Dent 1113 Test 2
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
What are the positions for patients in the dental chair?
Upright
supine
subsupine
What is upright position?
Used for patient entry and dismissal, exposed radiographs, and impressions taken
90 degree angle
What is supine position?
Most treatments completed in this position
Patient head and knee are at same level
What is subsupine position?
patient head lower than patient feet
recommended for emergency situations such as syncope and for treatments of unconscious patients
What is the proper working distance between operator and patient’s face?
12 - 14 inches
What is the chair position for the operator?
front edge of the stool touching the back of the knees
Seated far back as possible
thighs parallel to the floor
knees slightly lower than hips
backrest of chair positioned to support lower portion or small of the back
height of the chair maintained to keep operators forearms parallel to the floor
What is the chair position for the DA?
Seated back on stool
positioned as close as possible to the patient oral cavity
Hip at the patients left shoulder and legs parallel to the patient chair towards the patient head
eye level 4-6 inches above the operator
feet resting on base or foot ring of stool
What is the operator’s zone in right handed?
7 - 12 o’clock
What is the transfer zone in right handed?
4 - 7 o’clockw
What is the assistant’s zone in right handed?
2 - 4 o’clock
what is the static zone in right handed?
12 - 2 o’clock
What is the operators zone?
Area where the person who completes the procedure is seated
What is the transfer zone?
Area where instruments and dental materials are exchanged
What is the assistants zone?
Area where the da is positioned
What is the static zone?
located directly behind patient
What hand is used to transfer dental instruments, dental handpieces and dental materials?
Left hand
What hand is used for suction and to ready the next transfer of a dental instrument or material?
right hand
What way do you transfer instruments to the dentist?
Directing the working end of the instrument downward for the mandibular arch and upward for the maxillary arch
What instruments do you use for single handed technique?
hand instruments
dental handpieces
air-water syringes
what instruments do you use for two handed transfer?
rubber dam forceps
surgical forceps
orthodontic pliers
scissors
What is the procedure for single handed transfer?
Pick up the instrument from the tray setup using thumb and index finger and middle finger of left hand
Grasp the instrument at the end of the handle or opposite of the working end
Transfer instrument from tray into transfer zone instrument parallel to dentist hand
Use last two fingers of left to retrieve instrument from dentist tucking in to palm
position new instrument firmly within dentist hand
What is the procedure for two handed transfer?
Using right hand grasp instrument on the tray setup closer to the working end with your thumb and first two fingers
With left hand retrieve the used instrument from dentist using the reverse palm grasp to hold the instrument before placing it back on tray
Deliver new instrument to the dentitst so it is oriented with the working end i the appropriate position
Return the used instrument to its proper position on the tray
What is the patient head positioning for mand left occlusal?
chin up head turned toward operator
what is the patient head positioning for mand right occlusal?
chin down head turned toward operator
what is the patient head positioning for max left occlusal?
head turned slightly away from operator
what is the patient head positioning for max right occlusal?
chin up and head turned toward operator
when do you use indirect vision?
max right occlusal
max ant lingual
max left occlusal
What is a fulcrum?
finger rest to stabilize hand
Where do you put fulcrum working in posterior?
anterior to tooth working on
Where do you put fulcrum?
Same arch working on
close to working area
Where is it preferred to put fulcrum?
intra oral
What is class I in classifications of motions?
Movement of fingers only
What is class II in classifications of motions?
Movement of fingers and wrist
What is class III in classifications of motions?
Movement of fingers wrist and elbows
What is class IV in classifications of motions?
Use of the entire arm and shoulder
What is class V in classifications of motions?
Use of entire upper torso
What is an example of class I in classifications of motions?
Picking up an instrument or single object from a flat surface or picking up a pencil
What is an example of class II in classifications of motions?
placing or receiving instruments to the operator from the tray with use of a pen grasp or dental material
What is an example of class III in classifications of motions?
transferring instruments to the operator from the tray
What is an example of class IV in classifications of motions?
Reaching for items within the mobile unit, moving radiography unit, and filing patient records
What is an example of class V in classifications of motions?
bending over to see intraorally, retrieving dental materials from a tub or drawer, reaching to hand patients a from to complete
What are do the numbers indicate on the handle of instruments?
Width
Cutting
Length
Angle
What is the number is the width in 07.10.30.20
07
What number is the cutting edge angle in 07.10.30.20?
10
What number is the length in 07.10.30.20?
30
What angle is the angle in 07.10.30.20?
20
What are the different classifications of instruments?
Examination
Hand cutting
Restorative
Accessory
What instrument is this?
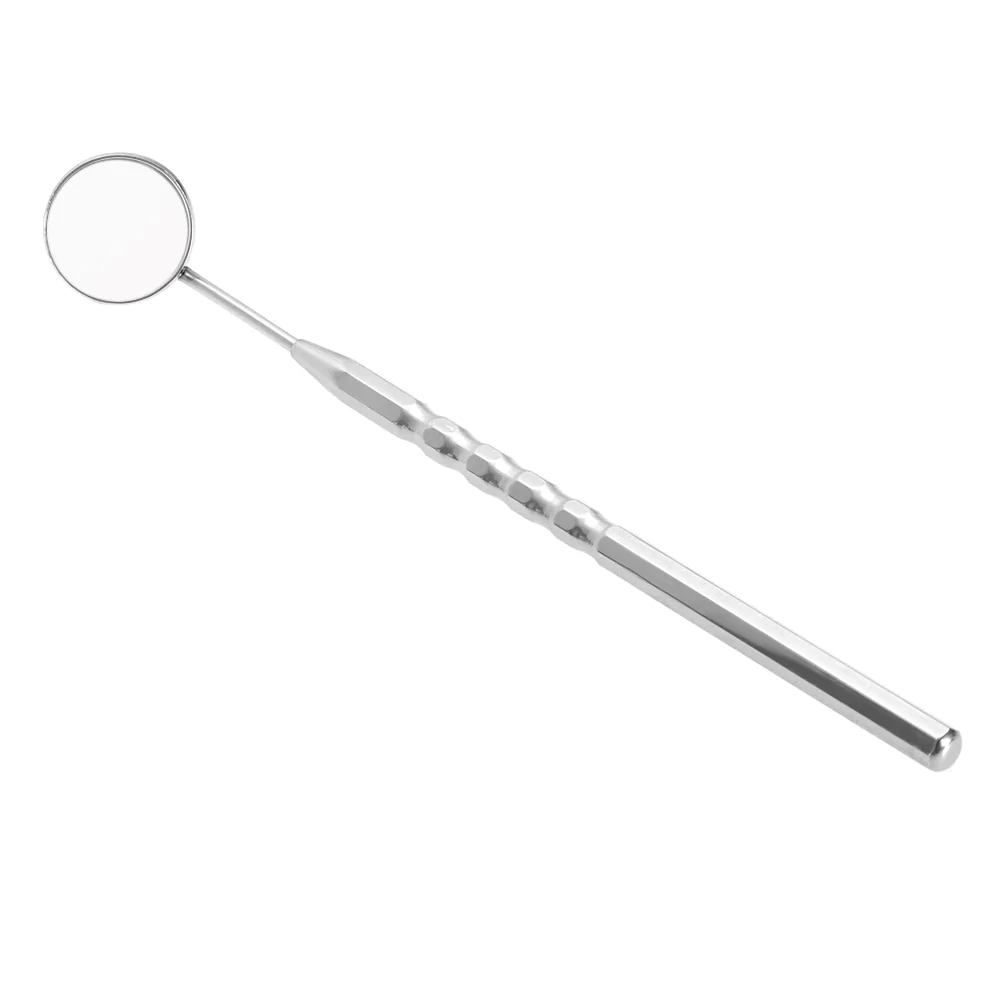

Mouth mirror
What instrument is this?
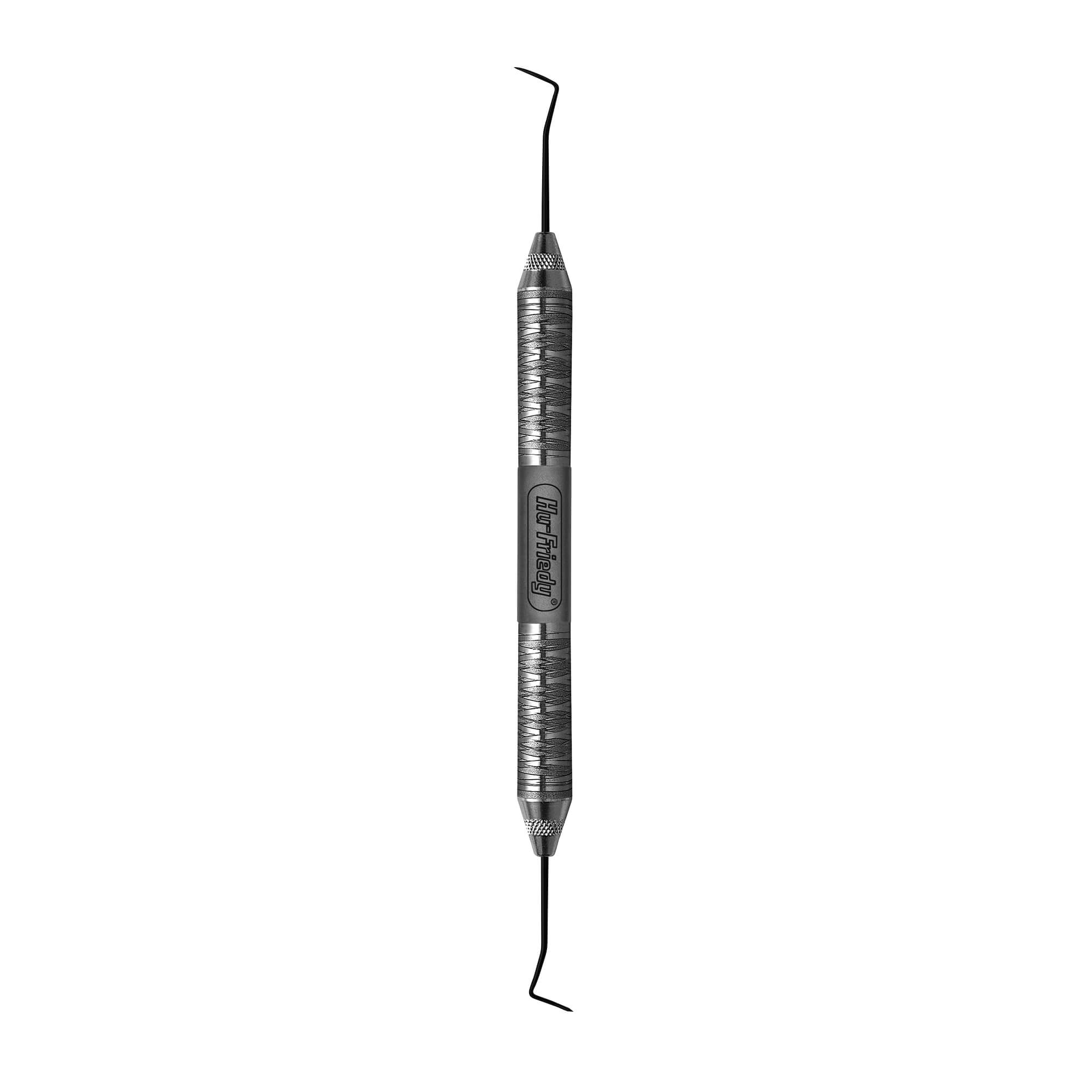
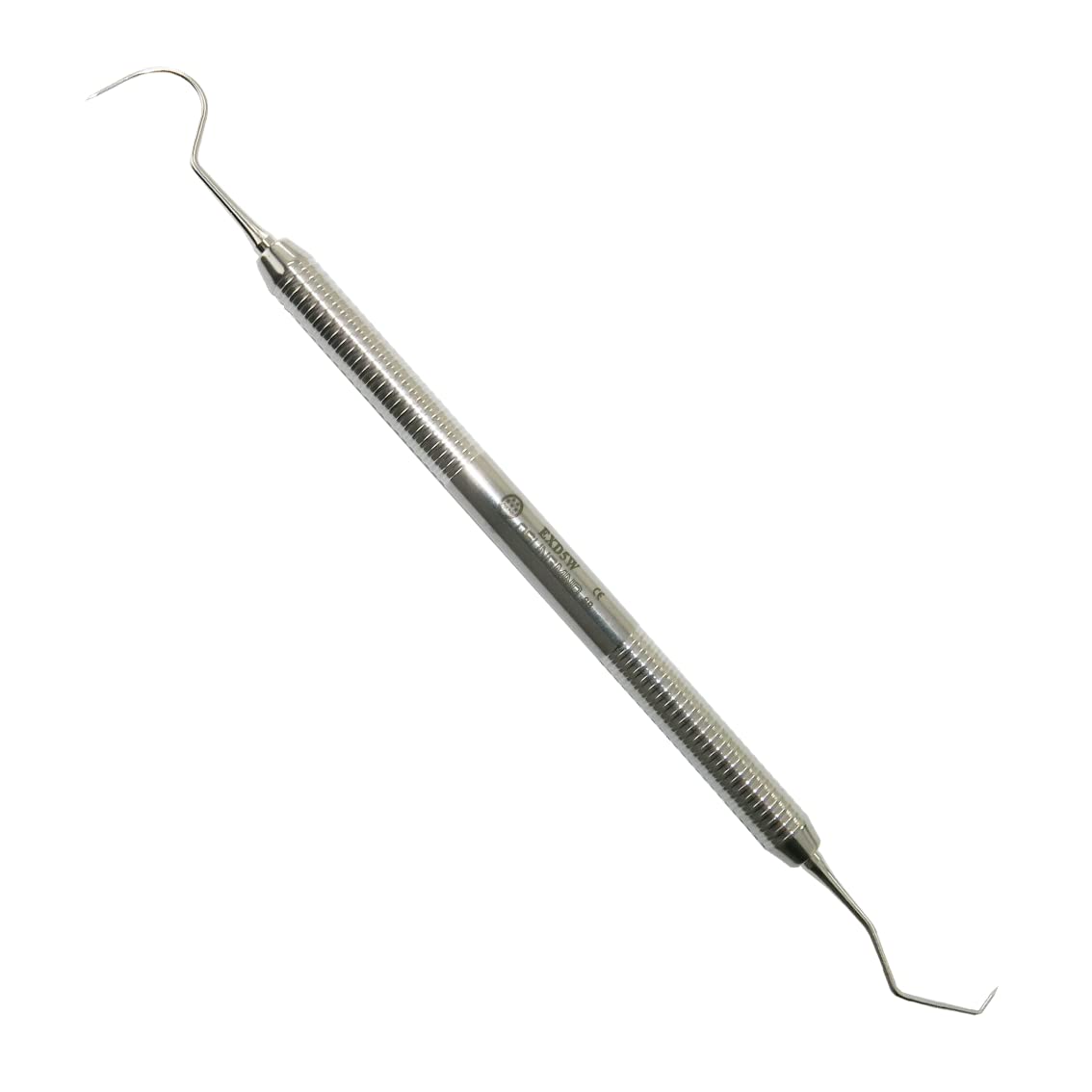
Explorer
What instrument is this?
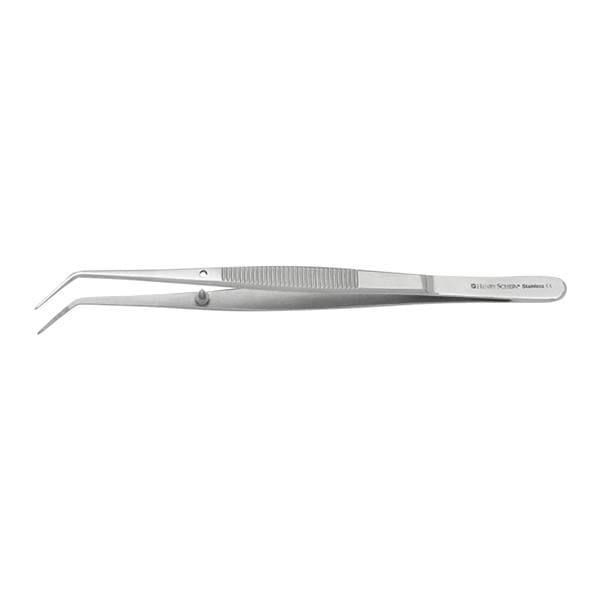
Cotton forceps (pliers)
What instrument is this?
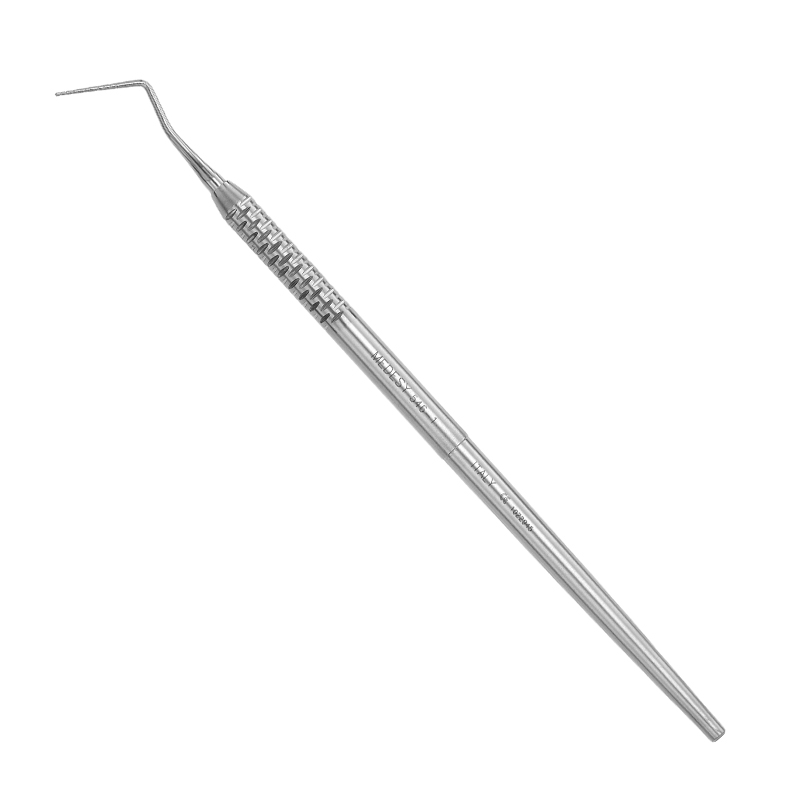

Periodontal probe
What instrument is this?
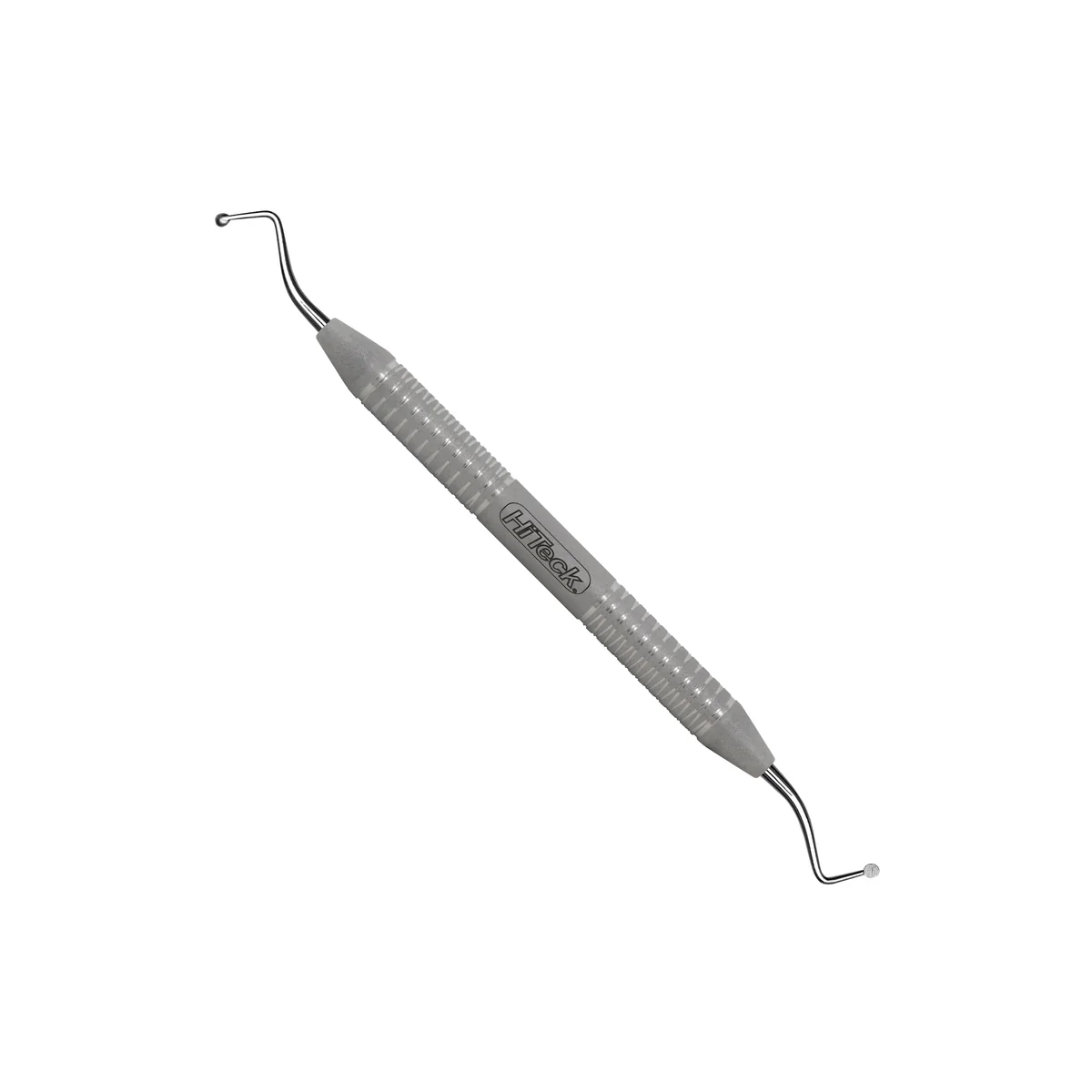

Excavator
What instrument is this?
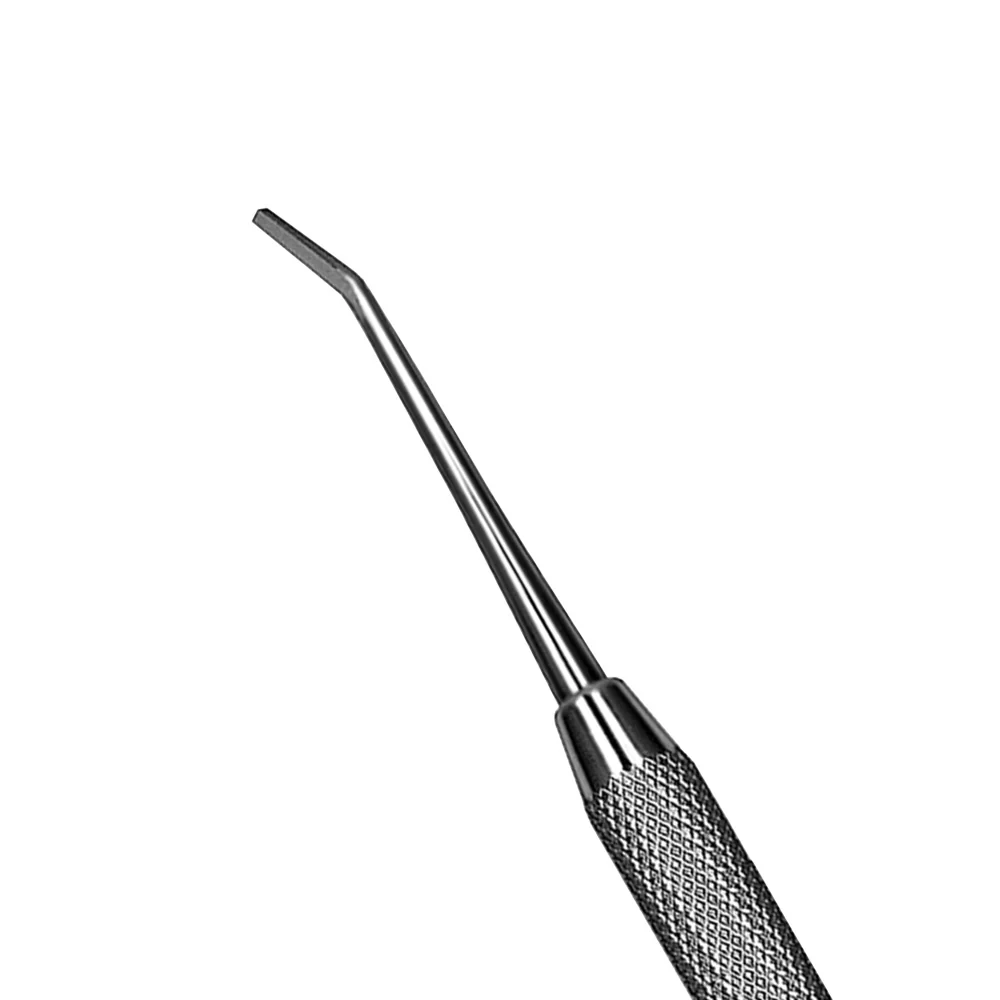

hoe
What instrument is this?

chisel
What instrument is this?
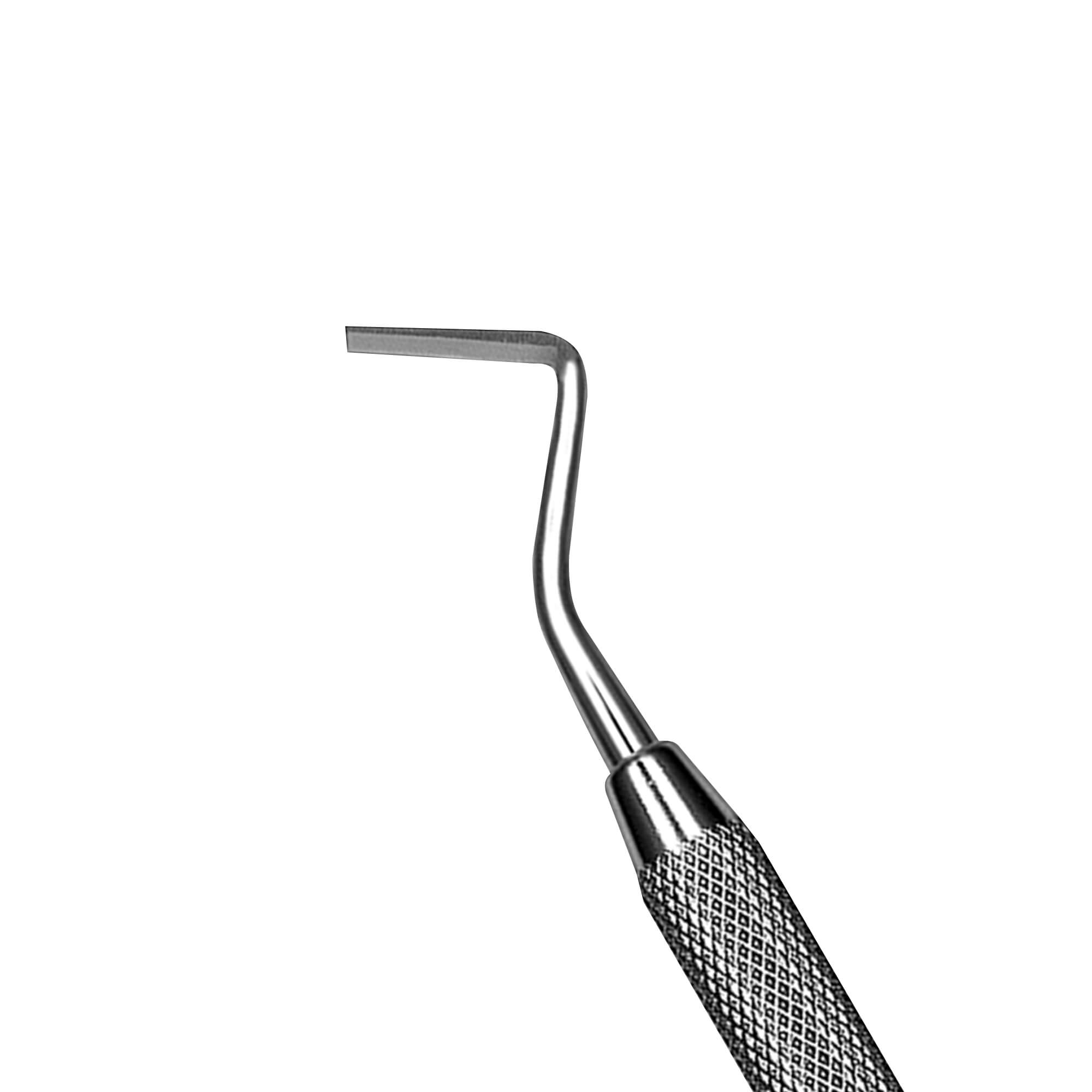
hatchet
What instrument is this?
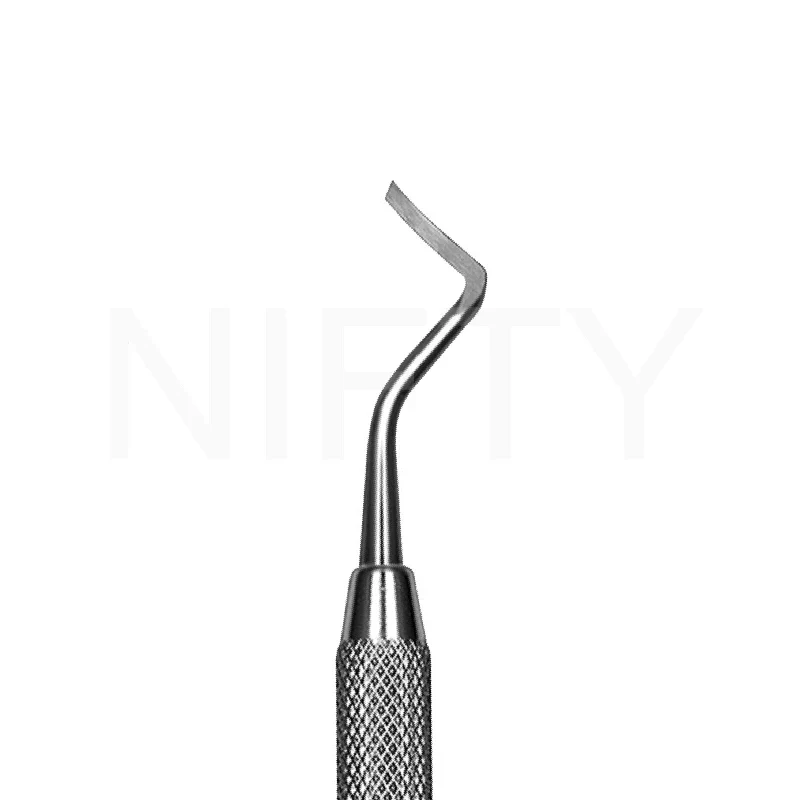
gingival margin trimmer
What instrument is this?
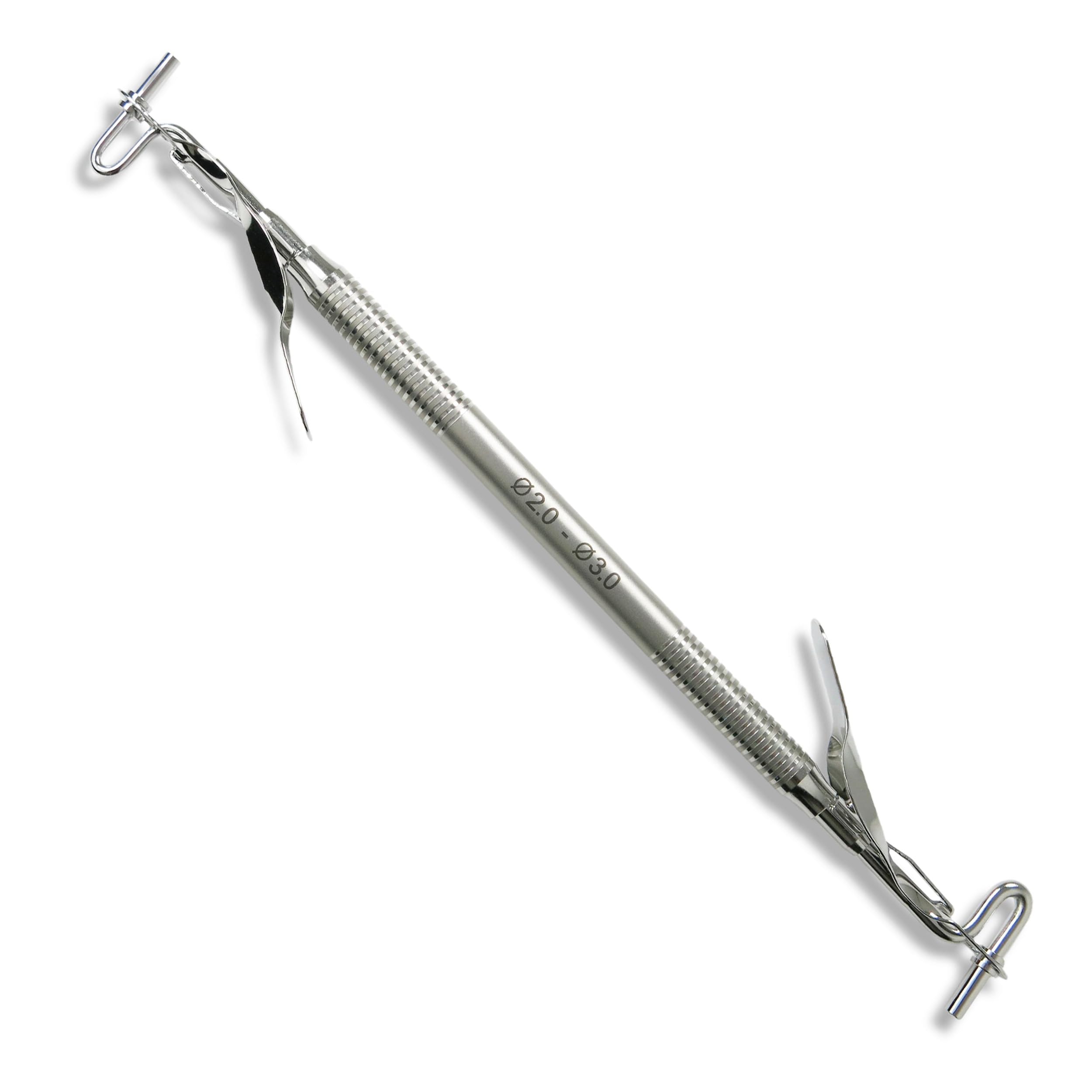

amalgam carrier
What instrument is this?
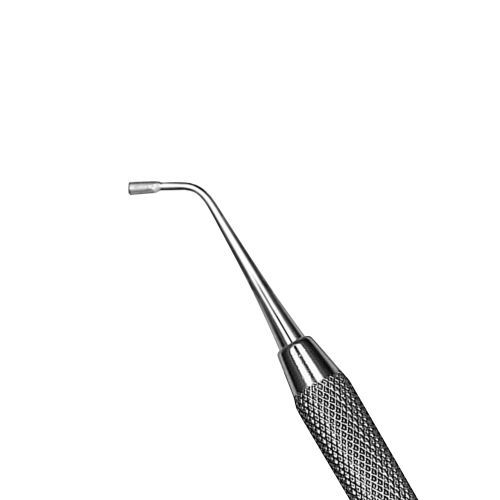
condenser
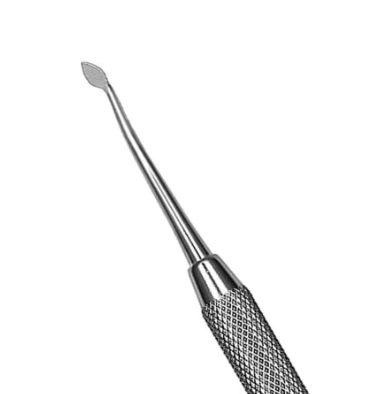
What instrument is this?
burnisher
What instrument is this?
discoid-cleoid carver
What instrument is this?
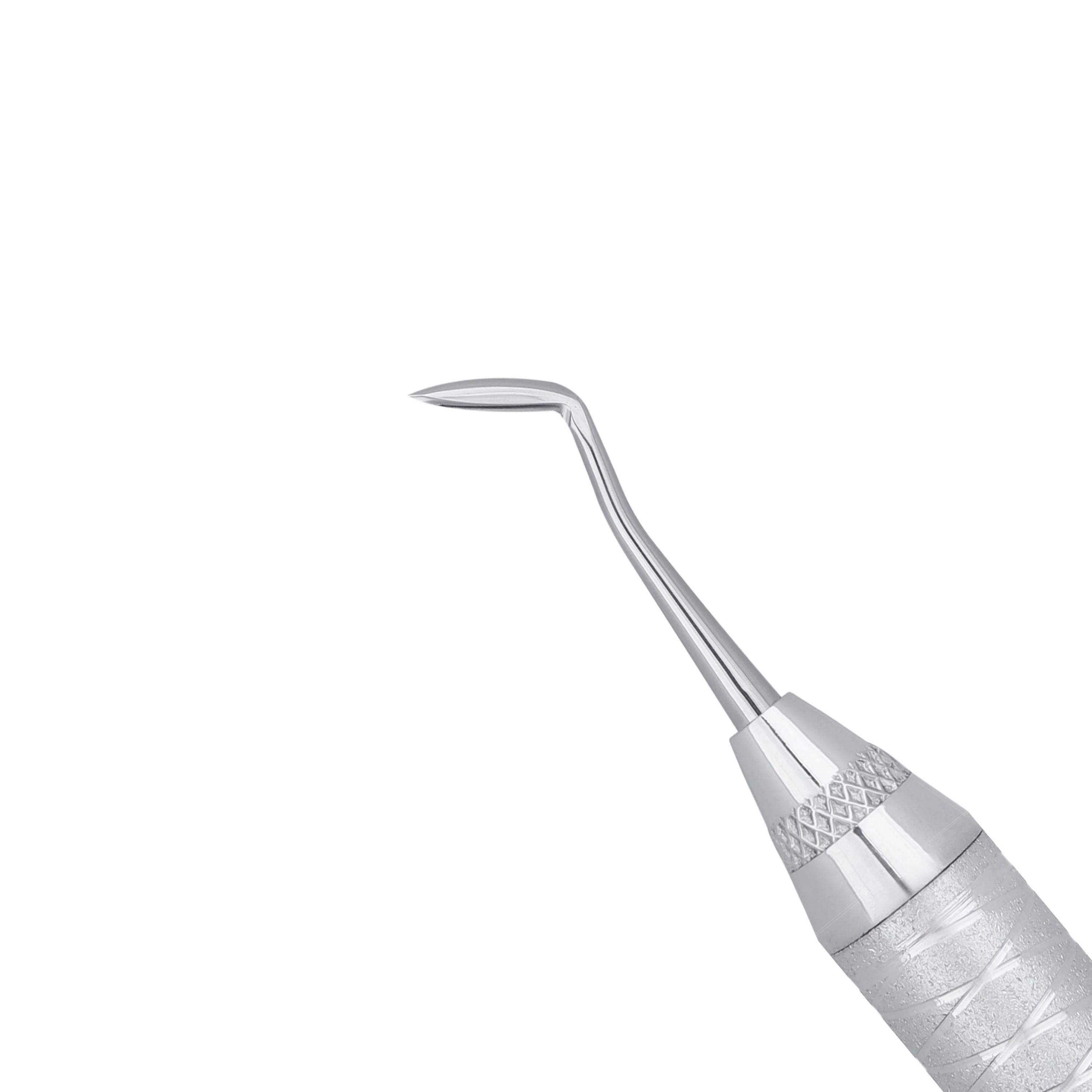
Hollenback carver
What instrument is this?
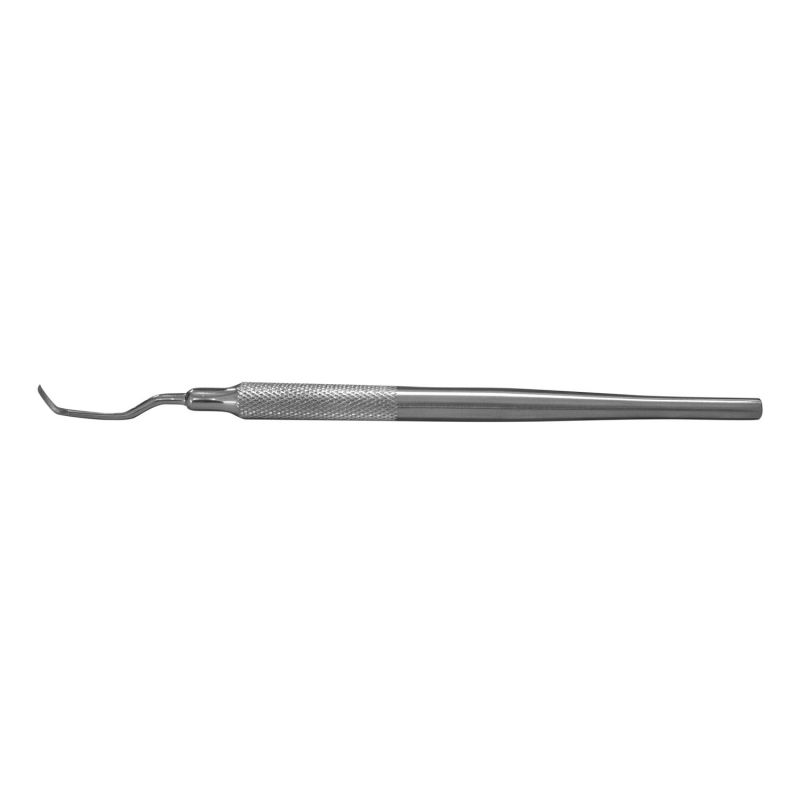

amalgam knife
What instrument is this?
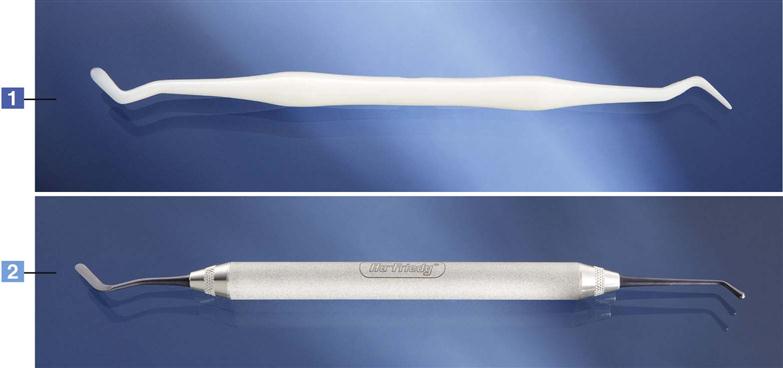
Composite placement instruments
What instrument is this?
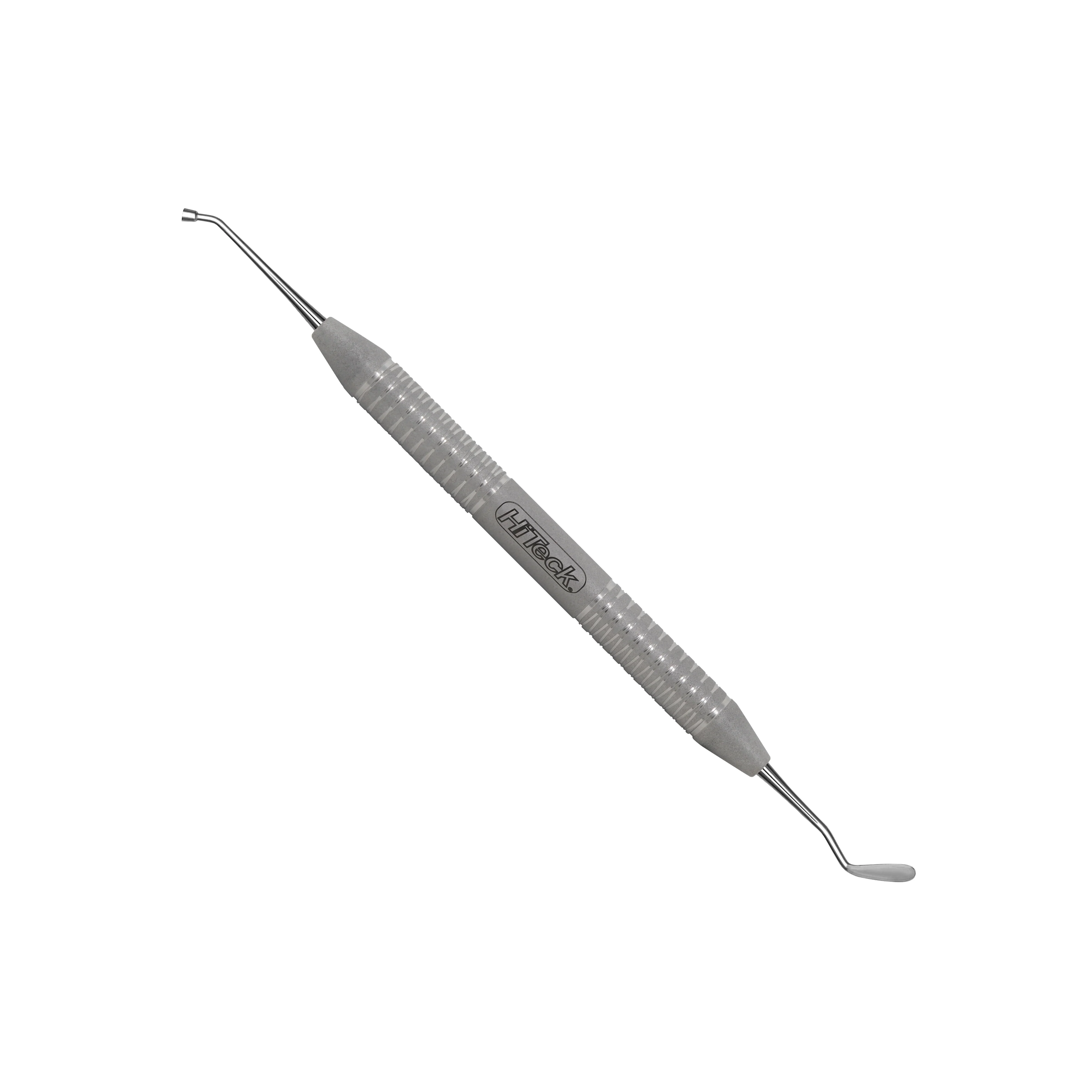

woodson (FP-1)
What instrument is this?
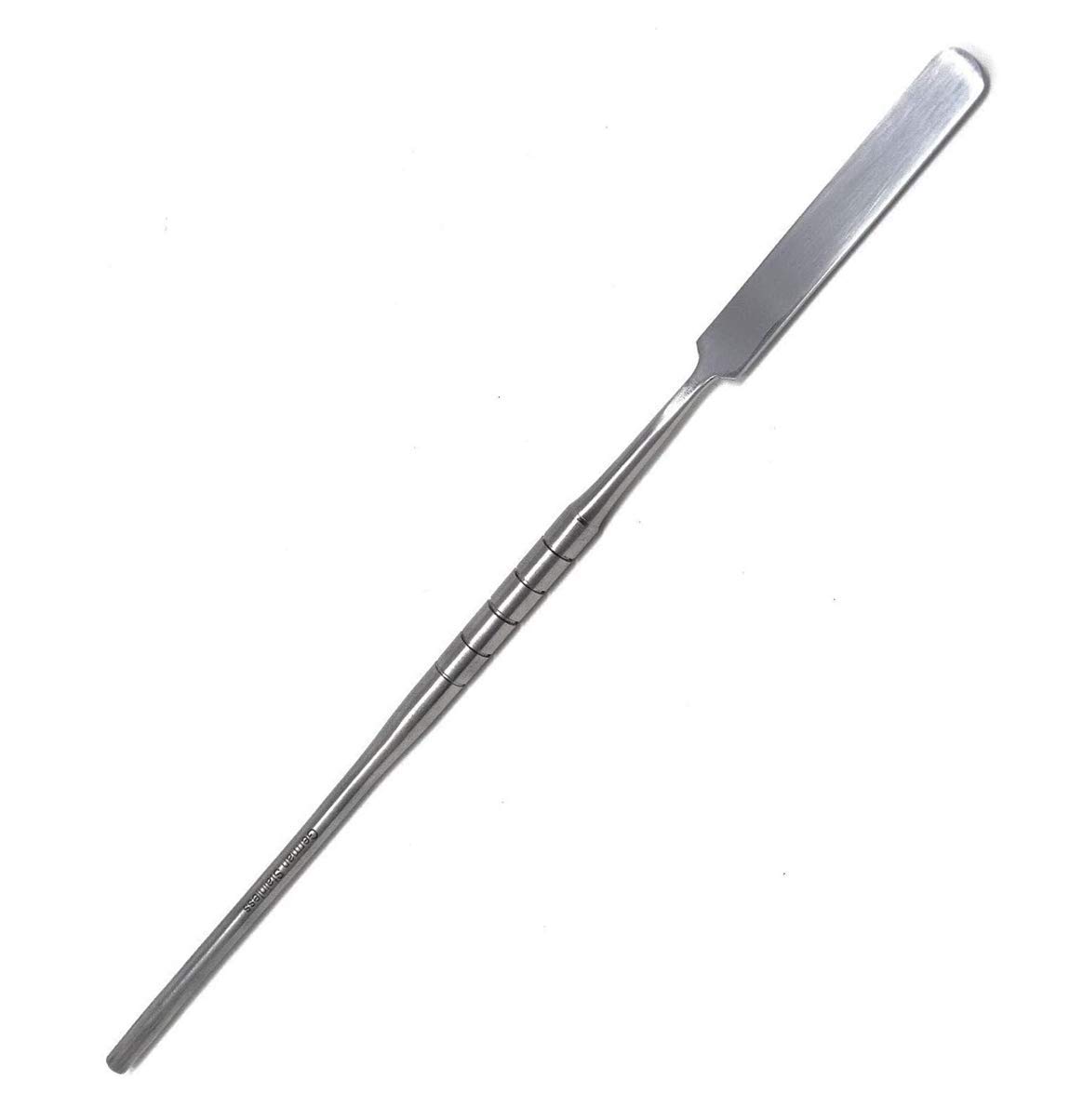

Spatula
What instrument is this?
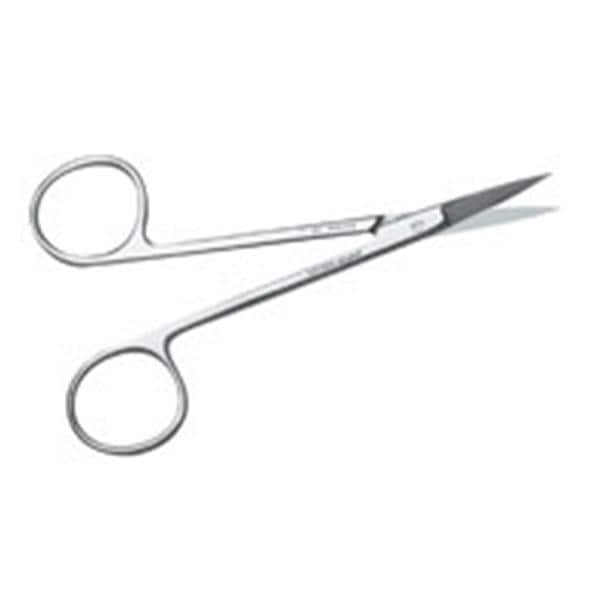
Scissors
What instrument is this?
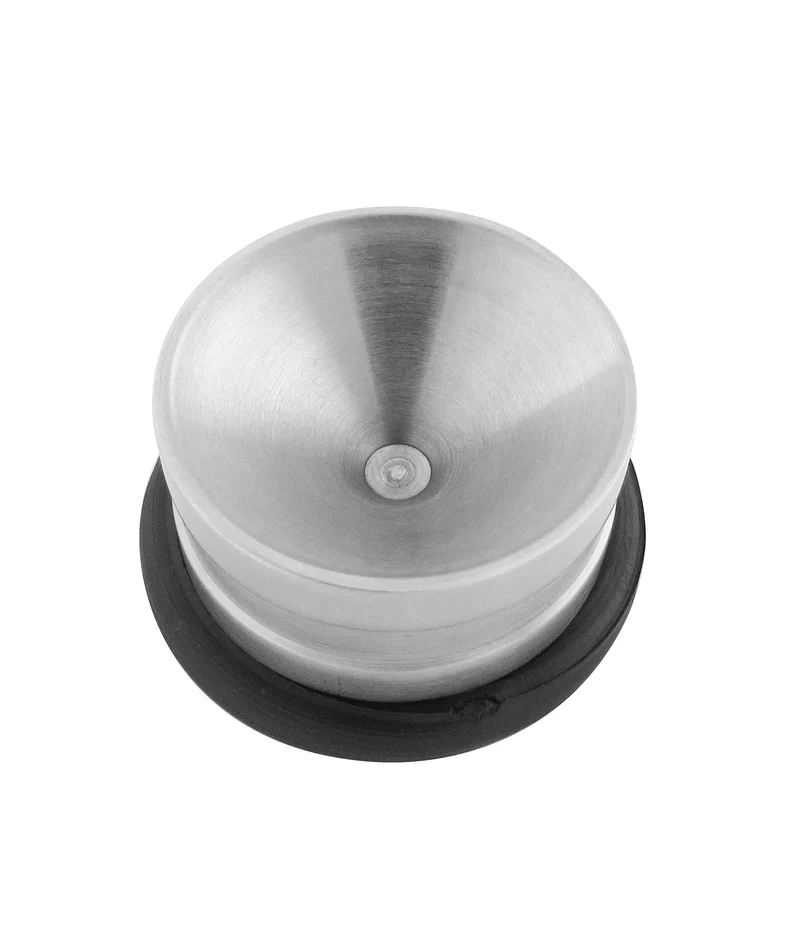

amalgam well
What instrument is this?
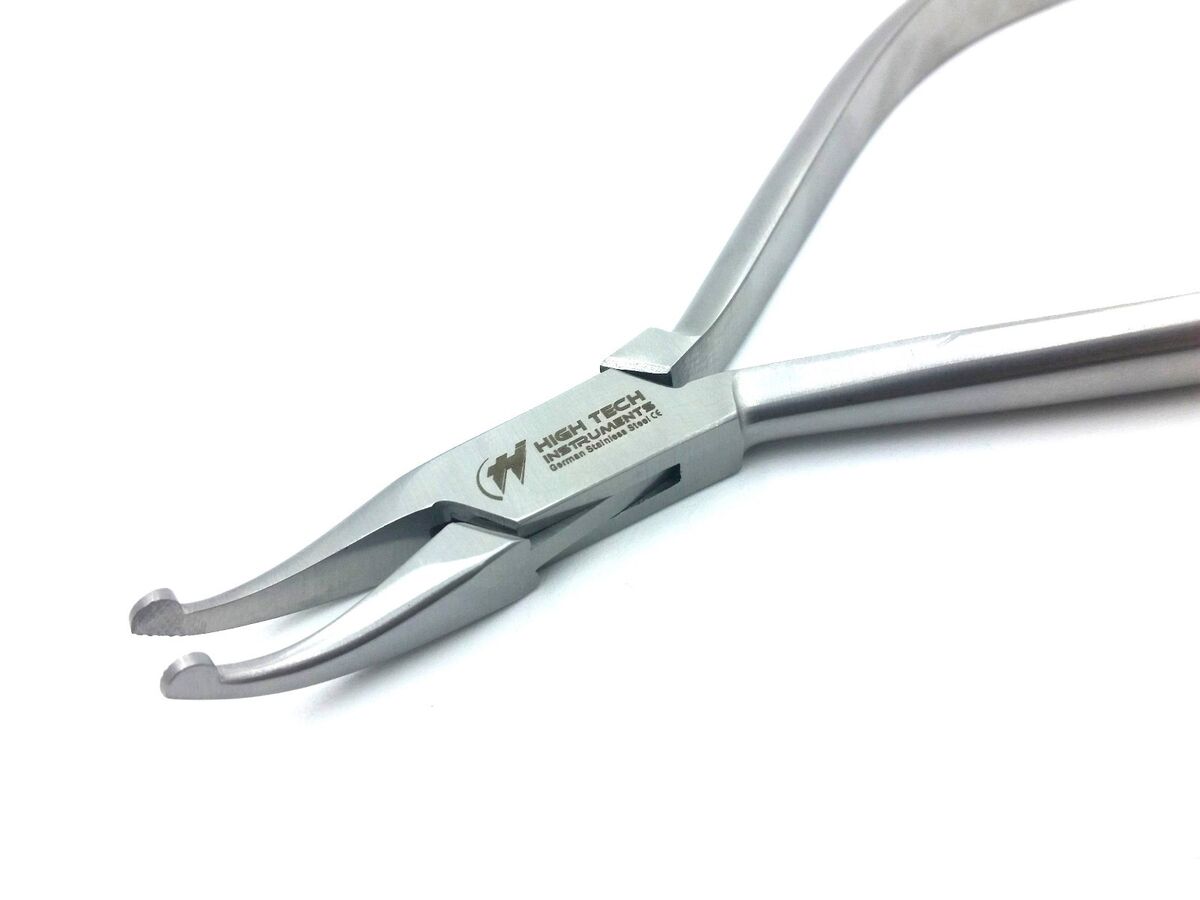

Howe pliers aka 110 pliers
What instrument is this?
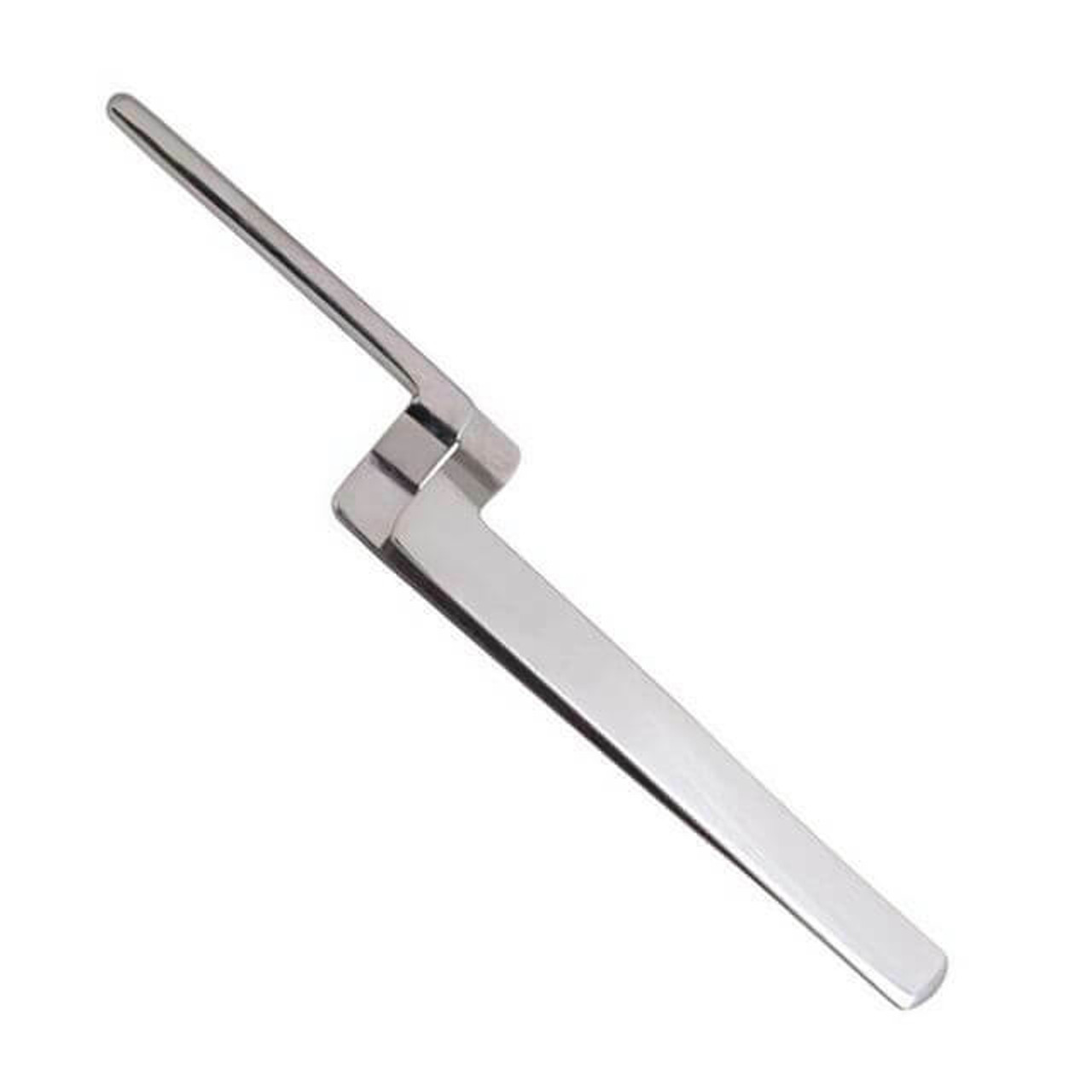

Articulating paper holder
What is the use of mouth mirror?
indirect vision, reflecting light onto surface, retraction of tongue and soft tissue
What is the use of explorer?
tactile sensitivity to distinguish areas of calculus or decay from discrepancies on the surfaces of teeth
What is the use of cotton forceps?
carry, place and retrieve small objects to and from mouth
What is the use of periodontal probe?
measure sulcus or pocket depth of the periodontium of each tooth
What is the use of the excavator?
removal of soft dentin, debris, and decay from tooth
What is the use of the hoe?
prepare the tooth and plane the walls and floors of the tooth preparation with push-pull action
what is the use of the chisel?
used to break down the enamel margin of the tooth preparation, form sharp lines and points angles, place retention grooves
what is the use of hatchet?
cut enamel and smooth the walls and floors of the tooth preparation
what is the use of gingival margin trimmer?
used cut enamel and place bevels along the gingival enamel margins of the preparation
what is the use of the amalgam carrier?
pack freshly mixed amalgam and carry it to the prepared tooth
what is the use of the condenser?
aka pluggers; composite side is used to prevent sticking and discoloration of restorative material; amalgam side is used to condense freshly placed amalgam into preparation
What is the use of the burnisher?
Used to smooth the surface of the restorative material
What is the use for the discoid-cleoid carver?
carving the restorative material on the occlusal surface
what is the use of the hollenback carver?
contour or remove excess restorative material interproximally
What is the use of the amalgam knife?
removal of excess restorative material along the margin where the material and the tooth structure meet
what is the use of the composite placement instruments?
placement of composite restorative materials
What is the use for the Woodson (FP-1)?
One end is a nib that resembles a condenser; other end is used for carrying dental materials to the prepared tooth structure
what is the use of the spatula?
mixing of a dental material is needed
what is the use of the scissors?
cutting dental dam material, retraction cords, and stainless steel crowns
what is the use of the amalgam well?
newly mixed amalgam is placed in and then picked up in the carrier for transfer
What is the use of the howe pliers?
used for carrying cotton products, removing matrix band, placing and removing wedge; useful for holding items
What is the use of the articulating paper holder?
carry and hold articulating paper
How do you properly transfer instruments working end?
Up for max arch
Down for mand arch
What is the use of the low speed motor with the straight attachment?
Trimming and contouring of custom impression, and whitening trays
What is the use of the low speed motor with the contra-angle attachment?
Removal of soft decay and fine finishing of a cavity preparation
Finishing and polishing restorations
Adjustments of porcelain and/or gold fixed restorations
Root canal treatment
what is the use of the low speed motor with the prophylaxis angle?
Coronal polishing procedures
What is the use of the high speed handpiece?
Used for restorative procedures and specialty procedures such as endodontics and fixed prosthodonticsW
What is the use the laboratory handpiec?
Use for finishing or polishing a cast restoration before cementation, removable prosthesis, or tray materials
What is the use of the ultrasonic handpiece?
Used for scaling and root planning procedures
What is the use of the laser handpiece?
Removal of decay and to prepare the tooth for the final restoration
Reshape or remove gingival tissue because of inflammation and disease
Removal of tissue intraorally for biopsy
Teeth whitening procedures
What is the use of the air abrasion handpiece?
Remove enamel, dentin, restorative materials without compromising healthy tooth structures