BIOL10212 Biochemistry
1/281
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
282 Terms
amphipathic
molecules having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
Aliphatic
The group of amino acid including glycine, alanine, valine, leucine and isoleucine. Only contrains hydrocarbon side chains
Aromatic
The group of amino acids including phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan and histidine
Hydroxyl
Amino acid group containing tyrosine, serine and threonine
Sulphur containing
The amino acid groups containing cysteine and methionine
Acidic
The amino acid group containing aspartate and glutamate
Amide
The amino acid group containing asparagine and glutamine
Basic
The amino acid group containing lysine and arginine
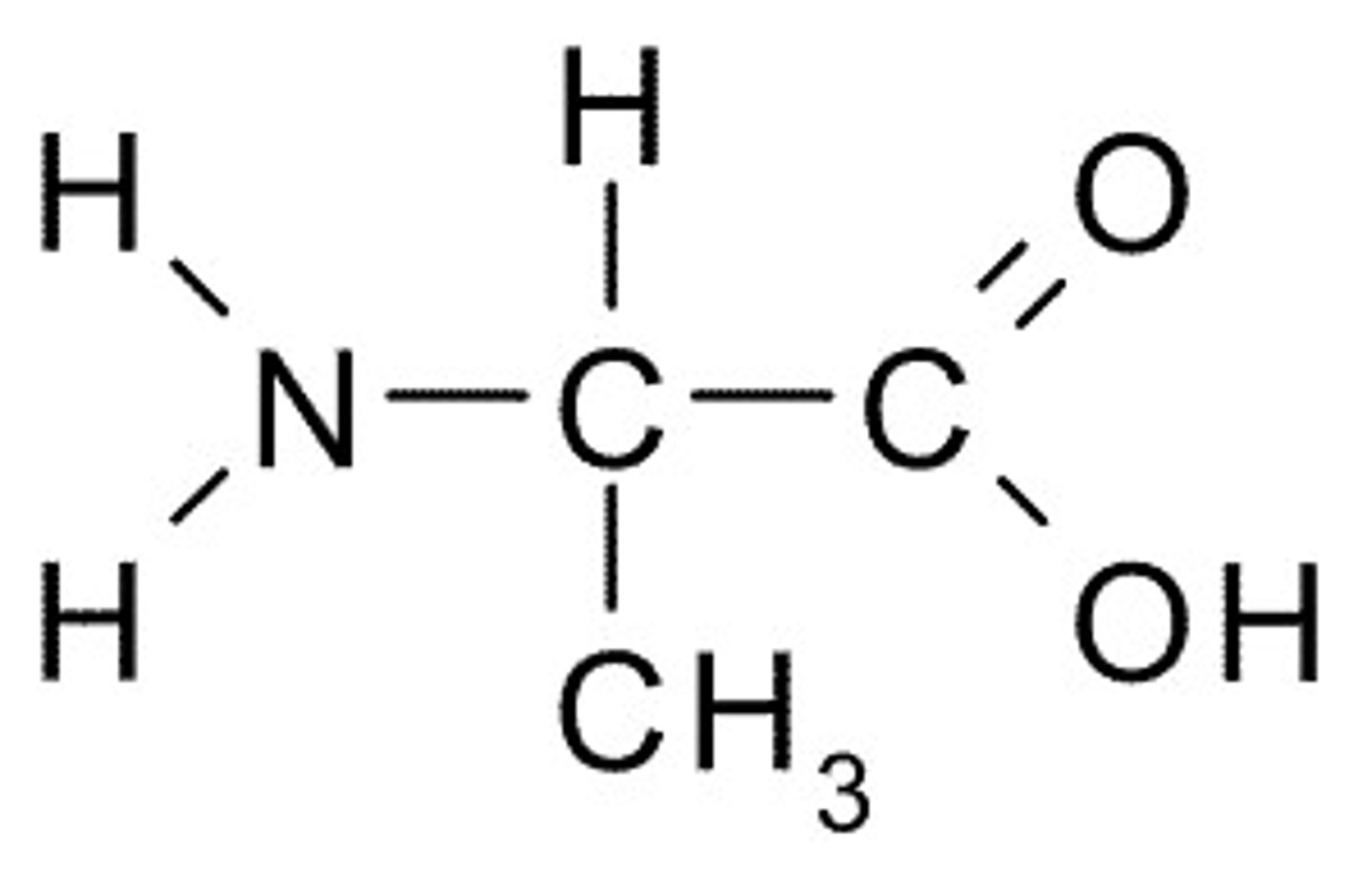
Alanine, Ala, A
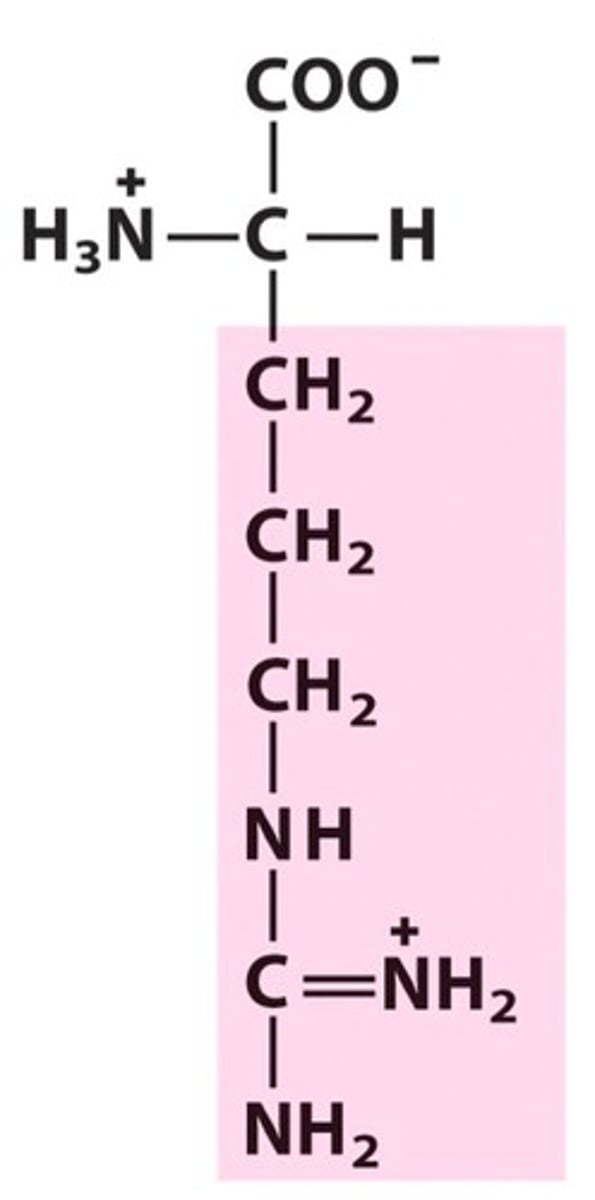
Arginine, Arg, R
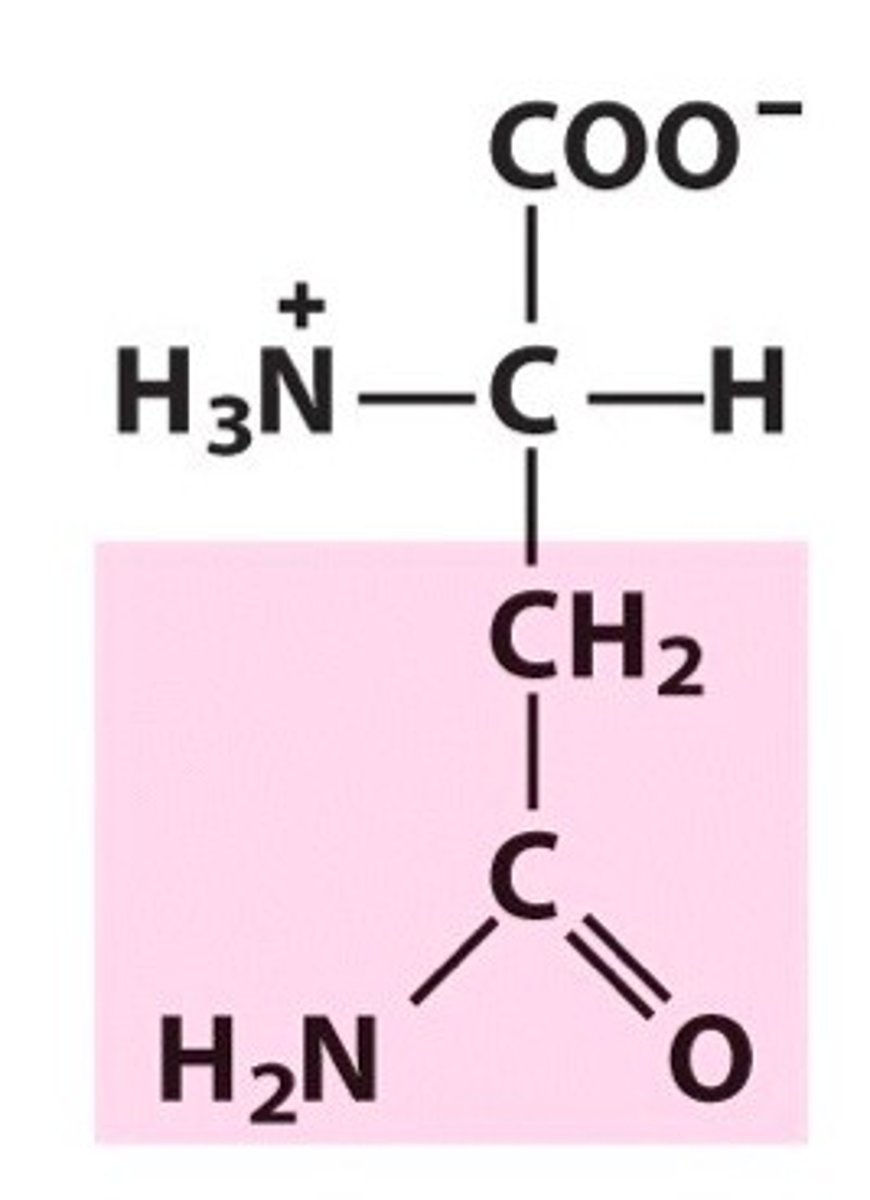
Asparagine, Asn, N
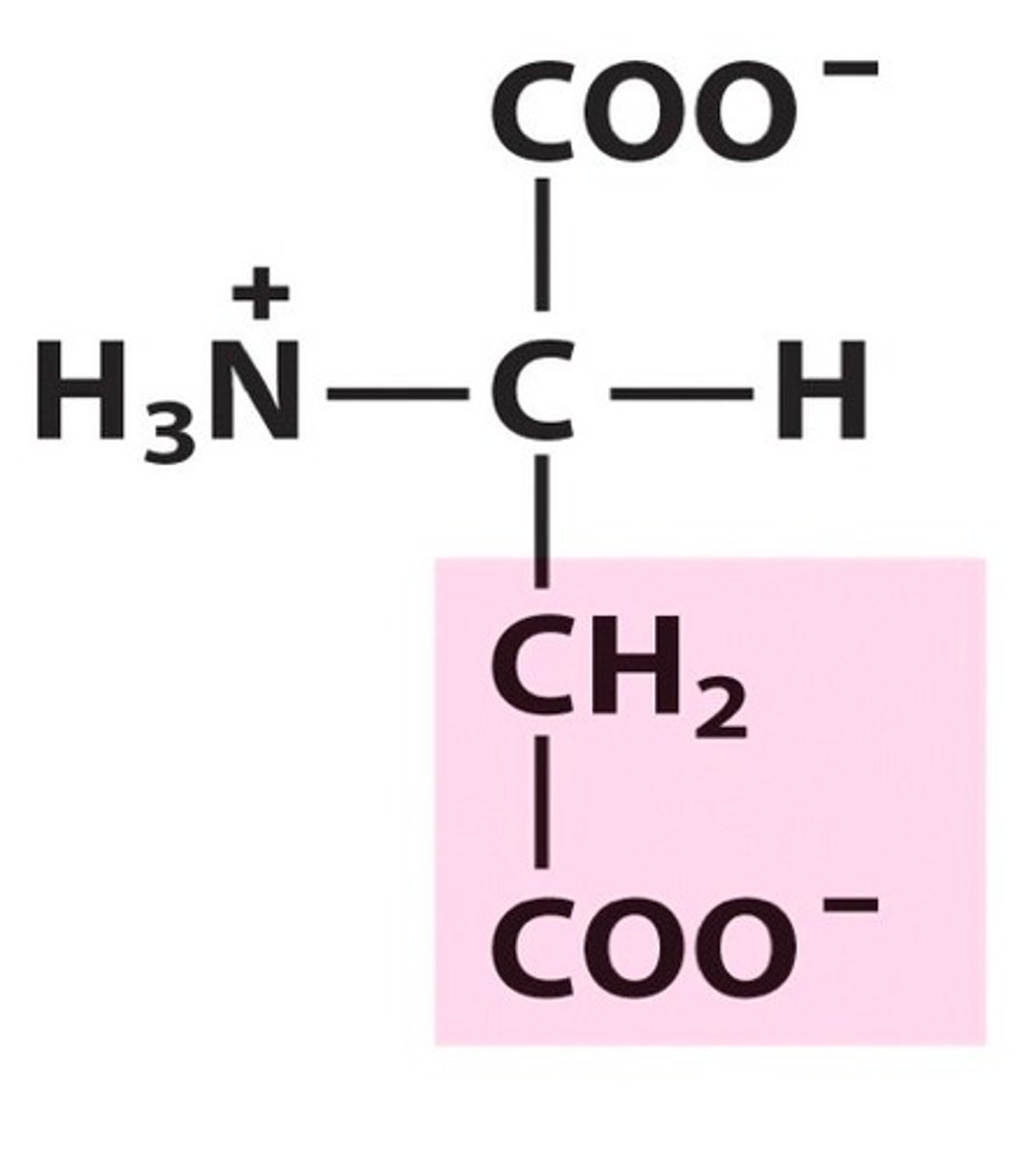
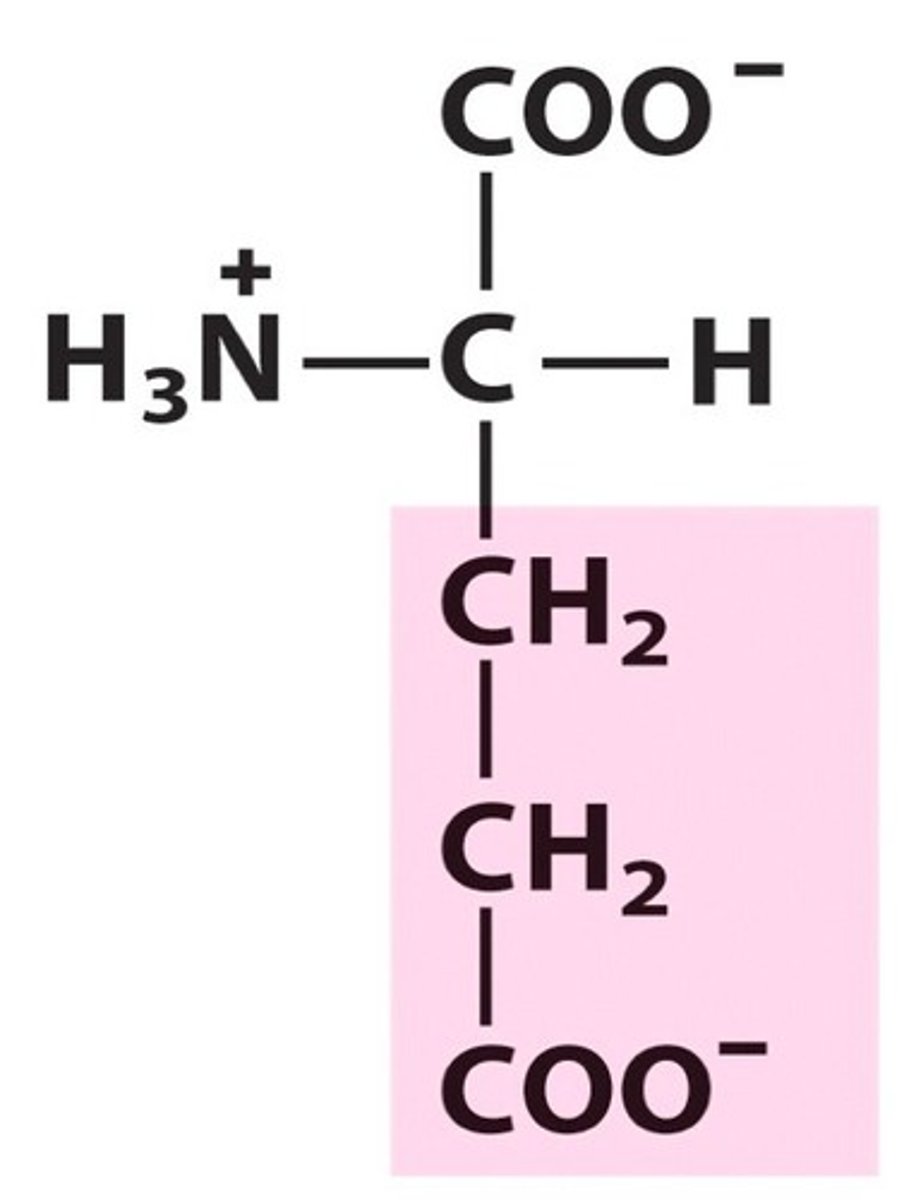
Aspartic acid, Asp, D
Cysteine, Cys, C
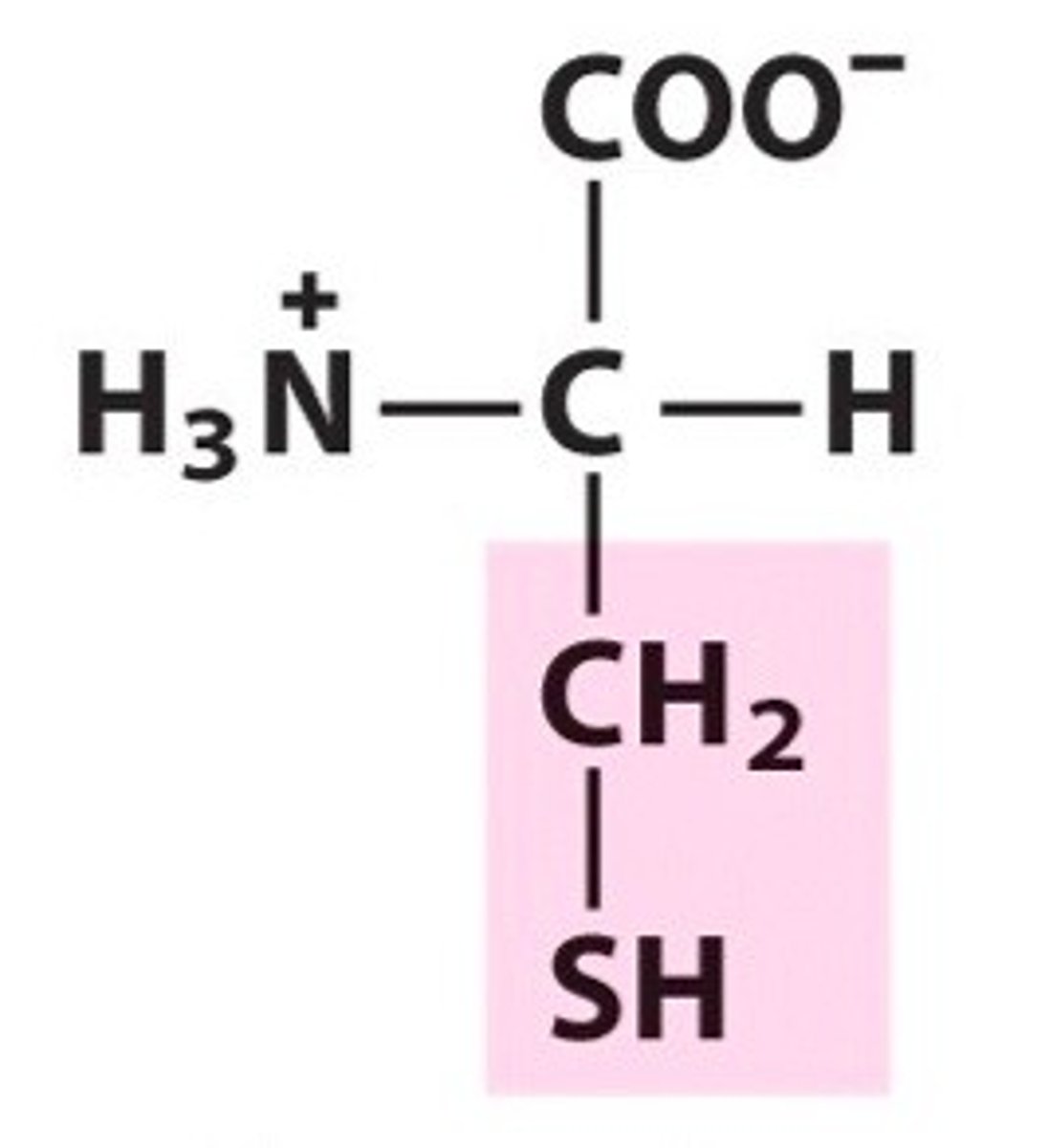
Glutamic acid, Glu, E
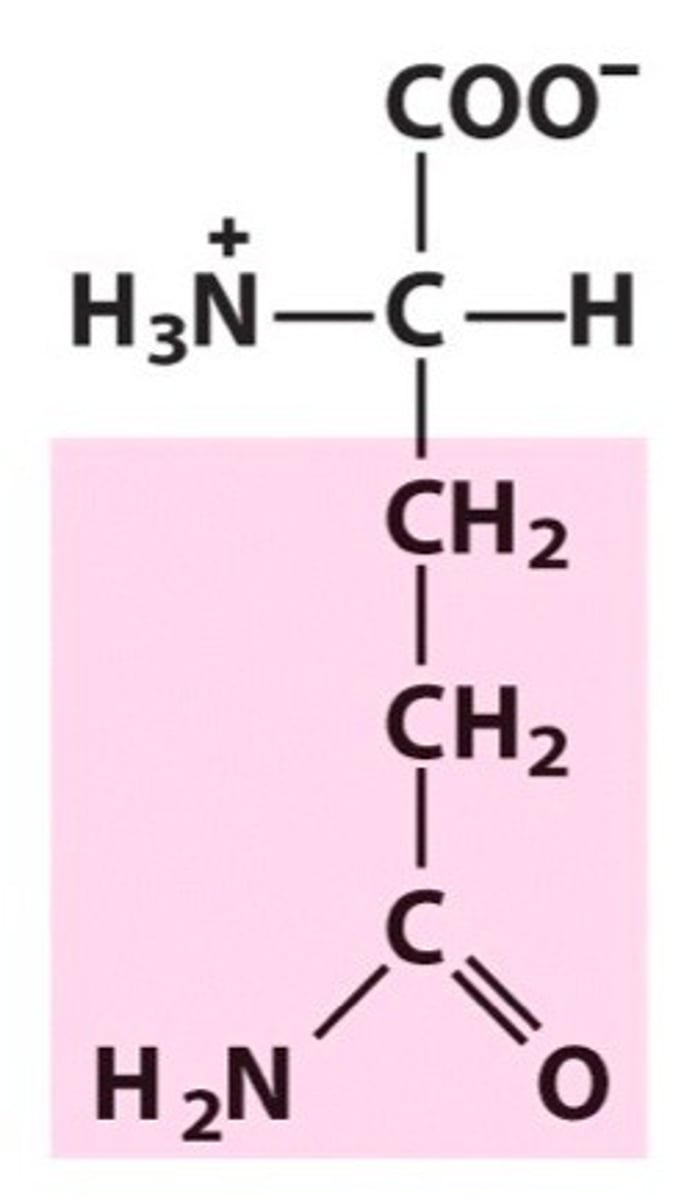
Glutamine, Gln, Q
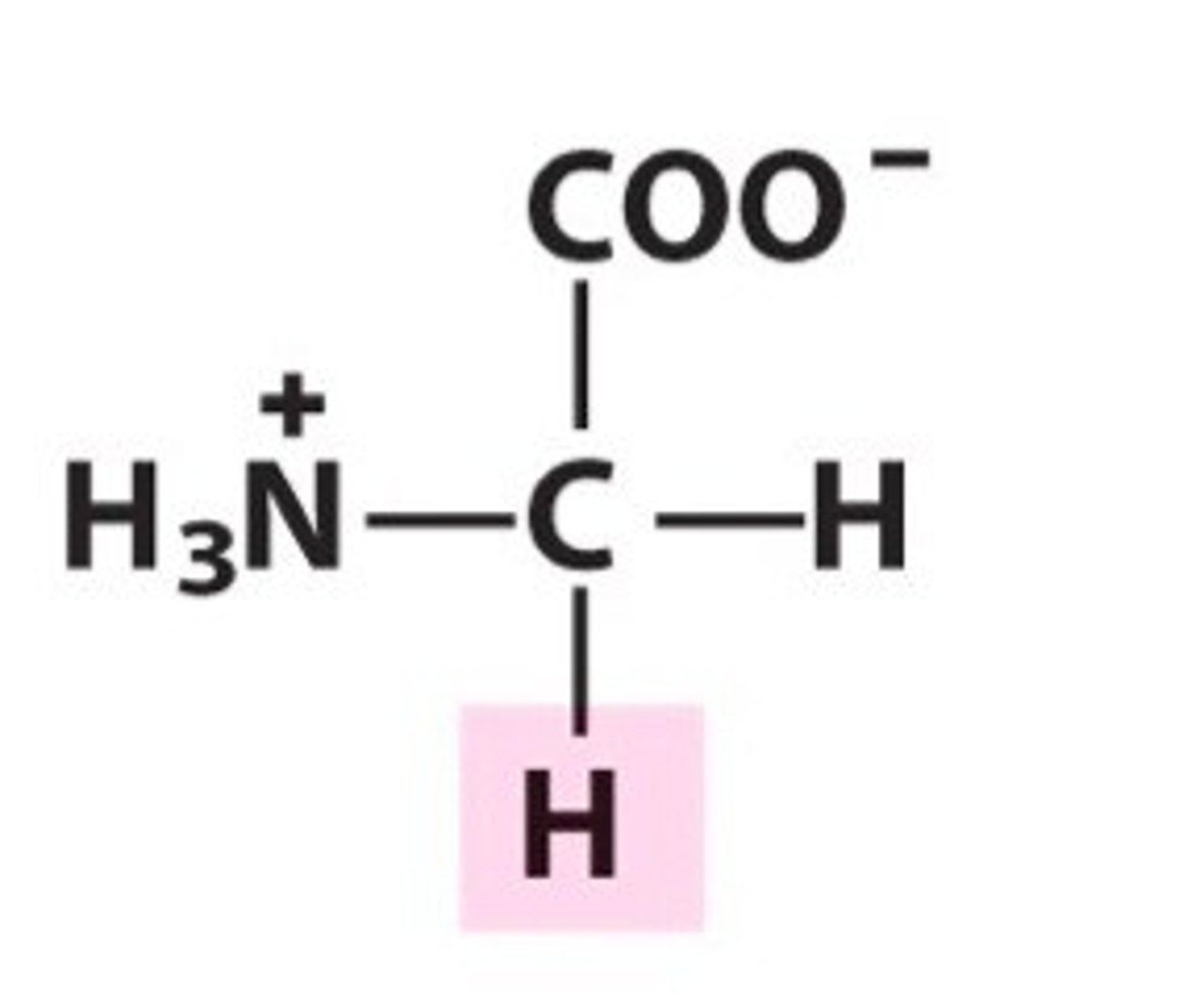
Glycine, Gly, G
Histidine, His, H
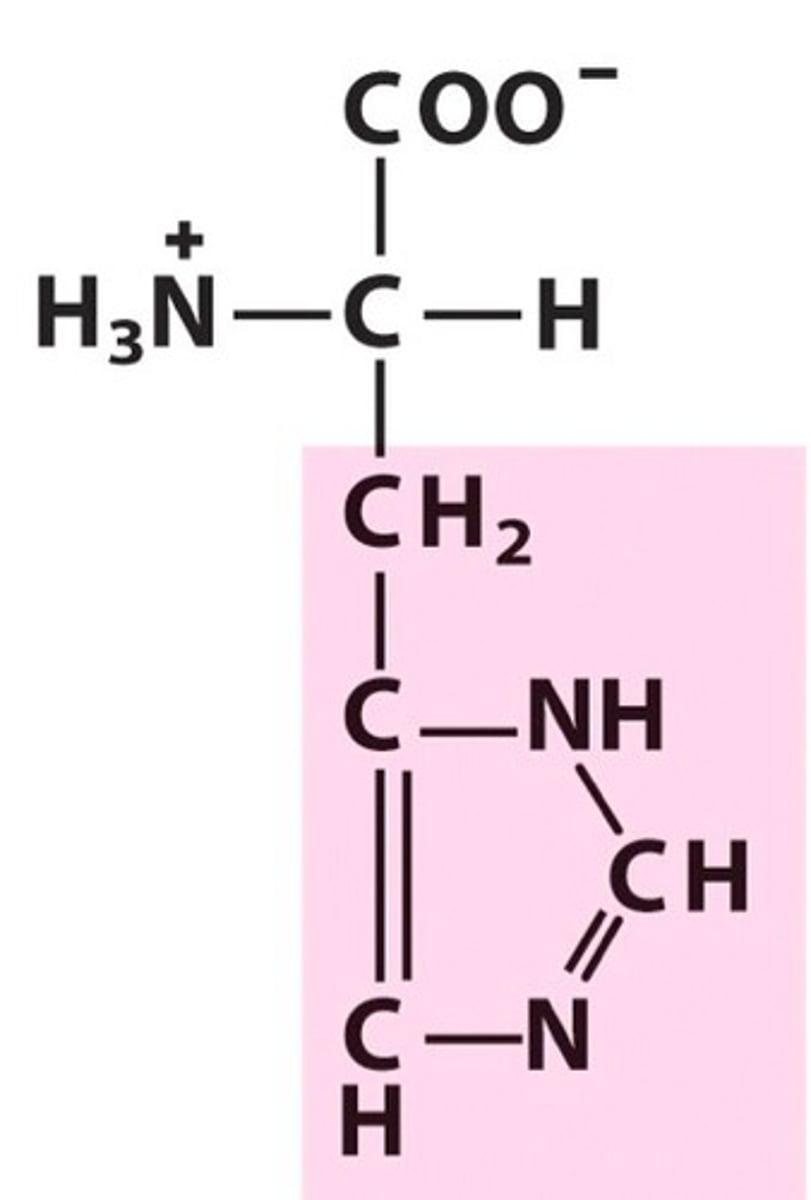
Isoleucine, Ile, I
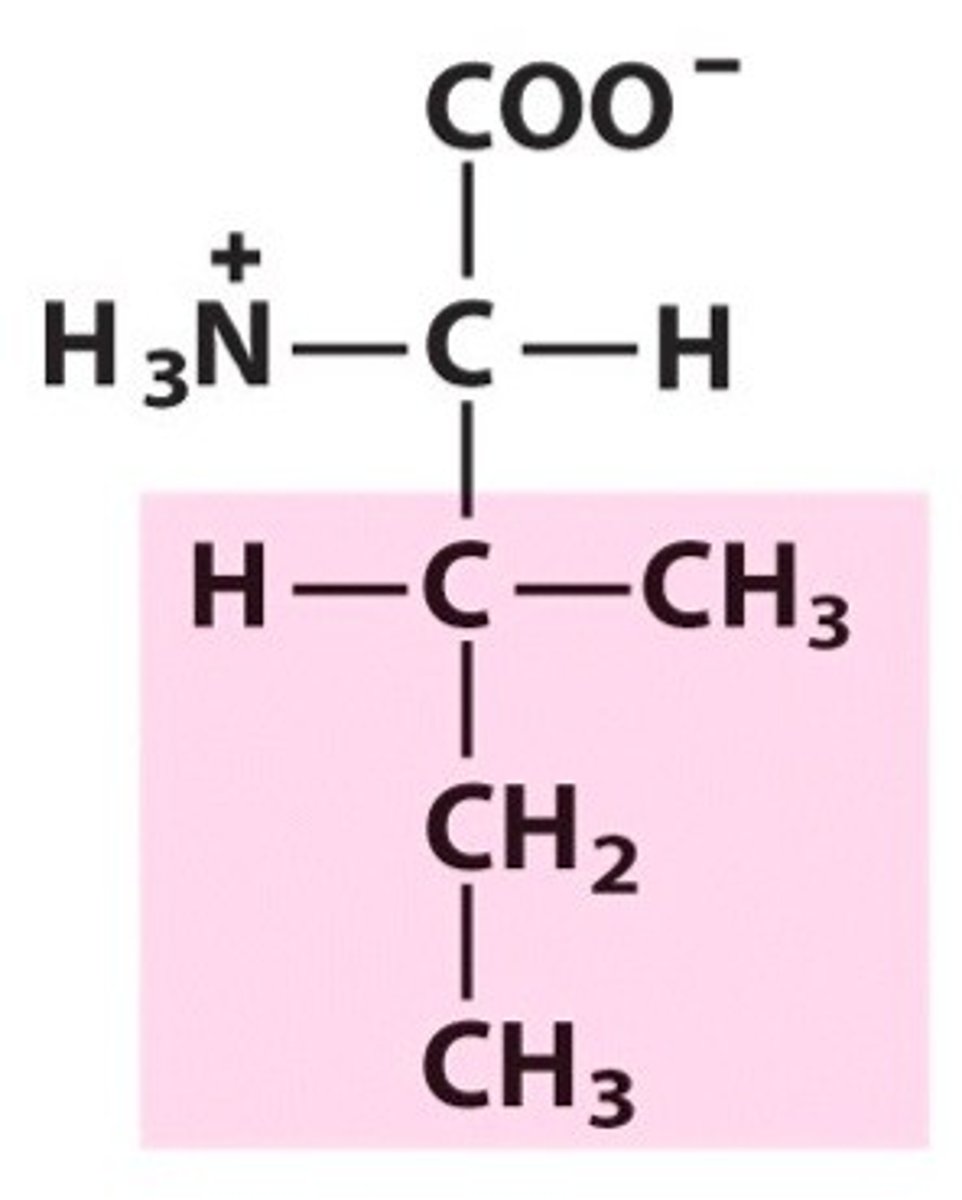
Leucine, Leu, L
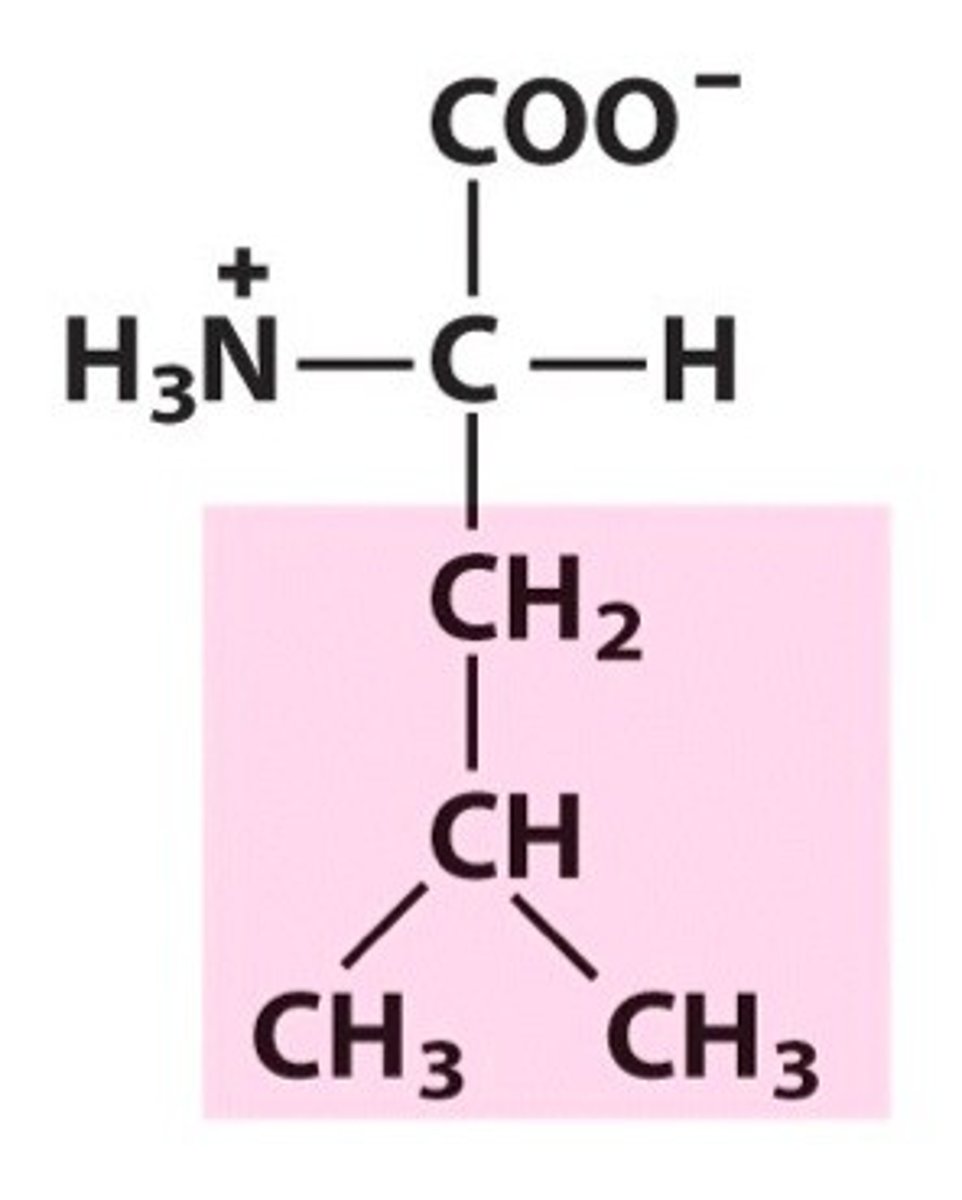
Lysine, Lys, K
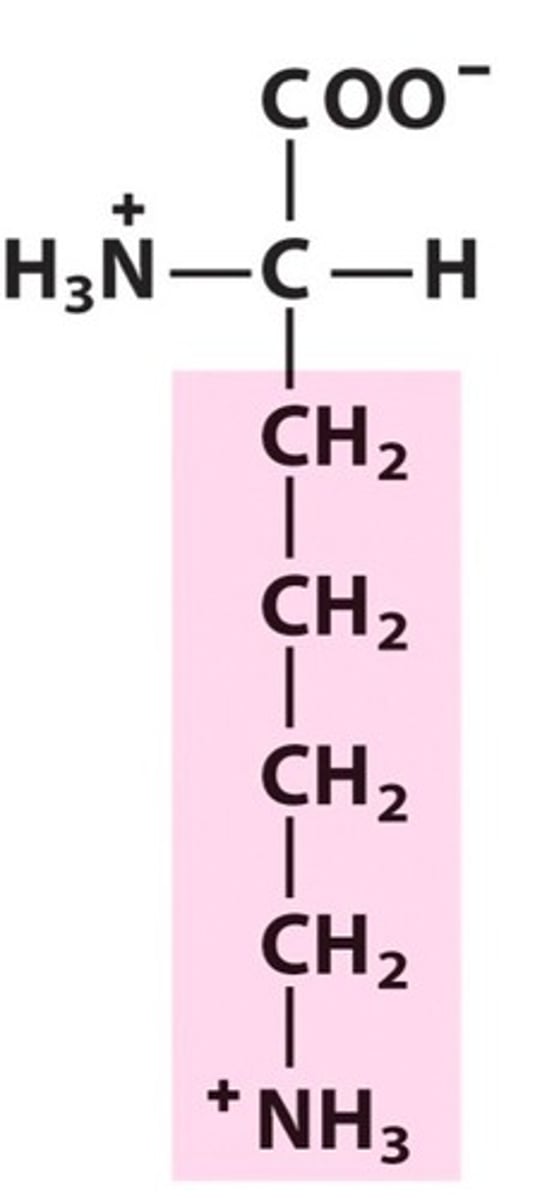
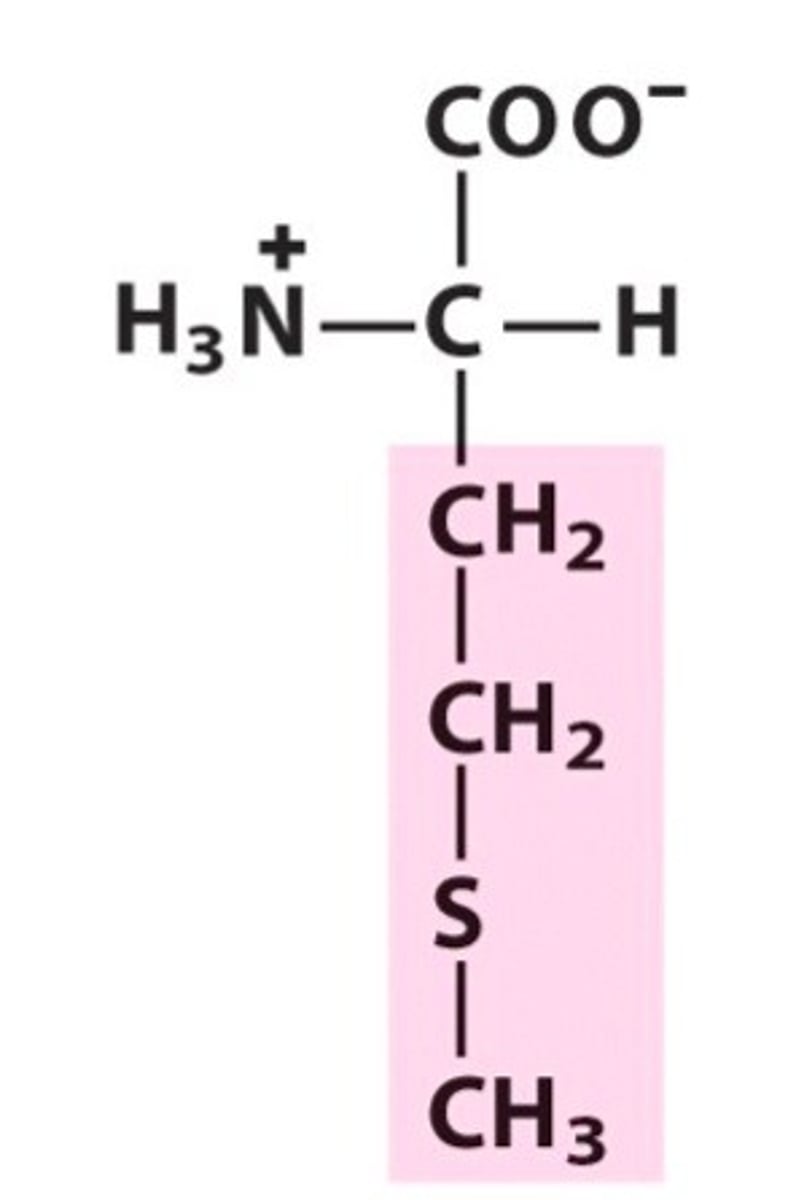
Methionine, Met, M
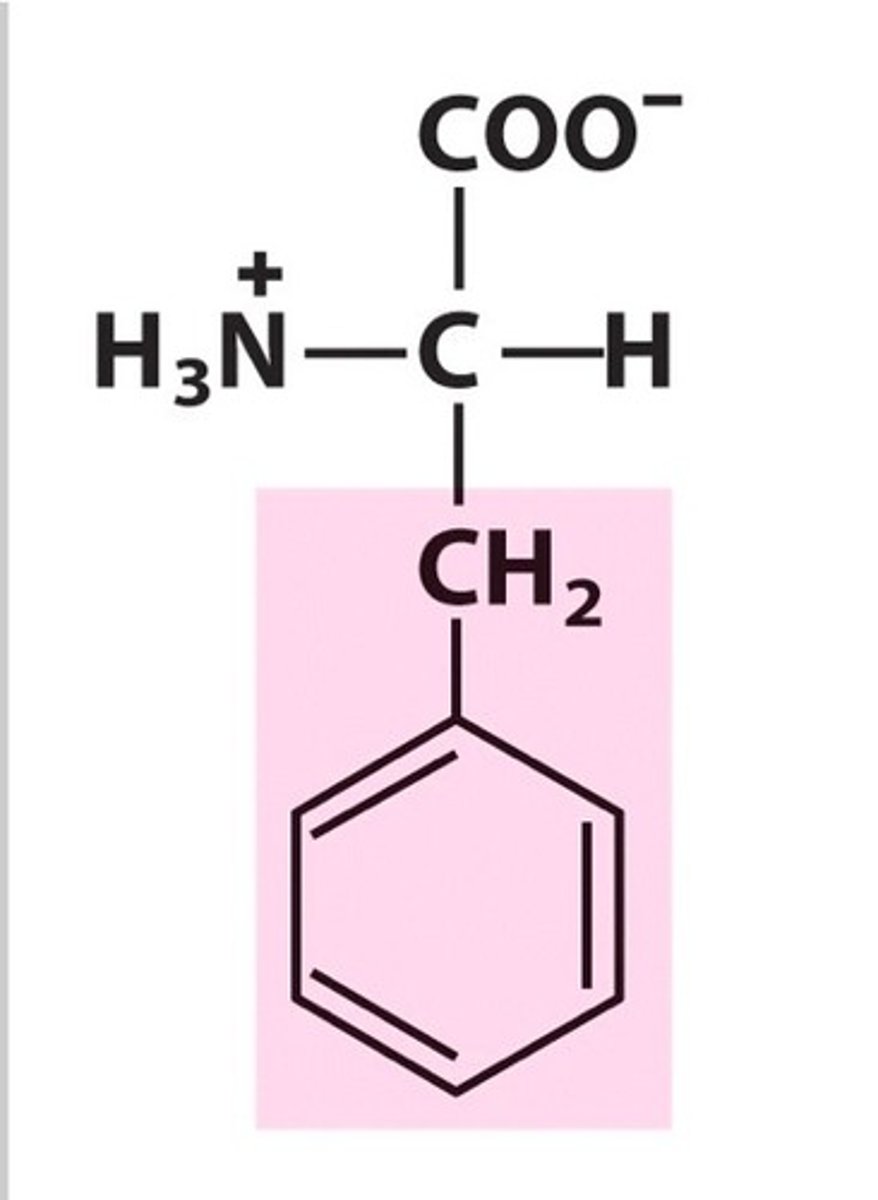
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
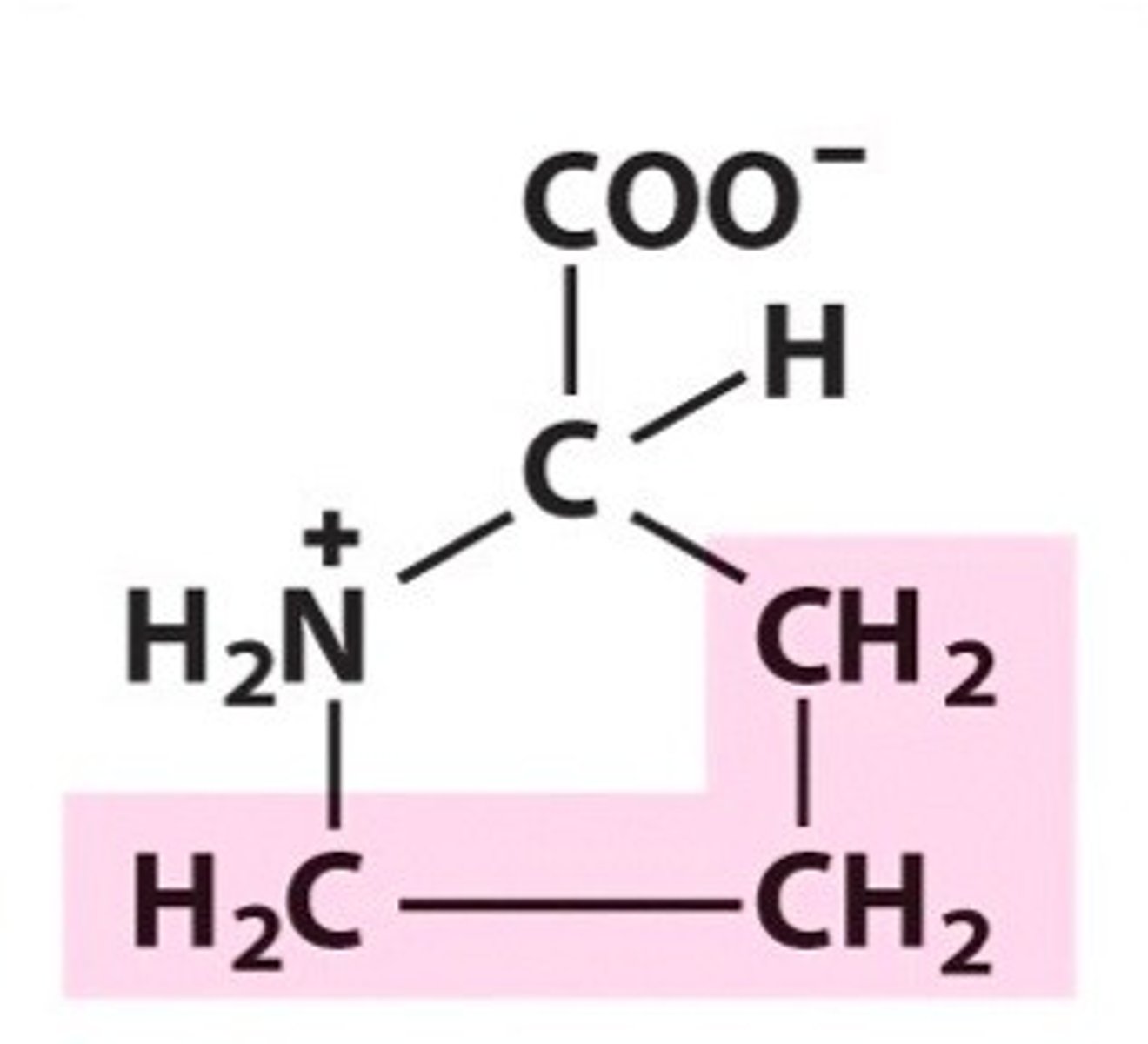
Proline, Pro, P
This is a unique amino acid as the R group forms a bond with the amide group to create a ring called a heterocycle.
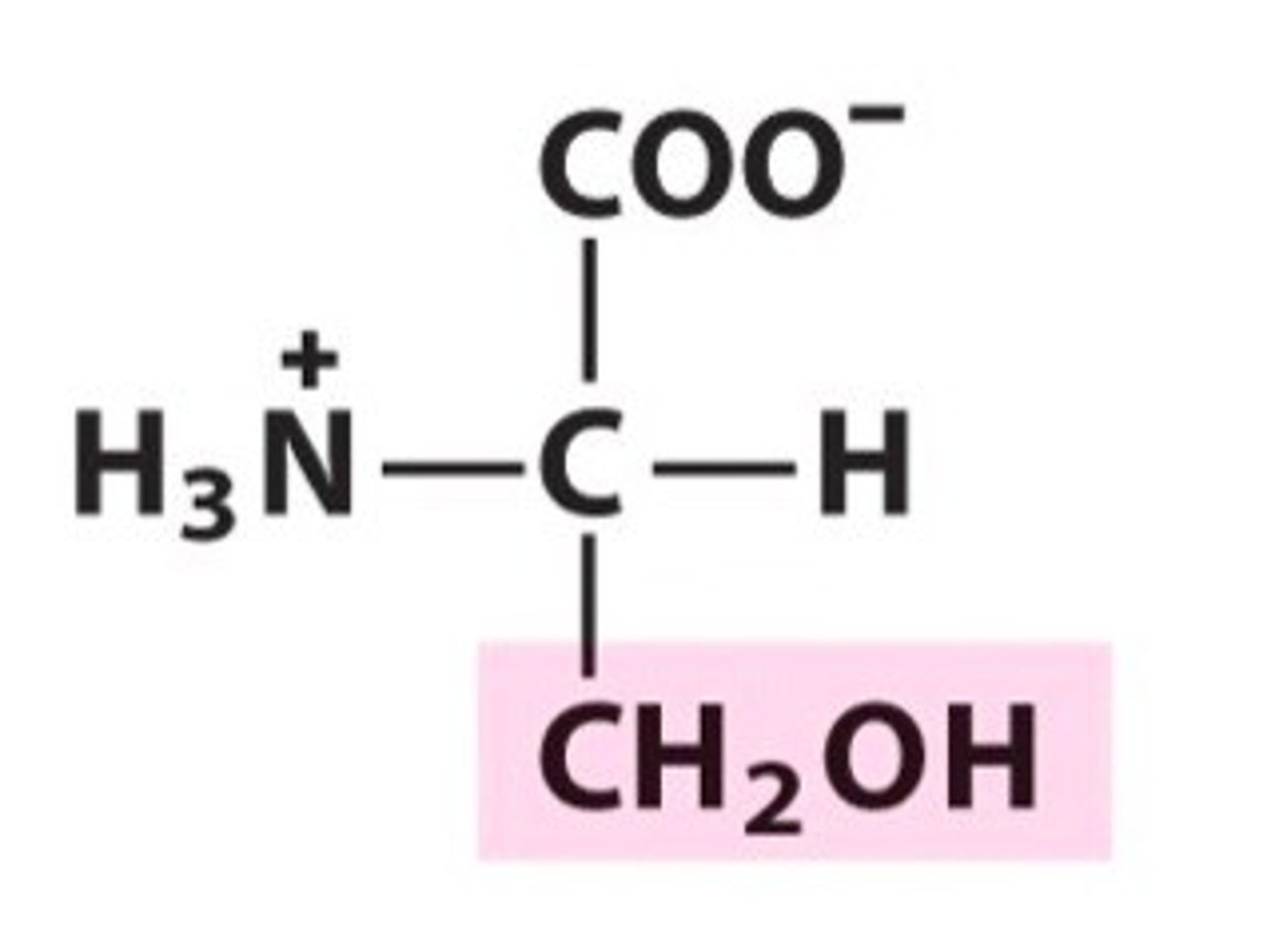
Serine, Ser, S
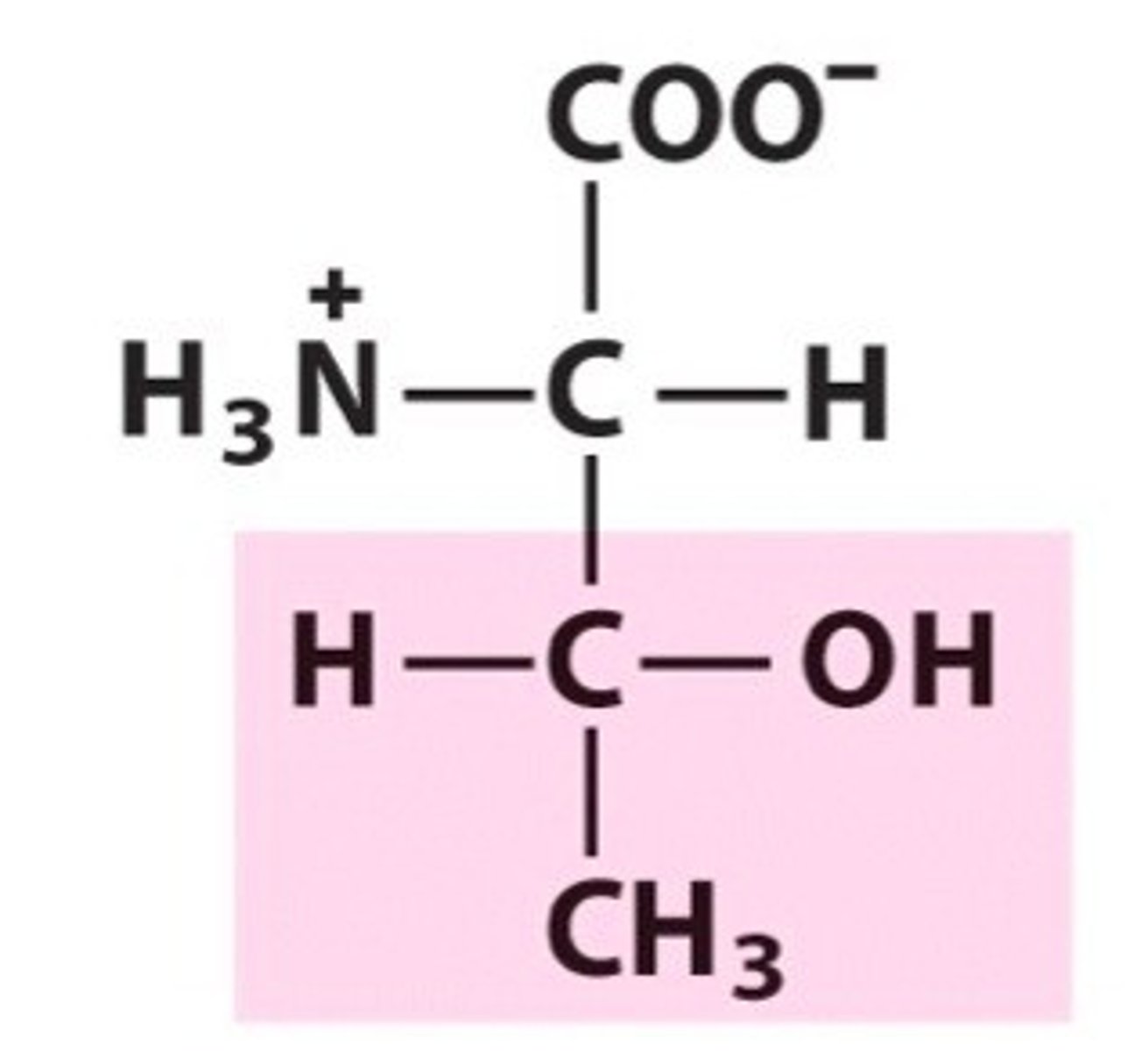
Threonine, Thr, T
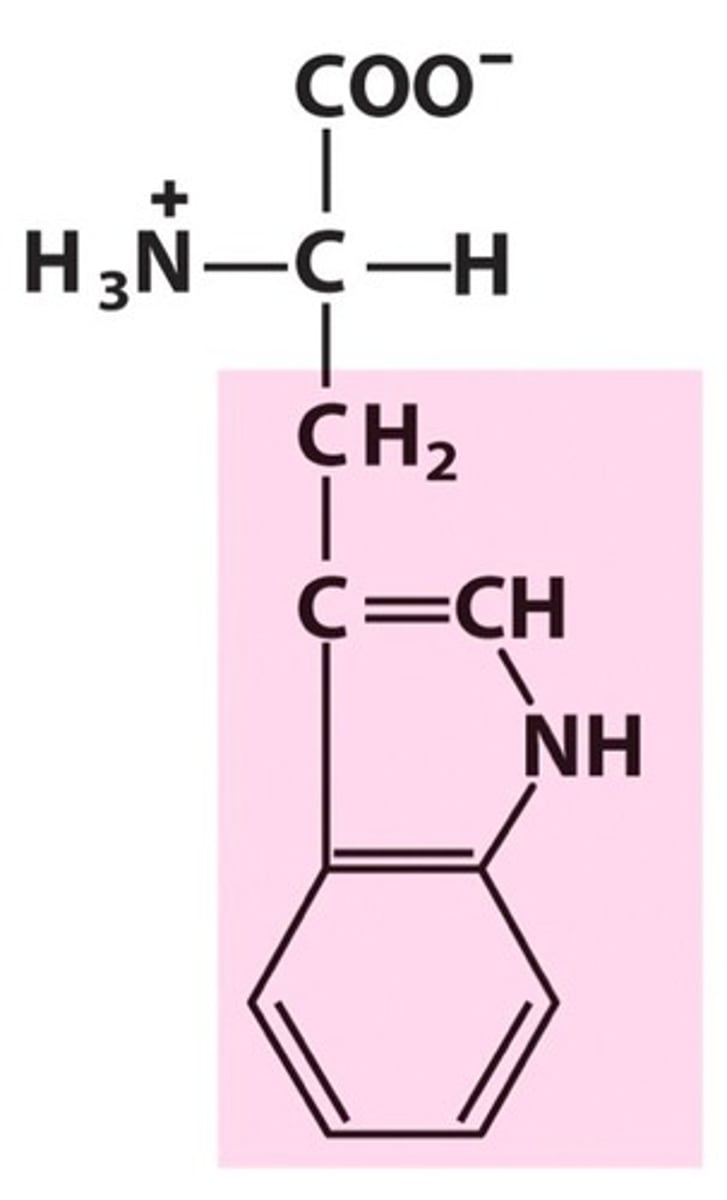
Tryptophan, Trp, W
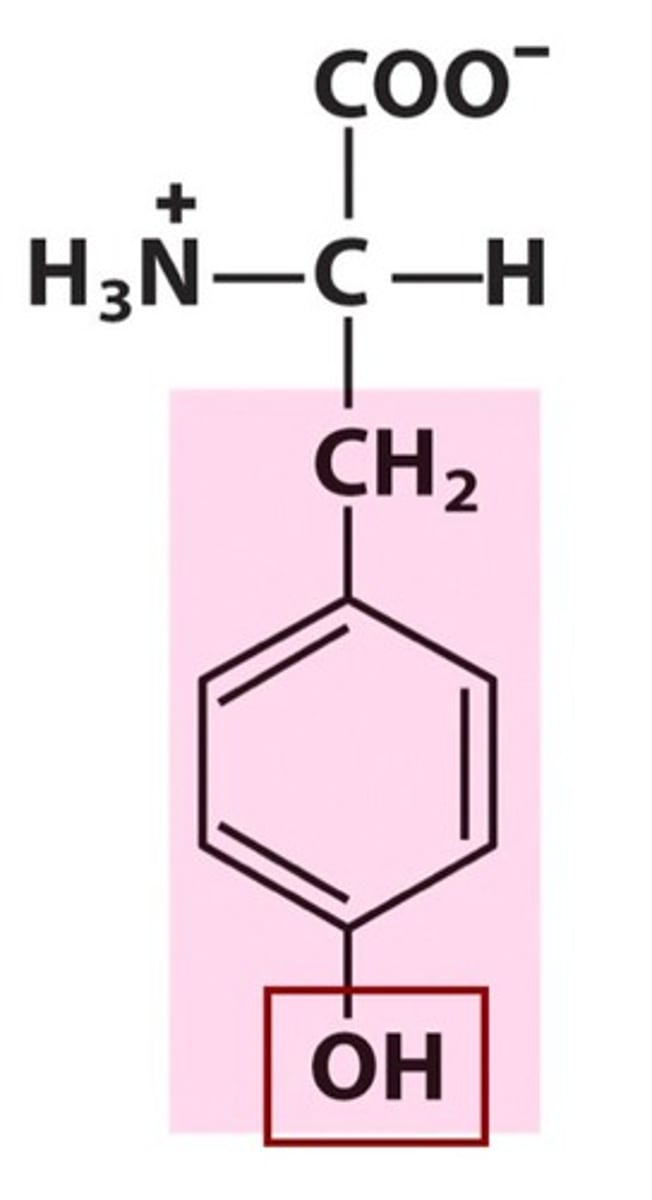
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
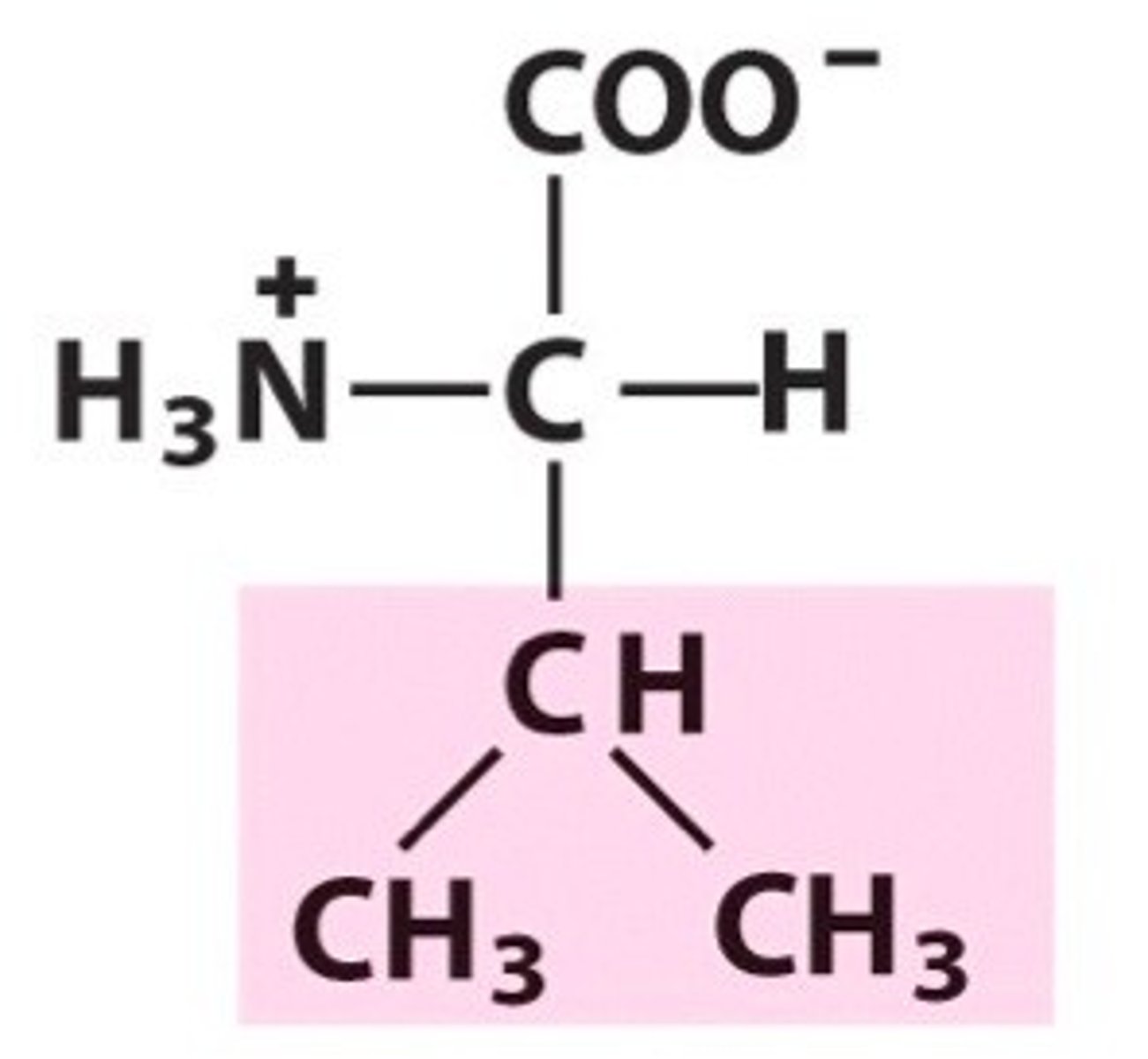
Valine, Val, V
Primary structure
The sequence of amino acids in a protein
Bioinformatics
A database of the primary sequences of proteins
Peptide bond
The bond formed between the alpha-carboxyl and alpha-amino of two amino acids in a condensation reaction
N-terminus
The start of a protein
Secondary structure
Regular repeats in folding patterns like alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
Native conformation
The single stable shape a protein folds to under physiological conditions.
Rotation
This is restricted in the amide bond due to double bond characteristic. It causes all backbone atoms to lie in one plane
Trans
The conformation preferred by amide bonds - the other conformation is less favoured due to steric interference of alpha carbon chains
Phi bond
The N-C(alpha) bond in a peptide chain. Rotation is possible around this
Psi bond
The C(alpha)-C bond in peptides. Rotation around this is possible too
Alpha helices
A right handed corkscrew in the secondary structure of a protein. Each carboxyl group of amino acid (n) forms a hydrogen bond with the amide group of amino acid n+4. All carboxyl groups point towards the C terminus which creates a dipole moment
3.6
The number of amino acids per turn in an alpha helix.
Beta strands
A polypeptide chain that is alost fully extended but not stable by itself
Beta sheets
Multiple beta strands running next to each other that are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Part of secondary structure. Side chains project above and below. One side is hydrophilic and the other is hydrophobic.
Antiparallel beta sheets
Secondary structure where strands run in opposite directions with hydrogen bonds between. These are closer and straighter so more strong than the other form
Parallel beta sheet
Secondary structure where strands run in the same direction and are stabilized by hydrogen bonds
Loops and turns
The short section of a protein that connect beta strands and alpha helices and allow the protein to fold back on itself. Often only 5 or less residues.
Tertiary structure
The 3D shape of a protein which is what makes the protein specific for its particular biological function. It is stabilized by non-covalent interactions - mainly hydrophobic ones. Also disulphide brdiges
Motifs
Reoccurring folding patterns in tertiary structures. Also known as supersecondary structures
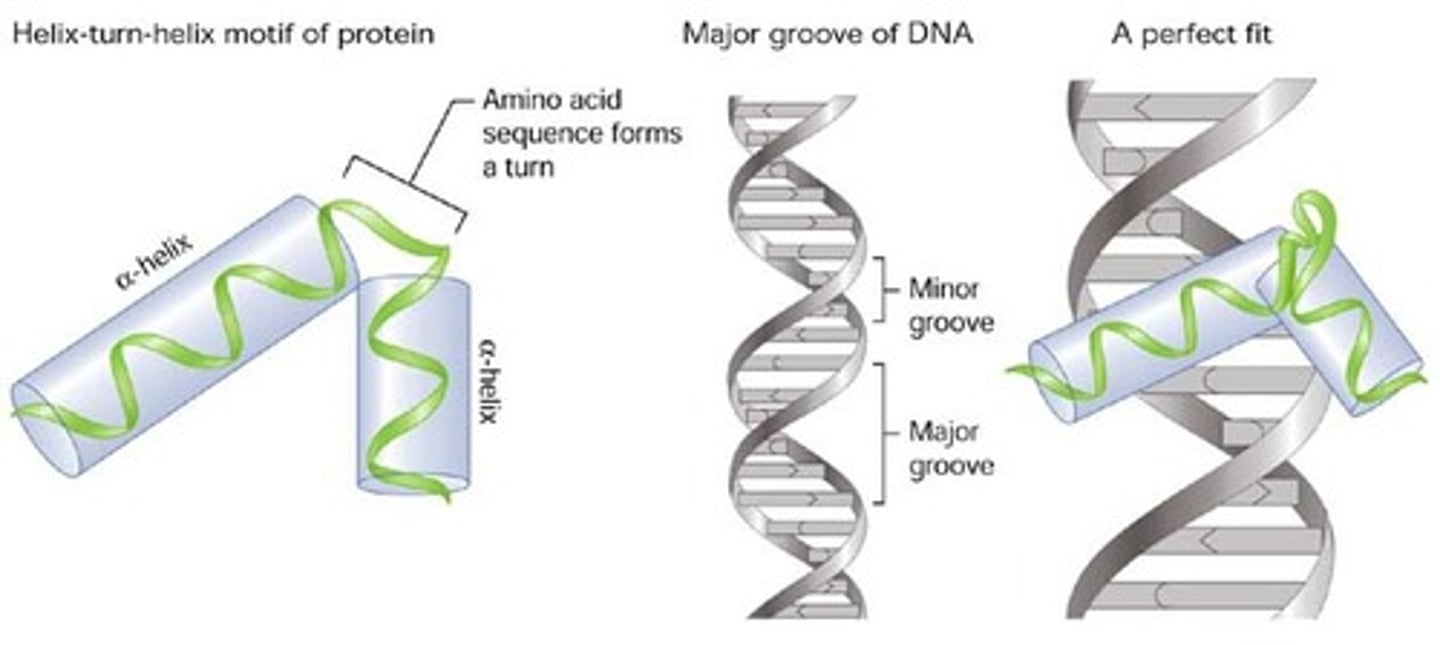
Helix-turn-helix
A motif that is common in proteins that bind to DNA
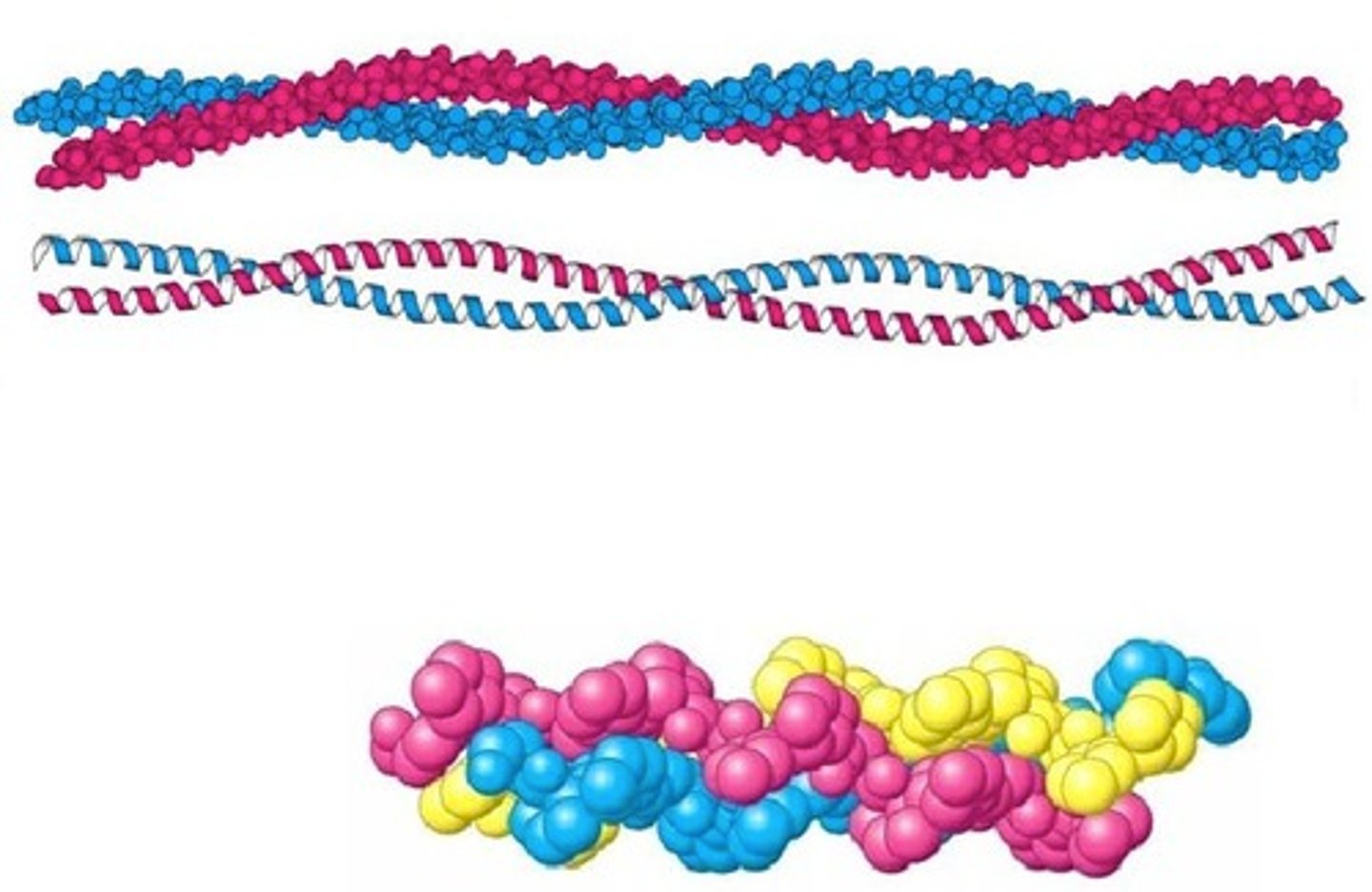
Coiled coil
A motif Where two alpha helices wrap around each other. Found in some proteins that bind to DNA and structural proteins.
Beta-alpha-beta
A motif found in metabolic proteins - a beta sheet followed by an alpha helix and then another beta sheet.
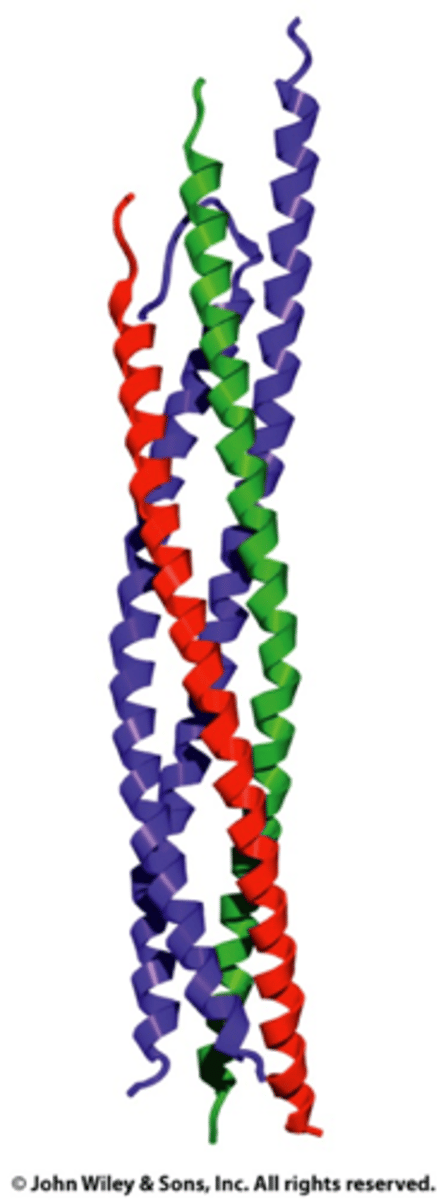
Helix bundle
A motif with mutiple alpha helices pressed together
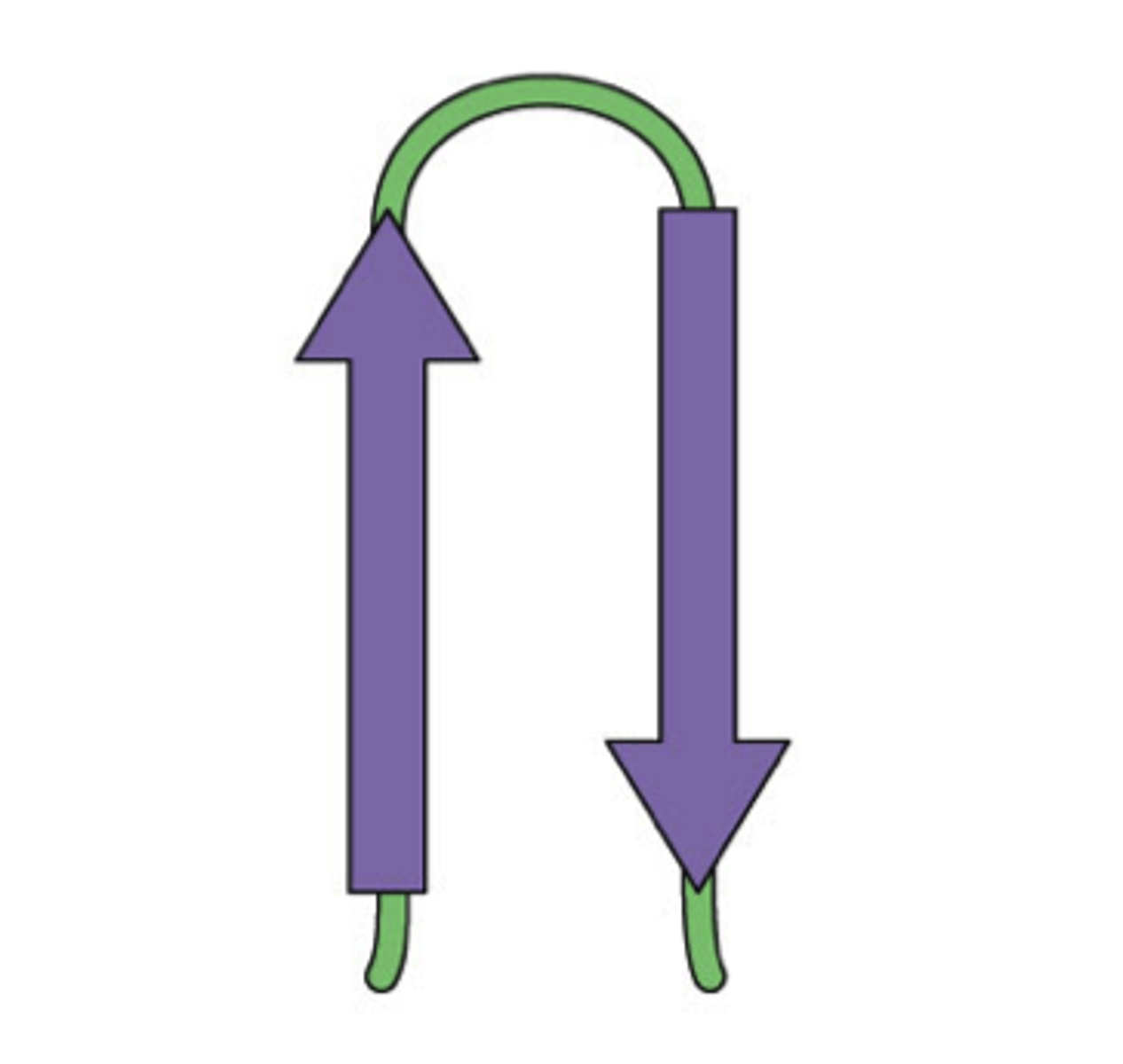
Beta-hairpin
A motif with two beta strips together
Greek key
A motif that is a variation of the anti parallel beta sheet where the strips don't need to form hydrogen bonds with their adjacent strip
Domain
An independently folded, compact unit in proteins that can be 25-300 amino acids in length. Proteins often have 3 domains with each having a different function. Domains can be shared between proteins that bind to the same ligand or catalyses the same reaction
Folding pattern
A part of tertiary structure that helps us identify This has 4 categories - all alpha, all beta, mixed alpha beta and alpha + beta
Quaternary strucuture
The organisation of subunits in a protein with multiple. These associate through weak noncovalent interactions and disulphide bonds.
Monosacharides (simple sugars)
A single unit of a carbohydrate - one monomer. They are in two forms: aldoses or ketoses
Triose
A monosaccharide with 3 carbons
Tetrose
A monosaccharide with 4 carbons
Pentose
A monosaccharide with 5 carbons. Forms a ring
Hexose
A monosaccharide with 6 carbons. Forms a ring
Heptose
A monosaccharide with 7 carbons
Oligiosaccharides
2-20 monosaccharides joined together
Polysaccharides
20+ monosaccharides joined together
Glycoconjugates
Carbohydrates that are covalently liked to proteins or lipids
Aldose
A monosaccharide with an aldehyde group
Ketose
A monosaccharide with a ketone group
D
The stereoisomer of sugars that are much more common in nature
hemiacetal
Forms when the aldehyde of aldose reacts with an alcohol
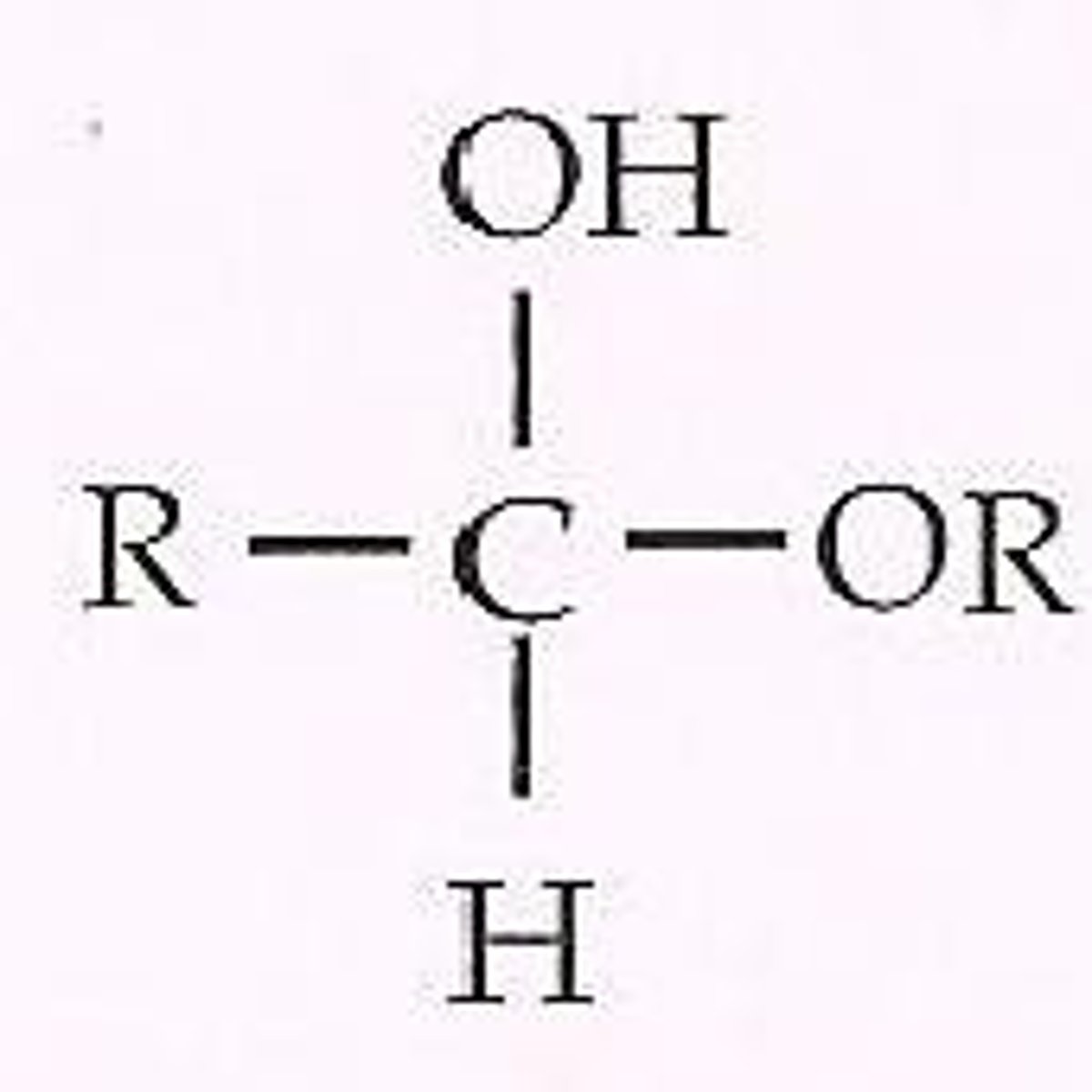
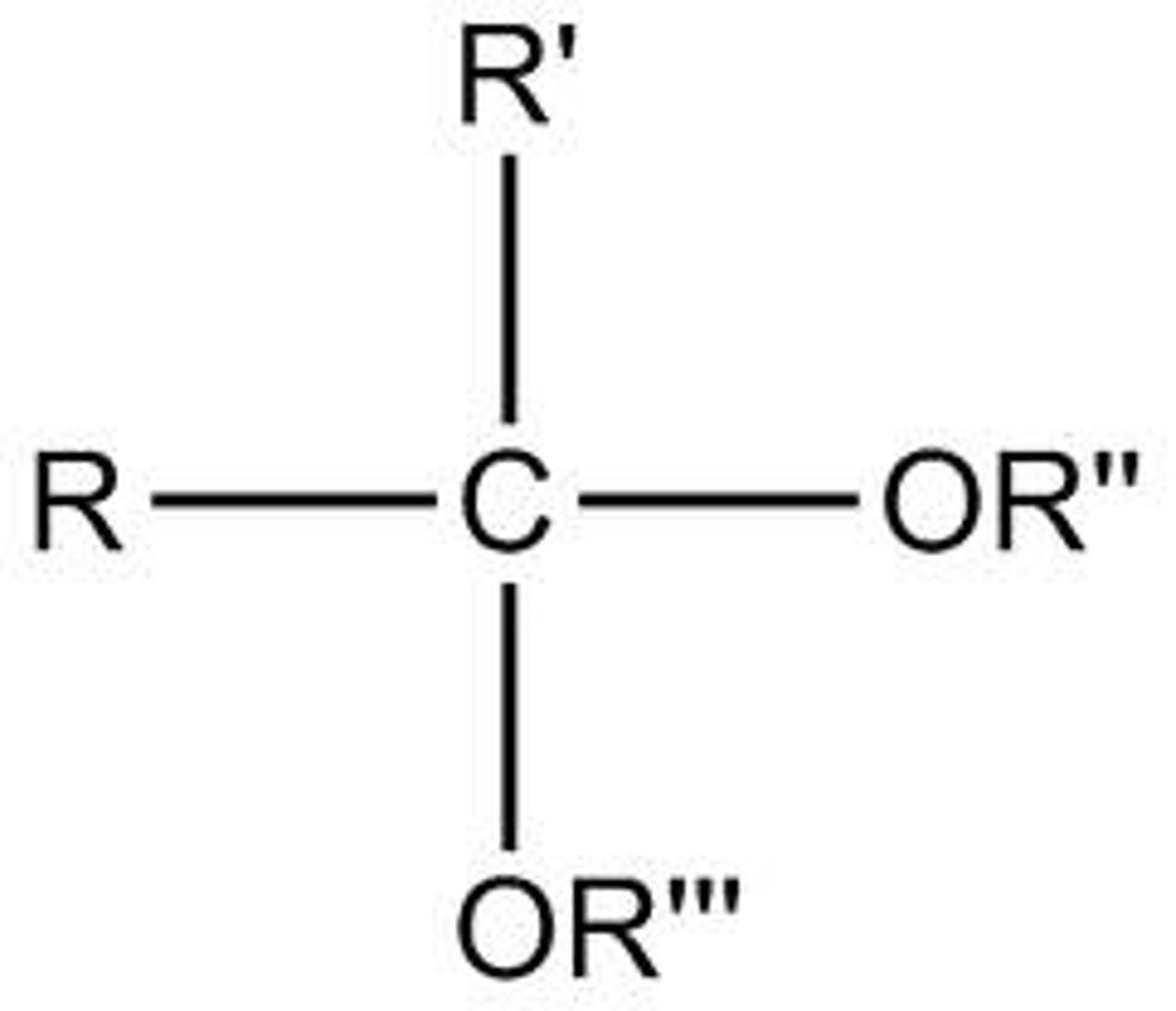
Acetal
Forms when a hemiacetal reacts with another alcohol in a condensation reaction
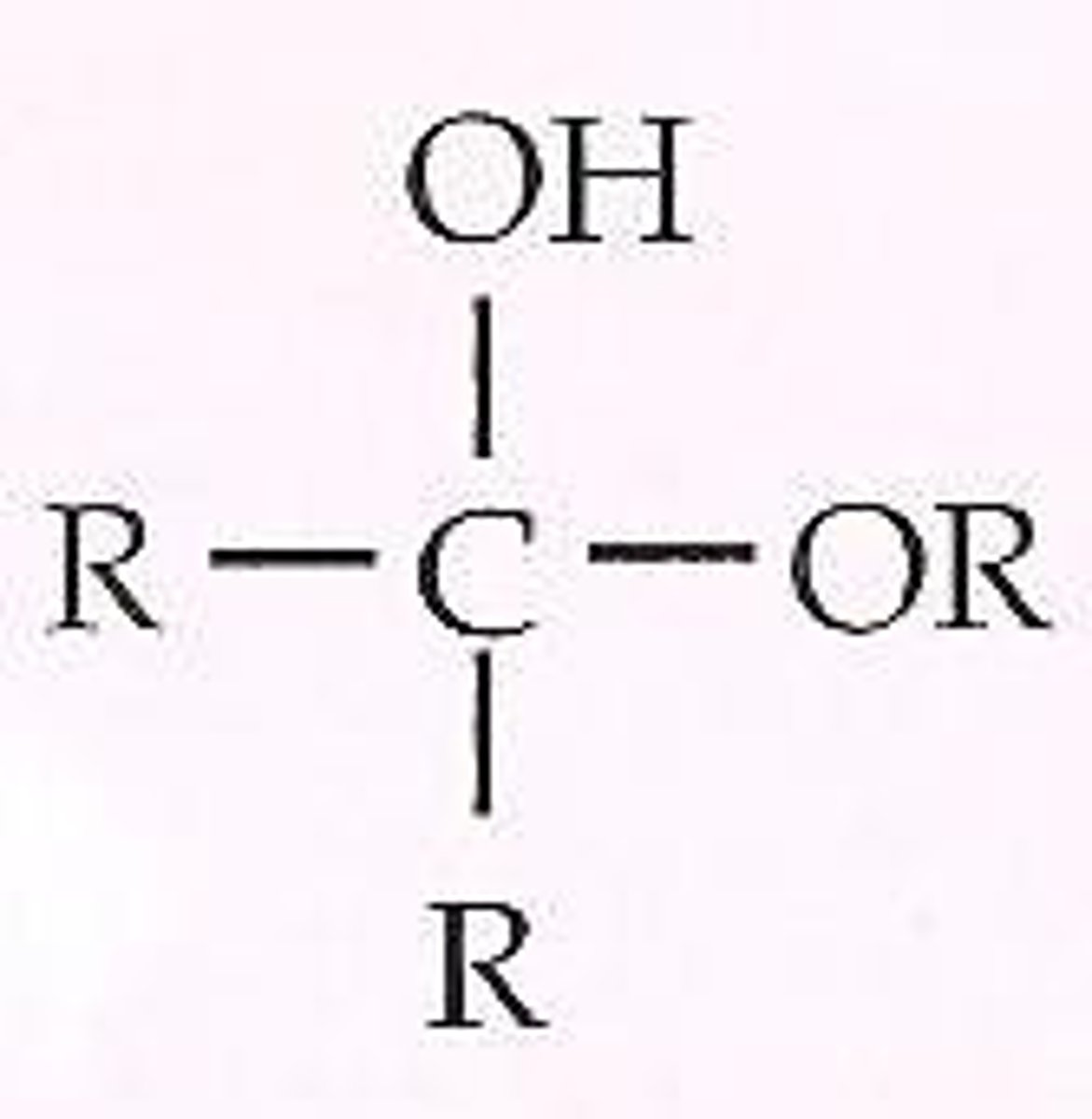
Hemiketal
Ketone reacts with an alcohol to form this.
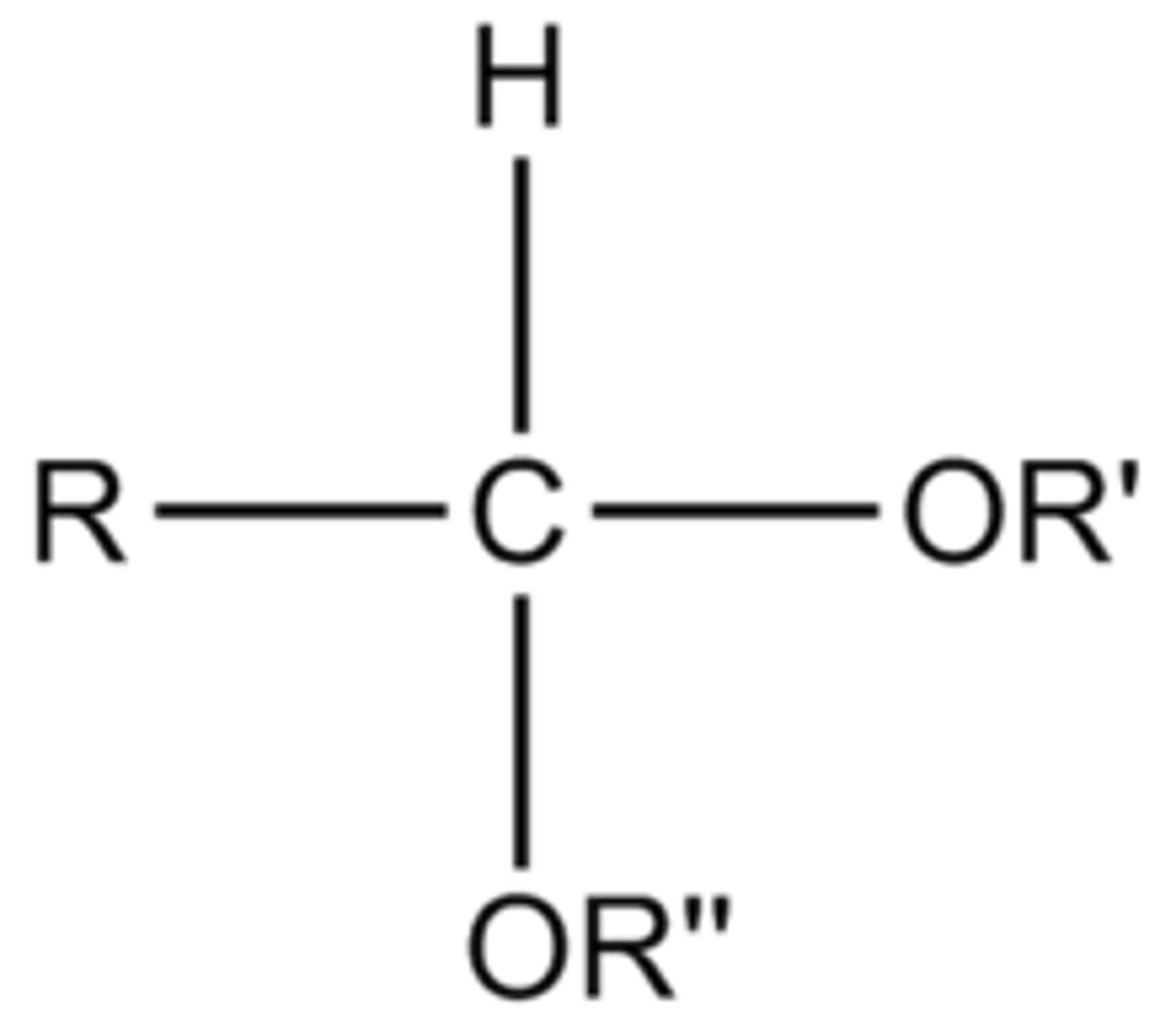
Ketal
A hemiketal reacts with an alcohol to form this in a condensation reaction
Pryranoses
A sugar with a 6 membered ring - 5 carbons and 1 oxygen
Furanoses
Sugars with a 5 membered ring - 4 carbons and oxygen
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond. Hemiacetal/ketals become acetals/ketals when this occurs
Homoglycans
Polysaccharides with only 1 monomer
Heteroglycans
Polysaccharides with more than one monomer
Glycogen
The way anials and fungi store glucose. Joined by a1-4 glycosidic bonds. Also branching at a1-6 glycosidic bonds every 8-12 residues
Starch
The way plants store glucose - a mixture of amylose and amylopectin
Amylose
Glucose joined by a1-4 glycosidic bonds to form a spiral chain but with no branches
Amylopectin
Glucose joined by a1-4 glycosidic bonds to form a spiral chain. Also a1-6 glycosidic bonds every 24-30 residues
cellulose
The most abundant biopolymer on earth. B glucose linked by b1-4 glycosidic bonds and little branches. Strong hydrogen bonds between strands.
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrates linked to proteins usually by an O-glycosidic linkage to the -OH group of Ser or Thr
Deoxyribose
The 5 membered ring carbohydrate monomer in DNA
Ribose
The 5 membered ring carbohydrate monomer in RNA.
Triacylglycerol
A lipid composed of a a glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acids. Used as a fuel source in the cell. Stored as fat droplets
Glycerophospholipids
A lipid composed of a glycerol backbone, a phosphate molecule connected to a polar head group and 2 fatty acids. The most abundant lipid in the ell membrane
Sphingolipids
A lipid built on a sphingosine backbone. They have 2 nonpolar tails and a polar head. Sphingosine is similar to an amino acid
Isoprenoids
A group of lipids including steroids, lipid vitamins and hormones
Fatty acids
Have 12-22 carbons with a carboxyl group at C1. Can be saturated or unsaturated.
Steroids
A class of isoprenoids that are derived from isoprene.
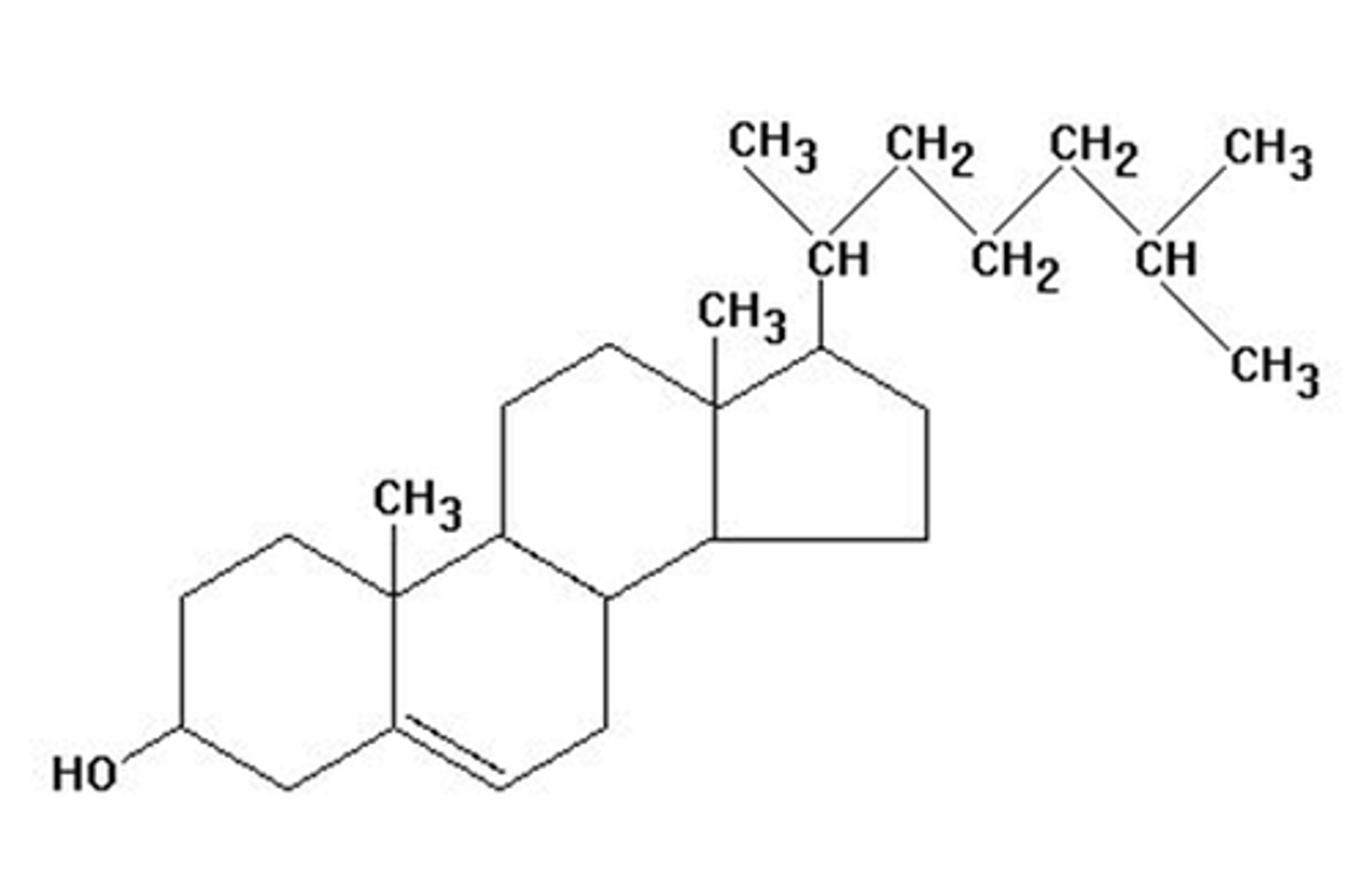
Cholesterol
An amphipathic molecule with a fused ring system that makes it less flexible than a fatty acid. Acts a fluidity buffer for membranes
Biological membranes
Defines boundaries between cells and subcellular compartments. Made up of proteins and lipids
25-50%
The percentage by mass of lipids in a membrane
50-75%
The percentage of proteins by mass in a membrane
Integral membrane proteins
proteins found in the lipid bilayer than span the entire bilayer. Must contain hydrophobic regions. Membrane spanning alpha helices are the most common motifs. Beta sheets can act as a channels through the membrane .
Peripheral membrane proteins
Associated with the membrane face with charge-charge or hydrogen bonding interactions. They can readily disociate
Lipid anchored membrane proteins
Proteins tethered to the membrane though a protein-lipid covalent bond.
Channels/pores
A passage that allows molecules and ions to move through the membrane passively. Molecules/ions must be the right size, charge and molecular structure
Induced fit
Where an active site of an enzyme fits better to the substrate after it has bound