electrophilic addition
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is an electrophile?
e- deficient species which will accept a pair of e-
what is a carbocation?
+vely charged C atom w/ only 3 bonds, making it unstable
what does electrophilic addition involve? what does it form?
alkene → dihaloalkane
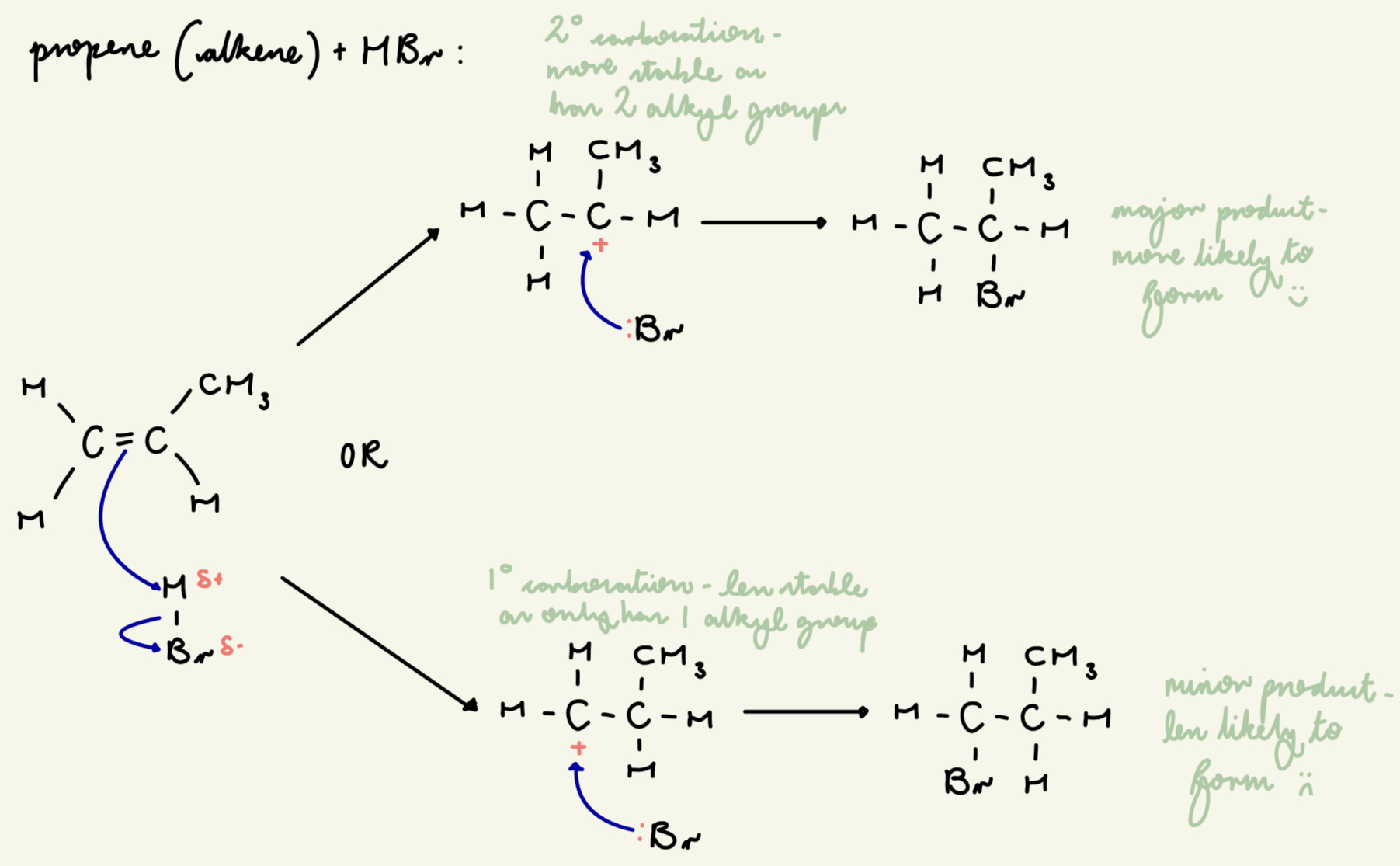
draw out the electrophilic addition mechanism between HBr and propene (for both the major and minor product):
draw out the electrophilic addition mechanism between Br2 and ethene:
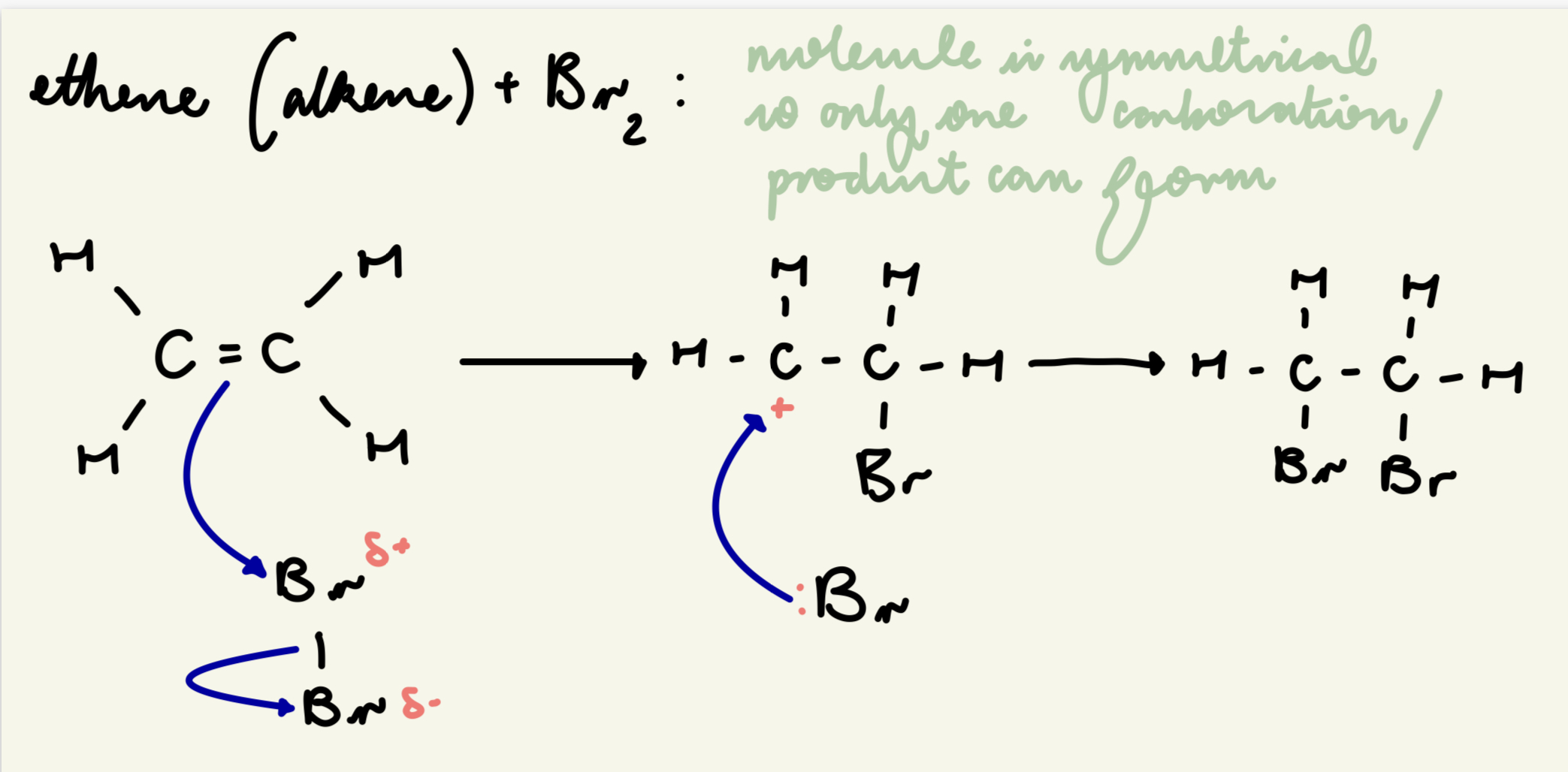
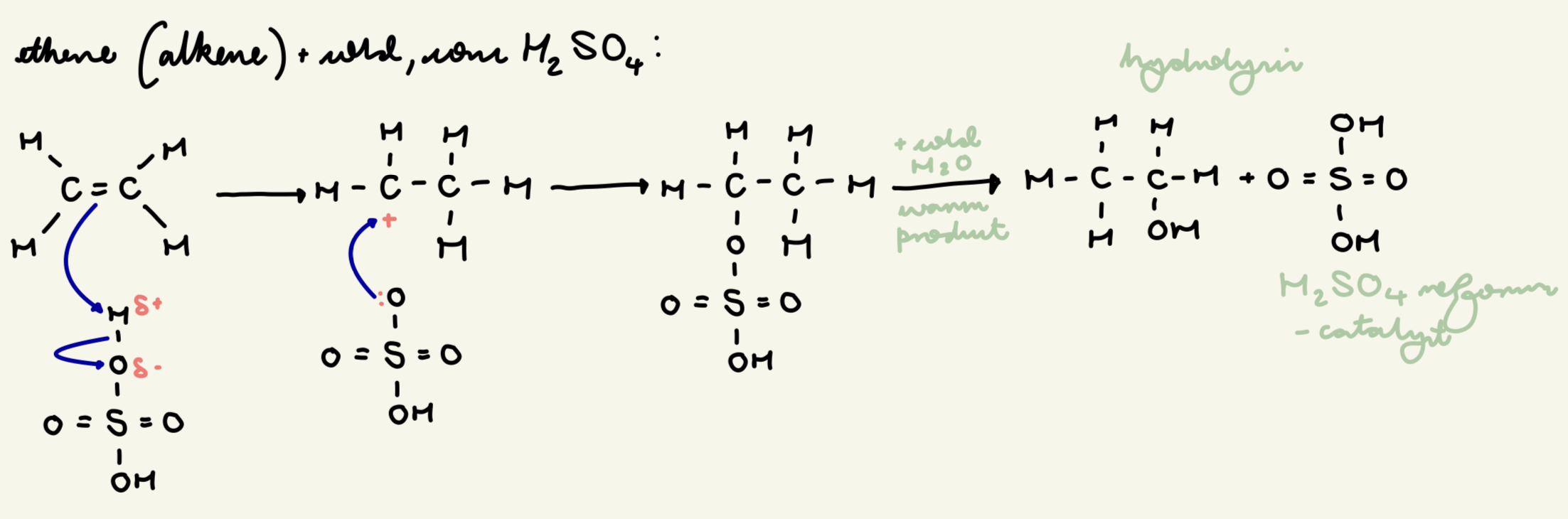
draw out the electrophilic addition mechanism between H2SO4 and ethene and state the conditions:
give the order of carbocation stability - why is this the case?
tertiary carbocations have the most stability as they have the greatest +ve inductive effect as they have the most alkyl/C groups
as they push e- density towards the carbocation and stabilise the +ve charge
the more alkyl groups, the more stable
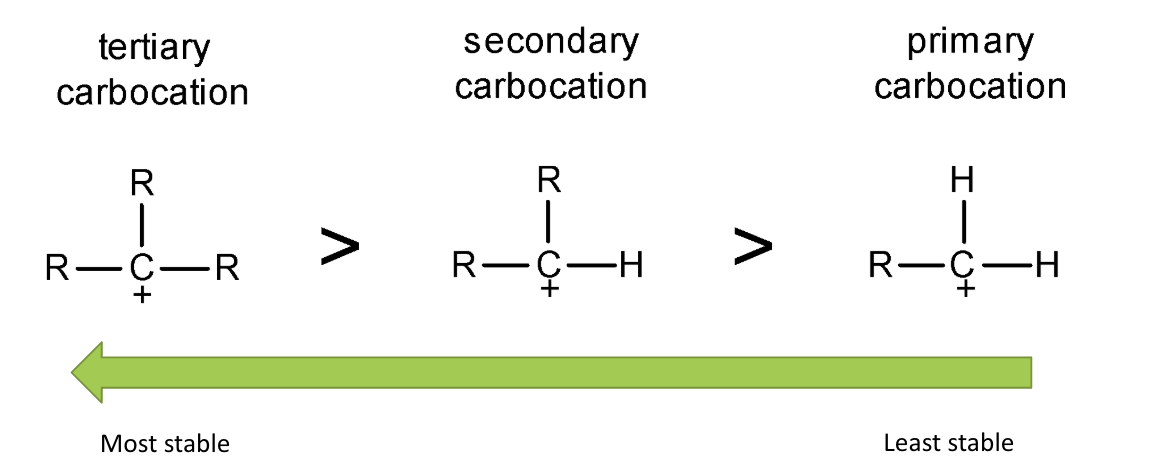
what is a primary carbocation?
carbocation w/ only 1 alkyl group
what is a secondary carbocation?
carbocation w/ 2 alkyl groups
what is a tertiary carbocation?
carbocation w/ 3 alkyl groups
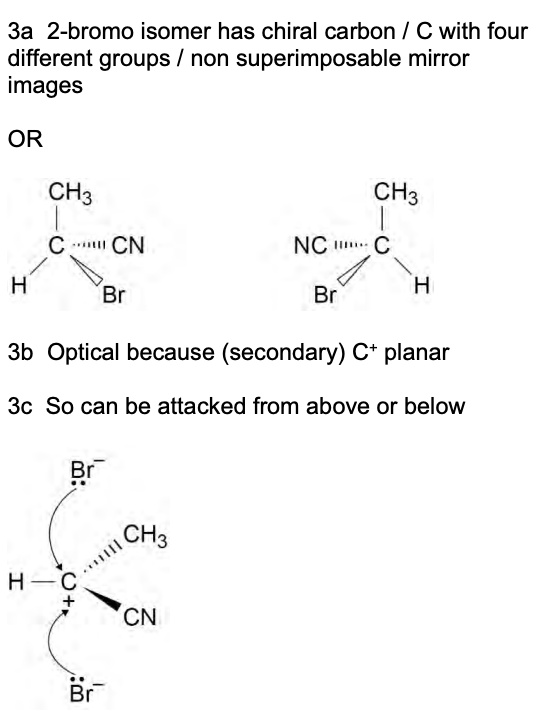
why may a product of electrophilic addition display optical isomerism?
electrophilic addition involving an alkene w/ one of the Hs substituted for a different functional group e.g. CN + HX
product is a haloalkane w/ one of the Hs subbed for the other functional group
one of the carbocations may form a product w/ a chiral C
optical as C+ on carbocation planar so can be attacked from above or below