chloroplasts and photosynthetic pigments
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Define photosynthesis
The production of carbon compounds in cells using light energy
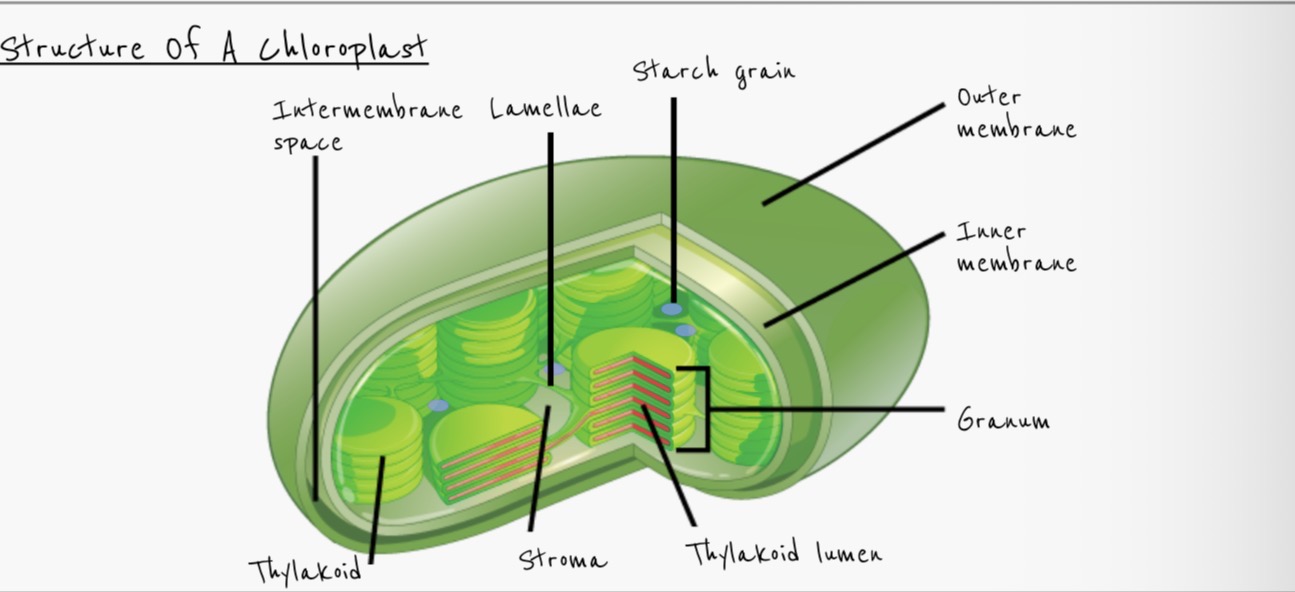
Describe the structure of a chloroplast
thylakoids
Thylakoid space/lumen
Granum
Stroma
Starch grains
Outer and inner membrane
70S ribosome
Circular DNA
How is the thylakoid adapted for its function
large surface area for light absorbing photosystems
Membrane provides site for electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
How is the thylakoid space/lumen adapted for its function
Very small volume so a steep proton gradient builds very fast (for accumulation of protons)
How is the grana adapted for its function
Stack of thylakoid membranes to maximise light absorption
How is the stroma adapted for its function
Contains enzymes used in Calvin cycle/light independent reaction
What is the function of the double membrane of a chloroplast
Allows separation from the rest of the cell
How is the presence of DNA and ribosomes useful in the chloroplasts
For protein synthesis for production of enzymes (eg RUBISCO)
What is the function of the starch grains in chloroplasts
To store carbohydrates produces in photosynthesis
What is a pigment
A substance that absorbs light
What is chlorophyll and how does it aid photosynthesis
pigment responsible for absorbing light
Releases electrons used to produce ATP
What photosynthetic pigments are found in the chloroplast (4)
Chlorophyll a (main pigment)
Chlorophyll b (accessory pigment)
Carotenoids (accessory pigment)
Xanthophylls (accessory pigment)
Where are the photosynthetic pigments found in the chloroplast
In photosystems
Where in a photosystem are accessory pigments found in the chloroplasts
In photosystems
What is the role of pigments in the light harvesting system
absorb light energy from a range of different wavelengths
Transfer energy to reaction centre (containing chlorophyll a)
What is the role of the reaction centre
releases high energy electrons
Used in light dependant stage of photosynthesis
Outline the role of pigments in the process of photosynthesis
pigments in photosystems absorb light energy
Light energy excites electrons
Energy passed from pigment to pigments
Energy reaches reaction centre where chlorophyll a is found
Accessory pigments allow for wider range of wavelengths to be absorbed
Compare chlorophyll’s absorption in the different parts of the visible spectrum
absorbs blue light most strongly, also absorbs red light
Reflects green light
Describe what an absorptionspectrum shows
Wavelengths of light absorbed by each pigment
Describe the shape of a photosynthesis action spectrum
graph shows overall rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength of light
Maximum at blue light, then red light
Lowest at green light
Define action spectrum
Graph showing overall rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength of light
Distinguish between absorption spectrum and action spectrum
absorption spectrum - wavelengths of light absorbed by each
Action spectrum - overall rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength
How can mixtures of photosynthetic pigments be separated
Chromatography
Describe the process of chromatography to separate coloured pigments
Place Spot of sample on pencil line on chromatography paper/plate
Repeat to concentrate extract
Suspend paper in suitable solvent (Solvent below base line)
Let solvent move up paper, remove before solvent reaches top
Mark solvent front
Calculate Rf value
Compare with data book value for Rf
Give a suitable solvent for extracting photosynthetic pigments from plant tissues
propanone
Alcohol
Ether