chapter 12 (part 2)- Protozoan diseases
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Protista (plant-like)
Kingdom of algae
Eukarya
domain of algae
unicellur, filamentous, or multicellular
Describe algae
photoautotrophs
Most algae are...
asexual reproduction in algae
Spore, fragmentation, fission
sexual reproduction in algae
Conjugation, gametes
Green algae
Photosynthetic protists that include unicellular, colonial, and multicellular species with grass green chloroplasts; closely related to true plants.
Brown algae
One of a group of marine, multicellular, autotrophic protists, the most common type of seaweed. Brown algae include the kelps.
red algae
marine algae in which the chlorophyll is masked by a red or purplish pigment
Phaeophyta (brown algae)
-multicellular (kelps and seaweed)
used as an emulsifier
- gas bladders
-cellulose and align
- laminator japonica
Rhodophyta (red algae)
-Cellulose cell walls
-Most are multicellular
-Chlorophyll a and d, phycobiliproteins
-Store glucose polymer
-Harvested for agar and carrageenan
Chlorophyta (green algae)
-Resemble plants, multicellular or unicellular, -flagellated gametes
- cellulose in cell walls
- red eye spot, photo detector pigment
- chloroplast for photosynthesis
Bacillariophyta
- diatoms
- pectin and silica (glass) in cell wall
- unicellular
- store extra oil for energy
- some produce domoic acid intoxication
Dinoflagellata
- cellulose in cell membrane
- unicellular
Alexandrium (dinoflagellate)
Saxitoxin, causing paralytic shellfish poising
Paralysis of respiratory muscle
Karelia brevis (dinoflagellata)
Causes fish to die
Produces a neurotoxin that gets into the gills of fish and suffocates them
Phytophthora infestans (dinoflagellata)
Irish potato blight, potato fields were failing
Algal bloom
an immediate increase in the amount of algae and other producers that results from a large input of a limiting nutrient
Protista
Kingdom of Protozoa
Eukarya
Domain of Protozoa
Unicellular, pellicle, they make cyst, in water and soil
Protozoa is...
Asexual reproduction in Protozoa
fission, budding, or schizogony
Sexual reproduction in Protozoa
Conjugation, gametes
Ciliates
A group of protozoans that move by waving tiny, hair-like organelles called cilia.
- cytostome oral: groove where food comes in
- anal pore: where waste exists
- micronucleus and macronucleus
- contractile vacuole: expand and contract
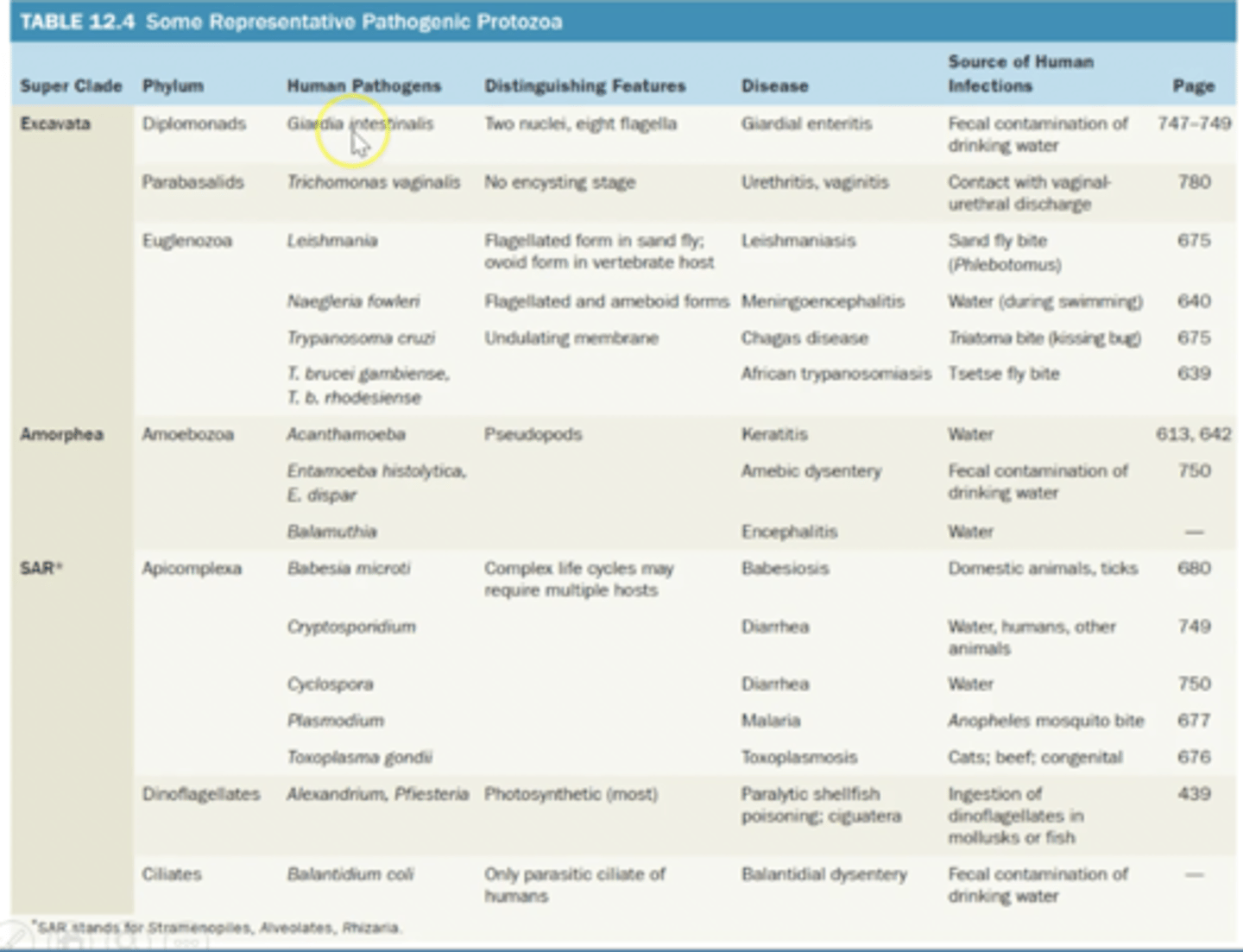
Balatidium coli (ciliates)
giant pig protozoan
Amoebozoa
--psuedopodia
--engulf food (phagocytosis)
--soil and water
--some parasitic
- amoeba proteus
Entamoeba histolytica (amebea)
- causes amoebic dysentery, blood in stool, fever, abdominal pain
- Found in water, so drinking contaminated water
- red blood cells in ambea
Acanthamoeba (amebea)
- Keratitis which can lead to blindness
- found in tap water
- inflammation of lens
- cornea infection
Parabasalids
A group of protistans, including the trichomonads, that lacks mitochondria.
Tricomonas vaginalis
- undulating membrane, motility
- no cyst stage
- no mitochondria
- causes urinary tract infection and genital tract infection (men and women)
Diplomonads
a protist that has no mitochondria, two equal-sized nuclei, and multiple flagella
Giardia intestinalis
- no mitochondria
- adjustive disk that's attached to epithelial cells of digestive tract, intestine
- found in contaminated water and moist soil
- severe diarrhea infection
- cyst can't be removed with chlorine
- in human stool
Apicomplexa
-nonmotile, Apical complex
- obligate intracellular parasites
- complex life cycle
Toxoplasma gondii (apicomplexa)
- Mild to no symptoms in health people
- If late in pregnancy it affects the fetus and mental retardation, blindness, seizures, under developed head
- affected by changing kitty litter
- others can get affected by eating poorly cooked beef
- cat is the host and rats cows & people are the intermediate host
definitive host
an organism that harbors the adult, sexually mature form of a parasite
intermediate host
an organism that supports the immature or nonreproductive forms of a parasite.
Apicomplexa Plasmodium vivax
malaria
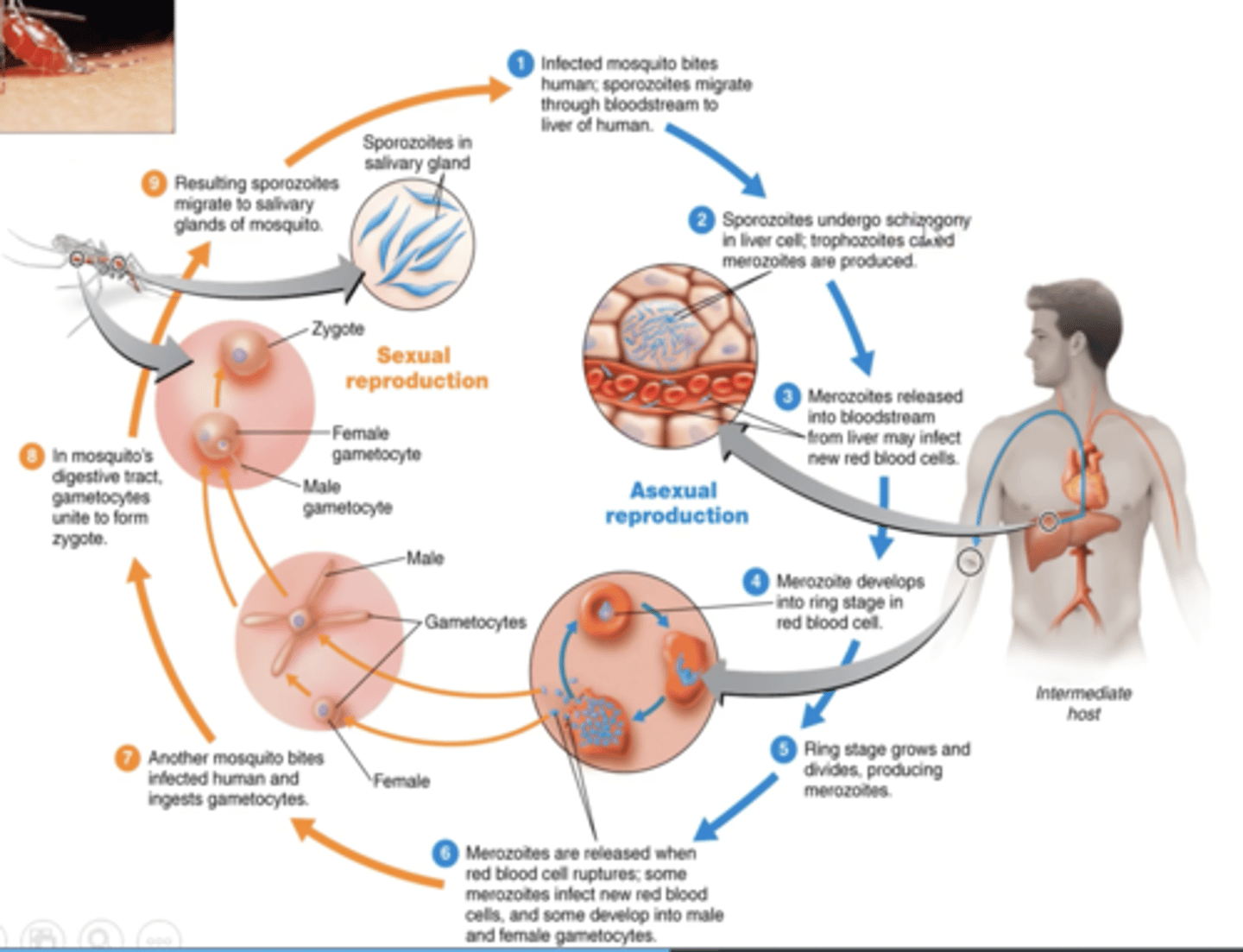
Plasmodium vivax
70-90% of cases in Asia & South America,
1-10% in Africa
P. ovale
8% of cases in Africa, stray cases in Asia
P.malariae
2-3% of the cases in Africa, sporadic in Asia & S.America
P.falciparum
80-90% of the cases in Africa, 40-50% in S.E. Asia, 4-30% in s. Asia and s. America
Sporozoites
Infective stage - Malaria
Merozoites
Ring stage- malaria
Cryptosporidium (apicomplexa)
- transmitted via feces; causes waterborne illness
- contaminated water of the cyst
- attaches to intestinal epithelial wall
- severe diarrheal infection
Euglenoza
- also known as Hemoflagellates
- no mitochondria
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (euglenozoa)
- trypanosomiasis or African sleeping sickness
- vectors: tsetse fly
- appear weak and last for many years
- affects the center nervous system, liver, spleen
- if not treated chronic fever headache, change of personality, difficulty to concentrate or walk
Trypanosoma cruzi (euglenozoa)
- American sleeping sickness (Chagas disease)
- vector: kissing bug
- bug bites on the face and defecates
- cardiac nerves affects and causes heart failure
- coma, difficult swallowing, enlarged colon
Leishmania tropica
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Papule that ulcerates and scars are
Sandflies
Leishmania braziliensis
Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis
Disfiguring, distribution of tissue
Sandflies
Leishmania donovani
visceral leishmaniasis
Fatal if untreated
Sandflies
Naegleria fowleri
- primary amoebic meningoencephalitis ("the brain-eating amoeba")
- Found in tap water, rare and fatal
- focal hemorrhage and necrosis in frontal cortex
Pathogenic Protozoa