M4 - U3 - S4 - Digital Certificates and Anti-Phishing
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
True
The public key can’t be used to decrypt the message once encrypted
Only the linked private key can be used to do that
True or False: When a web browser communicates with a secure (HTTPS) server, it accepts the server's digital certificate to use its public key to encrypt communications
Asymmetric Encryption
A method of encrypting and decrypting data using a pair of keys: a public key and a private key
The public key is used to encrypt plaintext
The private key is used to decrypt the resulting ciphertext
Certificate Authority
Third party/entity that issue digital certificates to verify the identity of users, computers, and organisations
Relied on by browsers and servers to vouch for server identity
True
True or False: Having a certificate is not in itself any proof of identity
Public Key Infrastructure
A set of technologies and processes that use encryption to protect and authenticate digital communications
Root Certificates
A browser is pre-installed with a number of ____ which are automatically trusted
These represent the commercial CAs that grant certificates to most of the companies that do business on the web
True
Third-party browsers such as Firefox and Chrome maintain their own stores
True or False: Windows has a certificate store that Microsoft Internet Explorer and Edge browsers use
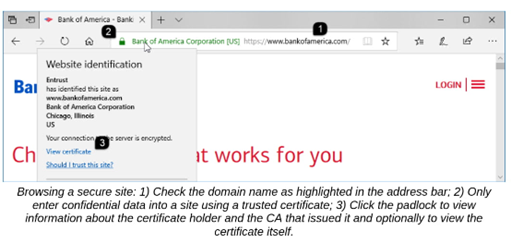
Padlock
Certificate is valid and trusted - click for info
Padlock + Green Address bar
Certificate is highly trusted - site owner has gone through even more rigorous identity validation procedure
Maroon Address Bar
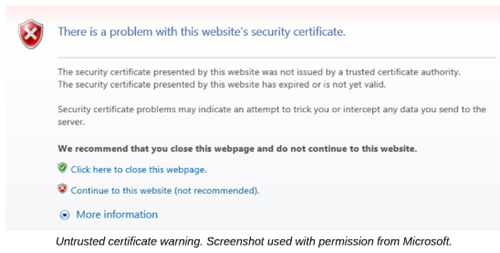
Certificate is untrusted
Site will be blocked by warning message
Indications of certificate validity
True
If a certificate has not been issued by a one of the trusted root CAs, Windows will warn you that the publisher cannot be verified
When you try to install an add-on or other type of application
True or False: Digital certificates are also used to verify the identity of software publishers
Domain name
Another important step in validating the identity of a site is to confirm its ________
Phishing/Pharming
Techniques to direct users to fake or manipulated websites
Often use well-known subdomains as part of the address
e.g. comptia. phishing. org
The browser highlights the registered domain part of the address so that you can verify it
Anti-phishing protection software
Most browsers run ______ to block access to URLs known to be the source of phishing attempts or that host malware