Miller and Levine Biology Chapter 8 - Organelles
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
cell
the basic unit of life
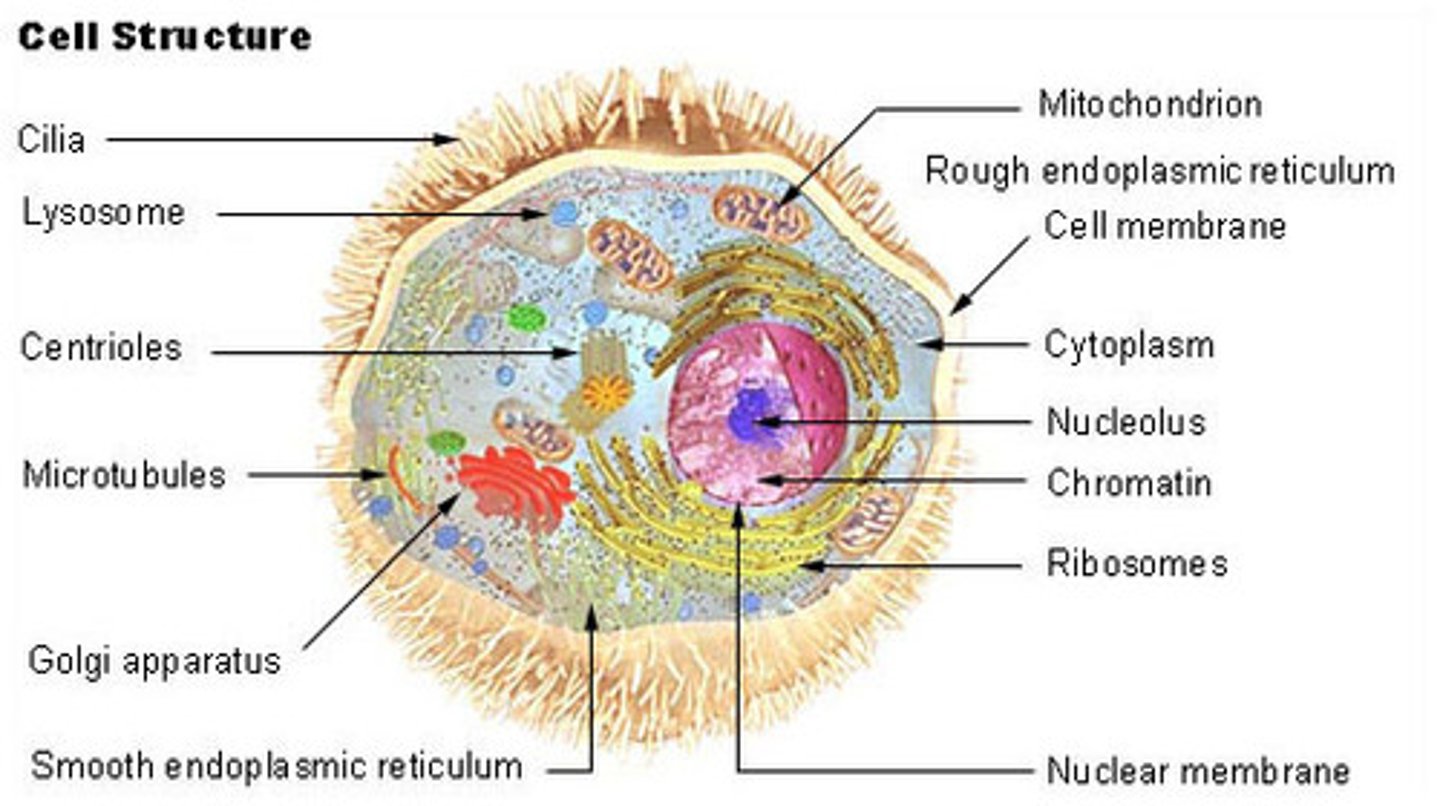
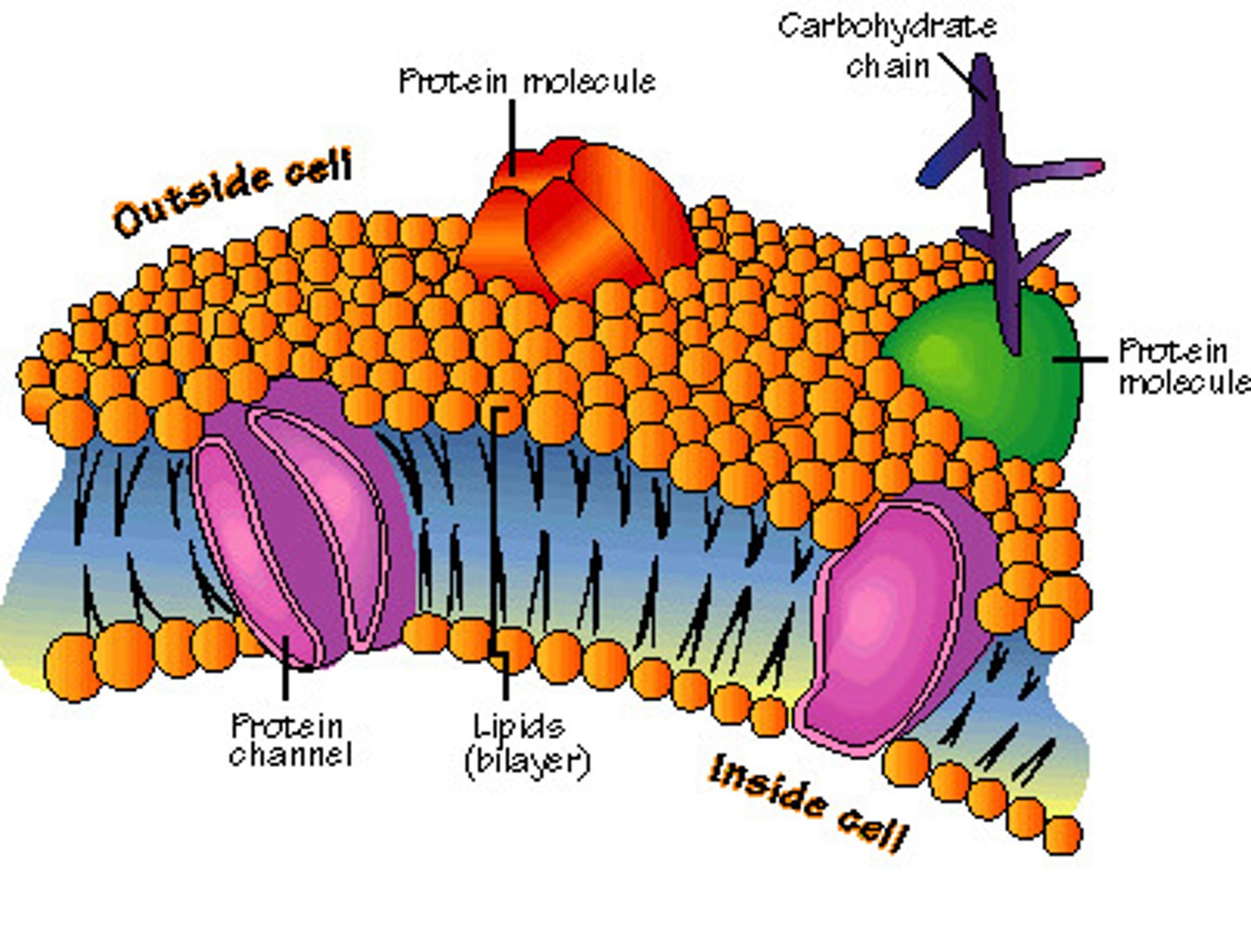
cell membrane/plasma membrane
a thin flexible barrier surrounding a cell (all cells) that controls what enters and leaves the cell; ALL cells have this!
cytoplasm (aka cytosol)
fluid portion of the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus; what the organelles "sit" in. (all cells); contains CYTOSOL, ORGANELLES, AND INCLUSIONS; ALL cells have this!

eukaryote
cell that encloses its DNA in nucleus; has membrane bound organelles, large, and complex.
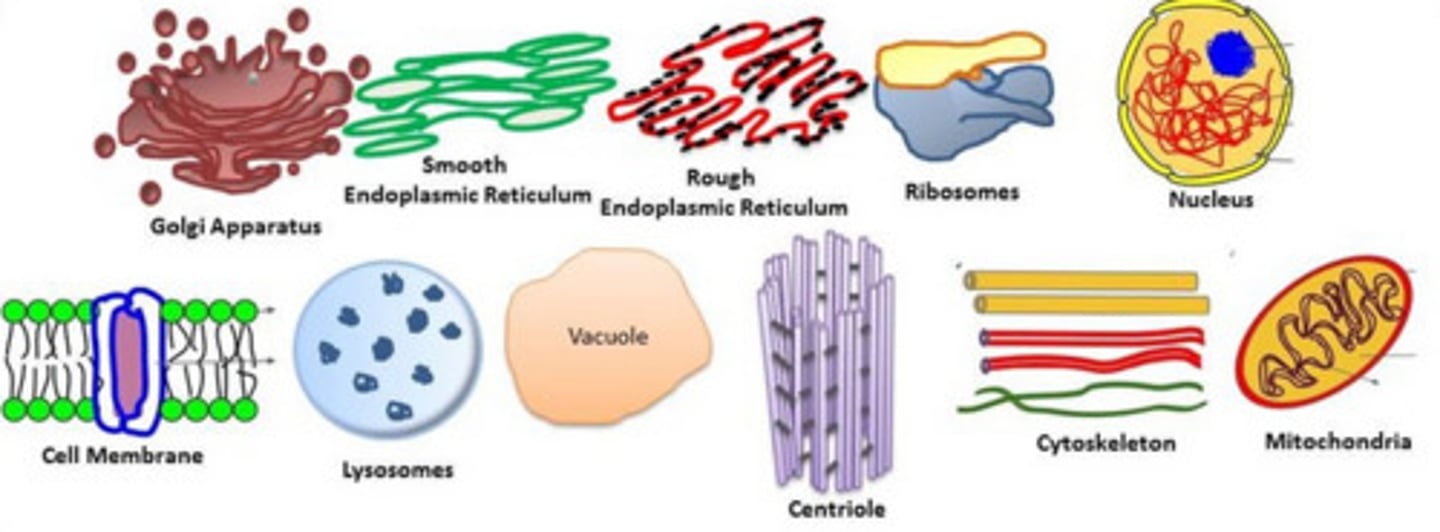
organelle
specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell (little cellular organs)
small vacuoles
Storage organelle for materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. (animal cells)
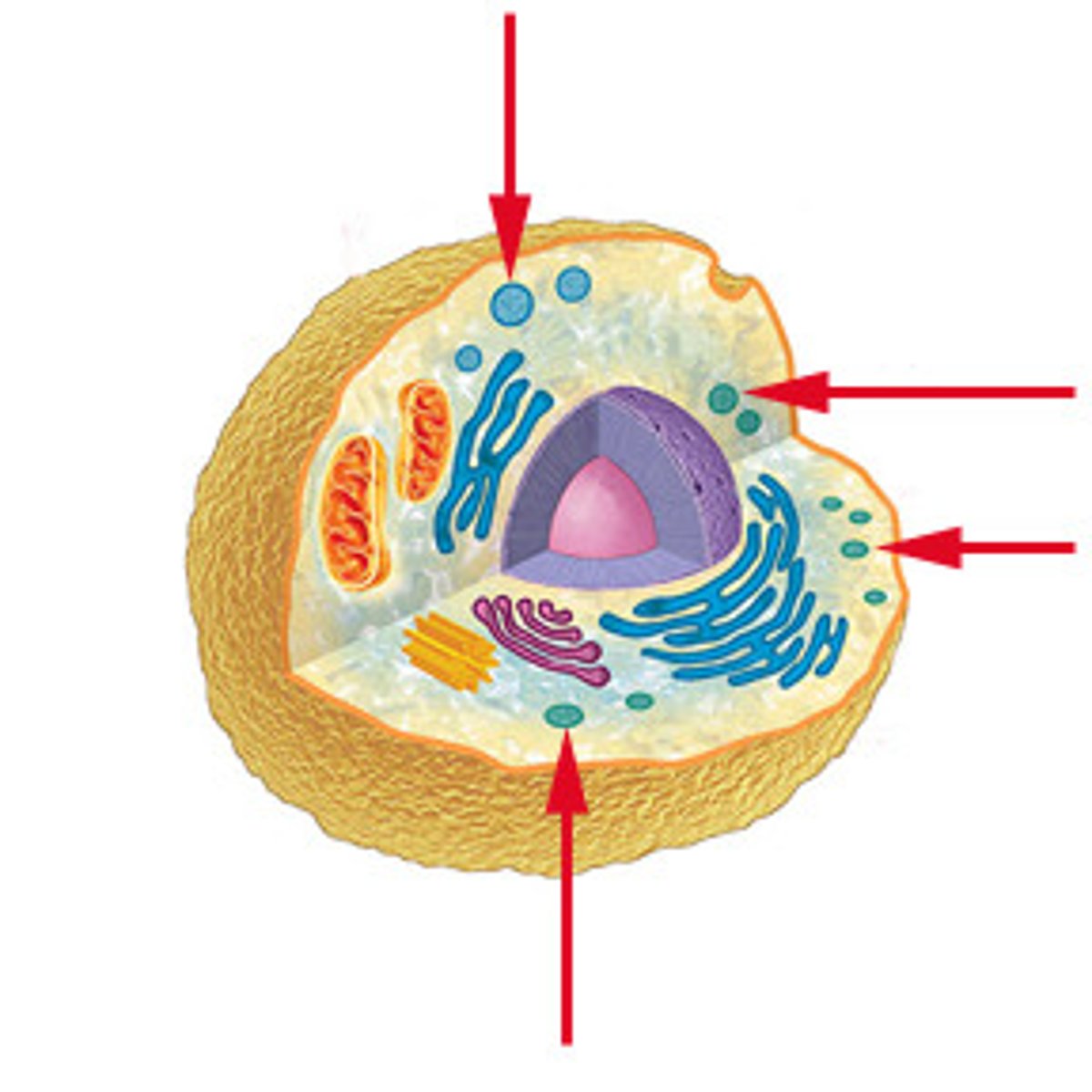
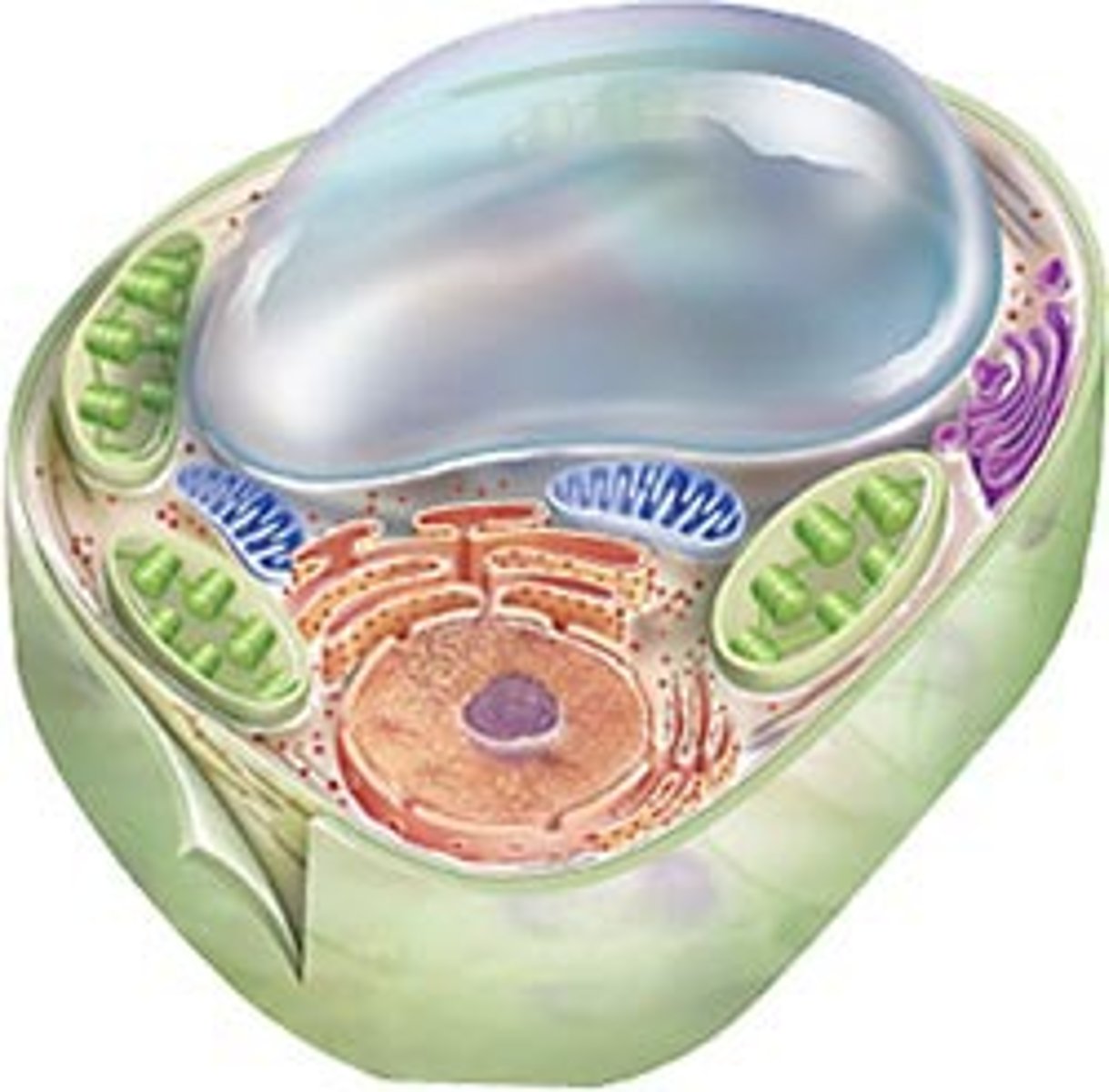
large central vacuole
storage area for nutrients and wastes as well as water to maintain cell shape; (plants); helps maintain turgor pressure
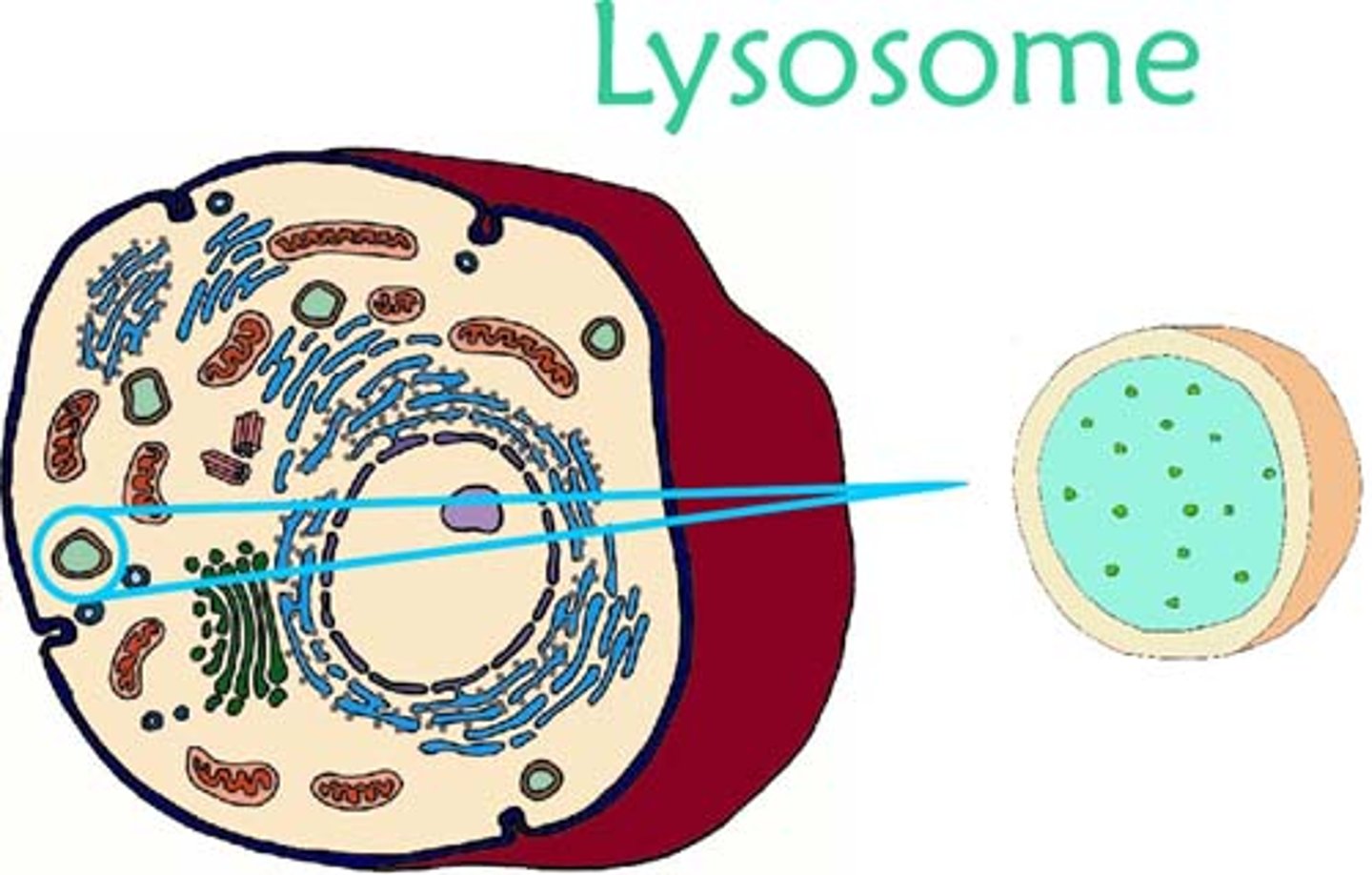
lysosome
organelle containing digestive enzymes that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins (from ingested material or worn out cell parts) into small molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell; excretes waste
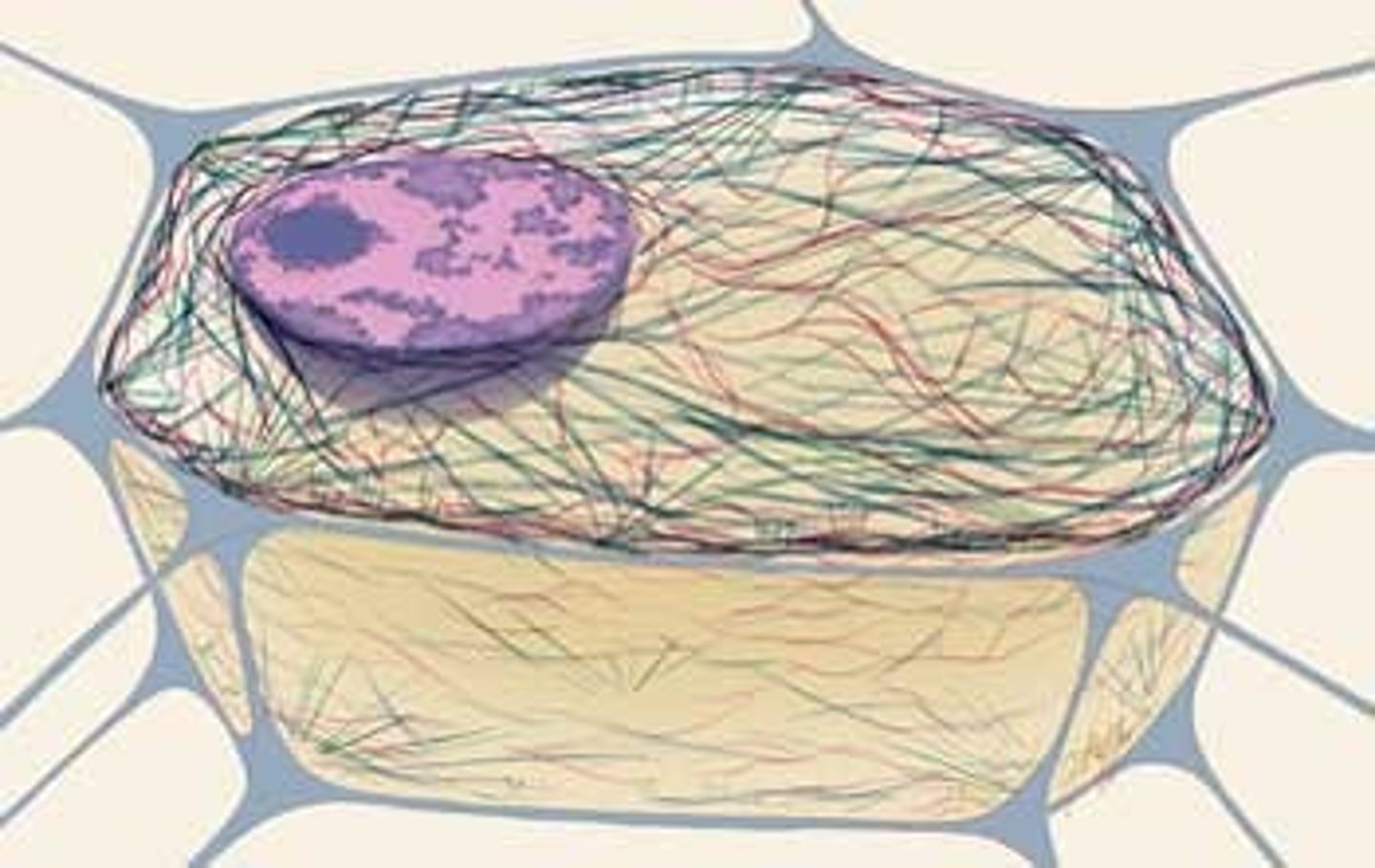
cytoskeleton
network of protein tubules or filaments that gives the cell its shape and internal organization and is involved in movement
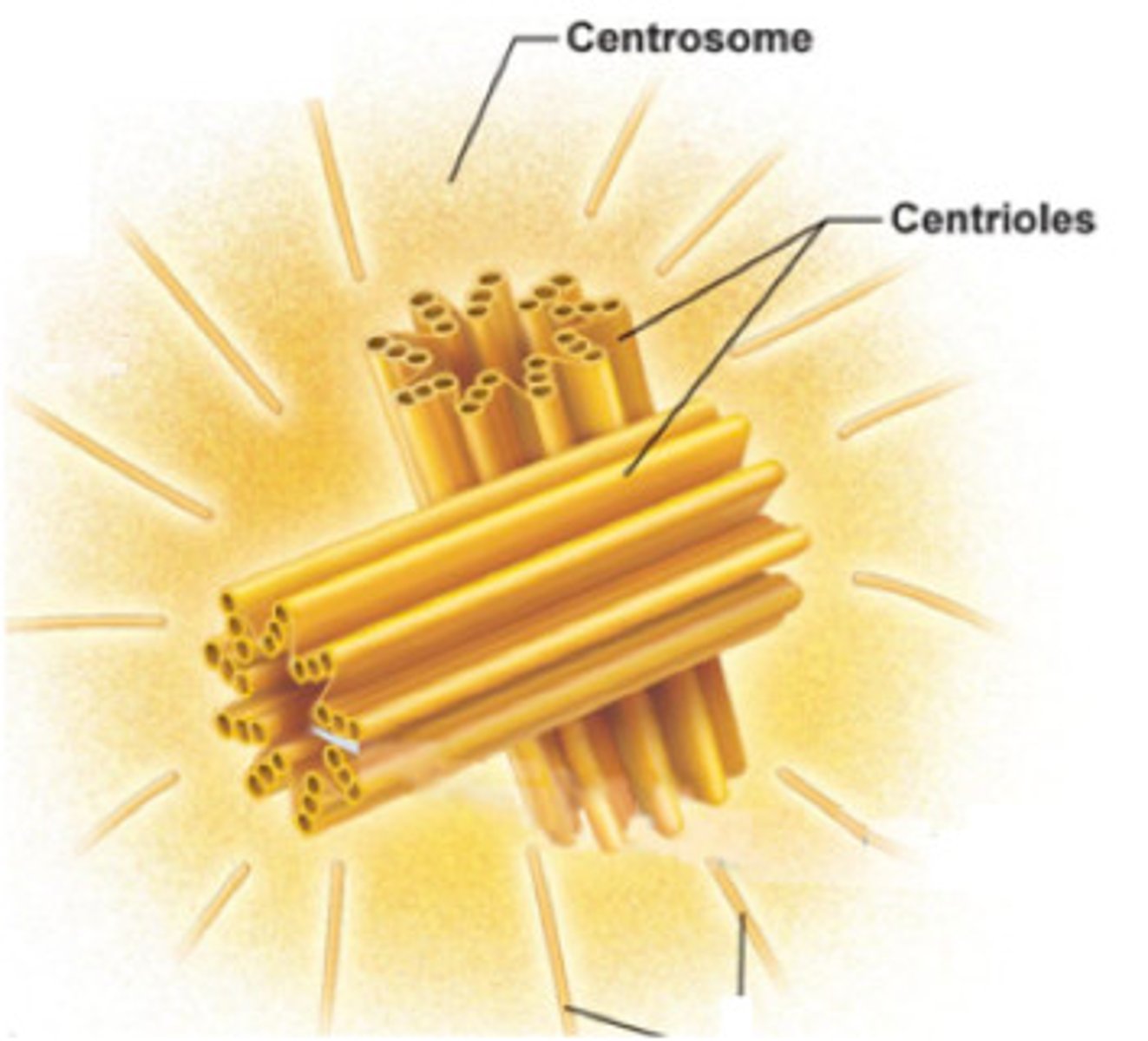
centrioles (centrosome)
structure in an animal cell, located outside the nucleus, that helps organize cell division
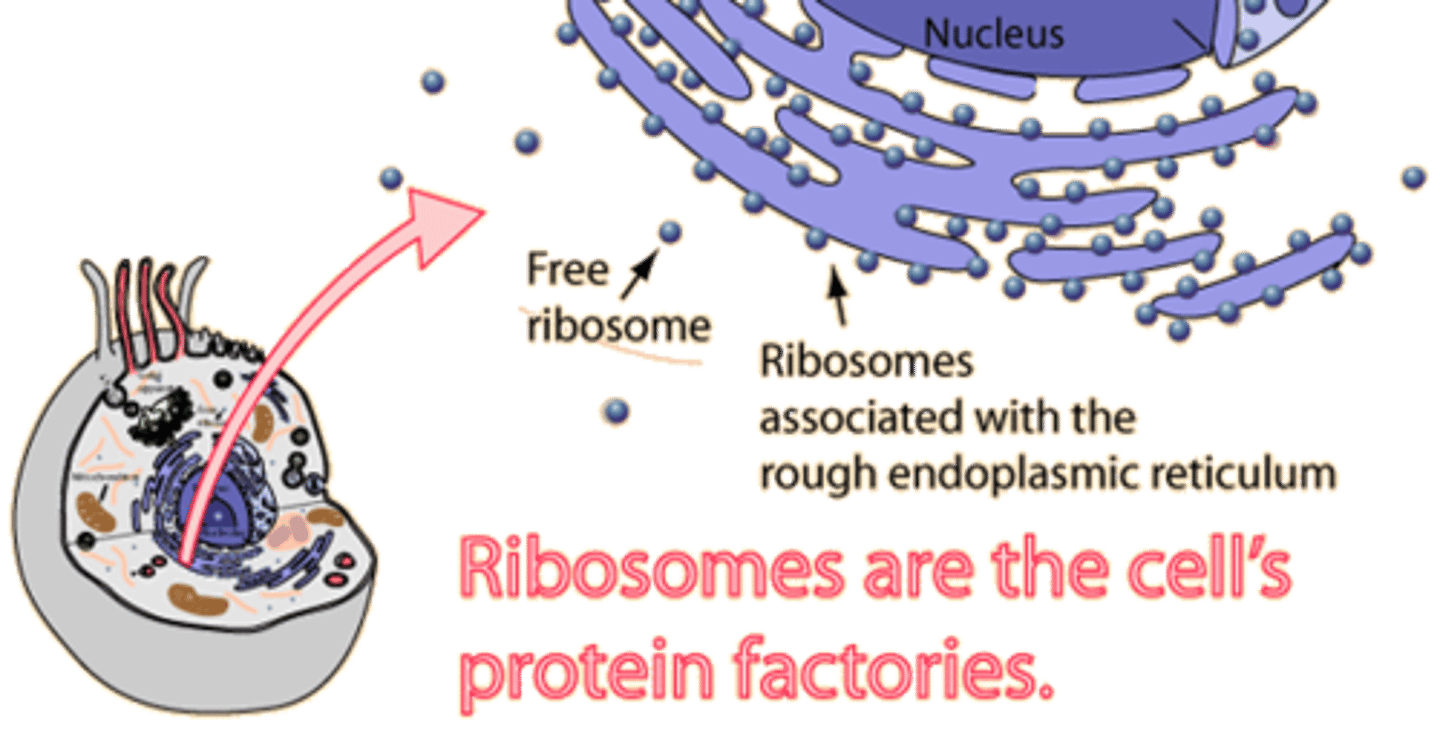
ribosome
organelle where proteins are made; can be free floating in cytoplasm or attached to the Rough ER (ALL cells have ribosomes!)
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
system of channels that transport materials like proteins and lipids to Golgi body
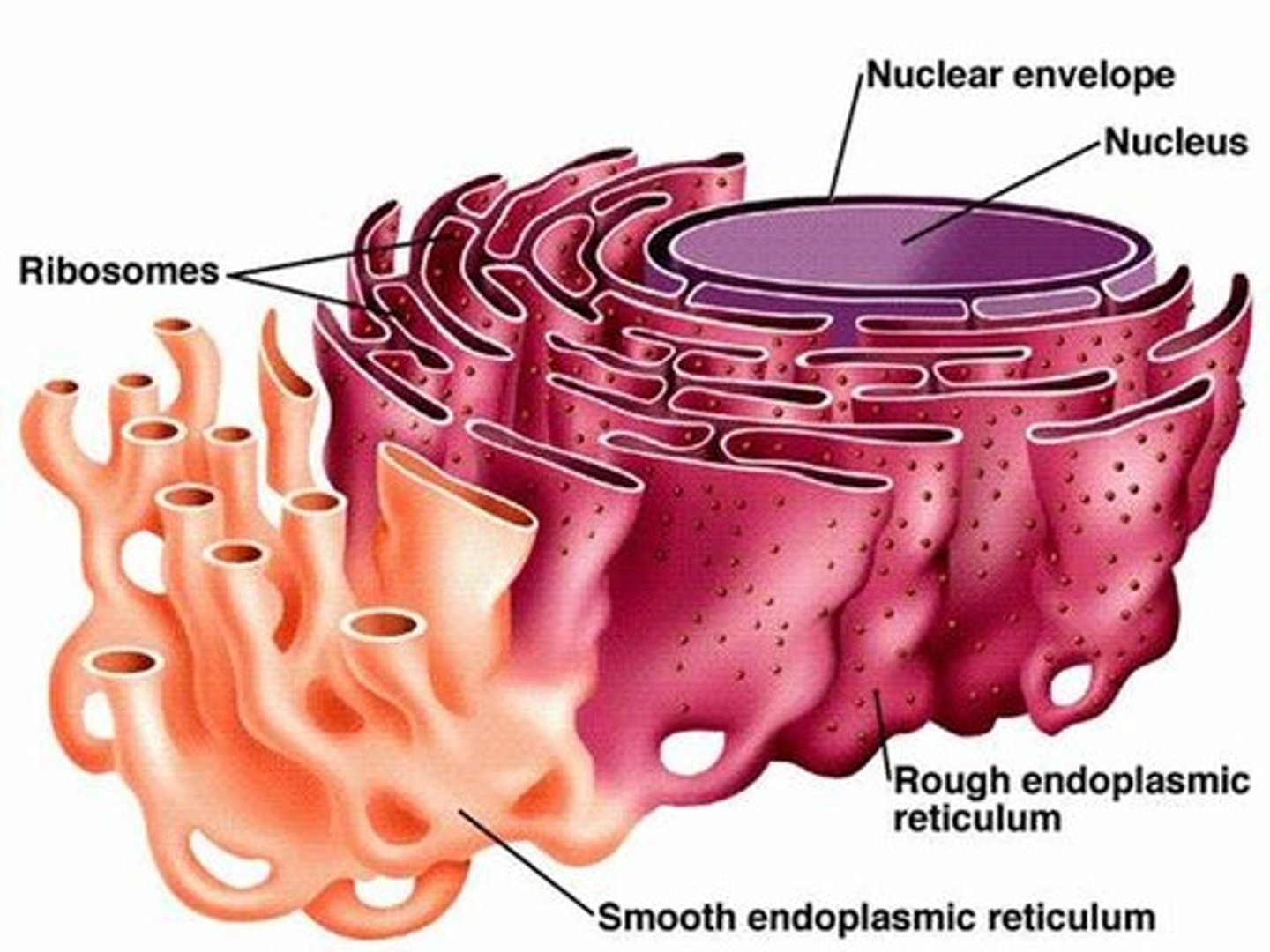
rough ER
part of the ER involved in the synthesis of proteins (named because of ribosomes found on its surface)

smooth ER
portion of the ER without ribosomes - contains enzymes that perform specialized tasks such as making lipids and detoxification of drugs
Golgi apparatus (or body)
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials coming from the ER; makes vacuoles for storage in the cell or release outside the cell.
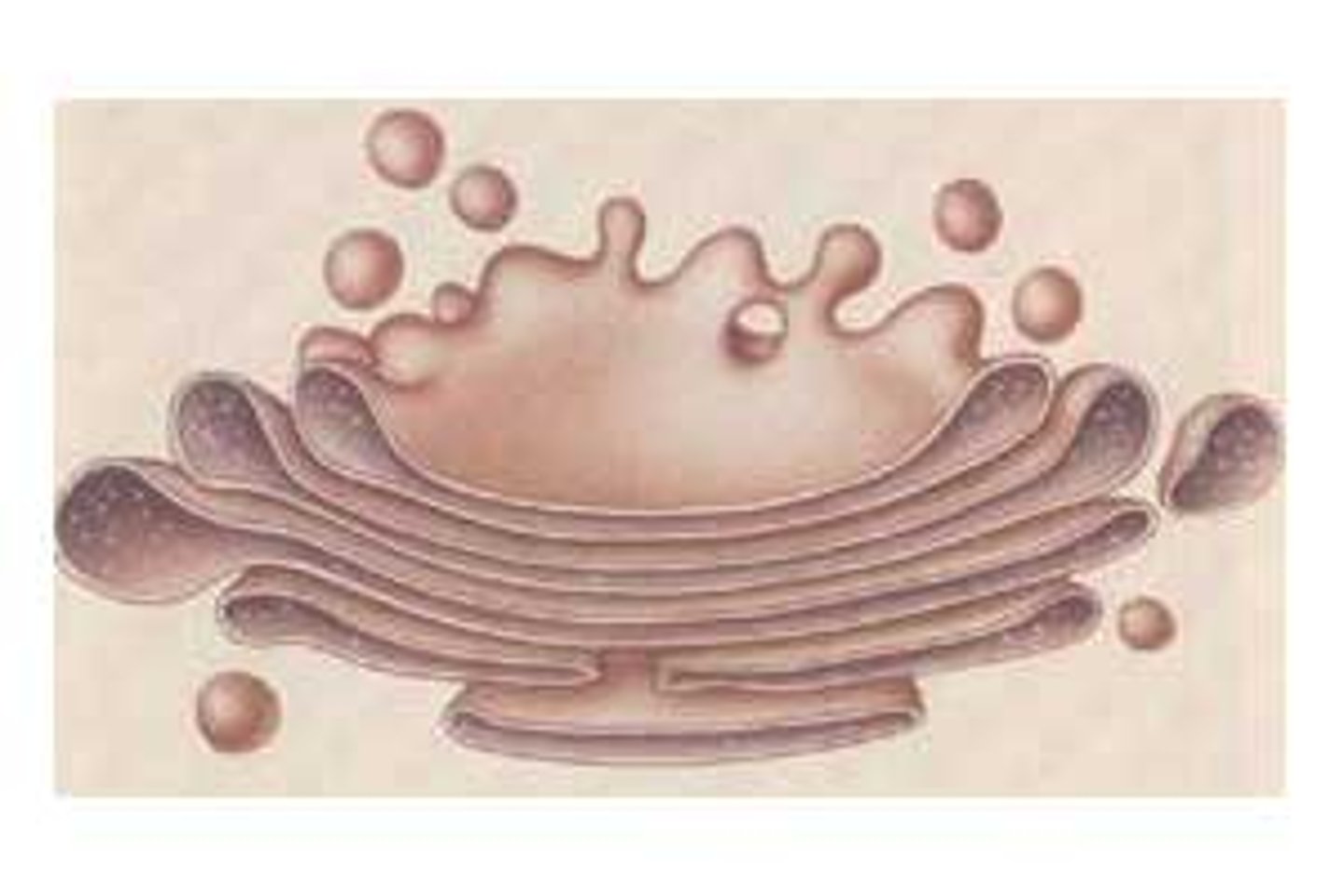
chloroplast
captures energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy (PHOTOSYNTHESIS); green in color; (plants and algae)

cell wall
strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane: (plants and bacteria)
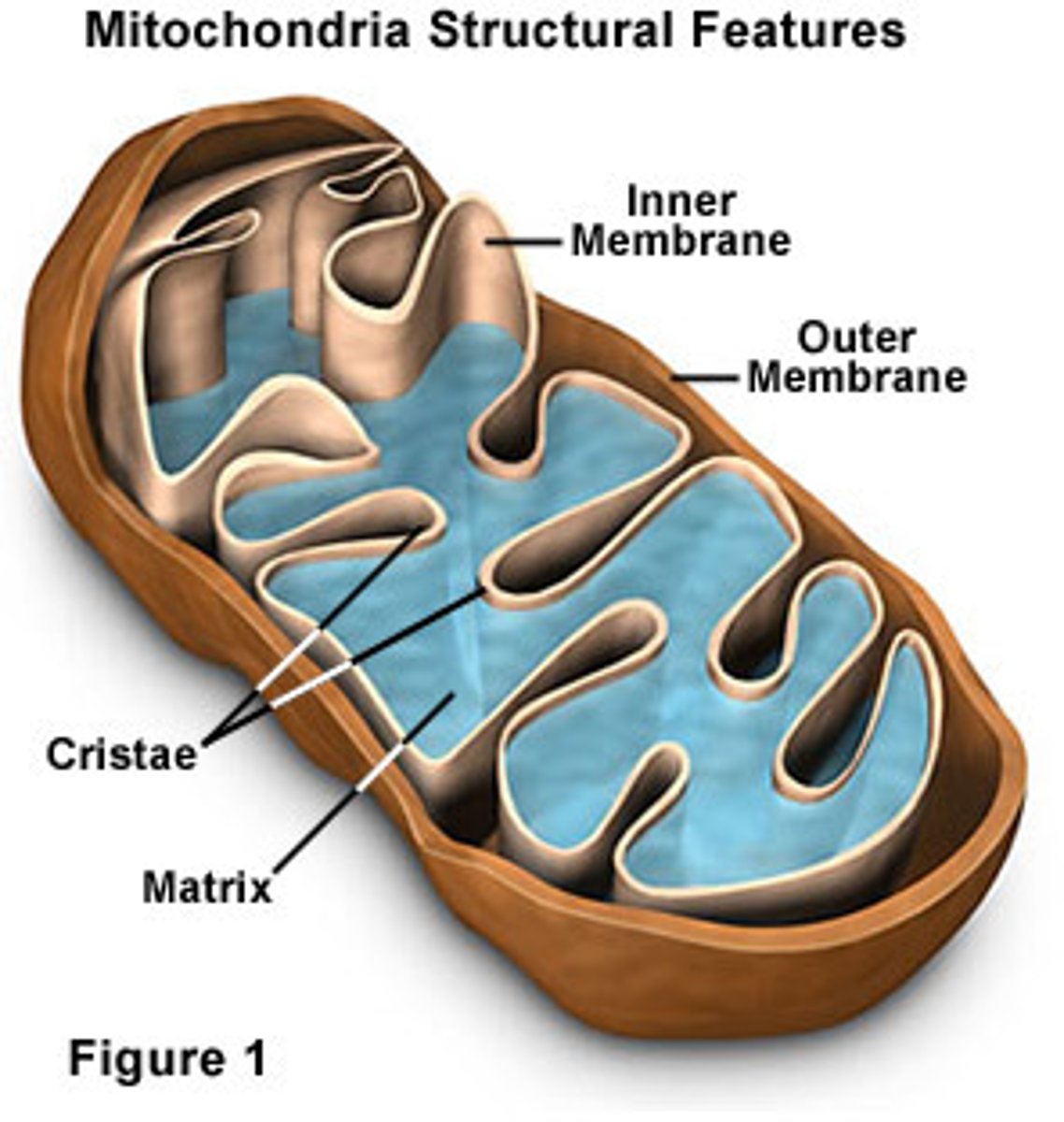
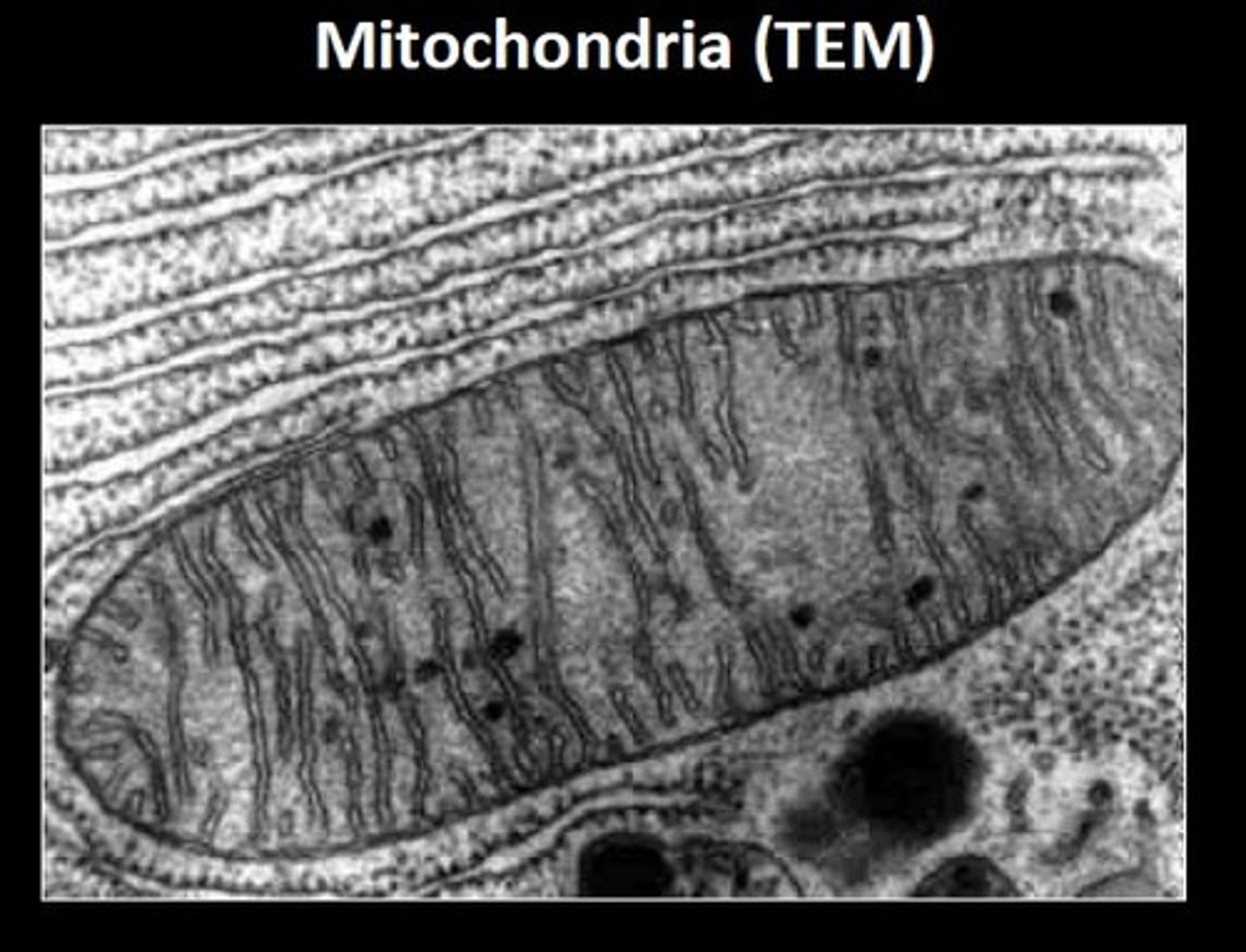
mitochondrion
converts the chemical energy of food (glucose) into compounds that the cell is able to use (ATP). CELLULAR RESPIRATION!
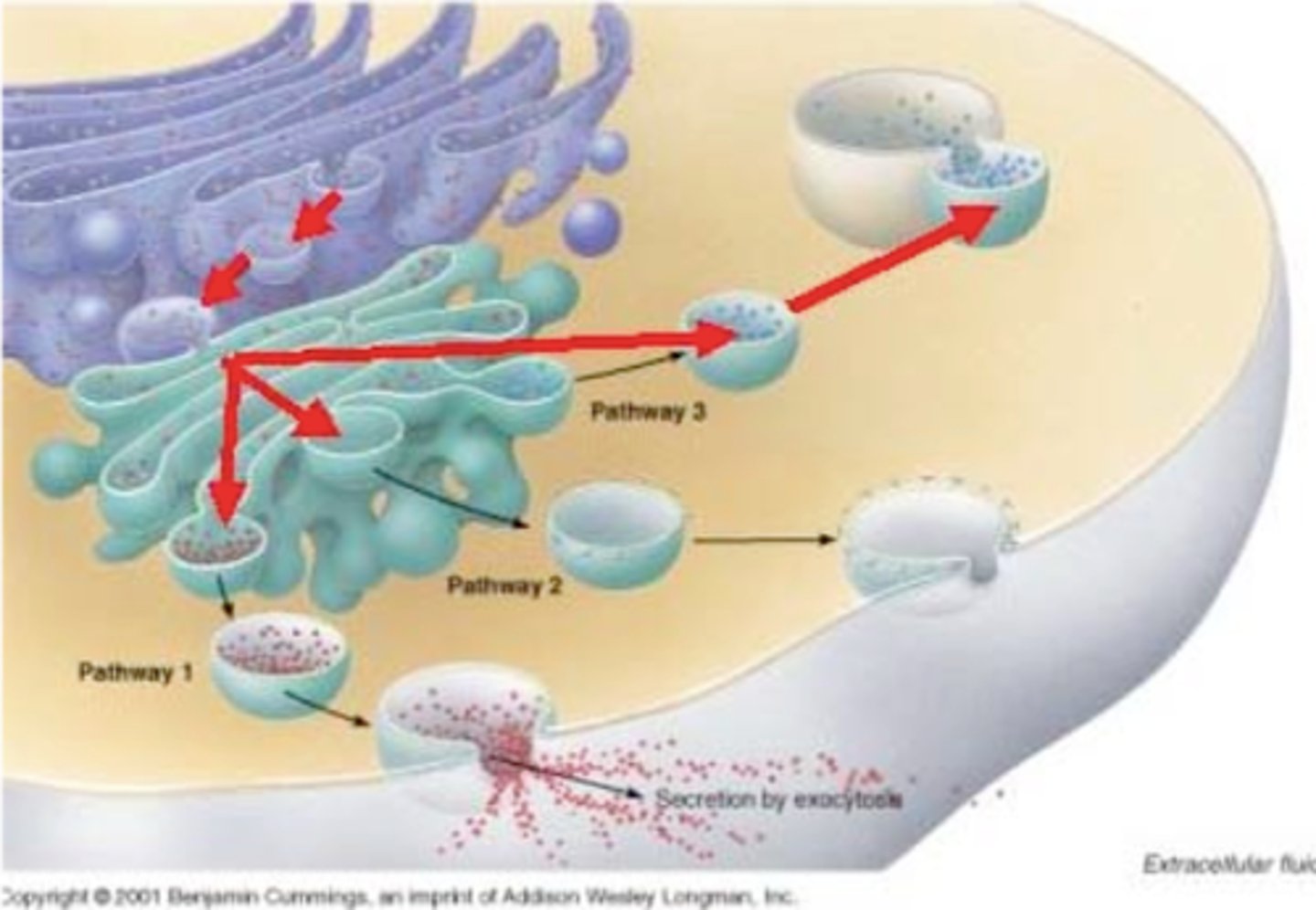
vesicle
Small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell.
nucleolus
A specialized structure in the nucleus, formed from various chromosomes and active in the synthesis of ribosomes
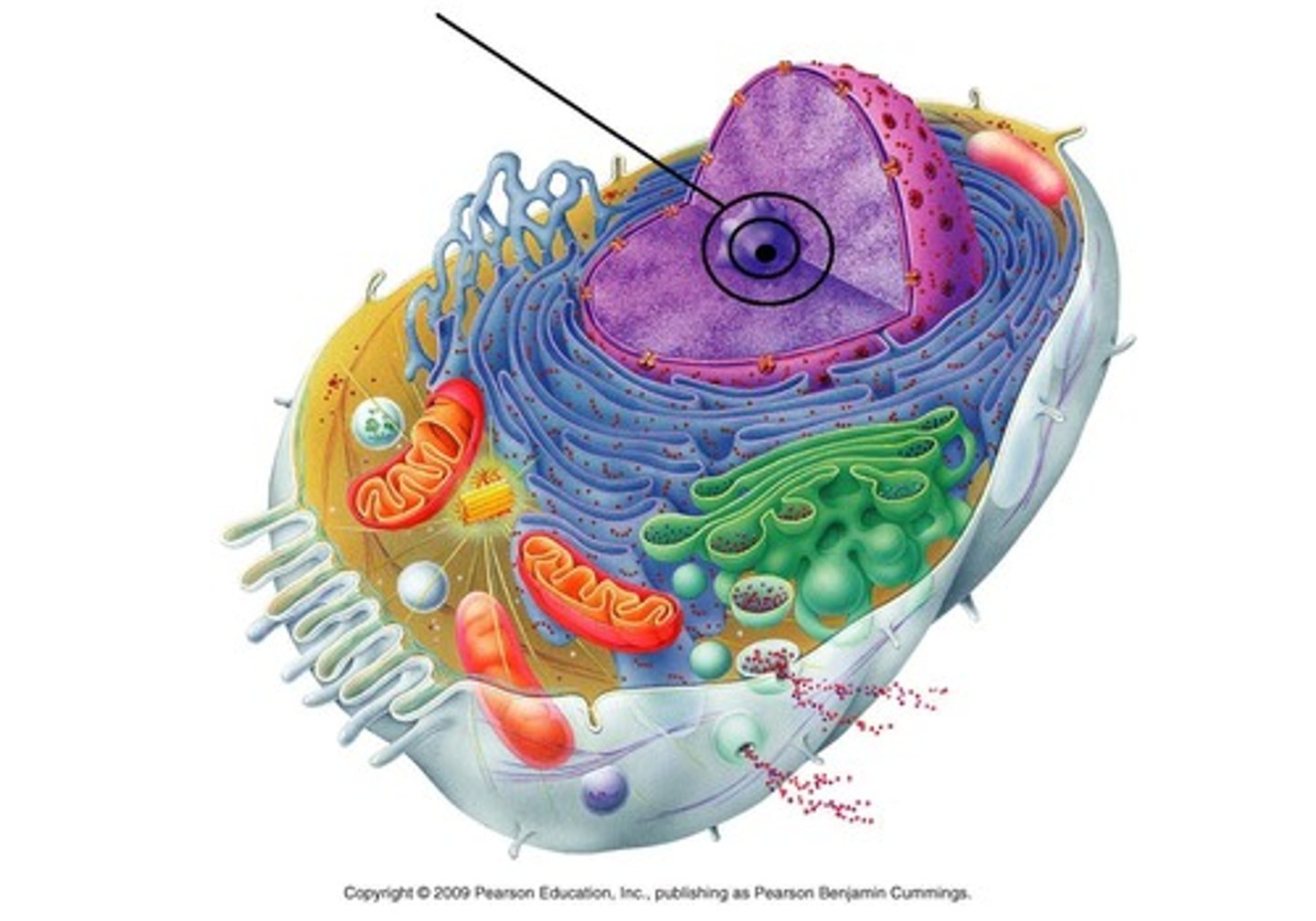
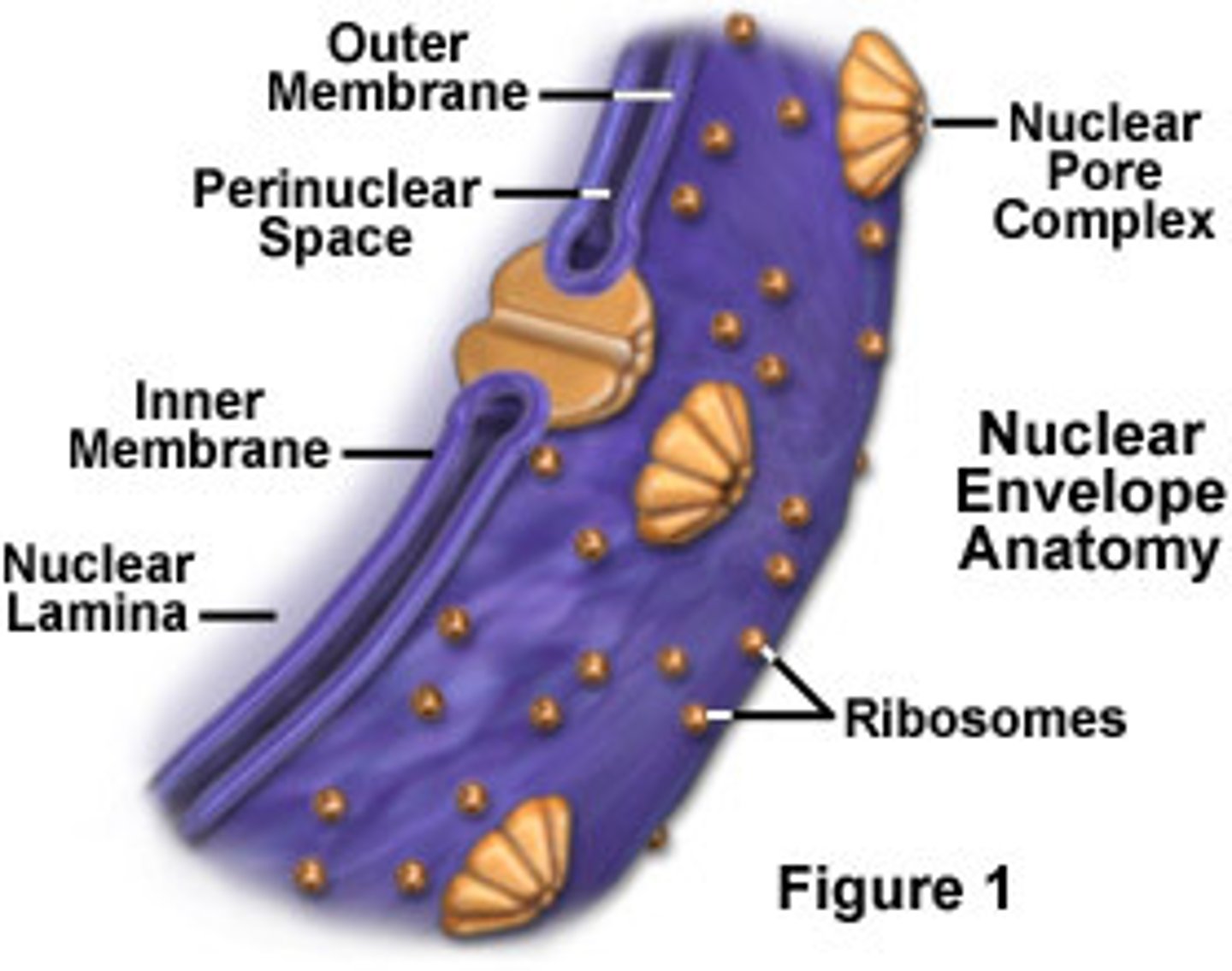
nuclear envelope/membrane
Barrier of the nucleus
Consists of a double membrane
Contains nuclear pores that allow for exchange of material with the rest of the cell
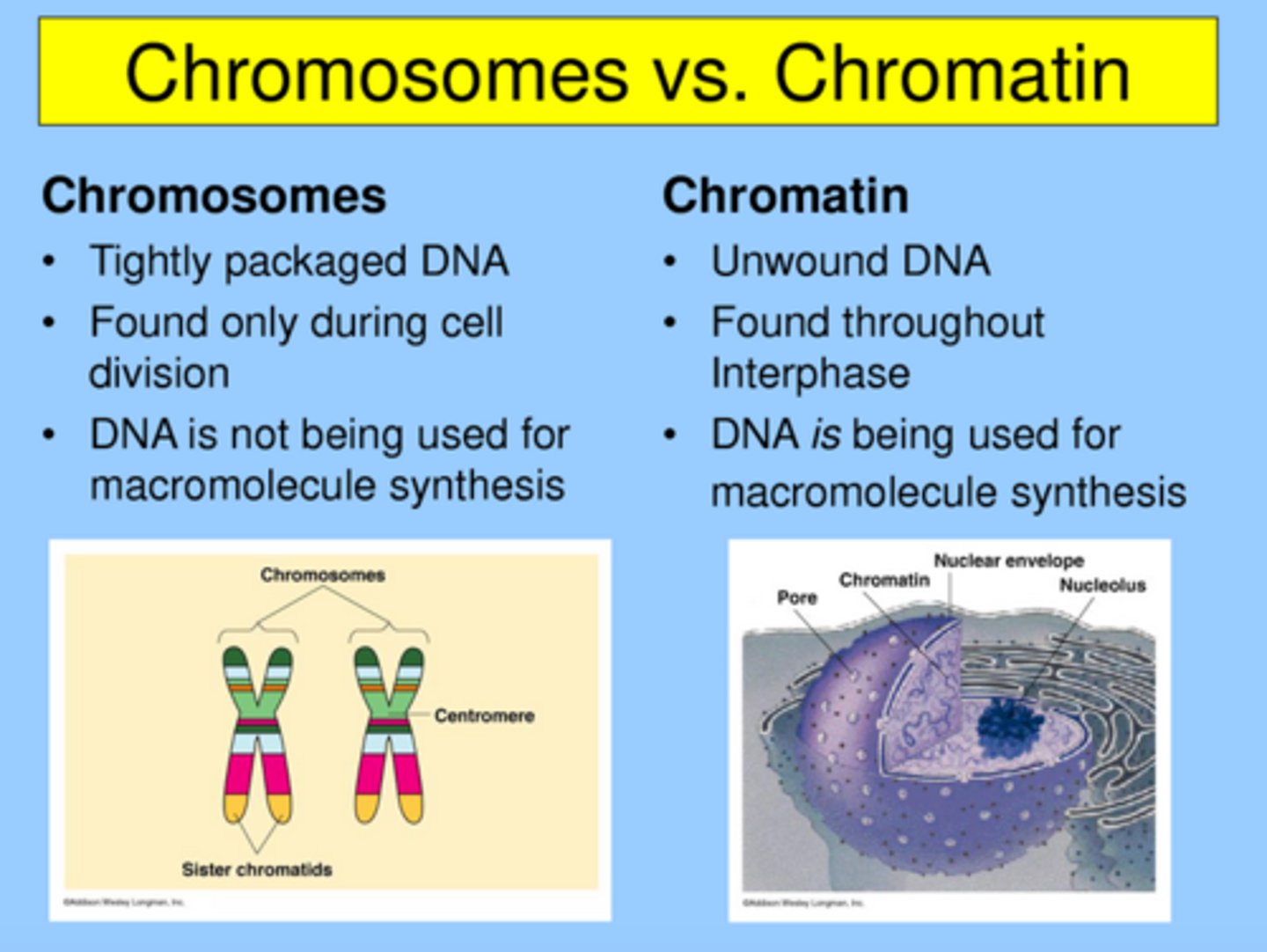
Chromatin/Chromosomes
The form of DNA coiled and packed in the nucleus (becomes individual chromosomes when it condenses before cell division)
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.

Cilia
The hair-like projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner, either propelling the cell forward or move substances past a cell

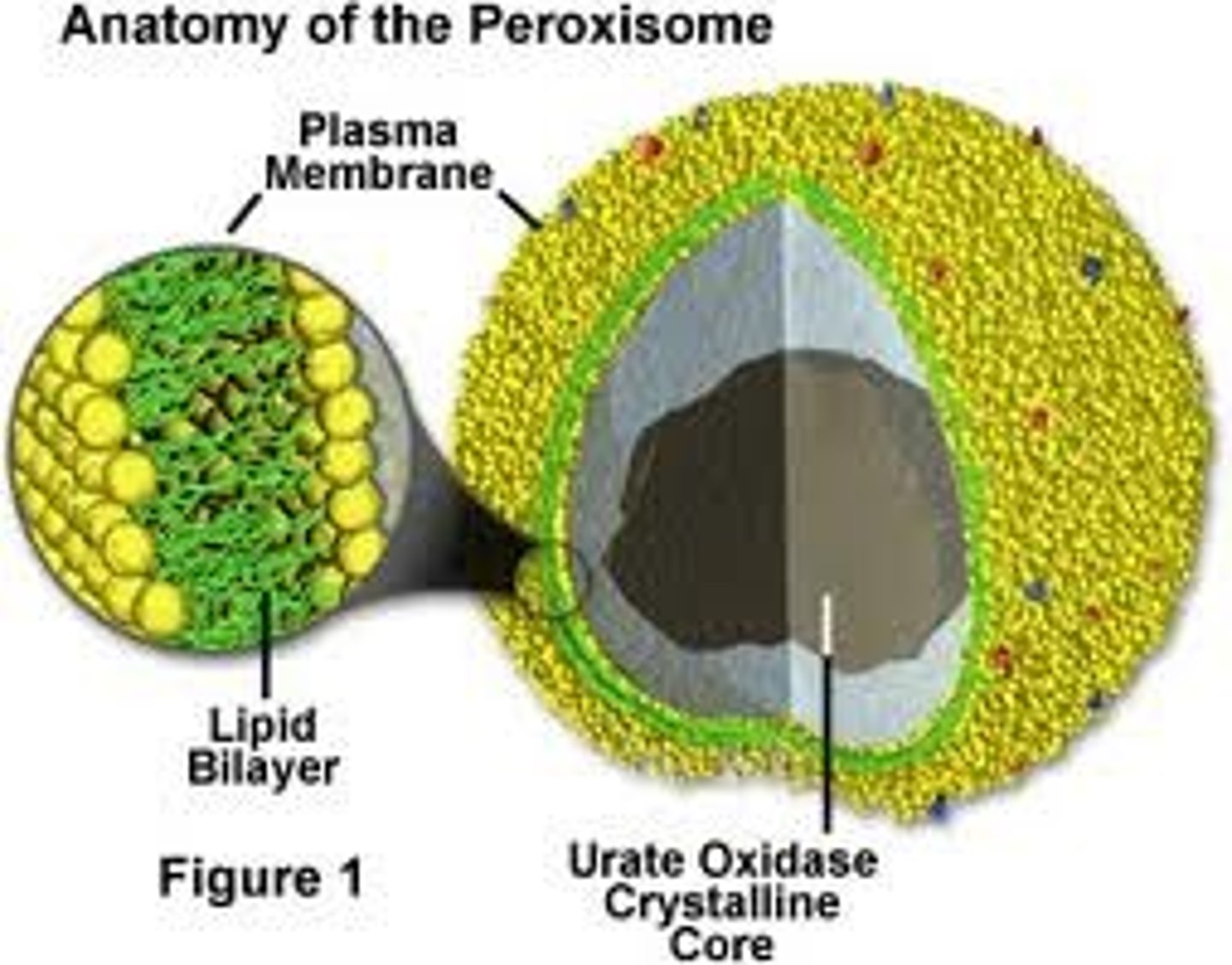
Peroxisome
A microbody containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, producing and then degrading hydrogen peroxide.
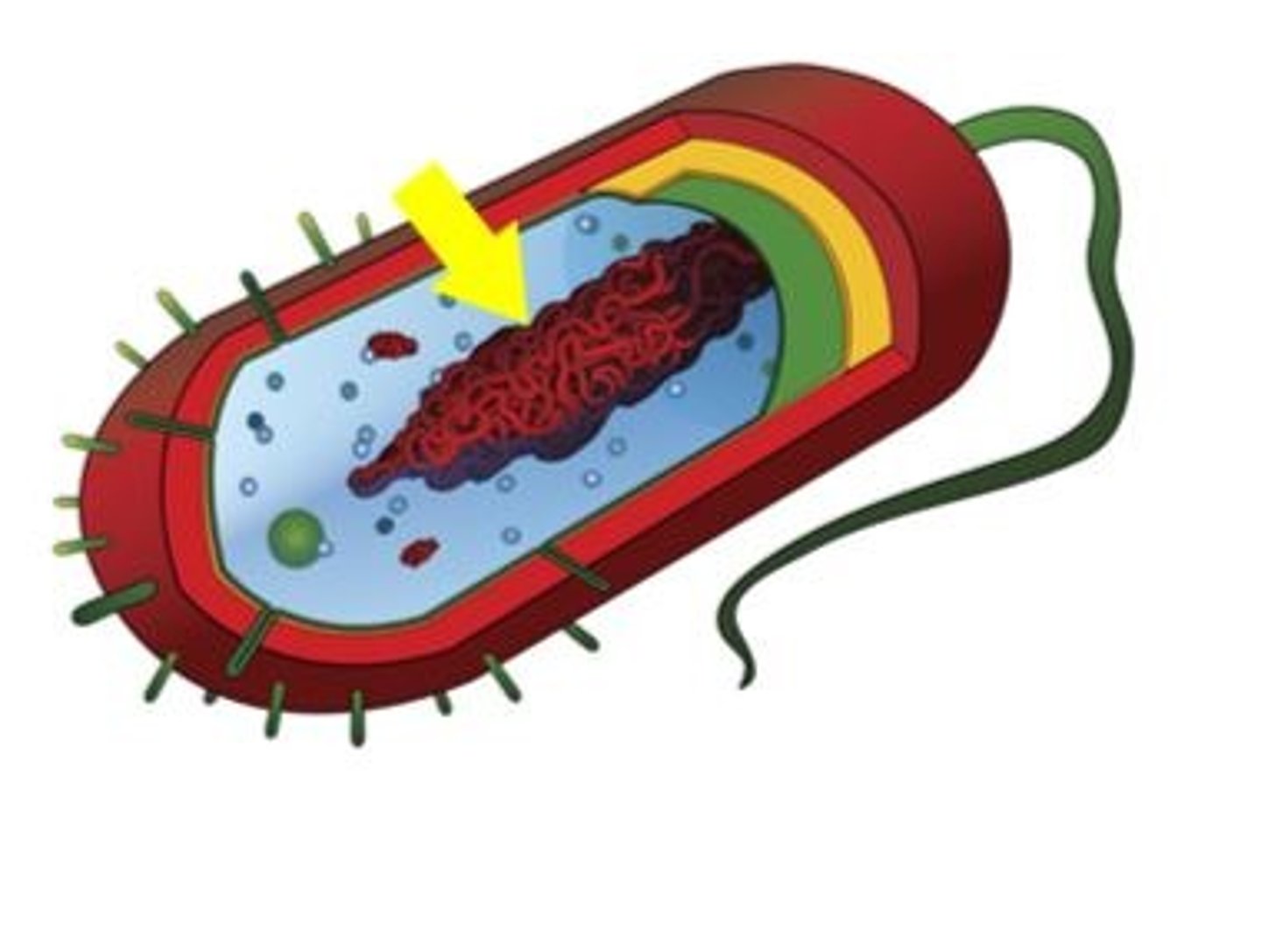
prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (Bacteria)

Cell Theory
idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
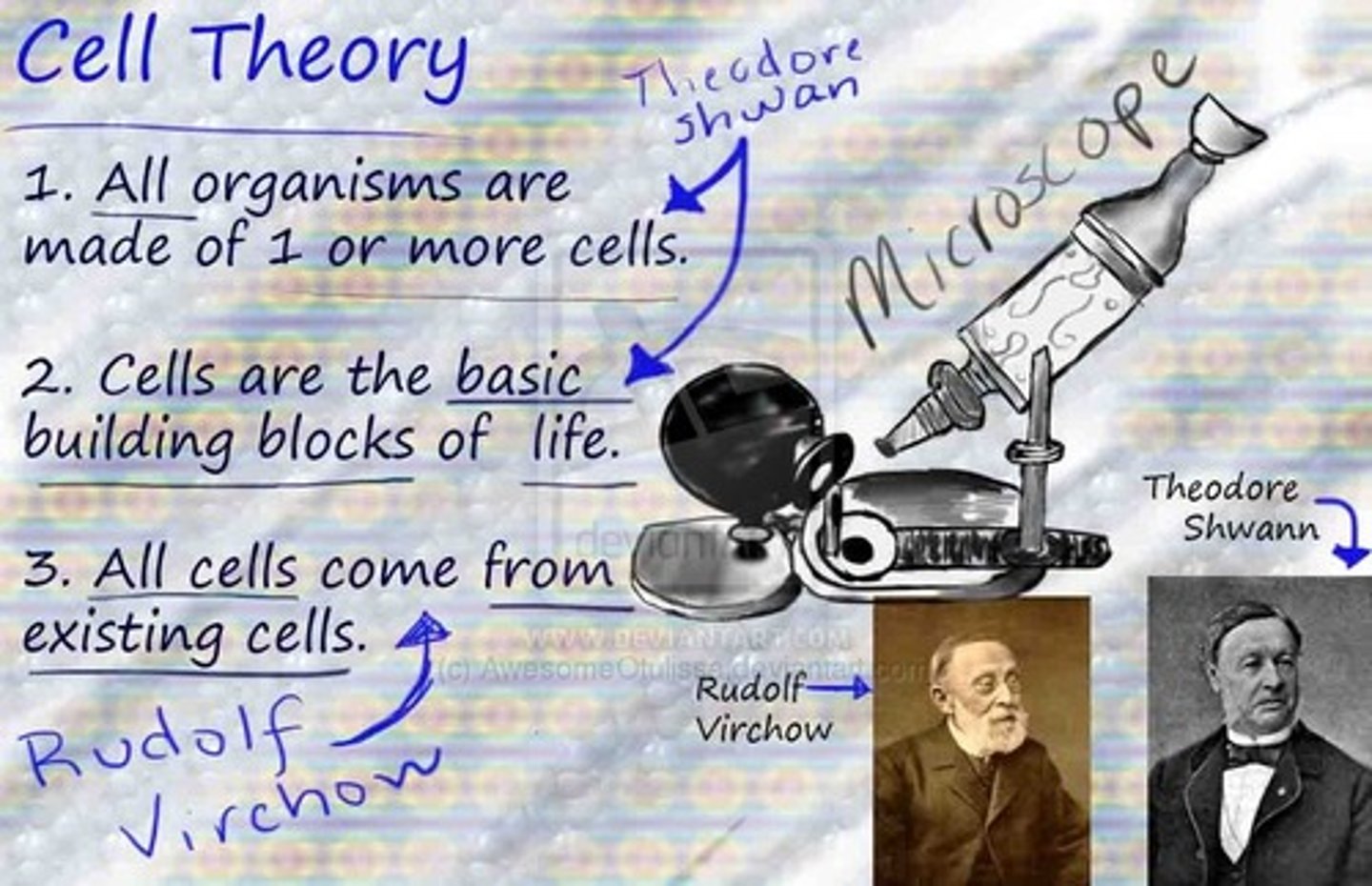
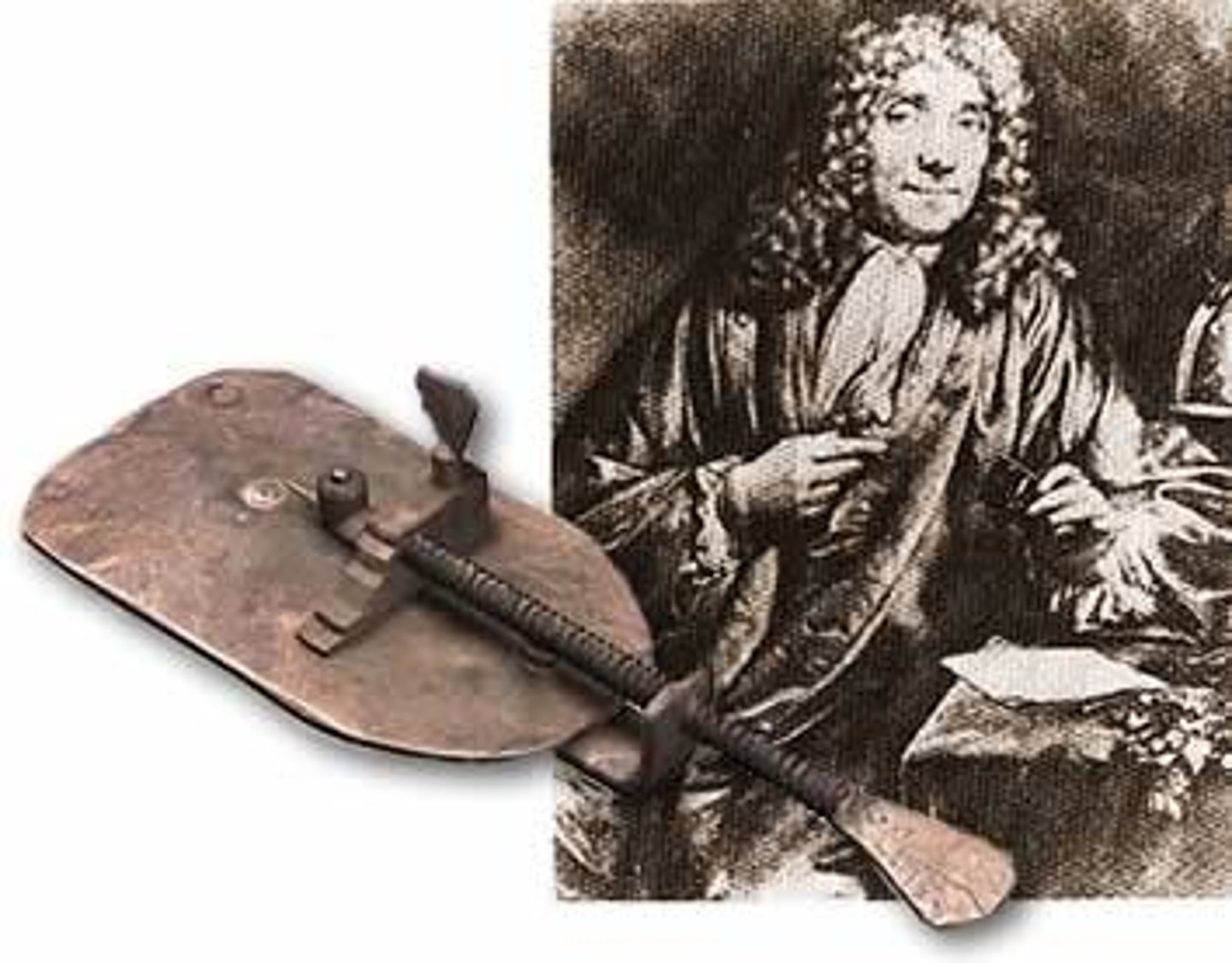
Robert Hooke
first to observe "small chambers" in cork and call them cells.

Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Invented the microscope

Nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
Stated that all plant and animal tissues were made up of cells.

Rudolph Virchow (1855)
determined that cells come only from other cells
compound light microscope
a microscope that shines light through a specimen and has two lenses to magnify an image up to 2000x; can observe living organisms in 2D
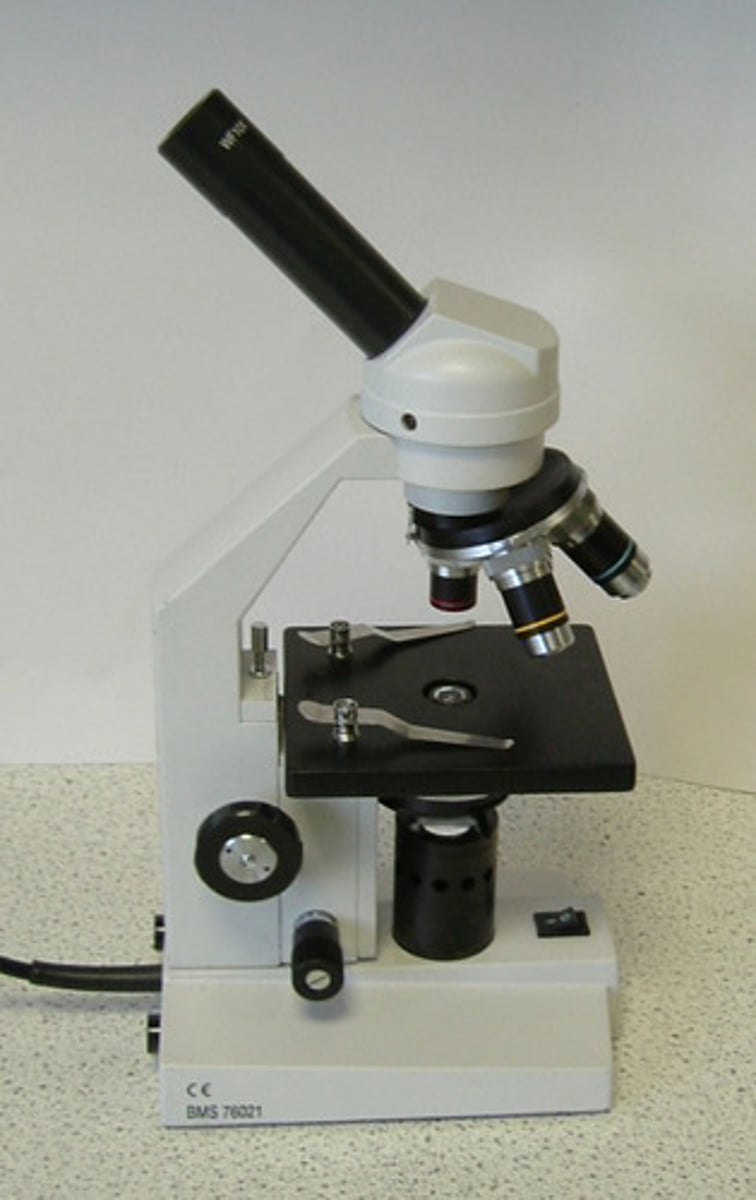

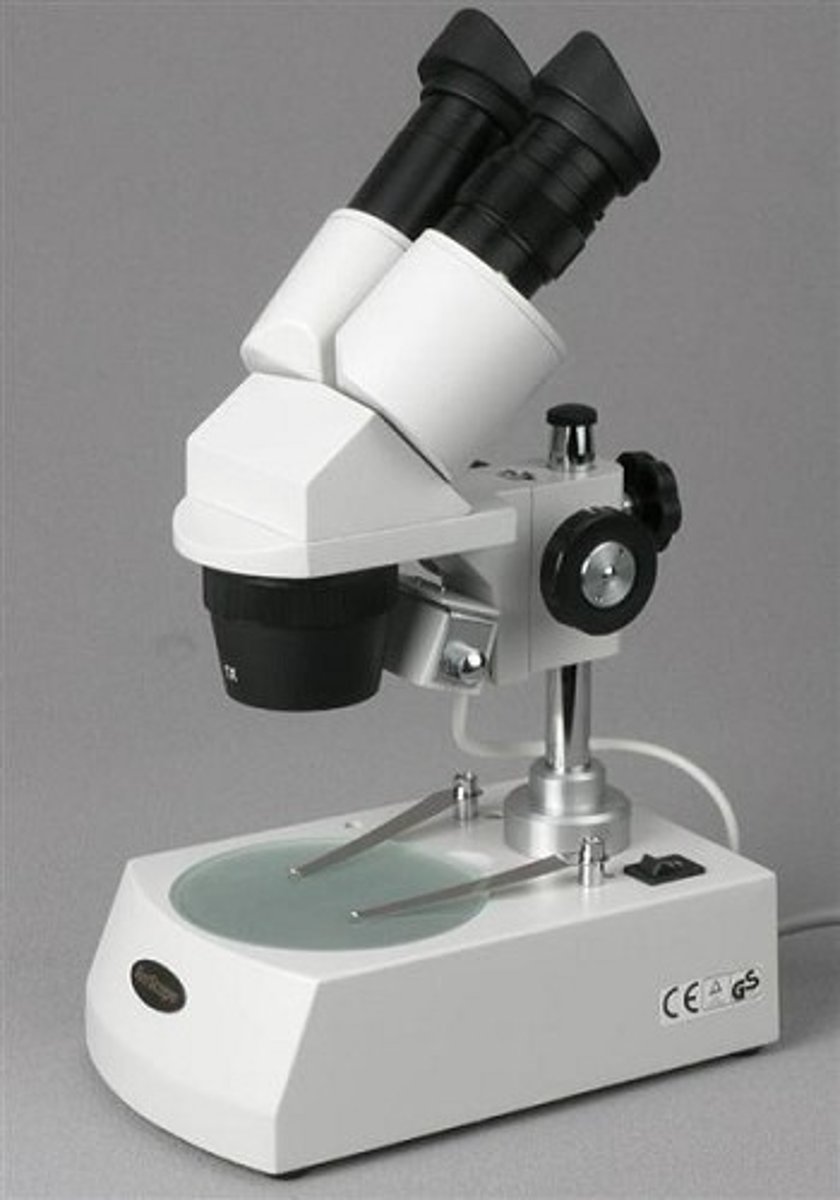
dissecting microscope
light microscope used for low magnifications up to 60x and larger objects; can observe living organisms in 2D
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a sample, coated with metal atoms, to study details of its topography; only dead specimens; up to 1,500,000x magnification; 3D image; on computer screen
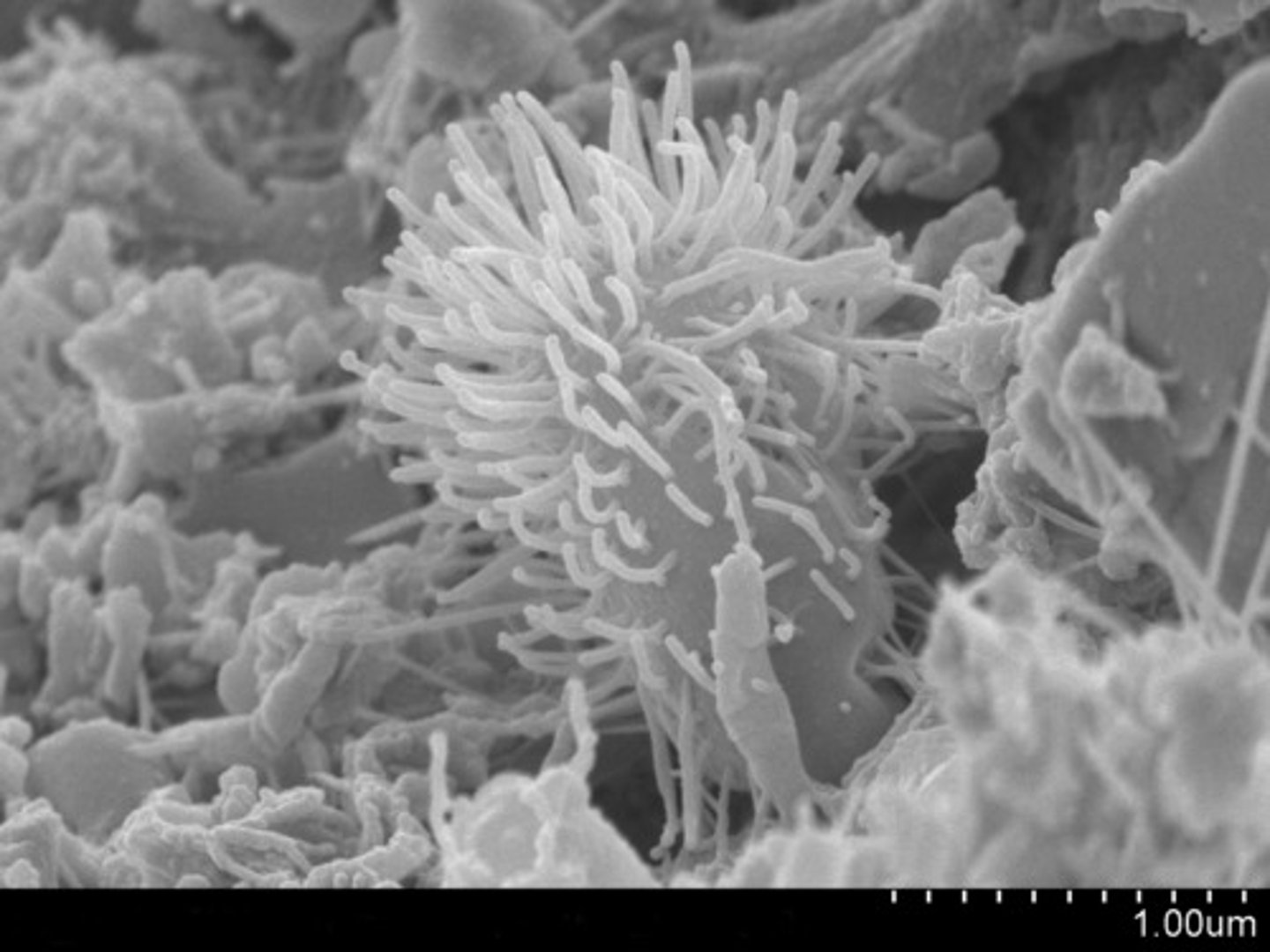
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
a microscope that passes an electron beam through very thin sections stained with metal atoms and is primarily used to study the internal ultrastructure of cells; only dead organisms; up to 200,000x magnification; 2D image; on computer screen.
Domain Eukarya
Domain of all organisms whose cells have nuclei, including protists, plants, fungi, and animals

Domain Archaea
One of the three domains of life; contains prokaryotic cells that often live in extreme habitats and have unique genetic, biochemical, and physiological characteristics; its members are sometimes referred to as archaea.

Domain Bacteria
One of the three domains of life; contains prokaryotic cells that differ from archaea because they have their own unique genetic, biochemical, and physiological characteristics.
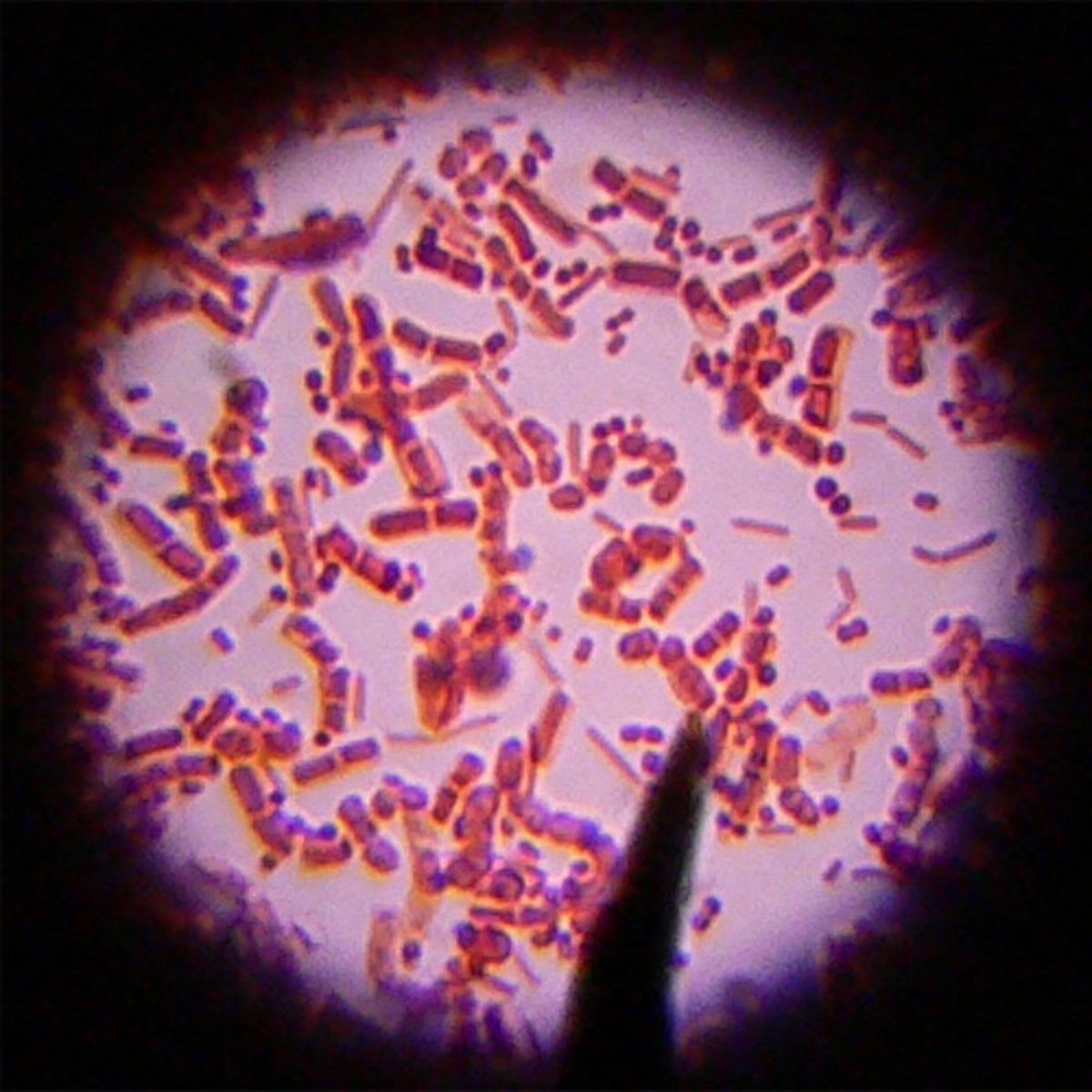
All cells have...
cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes

Unicellular
A single celled organism
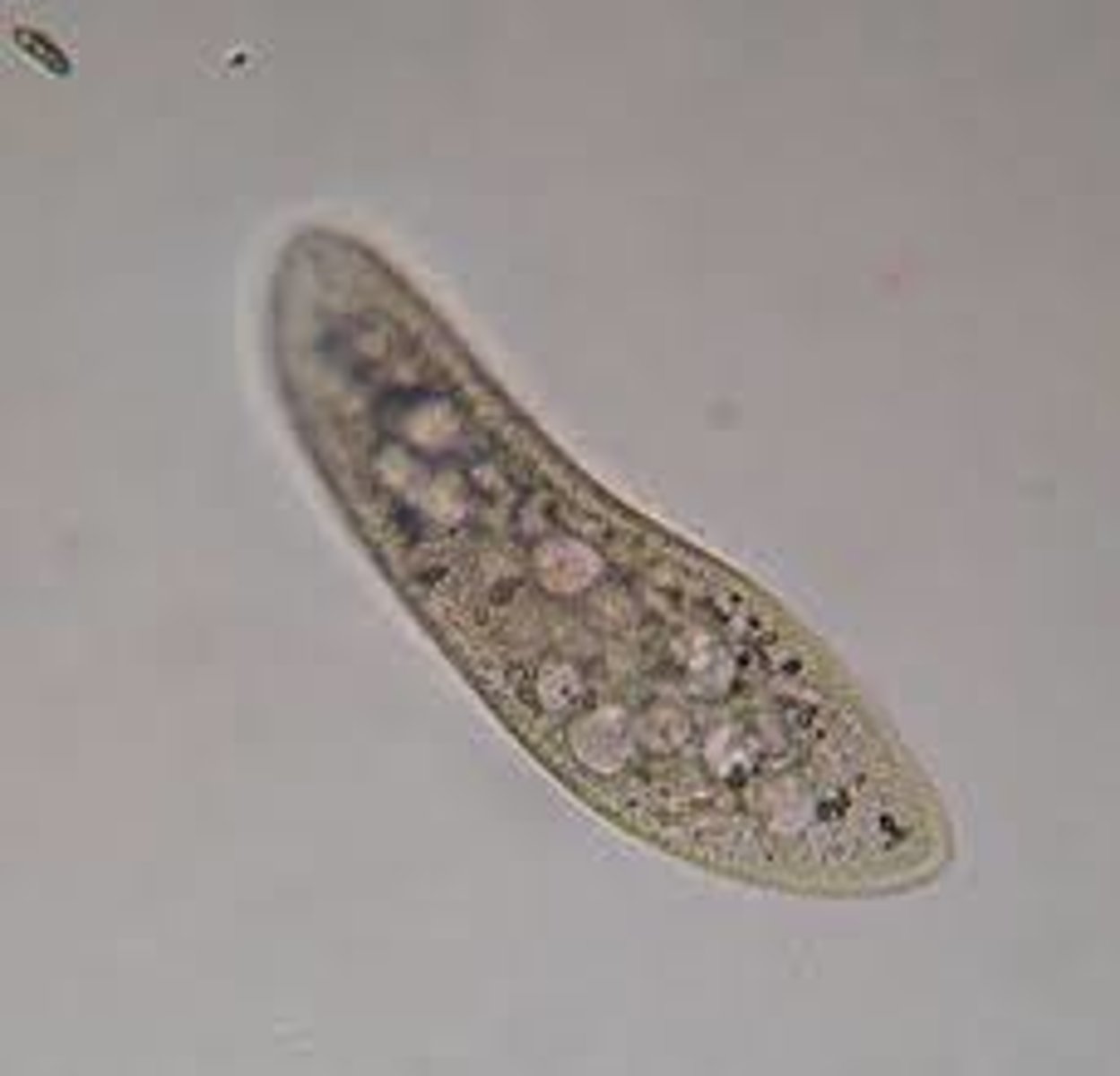
Multicellular
Consisting of many cells

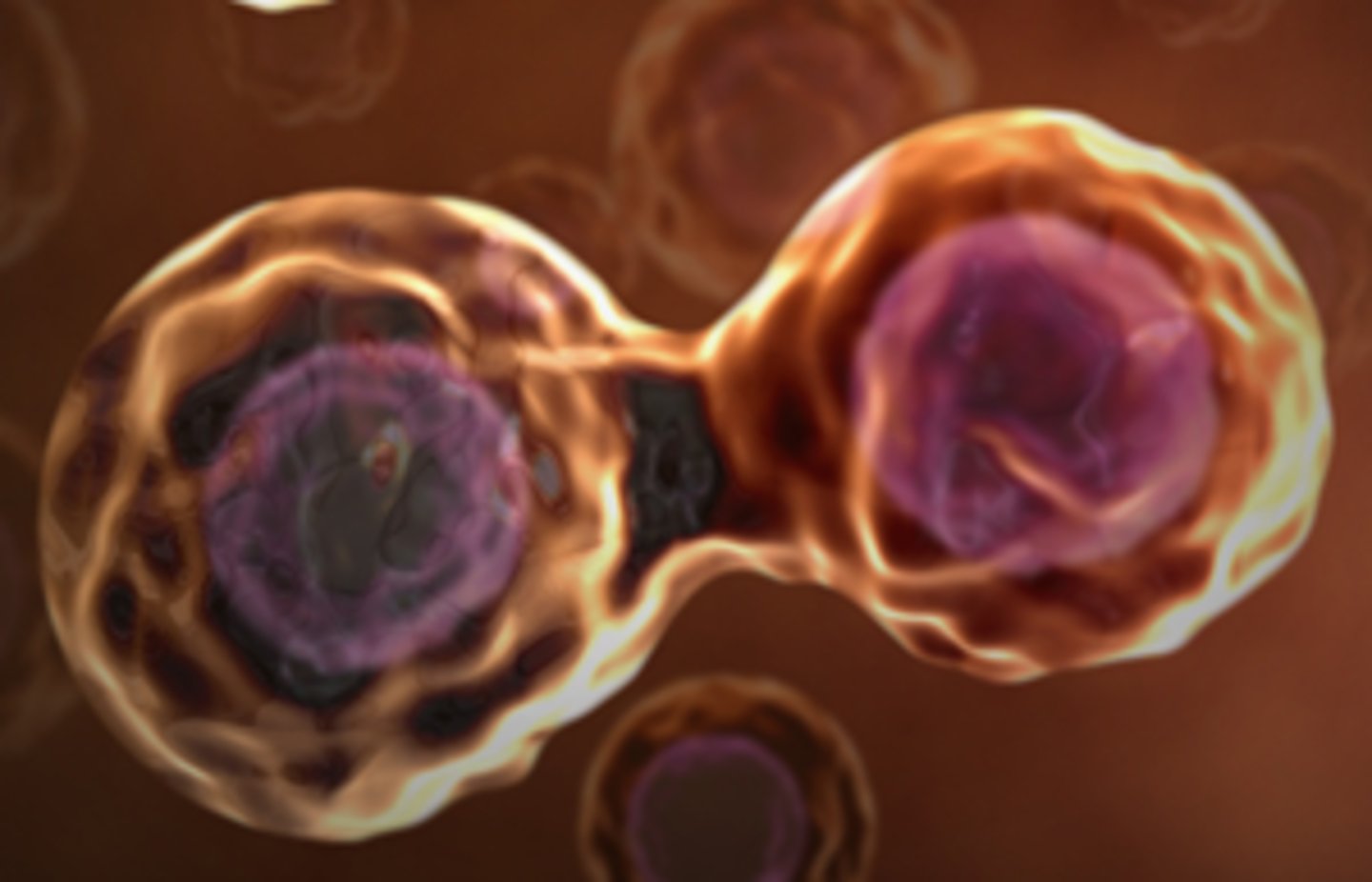
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size; performed by Prokaryotes.
