Emotion W3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
Autonomic specificity
* in line with James-Lange
* = each distinct patterns of ANS activation lead to experience of different emotion
* prove from recent research:
* →over a dozen of distinct ANS pathways tht actitivate different regions of body
* →different ways in which components of ANS could combine
* = each distinct patterns of ANS activation lead to experience of different emotion
* prove from recent research:
* →over a dozen of distinct ANS pathways tht actitivate different regions of body
* →different ways in which components of ANS could combine
2
New cards
Embodiement
* higher order thought processes (emotion and cognition) are largely influenced by bodily processes
* they are embedded in bodily representations
* emotions and body are intertwined
* they are embedded in bodily representations
* emotions and body are intertwined
3
New cards
Cannons Criticism on James
* ANS response not specific enough to differentiate between emotions
* Changes in bodily sensation to diffuse
* Changes to small to be meaningful
* ANS to slow to be source of emotion
* ANS response appear also regardless of emotion (fe: fever)
* We are not sensitive to all ANS responses
* Changes in bodily sensation to diffuse
* Changes to small to be meaningful
* ANS to slow to be source of emotion
* ANS response appear also regardless of emotion (fe: fever)
* We are not sensitive to all ANS responses
4
New cards
**Bart and cannon hypothesis: NS in 3 levels**
1. hindbrain, reflex pathways for simple functions such as movements
2. structures involved in emotion
3. cerebral cortex which controls and inhibtits lower levels
\
Prove:
* children are not fully able to control emotions as cortex is not fully developed yet
* no reduction of emotion occurs:
* if viscera is served (part of brain where James thought emotion would arise) and if disconnection between guts and brain → Critique on James)
* but if there is a disconnection between cortex and subcortical regions → emotion changes \n → his theory cortex inhibits subcortical regions
5
New cards
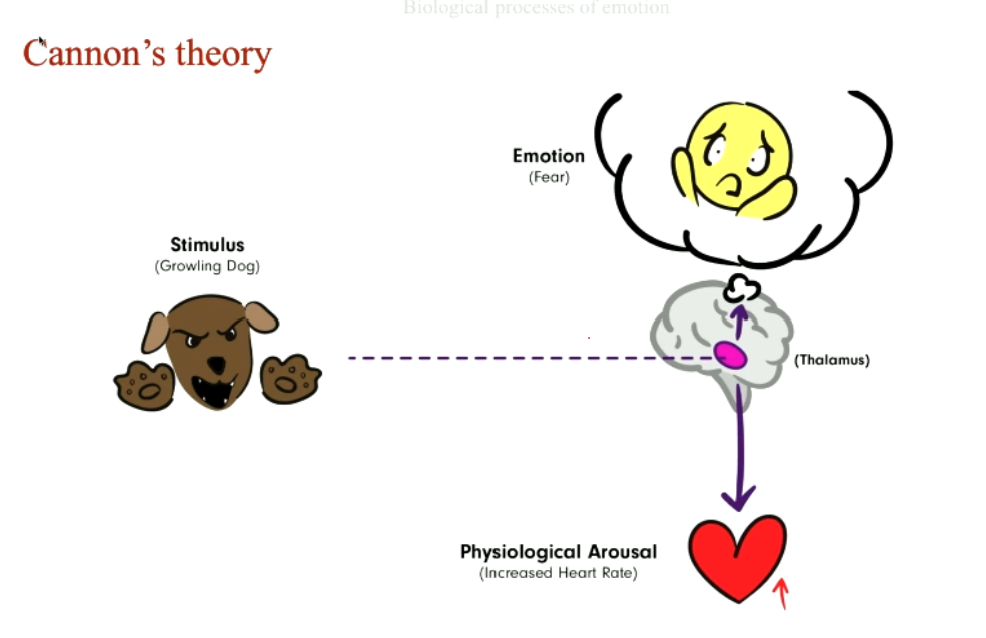
Cannon Bard Theory
* Look at model in picture
* Brain(thalamus) registers stimulus → produces the arousal and the emotion
* bodily sensations co-occur with emotions, yet independent
* autonomic specificity doesn't exist (one-arousal-fits-all model)
\
* Brain(thalamus) registers stimulus → produces the arousal and the emotion
* bodily sensations co-occur with emotions, yet independent
* autonomic specificity doesn't exist (one-arousal-fits-all model)
\
6
New cards
Facial action coding system (by Ekmann et al.)
=Muscle by muscle instruction to configure face in a specific emotion
\-> while that ANS was measured
results
* moving facial muscles change emotional experience
* different autonomic reactions (galvanic skin response and increasing heart rate differ) to different negative emotions (fe between anger and sadness)
* different autonomic reactions to different positive emotions
\->supports Autonomic Specificity
\-> while that ANS was measured
results
* moving facial muscles change emotional experience
* different autonomic reactions (galvanic skin response and increasing heart rate differ) to different negative emotions (fe between anger and sadness)
* different autonomic reactions to different positive emotions
\->supports Autonomic Specificity
7
New cards
Hohmann vs Bermond
Hohmann: participant with paralysis (as a result of spinal cord lesion)
* reduced fear and anxiety
→evidence for Autonomic Specifity
Boermond: If Hoehmann is right then all emotions should be reduced
also observed participants with paralysis:
* normal experience of sadness and happiness
* heightened fear and anger
→Increase post in-jury and not decrease
* reduced fear and anxiety
→evidence for Autonomic Specifity
Boermond: If Hoehmann is right then all emotions should be reduced
also observed participants with paralysis:
* normal experience of sadness and happiness
* heightened fear and anger
→Increase post in-jury and not decrease
8
New cards
__experiment: adrenaline injections__
\
some participants received info about effect on behavior some not
→ p who did not know about effect were influenced by behavior of accomplice of researcher who either behaved euphoric or angry
* different contexts elicit different emotions
→ no support for Autonomic specificity
* results not replicated
some participants received info about effect on behavior some not
→ p who did not know about effect were influenced by behavior of accomplice of researcher who either behaved euphoric or angry
* different contexts elicit different emotions
→ no support for Autonomic specificity
* results not replicated
9
New cards
Schachter and Singer influence
→their model is used today
* added to the interest in appraisal and in **misattribution of arousal** =when arousal does not have an obvious source people tend to label arousal accounting to situation
* **transfer of excitation= a**rousal can be transferred to other situations which can effect emotional experience in social world
* added to the interest in appraisal and in **misattribution of arousal** =when arousal does not have an obvious source people tend to label arousal accounting to situation
* **transfer of excitation= a**rousal can be transferred to other situations which can effect emotional experience in social world
10
New cards
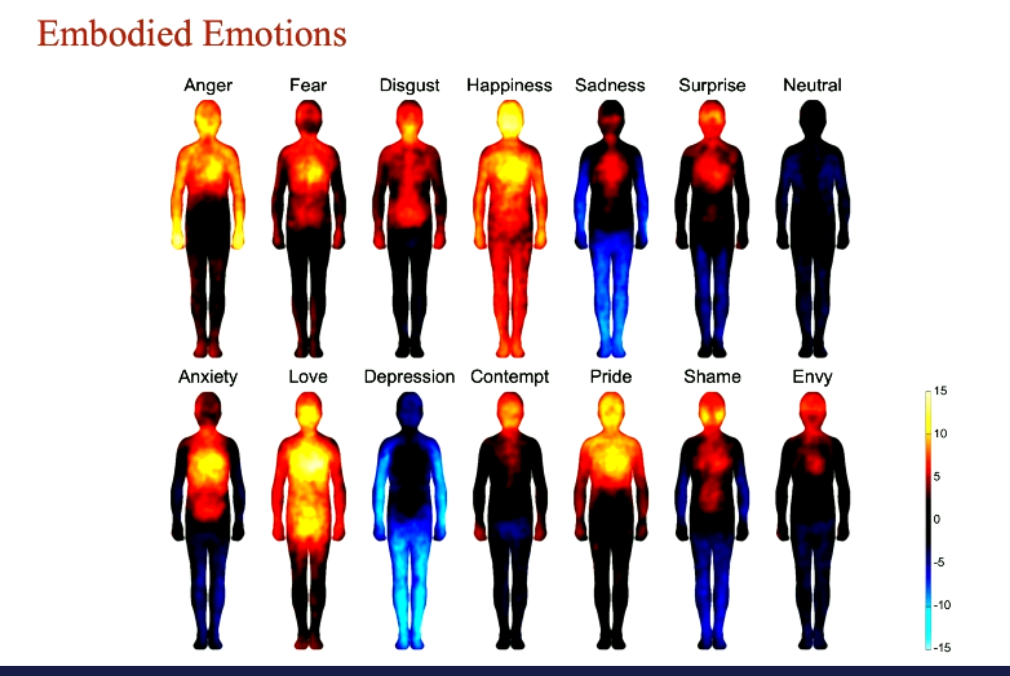
Bodily sensation map
* shows decreased and increased activity of body parts associated with an emotion
* each map of body is associated with different emotion
\
* each map of body is associated with different emotion
\
11
New cards
Bodily reverberations
term introduced by James
they are product of:
* ANS
* endocrine system
* immune system
* (=including breathing, blood flow, heart palpitation, trembles, goosebumps, lacrimal glands that produce tears, and different muscle movements)
they are product of:
* ANS
* endocrine system
* immune system
* (=including breathing, blood flow, heart palpitation, trembles, goosebumps, lacrimal glands that produce tears, and different muscle movements)
12
New cards
endocrine system
responsible for synthesis and distribution of hormones in body
(Pineal gland, Pituitary gland, Hypothalamus, Adrenal glands…)
(Pineal gland, Pituitary gland, Hypothalamus, Adrenal glands…)
13
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
ANS
* cortex -> limbc system + hypothalamus -> ANSS and body parts -> send feedback
* Regulate internal conditions of body: control digestion, blood flow, temperature, behaviour related to emotion (such as defensive behavior, aggression and sexual behavior
* maintains homeostasis of body in order for individual to adapt to fluctuations of environment
* originate from parts of spinal cord and are controlled by neurotransmitters
* two parts of the system
* cortex -> limbc system + hypothalamus -> ANSS and body parts -> send feedback
* Regulate internal conditions of body: control digestion, blood flow, temperature, behaviour related to emotion (such as defensive behavior, aggression and sexual behavior
* maintains homeostasis of body in order for individual to adapt to fluctuations of environment
* originate from parts of spinal cord and are controlled by neurotransmitters
* two parts of the system
14
New cards
2 Parts of the ANS
\
* **parasympathetic branch: responsible for restorative proces**s -> makes us relax
→ reduce heart ,rate blood pressure...
\+ activation of digestive processes
* **sympathetic branch: prepares individual for fight or flight response** (physically demanding activities) increasing processes that provide energy for body:
→increasing heart rate, blood pressure and cardiac output
\+ stops digestion
\+decreases activity of immune system by reduding natural urotransmitters
* **parasympathetic branch: responsible for restorative proces**s -> makes us relax
→ reduce heart ,rate blood pressure...
\+ activation of digestive processes
* **sympathetic branch: prepares individual for fight or flight response** (physically demanding activities) increasing processes that provide energy for body:
→increasing heart rate, blood pressure and cardiac output
\+ stops digestion
\+decreases activity of immune system by reduding natural urotransmitters
15
New cards
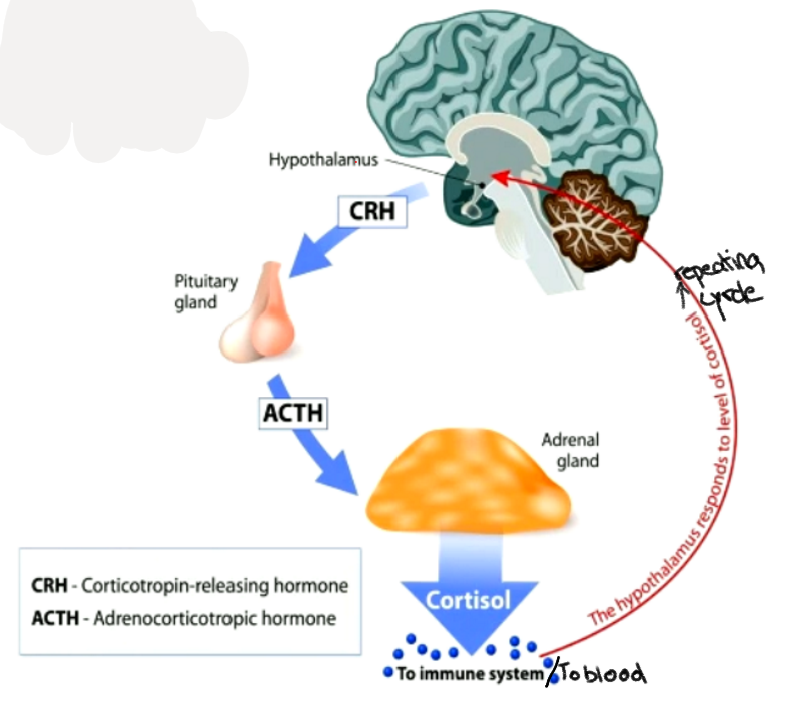
HPA Axis
* Hypothalamic-Pituitary-adrenal Axis →stress response system and part of endocrine system
* Linked to fear but large individual differences
* can have positive effects: increased focus performance generally
\
* Linked to fear but large individual differences
* can have positive effects: increased focus performance generally
\
16
New cards
Cortisol
increases gluose production (needed for metabolically demanding action fight- flight)
increases heart rate and blood pressure-> blood supply to relevant muscles
suppresses immune system
increases heart rate and blood pressure-> blood supply to relevant muscles
suppresses immune system
17
New cards
Trier social stress task
P must perform a spontaneous speech in front of a critical audience ->stressful event
* ACTH increase right afterwards and than bit later also cortisol increase (timeframe individually)-> proves that both are related to each other and to stressful task
* elicts emotion fear -> recent study show that cortisol is more correlated to anger than fear
* ACTH increase right afterwards and than bit later also cortisol increase (timeframe individually)-> proves that both are related to each other and to stressful task
* elicts emotion fear -> recent study show that cortisol is more correlated to anger than fear
18
New cards
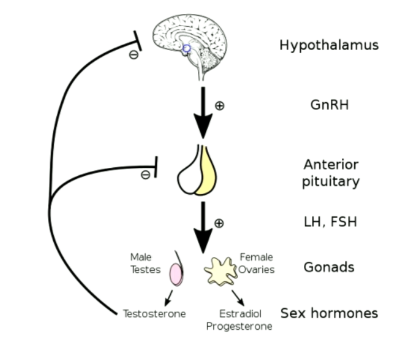
HPG axis
Hypthalamic-Pituritary-Goand-axis
\
\
19
New cards
testestorone
siehe pic

20
New cards
HPG vs HPA axis
siehe pic

21
New cards
Discovery of Neurochemicals by Galvani:
\
If electricity is passed onto dead frog legs they contract
\
\
If electricity is passed onto dead frog legs they contract
\
\
22
New cards
Discovery of Neurochemicals: Loewi
First experiment
* Electrical stimulation of a heart 1 → heart rate slows down
* heart 2 (is in same fluid as heart 1) → heart rate also slows down
→ he hypothised this happens bcs of neurochemicals
\
Second experiment
1. stimulation of vagus nerve of donor heart
2. donor heart rate slows down
3. Remove fluid sample from donor heart
4. add it to recipient heart
5. Recipient heart rate slows down
\
* Electrical stimulation of a heart 1 → heart rate slows down
* heart 2 (is in same fluid as heart 1) → heart rate also slows down
→ he hypothised this happens bcs of neurochemicals
\
Second experiment
1. stimulation of vagus nerve of donor heart
2. donor heart rate slows down
3. Remove fluid sample from donor heart
4. add it to recipient heart
5. Recipient heart rate slows down
\
23
New cards
Neurochemicals:
=located in different brain regions and related to behavior
\
1. Neurotransmitters
* Communication between neurons
* Norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, GABA
\
2. Hormons
* Communication via blood circuit
* take longer to act then neurotransmitters, but effects last longer
* Adrenaline, cortisol, peptides
* controlled by pituitary which is influenced by hypothalamus
\
3. neuromodulators
* Signal enhancers/ diminishers
* Most are peptides (like endogenous opiates) which modulate pain system
\
1. Neurotransmitters
* Communication between neurons
* Norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, GABA
\
2. Hormons
* Communication via blood circuit
* take longer to act then neurotransmitters, but effects last longer
* Adrenaline, cortisol, peptides
* controlled by pituitary which is influenced by hypothalamus
\
3. neuromodulators
* Signal enhancers/ diminishers
* Most are peptides (like endogenous opiates) which modulate pain system
24
New cards
Serotonin
* essential to emotional experience
* Processing of affective info of faces
* involved in processes that balance
* Heuristic processes/fast thinking in subcortex
* Deliberate procesess/ slow thinking in frontal lobes
\->when serotonin levels are low fast and intuitive levels weigh more
* Low levels of serotonin
* antisocial tendencies (-> dysregulation of frontal lobes of aggressive tendencies)
* Depression (frontal lobes not regulating negative emotions)
* ASD
* low levels of agreeableness and constraint high levels of neuroticism
* \
* Processing of affective info of faces
* involved in processes that balance
* Heuristic processes/fast thinking in subcortex
* Deliberate procesess/ slow thinking in frontal lobes
\->when serotonin levels are low fast and intuitive levels weigh more
* Low levels of serotonin
* antisocial tendencies (-> dysregulation of frontal lobes of aggressive tendencies)
* Depression (frontal lobes not regulating negative emotions)
* ASD
* low levels of agreeableness and constraint high levels of neuroticism
* \
25
New cards
Serotonin and Depression
SSRI increase serotonin levels in synaptic cleft by blocking its reuptake
→ less negattive affect im depression
\
early theories: insufficient serotonin might cause depression
\
→ less negattive affect im depression
\
early theories: insufficient serotonin might cause depression
\
26
New cards
Oxytocin
* Hormone produced in hypothalmus
__*Oxytocin release has effect on*__
* **social processes:** involved in lactation, maternal (mütterlich) bonding, sexual interaction, promotes social sensibilities to silent social cues and in Group prosocial behaviour
* **cognitive processes:** social and olfactory memory, also emotional memoories (because it makes certain experiences more emotional)
* **neurendocrine**: reduces activity of HPA axis→ less Cortisol produced if Oxitocin present, supresses hunger
* **autoregulation:** autoexcitation during birth and suckling
* **emotional:** reduces anxiety (by enhancing prefrontal circuits which inhibit limbic system) and increases pos. mood
* might increase generoyity and empathy
\
__*Oxytocin release has effect on*__
* **social processes:** involved in lactation, maternal (mütterlich) bonding, sexual interaction, promotes social sensibilities to silent social cues and in Group prosocial behaviour
* **cognitive processes:** social and olfactory memory, also emotional memoories (because it makes certain experiences more emotional)
* **neurendocrine**: reduces activity of HPA axis→ less Cortisol produced if Oxitocin present, supresses hunger
* **autoregulation:** autoexcitation during birth and suckling
* **emotional:** reduces anxiety (by enhancing prefrontal circuits which inhibit limbic system) and increases pos. mood
* might increase generoyity and empathy
\
27
New cards
Noreadrenaline/ Norepinephrine
= Neurotransmitter synthesised in Locus Coeruleus (LC)
→ 90% of neurons are noradrenergic
__*has widespread in projection:*__ variety of processes
* wakeful/sleep
* attention
→ higher order area
* pupil response: high LC activity pupils dilate, Less LC activity pupils constrict
* arousal
→subordinate areas
→ 90% of neurons are noradrenergic
__*has widespread in projection:*__ variety of processes
* wakeful/sleep
* attention
→ higher order area
* pupil response: high LC activity pupils dilate, Less LC activity pupils constrict
* arousal
→subordinate areas
28
New cards
noradrenaline cortical enhancer
Emotional arousal -> activation of LC -> increase noradrenaline -> noradrenaline modulates cortical circuits to enhance certain processes
29
New cards
Yerkes Dodson Curve
Low arousal on easy tasks -> no good performance
Low arousal on difficult task good performance
High arousal on easy task -Y good performance
High arousal on difficult tasks ->no good performance
Low arousal on difficult task good performance
High arousal on easy task -Y good performance
High arousal on difficult tasks ->no good performance
30
New cards
Noreadrenaline and Emotion
Pupil size increases during arousal
cognitive effortful tasks also influence pupil size
Noradrenaline: signalling accumulation of evidence (=thinking about evidence for other persons felt emotion )
Pupil dilation reflect the confidence in decision and predicts decision about pos/neg emotion
cognitive effortful tasks also influence pupil size
Noradrenaline: signalling accumulation of evidence (=thinking about evidence for other persons felt emotion )
Pupil dilation reflect the confidence in decision and predicts decision about pos/neg emotion
31
New cards
MacLean
* Forebrain and three distinct systems → “1 mind, 3 brains”
* sensory impulses from body and outside world reach thalamus and are directed into 3 main pathways
* each has a different evolotionary stage and species dependent functions
\
* sensory impulses from body and outside world reach thalamus and are directed into 3 main pathways
* each has a different evolotionary stage and species dependent functions
\
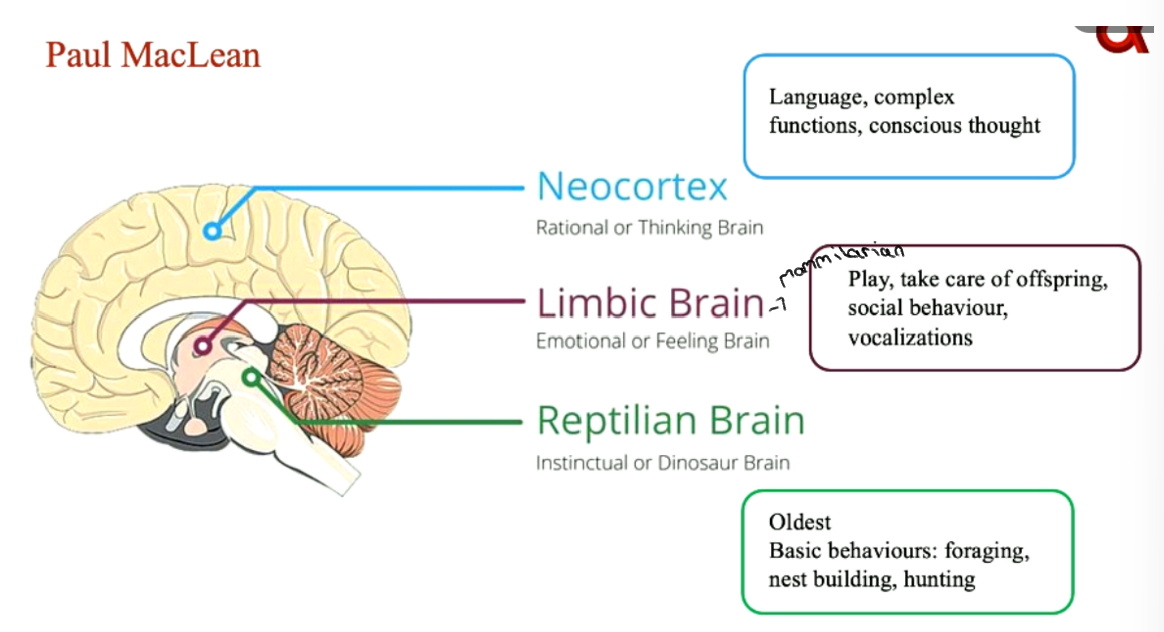
32
New cards
MacLean-Panksepp conjunction:
* each distinct type of emotion is based on particular part of limbic system brain circuity
* creating set of species characteristic brain systems and behaviors
* creating set of species characteristic brain systems and behaviors
33
New cards
limbic system
* Centre of emotions
* Includes thalamus, hippocampus and amygdala
* Closely connected to hypothalamus controls,
\
* Includes thalamus, hippocampus and amygdala
* Closely connected to hypothalamus controls,
\
34
New cards
Amygdala Fear Centre
* Early theories brains centre of fear
* helps to ensure survival
* amygdala damage no behavioral & physiological response to threat
* \
* helps to ensure survival
* amygdala damage no behavioral & physiological response to threat
* \
35
New cards
Amygdala sonstiges
\
* depressive individuals have heightened amygdala activity
* plays role in emotional memory and in assessing valence (goodness or badness of stimuli)
* More intense stimuli-> higher activation of amygdala
* emotional profile predicts intensity of amygdala activation in response to intense stimuli fe: looking at life in pos way -> greater activation to intense pos stimuli and
* depressive individuals have heightened amygdala activity
* plays role in emotional memory and in assessing valence (goodness or badness of stimuli)
* More intense stimuli-> higher activation of amygdala
* emotional profile predicts intensity of amygdala activation in response to intense stimuli fe: looking at life in pos way -> greater activation to intense pos stimuli and
36
New cards
Amygdala anatomy
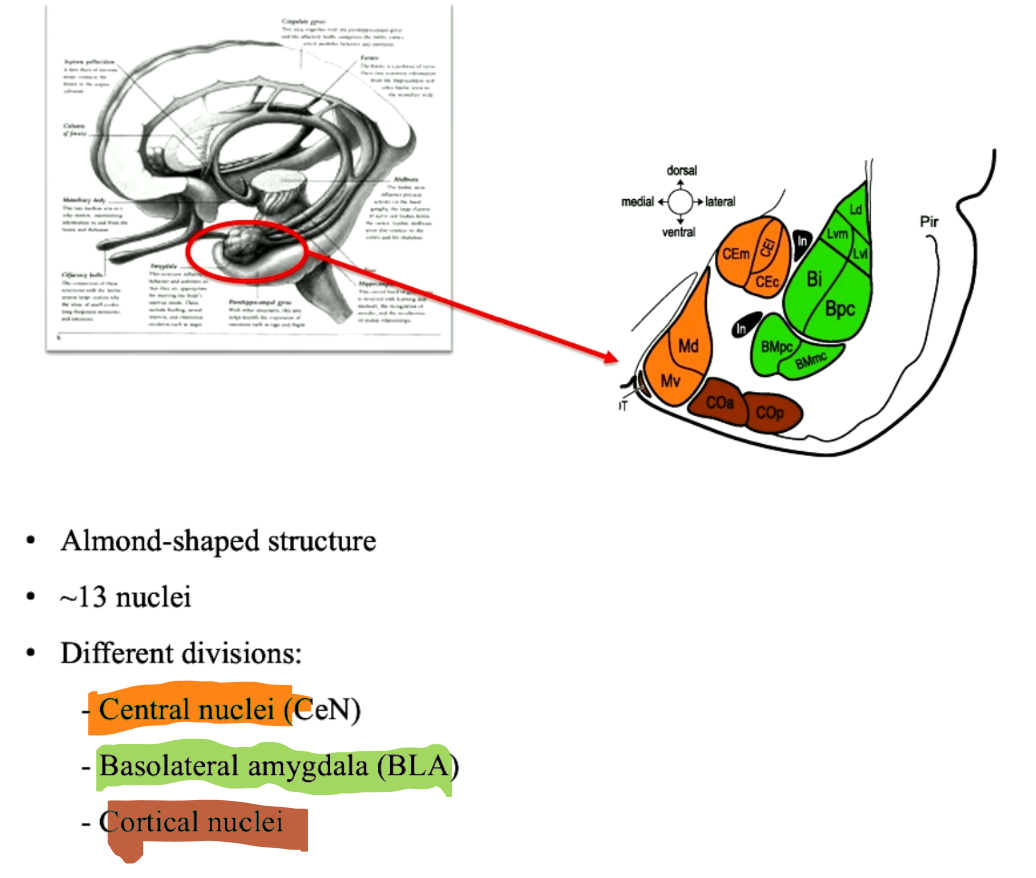
37
New cards
Basolateral amygdala
**Basolateral amygdala**
input - linked to prefrontal cortex
learning processes: **treat conditioning** (with Conditioned Stimulus - unconditioned stimulus associations) + **stimulus outcome**
\
\
\
input - linked to prefrontal cortex
learning processes: **treat conditioning** (with Conditioned Stimulus - unconditioned stimulus associations) + **stimulus outcome**
\
\
\
38
New cards
Central Nucleus
output produce fear response:
* ANS
* startle (erschrecken) reactions
* activation of neurotransmitter systems noradrenaline
* arousal
* ANS
* startle (erschrecken) reactions
* activation of neurotransmitter systems noradrenaline
* arousal
39
New cards
amygdala functions
Emotions
Fear/Defensive processing
* Pavlovian learning (dog) (stimulus-outcome)
* Instrumental learning (reward) (stimulus-response)
→ Fear conditioning acoustic startle and skin conductance
Attention
Autonomic reactions
Social cognition
* Emotions from faces, relevance
\
Fear/Defensive processing
* Pavlovian learning (dog) (stimulus-outcome)
* Instrumental learning (reward) (stimulus-response)
→ Fear conditioning acoustic startle and skin conductance
Attention
Autonomic reactions
Social cognition
* Emotions from faces, relevance
\
40
New cards
LeDoux Amygdala
* detection of fear, but no role in concious experience of fear
* Subjective responses (fear and anxiety are produced by higher-order brain circuits (prefrontal cortices)
Evidence: Damage to amygdala eliminates response, but not feeling of fear
+
* emotional conditioning is possible: especially connections between negative stimuli is quickly made and slow to extinguish
* Subjective responses (fear and anxiety are produced by higher-order brain circuits (prefrontal cortices)
Evidence: Damage to amygdala eliminates response, but not feeling of fear
+
* emotional conditioning is possible: especially connections between negative stimuli is quickly made and slow to extinguish
41
New cards
before LeDoux the fear centre view of amgdala function
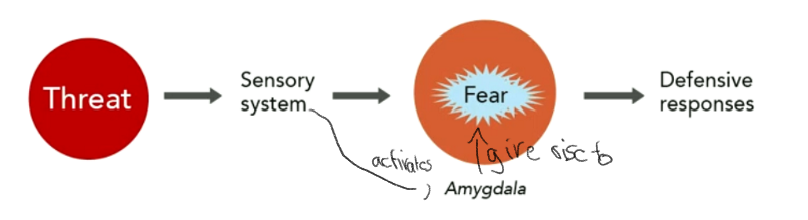
42
New cards
Le doux 2systems view of threat processing
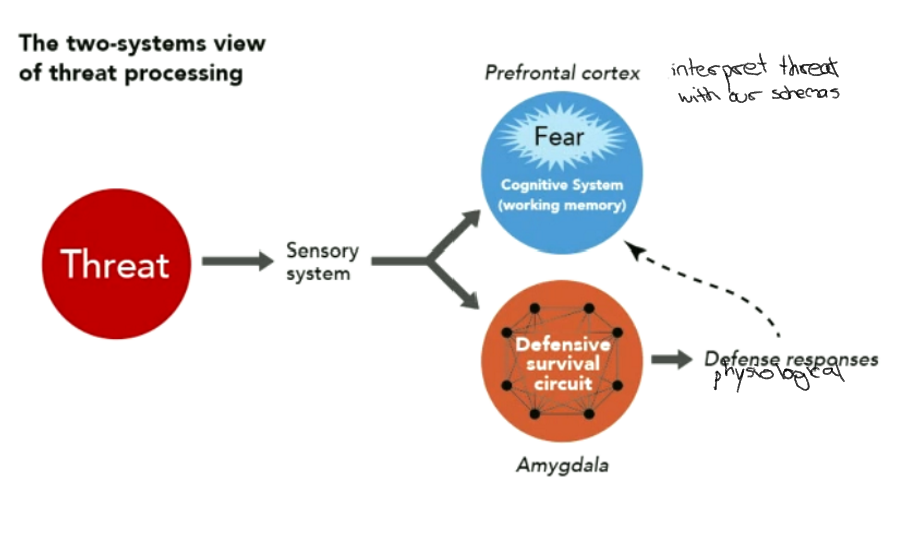
43
New cards
LeDoux Rethink fear
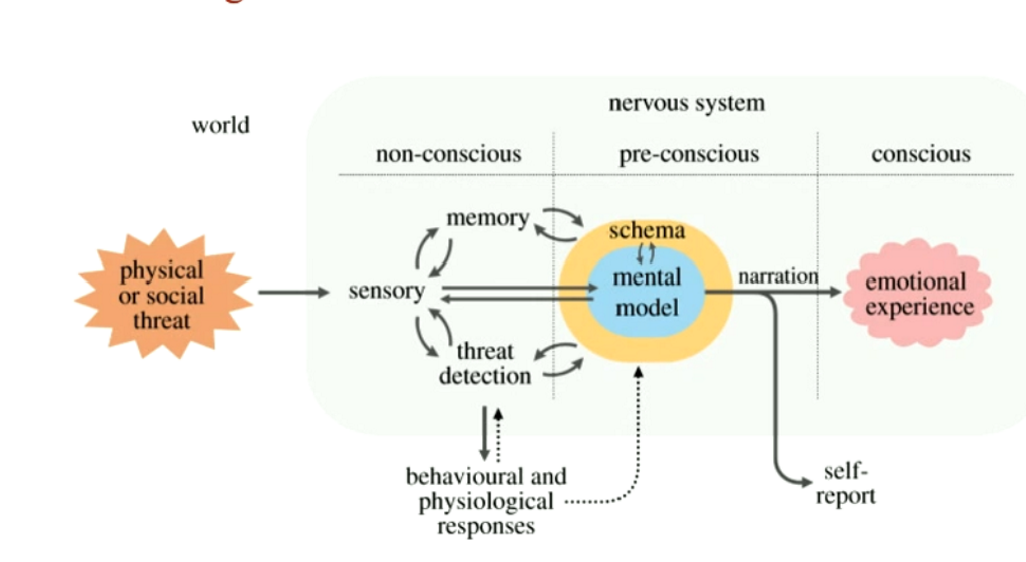
44
New cards
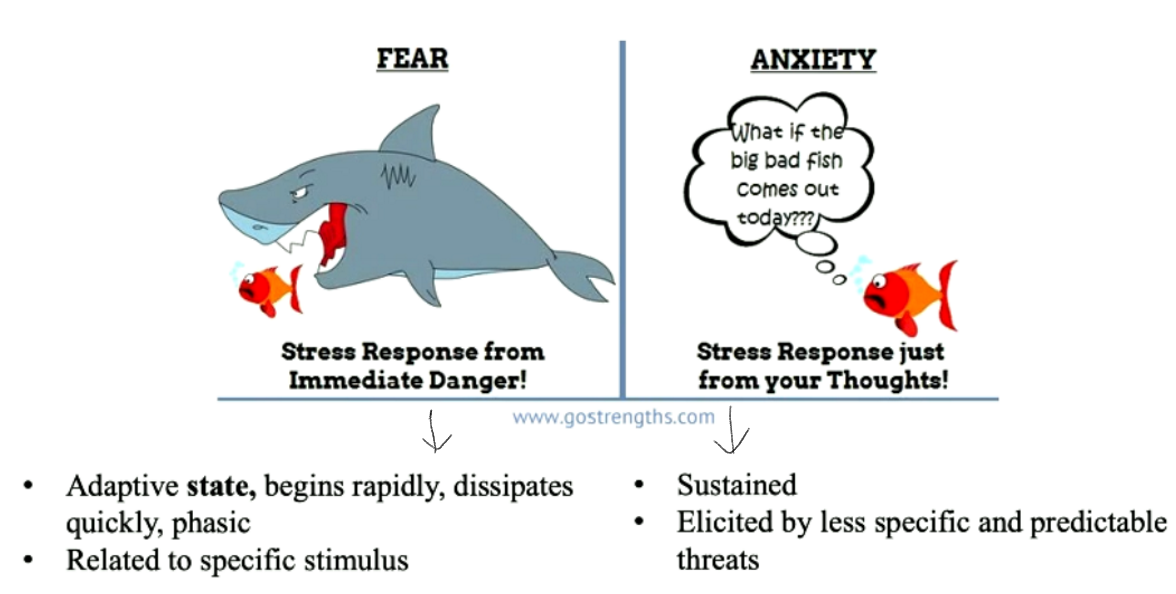
Fear vs Anxiety
45
New cards
anxiety today
* modern society requires active monitoring of potential harm
* new threats: financial security, politics, meaning of life
* (interplay of concious (LeDoux) underlies anxiety)
\
* new threats: financial security, politics, meaning of life
* (interplay of concious (LeDoux) underlies anxiety)
\
46
New cards
different meausurments to determine activity of ANS
\
* galvanic skin response measurement: measures electrodermal skin response fe sweating
* Facial action coding systems
* Blood flow of different parts of the body or temperature throughout the body
* galvanic skin response measurement: measures electrodermal skin response fe sweating
* Facial action coding systems
* Blood flow of different parts of the body or temperature throughout the body
47
New cards
ventral vagal complex/ vagal branch
* \
* controlled by the ventral vagus nerve
* part of parasympathetic nervous system
* is involved in compassion and love
* is unique to mammals and regulate facial muscle actions, head movements, vocalizations and heart rate declarations
* activity of vagus nerve = vagal tone is measured by measuring relationship between heart rate and respiration (Atmung
* compassion is associated with an elevated vagal tone
* controlled by the ventral vagus nerve
* part of parasympathetic nervous system
* is involved in compassion and love
* is unique to mammals and regulate facial muscle actions, head movements, vocalizations and heart rate declarations
* activity of vagus nerve = vagal tone is measured by measuring relationship between heart rate and respiration (Atmung
* compassion is associated with an elevated vagal tone
48
New cards
blushing
has highly social = showing reception (empfang) of a mistake to produce more positive responses in others
* *(Darwin:)* product of self focused attention: while we are ashamed we direct our attention to the face, which causes blushing
* *(Larry et al.:)* product negative self focused attention: we blush when we are object of undesirable attention
* *(Darwin:)* product of self focused attention: while we are ashamed we direct our attention to the face, which causes blushing
* *(Larry et al.:)* product negative self focused attention: we blush when we are object of undesirable attention
49
New cards
chills
goosebumps and piloerection (= contraction of small muscles surrounding hair )
triggered by awe-related experience or by experiences of horror
triggered by awe-related experience or by experiences of horror
50
New cards
flash
non social response
associated with physical arousal, temperature changes or alcohol
\
associated with physical arousal, temperature changes or alcohol
\
51
New cards
regions involved in emotion
cortical
* Prefrontal cortex
* Visual cortex
* (midline and) Anterior cingulate)
subcortical
* Amygdala
* hypothalamus
* Periaqueductual gray
* ( hippocampus)
* (Ventral striatum)
* Prefrontal cortex
* Visual cortex
* (midline and) Anterior cingulate)
subcortical
* Amygdala
* hypothalamus
* Periaqueductual gray
* ( hippocampus)
* (Ventral striatum)
52
New cards
hindbrain
regulates basic physiological processes
* medulla -> cardiovascular activity
* Pons sleep breathing
* cerebellum ->motor coordination and automatic movement
* medulla -> cardiovascular activity
* Pons sleep breathing
* cerebellum ->motor coordination and automatic movement
53
New cards
Forebrain
* thalamus -> integrating sensory memory
* hippocampus -> memory
* hypothalamus -> biological functions/ emotionladen behavior (eating, sexual behaviour, aggression body temperature) +controls ANS via pituitary glands and controls hormonal system
* Limbic system
* hippocampus -> memory
* hypothalamus -> biological functions/ emotionladen behavior (eating, sexual behaviour, aggression body temperature) +controls ANS via pituitary glands and controls hormonal system
* Limbic system
54
New cards
Lateralization Approach/Withdrawl
* looking at Emotion in term of approach or withdrawal
* approach → left regions (language located here central to goal directed behavior)
* withdrawal → right regions
Evidence:
* perception of happy faces activates left side
* perception of disgust activates right
* approach → left regions (language located here central to goal directed behavior)
* withdrawal → right regions
Evidence:
* perception of happy faces activates left side
* perception of disgust activates right
55
New cards
anterior cingulate cortex
=brains alarm system
* active during physical pain and activated in social pain (fe when socially rejected)
opiates used for physical pain can also relieve social pain
* active during physical pain and activated in social pain (fe when socially rejected)
opiates used for physical pain can also relieve social pain
56
New cards
opiod and dopamine
* nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area =dopamine rich networks)
* Reward circuit: ventral stratium receives input from prefrontal cortex, amygdala, hippocampus than sends info to hypothalamus
→ dopamine essential to wanting
→opioid receptors essential for liking
* Reward circuit: ventral stratium receives input from prefrontal cortex, amygdala, hippocampus than sends info to hypothalamus
→ dopamine essential to wanting
→opioid receptors essential for liking