2. Replication and Mendelian Inheritance I
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
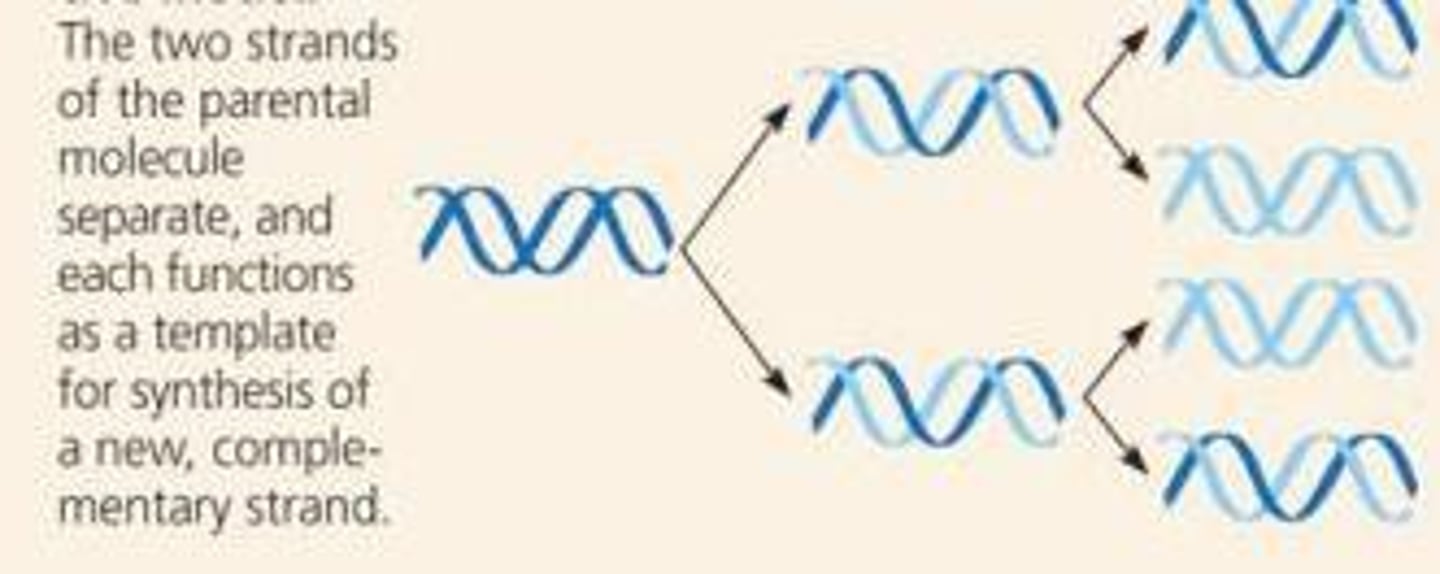
Semi-conservative replication
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new
What 5 things do you need for DNA replication
1. dNTPS (special type of nucleotide used during replication)
2. DNA polymerase (catalyzes DNA synthesis)
3. DNA template
4. DNA/RNA primer
5. Mg 2+ for polymerase activity
New DNA is made in what direction
5' to 3'
Replicator
A sequence of DNA that denatures (opens up) to form the replication bubble. It's where REPLICATION STARTS.
Where replication starts is called the
origin of replication
the denatured area where replication is happening is called the ________ and in it is the ________
replication bubble
replication fork
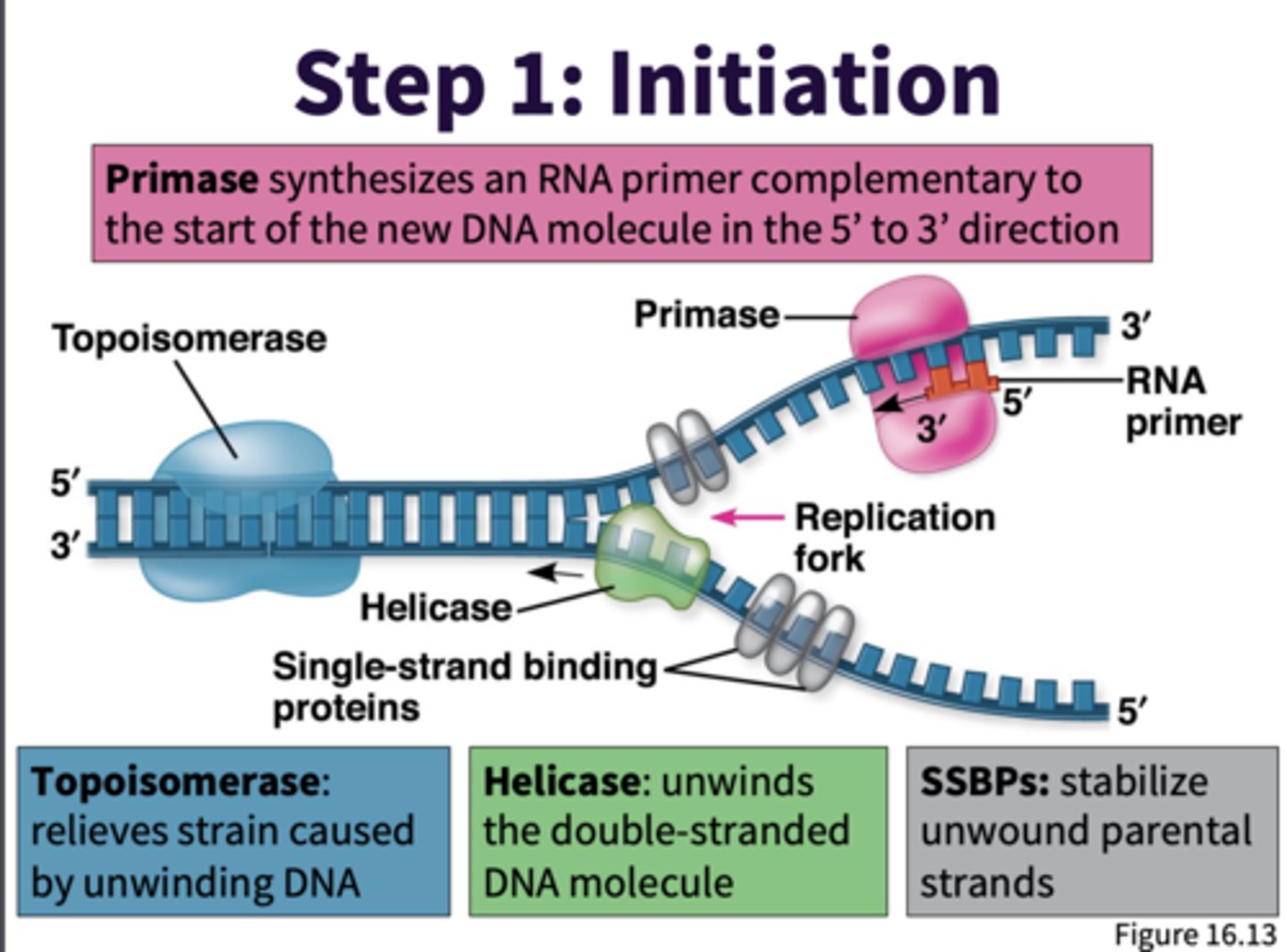
Step 1 of DNA Replication
Initiation:
- RNA primer made by DNA primase starts replication of lagging strand (synthesis of 1st okazaki fragment)
Step 2 of DNA Replication
Further untwisting and elongation of new DNA strands, 2nd okazaki fragment elongated.
Step 3 of DNA Replication
Process continues until entire strand is copied
Step 4 of DNA replication
primer removed by DNA polymerase I. When completed, single-strand nick remains.
Step 5
joining of adjacent DNA fragments by DNA ligase.
What stitches together the Okazaki fragments
DNA polymerase I and ligase.
DNA poly I uses the preceding okazaki 5' end fragment to add dNTPS and link it to the next fragment.
Ligase seals the last sugar phosphate backbone bond (called the nick).
Eukaryotes have
multiple origins of replication
telomerase
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=it8g9RU8KMM
An enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic germ cells.
It complementary bases to the overhang that's present when the primer is removed.
genotype vs. phenotype
genotype: sequence of bases (genetic composition)
phenotype: appearance (observable traits)
Phenotype depends on 2 things:
genes + environment
What happens when you breed 2 true breeding plants? (one homozygous dominant, one homozygous recessive)
F1: all heterozygous (Pp)
Which alleles are expressed in phenotype
dominant
the sequence of bases for dominant and recessive alleles are
dfferent
ex: the gene for flower color is found on the same chromosome but different sequence of bases at that locus leads to different phenotypes
F2 generation phenotype ratio
3:1
Mendel's Principle of Dominance:
Dominant alleles mask recessive alleles in phenotype. Recessive alleles do not show where dominant alleles are expressed.
Mendel's Principle of Segregation.
What cross shows this
each gamete only carries one allele. So in the gametes of the F1 generation, A separates from a, and when they combine to form F2, you get 3:1.
Production of F1 x F1 = F2 generation: 3:1
Mendel's Principle of Independent Assortment.
Which cross shows this and what ratio do you get
alleles of different genes assort into gametes independently of one another.
Crossing 2 heterozygotes that are heterozygous for both traits (SsYy x SsYy) = 9:3:3:1
9 is dom in both, 3 is dom in one, 3 is dom in another, 1 is recessive in both
Ratio of genotypes vs ratio of phenotypes
ratio of genotypes: heterozygous to homozygous
phenotypes: traits (like smooth: wrinkled)