Cell biology lecture 16
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
More signalling through cell surface receptors
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
3 types of cell surface receptors
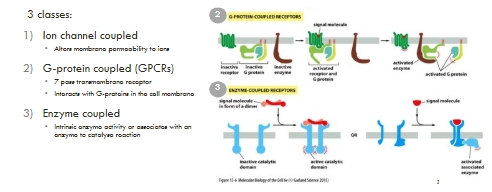
G-protein activation of downstream signalling pathways
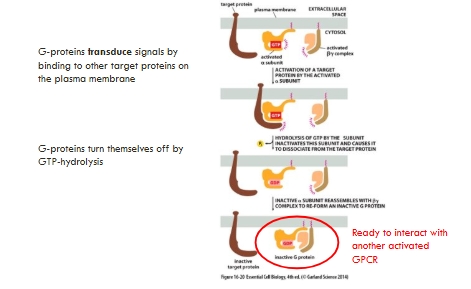
2 key proteins activated by the trimeric G proteins are:
Adenylyl cyclase
Phospholipase C
These enzymes pass information down the signalling pathway by producing 2nd MESSENGERS: See picture

Learning objectives
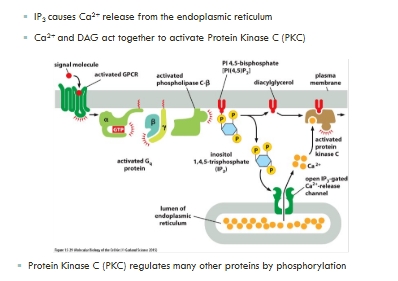
IP3 and DAG as secondary messengers
Protein kinase C
Calcium as a secondary messenger
What are Enzyme linked receptors?
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
The Ras-MAPK pathway and cancer
Activation of the G-protein linked receptor
Results in dissociation of the trimeric G-protein
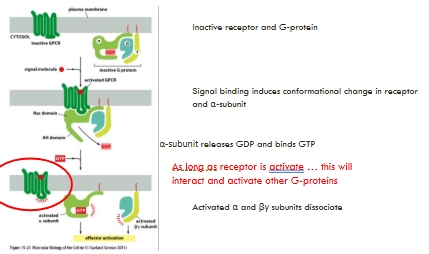
Transduction of G protein signals
Phospholipase action
Cleaves phosphoinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to produce IP3 and DAG
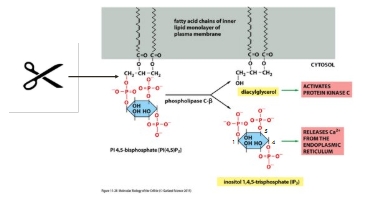
IP3 and DAG action
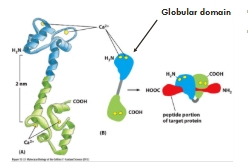
Ca2+ as a second messenger
Small changes in Ca2+ are easily detected, because cytosolic Ca2+ levels are maintained at a low level (~10-7M), compared to extracellular Ca2+ (~10-3M)
Ca2+ can bind tightly to proteins inducing conformational change
Calmodulin
Mediator of many calcium dependent effects
Each calmodulin molecule binds 4 Ca2+ ions
The resulting conformational change allows the calmodulin/Ca2+ complex to wrap around and activate target proteins
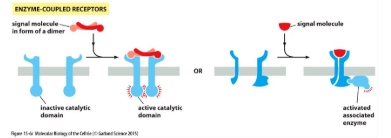
Enzyme linked receptors
Single-span transmembrane proteins
Cytosolic domain has intrinsic enzymatic activity or is associated with an enzyme
Receptor Tyrosine kinases (RTK)
most common type of enzyme linked receptors
The RTK family includes Insulin receptor and many growth factor receptors
Growth factor receptors control cell proliferation
Cancer is frequently associated with problems in growth factor signalling
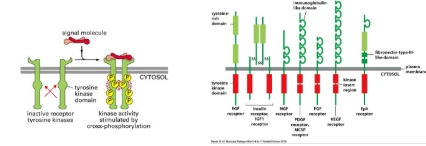
What does the cytoplasmic/cytosolic domain or receptor tyrosine kinases have?
Intrinsic kinase activity
Binding of the ligand to growth factor receptors leads to cross-linking of two receptor chains
Oligomerisation of the receptor chains allows cross-phosphorylation (autophosphorylation)
Insulin receptors are tetramers; ligand binding causes realignment of the polypeptide chains activating cross-phosphorylation
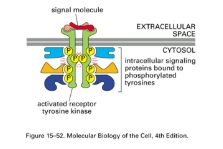
what do phosprylated tyrosine residues achieve?
Provide docking sites for other signalling proteins
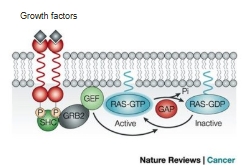
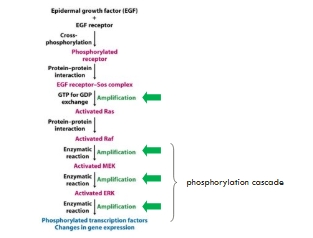
The RAS Signalling Pathway
Ras is the main signal-transducer protein for growth factors e.g. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF)
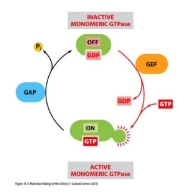
Ras is a small MONOMERIC G-protein (very small)
Trimeric protein
Like G protein coupled receptor (larger protein)
Bind directly to receptor
Receptor activates GDP release
GTP hydrolysis by intrinsic GTPase activity alone
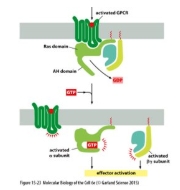
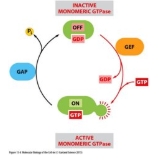
Monomeric protein
Like RAS
Not directly linked to receptor
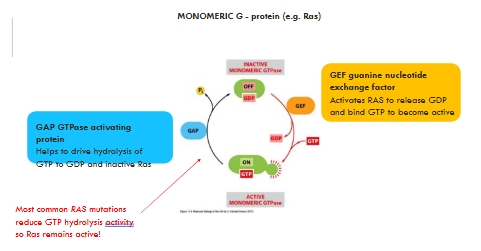
GDP release activated by GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor)
Weak intrinsic GTPase activity – needs GAP (GTPase activating protein) to drive GTP hydrolysis.
RTK mediated activation of the RAS-MAPKpathway
RAS and GEF do not bind directly to the RTK
Binding is mediated by an adapter protein, Grb-2
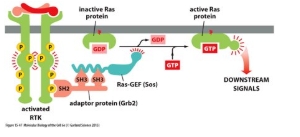
What does Ras activate?
A downstream phosphorylation cascade
Ras, Raf, Mek, Erk
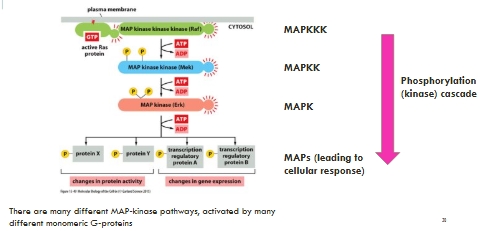
Amplification steps of the Ras-MAPK pathway:
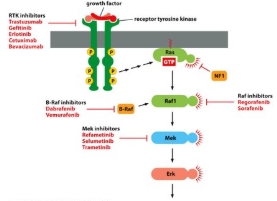
The RAS Signalling Pathway and cancer
RAS is a proto-oncogene (in cell growth)
RAS mutations are found in 20-30% of human cancers (~80% pancreatic)
Most common RAS mutations reduce GTP hydrolysis activity
GTP stays bound longer and the signalling pathway is continuously switched on
Leads to cell proliferation, even in the absence of growth factors such as EGF
RAS becomes an oncogene and causes cancer
Ras pathway
Inhibitors targeting The RAS Signalling Pathway
Don’t need to know specific drugs