OTH 5430–Exam 3: Cancer and Oncology Rehab
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
How is cancer treated?
surgical removal
radiation therapy
chemotherapy
immunotherapy
hormone therapy
stem cell transplants
patients can undergo many at once
Surgical removal
removal of cancer cells/tumors from body
Radiation therapy
focused on killing cancer cells and shrinking tumors
Chemotherapy
drugs to kill cancer cells
Immunotherapy
focused on strengthening and using persons immune system to fight cancer
Hormone therapy
uses hormones to slow or stop cancer cell growth
Stem cell implants
restores blood-forming cells destroyed by high-dose chemo or radiation
Impact of cancer treatment on body functions include
changes in HR and rhythm
dizziness
BP dysfunction (elevated or low)
changes in vision
changes in cognitive status
changes in appetite and perception of taste
changes in metabolic rate (lose/gain weight)
2 key measures of body functions in cancer treatment are _____ and _______.
vital signs and lab values
these help with developing treatment interventions
Cancer rehab: Precautions
lab values
-provide info on patient via chart review
tx implications
-lab values provide info on which tx interventions can be done
(accepted lab values - careful monitoring)
Cancer rehab: Contraindications
typically abnormal lab values that are extreme
-most likely defer tx
_______________ is contraindicated for lab values that are critically outside the normal range.
Functional activity
tests such as a CBC can help practitioners determine safe functional activity guidelines, particularly for patients who are undergoing or have just completed chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or bone marrow transplants
Cancer rehab: Medical complexity
safe tx options can change
-patient may safely exercise at one point and then may be under activity restrictions at other times
Common lab values in oncology that should be reviewed prior to implementing any interventions or treatment include .
platelets
WBC's
hematocrit
Platelet: Normal range
150 k/uL - 450 k/uL
Platelets: Accepted values for participation
140 - 440 k/uL
Platelets: Rehab implications
< 5 K only active assistive movements/no Valsalva maneuvers (pushing too hard, increases BP) – no resistance
< 20 K active movements – no resistance
> 50 K resistive movements
Fall risk assessments are paramount when platelets are low
What exercise do we give patients with a platelet count of less than 5k?
only active assistive movements (client moves partial way but then requires outside assistance to complete ROM)
no resistance
What exercise do we give patients with a platelet count of less than 20K?
active movements
no resistance
What exercise do we give patients with a platelet count of greater than 50k?
resistive movements
Platelets: Other findings
-fall risk assessments are paramount when platelets are low**
-check for petechiae (reddish, purple rash)
-check for any active signs of bleeding (nosebleeds, excessive bleeding from cuts, blood-tinged sputum, swollen joints, etc.)
-below 20k = increased risk for intracranial bleed
If a patient has a platelet count of below 20k, they are at an increased risk for ________.
increased risk for intracranial bleed
check for cog issues i.e. confusion, difficulty speaking, sudden vision changes
What type of assessments are paramount when platelets are low?
fall risk assessments
WBC's: Normal range
3.5 k/uL - 10.5 k/uL
WBC's: Accepted values for participation
4 - 11 k/uL
WBC's: Rehab implications
(+) Risk for infection
Neutropenia: absolute neutrophil countless than 0.5 cell/mm3
Adhere to hand hygiene and infection control policies
Patient may present with a fever when neutropenic
Hematocrit: Normal range
male: 37% - 49%
female: 36% - 46%
Hematocrit: Accepted values for participation
male: 40% - 54%
female: 37% - 47%
Hematocrit: Rehab implications
< 20% can result in cardiac failure/death
< 25% defer therapy
25% – 30% ADL and exercise as tolerated – no resistance
30% can add resistive exercises
A patient has a hematocrit level of 18%, what type of activities will we focus on?
none!!! can result in cardiac failure or death!!!!!
A patient has a hematocrit level of 23%, what type of activities will we focus on?
none, we defer therapy
A patient has a hematocrit level of 27%, what type of activities will we focus on?
ADLs and exercise as tolerated but with NO RESISTANCE
(range = 25% – 30%)
A patient has a hematocrit level of 33%, what type of activities will we focus on?
ADLs and exercise as tolerated but now WITH RESISTANCE
1) Radiology and imaging include_________.
2) Why should OT's consult and review imaging reports?
1) CT or CAT scans, MRIs, ultrasound, x-rays in the event of acute fractures, and metastasis (the spread of cancer to another part of the body)
2) because the test results may influence the type of testing that the occupational therapy practitioner performs or alter the intervention plan
An OT is performing a chart review and found evidence that their patient's MRI report shows a new metastatic disease to the brain. What should the OT do?
OT should reassess cognition
An OT is performing a chart review and found evidence in their MRI report exhibiting new pathologic fractures. What should the OT do?
OT should refrain from giving the patient WB activities and resistive exercises on the affected extremity
(fractures could alter activities of daily living (ADLs) that require weight bearing or lifting)
T or F: In general, OTs should verify blood counts, vital signs, and images before completing an evaluation and providing treatment.
true
Commonly used assessments in oncology
Activities of Daily Living Assessment Scales - Katz Index
A-one
Brief-Fatigue Inventory (BFI)
Executive Function Performance Test
Kettle Test
Multiple Errands Test (MET)
Pain scales
Katz Index of ADL
Assessment of level of independent functioning and type of assistance required in six areas of ADL.
Evaluator observes activity performance or interviews the individual about performance.
Population: Adults and elders with chronic illness.
A-one assessment
-cognitive assessment that directly links fxnl performance (BADLs and mobility) to neurobehavioral deficits including cognitive-perceptual and motor impairments
-appropriate to use for patients over the age of 16 who present with damage to the central nervous system
Brief-Fatigue Inventory (BFI)
short assessment of the severity of fatigue experienced over the previous 24 hours and its impact on function
Executive Function Performance Test
a performance-based standardized assessment of cognitive function available for free in the public domain
-assesses function deficits during the performance of real world tasks (cooking oatmeal, making a phone call, managing medications & paying a bill)
-uses a structured cueing & scoring system to assess initiation, organization, safety, & task completion & develop cuing strategies
Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT)
a general assessment of quality of life
Kettle Test
performance-based test that assesses cognitive functional performance
-the clinician observes while the patient completes the task of making two different hot beverages
-following the task, the clinician and the client discuss the task, how the client performed, and how difficult the client found the task
Multiple Errands Test (MET)
evaluates the effect of executive function deficits on everyday functioning through a number of real-world tasks
Pain scales
Visual Analogue Scale (VAS)
Numeric Rating Scale (NRS)
What is cancer-related fatigue (CRF)?
''a distressing, persistent, subjective sense of physical, emotional, and/or cognitive tiredness or exhaustion related to cancer or cancer treatment that is not proportional to recent activity and interferes with usual functioning.''
What worsens symptoms with CRF?
sleep and rest will worsen symptoms with CRF
What are the 4 subcomponents of CRF?
1) general fatigue
2) emotional fatigue
3) physical fatigue
4) mental fatigue
80% of patients report _________ as the most distressing symptom experienced as it can drastically decrease participation and performance of all occupations, roles, and routines.
CRF
it profoundly affects QOL due to inefficient use of energy, loss of control and identity, impaired volition and motivation, reduced ability to work, reduced self-efficacy, lack of social interaction, and loss of important roles.
What intervention can an OT provide for a patient with CRF using the create, promote approach?
Create educational materials to guide patients in management of cancer-related fatigue or cognitive impairment
What intervention can an OT provide for a patient with CRF using the prevent approach?
Screen for early signs of CRF and educate patients and family members on the potential for the onset of CRF with new treatments
What intervention can an OT provide for a patient with CRF using the establish, restore approach?
Examine daily routines and establish habits and patterns that incorporate rest and exercise to minimize cancer-related fatigue.
What intervention can an OT provide for a patient with CRF using the modify approach?
Simplify ADLs and IADLs and add cueing strategies to compensate for cancer-related cognitive impairments such as impaired short-term memory and lowered attention span.
What intervention can an OT provide for a patient with CRF using the maintain approach?
Identify occupations and roles important to the patient and prioritize involvement in meaningful occupations that will allow the patient to continue role fulfillment
Use lifestyle redesign approaches to maintain strength, endurance, and mobility during and after treatment.
What are some basic guidelines to follow in interventions for CRF?
-Remain client-centered, use active listening, and use a holistic approach focusing on therapeutic use of self.
-Assess the patient's motivation and volition for performance of occupations and roles.
-Assess all areas of function (physical, cognitive, psychosocial/emotional, etc.).
-Ensure that intervention will include an application of skills and use of occupation rather than remain solely didactic.
-Provide demonstrations and give homework to facilitate carryover of skills and learning.
-Assess response to treatment and indications that treatment or homework is too intense or counterproductive.
What is cancer-related cognitive dysfunction?
impairments in memory, executive functioning, and attention span due to cancer treatment
can vary from subtle to dramatic; can be temporary or permanent
Up to 75% of patients with cancer experience ________________ during or after cancer treatment with impairments in memory, executive functioning, and attention span.
cancer-related cognitive impairment
(nearly 4 million cancer survivors have some form of cognitive difficulty)
Patients who undergo chemotherapy may experience changes in cognition including __________.
inattention
lack of concentration
decreased working memory
impaired executive functioning

Patients who undergo radiation therapy may experience changes in cognition including __________.
inattention
decreased memory
impaired executive functioning
impaired visual perceptual skills

Patients who are on steroids may experience changes in cognition including __________.
behavioral changes
decreased verbal memory
inattention

Patients who are on sedative may experience changes in cognition including __________.
decreased level of arousal
delirium
confusion/disorientation

What intervention approaches can be used for cancer-related cognitive dysfunction?
cognitive-behavioral strategies
remediation/restoration
compensatory skills training
meaningful functional activity
Coping skills and relaxation techniques, sleep hygiene education, and self-management and goal-setting are examples of which type of intervention strategy used for patients with cancer-related cognitive dysfunction?
cognitive-behavioral strategies
Repeated practice of drills, exercises, or activities, relevant real-life tasks, and computer-based training are examples of which type of intervention strategy used for patients with cancer-related cognitive dysfunction?
remediation/restoration
Environment or task modifications, adjustment of task features/sensory cues, and involvement of the individual's mental operations i.e. use of imagery are examples of which type of intervention strategy used for patients with cancer-related cognitive dysfunction?
Compensatory skills training
Engaging in meaningful functional activities is an important intervention strategy used for patients with cancer-related cognitive dysfunction because it ___________.
Promotes and maintains focus; concentration
Decreases anxiety
Improves psychological well-being
What is chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN)?
experienced by patients undergoing treatment with certain neurotoxic chemotherapy agents that causes dysfunction or damage to the peripheral nerves
How does CIPN present?
-presents as motor, sensory, autonomic, or mixed impairments
-follows a symmetric stocking-glove distribution of impairment
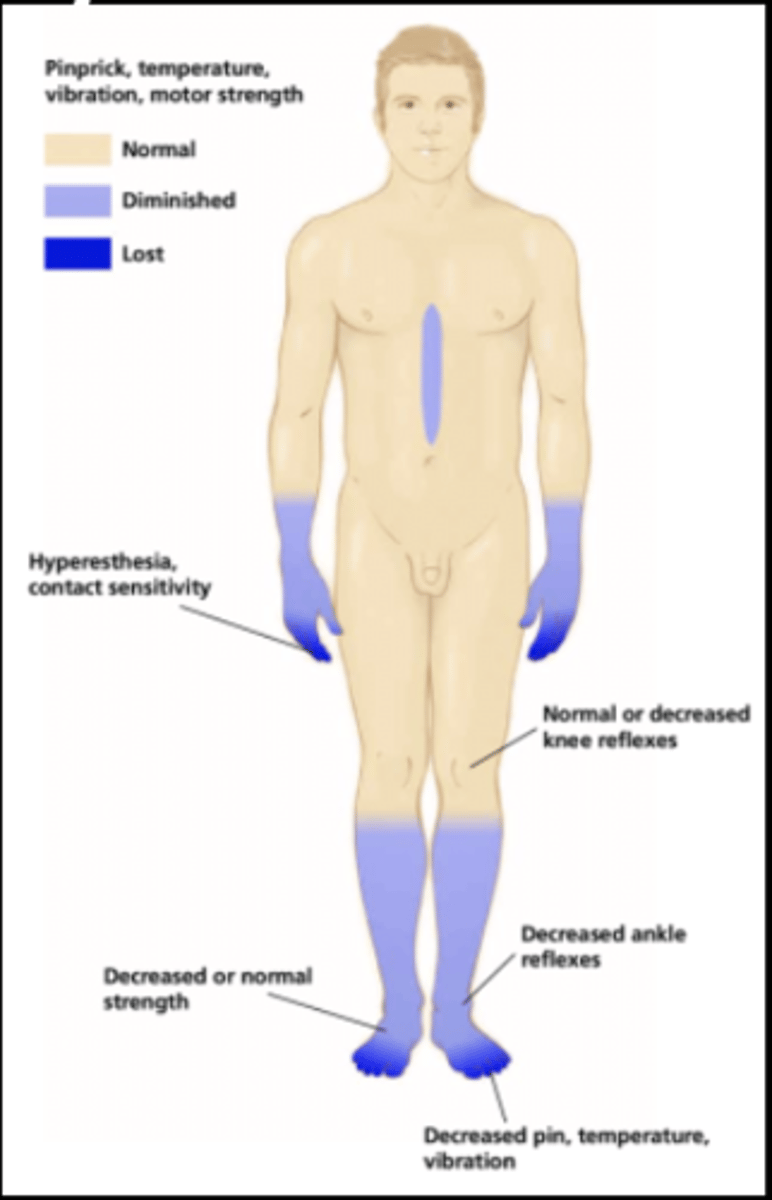
Earliest symptoms of CIPN develop at the ______ and ______. Symptoms include ________.
develops at fingertips and toes
symptoms include
-tingling
-numbness
-paresthesia
-temperature sensitivity
-pain
-feeling of wearing gloves/stockings
-weakness
-impaired balance (due to decreased ankle and knee reflexes as well as sensory impairments)
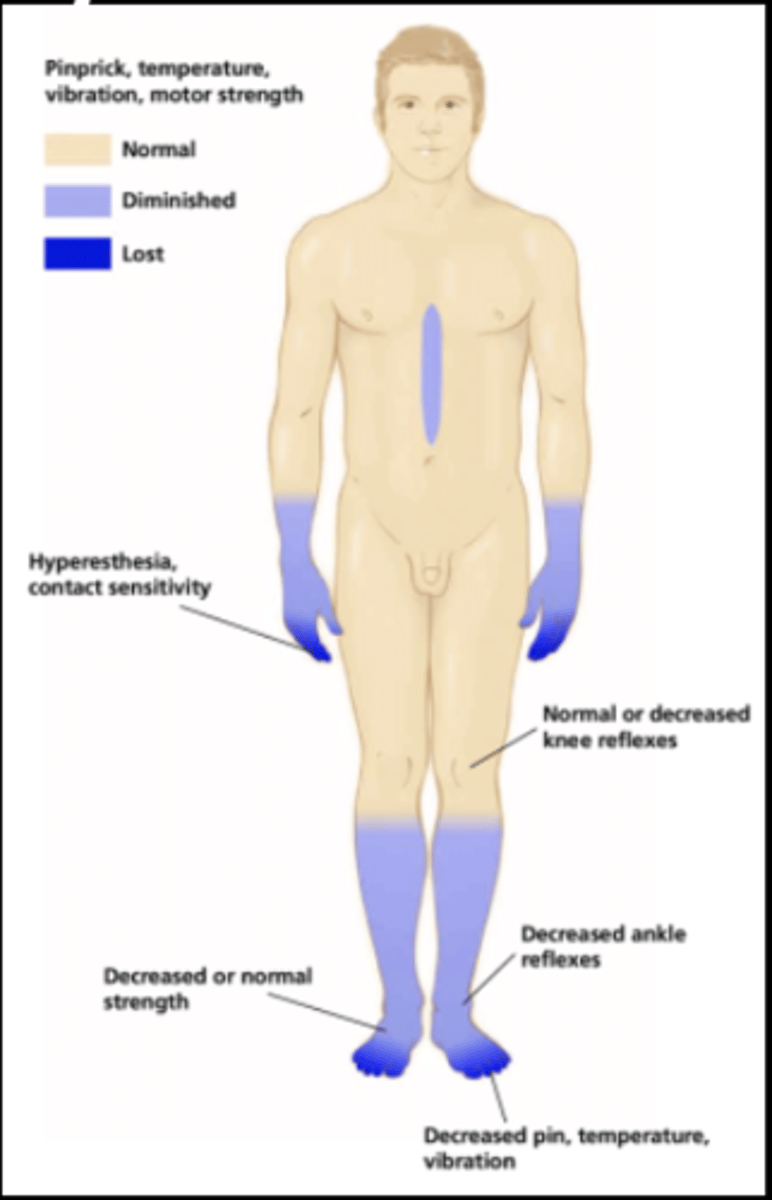
A person who has CIPN may experience normal, diminished, or lost sensation of ____________
pinprick (protective)
temp (protective)
vibration (protective and discriminative)
motor strength
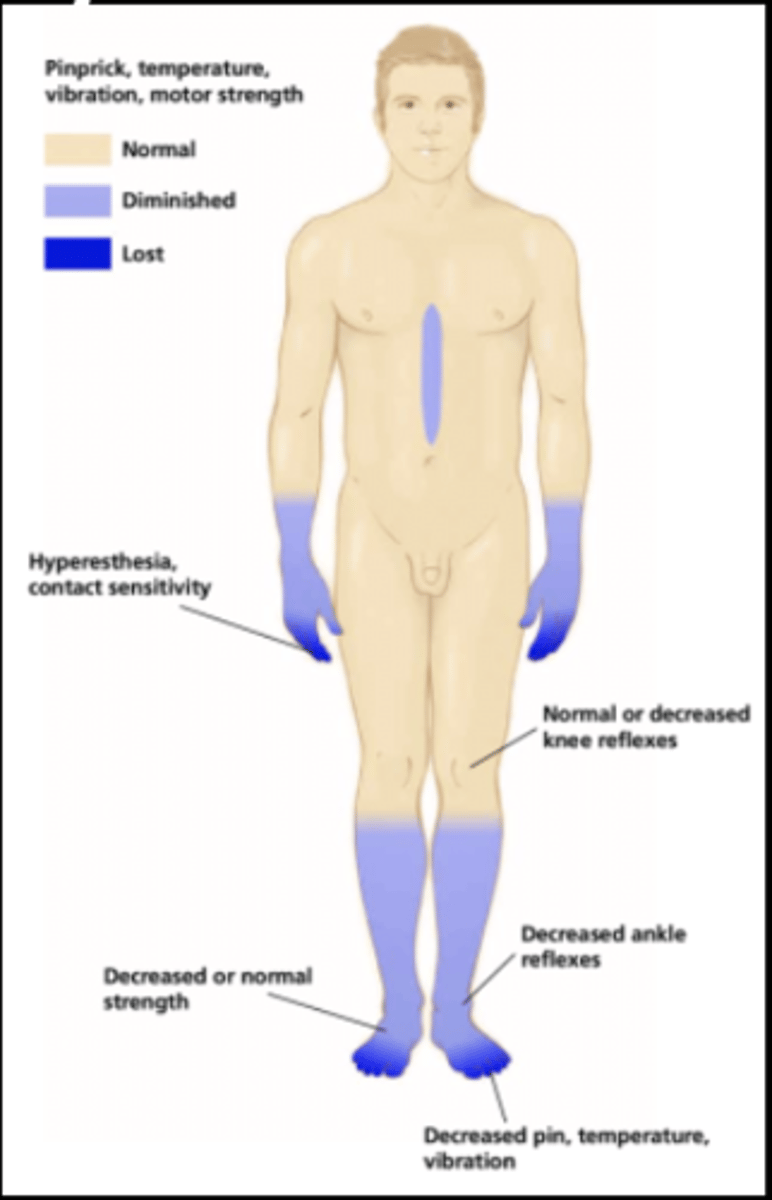
Compensation strategies for CIPN include.......
-foot care and proper shoes
-strategies to reduce ischemic and thermal injuries and management of symptoms of autonomic dysfunction
-fall prevention!!!
-use of AE to compensate for loss of sens., promote ind. and remain active in daily activities (gloves, mirrors for skin inspection, use of vision)
SAFETY IS ALWAYS FIRST
Sensory re-education is used with the ________ approach when working with individuals with CIPN.
restore
Compensatory is used with the ________ approach when working with individuals with CIPN.
modify
What is cancer-related pain?
-a complex symptom that affects a person's life, including physical functioning, the performance of ADLs, psychological, and emotional status and social interactions
-may be acute, chronic, or intermittent and often has a definable cause such as tumor invasion or neuropathy caused by the cancer treatment
How can OT help patients with cancer-related pain?
OT can evaluate the impact of pain on a client's desired activity and QOL and use this information to equip the patient with skills and strategies to manage the pain such as
-collaborative activity analysis w/ pt
-graded activities
-identifying pain triggers
-posture assessments
-visualization or mental strategies to overcome pain cycle
What is the goal of treating cancer-relating pain?
keeping pain at a manageable level
Deconditioning in oncology includes
-loss of functional capacity due to lack of activity
-associated with disease process and cancer-related tx, poor responses to cancer tx, and poor survival
-directional relationship between fatigue, inactivity, and deconditioning (cycle)
Through mobilizing activities, we can combat the cycle of deconditioning. What are some activities/strategies that we can teach patients?
-eating meals sitting up instead of lying down
-walking to bathroom instead of using bedside commode
-ADLs while standing instead of seated
-walking short and safe distances
Cardiopulmonary considerations
cardiopulmonary status directly relates to occupational performance and activity tolerance
rest = bad!!!!!!!!!1 try to remain active as tolerated
T or F: Physical activity, including occupational engagement and exercise, has been shown to increase cardiovascular and pulmonary measures as well as reduce fatigue, resulting in strong implications for the efficacy of skilled occupational therapy intervention in this patient population.
true
What are common psychosocial issues associated with cancer?
body image and depression
Psychosocial intervention focuses
-stress management and coping strategies to increase sense of control
-relaxation techniques, guided imagery, breathing techniques
-CBT
-interventions related to disturbances in body image
-psychosexual therapy
-expressive-supportive therapy
-educational interventions to increase knowledge on disease with aim of self-efficacy
Lymphedema
swelling due to an abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid within the tissues
requires adv. training and certification
Lymphedema is most common in what type of cancer?
breast cancer
Lymphedema tx approaches include ______________
gentle exercises
compression garments
lymphedema wrapping techniques
manual lymphedema drainage
Hospice and palliative care interventions are focused on ______________ with an emphasis on _____________.
intervention focus
-maximizing comfort
-minimizing pain
-optimizing QOL
emphasis on
-end-of-life goals (life review)
-self-determination
-increasing locus of control
Intervention Approaches for Cancer-Related Cognitive Dysfunction
Cognitive-behavioral strategies
Remediation/Restoration
Compensatory skills training
Meaningful functional activity
Cognitive-behavioral strategies
Coping skills/relaxation
Sleep hygiene and education
Self/goal management
Remediation/restoration
Repeated practice of drills, exercises, or
activities
Relevant real-life tasks
Computer-based training
Compensatory skills training
Environment or task modifications
Adjustment of task features/sensory cues
Involvement of the individual’s mental
operations; use of imagery
Meaningful functional activity
Promotes and maintains focus; concentration
Decreases anxiety
Improves psychological well-being