Fetal Echocardiography
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
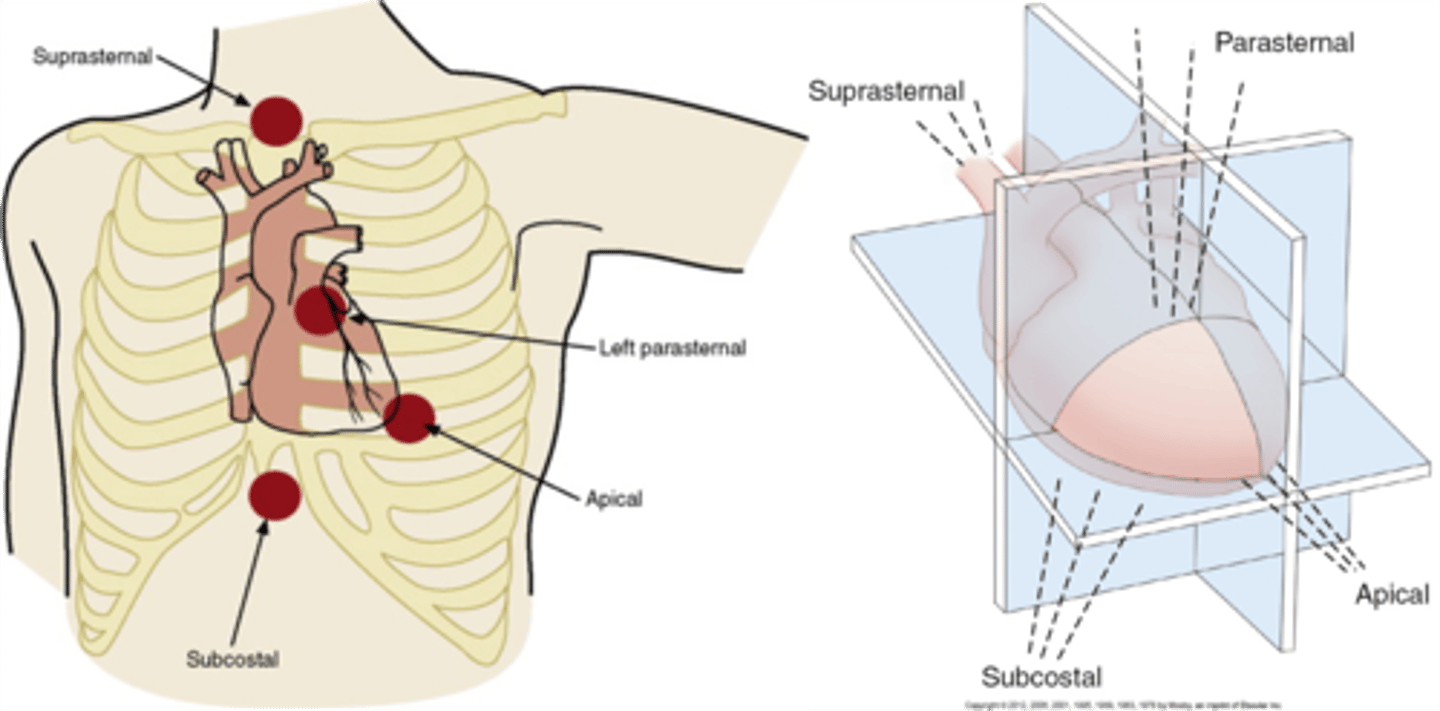
What are transducer locations for fetal echo?
1. suprasternal
2. subcostal
3. apical
4. parasternal
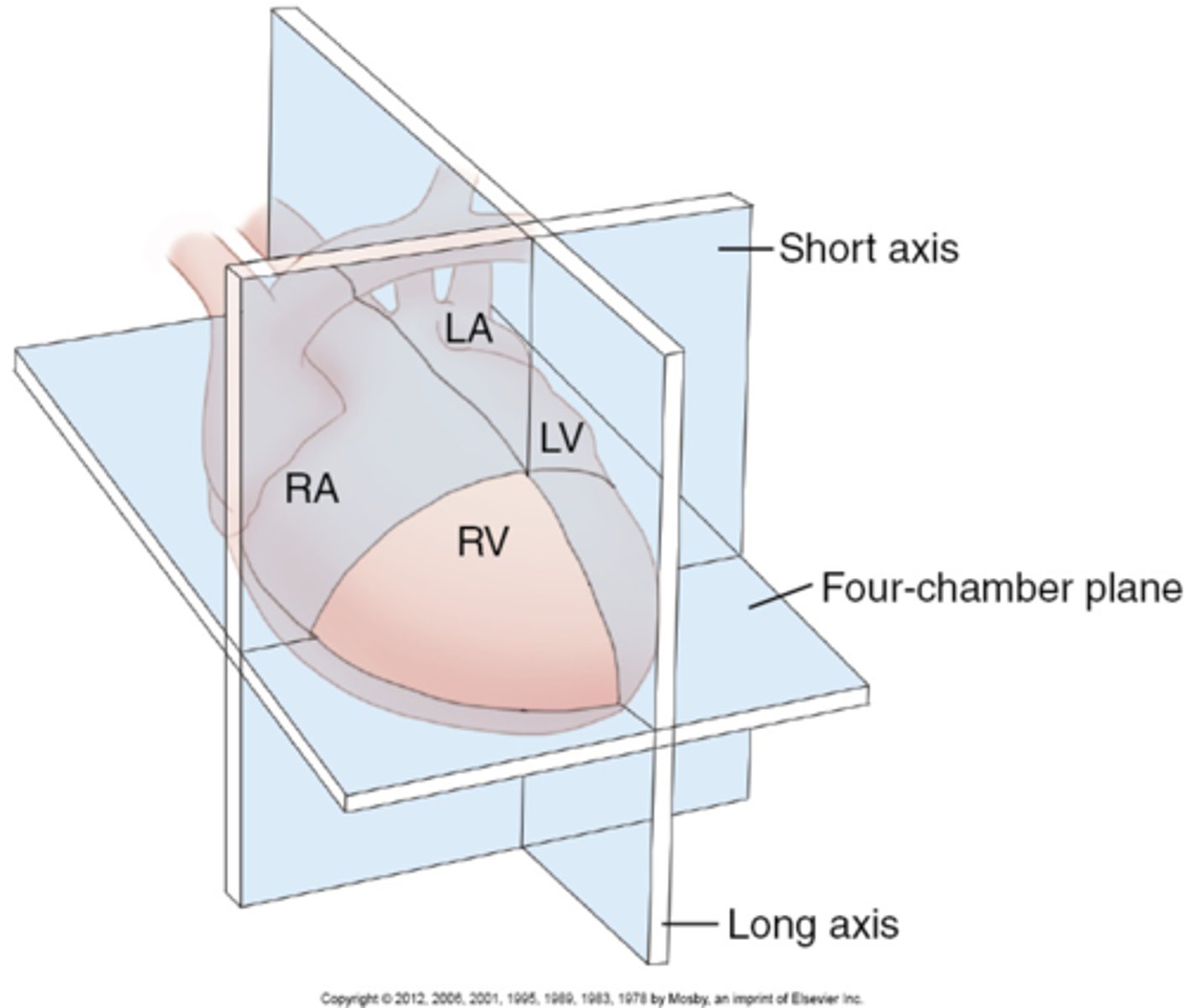
What are imaging planes for fetal echo?
1. long axis
2. short axis
3. 4CH
What is apical view?
transducer located over apex, giving a 4CH view
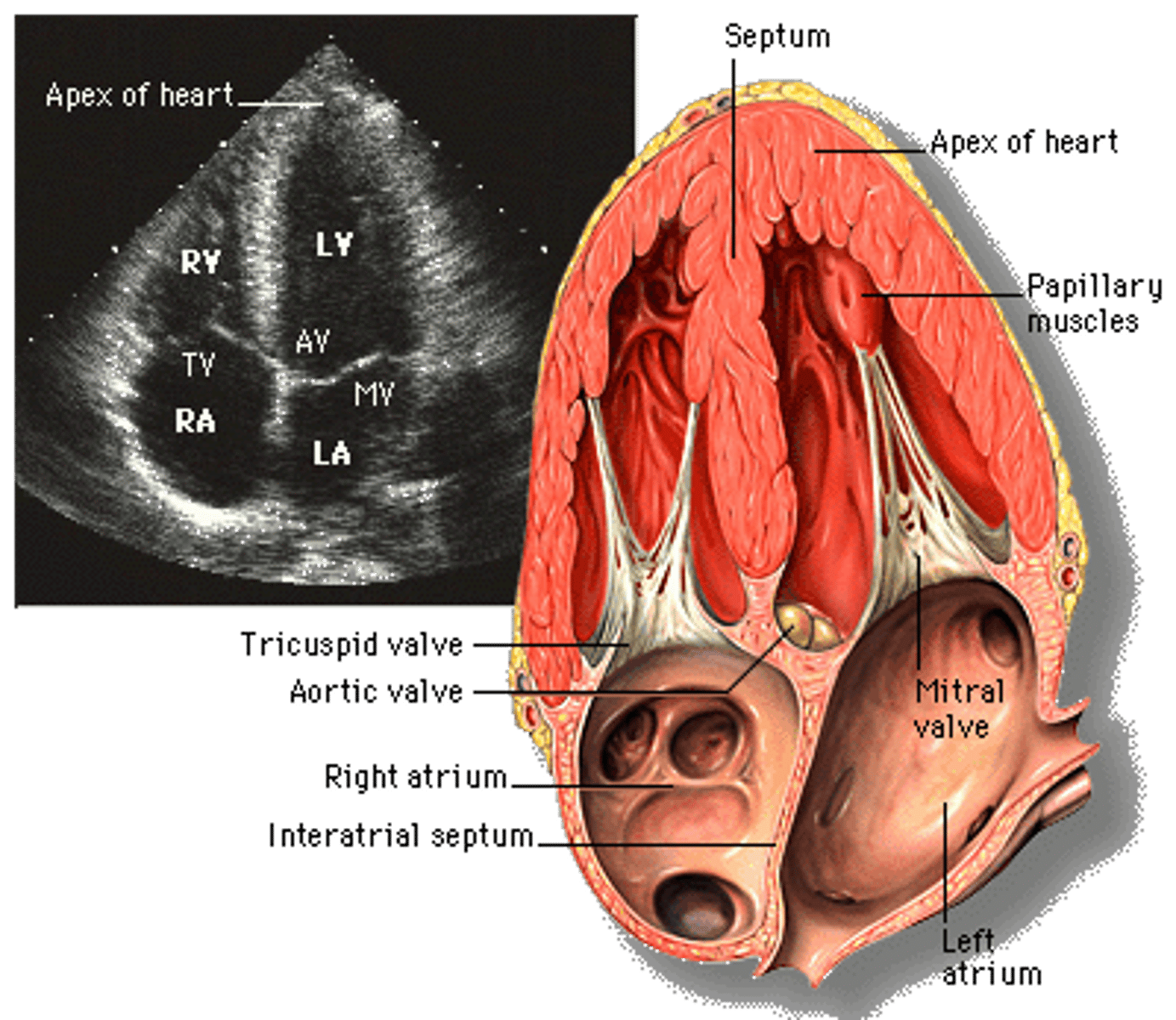
Label the fetal heart
https://www.purposegames.com/game/fetal-heart-quiz
When can fetal echo be performed transvaginally?
10-16 weeks
What is the optimum time for fetal echo?
18-22 weeks
The most sensitive period in the first trimester for cardiac development is between ___ weeks
3.5 and 6.5
The cardiovascular system is the first organ system to reach a ___ state
functional
By week __, blood circulation begins
3
By week __, heartbeat is seen
5
The primitive heart is a ___ structure that forms like a large blood vessel from the ___ cells in the cardiogenic area of the embryo
tubular; mesenchymal
Paired ___ ___ ___ develop before the end of the third week and begin to fuse, thus forming the primitive heart
endocardial heart tubes
The vascular system begins during the third week in the wall of the ___ ___, the ___ ___, and the ___
yolk sac; connecting stalk; chorion
Blood vessels begin to develop ___ after vascular system
2 days
___ ___ are then formed and cavities develop inside to form primitive blood cells and vessels
Blood islands
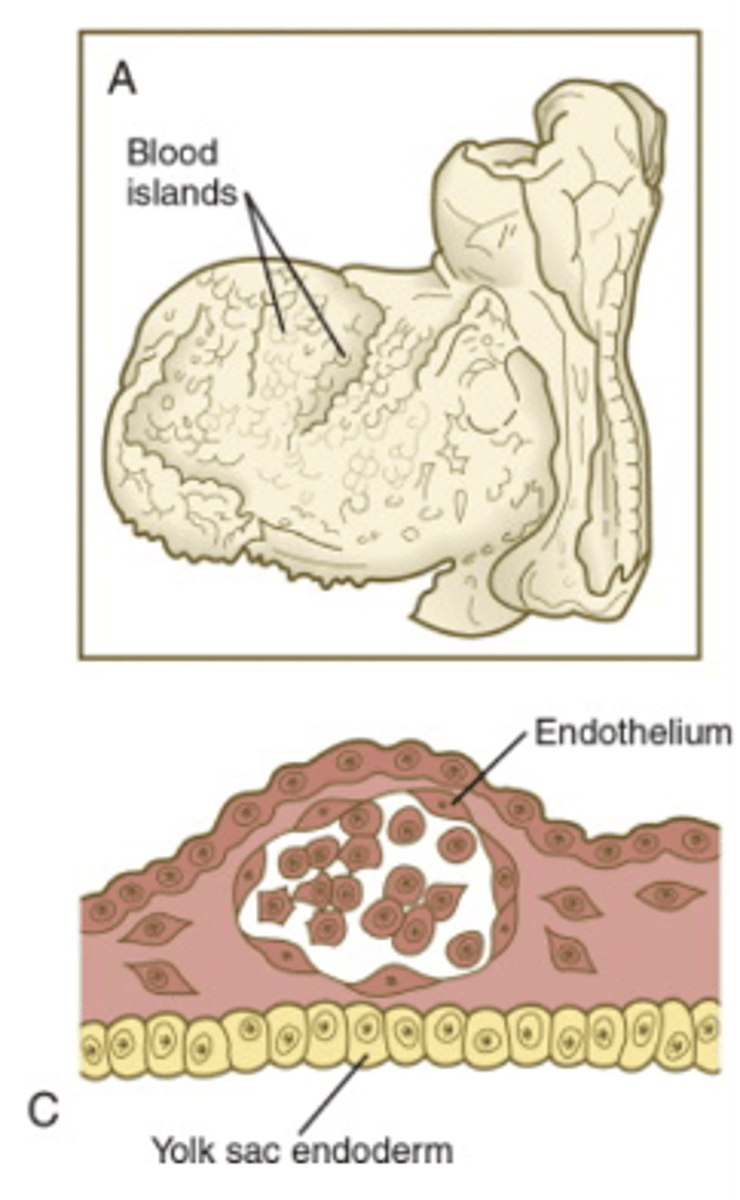
Primitive vessels form a vascular network in the wall of the ___ ___
yolk sac
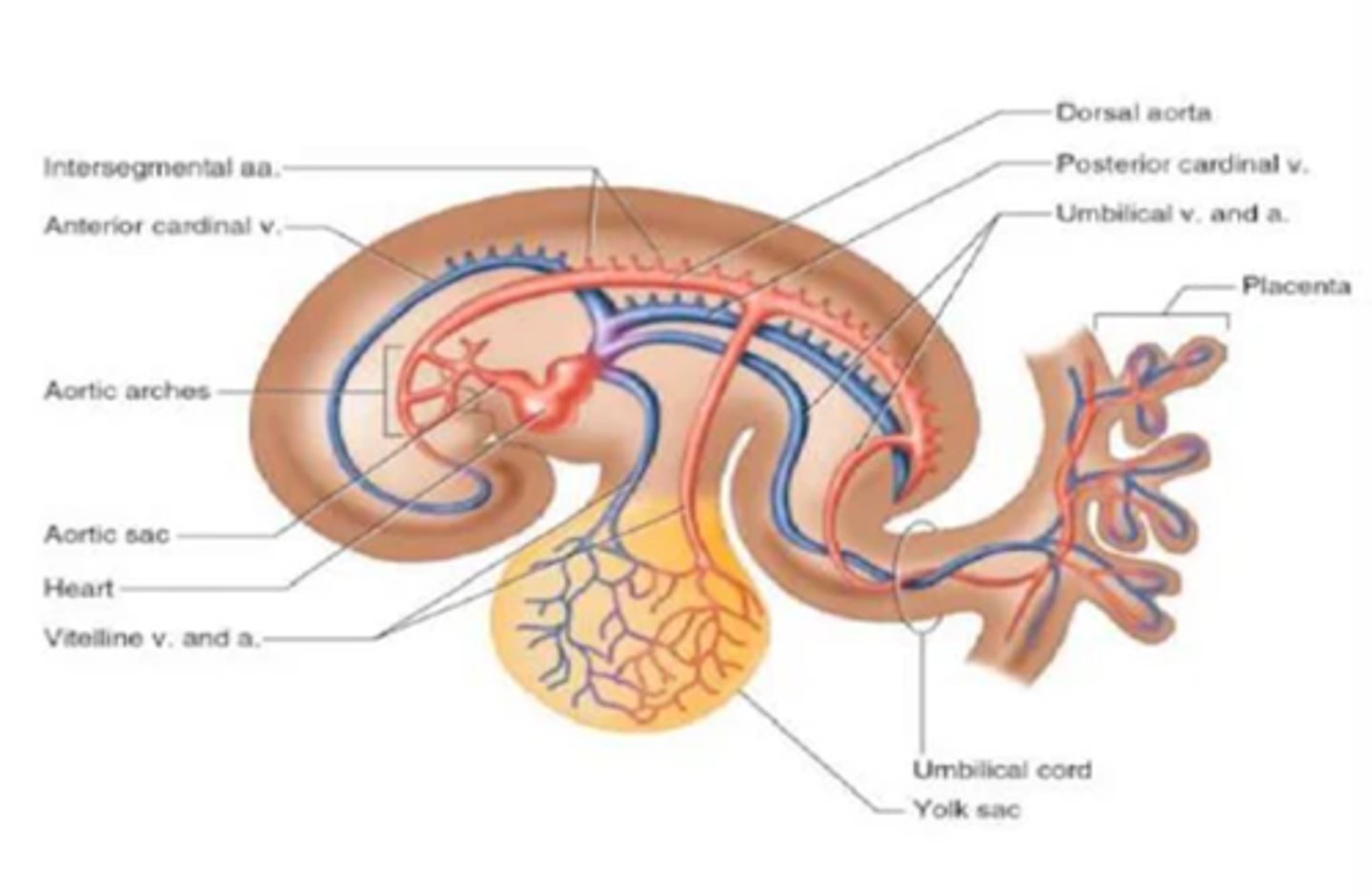
Cardinal veins return blood from the ___
embryo
Vitelline veins return blood from the ___
yolk sac
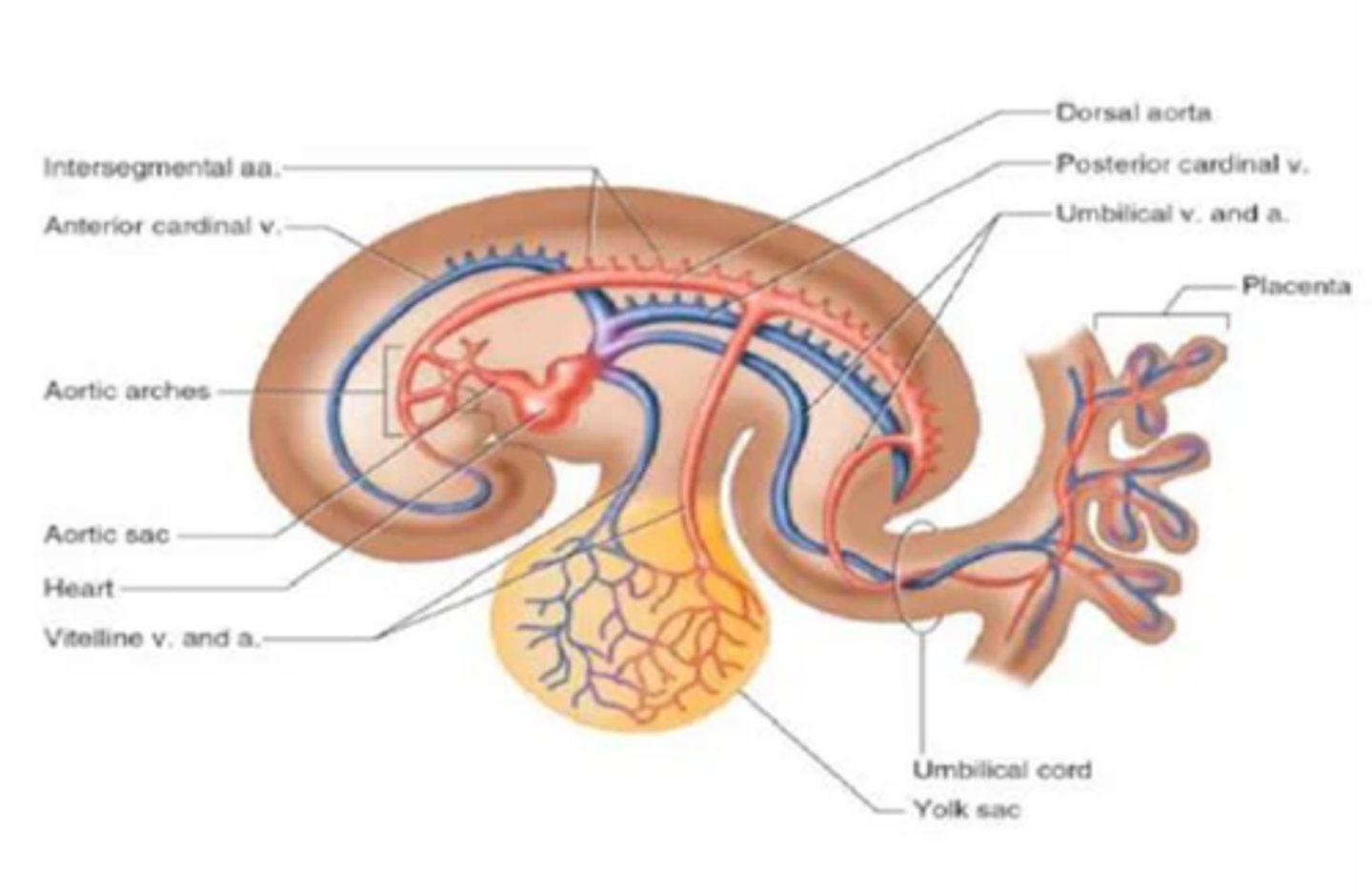
Umbilical veins return ___ blood from the ___ (only one umbilical vein persists)
oxygenated; placenta
Two dorsal aortas fuse in the caudal half of the embryo to form a ___
single dorsal aorta
What is sinus venosus?
caudal region of the primitive heart
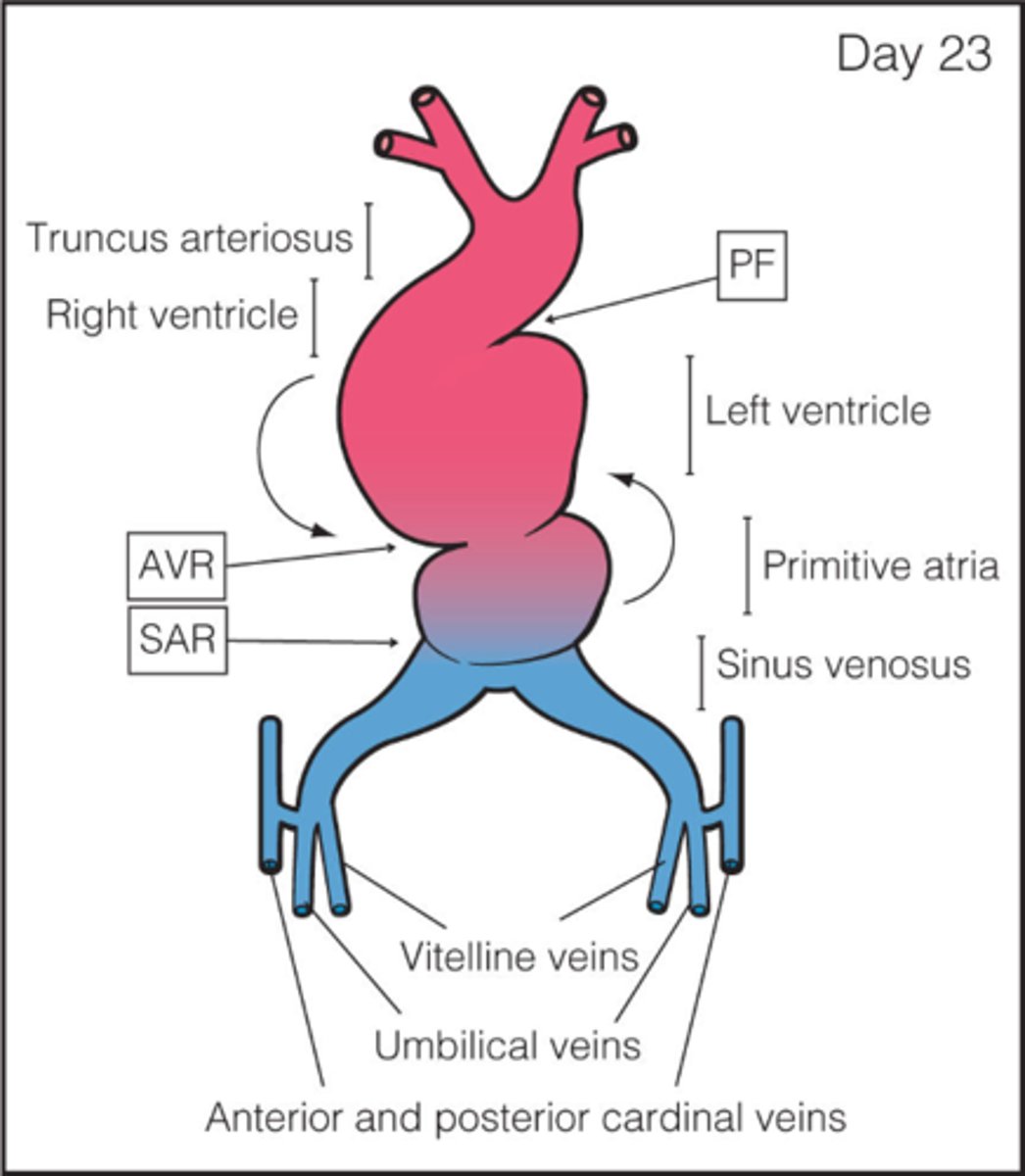
The sinus venosus receives all blood returning to the heart from ___, ___, and ___
common cardinal veins; vitelline veins; umbilical veins
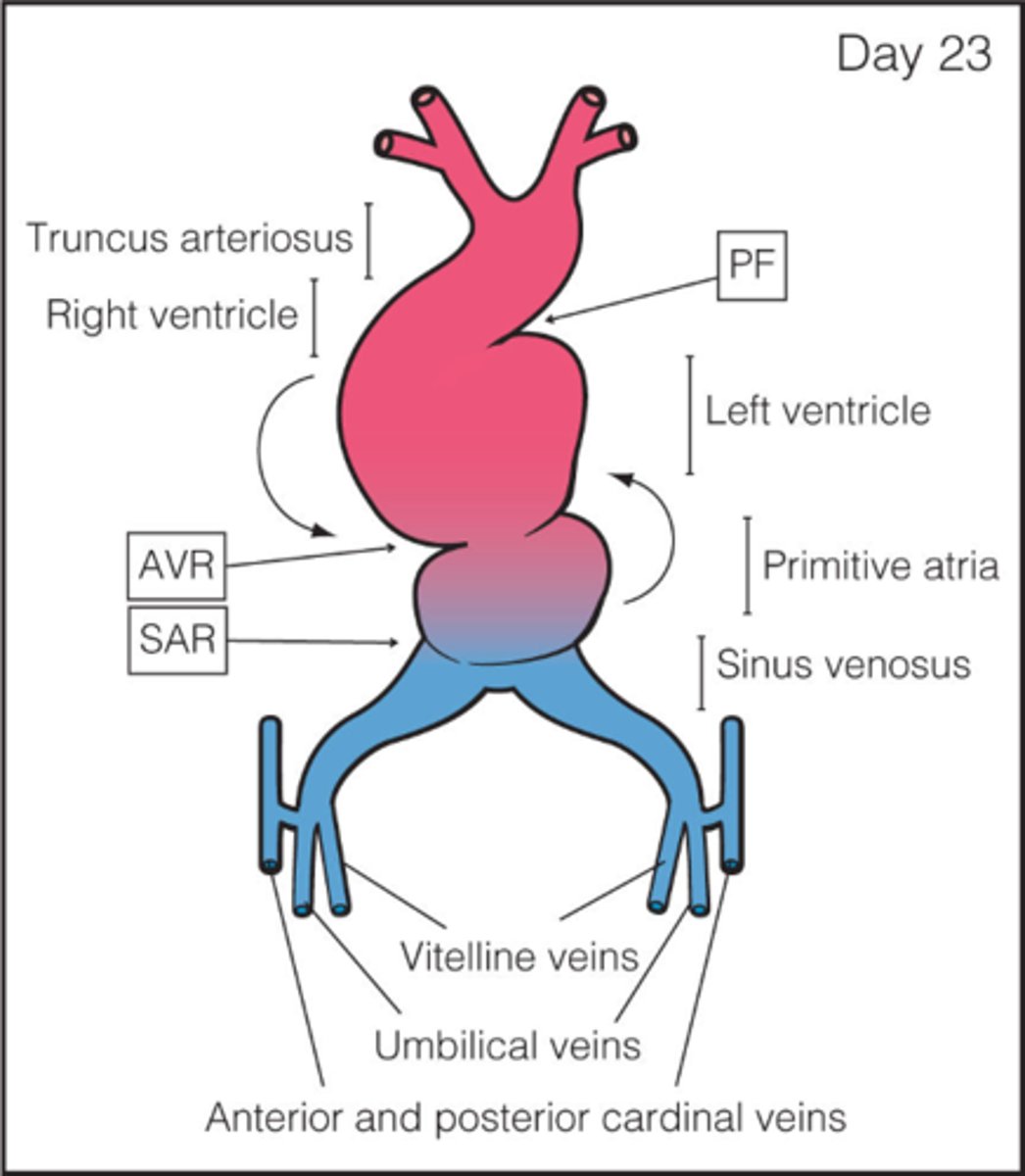
The primitive atrium develops into the ___
right and left atria
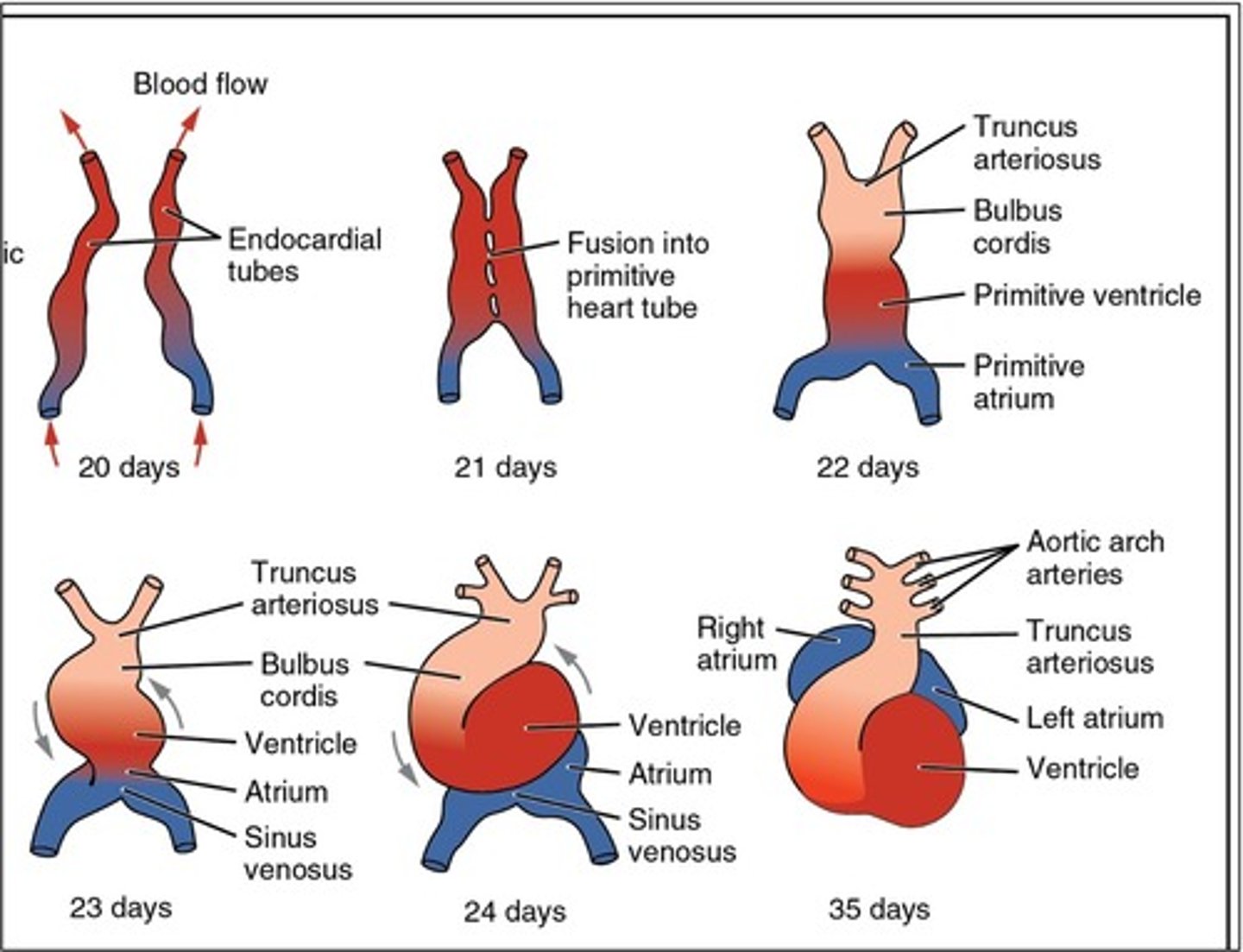
The primitive ventricle develops into the ___
left ventricle
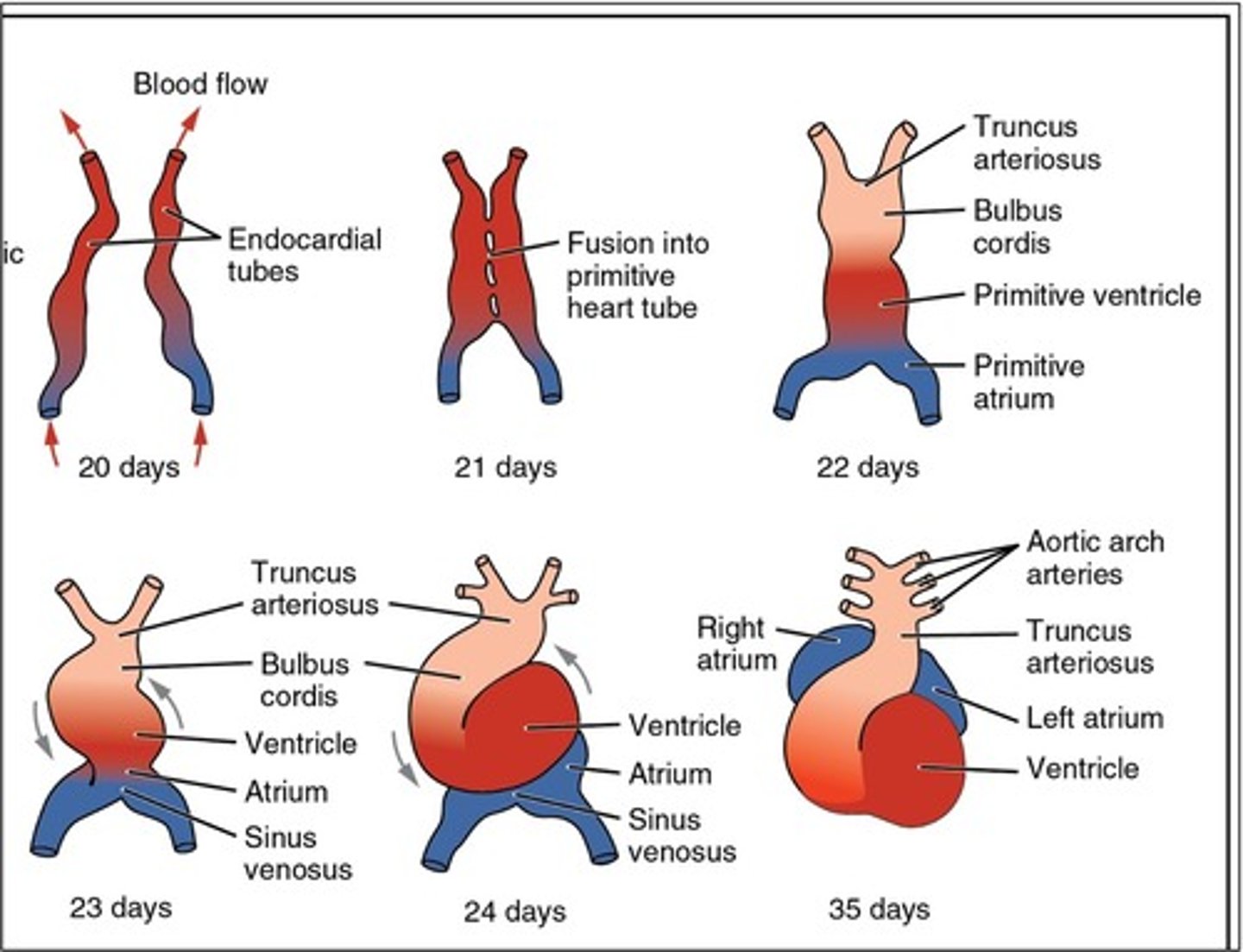
The bulbus cordis develops into the ___
right ventricle
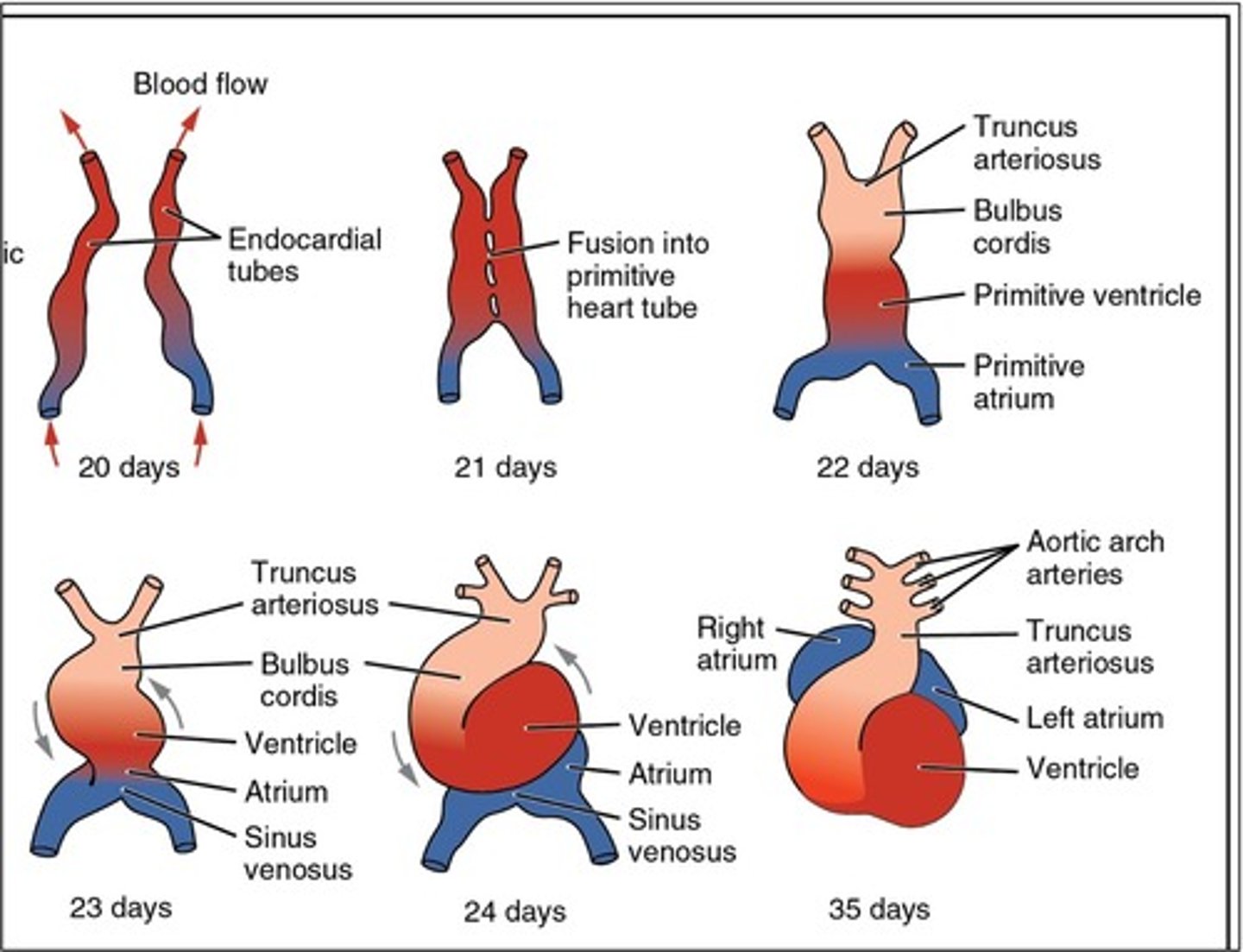
The truncus arteriosus dilates to form ___ from which ___ arise
aortic sac; aortic arches
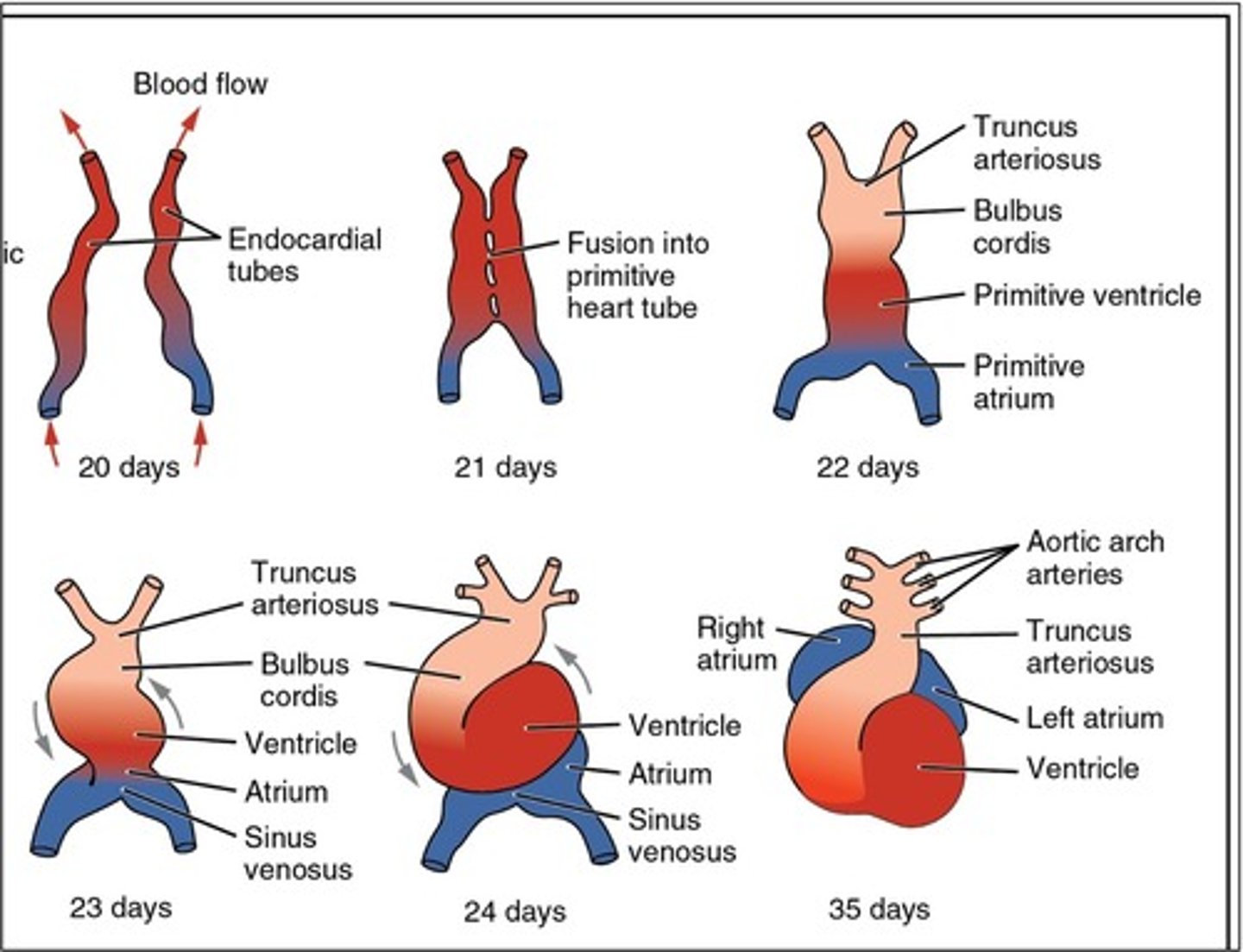
When does division of the heart into four chambers occur?
4-5 weeks
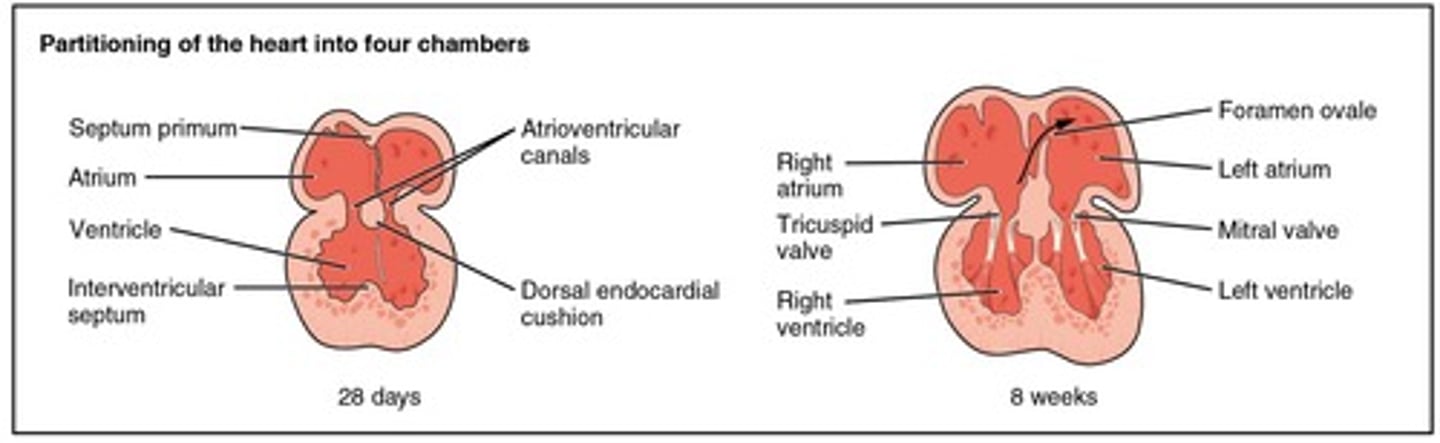
Communication is open between the right and left atrium of the fetal heart through the ___
foramen ovale
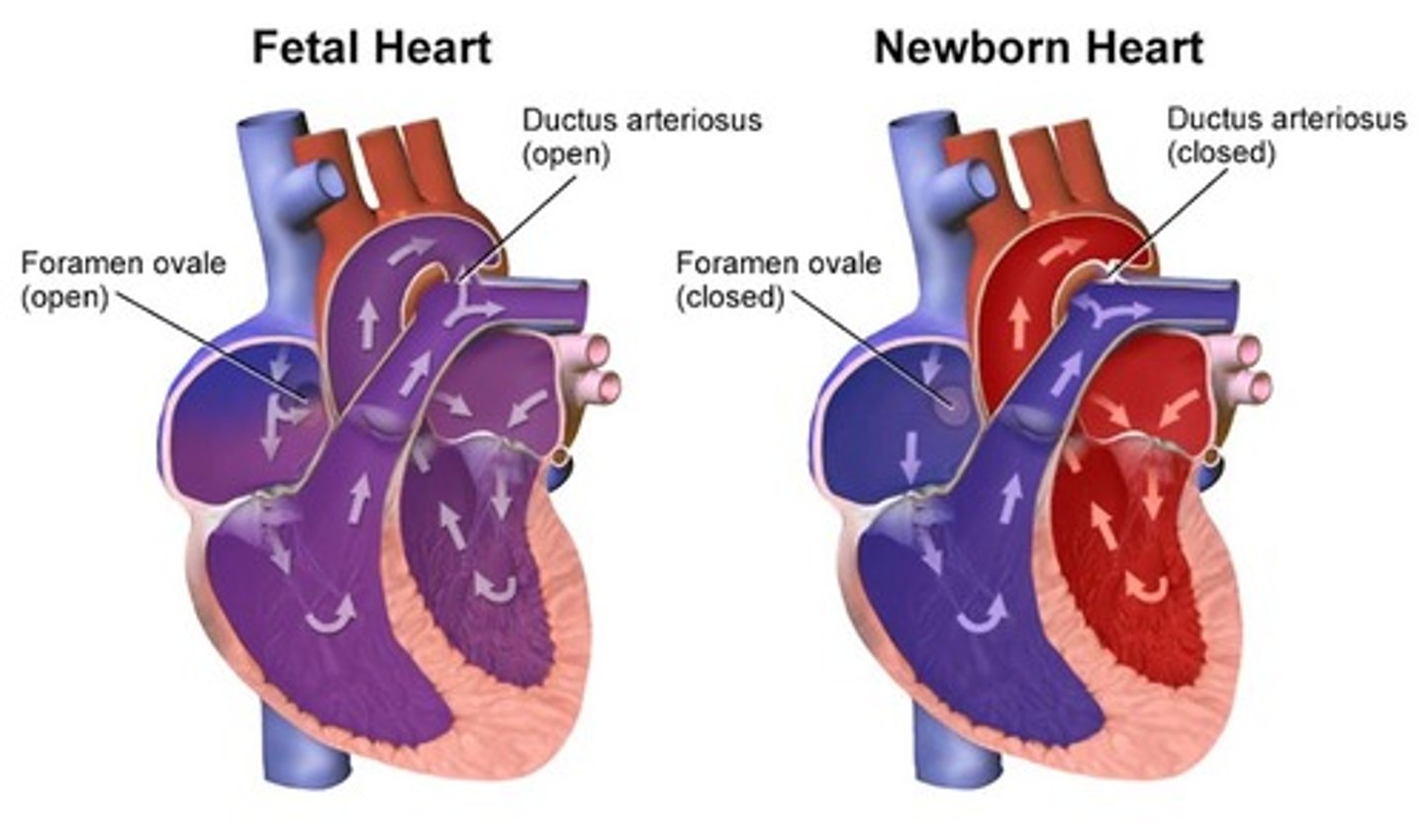
Communication is also open between the aorta and the ___ via the ___
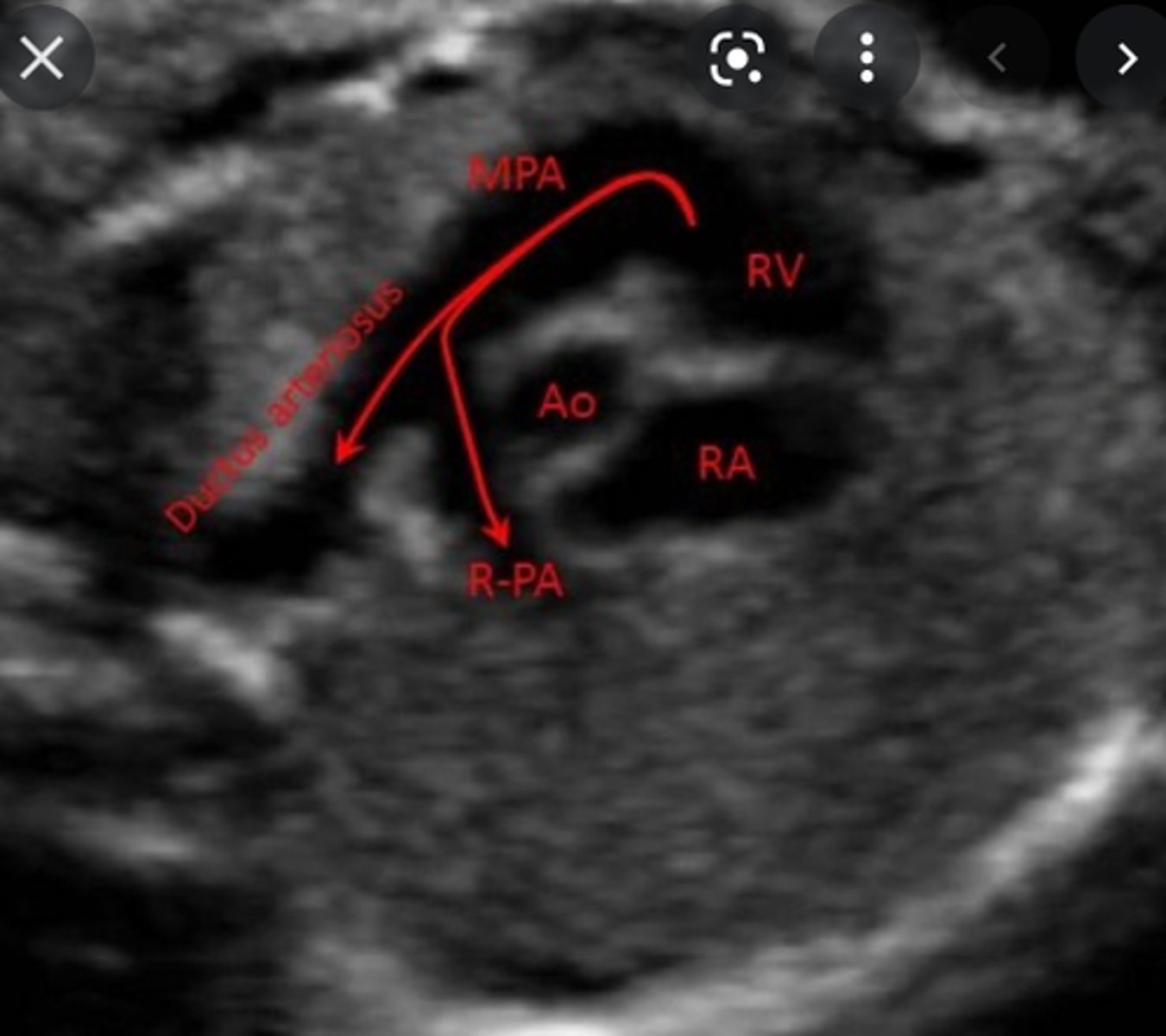
pulmonary artery; ductus arteriosus
Before birth, oxygenated blood is given to the fetus through the ___ from the ___ to the heart
umbilical vein; placenta
Half of the oxygenated blood passes through ___, the rest bypasses the liver to go through ___ into the ___
hepatic sinusoids; ductus venosus; IVC
The ductus venosus connects the ___ and ___
umbilical vein; IVC
Blood flows from the IVC and SVC and enters into the ___
right atrium
Blood in the right atrium is ___ oxygenated than blood in the umbilical vein
less
Small amount of oxygenated blood from IVC is diverted by the ___ and remains in the ___ to mix with deoxygenated blood from the ___ and ___
crista dividens; right atrium; SVC; coronary sinus
Most of the blood from IVC is directed by lower border of ___ through the foramen ovale into ___
septum secundum; left atrium
Blood in RA flows through the ___ valve into the ___ and leaves through the ___
tricuspid; right ventricle; main pulmonary artery (MPA)
MPA bifurcates into right and left pulmonary artery branches that lead to their respective ___
lungs
Most of this blood passes through the connection of the ___ into the ___; only a very small amount goes to the lungs
ductus arteriosus; descending aorta
Blood mixes with a small amount of ___ blood as it returns from the lungs via the four ___ into the ___
deoxygenated; pulmonary veins; left atrium
Pulmonary veins enter the posterior of the ___
left atrium
The four pulmonary veins are named according to their locations:
right upper, left upper, right lower, and left lower
Blood then flows from LA into LV through ___ and leaves heart through ___
mitral valve; ascending aorta
What are branches of fetal ascending aorta?
- innominate artery
- left carotid artery
- left subclavian artery
The rest of the mixed blood in the descending aorta passes into the ___ and is returned to the placenta for ___
umbilical arteries; reoxygenation
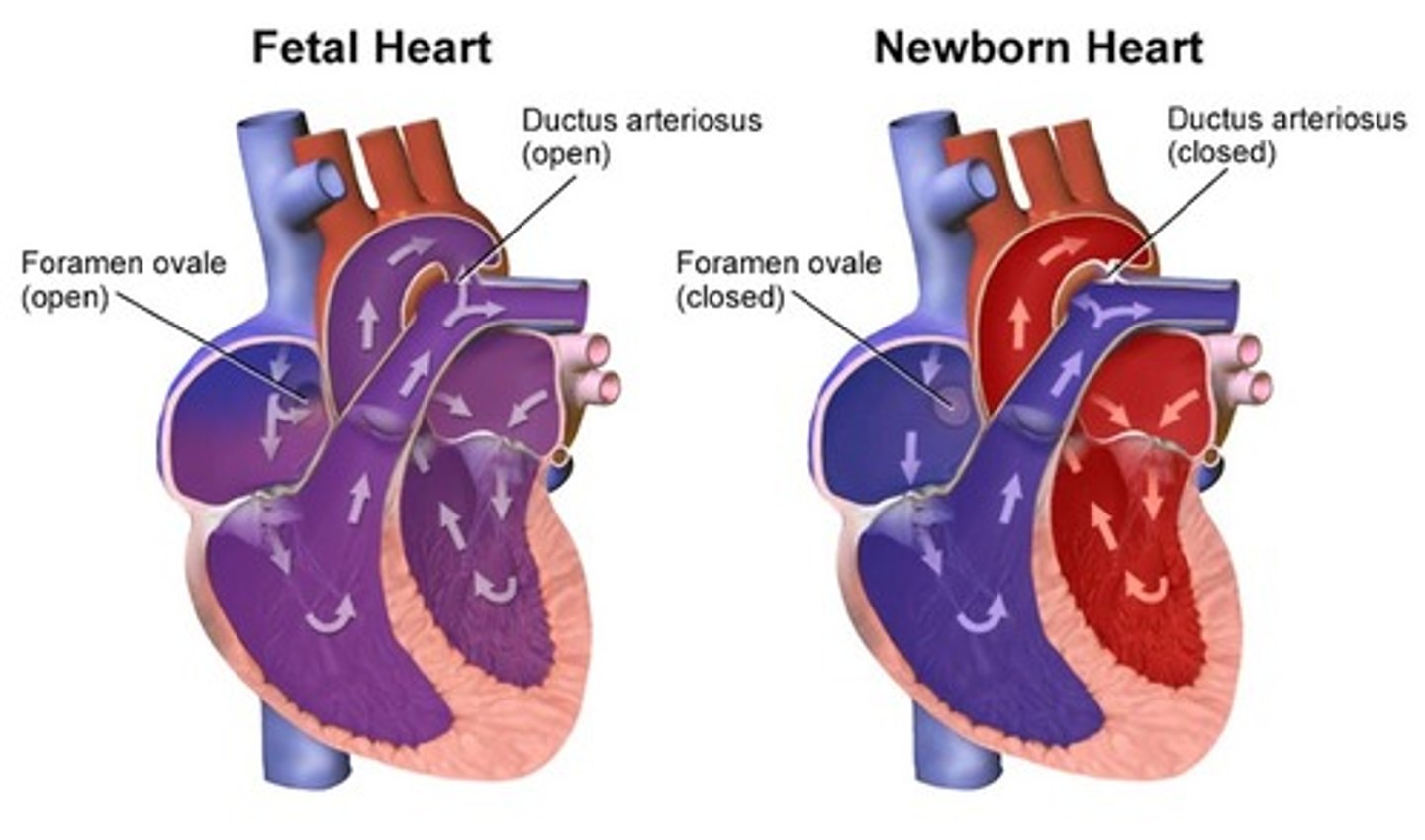
Circulation of fetal blood through placenta ceases at birth when the ___ begin to function
neonatal lungs
What fetal cardiac structures are no longer necessary at birth?
- foramen ovale
- ductus arteriosus
- ductus venosus
- umbilical vessels
Omission of placental circulation causes an immediate fall of blood pressure in newborn's ___ and ___
IVC; RA
As lungs expand with air, there is a ___ in pulmonary vascular resistance. This causes an ___ in pulmonary blood flow and progressive ___ of walls of the pulmonary arteries
fall; increase; thinning
Pressure in the left atrium becomes ___ than that in the right atrium. This causes the ___ to close
higher; foramen ovale
With time, complete closure of foramen occurs from adhesion of the septum ___ to the left margin of the septum ___
primum; secundum
Septum primum forms the floor of the ___
fossa ovalis
Ductus arteriosus constricts ___ after birth, once ___-sided pressures exceed the ___-sided pressures
24-48 hours; left; right
There is a small shunt of blood from aorta to ___ until these pressures adjust to neonatal life
PA
Once the ductus arteriosus closes, it turns into ___ in the neonate
ligamentum arteriosum
If ductus arteriosus communication persists, it is called a ___
patent ductus arteriosus
Umbilical ___ also constrict after birth to prevent blood loss from the neonate
arteries
Umbilical ___ may remain patent for some time after birth
vein
What is normal fetal heart rate?
120-160 bpm
In first trimester, heart rate begins around ___ and increases to ___ before returning to normal rate and sinus rhythm
90 bpm; 170 bpm
Heart rate less than ___ is bradycardia
100 bpm
Heart rate greater than ___ is tachycardia
200 bpm
What are fetal risk factors indicating fetal echo?
- IUGR
- cardiac arrhythmias
- abnormal amniocentesis
- abnormal amniotic fluid collections
- hydrops fettles
Presence of extracardiac abnormalities in the fetus are associated with ___
congenital heart disease
What are maternal diseases indicating fetal echo?
- diabetes
- lupus
- infections during pregnancy
If one parent has congenital heart defect, recurrence risk ranges from ___%
2.5 to 4
What is LVOT?
connects left ventricle to aorta
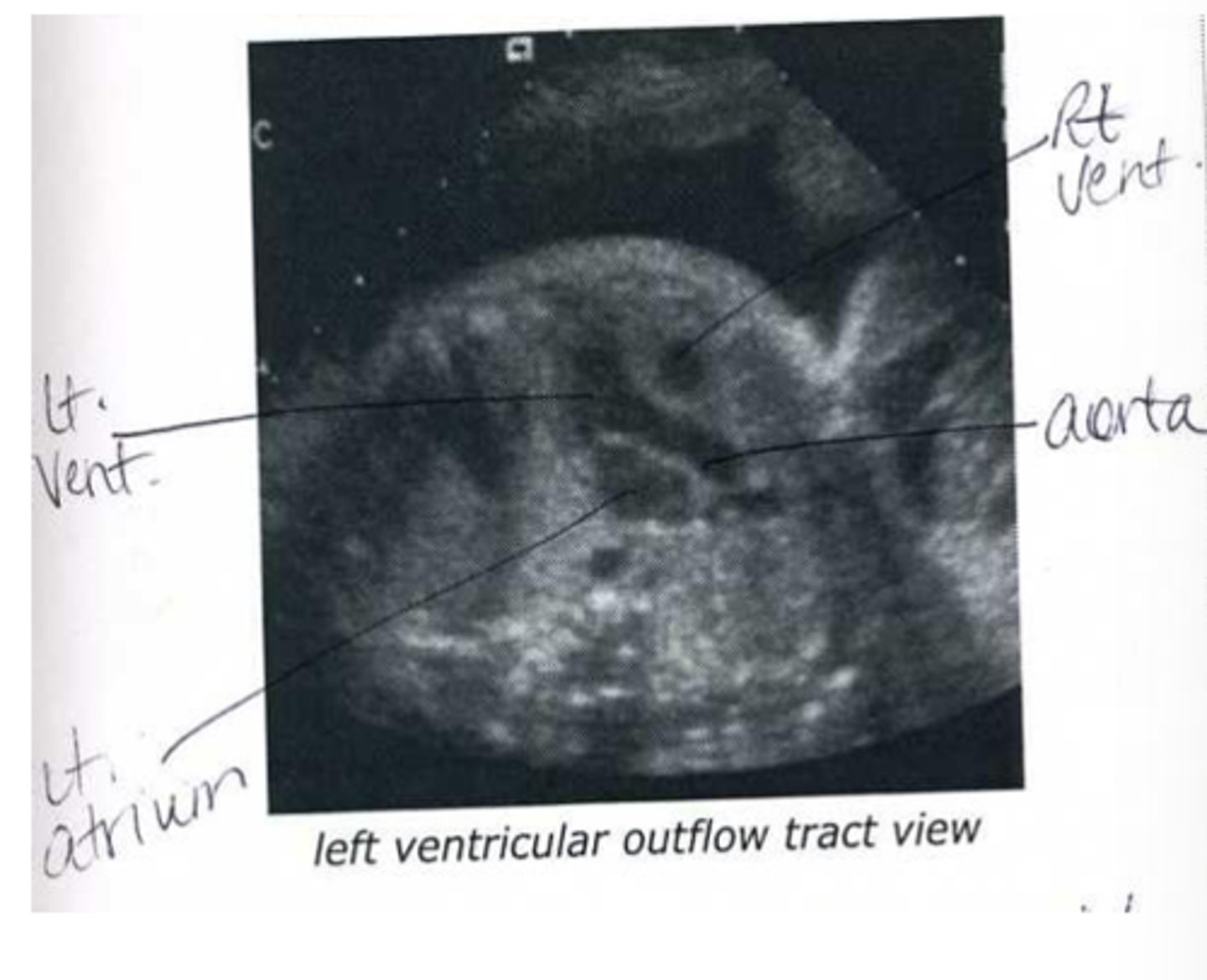
What is RVOT?
connects right ventricle to pulmonary artery