World History Semester 1 Final Review
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
Agricultural Revolution
when humans stopped hunting/gathering and began to farm and domesticate animals
around 10,000 BCE
originated in the Mesopotamian civilization of Sumer
Civilization
complex society characterized by advanced cities, organized governments, specialized workers, complex institutions, record keeping, and improved technology
began around 4,000 - 3,000 BCE
first civilizations - Mesopotamia, Egypt, Indus Valley, China
Advanced city
place with a large population and a center of trade for a larger area
Specialized worker
someone skilled at a certain type of work
farmers, priests, soldiers, etc
Complex institutions
things that maintain social order
government, religion, and education
Record keeping
a way to keep track of transactions, laws, and historical events
Improved technology
innovations that increased efficiency in communication, transportation, and production in society
ex: pottery wheel - used for vases, bowls, etc
Sahara Desert
large desert in North Africa with sand dunes and dry conditions
Savannas
grassland that is home to wildlife and used for grazing and agriculture
can be swampy or dry
African civilizations
Nomadic lifestyle
way of life where humans move from place to place in search of food, water, and other resources
instead of settling in one spot
indigenous peoples, Mongol Empire, Bedouins
Animism
the belief that there are spirits within natural objects (animals/plants) and phenomena
practiced in traditional and indigenous religions
indigenous peoples of Africa, Native American cultures
shows a connection between humans and nature
Griots/oral tradition
people who preserved historical events and traditions by speaking about them and telling stories
Mali Empire
Migration
movement of people from one region to another
often influenced by climate, resources, conflict, or opportunity
Bantu migration, Indo-European migrations, and the Mongol Empire which caused others to migrate because of its conquests and trade
Push-pull factors
things that bring people out of their homeland (push)
things that attract them to a new area (pull)
Bantu-speaking peoples
group of people who migrated across Africa
spreading their language, culture, and ironworking technology
significantly influenced the regions in which they settled - Sub-Saharan Africa
from around 1000 BC to 500 AD
Fertile Crescent
rich soils and agriculture led to Mesopotamia developing here
located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers
known for its early civilizations: Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians
City-state (Middle East)
self-governing urban center
own government, social structure, gods
Sumerian civilization used these
Cuneiform
one of earliest systems of writing
developed by the Sumerians
used wedge-shaped symbols on clay tablets
used for record keeping, communication
Ziggurat
large temple complex, built in the center of each Sumerian city-state
many people went there to pray
it served as a religious and administrative center
Cultural diffusion
spread of cultural beliefs, ideas, and technologies from one society to another through trade, migration, or conquest
knowledge in math, medicine, astronomy
origins of Judaism, Christianity, Islam
art - mosaics and sculptures
3500 - 500 BCE
was big in Middle East but also Ancient Greece
Hammurabi
Babylonian king (Babylonian civilization)
known for creating one of the first written legal codes, the Code of Hammurabi
Code of Hammurabi focused on aspects of society: family law, property rights, trade, civil rights. Emphasized justice and “eye for an eye” principle
he strengthened Babylonian state - expanded, established central government, unified Mesopotamian city-states
about 1792 - 1750 BCE
Empire
political unit where one state or ruler controls multiple territories or peoples, often through conquest
Roman Empire, Persian Empire, Mongol Empire, Ottoman Empire, British Empire
Cyrus
founder of the Persian Empire
known for his tolerance of conquered peoples and innovative administrative policies
mid 6th century BCE: about 559 BCE - 530 BCE
Darius
Persian ruler
became king in 522 BCE after Cyrus’s son Cambyses II
expanded the empire, standardized currency, and built the Royal Road for efficient communication
ruled from 522 - 486 BCE
Satraps
provincial governors in the Persian Empire
ruled locally under the king's authority and made the empire more efficient
during the empire: about 550 - 330 BCE
Royal Road
vast network of roads built by the Persian Empire
facilitated trade, communication, and military movement
during Darius’s reign: 522 - 486 BCE
continued to be used until 330 BCE when the empire fell to Alexander the Great
Zoroastrianism
ancient Persian religion based on teachings of Zoroaster
introduced Monotheism
emphasizing the struggle between good (Ahura Mazda) and evil (Ahriman)
emphasis on good deeds, good words, good thoughts
around 6th century BCE (Persian Empire)
Torah
central religious text of Judaism
consists of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible
outlines laws, teachings, moral principles of Jewish society
relationship with God and ethical behavior
Hebrew civilization
Temple or synagogue
places of worship in Judaism
temples being ancient central places of worship and synagogues serving local congregations
First temple built in Jerusalem by King Solomon: central place of worship for Israelites. Sadly destroyed by Babylonians in 586 BCE.
Synagogues became primary places of worship after second temple destroyed in 70 CE
Rabbi
Jewish religious teacher and leader
responsible for interpreting Jewish law and traditions
Rabbis emerged more during 1st century CE
Abraham
considered the patriarch of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam
he established a covenant with God - promised to be the father of a great nation
lifetime dates are controversial but around 2000 BCE - 1800 BCE
Israelites
ancient people who formed the Jewish nation and followed the teachings of the Torah
Famous events:
Egyptian Exile: they settled in Egypt during famine and became enslaved
Exodus: Moses led them out of Egypt and slavery to establish their land, and they wandered in the desert for 40 years
Overall lasted from 2000 - 586 BCE
Covenant
sacred agreement or promise
the covenant between God and Abraham in Jewish tradition - where Abraham promised to be the father of a great nation
Ten Commandments
set of moral and religious laws given to Moses by God, foundational to Jewish and Christian ethics
given to Moses during Israelites’ Exodus
the Ten Commandments (paraphased):
No other gods before God
No images or representations of God or an idol
Don’t take the name of the Lord your God in vain
Remember to keep Sabbath holy
Respect your parents
Don’t murder
Don’t commit adultery
Don’t steal
Don’t bear false witness against your neighbor
Don’t covet your neighbor’s house
Monotheism
the belief in a single god, foundational to religions such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam
originated around the 14th century BCE or 13th century BCE (from the Israelites and the Ten Commandments)
unified belief and understanding of God
Jesus (Christ)
central figure of Christianity, believed by Christians to be the Son of God and the Messiah
believed to have lived during first century CE
crucified around 30 - 36 CE and somehow disappeared
Crucifixion
Roman method of execution in which Jesus was put to death - being hung on a cross
central to Christian belief in his sacrifice for humanity's sins
Jesus’ crucifixion took place around 30 - 36 CE, scholars agree it likely happened during the Passover festival
Bible (Old and New Testament)
sacred scripture of Christianity
consisting of the Old Testament (shared with Judaism) and the New Testament
Old Testament written between 1400 - 400 BCE
history of Israel, laws, poetry, prophecies
Moses, David, prophets
New Testament written in first century CE: about 50 - 100 CE
life, teachings, death, resurrection of Jesus Christ
early Christian church
letters of Paul and Gospels
Priest
religious leader authorized to perform sacred rituals and offer guidance in Christianity and other religion
after Jesus’ resurrection, apostles and their followers began to establish Christian communities. Priests emerged in these early churches
from the 5th century and later (Middle ages), priests got more established in their roles in the RCC (Roman Catholic Church)
Messiah
savior or liberator expected by the Jewish people
Christians believe this is Jesus because he sacrificed for humanity’s sins and fulfilled the prophecies
Disciples
followers of Jesus who learned from and spread his teachings after his death
important figures in the early Christian church after Jesus’ resurrection
Apostles
the primary early Christian missionaries, including Jesus' closest disciples
during Jesus primarily: learning from and spreading his teachings
laid the foundation of Christianity after Jesus’ resurrection
Paul
apostle who played a key role in spreading Christianity beyond Jewish communities through his letters and missions
converted from Judaism to Christian when he had a vision of Jesus
about 30 - 65 CE
Pope
leader of the Roman Catholic Church (RCC)
makes important decisions, represents church
Democracy
form of government in which power is determined by citizens, who exercise it through elected representatives or directly
first known democracy: in Ancient Greece, in Athens
around 507 BCE
Roman Republic - had democratic elements after Athens: 509 - 27 BCE
Citizens vs Subjects
citizens participate in governance and have rights, while subjects are ruled without direct participation
citizens: active participates in government
right to vote, run for office, make decisions
based on birth or legal status
subjects: under a monarchy or authoritarian regime
way less rights, especially not participating in government
limited ability to influence laws/policies and expected to follow rules
this is most commonly associated with Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome
City-state/polis (Greece)
self-governing urban entity typical in ancient Greece
has its own government and military
most famous city-states: Athens and Sparta
emerging democracy in Athens
8th century BCE to 4th century BCE
Pericles
Athenian statesman who promoted democracy and led Athens during its Golden Age
lived from about 495 - 429 BCE
prominent political leader in 461 BCE
Golden Age of Athens: leader during the height of Athenian democracy and culture
especially 450 - 430 BCE
Assembly
gathering of citizens in a democracy to discuss and decide on laws and policies
one of the earliest forms of direct democracy
in Athens
only male citizens over the age of 18
voting by hands or colored stones
Socrates
Greek philosopher who emphasized questioning and ethics
known for his Socratic method
a way to stimulate critical thinking and illuminate ideas
questioning, critical thinking
lived from about 469 - 399 BCE
during Golden Age of Athens, when democracy flourished and arts thrived
he was put on trial in 399 BCE for corrupting youth
sentenced to death and chose to drink poison instead of taking back his beliefs
Parthenon
temple dedicated to goddess Athena in Athens
built under leadership of Pericles
an example of classical Greek architecture
built between 447 and 432 BCE, during Golden Age of Athens
impressive columns
became a symbol of Athenian democracy
Republic
form of government where citizens elect representatives to make decisions
in ancient Rome
about 509 to 27 BCE
Senate
legislative body in the Roman Republic composed of elder statesmen who advised on laws and policies and controlled finances
Patrician
member of the wealthy, noble class in ancient Rome
they were born into their role/class
typically the only ones eligible for high government positions
Plebeian
commoner in ancient Rome, often with limited political power initially (fewer rights than patricians)
majority of the population: farmers, laborers, merchants
could not hold high government positions or fully participate in the political process
over time, they fought for more rights - formed their own assemblies, gained the right to elect officials to protect their rights
eventually gained more equality and influence in society
Pax Romana
period of peace and stability throughout the Roman Empire lasting about 200 years
about 27 BCE - 180 BCE
“Pax Romana” translates to “Roman Peace”
a time with little military expansion and less internal conflicts
Emperor Augustus established a strong centralized government and effective administration
trade flourished, which led to economic growth, cultural exchange, advancements in engineering and architecture
artistic achievements, literature, spread of culture and law
Colosseum
large amphitheater in Rome used for gladiatorial games and public spectacles
people and animals were killed for entertainment - part of Roman culture
aqueducts built in for water activities
huge size, impressive design - arches and vaults
can hold 50,000 - 80,000 people
built between 70 - 80 CE
today, it still stands as a symbol of Rome’s architectural and cultural achievements
Aqueduct
Roman engineering structures that transported water over long distances to cities and towns
supplied water for drinking, bathing, irrigation, bathrooms, and other things - overall improving public health and sanitation
the Romans used gravity to move the water since it just flowed through
some aqueducts had high arches that stood up above the ground
showed the Romans’ advanced engineering and helped cities thrive
mostly built between 4th century BCE and 3rd century BCE
Subcontinent
large, distinguishable part of a continent, such as the Indian subcontinent
sometimes densely populated
different culture and language between subcontinents
different resources - fertile land, minerals, or waterways
different wildlife in different subcontinents
Monsoon
seasonal winds that bring heavy rains and influence agriculture in South Asia
summer monsoon: between June and September. In India, moisture-full winds from the ocean trigger heavy rain, which is great for agriculture
winter monsoon: from October to April. It brings dry winds from the land, leading to cooler, drier weather
monsoons are crucial for farming - they provide water for crops. But they can also cause flooding and natural disasters from excessive rainfall
monsoons impact climate, which in turn impacts temperature, ecosystems, and lifestyles
Harappan civilization
early urban culture of the Indus Valley known for planned cities and advanced infrastructure
well-constructed roads, advanced drainage systems, public baths
also known as the Indus Valley civilization
peaked between 2500 and 2000 BCE
developed urban centers - Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro
declined around 1900 BCE due to climate change or less resources
Mohenjo-Daro
major city of the Harappan civilization, featuring sophisticated urban planning
grid layout with streets laid out in right angles
sophisticated drainage systems
public buildings
houses from baked bricks
granaries for storing grain
great public bath
trade with Mesopotamia
had its own writing script but is still undeciphered
built around 2500 BCE
Aryans
Indo-European nomadic peoples who migrated to India and introduced the caste system and Vedic culture
believed to have migrated to India around 1500 - 1000 BCE
their arrival marked the beginning of the Vedic period (named after the Vedas)
lasted from 1500 - 500 BCE
they were primarily pastoral and agricultural
lived in tribes, practiced cattle herding, settled into farming
they practiced a polytheistic religion - worshipped different deities/gods related to nature
rituals centered around sacrifices
Vedas
ancient sacred religious texts forming the foundation of Hinduism
composed in Sanskrit between 1500 - 500 BCE
passed down orally before being written down
they cover cosmology, philosophy, ethics and guidance for rituals
Castes
social groups in Hindu society that are determined by birth and rigidly divided
also based on occupation
Brahmins: highest caste
mainly priests and scholars
responsible for religious rituals and teaching sacred knowledge
Kshatriyas: warrior and ruler caste
kings and soldiers
responsible for protecting the land and governing society
Vaishyas: merchant and landowner caste
involved in agriculture, trade, and commerce - contributing to the economy
Shudras: lowest caste
laborers and service providers
performed manual work and provided services to the other castes
Untouchables: outside of the four main castes
experienced severe social discrimination and exclusion
assigned dirty tasks - working with leather, handling waste, etc
forced to live separately from other castes
touching or coming into contact with an untouchable was thought to pollute someone from a higher caste
Polytheism
the belief in and worship of multiple gods/deities, common in ancient and traditional religions
each god might be associated with different aspects of life, nature, or human experience
Ex: Hinduism is polytheistic
Karma
the belief that actions in life determine one's fate in future lives
found in Buddhism and Hinduism
good karma - positive actions lead to beneficial outcomes in this life or future lives
bad karma - negative actions can result in suffering or difficulties later on
Brahman
the ultimate, unchanging reality or world soul in Hinduism
considered infinite, formless, and beyond human comprehension
different from Atman - this is a world soul while Atman is the individual’s soul
Dharma
one's duty or righteousness according to Hinduism
the right way of living - one’s responsibilities towards family, society, and the universe
varies based on age, gender, social class (varna), and situation
following Dharma is believed to lead to harmony in life, societal stability, and spiritual progress
Reincarnation
the cycle of rebirth of the soul into a new body or the belief that a soul is reborn into a new body after death
prevalent in the religions of Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism
the goal is to learn and grow spiritually and for the soul to reach moksha
Moksha
attaining knowledge, wisdom, and liberation through and from reincarnation
getting union with Brahman
freedom from all suffering, karma, and worldly attachments
realizing one’s true nature (Atman) and its oneness with the ultimate reality (Brahman)
Atman
the individual soul in Hindu philosophy
the true essence of a person - the part that is eternal and unchanging
different from Brahman - this is the individual’s soul while Brahman is the world soul
Ganges River
a sacred river in India, central to Hindu spirituality
considered sacred - people believe that bathing in its waters purifies the soul and helps achieve moksha
originates from glaciers in the Himalayas and flows through northern India before it empties into the Bay of Bengal
Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama)
the founder of Buddhism, who attained enlightenment and taught the path to overcome suffering
lived around the 6th - 4th centuries BCE in modern-day Nepal and India
born into royal family, lived a sheltered life
protected from suffering until 29 years old, when he went outside for the first time and came across old age, sickness, and death
sat under a tree and meditated, reached enlightenment after 49 days
shared his insights - the Four Noble Truths
Enlightenment/nirvana
Nirvana: a state of liberation and freedom from suffering, the ultimate goal in Buddhism
Enlightenment: gaining a true understanding of nature and oneself
realizing the Four Noble Truths
gaining wisdom, compassion, and insight, leading to a higher perspective on life and suffering
Noble Eightfold Path or Middle Way
Buddhism's guide to ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom, leading to enlightenment
right understanding
right intent
right speech
right action
right livelihood
right effort
right mindfulness
right concentration
Four Noble Truths
the core teachings of Buddhism explaining the nature of suffering, its cause, its cessation, and the path to liberation
life is filled with suffering and sorrow
the cause of all suffering is people’s desire for the temporary pleasures of the world
the way to end all suffering is to end all desires
the way to enlightenment is to follow the Eightfold Path, which is called the Middle Way between desires and self-denial
Mauryan Empire
an ancient Indian empire founded by Chandragupta Maurya, known for its centralized governance
founded in 321 BCE
known for unifying most of India under a centralized government
Asoka
Mauryan emperor who spread Buddhism across Asia following the bloody Kalinga War and promoted peace and tolerance
ruled from 268 - 232 BCE
Gupta Empire
an ancient Indian empire noted for advancements in science, art, and mathematics, considered a “Golden Age” of India
320 - 550 CE
Oracle bones
animal bones or shells used by ancient Chinese priests to predict the future
1600 - 1046 BCE
Mandate of Heaven
in Chinese philosophy, the belief that heaven granted emperors the right to rule based on their virtue
if a ruler became corrupt, they could lose this divine approval
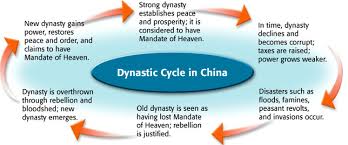
Dynastic cycle
traditional Chinese political theory that explains the rise and fall of dynasties
suggests that dynasties are born, rise to power, flourish, decline, and fall
Feudalism (China)
social hierarchy
king, then nobles, then peasants
king owns all land, grants large pieces to nobles in exchange for loyalty and military support
nobles then own the land and have power over peasants living in it
nobles protect peasants, ensure they paid taxes and provided military service
peasants worked and produced food. In return, they received protection and a place to live, but part of their harvest had to be given to the nobles
at first, Feudalism helped maintain social order and stability, but over time it weakened as merchants’ power increased
Confucius
Chinese philosopher
551-479 BCE
teachings on morality, government, family loyalty, and respect for elders (filial piety)
shaped Chinese thought and culture
Bureaucracy
system of government where decisions are made by state officials rather than elected representatives, often involving a hierarchy of offices and specialized roles
Legalism
Chinese philosophy advocating strict laws and harsh punishments to maintain social order
was influential during the Qin Dynasty under Shi Huangdi
221 - 206 BCE
Autocracy/authoritarian
system of government where one person or a small group has absolute power without checks or balances
Shi Huangdi’s rule is an example of autocracy
Filial piety
central value in Confucianism that emphasizes respect, obedience, and devotion to one's parents and ancestors
Daoism
Chinese philosophy emphasizing harmony with nature and the Dao ("the Way"), which refers to the natural order of the universe
founded by Laozi
Shi Huangdi and Qin Dynasty
Shi Huangdi - founder of the Qin Dynasty, China’s first emperor
known for unifying China and initiating the construction of the Great Wall
Qin Dynasty lasted from 221 - 210 BCE
characterized by centralized power, Legalism, and large-scale construction projects like the Great Wall
The Great Wall
massive fortification built across northern China to protect against invasions from nomadic tribes
it was expanded significantly during the Qin Dynasty
Han Dynasty
Chinese dynasty that followed the Qin
known for:
advancements in technology
trade (Silk Roads)
establishment of the civil service system
lasted from 206 BCE – 220 CE
Monopoly
exclusive control of a commodity or service in a particular market, often by a single entity
ex: the Han Dynasty had a monopoly on the production of silk
Silk Roads
ancient network of trade routes connecting China with the West
facilitated the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas between the Roman Empire, India, and China
Civil service
system in which government officials are selected based on merit, often through examinations
this was first implemented in China during the Han Dynasty
Assimilation
the process by which a group or culture becomes similar to another, often through the integration of one culture into a dominant one
this occurred during the Han Dynasty with the spread of Chinese culture to conquered peoples
Allah
the Arabic word for God in Islam, signifying the monotheistic belief in a single, all-powerful deity
Muslim/Islam
a Muslim is a follower of Islam
monotheistic religion founded by the prophet Muhammad in the 7th century
based on submission to the will of Allah
Ka'aba
sacred Islamic shrine in Mecca
central to Islamic worship and pilgrimage
believed to have been built by Abraham and his son Ishmael
Muslims face the Ka'aba during prayer