CSF, Intracranial Pressure and the Blood Brain Barrier
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is cerebrospinal fluid?
specialised type of extracellular fluid (ECF)
function of CSF
cushioning for the brain (allows the brain to withstand normal minor traumas)
provides constant external environment for neurons and glia
major route for removing harmful brain metabolites
distributes hormones (secreted by hypothalamic neurons)
where is CSF found?
sub-arachnoid space
ventricles (brain)
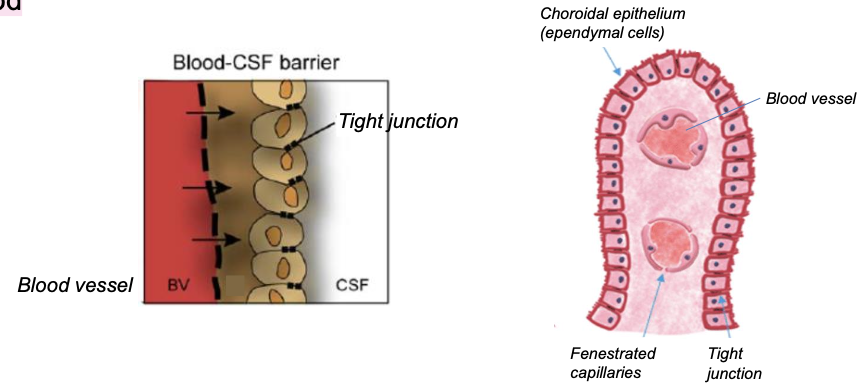
CSF is formed mainly by the choroid plexus, name another structure that is responsible for CSF formation
other brain capillaries
describe the circulation of CSF in the brain
produced by choroid plexus
flows through ventricles (lateral→ third → fourth)
exits fourth ventricle (base of brain)
flows into sub-arachnoid spaced
absorbed into venous blood across arachnoid vili
explain how CSF is formed
CSF is formed as a filtrate following active transport and passive diffusion across the wall of the choroid plexus
choroid plexus permeability
permeable to lipid-soluble solutes (anaesthetics, O2, CO2)
what is the blood-CSF barrier?
Barrier formed by tight junctions between the ependymal cells of the choroid plexus
total volume of CSF
125-150ml
25ml in ventricles
125ml in sub-arachnoid space
rate of CSF production
~0.35 ml/min
CSF pressure
10 mmHg
hydrocephalus
build up of CSF in brain → enlargement of ventricles
→ brain compressed →brain damage
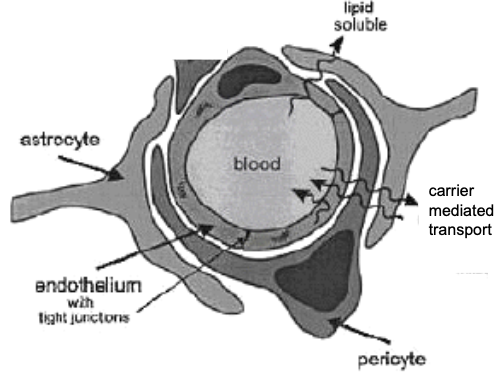
function of the blood brain barrier (BBB)
excludes toxic substances from brain tissue
protects brain from chemical fluctuations in blood
protects brain from certain circulating neurotransmitters/hormones (e.g. after stress)
maintains a constant environment for neurons to function effectively
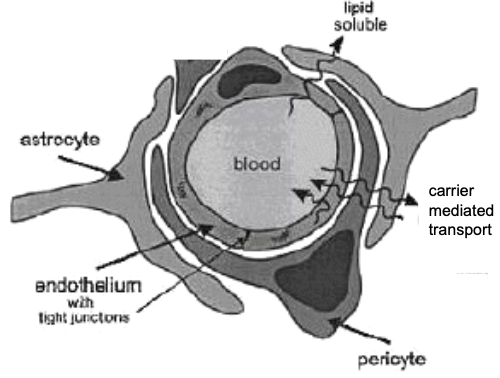
brain capillary
transport system (highly specific)
no holes
interconnected by tight junctions
lack of vesicular transport
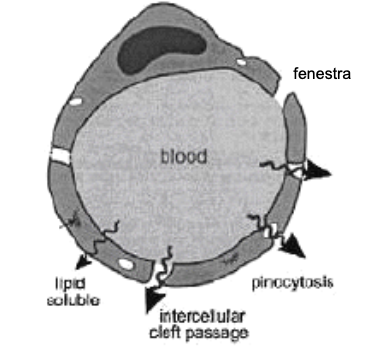
peripheral capillary
non selective diffusion across capilary wall
small holes (fenestra/ inter-endothelial clefts)
pinocytotic vesicles
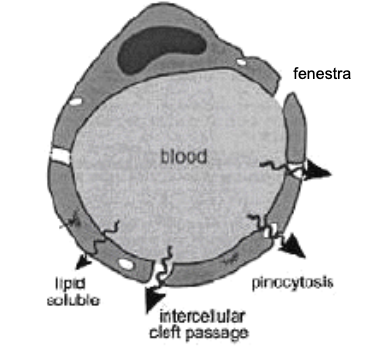
importance of BBB permeability
protects brain from harmful substances
limits use of drugs to treat CNS disorders
CNS side effects can be avoided in peripheral drugs
difference of BCSF and BBB barriers
BCSF: formed by tight junction between chroroidal epithelial/ependymal cells
BBB: formed by tight junctions between endothelial lining of capillaries and surrounded by astrocytic foot processes
the rigid cranium contains
brain
blood in cerebral vessels
CSF
intercranial pressure (ICP)
pressure exerted by fluids inside skill and on brain tissue
maintenance ICP
~10 mmHg (directly proportional to cranial contents volume)
monro-kellie doctrine
explains the relationship of the total cranial content (brain, blood and CSF)
increase in the volume of one component causes a compensatory decrease in the volume of the others
increased ICP means
cerebral vessels compressed
reduced blood supply to brain → cerebral ischemia
cushing’s reflex occurs
cushing’s reflex
NS response to increased ICP
reduced blood supply to brain = increased CO2, decreased O2
activates sympathetic and parasympathetic NS
results in: increased arterial BP, reduced HR, reduced respiration