IGCSE Biology 0654 B1 and B2
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms

Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining movement
an action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place


Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining respiration
the chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism


Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining sensitivity
the ability to detect and respond to changes in the internal or external environment


Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining growth
a permanent increase in size and dry mass

Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining reproduction
the processes that make more of the same kind of organism

Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining excretion
the removal of waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements

Describe the characteristics of living organisms by defining nutrition
the taking in of materials for energy, growth and development

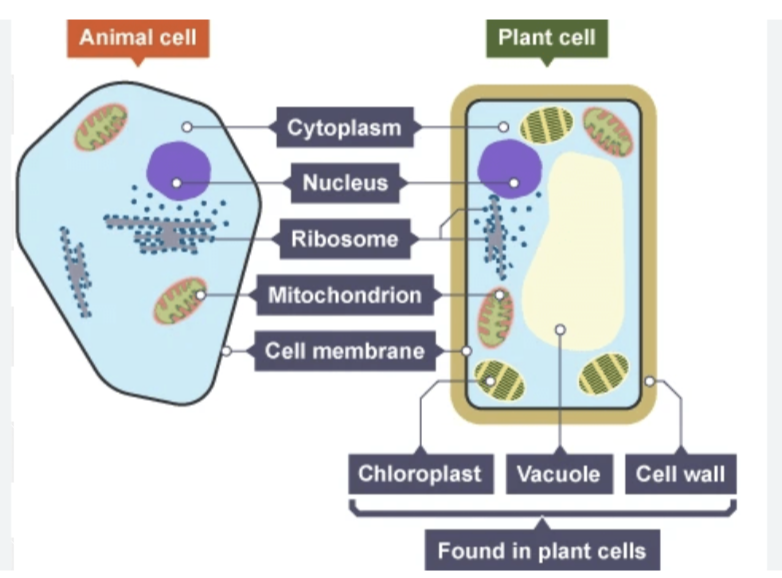
Explain the similarities and differences between a plant and animal cell
Similarities: Both contain a nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes and a cell membrane
Differences: plant cells have a cell wall (made of cellulose) vacuole and chloroplasts. Plant cells have a more regular shape and are larger
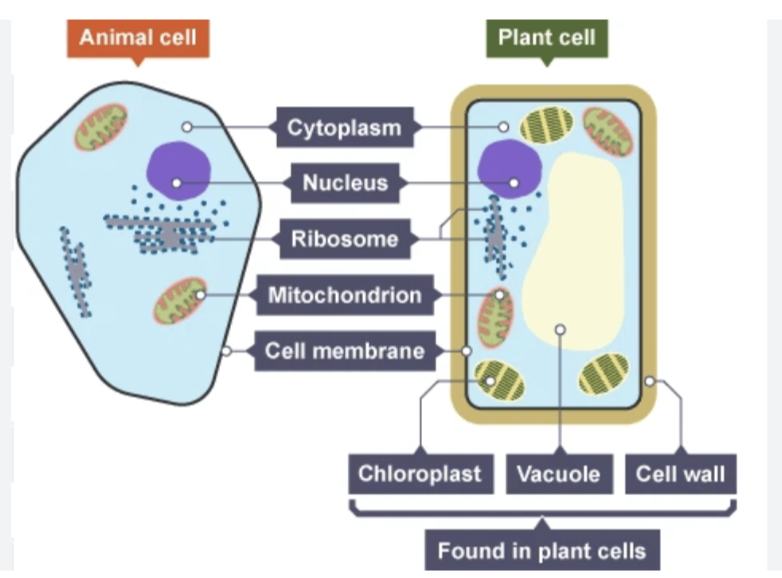
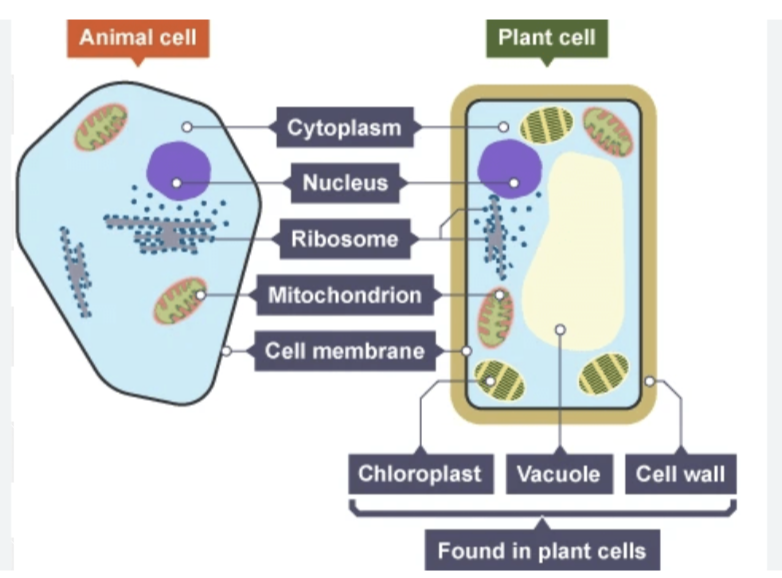
Describe the functions of the structures (parts) of an animal and plant cells
• Cell membrane
Controls which substance goes into and out
• Nucleus:
Contains genetic material (DNA) which codes for proteins.
Controls activities and characteristics of cell
• Cytoplasm:.
A jelly-like substance where chemical reactions occur
Contains mitochondria for aerobic respiration. Make proteins
• Ribosomes:
Build proteins for the cell from amino acids
• Mitochondria:
Where aerobic respiration occurs.
Provides energy for cells activities
• Cell wall:
Made of cellulose.
Protects and supports the cell, prevents bursting
• Chloroplasts
Contains the green chlorophyll. The site of photosynthesis.
Contain enzymes to produce glucose through photosynthesis
• Vacuoles:
Store cell sap (solution of sugar and salt). Support the shape of the cell.
Contains pigments which colour the cell and attract polinating insects
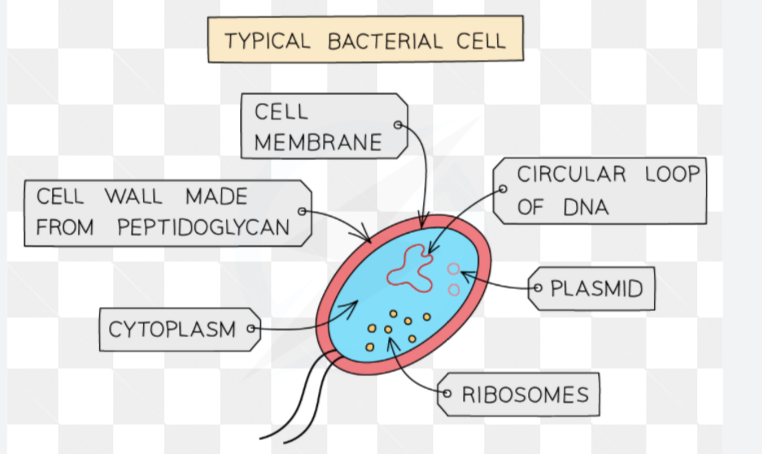
Describe and identify the structure of a bacterial cell
No nucleus, no mitochondria, no chloroplasts, no vacuole
• Cell wall Protects and supports the cell (not made of cellulose)
• Cell membrane Controls which substance goes into and out
• Cytoplasm Where most chemical reactions of the cell occur
• Ribosomes where protein for the cell is made
• Circular DNA Contains most of the genetic material in the cell
• Plasmids Tiny rings of DNA that float in the cytoplasm.
State how new cells are produced
by division of existing cells
State the functions of the following specialized cells:
Ciliated cells, root hair cells, palisade mesophyll cells, neurons, red blood cells, sperm and egg cells.
• ciliated cells: move of mucus out of the trachea and bronchi
• root hair cells: absorb mineral ions by active transport and water by osmosis
• palisade mesophyll cells: photosynthesis
• neurones: conduct electrical impulses
• red blood cells: transport O2 around the body for respiration
• sperm and egg cells (gametes): reproduction
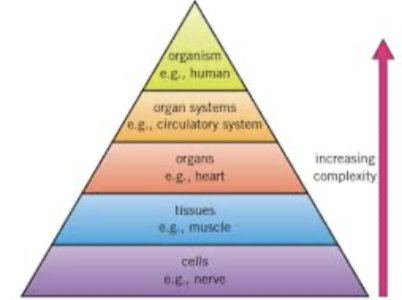
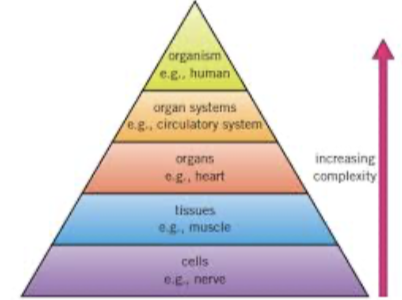
Describe cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Cell: the smallest functional unit of an organism. All living things are made of cells
Tissue: group of cells with similar structures that work together to perform the same function (e;g; tubes and glands)
Organ: group of tissue that work together to perform a specific function (brain, roots, leaves…)
Organ system: group of organs with related functions that work together to perform a specific body function (e.g the heart and blood vessels make up the circulary system)
Organism : a complete living thing made up of multiple organ systems
The image of a leaf cell is 50 cm long. The actual cell is 25 mm long. What is the magnification?
Step 1 – Convert 50 cm to mm:
50 cm = 500 mm
Step 2 – Apply formula:
Magnification = 500 mm/ 25mm = 20
Answer: 20×
The image of a cell is 90 mm long. The magnification is ×300. What is the actual size of the cell in cm?
Step 1:
Actual size = 90 mm / 300 = 0.3 mm
Step 2 – Convert to cm: 0.3 cm = 0.03 cm
Answer: 0.03 cm
A mitochondrion is 0.005 mm long. Convert this to micrometres (µm).
0.005mm×1000=5μm
A bacterial cell is 1800 µm long. Convert this to mm and then to cm.
Step 1: µm to mm:
1800μm÷1000=1.8mm
Step 2 – mm to cm:
1.8mm=0.18cm
Answer: 0.18 cm