ENSO - El Nino Southern Oscillation & Global Oceanic Circulation
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Ocean Currents
large scale flows of sea water that move across the surface and depths of the ocean and are driven by numerous forces including wind, earths rotations, and differences in water temperature and salinity.
Surface Currents
Comprise 10% of all the water in the ocean
Restricted to the upper 400m (1300ft) of the ocean
Driven by wind, major part of global circulation (global convier belt)
Deep Water Currents
The movement of deep water (currents) in the ocean basins is by density driven forces (temperature and salinity) and gravity.
theromohalien circulation
Driven by differences in water density.
True or False, Deep water currents sink into the deep ocean basins at high latitudes where the temperatures are cold enough to cause the density to increase.
True, deep water currents sink causing density to increase
Density difference in currents is caused by..
Different temperatures and salinity
Warm Water Currents
As ocean currents move westward along the equator, they absorb solar energy, heat up, and become warm currents.
As they turn away from the equator, the reverse happens, causing colder currents.
The currents radiate more heat than they gain (slowly).
Ex: Gulf Stream
True or False, Currents remain pretty warm after they have left the tropics?
True, the currents retain the heat.
Cold Water Currents
Transfer cold water from polar regions to the equator. These cool currents cool the atmosphere above them and often create cooler and drier conditions in the coastal regions.
Ex: California Current in Pacific
True or false, currents also move nutrients
True, they do not just move heat, they move nutrients to the surface in a process called upwelling.
True or False, Tropical waters are warmest during the Northern Hemispheres late winter and early spring seasons.
True, feburary and march are typically warmest seasons for tropical regions. Caused by tilt of the earth, thermal inertia, global climate dynamics and oceanic heat.
Thermal Inertia
Waters ability to store and slowly release heat
True or False, Equatorial cold tongues are prominent in the Eastern Pacific and Atlantic
True, this is the strongest during the southern hemispheres winter/spring from July-October
The Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
Naturally occurring cyclical change in global circulation patterns
Paleorecords indicate it has been occurring for 100,000 years
Oscillation of water temp and global pressure/wind patterns in pacific
Has global teleconnections (correlation between meteorological or other environmental phenomena)
Oscillation
Changes in water temperature and shifts in global pressure and wind patterns.
Primarily in Pacific Ocean.
True or False, ENSO occurs ever 2-7 years
True, it operates on a temporal time scale that is larger than typical seasonal changes
What are the the two Main phases of ENSO?
El Nino
La Nina
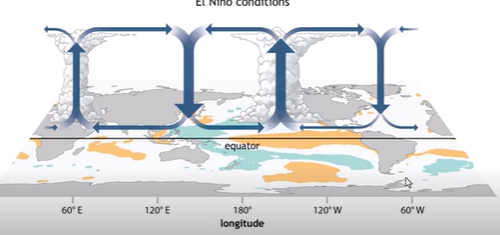
El Nino - ENSO
Characterized by warmer ocean temperatures in the pacific
Reversal of “average” conditions/walker circulation
tradewinds slow and blow in reverse direction (W to E instead of E to W)
La Nina - ENSO
Brings cooler ocean temperature into the pacific
Amplification of “average” conditions/walker circulation
True or False, ENSO is driven by trade winds.
True, it is driven by easterly surface winds in the tropics. (trade winds)
Trade Winds blow from..
the northeast in the NH and from the southeast in the SH.
True or False, Trade winds are stronger during the winter time.
True, they are stronger during the winter and play a crucial role in influencing ocean temperatures and circulation patterns in the pacific.
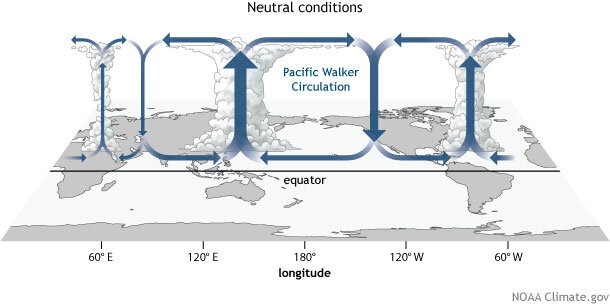
Walker Circulation aka Walker Cell
conceptual model of the air flow in the tropics (trade winds). Air follows a closed circulation in the zonal and vertical directions. .
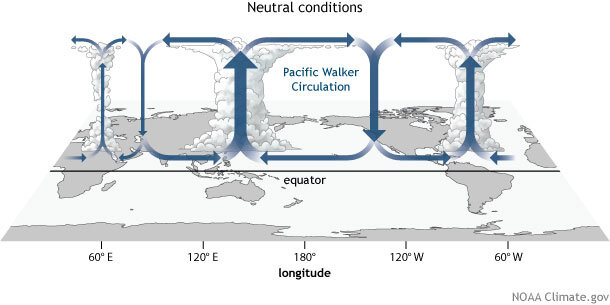
What causes the “Walker Circulation”?
This circulation is caused by difference in the heat distribution between ocean and land. Causes variations in air pressure which guide the flow of air.
Characteristics of Walker Circulation under normal/average conditions in WEST PACIFIC
Warm ocean water
Low Pressure
Unstable atmospheric Conditions
Characteristics of Walker Circulation under normal/average conditions in EAST PACIFIC
Cold water upwelling
High Pressure
Stable atmospheric conditions
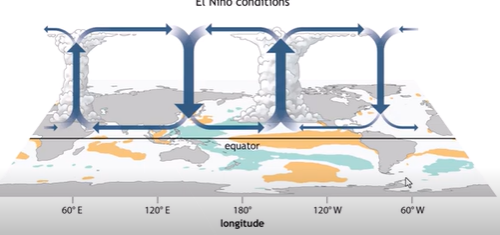
El Nino Conditions in the EASTERN PACIFIC
Upwelling ceases
Warmer Surface Water
STHP weakens
Wet and Unstable Conditions
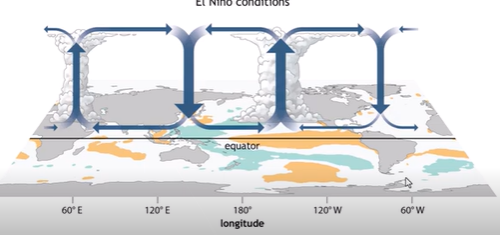
El Nino conditions in the WESTERN PACIFIC
Cooler Surface water
Low Pressure Weakens
Drier and Stable Conditions
El Nino conditions can lead to..
Eastern: Warmer surface waters, increases evaporation/moisture, more precipitation leads to:
Flooding and Mudslides
Western: Cooler surface waters and weakened pressure system, reduced rainfall, dry conditions leads to:
Droughts and Wildfires
True or False, El Nino causes weakened/reverse trade winds which causes the loss of cold water upwelling in the Eastern Pacific
True, this upwelling is a very crucial process for nu
Phytoplankton
Primary Producers of the Ocean - Vital role in our Ecosystem
Photosynthesizers
Cold water upwellings bring nutrients up to surface and cause them to bloom
serve as food for zooplankton and higher trophic levels
True or False, Collapse of fisheries along the South American coasts are due to the loss of cold water upwelling from El Nino
True, without the cold water upwelling, there are less nutrients being brought to the surface, which effects our ecosystem and marine life.
True or False, El Nino causes increased rainfall and vegetation cover in arid regions of the Western United States.
True, these areas typically lack a lot of moisture but warmer conditions in pacific create more moisture in the atmosphere that are transported inland, which can result in frequent and intense storms.
Can boost vegetation cover
El Nino and SouthEASTERN US weather
More azonal (not divided) polar jet stream: strong periodic incursions of cold air
Stronger Subtropical jet stream: more warm, moist air in region
Colder, wetter winters
Increased liklihood of strong fall and spring thunderstorns with tornados
Where does to polar jet stream stay during La Nina events?
Stays in Zonal Flow
Stays in its Zones
(More Straight lines)
Where does to polar jet stream stay during El Ninoevents?
Azonal Flow
Does not stay in zones
(more curved flows)
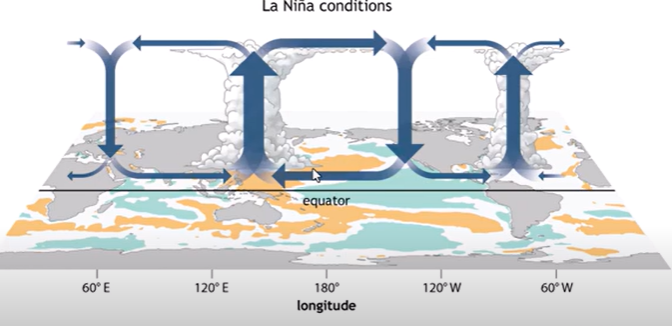
La NIna
Amplification of normal Walker Circulation
Easterly tradewinds grow stronger (E to W)
More Warm Water Piles up in Western Pacific
Lower Pressure, More Wet and unstable in western pacific
STHP in eastern pacific grows stronger, cooler and drier conditions
Greater Upwelling
La NIna and SOUTHEASTERN US weather
-More zonal Jet Stream
Weakened subtropical jet stream
Warmer, dryer winters (north of country is very cold)
Drier Conditions
What does ENSO mean for OUR weather during EL NINO?
Texas typically experiences wetter than average conditons (especially in fall and winter months)
Cooler temperatures (Retains soil moisture)
What does ENSO mean for OUR weather during LA NINA?
Texas experiences drier, warmer conditions (especially during winter and spring)
Increased chances of drought (affects crops, water resources, ag, and wildfires
Less rainfall and higher temperatures
True or False, ENSO is a natural cycle and is not caused by global warming
True, this naturally occurs but global warming may influence how intense and frequent El Nino events are