FMLec M3 | Shelf-life indicators
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
_ is the time between the production of the product and the point at which the product becomes unacceptable to consumers
Shelf life
Explain microbiological limits for end of shelf life
*product = typical shelf life
bsp cfc
Bread = up to 1 week at ambient
Sauces & dressings = 1-2 yrs at ambient
Pickles = 2-3 yrs at ambient
Chilled food = Up to 4 months at 0-8 C
Frozen food = 12-18 months in freezer cabinets
Canned food
Unlacquered = 12-18 months
Lacquered = 2-4 yrs
_ is a systematic way of determining how long a product can be kept under specific storage conditions, while still maintaining its quality
Shelf life testing services

Purposes of shelf life testing services
Compliance to regulatory standards
Product registration
Establishing mode of deterioration
Establishing suitability of packaging
3 analyses done in shelf life testing
mps
Microbiological
Physiological
Sensory
Enumerate & explain 2 approaches to shelf-life determination
Direct shelf life determination & monitoring
Applicable for products with short shelf lives
Batches of samples are taken at specified stages of product development
Samples are stored under controlled conditions until quality becomes unacceptable
Tests (M, P, S)
Accelerated shelf life estimation
Performed to meet product launch dates
Storage temperature is increased to increase ageing process
_ is an approach to shelf life determination that is applicable for products with short shelf lives
Direct shelf life determination & monitoring
Describe process of direct shelf life determination & monitoring
Batches of samples are taken at specified stages in their product development
Samples are stored under controlled conditions until quality becomes unacceptable
Tests (M,P,S)
_ is an approach to shelf life determination where storage temperature is increased to increase ageing process
Accelerated shelf life estimation
Enumerate 3 chemical indicators of spoilage
dpv
Depletion of glucose (e.g., red meat)
Production of lactic acid, acetic acid, ethanol (e.g., pork, beef)
Volatile compounds (e.g., proponol in beef)
Explain 3 analyses making up microbiological determination of shelf life
scp
Storage trials
Samples are taken at specified timed intervals and analyzed for:
Total microbial count
Specific spoilage organisms (Pseudomonads, LAB)
Viable count is compared with sensory evaluation
Challenge tests
Samples are incubated under conditions that replicate/reproduce large-scale food production & storage period
May be inoculated with target organisms (C. sporogenes)
Predictive modelling
Simultaneously predict growth of microorganisms over a range of conditions
Valide the model using published & in-house lab data
Part of microbiological shelf life determination
Samples are incubated at conditions replicating large-scale food production & storage period
May be inoculated w/ target organisms (C. sporogenes)
Challenge tests
Part of microbiological shelf life determination
Samples are taken at timed intervals & analyzed for
Total microbial count
Specific spoilage organisms (Pseudomonads, LAB)
Viable count compared with sensory evals
Storage trials
Part of microbiological shelf life determination
Simultaneously predicts growth of microorganisms over range of conditions
Validate model with published & in-house data
Predictive modelling
2 aspects to consider in causative agents of disease & associated food vectors
Indicator organisms
Foodborne pathogens & agents
The presence or absence of _ provides indirect evidence concerning a particular feature in the history of the sample
Indicator organisms
Indicator organisms can be any _ group of organisms
tpe
taxonomic, physiological, or ecological
T/F: Indicator organisms are used to assess food quality than food hygiene and safety
FALSE
Indicator organisms are used to assess food hygiene and safety, rather than food quality
Enumerate & explain 7 important characteristics of a food safety indicator
eead gpa
Easily & rapidly detectable
Easily distinguishable from other members of food flora
Always present when pathogen of concern is present
Density correlates with that of pathogen of concern
Growth requirements & rates should be equal to that of POC
Persists slightly longer than POC (to prevent false negatives)
Absent from foods free of POC (to prevent false positives)
Enumerate 4 common indicator organisms
ceeb
Coliforms
Enterobacteriaceae
Enterococci
Bacteriophages
_ is an indicator organism that ferments lactose to acid & gas at 35 C, 48 hrs
Gram-negative, rod-shaped, facultatively anaerobic bacteria
Coliforms
Coliforms are indicators of _
epf
Enteric pathogens
Post-processing contamination
Fecal contamination
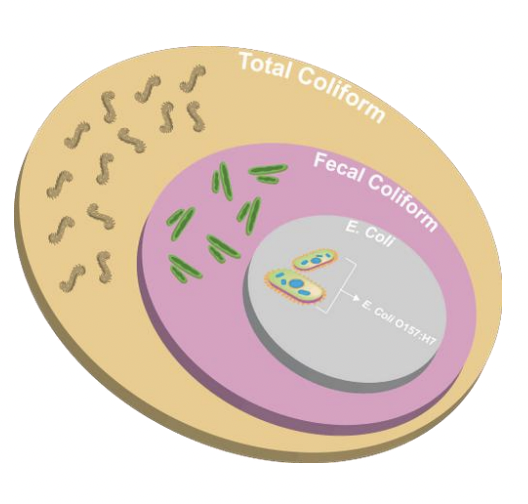
Total coliform vs. Fecal coliform vs. E. coli
Total coliform = general environmental contamination
e.g., ekec Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter
Fecal coliform = fecal pollution
e.g., E. coli = best indicator of recent fecal contam
E. coli O157:H7 = pathogenic strain
_ is the best indicator of fecal contamination
E. coli
Explain multiple tube fermentation technique as coliform test
*35C for 24-48h
Presumptive test: to detect possible coliforms via lactose fermentation
Lauryl Sulfate Tryptose Broth (LSTB) broth with Durham tube
(+)= Gas prod + turbid
Confirmed test = to confirm if gas production was due to coliforms or not
Brilliant Green Lactose Bile Broth (BGLBB) with Durham tube
(+)= Gas prod
Completed test = to confirm E. coli presence
EMBA
(+) colonies w/ dark center & metallic green sheen
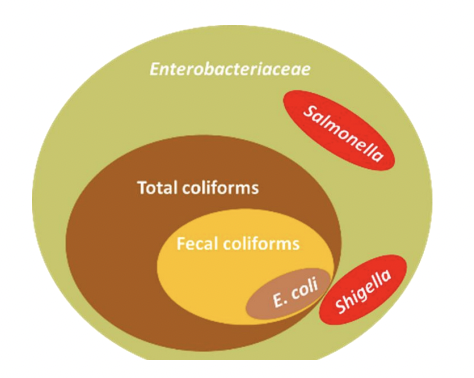
Enterobacteriaceae vs. Total vs. Fecal vs. E. coli
Enterobacteriaceae
Gram (-), bacilli, facultative anaerobe
Total coliforms + Salmonella & Shigella
Total coliforms = ekec Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter
Fecal coliform
E. coli
T/F: Salmonella & Shigella are total coliforms
FALSE
Salmonella & Shigella are not total coliforms but are part of Enterobacteriaceae
_ is an indicator of enteric pathogens
Enterobacteriaceae
part of this group are essey Escherichia, Salmonella, Shigella, Enterobacter, Yersinia
Gram (-), basilli, facultative anaerobes
Indicators of enteric pathogens
Enterobacteriaceae
_ is an indicator of fecal contamination in water
Enterococci
_ is an enterococcal species that indicates presence of human & animal feces
Enterococcus faecium
_ is an enterococcal species that indicates presence of human feces
Enterococcus faecalis
_ is an indicator of waterborne viruses and is present in human fecal matter
Bacteriophages
T/F: Bacteriophages are present in human fecal matter
TRUE
_ is an indicator for hygienic quality of frozen, dried, heat-treated food because they are more resistant to drying than coliforms, die more slowly than E. coli, survives better than pathogens, hence their detection may have little consequence
Enterococci
Enterococci is an indicator for hygienic quality of frozen, dried, heat-treated food because they are _
mds
More resistant to drying than coliforms
Die more slowly than E. coli
Survives better than pathogens, thus detection may be of little consequence
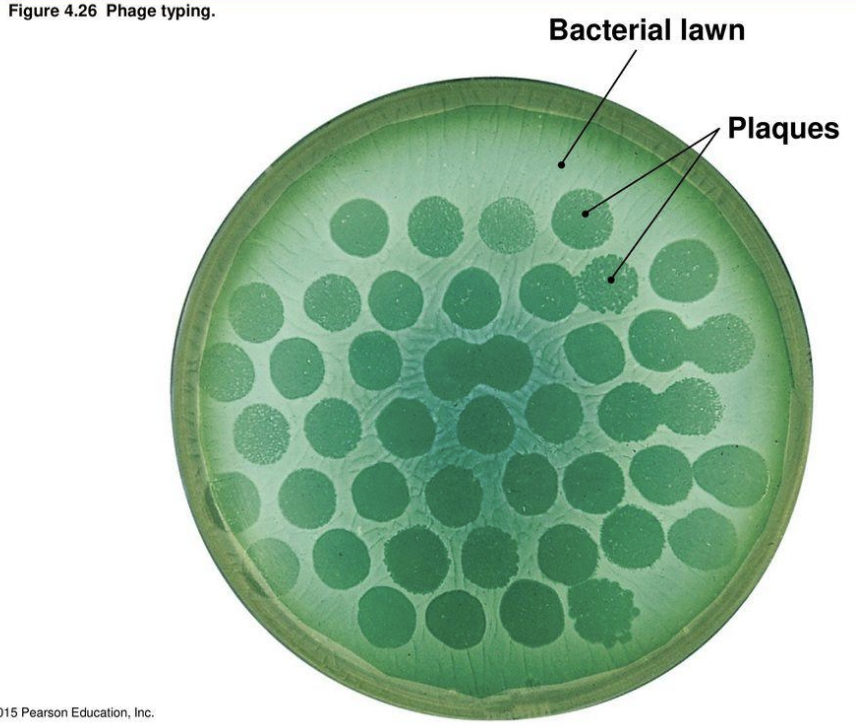
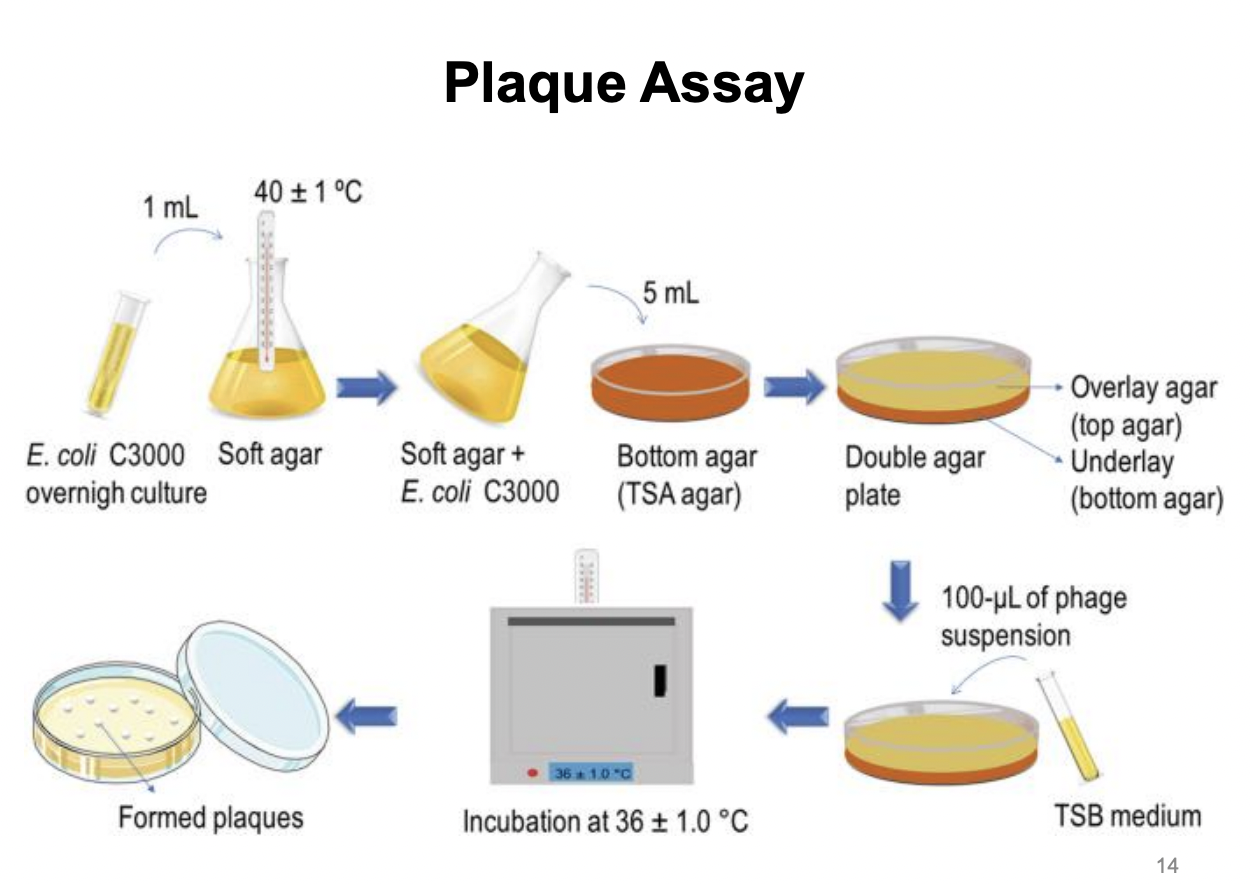
Explain plaque assay pipeline
Create double agar plate by
first pouring TSA agar onto an empty plate as bottom agar
then creating a mix of E. coli overnight culture + soft agar, then pouring this mix on top of solidified bottom TSA agar
Pipette 100 uL phage suspension on top of solidifed E. coli + soft agar mix
Incubate at 36C
Observed formed plaques (indicative of bacterial cells lysed by viruses)
Enumerate 5 foodborne pathogens & agents
bvptp
Bacteria
Viruses
Parasites
Toxins
Prions
Enumerate 15 foodborne bacteria
cam sal e
Campylobacter
Salmonella
E. coli
shi cro vi
Shigella
Cronobacter
Vibrio
bru ye ae
Brucella
Yersinia
Aeromonas
lis sta clo
Listeria
Staphylococcus
Clostridium
bac strep ent
Bacillus
Streptococcus
Enterococcus
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Cause sporadic & self-limiting gastroenteritis
Raw chicken, beef, milk, mushrooms, rbmm
clams, hamburger, water, cheese, pork,
shellfish, eggs, cake icing
Campylobacter
T/F: C. coli cause 80% of Campylobacter self-limiting gastroenteritis, while C. jejuni cause 15%
FALSE
C. coli cause 15% of Campylobacter self-limiting gastroenteritis, while C. jejuni cause 80%
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Cause gei
Gastroenteritis =
Enteric fever =
Invasive systemic disease =
Raw poultry, meat, eggs, milk and dairy
products, vegetables, fruits, chocolate,
coconut, peanuts, fish, shellfish
Salmonella
Cause gei
Gastroenteritis = serovar Enteritidis, Typhi
Enteric fever = Typhi, Paratyphi
Invasive systemic disease = Choleraesuis
Explain the different types of E. coli & disease they cause
Gram (-)
EPEC (Enteropathogenic)
Infant diarrhea
• Raw chicken and beef, fecal-contaminated food or
water
ETEC (Enterotoxigenic)
Traveler’s diarrhea
• Human sewage-contaminated food
• Infected food handlers
EIEC (Enteroinvasive)
Shigellosis-like
Fecal-contaminated food or water, hamburger meat,
unpasteurized milk
STEC (Shiga toxin-producing E. coli)
Hemorrhagic colitis
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (Complication)
• O157:H7 (Strain of major concern)
• Ground beef, poultry, apple cider, raw milk,
vegetables, cantaloupe, hot dogs, mayonnaise, salad
bar items
T/F: Shigella and EIEC both cause hemorrhagic diarrhea
TRUE
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Cause blood/nonbloody diarrhea
Salads, raw vegetables, bakery
products, sandwich fillings, milk,
and dairy products, poultry
Shigella
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Powdered infant formula, plant-based ingredients, vegetables, salads
Infants = meningitis, necrotizing enterocolitis
Elderly = Gastroenteritis, appendicits
Cronobacter
Explain the different types of Vibrio & disease they cause
V. cholerae = watery diarrhea
Seafood, vegetables, cooked rice, ice
V. parahaemolyticus = watery diarrhea + fever + vomiting
Raw or undercooked fish and fishery product
V. vulnificus = watery diarrhea + blood
Seafood, particularly raw oysters
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Sweating, headache, lack of appetite, fatigue, fever (_)
Raw or unheated processed foods of
animal origin (e.g. milk, milk products,
cream, cheese, butter)
Brucella
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Gastroenteritis w/ diarrhea and/or vomiting
Pork products, cured or uncured, milk and dairy
products
Yersinia
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Gastroenteritis
Seafood, snails, drinking water
Aeromonas
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Gastroenteritis
Freshwater fish, shellfish
Plesiomonas
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (-)
Meningitis, sepsis
Can cross the placental barrier
Can grow and survive over a wide range of environmental
conditions (4°C, Low pH, High-salt)
Soft‐ripened cheese, ground meat, poultry, dairy products,
sausages, potato salad, chicken, seafood, vegetables
Listeria
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (+)
Food poisoning
Workers handling foods, meat (especially sliced meat) poultry, fish, canned mushrooms, dairy products, prepared salad dressing, ham, salami, bakery items, custards, cheese
Staphylococcus aureus
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (+), endospore-forming (anaerobic), describe 2 types
Clostridium
C. perfringens (enterotoxins) = food poisoning
Meat, chicken gravies, beans,
seafood
C. botulinum (neurotoxin) = botulism
Improperly canned or
fermented goods, honey
Neurological condition characterized by weakness or paralysis, reduced muscle tone (hypotonia)
Botulism
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (+), endospore-forming
Diarrhea
Food infection (not only toxins)
Meats, milk, vegetables, and fish
Emetic toxin/syndrome
Food poisoning/food intoxication
Rice products, starchy foods (e.g. potato, pasta and cheese products)
Bacillus cereus
Streptococcus (Gram + cocci) species of concern that is B-hemolytic
Temperature‐abused milk, ice cream,
eggs, steamed lobster, ground ham,
potato salad, egg salad, custard, rice
pudding, shrimp salad
Sore throat and scarlet fever
S. pyogenes
Foodborne bacteria
Gram (+) fecal streptococci
Meat, sausage, evaporated milk,
cheese, raw and pasteurized
milk
Acute and self-limiting diarrhea
Enterococcus
Foodborne viruses are likely _
phage and animal viruses
In foodborne viruses, food serves as _
vehicle of transmission
Don’t replicate in food/water
Numbers don’t increase during transport/processing
Low infectious dose (implies that minimal contam → widespread illness)
_ are environmentally stable, relatively resistant to heat, disinfection, pH changes
Retains their infectivity over time and within the food matrix
Human fecal contamination shed in large amounts in
feces
Foodborne viruses
What are the viruses associated with the ff. foods?
Salad + fruits = ?
Salad + shellfish = ?
Raw shellfish + raw/undercooked pork products = ?
Fruits + vegetables + clams = ?
Salad + fruits = Rotavirus
Salad + shellfish = Norovirus
Raw shellfish + raw/undercooked pork products = Hepatitis E
Fruits + vegetables + clams = Hepatitis A
Explain 5 ways thru which viruses get into food supply
fhpaf
Shellfish contamined with fecal-polluted marine water
Human sewage pollution of drinking & irrigation water
RTE & prepared foods contam by poor personal hygiene
Aerosolization of vomit
Contact with fomites
_ include eukaryotes such as protozoa and helminths
Parasites
Protozoa
Hydrocephalus and blindness in children
Transplacental infection
Raw or undercooked meat, vegetables, goat’s milk, food and water contaminated with cat feces
Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasmosis
Protozoa
Watery and explosive diarrhea
Raspberries, lettuce and basil or basil‐containing products
Cyclospora cayetanensis
Protozoa
Fever, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia
Raw milk, drinking water, apple cider
Cryptosporidium parvum
Beef tapeworm
Taeniasis
Raw or undercooked beef
Taenia saginata
Pork tapeworm
Taeniasis
Cysticercosis (larval cyst in the brain, muscle, or other tissues)
Raw or undercooked pork
Taenia solium
Helminth
Nematode (roundworm)
Nonspecific abdominal stress
Raw/undercooked fish
Anisakis simplex
Food poisoning vs. Food infection
Food poisoning = toxins cause illness; does not require infection by viable cell
Food infection = illness caused by viable cells
T/F: Food infection occurs when it’s the microbial toxin that cause the illness itself and not viable cells
FALSE
Food poisoning occurs when it’s the microbial toxin that cause the illness itself and not viable cells
Toxins cause food poisoning and can be produced by which groups of organism?
paf
Protists
Algae
Fungi
Enumerate & explain 4 types of seafood and shellfish poisoning (due to toxins); primary causes
*primarily caused by algae, protists
dpan
Diarrheic shellfish poisoning
Mussels, oysters, scallops, clams mosc
e.g., Dinophysis fortii (okadaic acid) protist
Paralytic
Mussels, oysters, clams, fish mocf
e.g., Alexandrium catenella (saxitoxin) protist
Amnesic
Mussels
e.g., Pseudonitzschia pungens (domoic acid) algae
Neurotoxic
Mussels, oysters, scallops, clams
e.g., Cymnodinium breve (brevetoxin) protist
Type of seafood & shellfish poisoning you can get from consuming:
Mussels
Amnesic
diarrheic (mosc), paralytic (mocf), neurotoxic (mosc)
Type of seafood & shellfish poisoning you can get from consuming:
Mussels, oysters, clams, fish
Paralytic
diarrheic (mosc), neurotoxic (mosc), amnesic (m)
Type of seafood & shellfish poisoning you can get from consuming:
Scallops
Diarrheic, neurotoxic
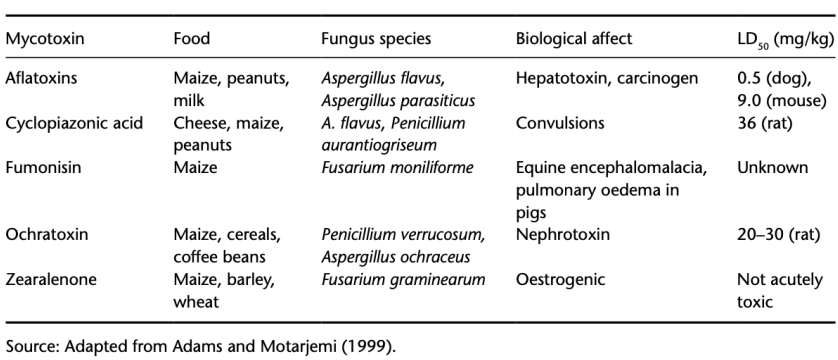
_ are fungal secondary metabolites that can cause fungal diseases called _
Mycotoxins
Mycotoxicosis
Enumerate most common mycotoxins
acofz
Aflatoxin
Food: Maize, peanuts, milk
Bio effects: Hepatoxins (liver), carcinogens
LD50: 0.5 (dog)
Cyclopiazonic acid
Maize, peanuts, cheese
Convulsions
9 (rat)
Ochratoxin
Maize, cereals, coffee beans
Nephrotoxins (kidney)
20-30 (rat)
Fumonisin
Maize
Equine encephalomalacia, pulmonary edema in pigs
Unknown
Zearalenone
Maize, barley, wheat
Oestrogenic
Not acutely toxic
_ are small proteinaceous infectious agents with no nucleic acids but is a modified form of normal cellular protein (misfolded protein); can come from cattle meat and milk
Prions
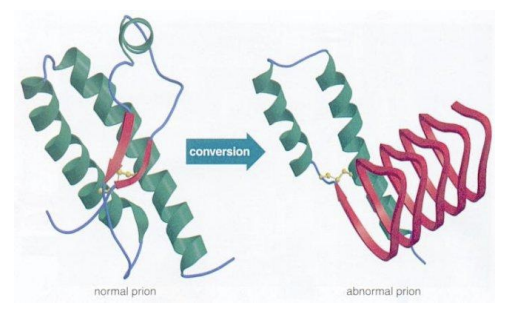
T/F: Prions are subviral agents with proteins and nucleic acid
FALSE
Prions are subviral agents with proteins and NO nucleic acid
Prions are proteins normally expressed in the _; however, infectious, misfolded ones can cause _
Brain
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy
T/F: Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are known to affect only humans and animals
TRUE
The native form of prion protein is not only expressed in humans but also in _
mammals, birds, reptiles mbr
Enumerate & explain 4 major characteristics of prion diseases
lldp
Long incubation period (years)
Loss of muscle coordination (cerebellum)
Dementia (loss of memory, intellect, poor judgment)
Progressive insomnia (marked loss of slow-way-eye-movement phases)
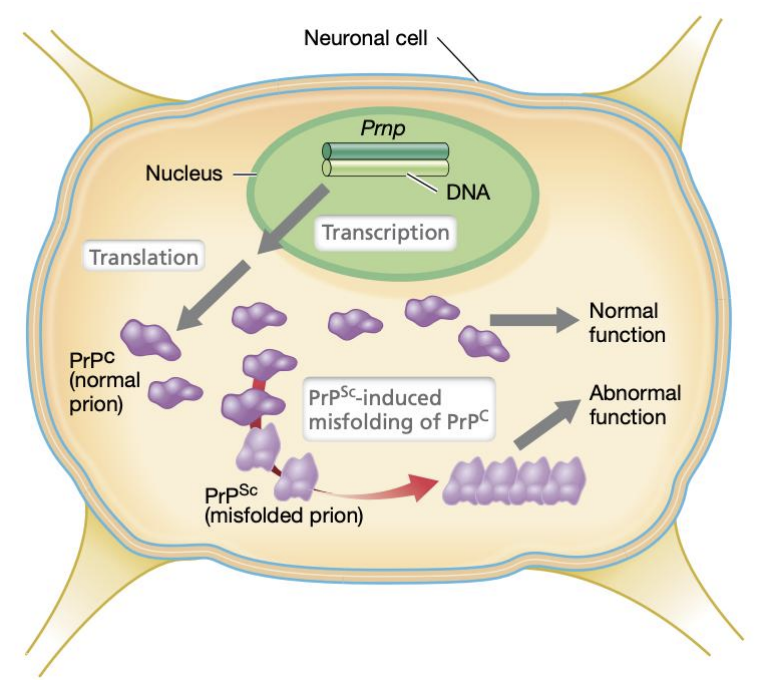
_ is the gene coding for prion protein cellular (PrPC)
Prnp (prion protein gene)
Prnp is the gene coding for _
Prion protein cellular (PrPC)
T/F: Mammals, birds, and reptiles have Prnp gene and thus express PrPC
TRUE
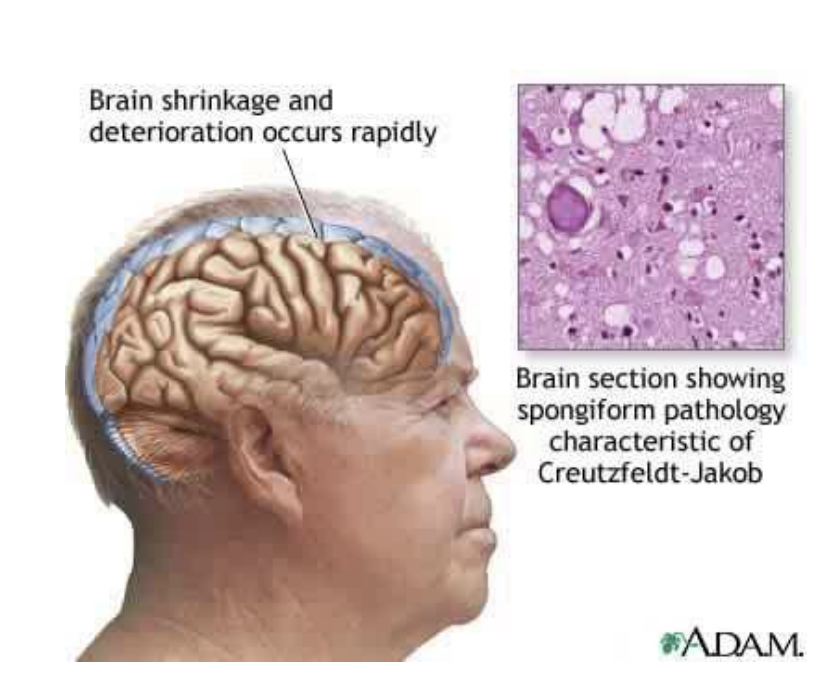
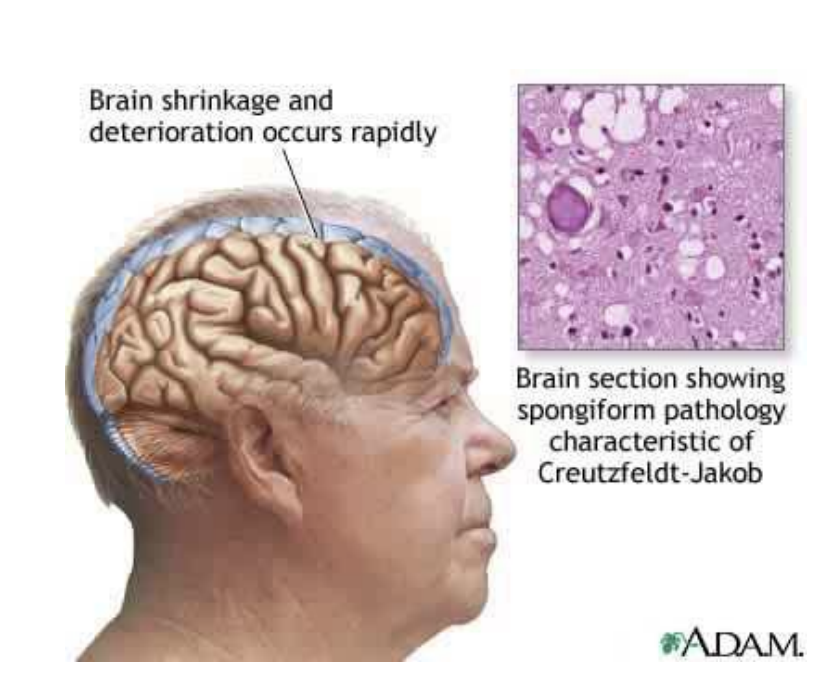
Enumerate 7 symptoms/manifestations of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
mbv pp cd
Memory problems
Behavioral changes
Vision problems
Poor muscle coordination
Progress quickly to dementia
Coma
Death
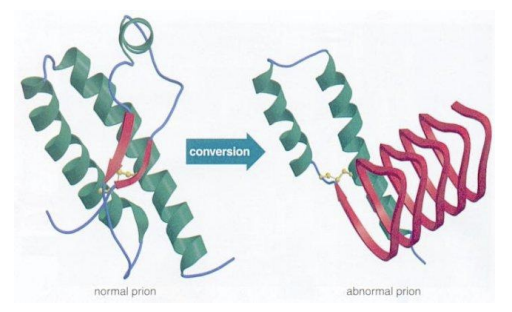
_ is the normal cellular prion, while _ is its pathogenic form
PrPC (prion protein cellular)
PrPSc (prion protein scrapie)
_ is the name of the disease caused by prion in sheeps
Scrapie
T/F: It is hypothesized that normal cellular prions (PrPC) only have to be exposed to misfolded prions (PrPSc) to become infected
TRUE
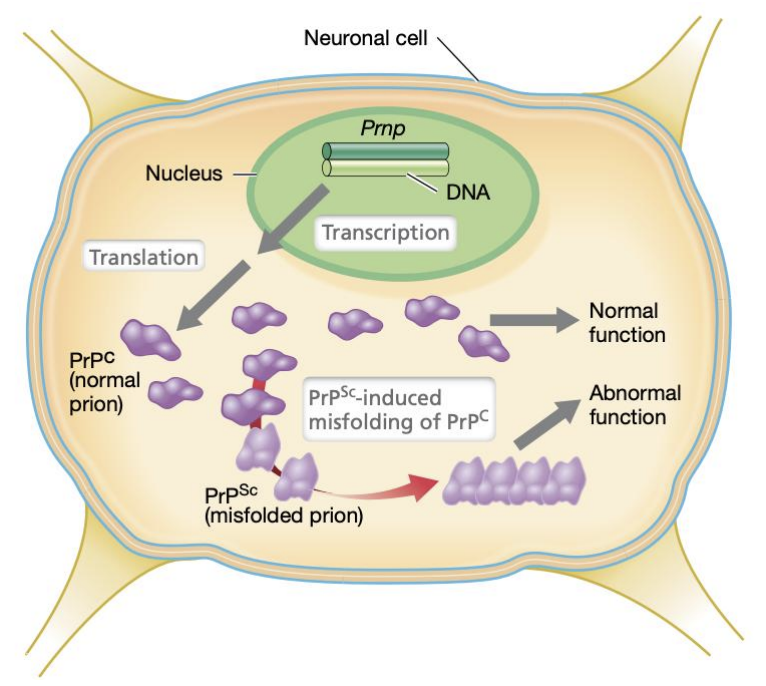
Enumerate & explain 3 common characteristics of misfolded prions
pia
Protease-resistant (doesn’t undergo degradation)
Insoluble
Form amyloids → insoluble crystalline fibers; prion aggregates; sponge-like structure
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, include _
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (humans)
Familial insomnia
Scrapie (sheeps)
BSE (cattles)
Kuru “laughing disease” = get when u eat brains (result of cannibalism)
What are the limitations to studying prions?
LS
Require a long incubation period
Subject of study is hard to obtain, e.g., humans and mammals
Not culturable = a living organism is needed