Hearing and Balance Mechanoreceptors
5.0(3)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
What is the difference between Optic and Otic
Optic refers to eye and Otic refers to ear
2
New cards
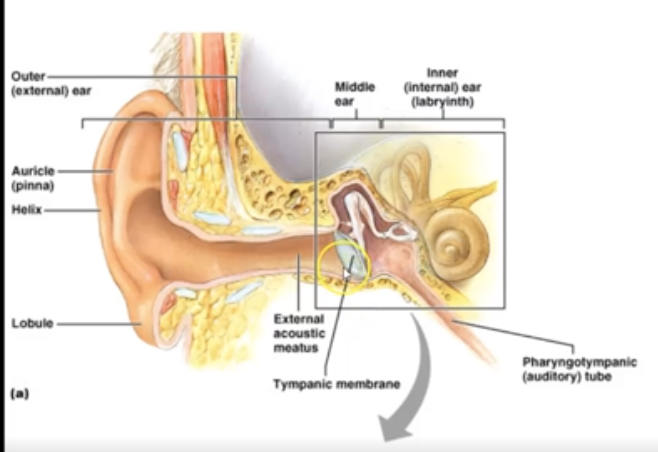
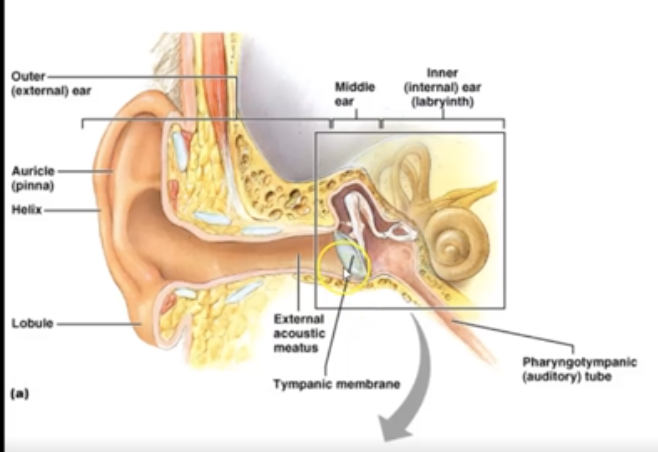
What are the 3 section of ear?
Outer (external) ear, Middle (ossicles) ear for hearing and inner (labyrinth) ear for hearing and equilibrium
3
New cards
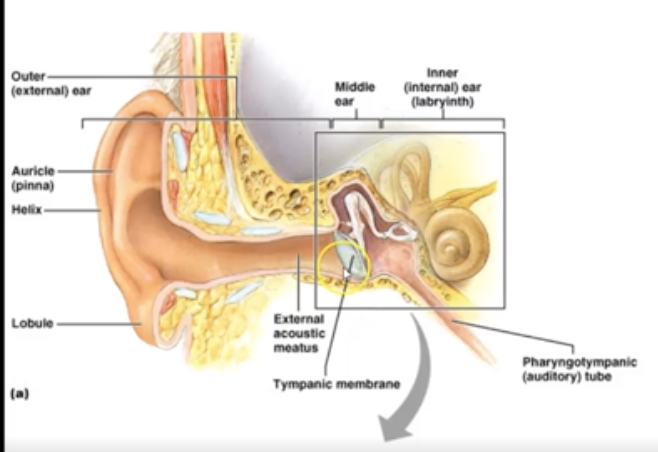
What are the 7 main parts of ear?
Tympanic Membrane, Malleus (Hammer), Incus (Anvil), Stapes (stirrup), Oval Window, Cochlea and Semicircular Canals.
4
New cards
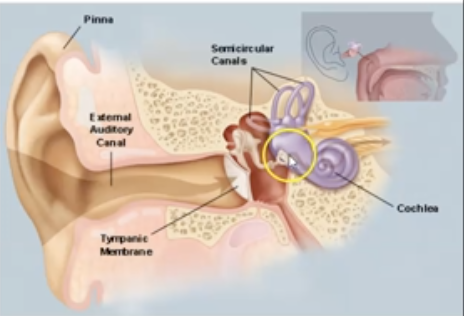
What is the function of 3 small bones (Malleus, Incus and Stapes)
Tympanic membrane vibrates in response to sound waves
Malleus vibrates due to change in Tympanic Membrane
Incus vibrates due to change in Malleus
Stapes vibrates due to change in incus
Malleus vibrates due to change in Tympanic Membrane
Incus vibrates due to change in Malleus
Stapes vibrates due to change in incus
5
New cards
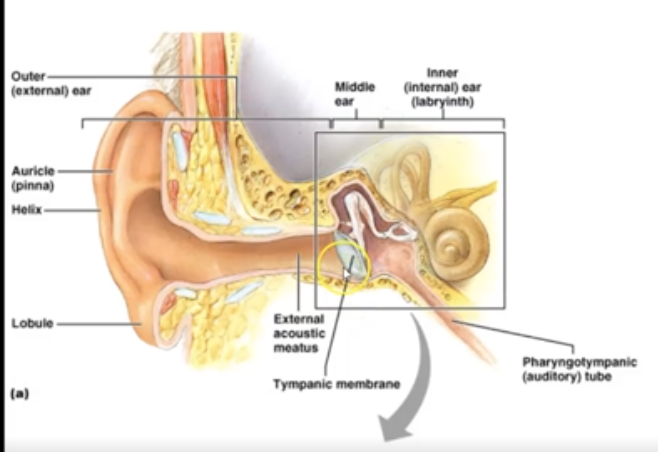
What is the function of Oval Window?
Oval Window moves fluid within cochlea in response to vibrations from stapes
6
New cards
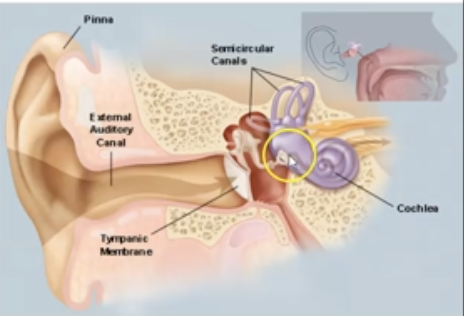
What in the function of Cochlea?
Contains receptors that react to changes in sound waves
7
New cards
What is of Semicircular Canals and its function in ear?
Fluid-filled structures that respond to changes in body position.
8
New cards
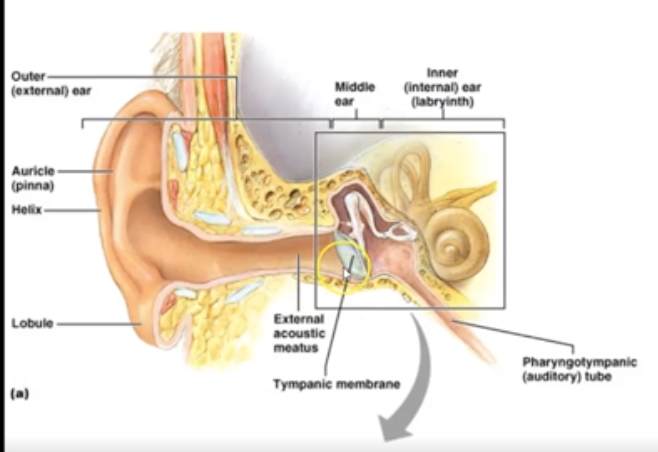
What happens after sound waves enter oval window
Vibrations cause disturbance in:
- perilymph → endolymph → basilar membrane → tectorial membrane → hair cells
- perilymph → endolymph → basilar membrane → tectorial membrane → hair cells
9
New cards
_____ frequency is detected close to oval window
Highest
10
New cards
_____ frequency is detected further from oval window
Lowest
11
New cards
What are mosquito ring tones?
High pitched ring tones
12
New cards
Fire alarms use _____ frequency tones so that older people can hear them
low
13
New cards
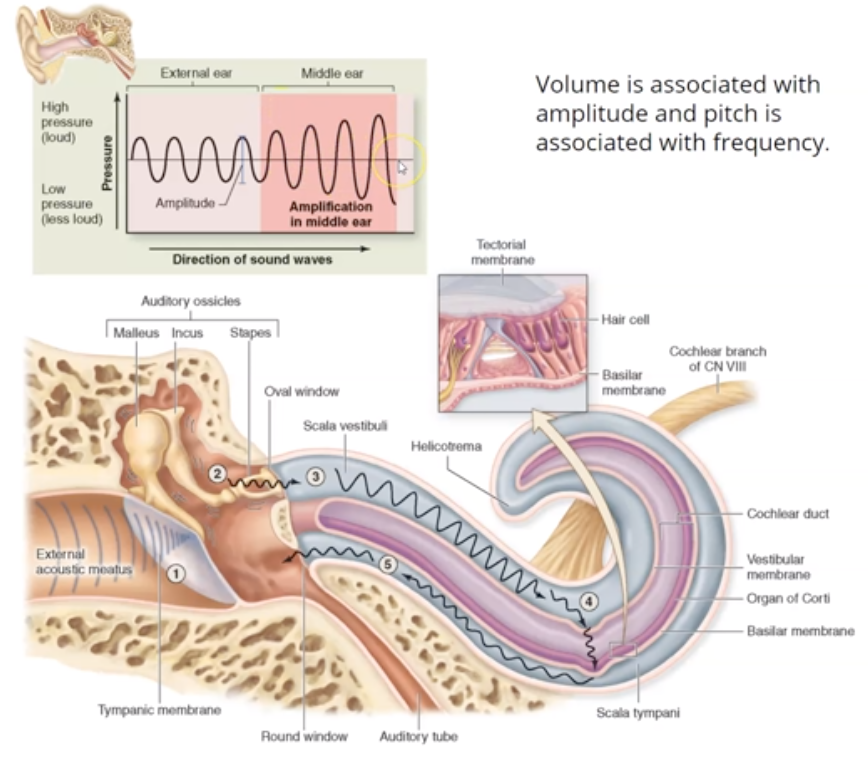
Volume is associated with ______ and pitched is associated with ______
Volume is for Amplitude
Pitch is for frequency
Pitch is for frequency
14
New cards
Movement of fluid surrounding the receptors causes ______ to move and triggers an action potential in ear
Sterocilia
15
New cards
What are ossciles
3 small bones on our body: Malleus (hammer), Incus (anvil) and Stapes (stirrup)
16
New cards

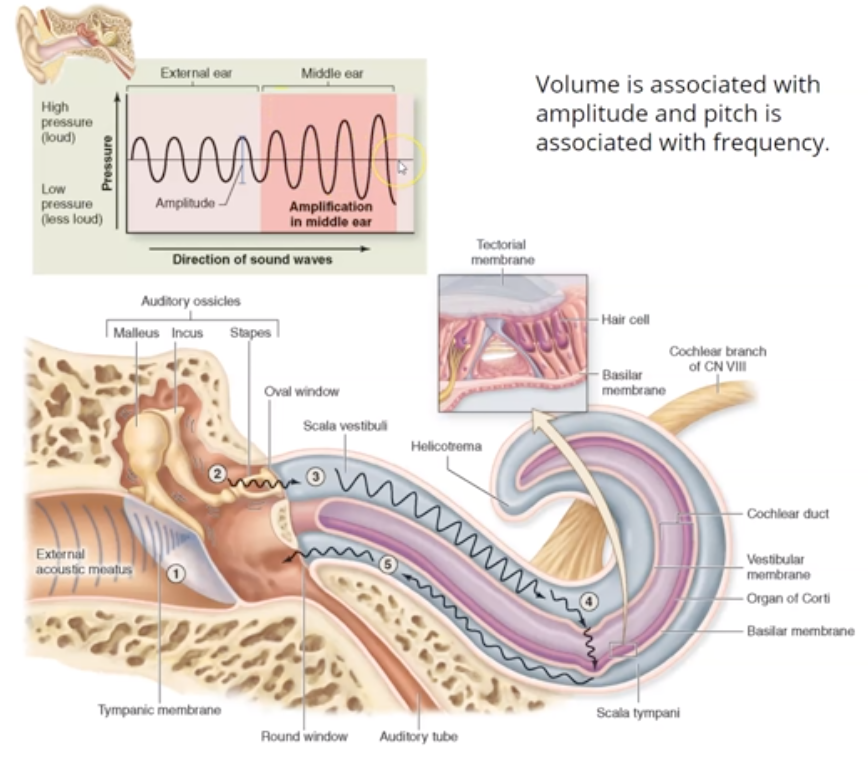
What are the First 3 steps sound transmission?
1. Sound in the external acoustic meatus hits the tympanic membrane (eardrum), causing it to vibrate.
2. Pressure is equalized by the pharyngotympanic tube (aka eustachian or auditory tube), which is about 45 mm long
3. The TM (aka eardrum) causes the ossicles in the air-filled middle ear to move.
2. Pressure is equalized by the pharyngotympanic tube (aka eustachian or auditory tube), which is about 45 mm long
3. The TM (aka eardrum) causes the ossicles in the air-filled middle ear to move.
17
New cards
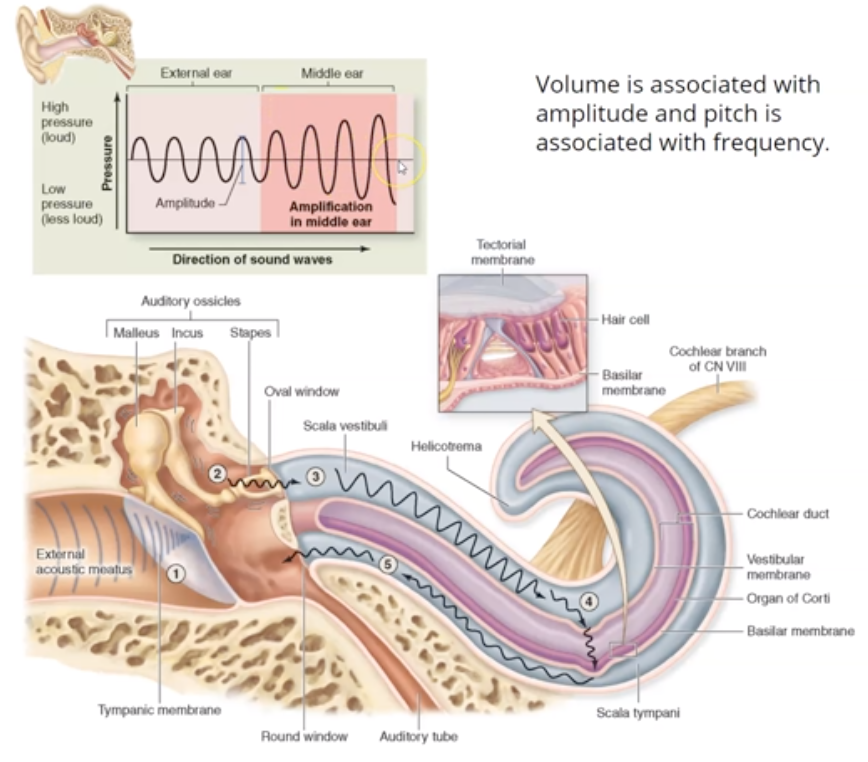
What are the last 4 steps in sound transmission?
4. The ossicles articulate to form a lever system that amplifies and transmits the vibratory motion of the TM to fluids of the inner ear cochlea via oval window
5. Vibration of the stirrup (stapes) at the oval window causes waves to start traveling in the fluid filled cochlea
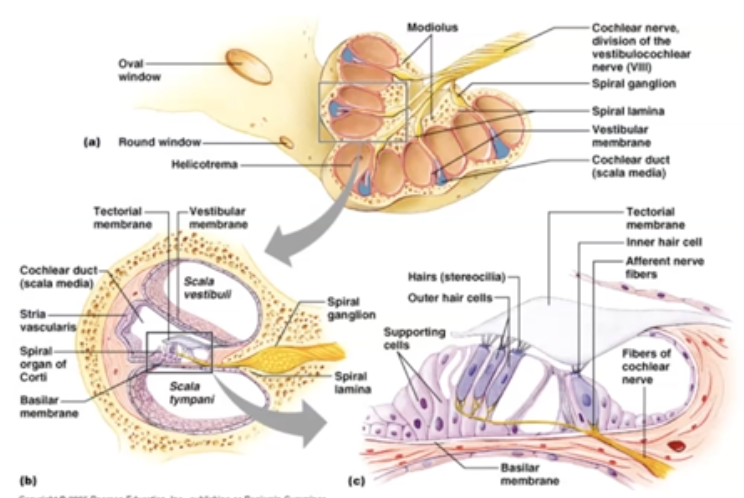
6. Sensory hair cells (stereocilia) are stimulated
7. The stereocilia send impulses to the cochlear nerve, a division of Nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve)
5. Vibration of the stirrup (stapes) at the oval window causes waves to start traveling in the fluid filled cochlea
6. Sensory hair cells (stereocilia) are stimulated
7. The stereocilia send impulses to the cochlear nerve, a division of Nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve)
18
New cards
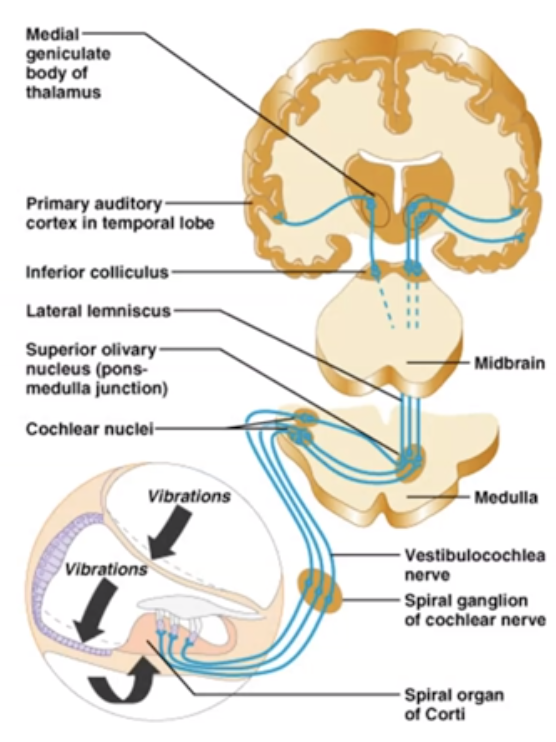
What does information go from cochlear nerve?
Cochlear Nerve -> Medulla -> Pons -> Midbrain -> Thalamus -> primary auditory cortex (temporal lobe)
19
New cards
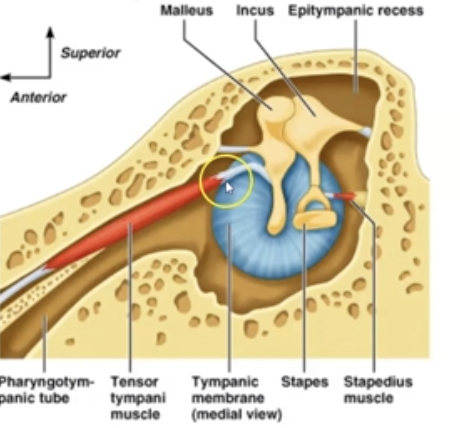
What are the 3 parts of the middle ear and their fuctions?
1. Cochlea: hearing
2. Vestibule: equilibrium
3. Semicircular canals: equilibrium
2. Vestibule: equilibrium
3. Semicircular canals: equilibrium
20
New cards
What is the difference between semicircular canal and vestibule?
Semicircular canal: Determines kinetic (rotational) equilibrium
Vestibule (ortholitic organs of utricle & saccule): Determine static equilibrium
Vestibule (ortholitic organs of utricle & saccule): Determine static equilibrium
21
New cards
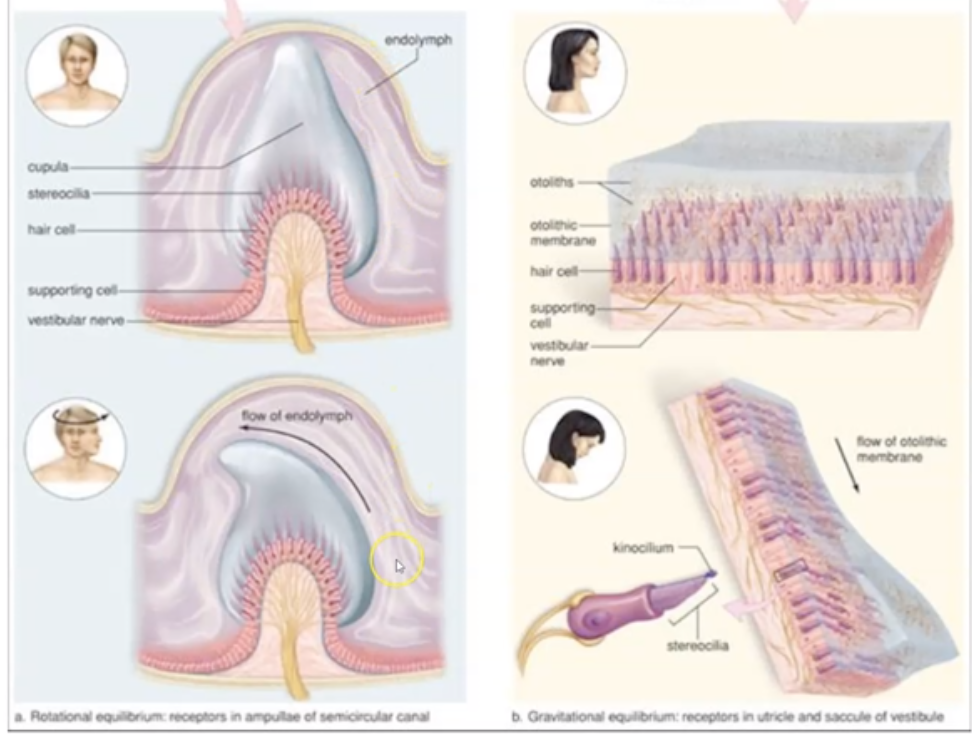
What are the 3 parts of Semicircular canal and functions?
- Transverse - right/left movement
- Coronal - tilting
- Sagittal - forward / backward
- Coronal - tilting
- Sagittal - forward / backward
22
New cards
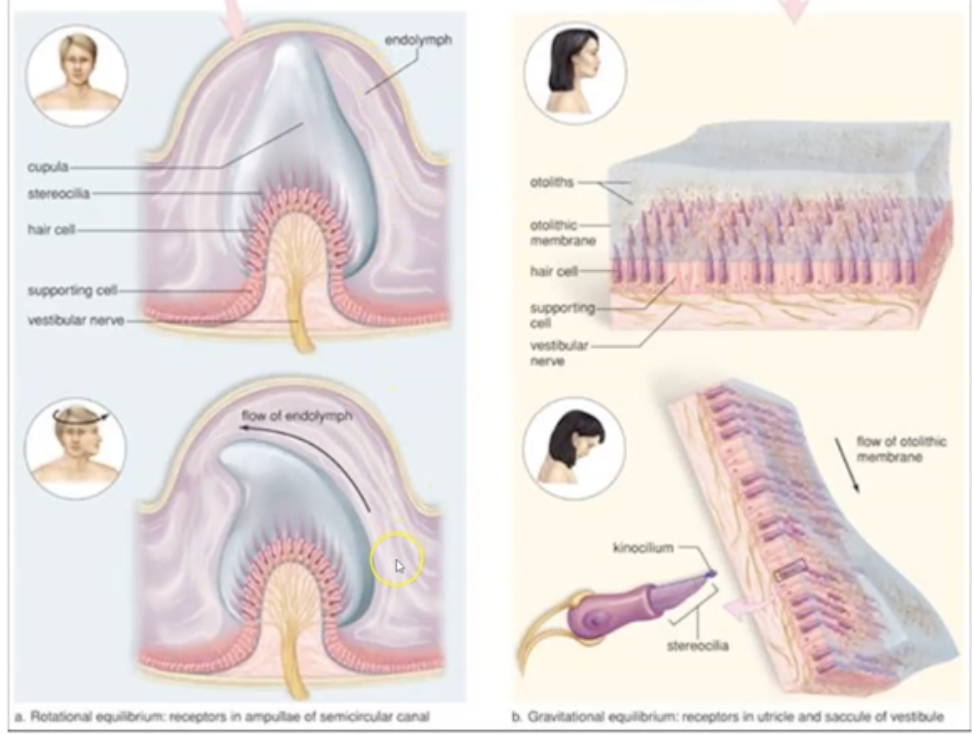
What are the 2 parts of the Vestibule?
Utricle - manages body position due to horizontal gravity
Saccule - manages body position due to vertical gravity
Saccule - manages body position due to vertical gravity
23
New cards
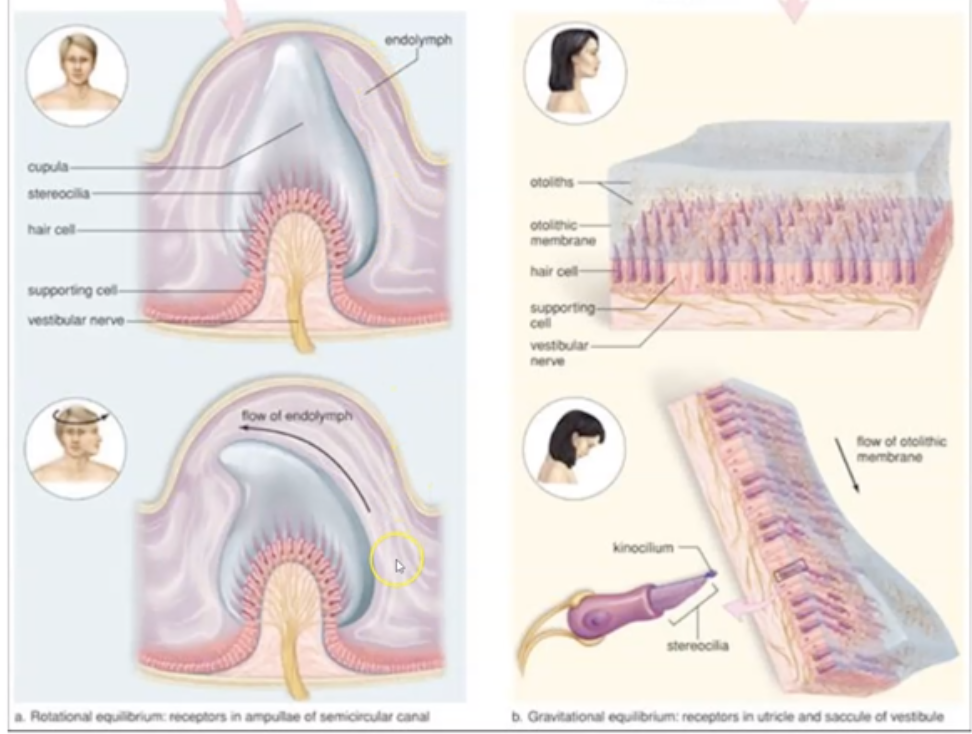
How does vestibule and semicircular canal assist in signal transmission to brain?
1. When your head moves, fluid inside of the vestibule and semicircular canals moves.
2. The movement of the fluid causes the hair cells to move
3. The movement of the hair cells sends an electrical impulse to the vestibular nerve
4. The vestibular nerve (via the vestibulocochlear never) transmits the signal to the cerebellum, brain stem, and spinal cord.
2. The movement of the fluid causes the hair cells to move
3. The movement of the hair cells sends an electrical impulse to the vestibular nerve
4. The vestibular nerve (via the vestibulocochlear never) transmits the signal to the cerebellum, brain stem, and spinal cord.
24
New cards
What are the 2 types of vestibular disorders?
Vertigo and Nystagmus
25
New cards
What is Vertigo?
a sensation of spinning.
26
New cards
What causes vertigo?
Vertigo is often caused by inner ear problem (build up of fluid, clumping of calcium particles or an infection)
27
New cards
What is Nystagmus?
"dancing eyes."
Eyes move uncontrollably up and down, side to side, or in a circle.
Eyes move uncontrollably up and down, side to side, or in a circle.
28
New cards
What causes Nystagmus?
Cataracts, strokes, head injuries, inner ear problems, or certain medications.