Topic 3- Gas Exchange in Humans
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Function of ciliated cells in trachea
to move microorganisms and dust particles along with the mucus in the trachea
Ficks law of diffusion
Rate of diffusion ∝ (area of surface x difference in concentration) / thickness of surface
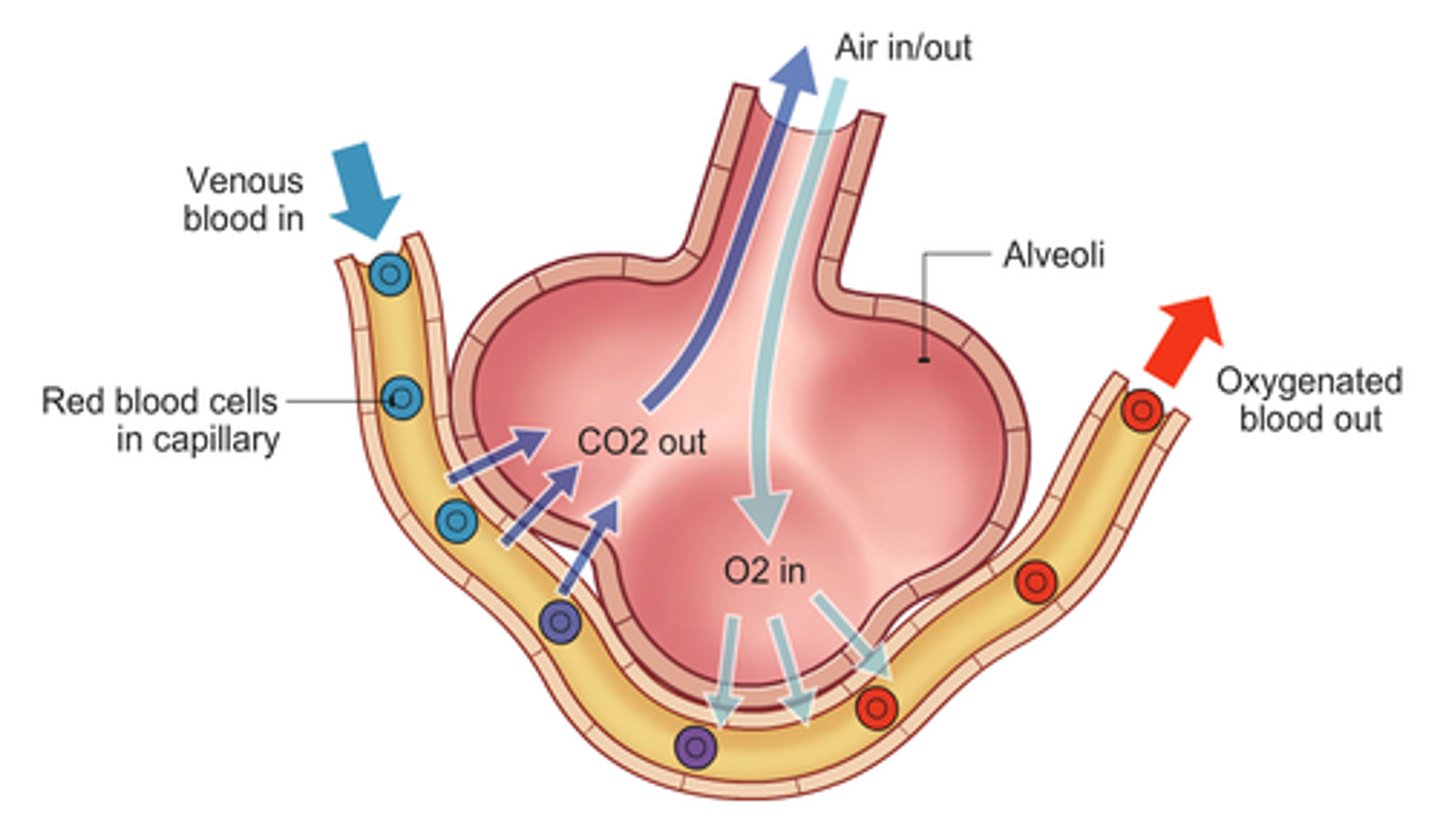
Lungs adaptations for gas exchange
1- Alveoli have large Surface area
2-Diffusion gradient maintained (capillaries constantly ventilated)
3-Thin alveoli walls so short diffusion pathway
4-Red blood cells are slowed as they pass alveoli so more time for diffusion
5-Red blood cells flattened against capillary walls to reduce diffusion distance
6-Alveoli and capillaries are close together to reduce diffusion distance
Structure of alveoli
-One cell wall thick, creating short diffusion pathway.
-Moist and extremely large surface area.
-Lots of capillaries around alveoli.
-High blood supply.
Lung surfactant
A phospholipid that coats the lung
Thins the watery lining of the alveoli preventing surface tensions creation which would cause alveoli to stick together
Structures in the mammalian respiratory system
Trachea, rib, rib muscle, bronchus, bronchiole, alveolus, diaphragm, heart
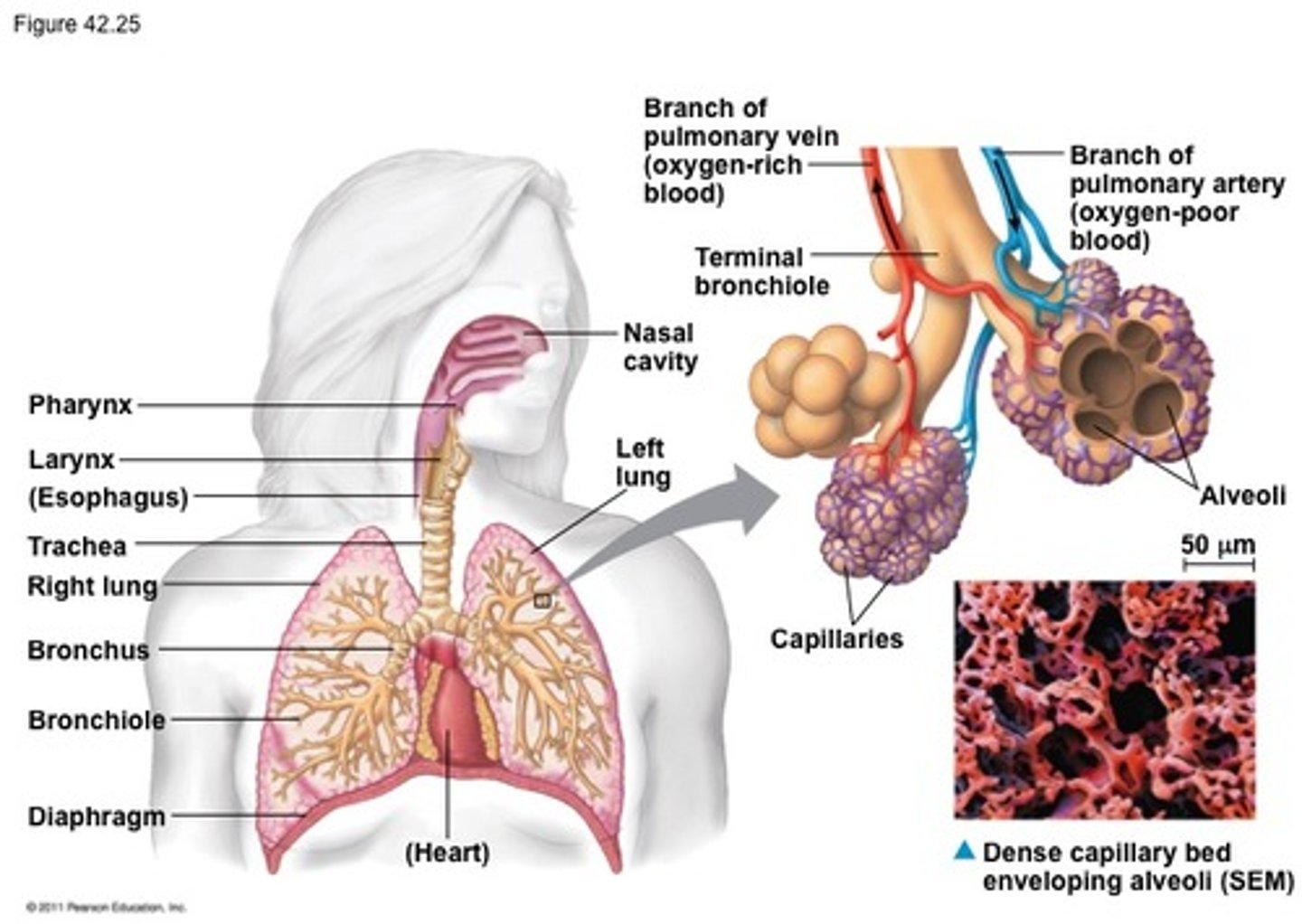
Adaptations of the trachea
Cartilage rings to prevent the trachea from collapsing
Goblet cells and ciliated cells to keep airway clear
Function of Goblet cells in trachea
produces mucus to trap microorganisms and debris, keeping the airway clear
Inspriation
-Diaphragm contracts and flattens
-external intercostal muscles contract, pulling ribs up and out
-Volume of the thorax INCREASES and pressure DECREASES
-Air pushed in to equalise pressure (pressure gradient)
Expiration (Normal)
-Diaphragm relaxes and forms a dome shape
-External intercostal muscles relax, pulling ribs down and in
-Volume of the thorax DECREASES so pressure INCREASES
-Air pushed out to equalise pressure (pressure gradient)
Spirometry
a measurement of breathing
Tidal volume
The volume of air breathed in and out without conscious effort.
Ventilation rate
The number of breaths per minute
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
volume of additional air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal inhalation
Vital capacity
The total volume of air that can be exhaled after maximal inhalation.
Residual Volume
The volume of air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation.
Total lung capacity
vital capacity + residual volume
Examples of lung disease
Lung cancer, emphysema, Asthma, TB, Pulmonary fibrosis