Habitat Loss, Degradation, and Fragmentation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the causes of habitat loss/modification?
over exploitation
agricultural activity
urban development
invasion/disease
resource extraction (ex. mining)
pollution
system modification (ex. fire, dams)
climate change
What is the primary driver of habitat loss?
agricultural expansion
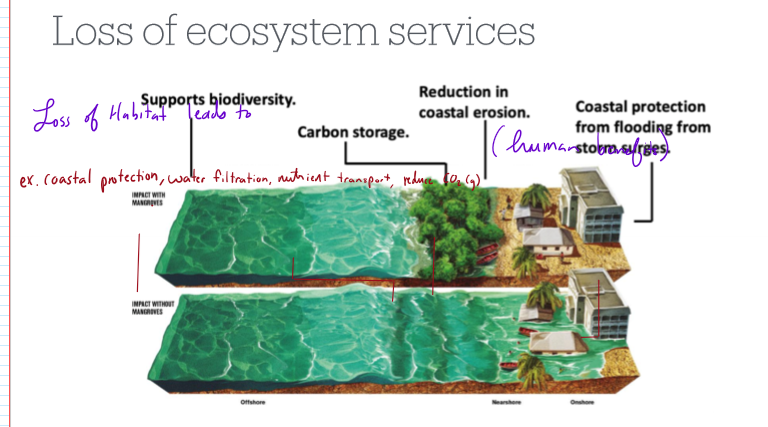
How does habitat loss reduce ecosystem services?
Can lose species providing coastal protection, carbon storage, water filtration, etc.
How can habitat loss/degradation shift communities?
can decrease/increase populations of species
migrants can increase
What are causes of habitat degradation?
pollutants ie. pesticides, oil spills, heavy metals
chemicals ie. hormones, detergents, antibiotics
plastics
eutrophication (algae turning water anoxic)
acid rain
desertification
erosion
How does increased farmland affect native species?
overall decline in native species, but some species do better. downstream trophic affects must be considered
What can pollutants likes DDT result in for top predators?
Biomagnification/bioaccumuation in individuals at higher trophic levels
How are different biomes affected by habitat degredation?
tropics and subtropics have much more annual forest loss
temperate forests are increasing
Why is habitat loss occurring at a higher rate for tropics/subtropics than temperate forests?
tropic species aren’t as accustomed to high-distrubance events
more removal of native land for agriculture than temperate forests
Why is habitat loss occurring at a lower rate for temperate forests than in the tropics/subtropics?
species more accustomed to high-disturbances
humans leaving for urban centers
What are causes of habitat loss/degradation in coral reefs?
destruction
chemical pollution
tourism
sedimentation
coral bleaching
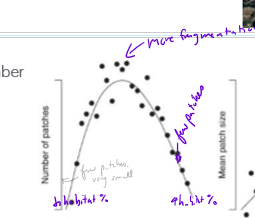
How does the number of patches correlate to habitat amount?
high and low habitat percents associated with few patches
50% habitat amount has more patches
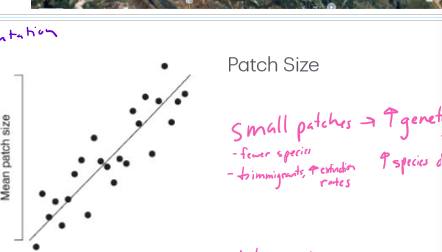
How does patch size correlate to habitat amount?
low habitat amount = small patches
high habitat amount = large patches
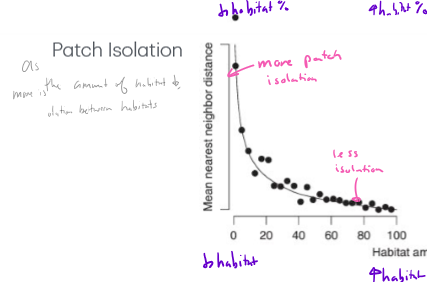
How does patch isolation correlate to habitat amount?
less habitat = more isolated, further from neighbors
more habitat amount = less isolated, closer to neighbors
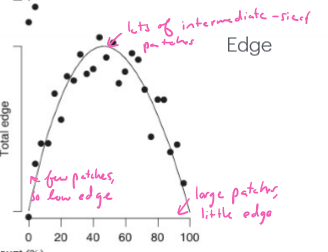
How does the total edge amount of a patch correlate to habitat amount
small and large habitat amount = little edge
medium habitat amont = lots of edge (many intermediate patches)
What effects does a small patch size have on the species present?
reduced immigration, higher extinction rates
increased genetic drift
increased species distinction over time
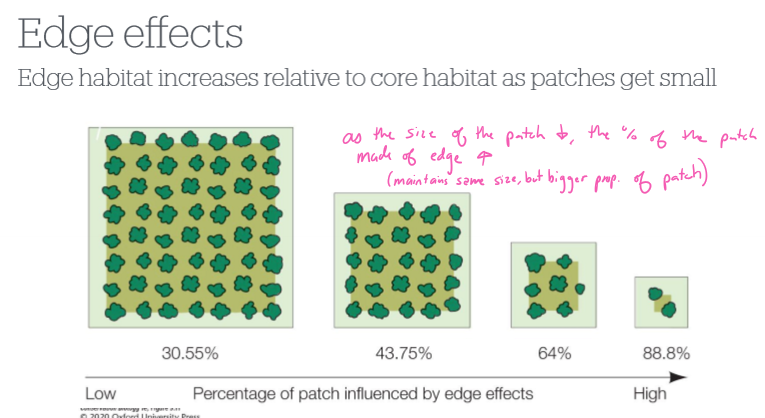
What happens to the edge of the habitat as the habitat size decreases?
the percent of the patch made of edge increases
What is the interior habitat of a patch affected by?
size and shape of patch
What are the effects of edge habitats?
changes in microclimate ex. lack of foliage coverage
less buffering of climatic variation ex. more exposure to sun, wind
increased disturbance ex. human interactions, chemicals, pollutants
increased susceptibility to invaders, pests, etc.
What are ecological traps and where do they often occur?
when organisms are attracted to poor-quality habitats because of previously reliable cues misleading them. reduces their survival and reproduction (lowers fitness)
ex. sea turtles following house lights
How has past natural selection in high-disturbance environments impacted the effects of fragmentation?
species that have persisted in high-disturbance environments (ex. storms, fires, glaciers) are less sensitive to edge effects (species sensitive to disturbance already lost by natural selection)
What are metapopulations?
collection of subpopulations connected by the movement of individuals
what can impact metapopulations within patches?
resource availability
size/shape of the patch
increased genetic drift
life history (density effects for mating)
What can impact population connectivity among patches?
barriers
distance
types of intervening matrix (urban vs rural)
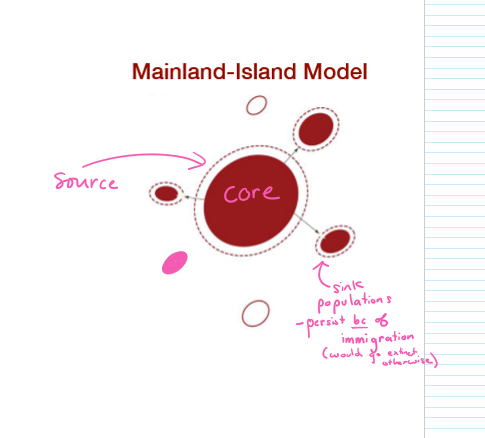
What is the mainland-island model of metapopulations?
when a large, stable population (the source) acts as a continuous source of individuals that disperse to smaller, isolated populations (sink)
How do sink populations within metapopulations persist?
solely because of immigration from source populaton
In what ways does habitat loss impact all levels of biological diversity?
local extinction
population declines from loss of resources
reduced genetic diversity
How does habitat loss impact community and ecosystems?
changes in species interactions, ex. increased competition
decreased connectivity between patches
less nutrient retention
How can habitat loss impact human well-being?
decreased ecosystem services ex. air quality, water purification, aesthetic value, reduced pollination
increased aridity
increased pollution
reduced crop yields
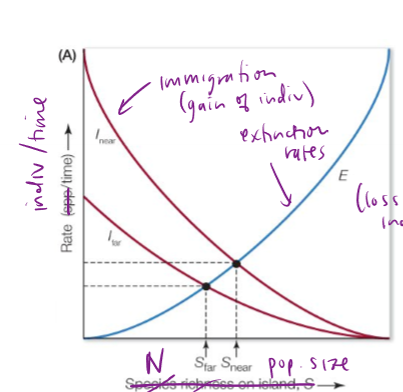
How does population size on islands and patches correlate to immigration and extinction rates over time?
low population: high immigration, low extinction
high population: high extinction rates
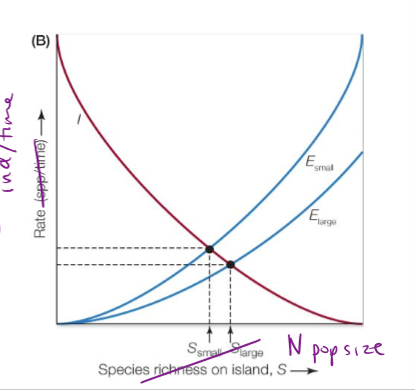
Are extinction rates on large patches or small patches higher? How is the immigration rate?
higher extinction rates on small patches. equal immigration rates
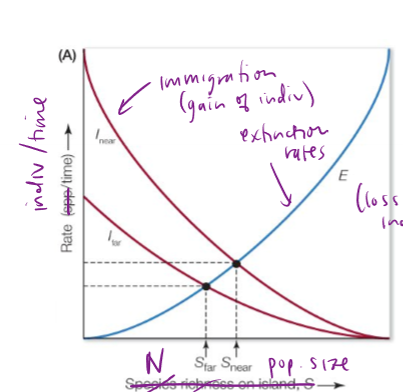
Are immigration rates higher for far or near islands/patches? How is the extinction rate?
Higher immigration rates for far islands, but equal extinction rates
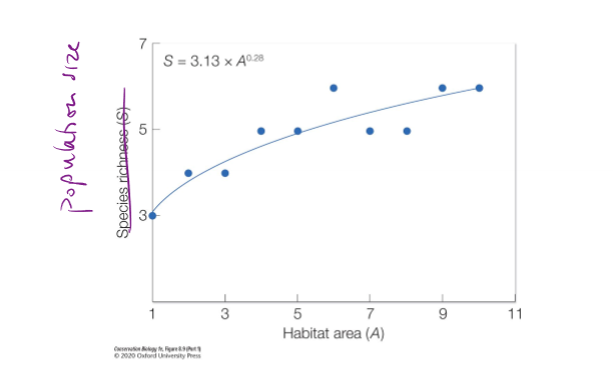
How does population size change with habitat area?
Population size increases logistically with habitat area
Why is experimental fragmentation important?
can control for influencing habitats (ex. rivers), pollution, climate, cause
can vary size/edge/isolation
can replicate
What are consistent effects of fragmentation across all sizes/habitats/isolation?
decreased diversity
loss of specialists
simpler/less resilient communities
extinction debt
What is extinction debt?
future extinction of species due to events in past ex. fragmentation, reducing long term species richness
How does reduced fragment area affect patches?
reduced species persistence
reduced species richness
reduced nutrient retention
changes to success rate
changes to trophic dunamics
How does increased isolation in fragments affect patches?
reduced movement between fragments
reduced abundance
reduced species richness
reduced pollination
changes to microclimate
reduced nutrient retention
How does increasing edge affect patches?
degraded community composition
changes in trophic dynamics
What is immigration lag?
a delay in the arrival and establishment of new species into a habitat following a disturbance or environmental change, resulting in a decrease in species richness
What is ecosystem function debt?
the delayed loss of biomass and nutrient cycling after a disturbance/fragmentation
What are some approaches to habitat management?
land sparing
land sharing
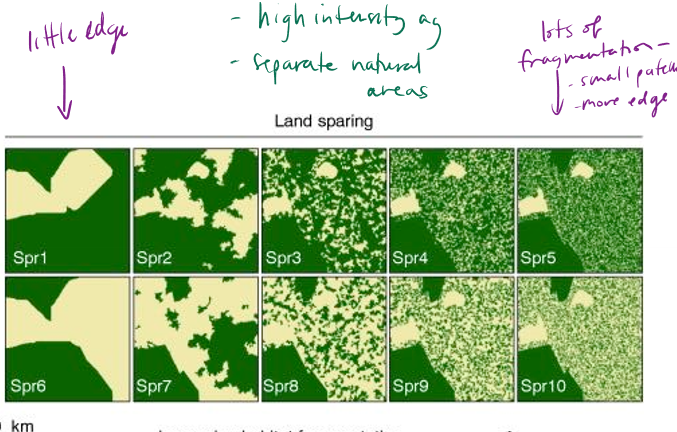

What is land sparing?
conservation strategy that aims to maximize biodiversity by setting aside areas of land for nature while intensifying agriculture on other areas to meet food production needs. The idea is to create a clear distinction between high-yield farming areas and untouched natural habitats, rather than mixing conservation efforts within farmland
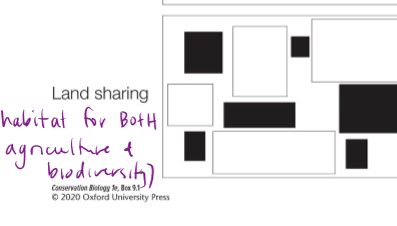
What is land sharing?
conservation strategy that integrates biodiversity conservation with agriculture by creating wildlife-friendly farming practices. Instead of separating high-intensity farming and natural habitats (as in land sparing), land sharing involves using lower-intensity, sustainable farming methods that allow wildlife to coexist with agriculture
What are benefits of a single patch?
large core habitat
positive alle effects
habitat homogeneity
What are benefits and downsides of several small habitats?
local extinction
lower diversity
decreased connectivity
resilience to disturbance events
reduced habitat homogeneity
What are the historical effects of racial redlining?
luxury effect - positive relationship between affluence and biodiversity
legacy effect - environmental changes result from historical human activities