Week Seven: Populations
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
distribution and abundance
The main goal of ecology is to understand the __________ and _________ of organisms
ecology
The study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment
Biotic Factors
living organisms (predators, competitors, etc.)
Abiotic factors
nonliving aspects (sunlight, temperature, humidity, water, etc.)
population
A group of individuals of the same species that lives in the same area at the same time, where it can tolerate abiotic environment
evolution
________ of new traits determine population growth or decline under local biotic and abiotic conditions
Population ecologists
___________ __________ ask questions about how and why the numbers of individuals in a population change over time
species
All populations, collective
size
Total number of individuals of all ages present at same time and in same area
range
area over which population is spread, driven by abiotic and biotic factors
density
size divided by range, can affect population size
random
in this distribution an individual has equal chance of occupying any position within range
plants
random distribution is normally seen in _____
clumped
in this distribution is seen in individuals grouped close together for safety or resources
meerkats
Clustered distribution is typically seen in _______
uniform
in this distribution is seen in individuals that may prevent from others being near by, and is more even than predicted by chance
count
How do ecologists measure size with sessile species?
mark and recapture
How to ecologists measure size with mobile species?
N = (C/R)M
What is the mark and recapture formula?
population size
What does N stand for in the mark and recapture formula?
total number caught
What does C stand for in the mark and recapture formula?
Number of marked recaptured
What does R stand for in the mark and recapture formula?
Marked on day one
What does M stand for in the mark and recapture formula?
N=(B-D)+(I-E)
What is the formula for population size changing with time?
change in population size/time
Rate of change of population size is given as:
Per capita growth rate (r)
Rate of population change divided by population size gives
Continuous
______ growth is when population increases or decreases continuously
discrete
______ growth is when population increases or decreases in steps
asynchronous
Species with ________ life cycles have continuous growth
synchronous
Species with ________ life cycle have discrete growth
synchronous
seeds germinating, growing, maturing, and then reproducing is an example of ________ lifecycle
asynchronous
being born and develop at different times like people, is an example of ________ life cycles
exponential
This formula is the equation for ________ growth
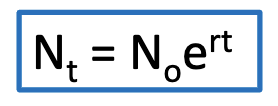
size, growth rate constant
Exponential growth is the simplest model as it assumes no constraints of ____, _______ ____ _______
Intraspecific
Competition for resources within species
interspecific
Competition for resources among species
Carrying capacity
(K) – max # of individuals habitat can sustain without degradation
S
Logistic growth produces and _ shaped curve
K
Logistic growth allows for _ to be displayed in the graph
Density-dependent factors
change in population related to size, due to competition (for food and other resources) and predation
Density-independent factors
change in population not related to its size
predict changes in population
Ecologists ______ _____ __ _______ using – 1) birth rate, 2) longevity of individuals, 3) proportion able to reproduce
age structure of population
divide population into age classes, structure allows predictions of growth
socioeconomics
Age structure of human populations partly driven by ___________
demography
study of size, structure, distribution of population
cohort
group of individuals born at the same time
Survivorship
proportion of individuals from initial cohort that survive each successive stage of life cycle
life table
This table shows number of individuals of cohort that are alive at different points
Survivorship
proportion of individuals from initial cohort that survives
Type I
What type of survivorship has high mortality at later stages
Type II
What type of survivorship has equal mortality throughout
Type III
What type of survivorship has high mortality at early stages
r
_-strategists are:
unpredictable environment
many young
type III survivorship curve
Reduce at rates approaching rmax
k
_-strategists are:
predictable environment
fewer young, larger, better-cared-for
type I survivorship curve
population commonly near carrying capacity
life history
typical pattern of resource investment in individuals to growth, maintenance or reproduction
Metapopulation
Collection of local populations, linked by corridors and movement between patches
Patch
Islands of habitat separated by uninhabitable corridors
vacant habitat
Metapopulation survives through recolonization of ______ ______
connected
When studying patches of moss that are connected and disconnected, the _________ patches survived better
island
any habitat patch surrounded by expansive inhospitable environment