Biopsychology Exam 2
1/436
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
437 Terms
research method framework for all studies
biopsych seeks to understand these relationships
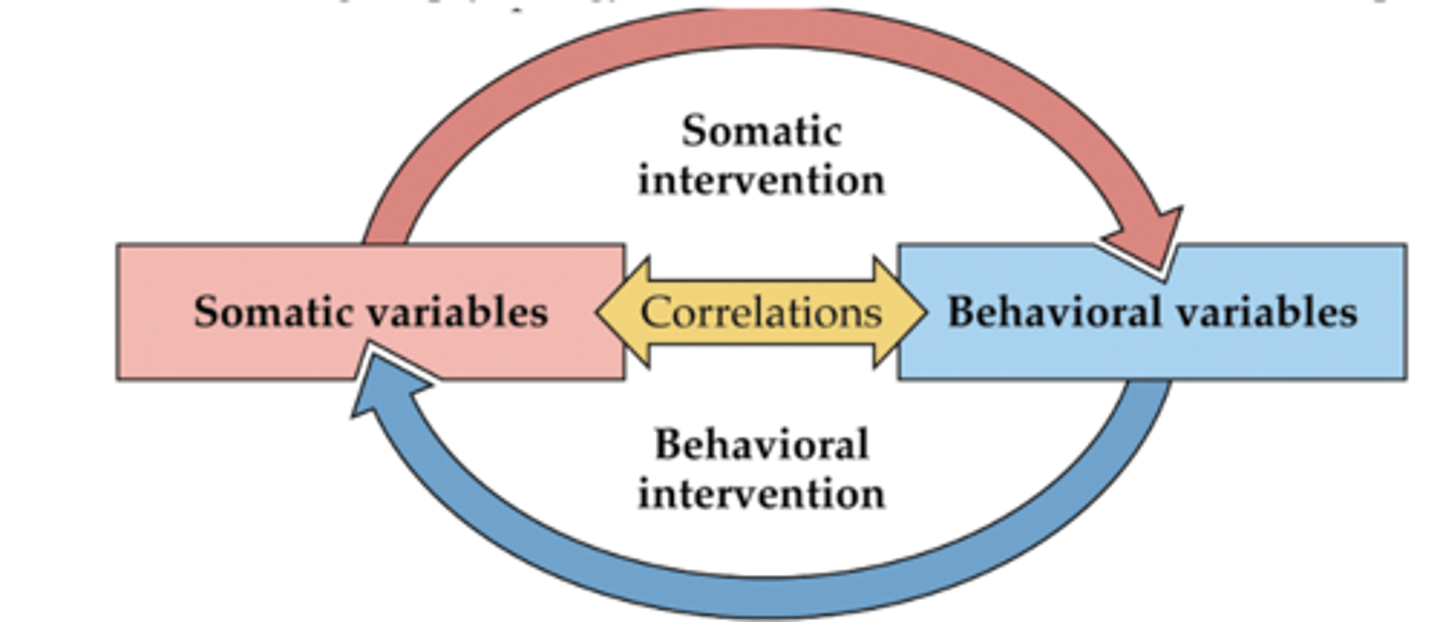
ways to relate brain to behavior
correlation and causation
correlation
- Brain changes co-occur with behavioral changes
- 3rd variable problem – correlation does NOT equal causation
causation tests for...
necessity and sufficiency
4 research techniques
1. Anatomical techniques
2. Functional removal of structure
3. Functional activation of structure
4. Recording of activity of structure (correlational)
anatomical techniques (1)
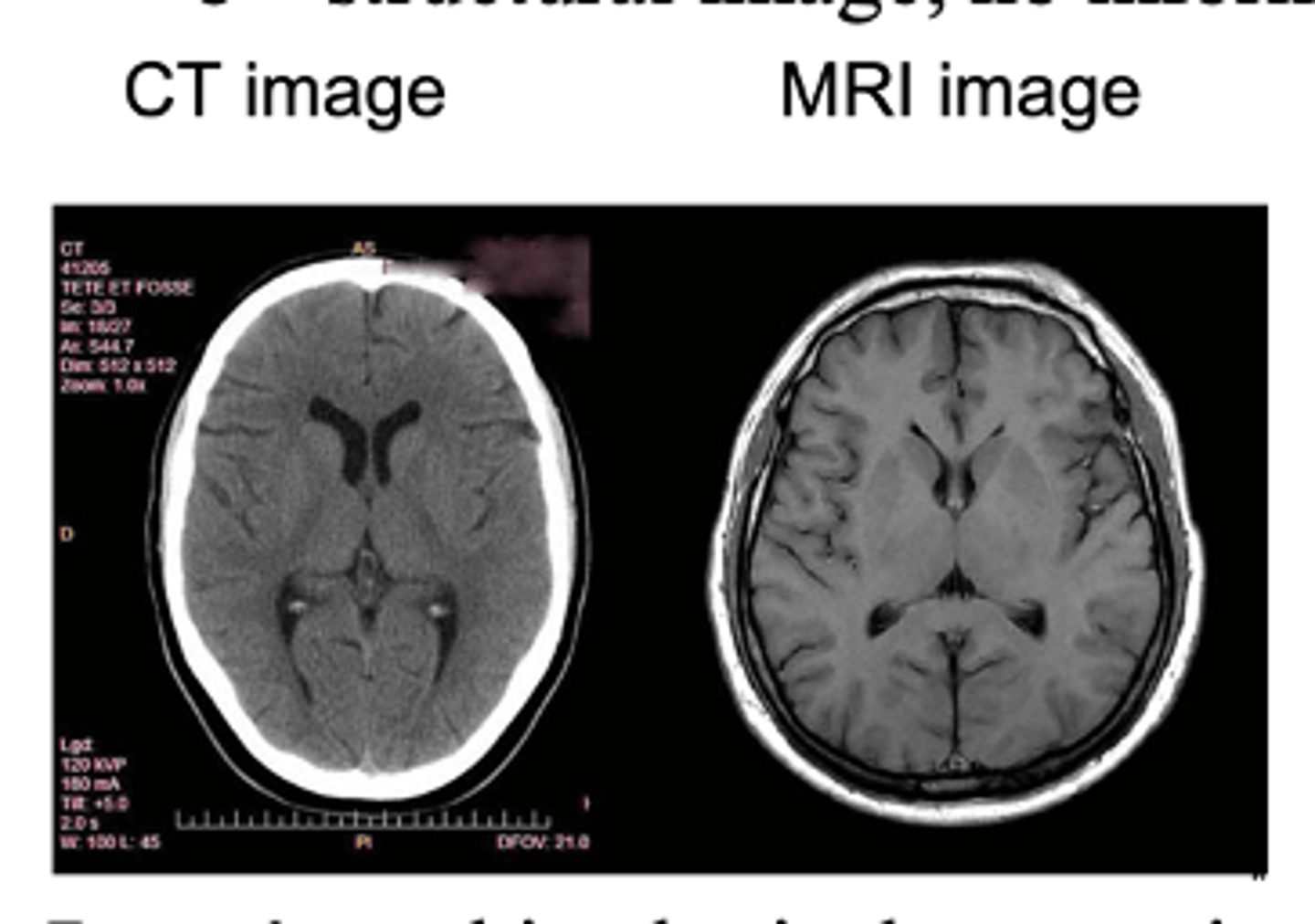
non-invasive: CT & MRI scans
invasive: histological processing
CT & MRI scans
provides precise images of brain STRUCTURE (no info on activity)
- can differentiate between white and gray matter
histological processing
brain 'staining'
- includes Nissl, Myelin, Golgi
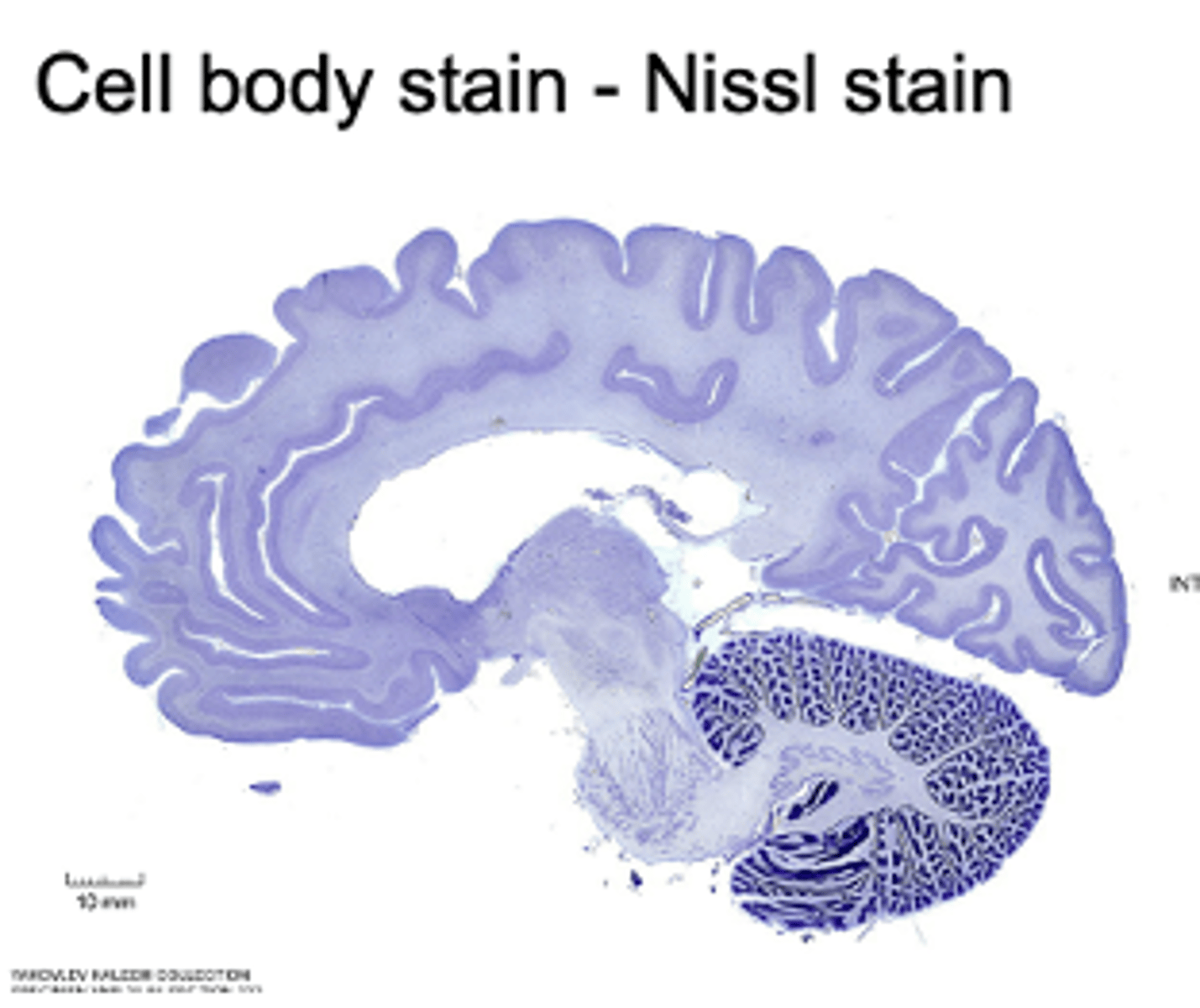
Nissl stain
stains DNA and RNA
- cell nucleus (cell body) and endoplasmic reticulum
- can see that cortex has a lower density of cells than the cerebellum
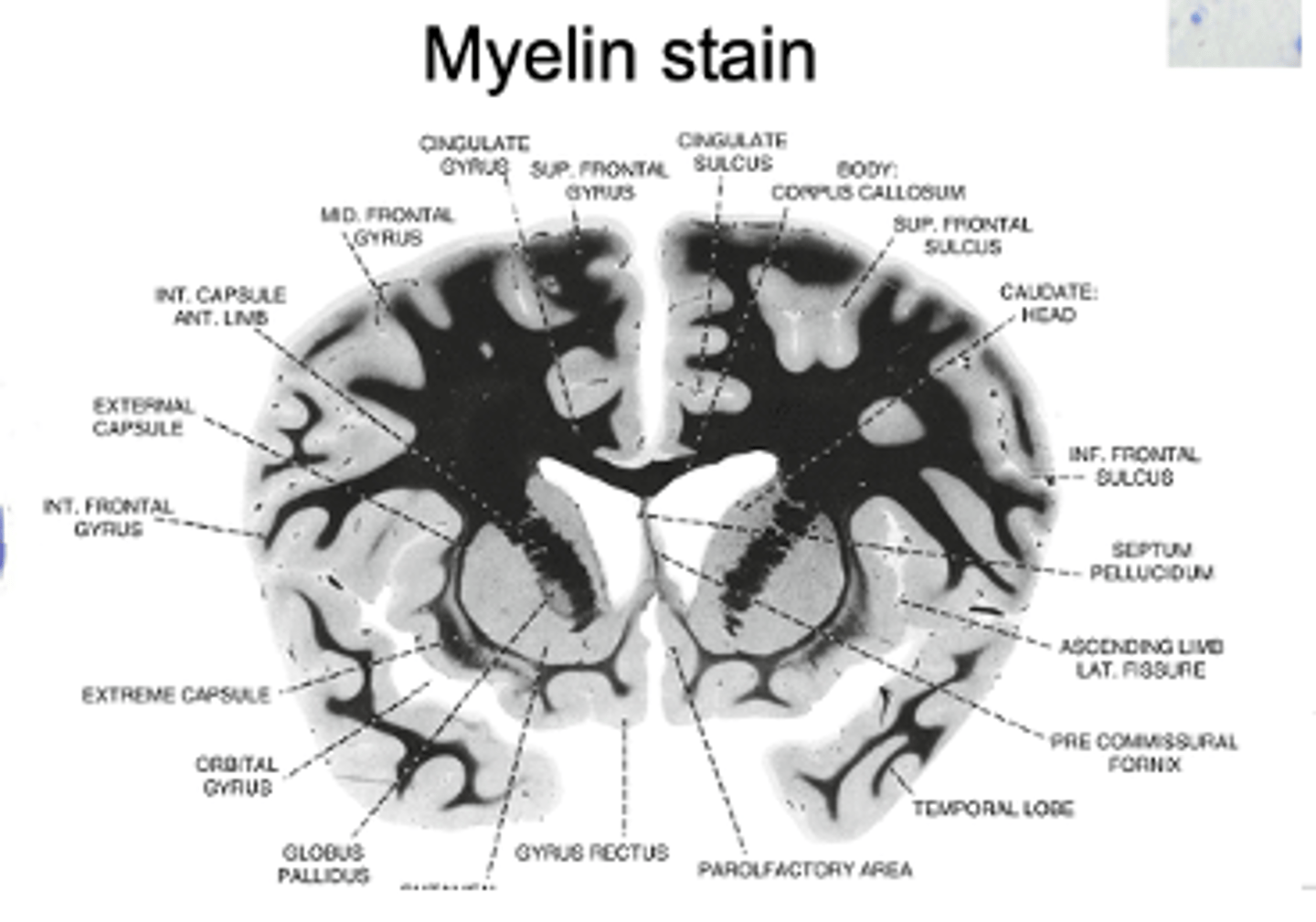
Myelin stain
all axons are stained, no contrast
- so, cannot make out neuron structure
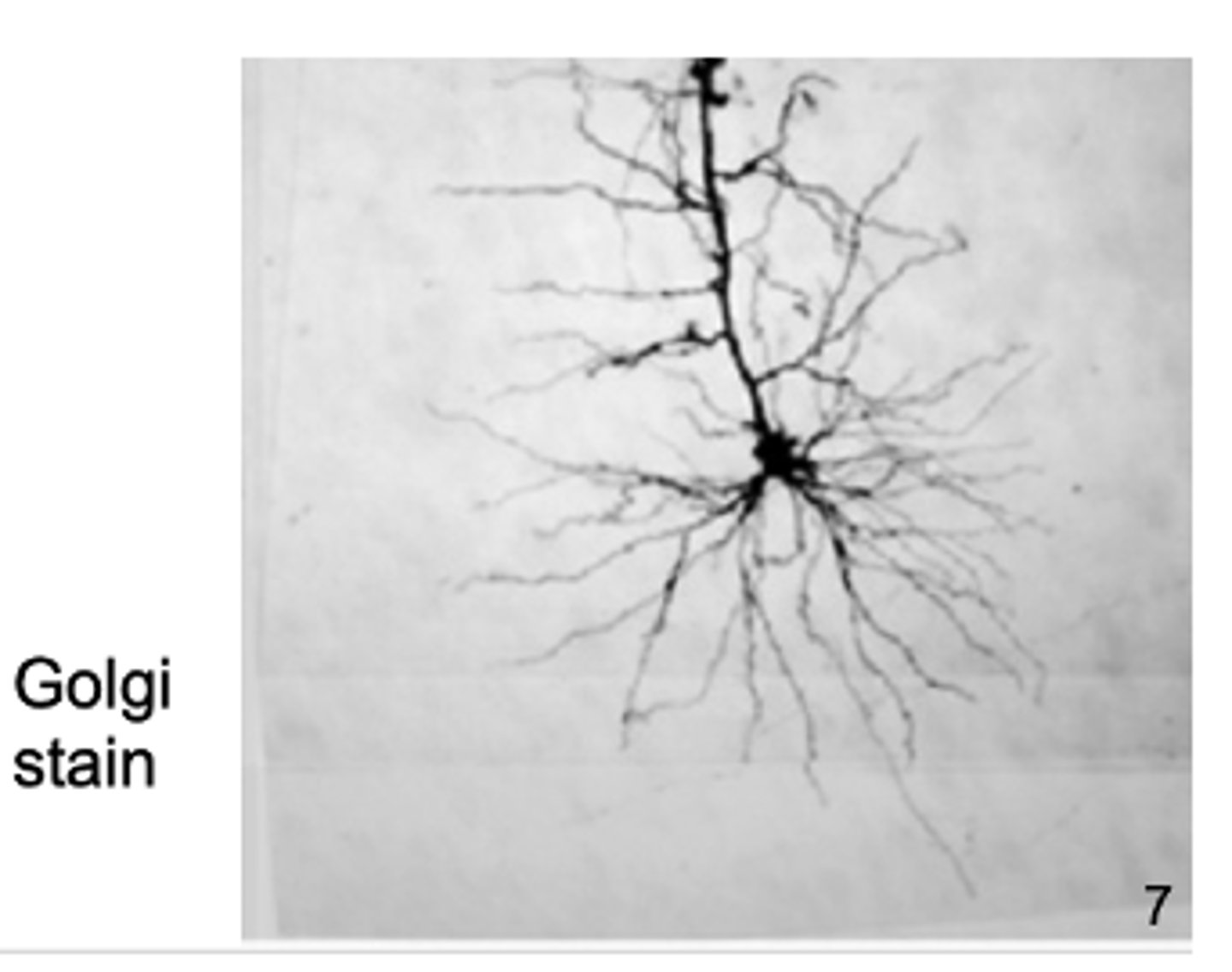
Golgi stain
shows dendritic branches and actual neuronic structure
- only certain neurons stain (we are unsure why, low % of them stain)
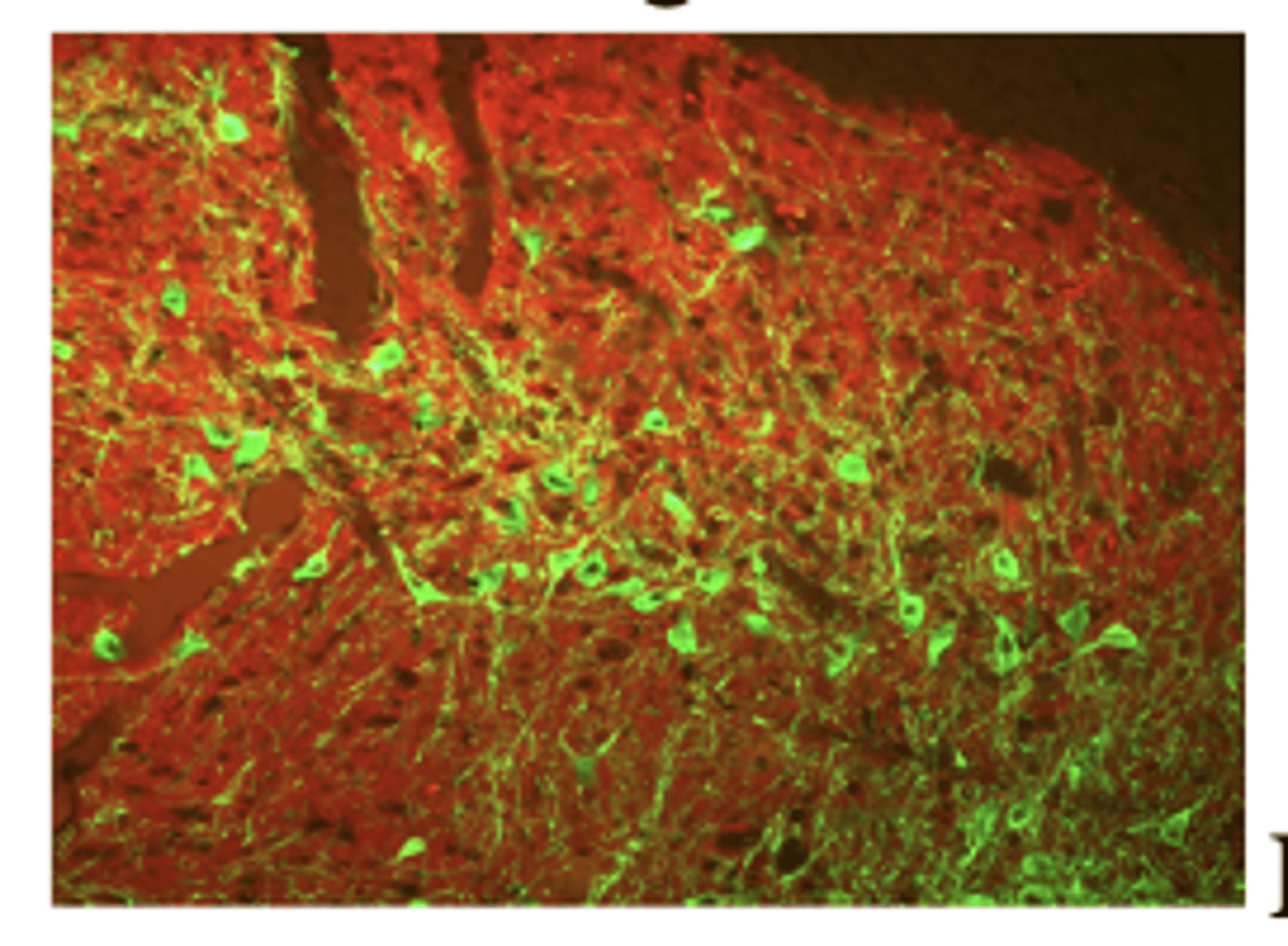
Immunocytochemistry
technique for detection and visualization of proteins or antigens in cells using antibodies specifically recognizing the target of interest
- using immune response to manufacture antibodies
- Dopamine in green, GABA in red
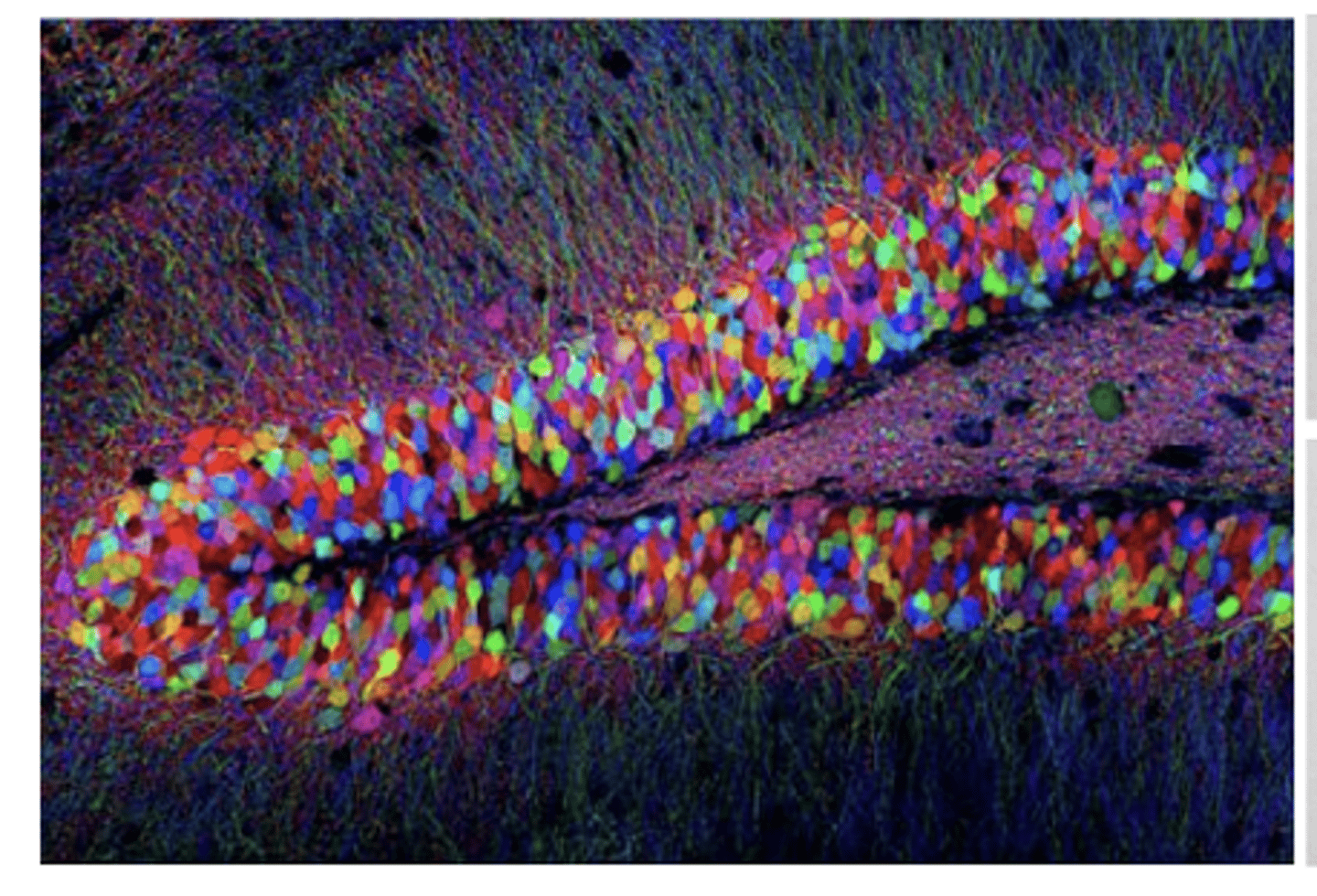
gene insertion and expression
uses fluorescent imaging
- brainbow, clarity
fluorescent imaging
shining one wavelength of light on a fluorescent substance causes it to emit light of a different wavelength
- via filters, you can see just the emitted light
brainbow
random expression in each neuron of several fluorescent proteins results in variety of colors
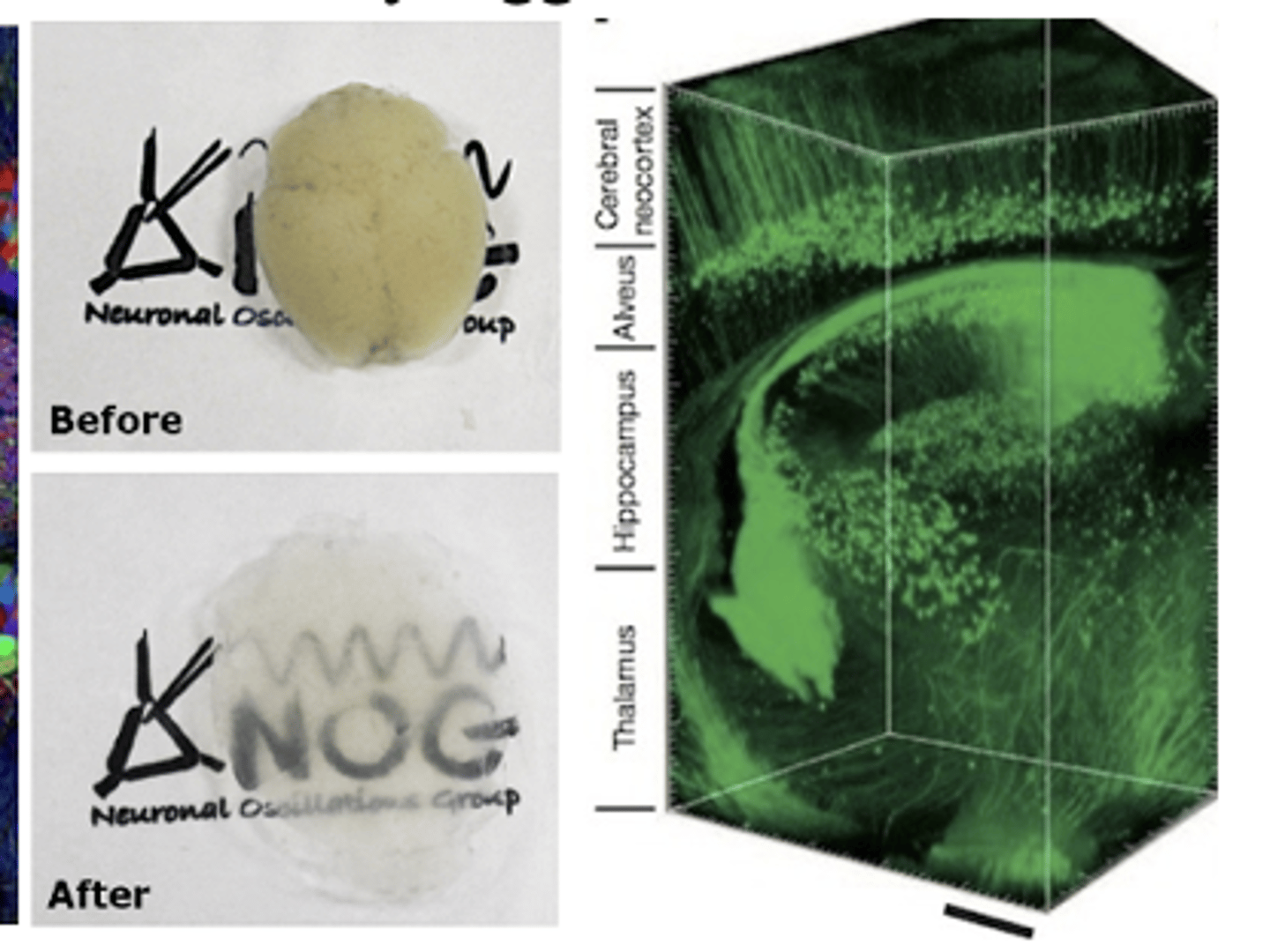
clarity
hydrogel mesh holds brain intact and opaque fats are removed
- producing transparent brains that can then be fluorescently tagged
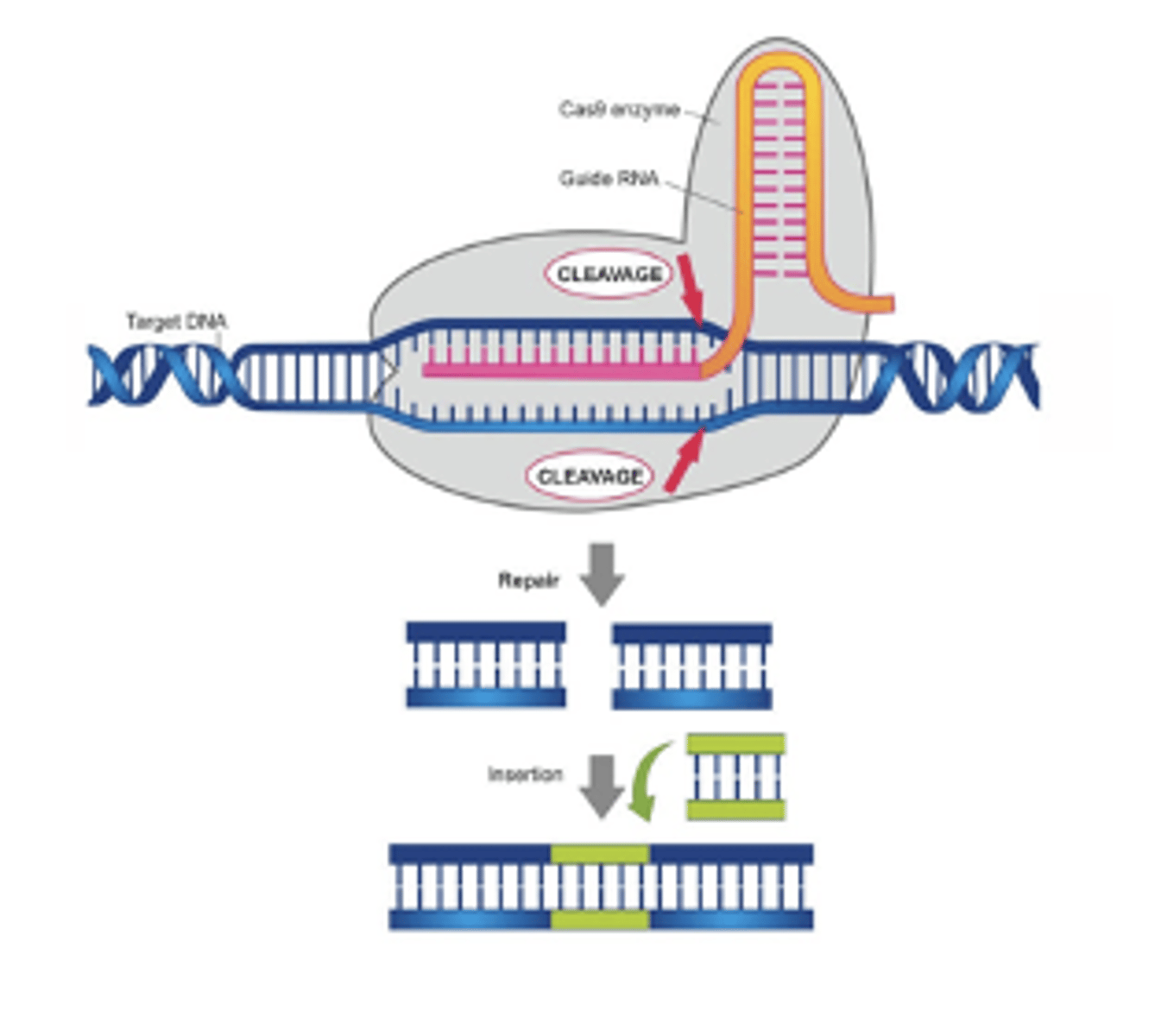
what does CRISPR-Cas9 stand for?
clustered, regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
CRISPR-Cas9
in bacteria, serves as primitive immune system
- Bacteria incorporate foreign viral DNA within these palindromic repeats
role of Cas9 protein
recognizes this DNA sequence between the repeats, and then cuts this pattern in the host DNA
example of CRISPR-Cas9
This Cas9 enzyme is bound to a guide RNA, which is complementary to a desired sequence in the DNA. The Cas9 protein can then cleave out the matching DNA, leading it to repair itself or insert a gene.
tract tracing
staining method that can be used to determine projections of neurons - not just where they are located, but WHO they are talking to
2 types of tract tracing
anterograde and retrograde
anterograde tracing
inject into cell body, moves down axon towards axon terminal, stains the terminal at the target site
retrograde tracing
inject into target site, taken up by axon terminal, and moves backwards into the cell body
removal of structure / functional group (2): necessity or sufficiency?
necessity
experimental lesions
neurotoxins
non-experimental lesions
case studies
drug administration
systemic or microinjections
microinjections
antagonists or channel blockers
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
non-invasive, handheld probe that induces magnetic field that briefly shuts down neuron activity
2 types of genetic knockout animals
conventional and conditional / inducible
conventional knockout
point mutation of amino acid sequence, changing protein function; removing gene early in development (substantial effect)
conditional / inducible knockout
gene is present / active until drug disrupts
*gene in red mouse (offspring) turns into loxP

optogenetics
a treatment that uses a combination of light stimulation and genetics to manipulate the activity of individual neurons
step 1/5 of optogenetics
Piece together genetic construct (promoter (to drive expression) + gene encoding ospin (light-sensitive ion channel)
step 2/5 of optogenetics
Insert construct into virus
step 3/5 of optogenetics
Inject virus into animal brain; opsin is expressed in targeted neurons
step 4/5 of optogenetics
Insert 'optrode' (fiber-optic cable plus electrode)
step 5/5 of optogenetics
Laser light of specific wavelength opens ion channel in neurons
insertion of halorhodopsin gene
reversibly shuts down cell activity (sleep)
insertion of channelrhodopsin gene
turns on cell activity (wake); opposite of halorhodopsin
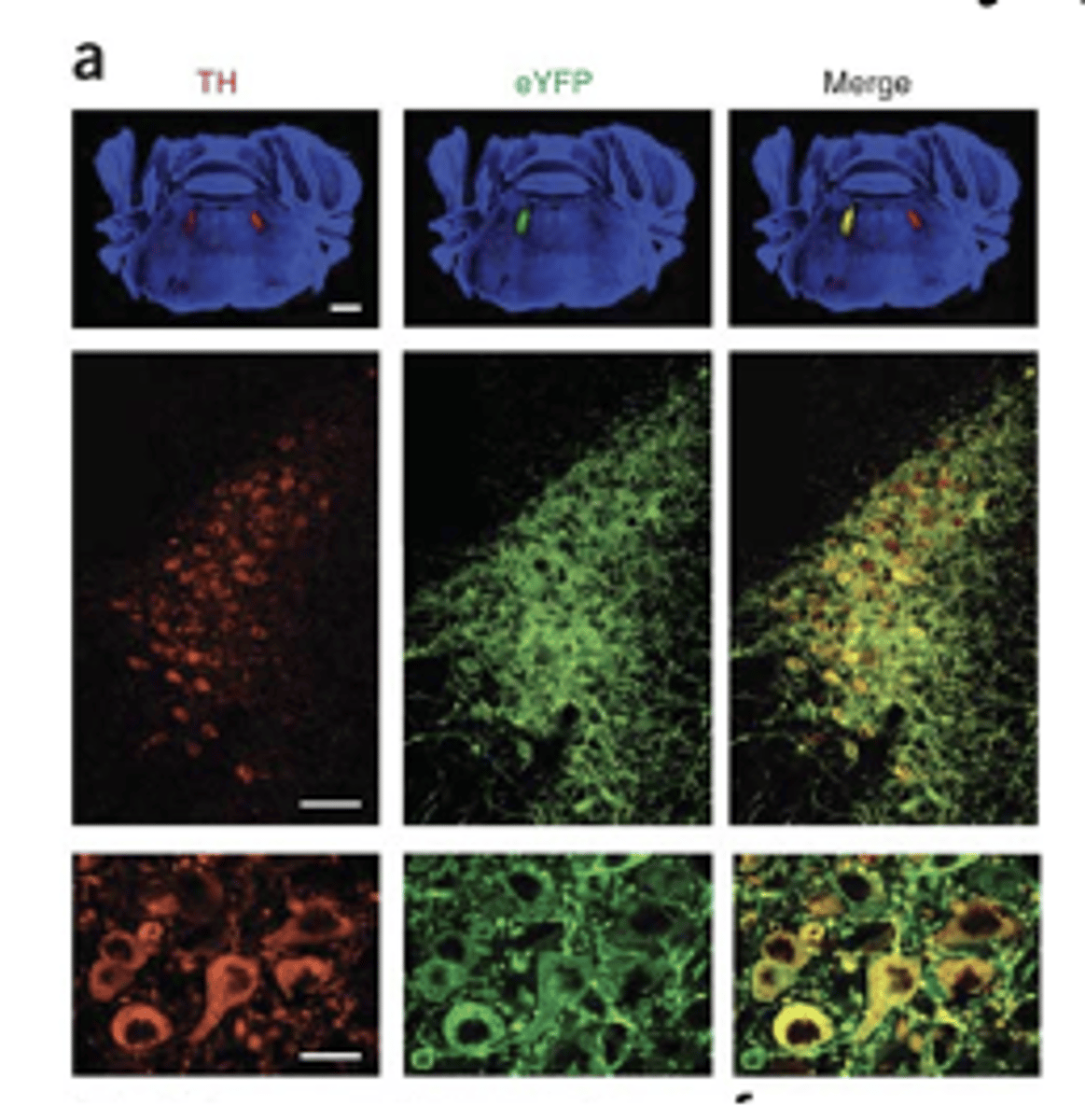
optogenetic activation and inactivation of Locus Coeruleus neurons
- blue light = activation
- yellow light = inactivation
- also using fluorescent tracer and immunocytochemistry
activation of structure / functional group (3)
- Electrical stimulation
- Drug administration
- TMS
- Transgenic mice (conventional & inducible)
- Optogenetics
- Chemogenetics - DREADDs
does drug administration for activation use antagonists or agonists?
agonists; whereas removal of structure uses antagonists
recording activity (4)
- Intracellular and extracellular recording (single or multisite)
- Local field potential
- Calcium imaging
- EEGs and ERP
- MEG (magnetoencephalography)
- Microdialysis (voltammetry)
- fMRI, PET, rCBF
- autoradiography (2-DG)
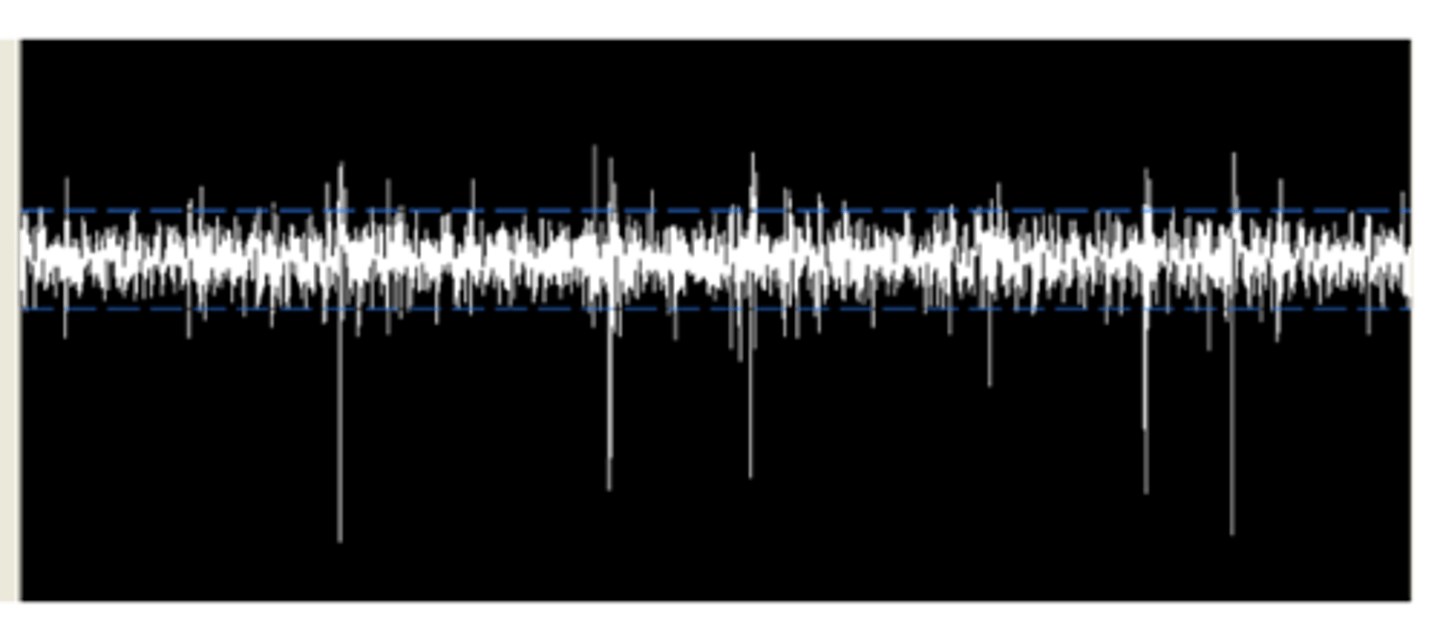
single extracellular recording
recording from single neuron with extracellular electrodes
- voltage potential from extracellular recording in striatum over time
- indicate time at which 'spike' (action potential) occurred
spike sorting
detecting and separating spikes corresponding to different neurons
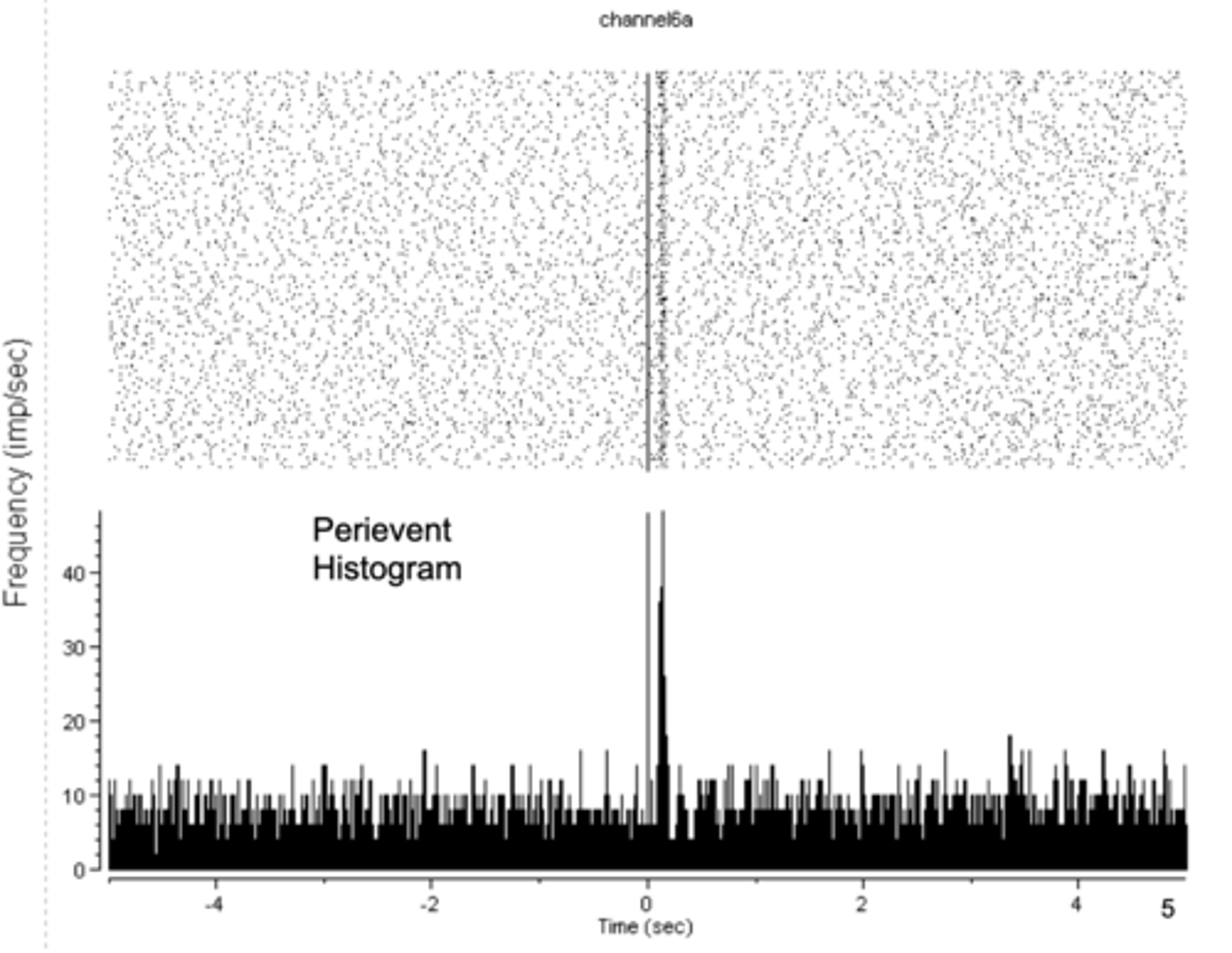
peri-event raster
response to a light onset
peri-event histogram
culmination of many peri-event raster events
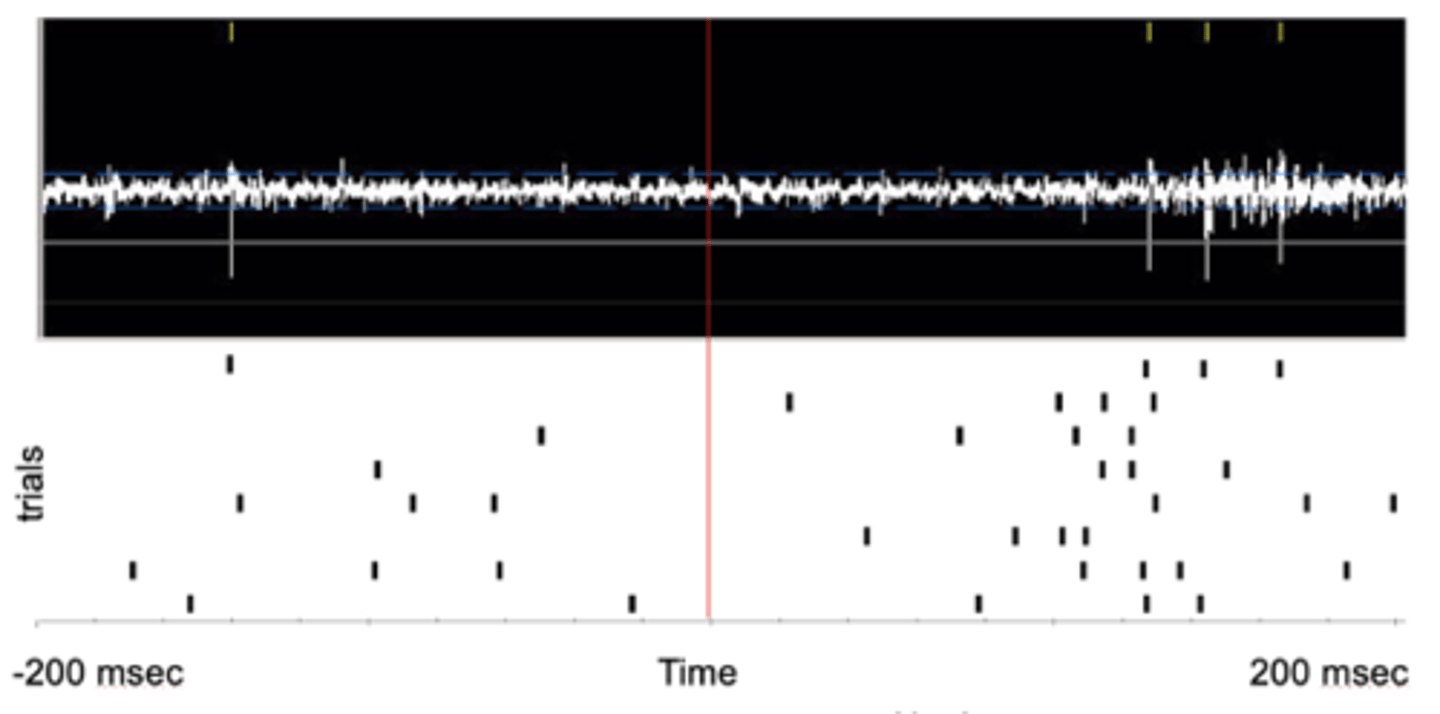
extracellular recording with peri-events
- red line = onset of a light
- each row of the peri-event raster = a different trial
- each tic = an action potential
- high rate of spike after light went on, low rate of spike before light came on
- performed many times to prove that light is inducing activity in neuron
neuropixels probe 1.0
simultaneously records AP (action potential) and LFP (local field potential)
- signals from 960 selectable, low-impedance TiN electrodes densely tiled along a 10-mm long, 70 x 24 µm cross-section straight shank
local field potential
primarily reflects inhibitory neuron activity in human / monkey cortex
- low frequency waves, slow fluctuation
- aggregate activity of spatially restricted (??) dendritic potentials
calcium imaging
genetically encoded calcium indicator
2-photon microscopy in calcium imaging
stimulate micrometer sized area with two different long wavelength light using laser and scan across area
- can image deeper than the surface
steps of calcium imaging
1. GECI expression
2. Cranial window & 2P calcium imaging
3. Signal analysis
EEGs
surface electrodes
what do EEGs induce?
induce EPSPs and IPSPs in target neurons
- leads to voltage fluctuations that are picked up on the scalp
fluctuation of EEGs at different states
- Deep sleep = delta waves
- Asleep = theta waves
- Relaxed = alpha waves
- Aroused = beta and gamma waves
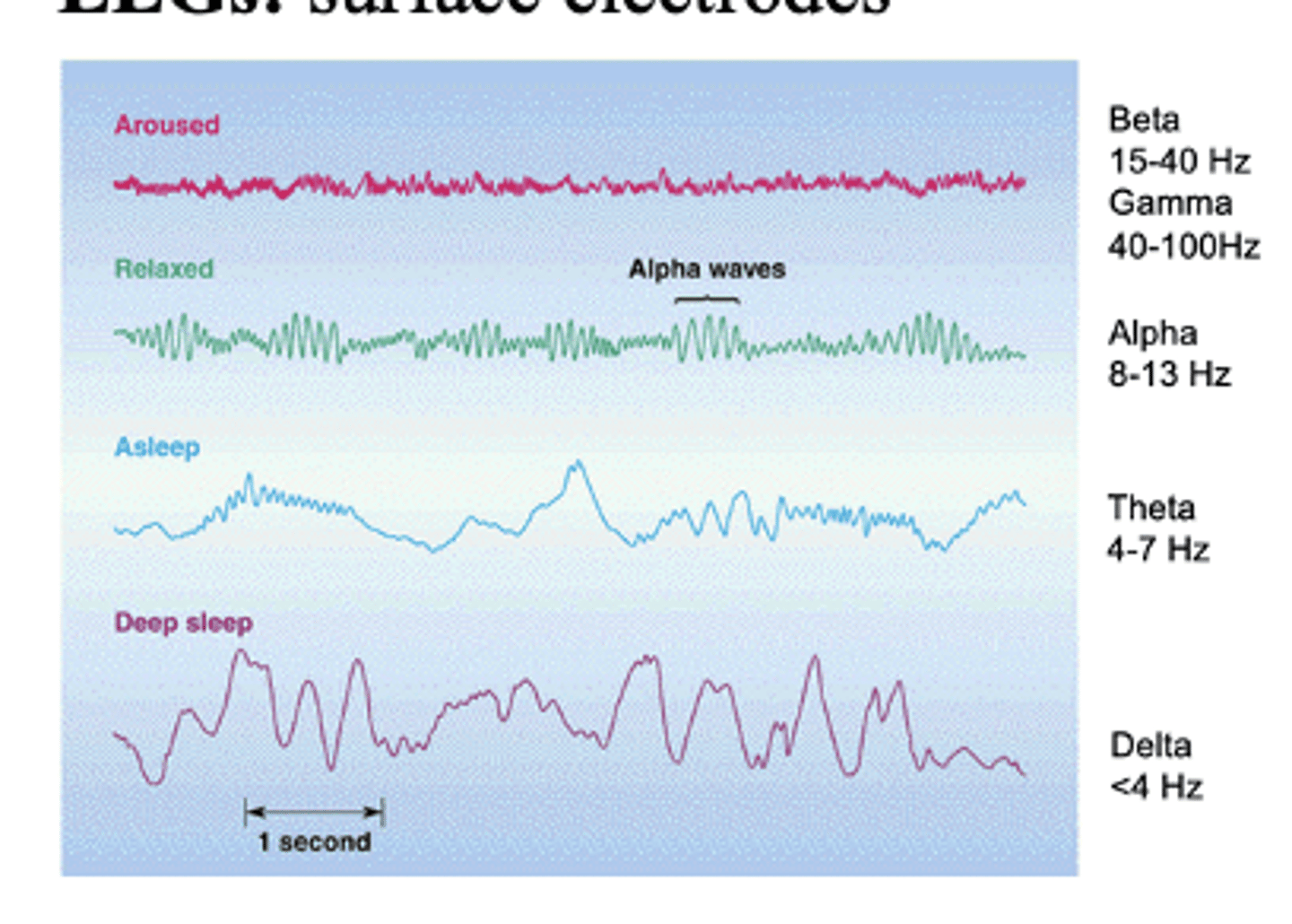
event-related potential (ERP) technique
EEG and ERP have high temporal resolution (i.e., millisecond precision) but bad spatial resolution due to electrodes on outside of skull and the “inverse” problem
- LFP is similar but is in vivo
Microdialysis
a technique for assessing the chemical composition of a very small area of the brain
more on microdialysis
- Resolution in the several seconds to minutes range
- Perfusion with artificial CSF + dialysate sample with serotonin (5-HT)
- Probed into mouse brain (concentric microdialysis)
- At the tip of the probe: 1 mm long membrane
- In vivo voltammetry (newer) provides similar information (neurochemical amount at site)
functional MRI (fMRI)
non-invasive dynamic measure that investigates human neural activity
- identifying specific areas of brain that are active
how is an fMRI different from MRI?
fMRI can track blood flow
what is an fMRI a result of?
difference between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin's magnetism
contrast of fMRI
BOLD
- blood-oxygen level dependent
fMRI image
fMRI results to the left reflect the difference between experimental (auditory stimulation) and control conditions
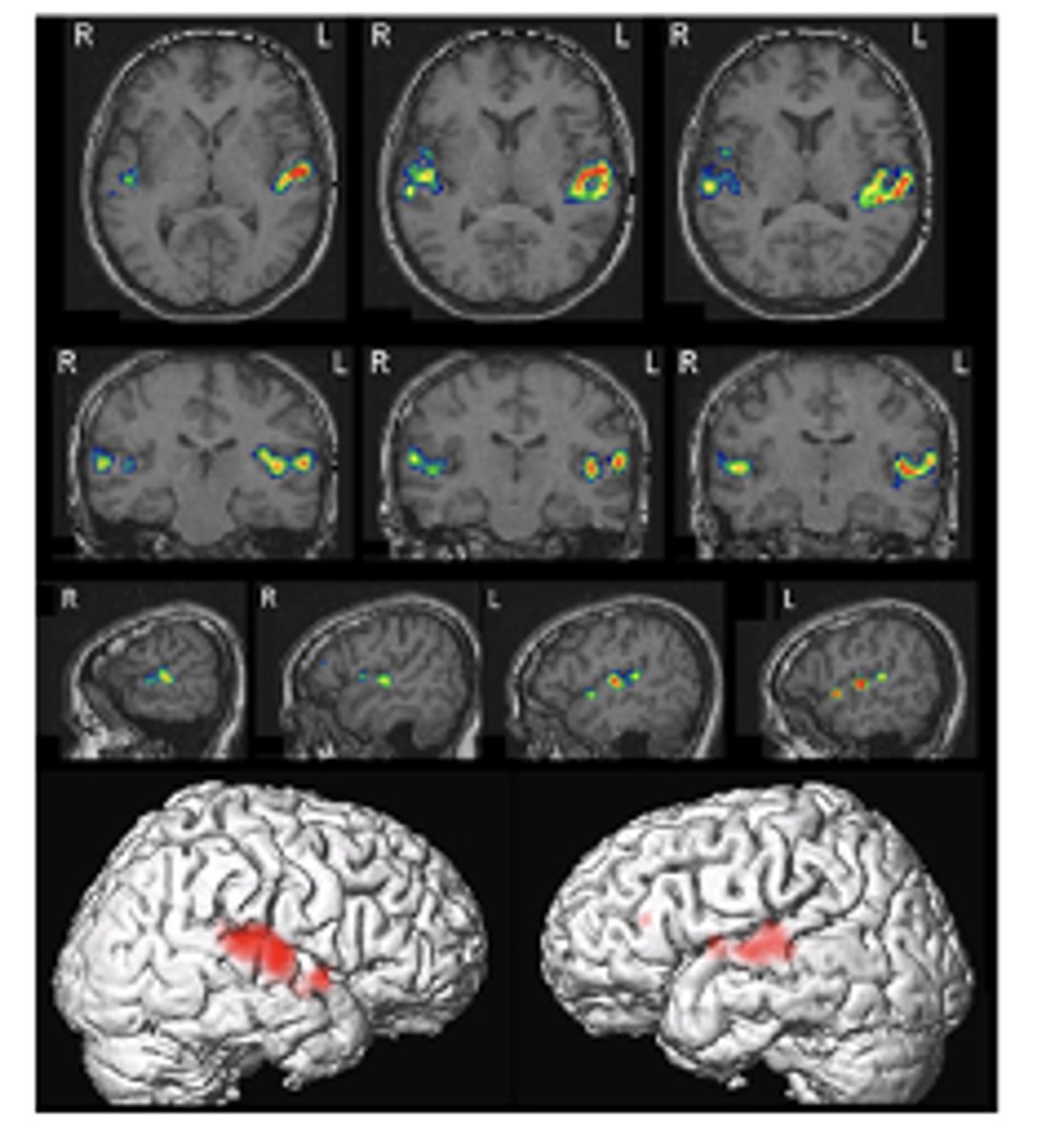
fMRI issues
1. oxygenated vs un-oxygenated hemoglobin differentially alters the magnetic field, leading to difference in rate of decay
2. change in BOLD activity of 1-4%: so, signal strength / noise is a prevalent issue
3. 100,000 + voxels in brain: needs statistical correction (many fluctuations due to chance)
4. Type 2 errors occur using fMRI (ex: failure to detect signal)
PET and fMRI subtraction method
Stimulation activity - control activity = difference activity
what does 'difference activity' signify?
brain activity due to the experimental manipulation
- brain is not 'dead' in scanner, it's highly active
issue of the PET and fMRI subtraction method
losing individual differences
Canonical Hemodynamic Response
fMRI has poor temporal resolution but “good” spatial resolution
- peak = increased oxygenated blood 6-7 seconds after stimulus is presented
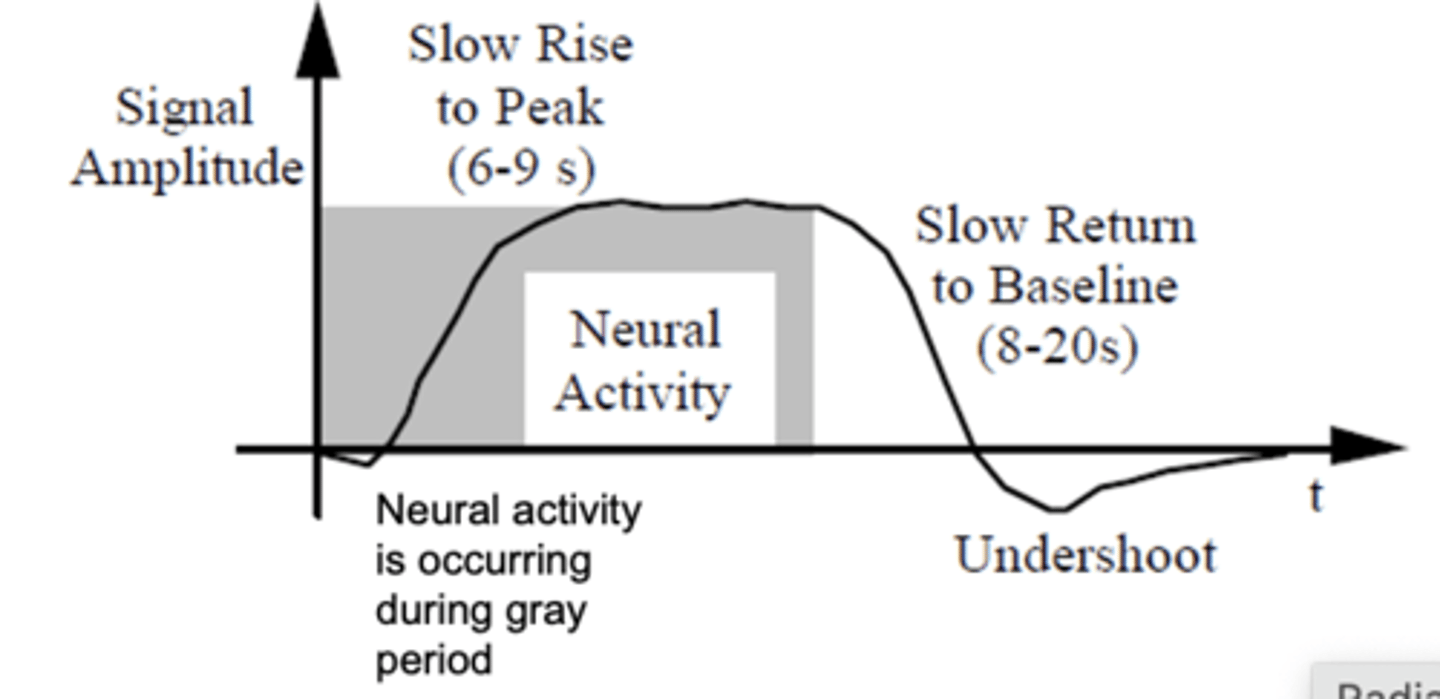
voxel
a cubic millimeter
(but this corresponds to a million neurons)
does an fMRI pick up individual neuron firing?
no, just mass blood flow
animal tasks
- Pavlonian and operant conditioning
- Radial arm maze
- Open field and conditioned place preference
- Forced swim test
operant conditioning
rewards and punishments to modify behavior
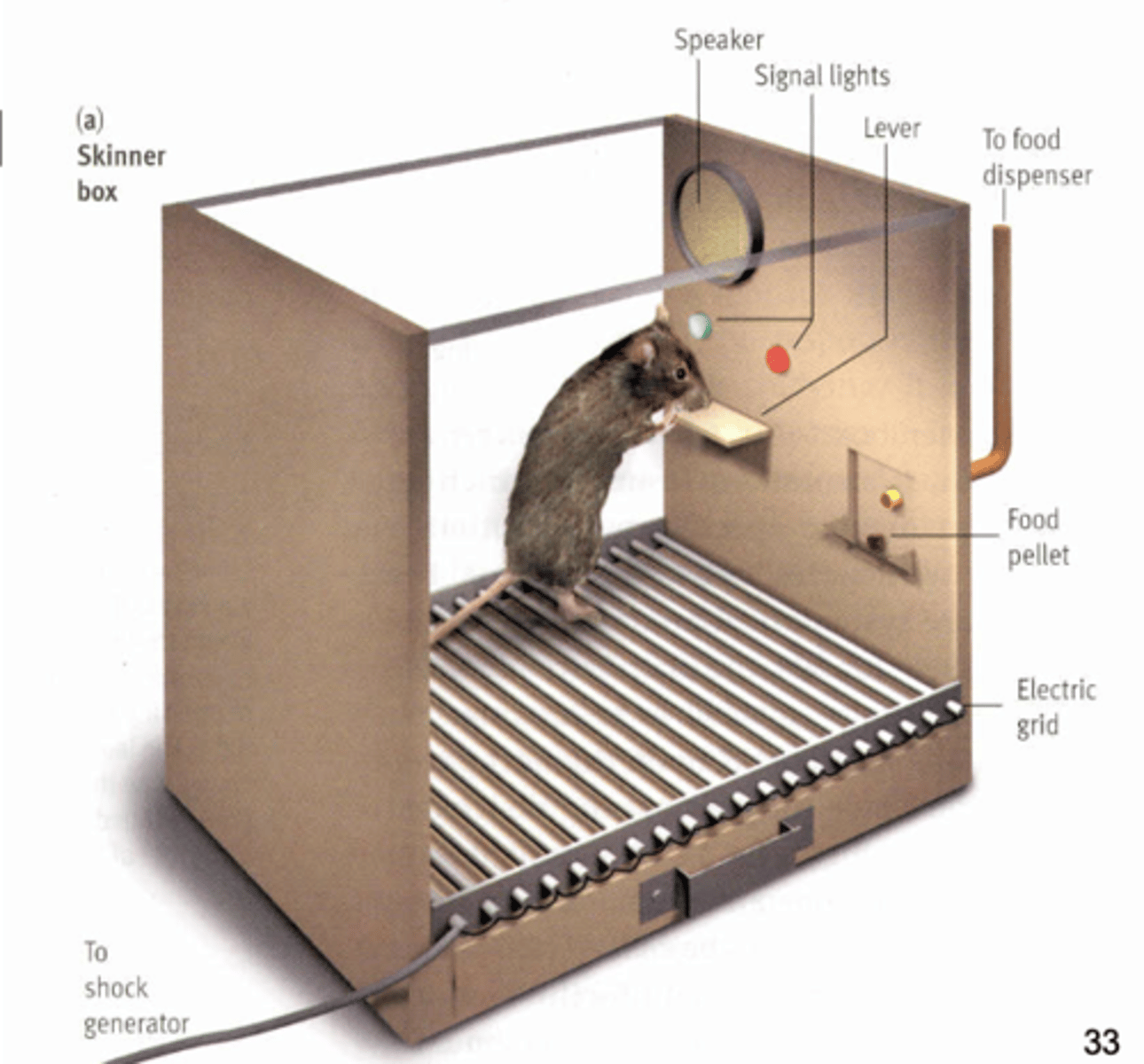
pavlonian conditioning
ring bell = give dog food (dog salivates) -> ring bell = dog salivation
radial arm maze
spatial reference memory and working memory
- animal learns where in maze food is, so will visit those ‘arms’ of the maze, even if food is not there now
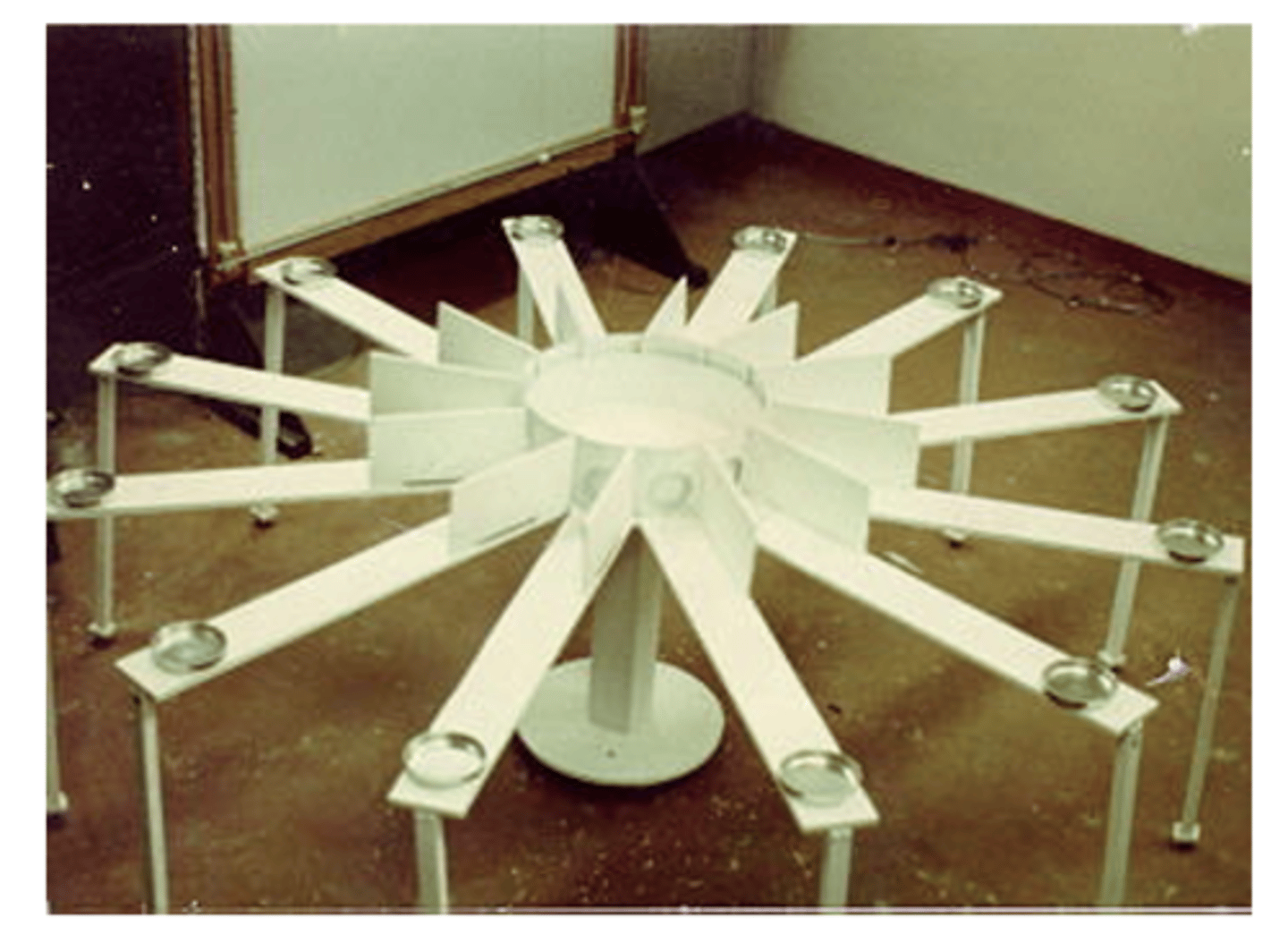
open-field system
testing anxious behavior through reinforcement potential of novel drugs
- put animal in open space (which they dislike)
- see if drug (increasing dopamine) will cause animal to venture more in open space
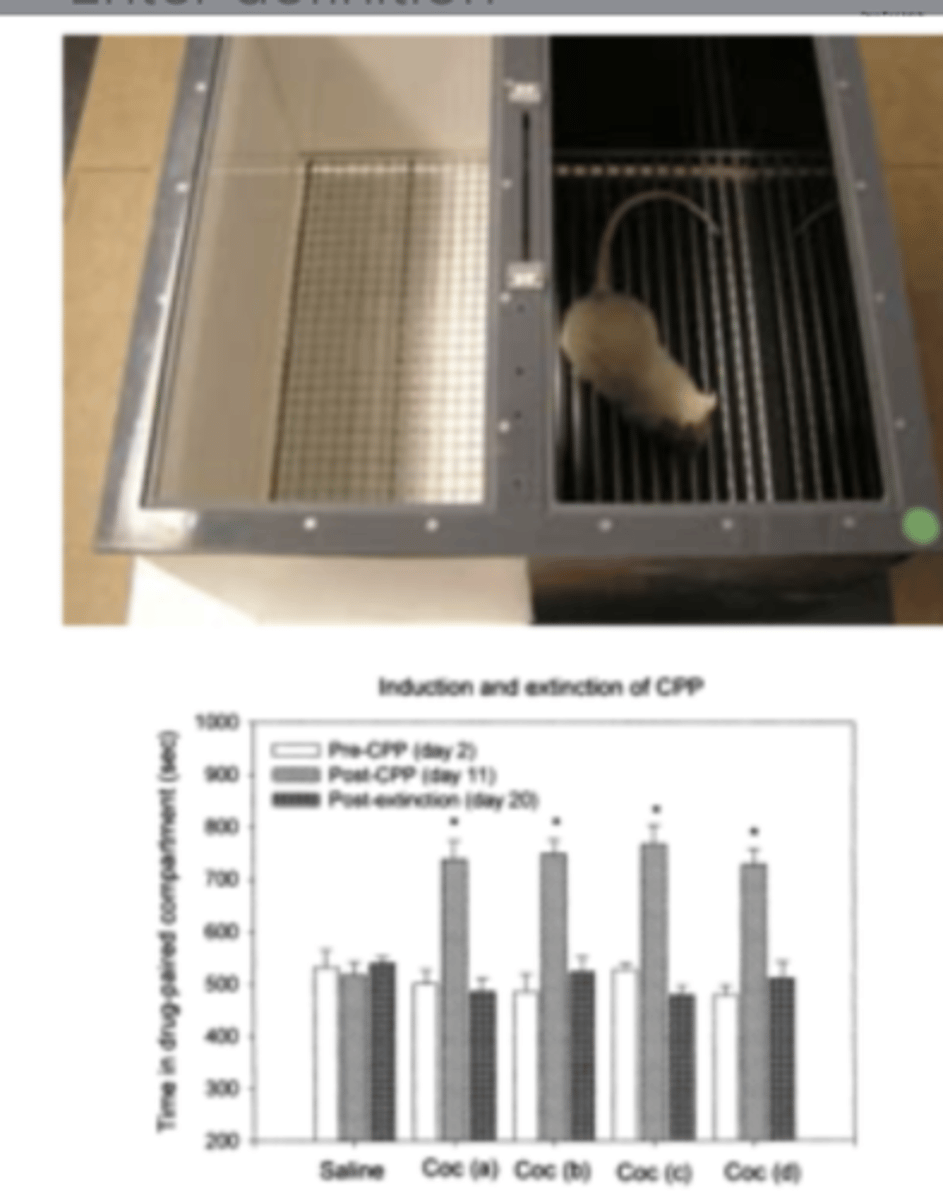
conditioned place preference
reinforcement potential of novel drug
- one light one dark space (preference = dark)
- give drug that increases dopamine and force rat in light space
- then rat prefers the light space
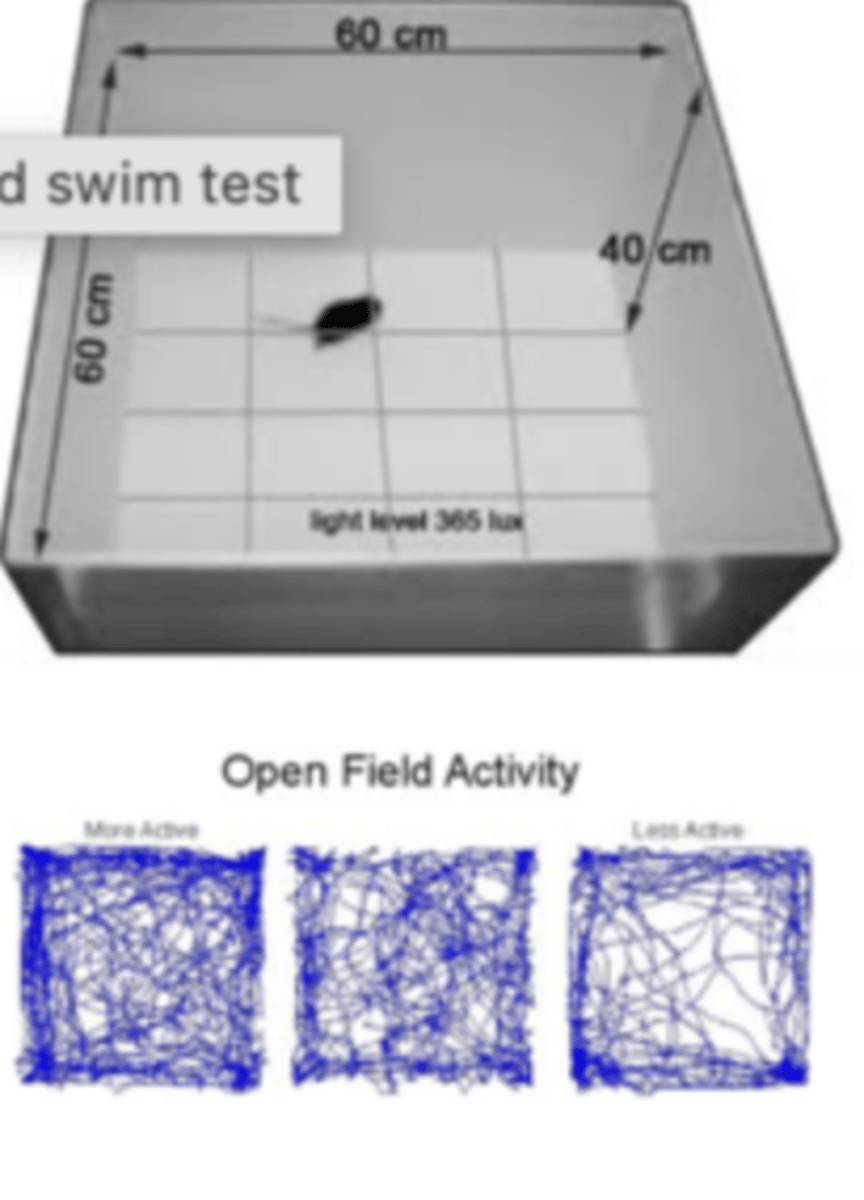
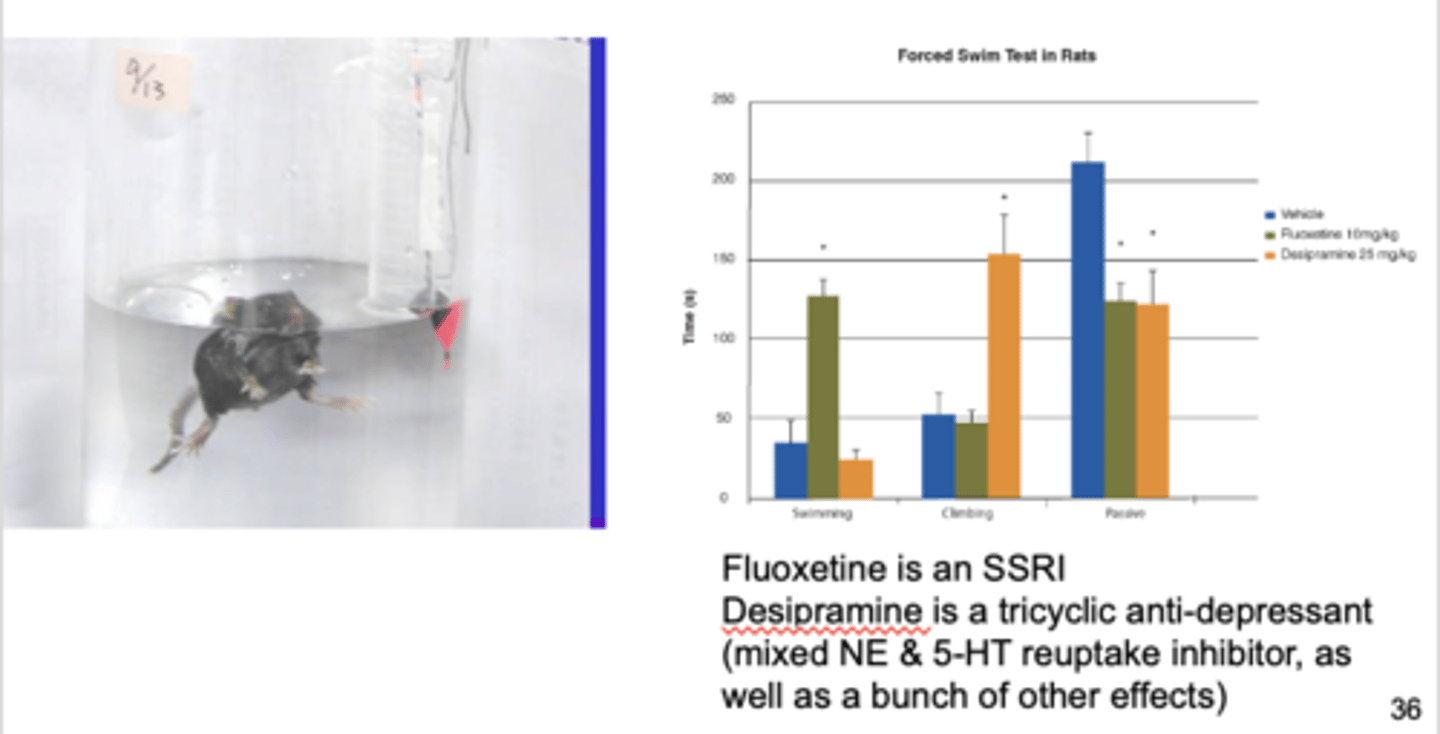
forced swim test
testing anti-depressant activity; measures behavior change with novel drug
- put mouse in beaker of water, mouse will struggle to swim and then give up
- if you give mouse anti-depressant, they will struggle longer / not give up as easily
- Fluoxetine = SSRI
Desipramine = tricyclic anti-depressant
(mixed NE & 5-HT reuptake inhibitor)
neuropsychology techniques
Wisconsin Card Sort Test and Iowa Gambling Taslk
Wisconsin Card Sort Test
Testing efficacy of frontal lobe
- presented 4 cards, put new card in 'appropriate' deck (could be based on number, color, or shape) & experimenter picks rule
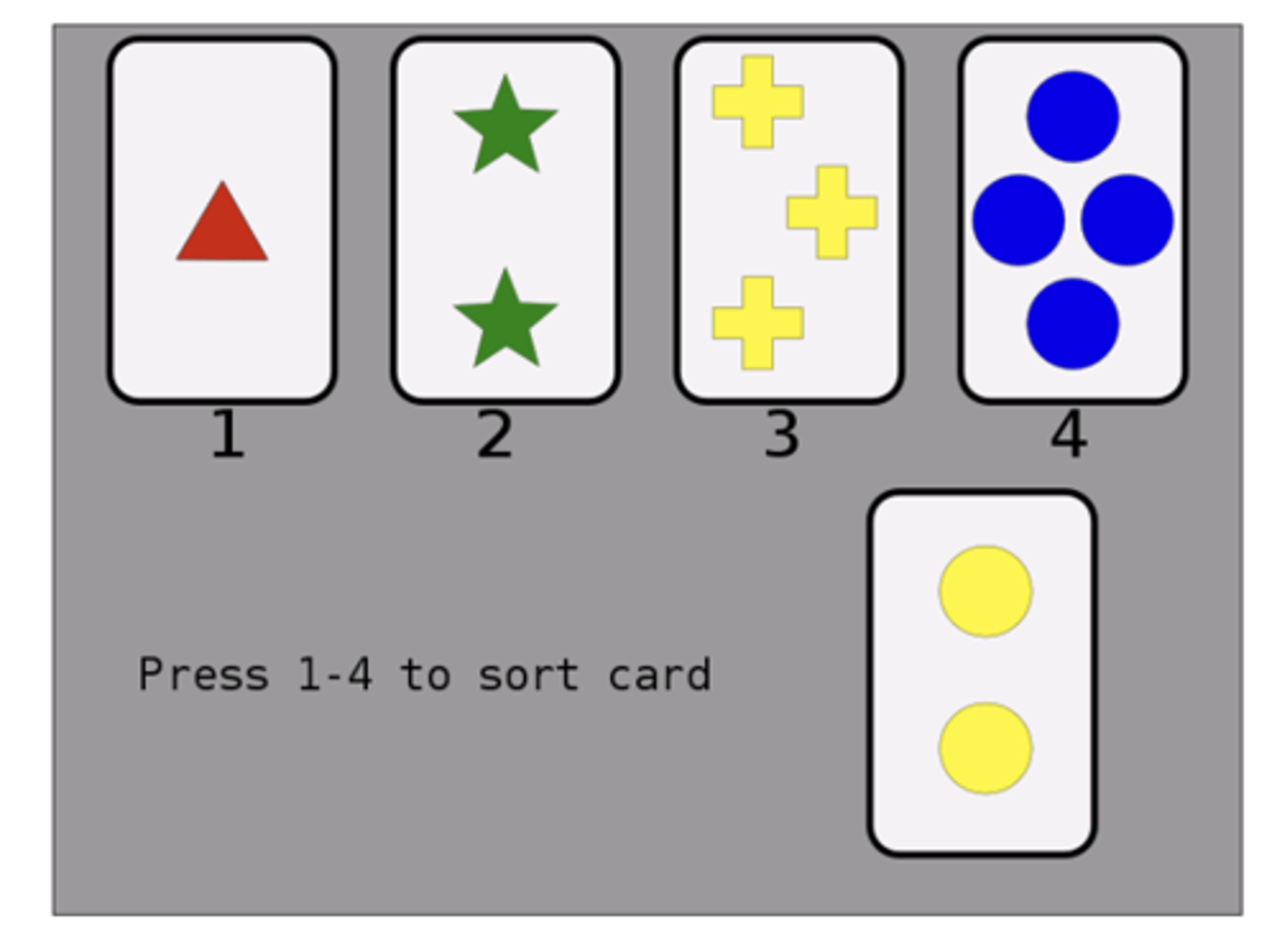
what happens to frontal lobe lesion patients in the Wisconsin Card Sort Test?
they will perseverate in their strategy
- ex will continue to use ‘shape’ rule even if it becomes incorrect after that round
Iowa Gambling Task
- Flip over card (large win/loss or small win/loss) (ex: decks A and B have high winning at first, but average loss over time (opposite with C and D))
- autonomic galvanic skin response: average person sweats more picking A/B and less in C/D (suggesting A and B are risky), then eventually consciously realize

what happens to frontal orbital patients in the Iowa Gambling task?
- will state that decks A & B are "bad" but continue to choose losing decks (have knowledge but do not match their behavior)
- don't show galvanic skin response to bad choices
- patients are more likely to participate in risky behavior in life generally
spikes =
action potentials
listening to the nervous system
- Picking up spikes (aps), and fluctuating baseline
- Use ‘filtering’ (high pass and low pass) to differentiate frequencies from slower fluctuations
- Relate spike rates to an outside event (stim)
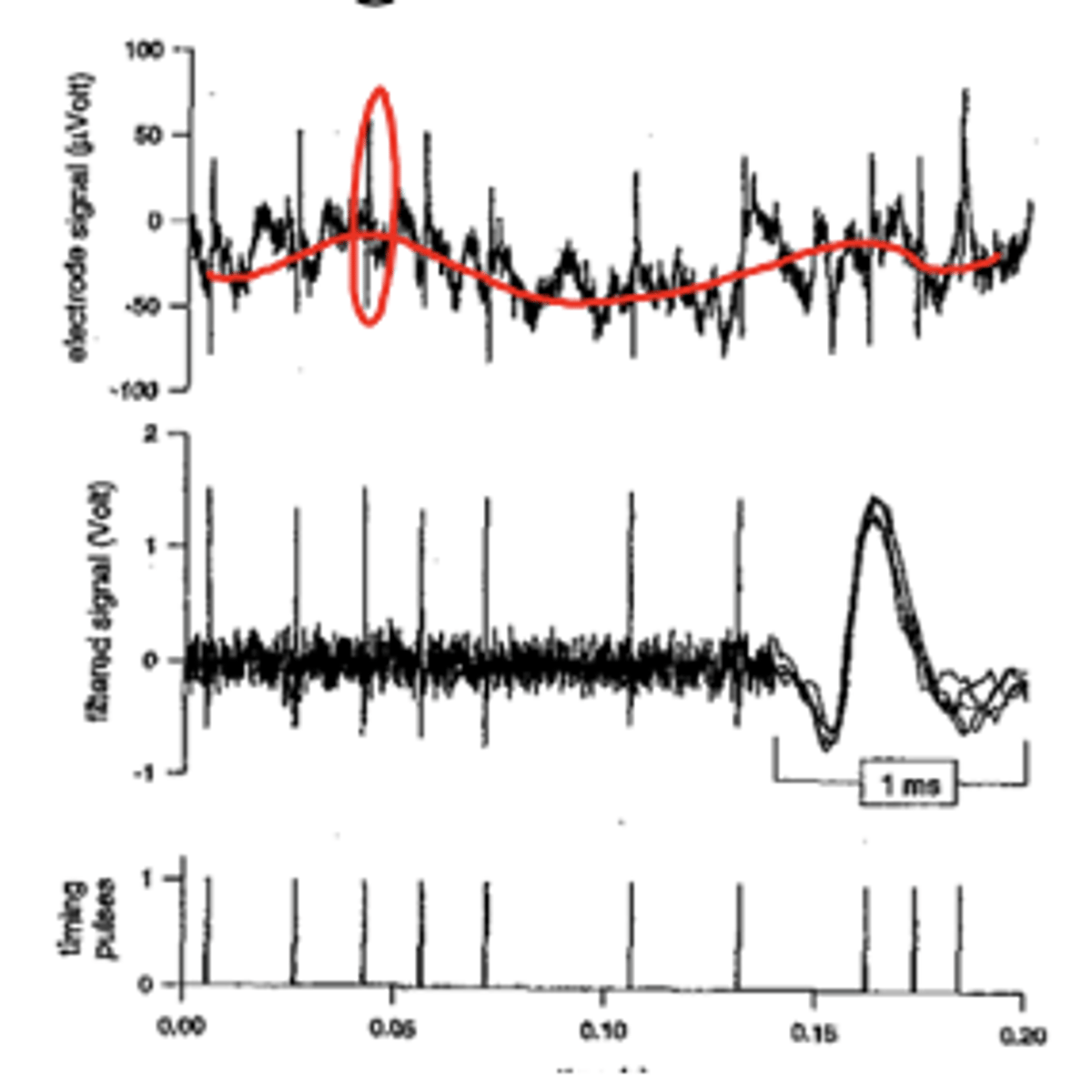
neuron recording movies
allow you to hear pop-like sound every time there is a spike - we can listen for the frequency of popping (aka how much cell is firing action potential)
for what/why do action potentials fire?
only fire for a particular stimulus in a particular place
perievent histogram
- there is a baseline firing rate
- when stimulus is presented, fires at a greater (or less) rate, then drops down to baseline rate again
- looking for how stimulus changed neural activity
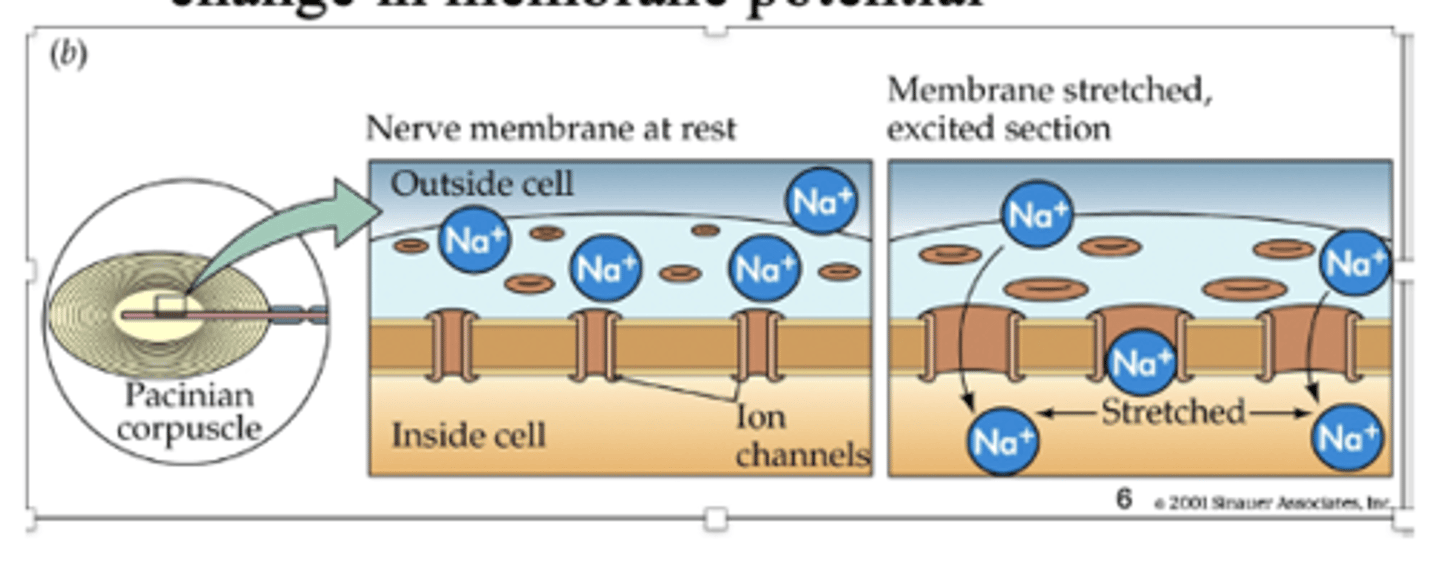
sensory receptor
converts one type of energy (ex: mechanical - pressure on skin) to a change in membrane potential
sensory transduction
when the membrane is stretched, there is an excited section and the pores stretch open (easier for ions to flow through)
- ex: when we put pressure on skin
Sensory receptors elicit ___ potentials that are proportional in amplitude to sensory event (i.e., like EPSPs)
graded
graded membrane potential producing an AP
- ap produced at some threshold voltage
- The graded potential produces NT release in proportion to strength
- weak stim = cannot reach threshold
- moderate stim = just under threshold
- strong stim = spike potential
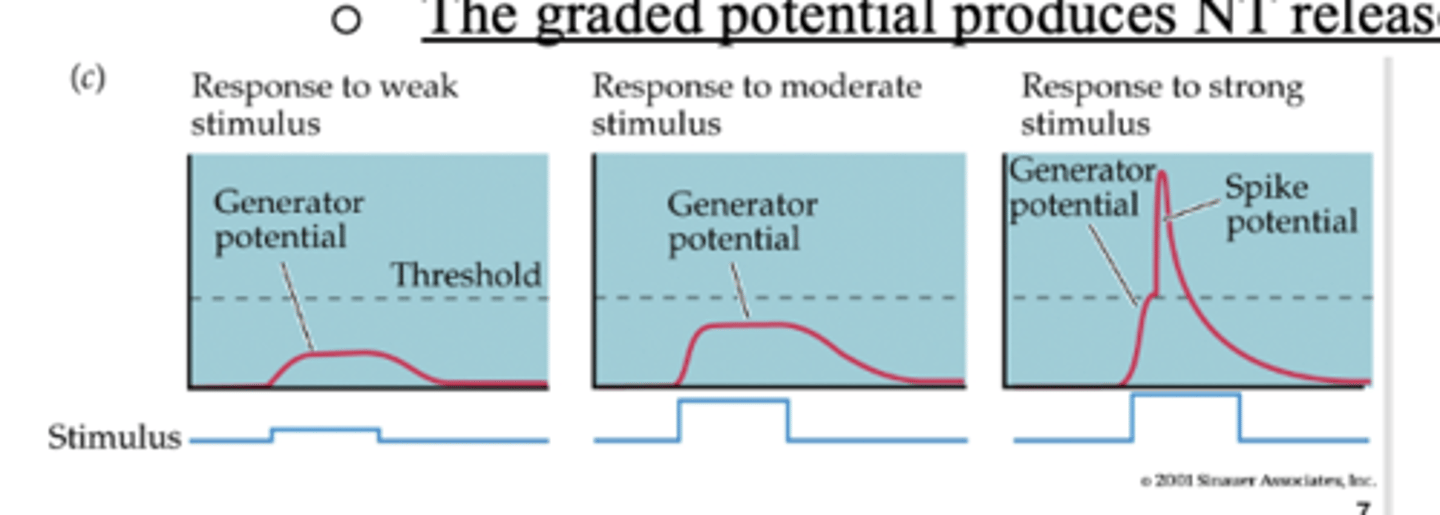
are there action potentials in visual and auditory systems?
no
a sensory event is transformed into a representation by...
spikes
how is information coded?
1. rate coding (firing rate)
2. temporal coding (spike timing)
rate coding (firing rate)
frequency = # of spikes/time
- Labeled lines
what do labeled lines represent in rate coding?
visual information is carried by neurons that project to visual cortex, auditory info projects to auditory cortex
what is the labeled lines coding scheme also for?
different qualities/positions within a modality (i.e., temperature vs. pressure for somatosensory system)