Academic Team Science Formulas
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
heat change formula
q=mcΔT

sqrt(1-v^2/c^2)
formula for apparent length percent of object traveling at speed v to a stationary observer
Y=(F/a)/(deltaL/L)
youngs modulus equation. use deltaL for stretch distance
(m2-m1)g/m1+m2
atwood machine acceleration formula
1/2kx^2
formula for elastic potential energy of a spring using hookes law
deltaC/deltaT
this formula finds the reaction rate from the before and after concentrations and the time passed
P=I^2*Rn
power dissipated by resistor formula
P=IV=I^2/R
formula for power of circuit
v^2/r
formula for centripetal acceleration around a curve based on the radius of the curve and the object's linear velocity
torque formula
this formula states: torque=force distance sin(angle of force) (must be meters)
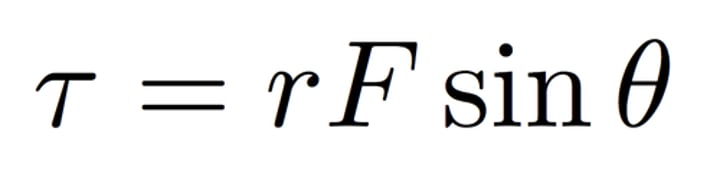
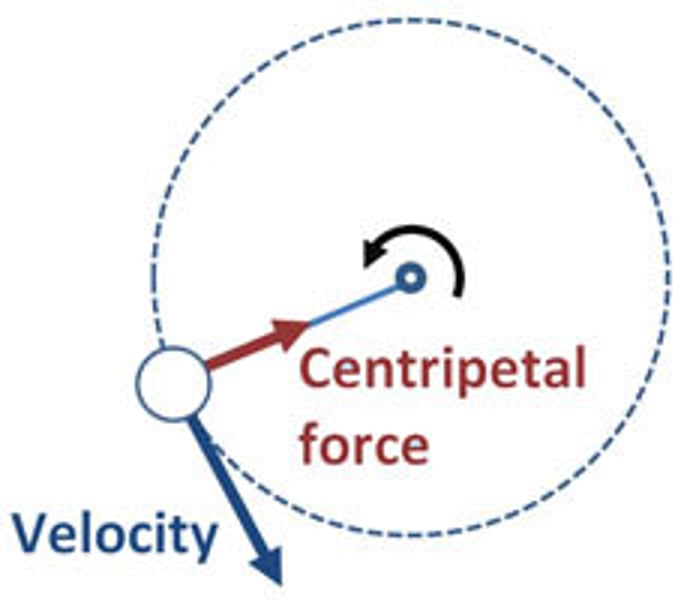
mv^2/r
formula for centripetal force (force to keep an item spinning in a circle)
KE=mgh
formula for kinetic energy of freefall at moment of impact (KE=)
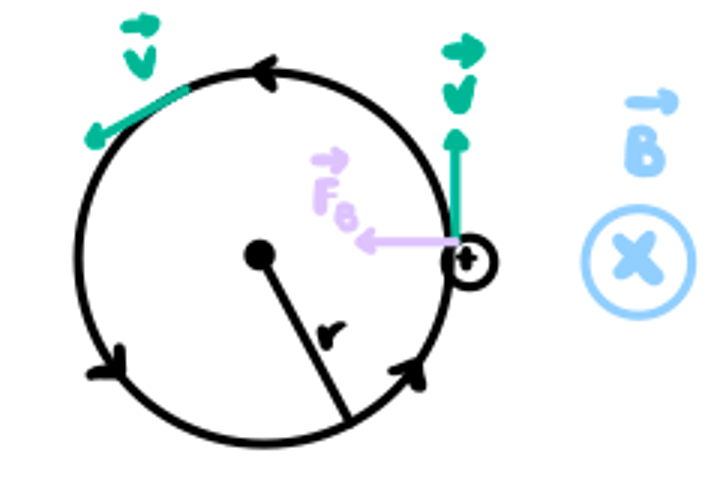
mv/qB
formula for radius of path for moving charged particle in magnetic field (depends on m,v,Q (charge),B (magnetic field strength))
v^2sin^2theta/2g
this formula calculates maximum height of projectile from initial velocity v, angle theta, and gravity g.
P=FV
this is the formula for power from force and velocity
W=mgh
formula for work done by gravity.
KE=1/2mv^2
formula for kinetic energy using mass and velocity (KE=)
t=2pi*sqrt(l/g)
this is the formula for the period of a pendulum (t) from the length (l) and gravity (g)
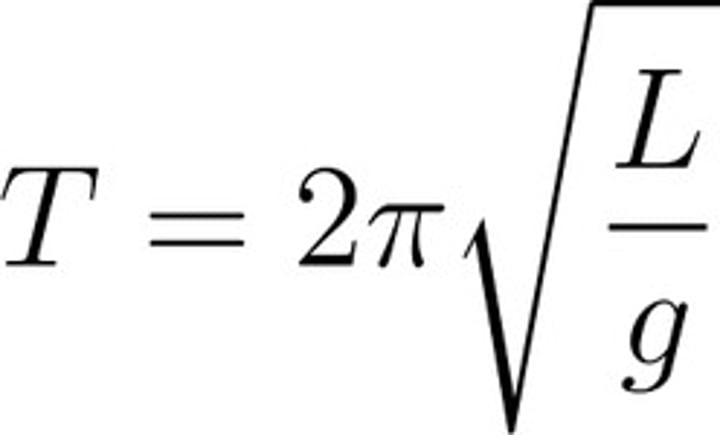
kinematic equations
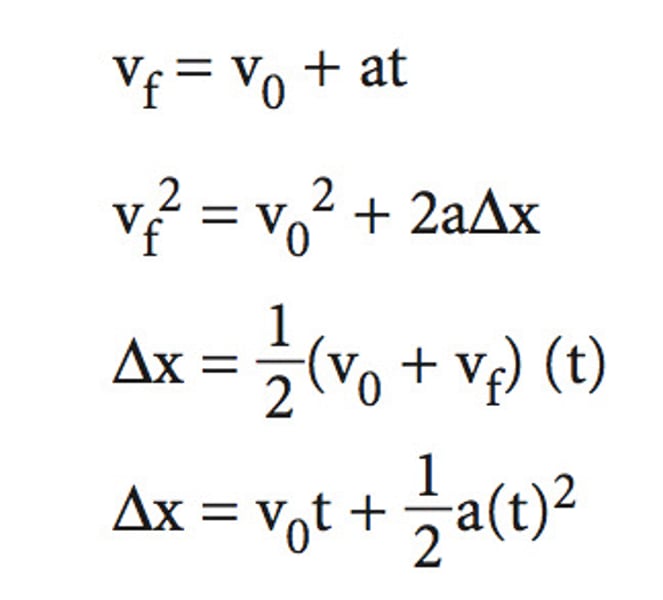
power formula
P=W/t or P=Fd/t
fluid pressure formula
pressure = density gravity height + atmospheric pressure
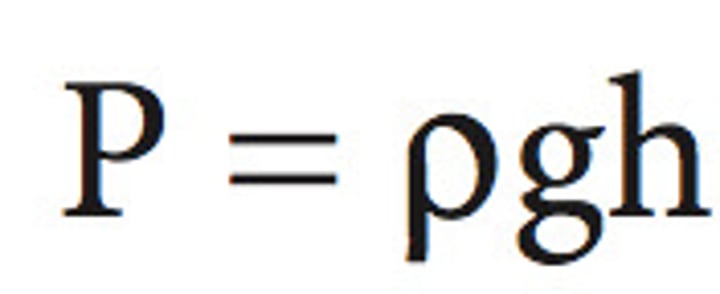
1/2gt^2
formula for distance traveled by a free falling object
U=qV
electric potential energy (U) formula from charge (q) in coulombs and voltage (V) in volts
buoyancy formula
formula = fluid density (p) displaced fluid (V) gravity (g). finds buoyancy force in newtons for an object. V MUST BE IN m³
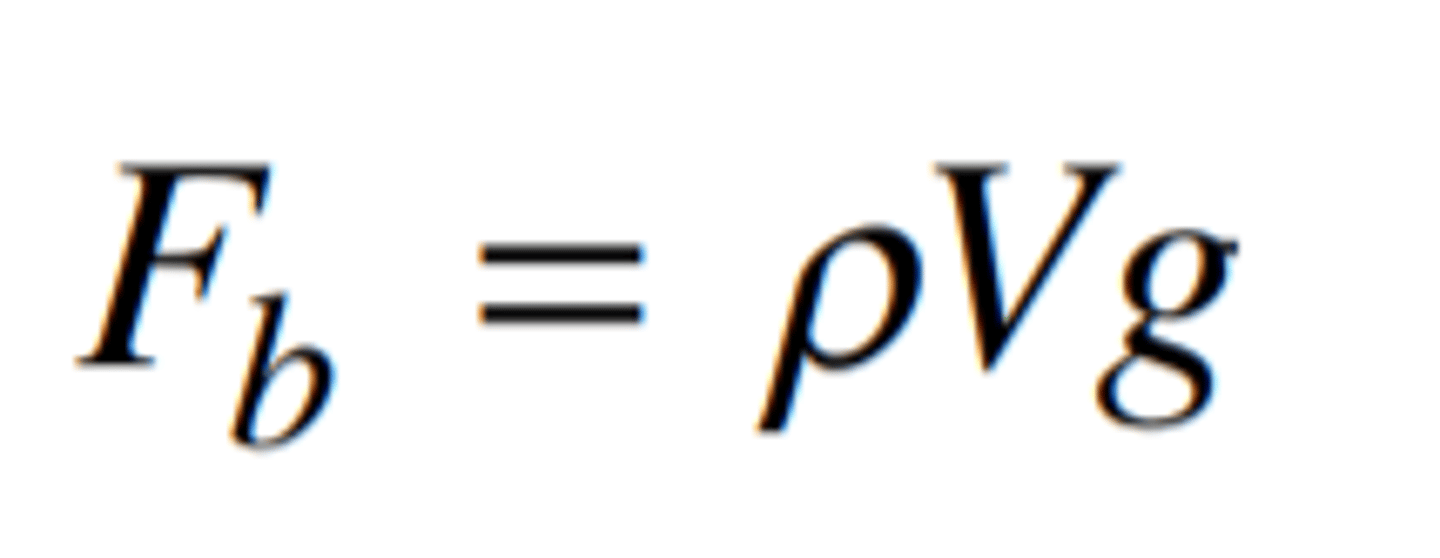
capacitance of parallel circuit
C=∑Cn
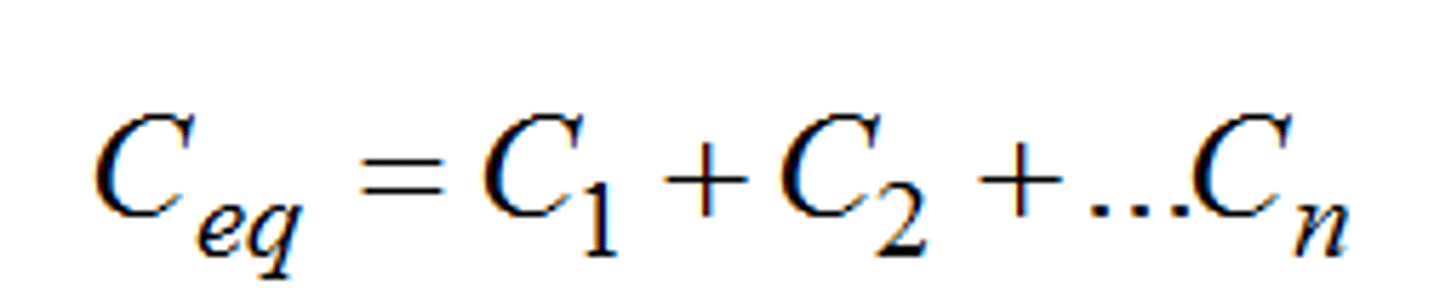
capacitance of series circuit
1/C=∑(1/Cn)
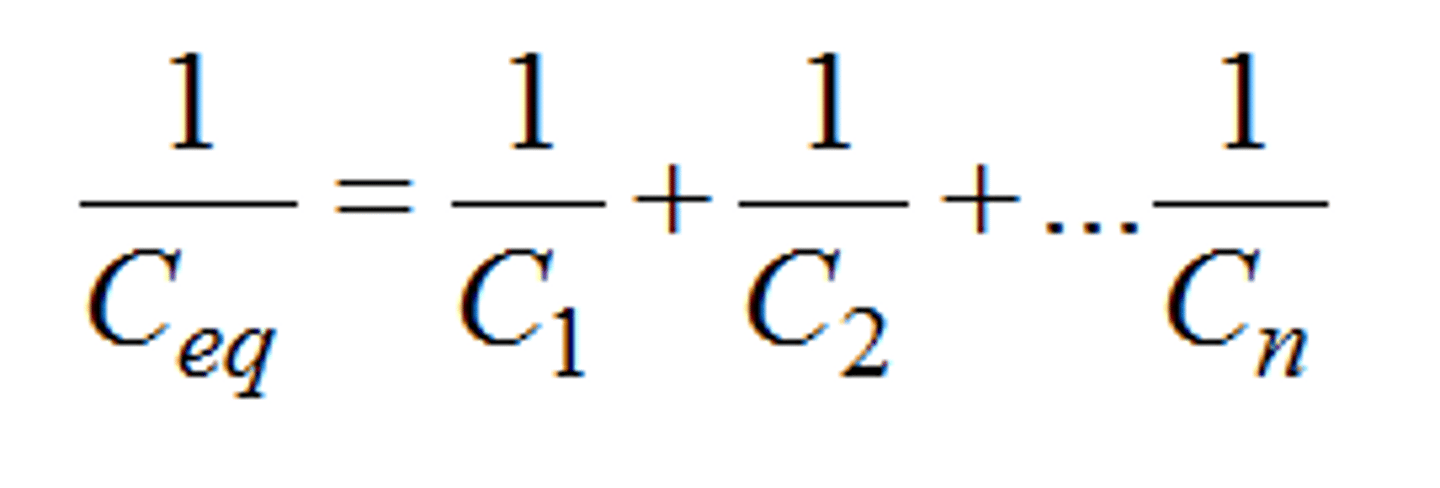
henderson hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log [base]/[acid],
pKa = -log Ka
Ka = dissociation constant (given)
finds pH of buffer
w=fd
formula for work from distance (meters) and force (newtons)
F=uN
force due to friction formula (F=), uses u (coefficient of friction) and N (normal force). N=mg or mgcostheta on inclined plane
lens equation
this equation relates the actual and image distances to the focal length. f=focal length, d0=actual distance, di=image distance
ALSO, hi ho di do: h is the magntification
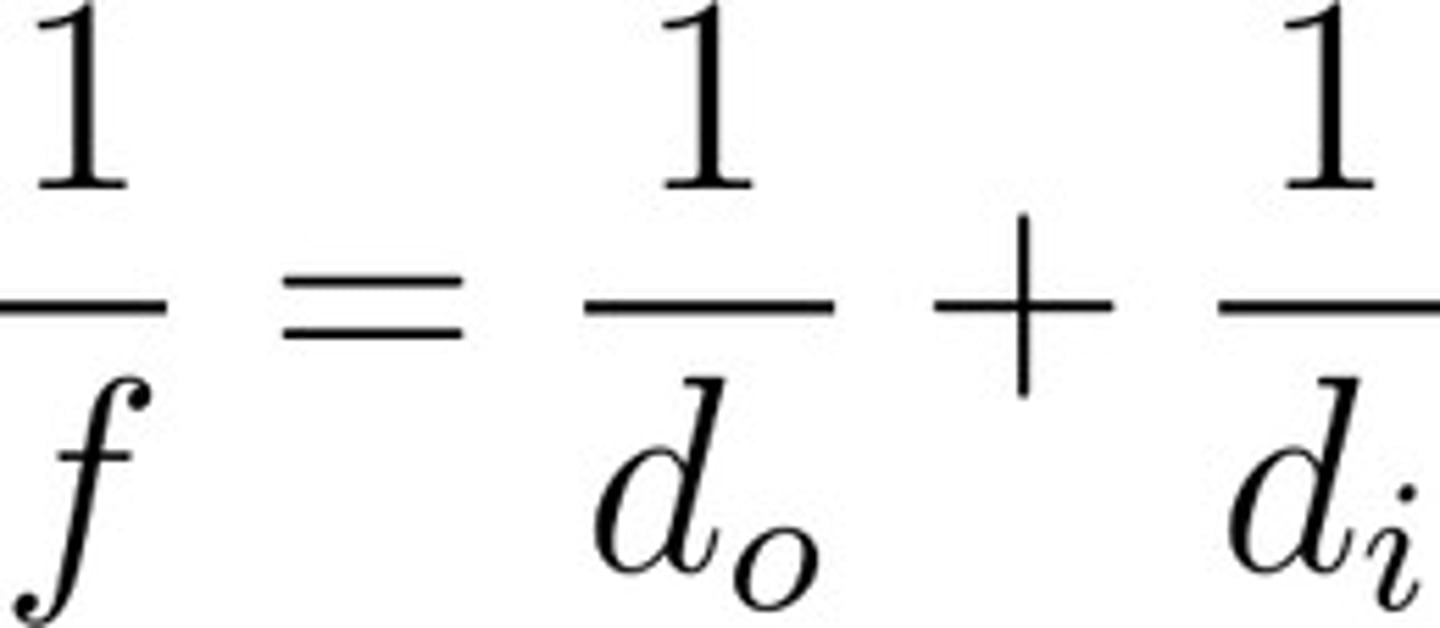
conservation of momentum equation
m1v1 + m2v2 = (m1 + m2)vf
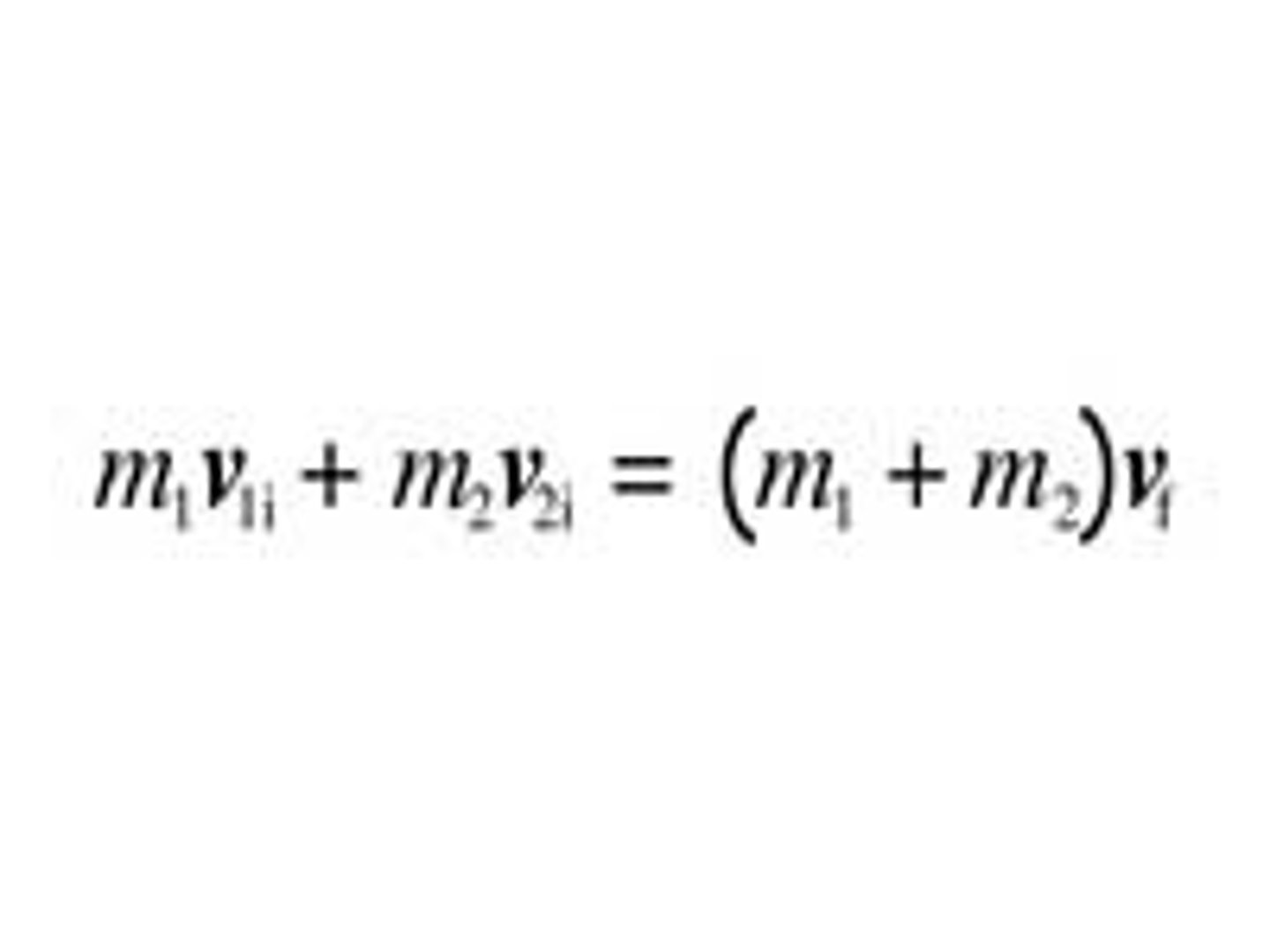
f=r/2
formula for focal length from radius of curvature of spherical mirror
moment of inertia formula
solid sphere: 2/5MR^2
hollow sphere: 2/3MR^2
cylinder: 1/2MR^2
hoop/hollow cylinder: MR^2
rod: 1/12ML^2
solid disk: 1/4MR^2
f=m(a+g)
formula for force OR tension from mass, acceleration, and gravity
Q=CV
formula for charge (coulombs) (Q) stored on the plates of a capacitor from voltage (volts) (V) and capacitance (farads) (C)
(v+-vo)f/(v+-vs)
doppler effect formula to find new frequency from speed of sound (v), observer velocity (vo), source velocity (vs), and base frequency (f). if moving towards, use plus, else, use minus
hardy weinberg equilibrium
this equation predicts the frequencies of genotypes.
p = homozygous recessive as decimal
2pq = heterozygous as demical
q = homozygous dominant as demical
p + q equals 1
p^2+2pq+q^2 equals 1 to find genotypic frequencies
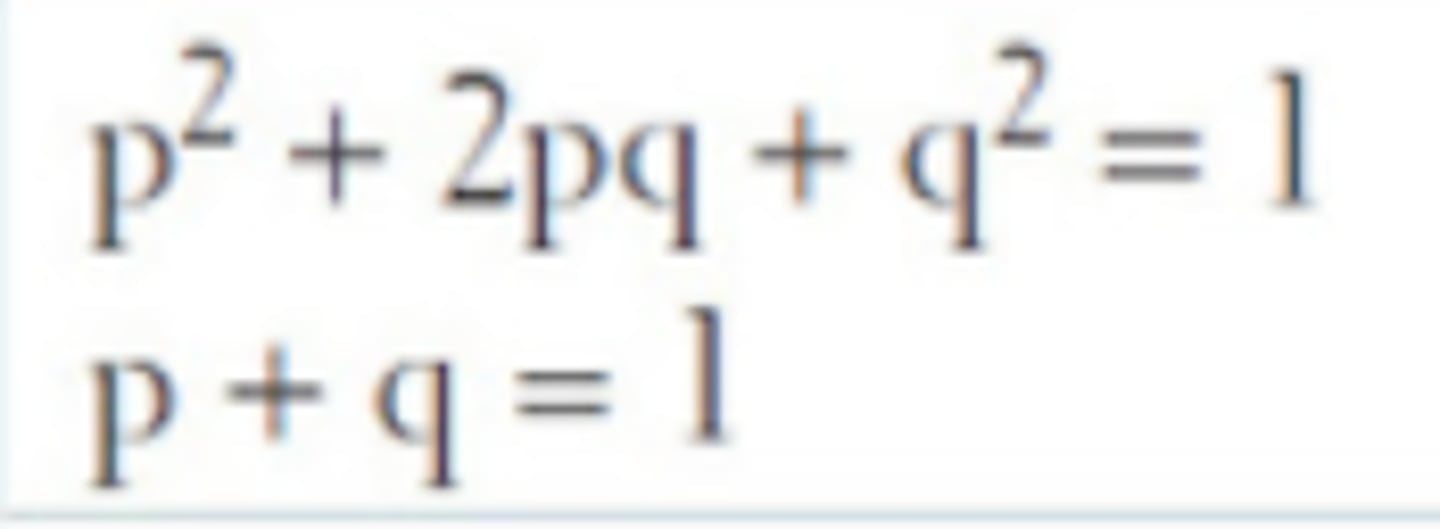
sum mr^2
formula for moment of inertia from all masses and radii (distances) from point acting on that point
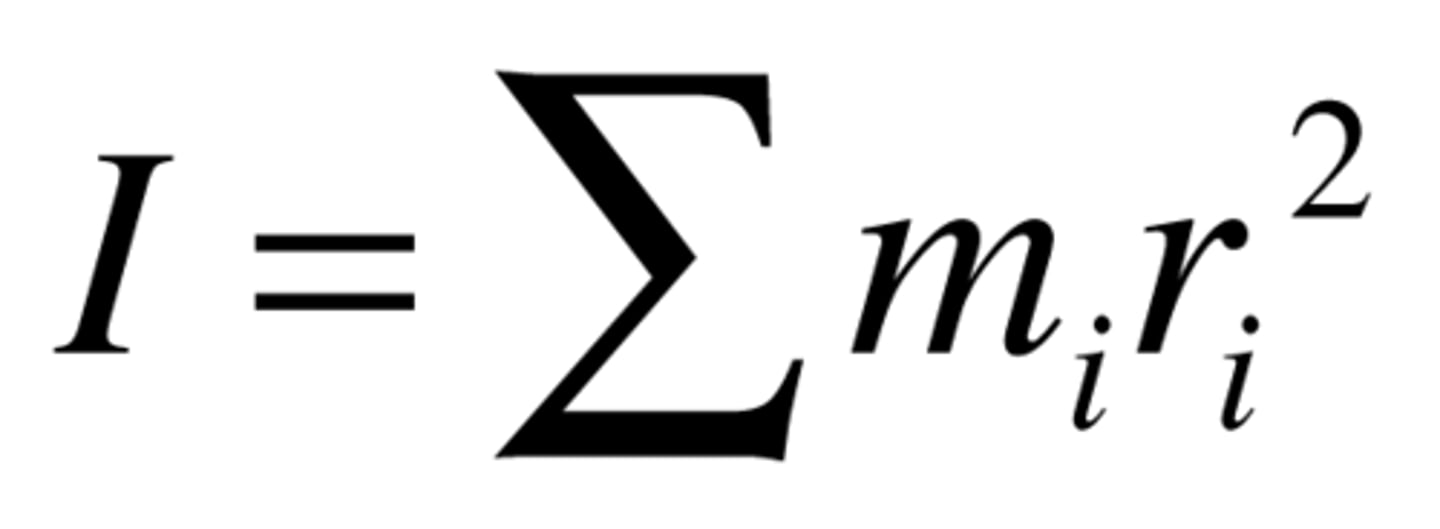
v=f*lambda
formula for velocity of standing wave from frequency and wavelength.
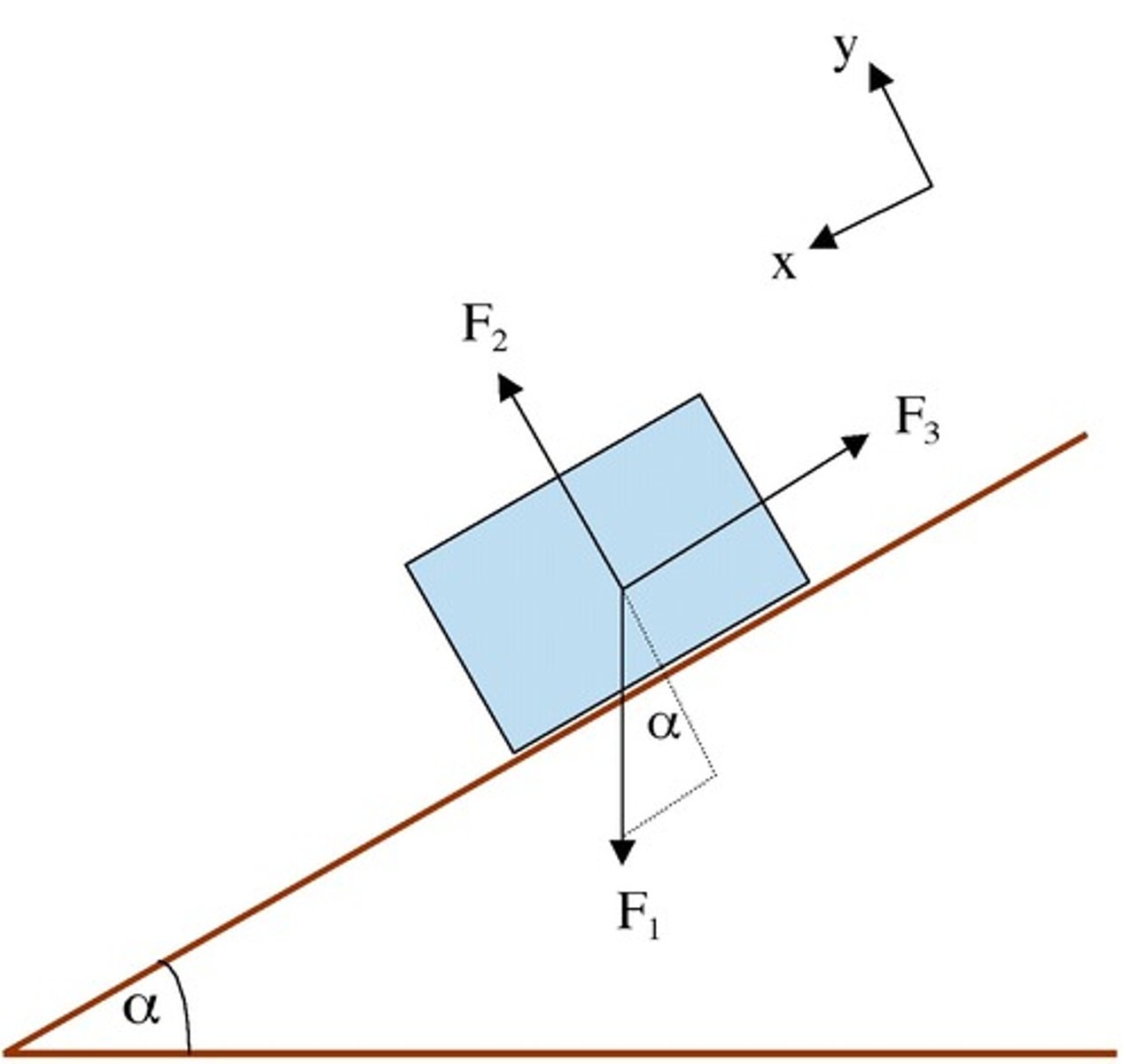
mgcostheta
normal force formula on inclined plane
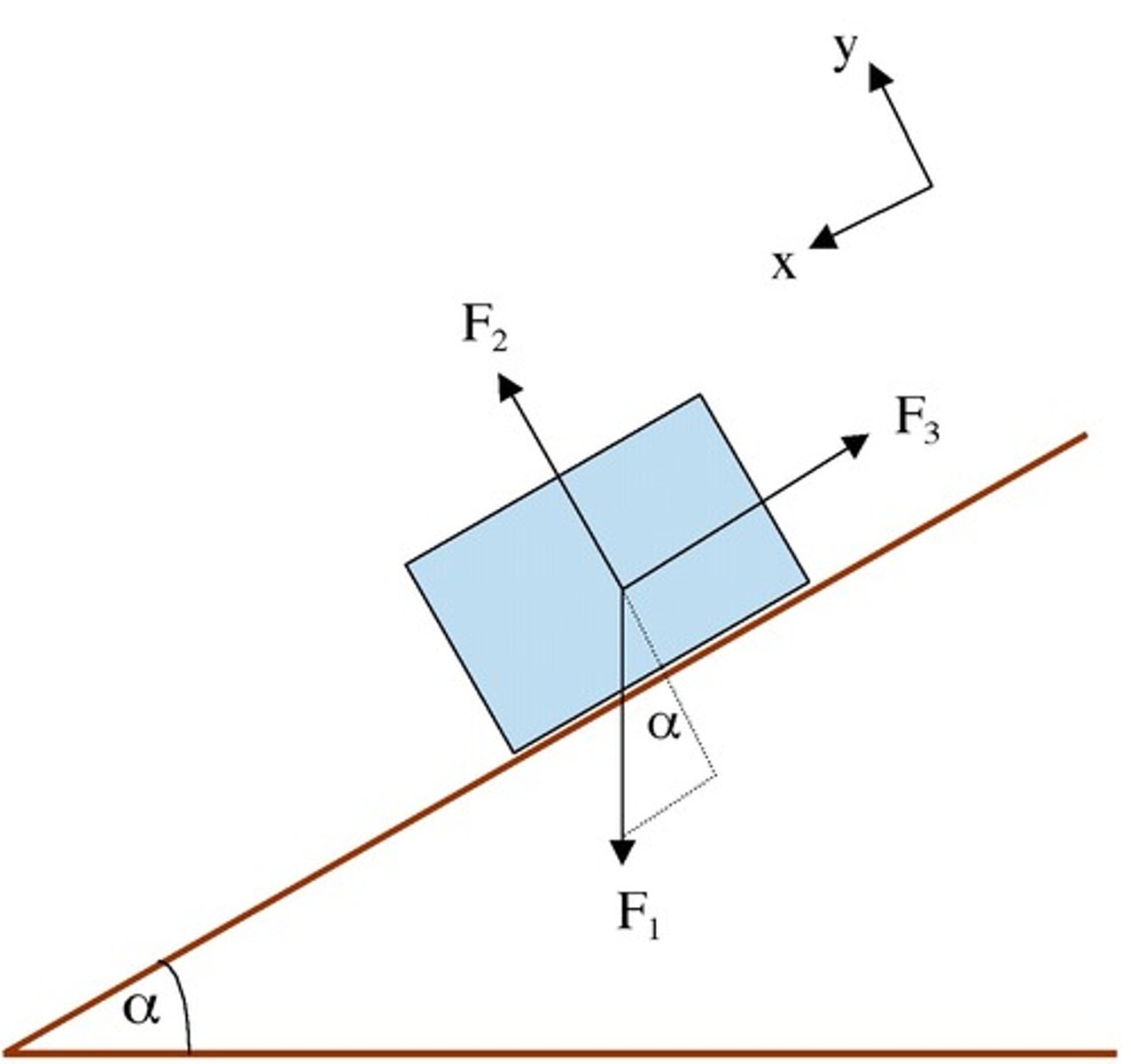
mgsintheta
net force down an inclined plane due to gravity
mgh=1/2mv^2
equation for pendulum motion relating PE and KE. h = height from resting position.
paulings rule
for oxoacids, pKa = 8 - 5p. Rewrite acid as (O)_pC(OH)_q.