3 Steady Heat Conduction
How can HT be modelled in plane walls?
steady
one-dimensional
temperature is normally expressed as T(x)
What is thermal resistance?
The resistance of a surface against conduction, convection, or radiation. It can be thought of using the analogy of electrical circuits:
rate of heat transfer → electrical current
thermal resistance → electrical resistance
temperature difference → voltage difference
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How can HT be modelled in plane walls?
steady
one-dimensional
temperature is normally expressed as T(x)
What is thermal resistance?
The resistance of a surface against conduction, convection, or radiation. It can be thought of using the analogy of electrical circuits:
rate of heat transfer → electrical current
thermal resistance → electrical resistance
temperature difference → voltage difference
What are the equations for thermal resistance in walls?
Rcond = L/kA
Rconv = 1/(hA)
Rrad = 1/(hradA)
What happens when there is a very large convection coefficient?
Convection resistance tends to zero and so there is no resistance against convection in the surface
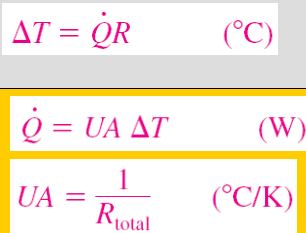
What is the temperature drop equation?
where U is the overall heat transfer coefficient
What is the equation for heat conduction in a cylinder?
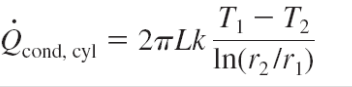
What are the equations for resistance in a cylinder?
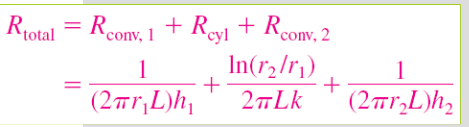
What are the equations for resistance in a sphere?
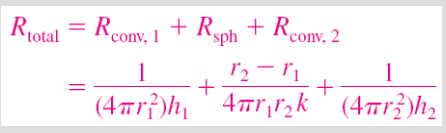
What is fin efficiency?
A judgement of how good a fin is working
η = Actual HT from the fin ÷ Ideal HT from the fin if entire fin were at base temperature
What is fin effectiveness?
This is judging if having the fin is better than not having the fin
ε = HT rate from fin ÷ HT rate from surface (w/out fin)
What is thermal contact resistance?
Interfaces between bodies are not always perfectly in contact which leads to thermal contact resistance
What causes the critical radius of insulation in cylinders/spheres?
The additional insulation increases the conduction resistance of the insulation layer, but decreases the convection resistance of the surface due to the increase in outer surface area.
What is the critical radius for cylinders and spheres?
cylinders r =k/h
spheres r =2k/h
Why may fins be added to a design?
If temperatures are fixed, adding fins increases the surface area and thus the heat transfer rate
What makes an effective fin?
high k
large p/Ac (ratio of perimeter to cross section area)
low h
How can you increase heat transfer rate?
increase surface area As using fins
increase convection coefficient h (using a pump or fan)
Name a dinosaur with fins
stegosaurus used fins to cool its blood
What is the best fin length?
when mL=1 as 76.2% of heat transferred by an infinitely long fin will be transferred and it uses less material
What is the heat transfer circuit analogy?
Heat transfer, like current, is the same everywhere