unit 5 ap human
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
subsistence agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family
2
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
the production of food primarily for sale off the farm
3
New cards
market gardening- intensvie
some of the fruits and vegetables are sold fresh to consumers, but most are sold to large processors for canning or freezing.
4
New cards
tropical climate
hot humid climate that produces certain plants, such as cassava, banana, sugar cane, sweet potato, papaya, rice, maize
5
New cards
Mediterranean climate
dry-summer climate that produces certain fruits, vegetables, and grains such as grapes, olives, figs, dates, tomatoes, zucchini, wheat, barley and prevails along the shores of the Mediterranean, in parts of California and Oregon, in central Chile, at South Africa's Cape and in parts of southwestern and southern Australia
6
New cards
shifting cultivation
A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another; each field is used for crops for relatively few years and left fallow for a relatively long period.
7
New cards
Pastoral Nomadism
seasonal migration of domesticated livestock, usually fixed territory between highlands and lowlands.
8
New cards
Ranching-extensive
the business of raising livestock (cattle, sheep)
9
New cards
agriculture innovations
-biotech
-gmo
-aquaculture
-soil and water use
-reductions in biodiversity
-extensive fertilizer and pesticide use
-gmo
-aquaculture
-soil and water use
-reductions in biodiversity
-extensive fertilizer and pesticide use
10
New cards
Fertile crescent
hearth of early agriculture and early civilization
southwest asia
southwest asia
11
New cards
First Agricultural Revolution
When humans achieved plant and animal domestication
12
New cards
intensive agriculture
large amounts of capital and/or labor per unit of cultivated land; may be part of either subsistence or commercial economy (next to people)
13
New cards
extensive agriculture
characterized by low inputs of labor per unit land area. (away from people)
14
New cards
Columbian Exchange
facilitated the global diffusion of plants, animals, diseases, human population, culture, technology, and ideas
15
New cards
Globalization of Agriculture
improvements in transportation and communication technologies create a variety of goods offered year-round, when they traditionally were only available seasonally-strawberries in winter
16
New cards
community-supported agriculture (CSA)
individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that the growers and consumers provide mutual support
17
New cards
Enclosure Movement
The 18th century privatization of common lands in England, which contributed to the increase in population and the rise of industrialization.
18
New cards
Second Agricultural Revolution
improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of food that started in the Middle Ages and then benefited from the industrial revolution with the use of machines and new technology.
19
New cards
Industrial Revolution
the transformation from an agricultural society to an industrial society with the introduction of power driven machines in manufacturing, mining, transportation, and agriculture.
20
New cards
double cropping
2 or 3 crops grown on the same piece of land in 1 year
21
New cards
vertical integration
one company or corporation owns all of the steps of production
(starbucks, Frito-Lay, Purina)
(starbucks, Frito-Lay, Purina)
22
New cards
Green Revolution (Third Agricultural Revolution)
high yield seeds(hybrid and/or GMOs) increased use of chemicals, mechanized farming, and elaborate irrigation systems.
23
New cards
Monoculture
growing one crop in a farm system at a given time
24
New cards
Mono-cropping
growing one crop in a farm system year after year
25
New cards
Land cover change
process by which agricultural areas are lost to development
26
New cards
soil salinization
process by which the amount of salt increases in the soil (irrigation)
27
New cards
multi-cropping
growing several crops in a farm system
28
New cards
Bid rent theory
theory that shows what various land users are prepared and able to pay for access to the center market
-intensive and extensive farming practices are in part by land costs
-extension of the von Thünen model
-intensive and extensive farming practices are in part by land costs
-extension of the von Thünen model
29
New cards
Agribusiness
system of commercial agriculture that links various industries to the farm
30
New cards
feedlots/Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs)
animals kept and raised in confined spaces and given hormones and/or antibiotics and/or fattening grains to prepare them for slaughter at a much quicker pace than traditional forms.
31
New cards
Desertification
process by which fertile land becomes desert as a result of human activity
32
New cards
commodity chain
activities involved in the creation of a product: design, production of raw materials, manufacturing and assembly, distribution
33
New cards
global supply chain
a worldwide network to maximize profits in production
34
New cards
Von Thunen Model
helps to explain rural land use by emphasizing the importance of transportation costs associated with distance from the market
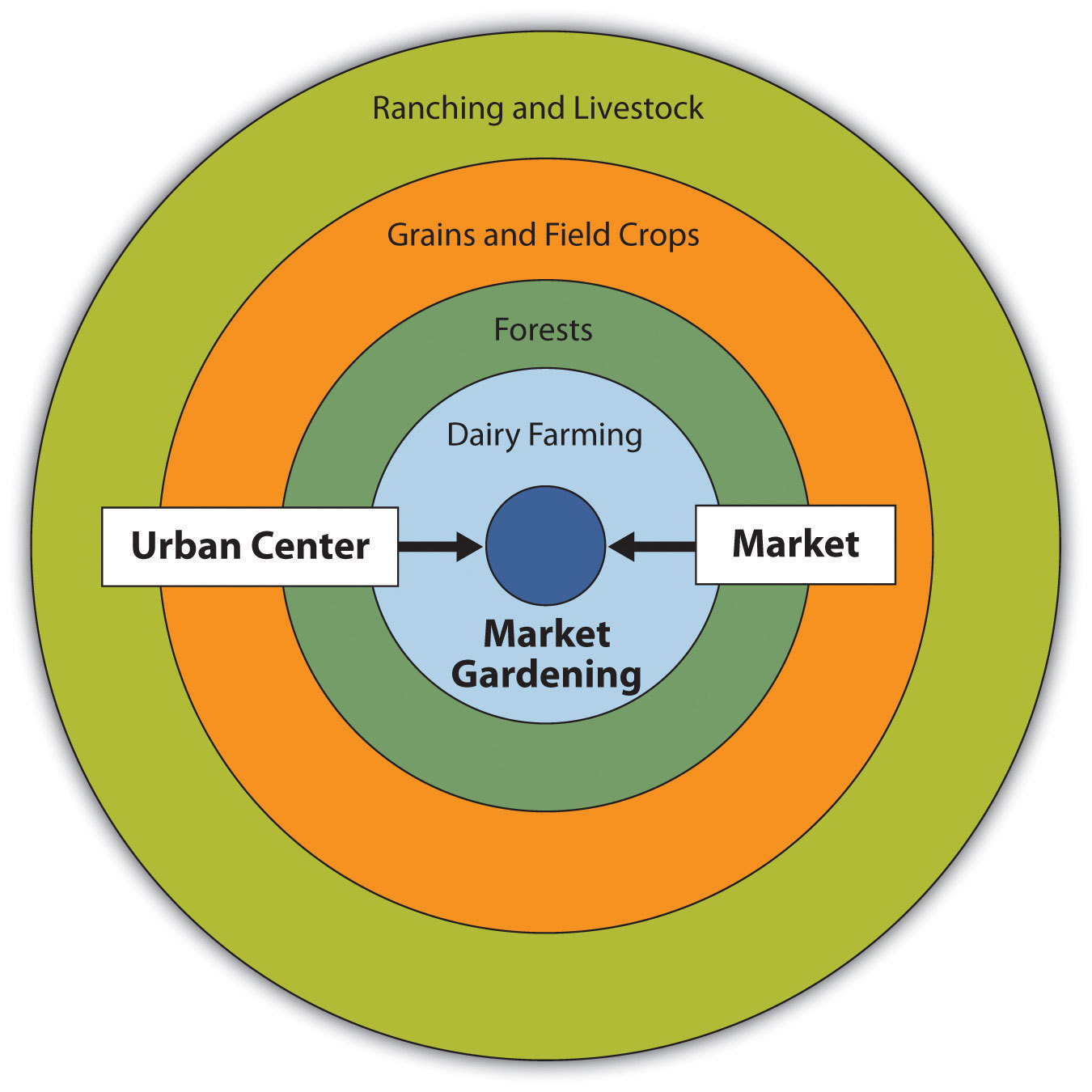
35
New cards
economies of scale
more efficient to own large farms because you can buy supplies in bulk
36
New cards
pollution
process by which soil in contaminated by chemicals
37
New cards
Terraces Farming
flat steps are created on the sides of hills to create more land for farming
38
New cards
irrigation
artificial application of water to land for the facilitation of agriculture
39
New cards
changing diets in LDCs and MDCs
MDCs-growing demand for meat, as well as convenient, processed foods
LDCs- continued demand for meat
LDCs- continued demand for meat
40
New cards
food insecurity
a condition in which people do not have adequate access to food
41
New cards
organic farming
crops produced without the use of synthetic or industrially produced pesticides and fertilizers or genetically engineered seeds
42
New cards
genetically modified organism (GMO)
plants or animals whose DNA has been genetically modified, often through combination of DNA from a similar plant or animal species for desired traits
43
New cards
subsides
public financial support
44
New cards
luxury crops
not essential to human survival but have a high profit margin
45
New cards
single crop economy
Reliance on one crop only
46
New cards
(economic) complementarity
degree to which one place supplies/produces something that another place demands/wants
47
New cards
export commodity
goods sent from one country to another for sale (some countries have become highly dependent on one or more export commodities including Haitian coffee, Sri Lanka tea, and Cuban sugar)
48
New cards
sustainable agriculture
farming that protects natural enviornment
49
New cards
conservation
the protection of wildlife and natural resources
50
New cards
fair trade
trade in which fair prices are paid to producers in developing countries. (high income, sustainable farming)
51
New cards
value added specialty crops
crops transformed from original state to more valuable state.
ex: milk to cheese
ex: milk to cheese
52
New cards
vertical farms
grow crops inside in stackable trays, using greenhouses, artificial lights, and hydroponics.
53
New cards
food deserts
Areas where it is difficult to find affordable, healthy food options. less than a mile
54
New cards
long lot survey system
divided and into narrow parcels stretching back from rivers, roads, or canals giving each household equal access to water resources
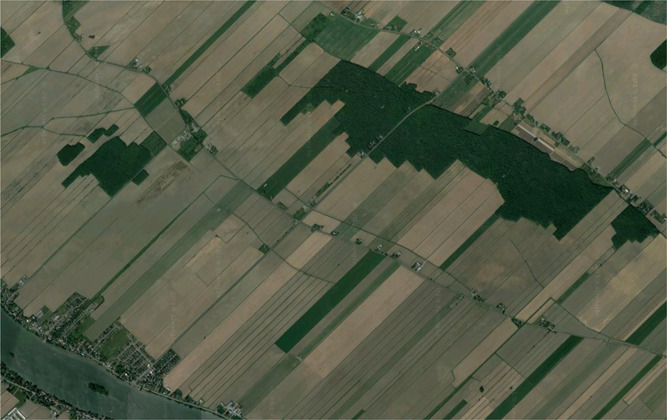

55
New cards
metes and bounds survey system
irregularly shaped tracts of land
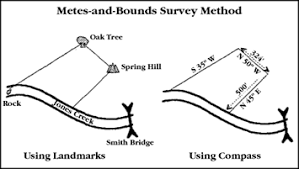
56
New cards
township and range survey system
rectangular survey system- divides the land into a grid like pattern

57
New cards
plantation agriculture-intensive
A plantation specializes in one crop that is transported for sale on the global market.
58
New cards
mixed crop/livestock- intensive
commercial farming characterized by integration of crops and livestock; most of the crops are fed to animals rather than consumed by humans.
59
New cards
nomadic herding-extensive
nomads move herds to different pastures to trade meat, milk, and hides. Rely upon animals for survival, not profit.
60
New cards
commercial grain farming-extensive
crops are grown primarily for human consumption. Farms sell their output to manufacturers of food products, such as breakfast cereals and bread.
61
New cards
agricultural biotechnology
the use of scientific tools and techniques to modify plants and animals (pesticide resistant crops, antibiotics, and biofuels)