Restorative Art 1 Final
1/315
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
316 Terms
restorative art
the care of the deceased to recreate natural form and color
form
refers to the general shape; it includes various dimensions such as length, width, and projection
color
refers to those rays of light reflected from the surface
physiognomy
the study of the structures and surface markings of the face and features
norm
the most common characteristics of each feature; typical, common, average
anatomical position
the erect position of the body with face directed forward, the arms at the side, and the palms of the hands facing forward
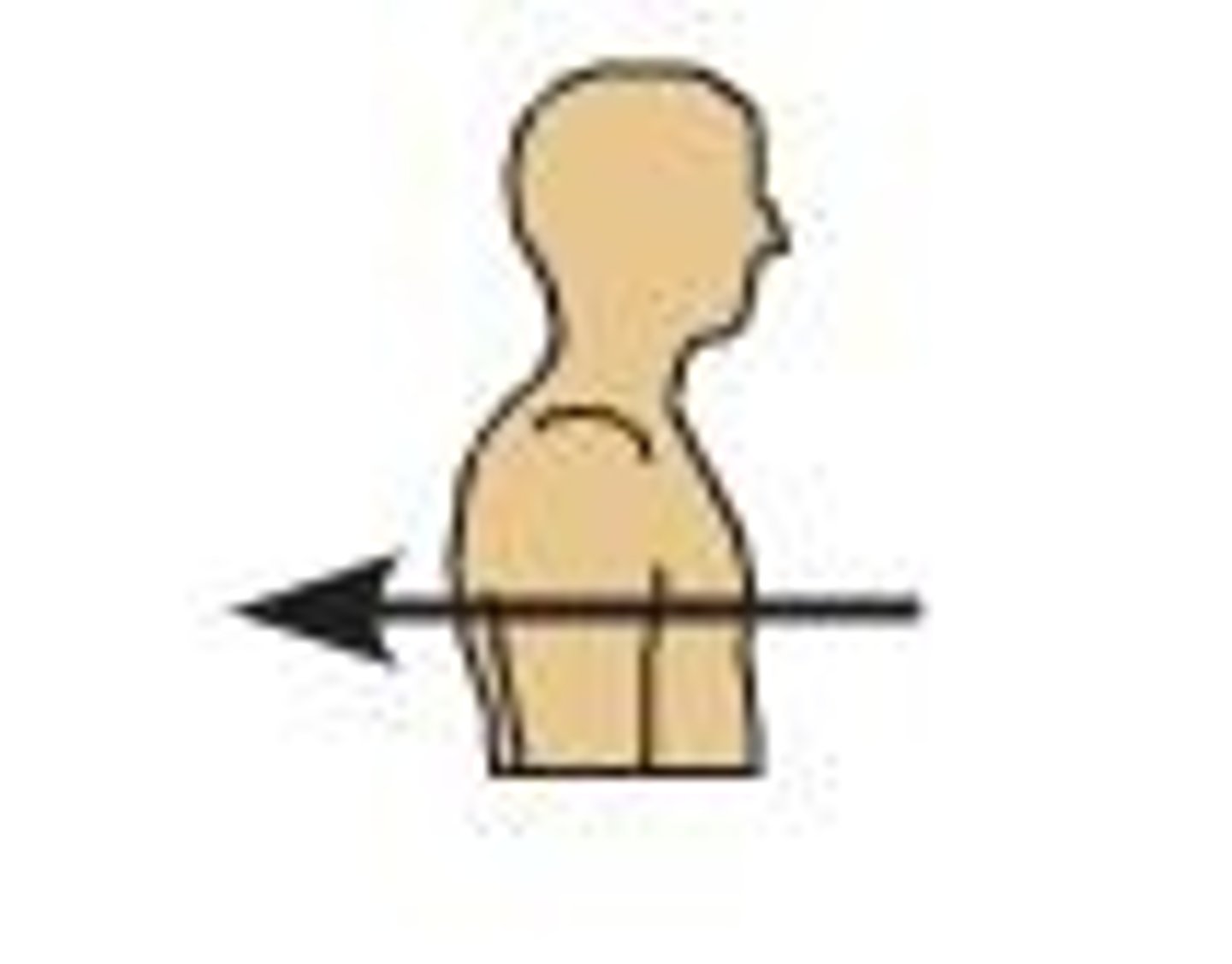
anterior (ventral)
describes the front or direction toward the front of the body
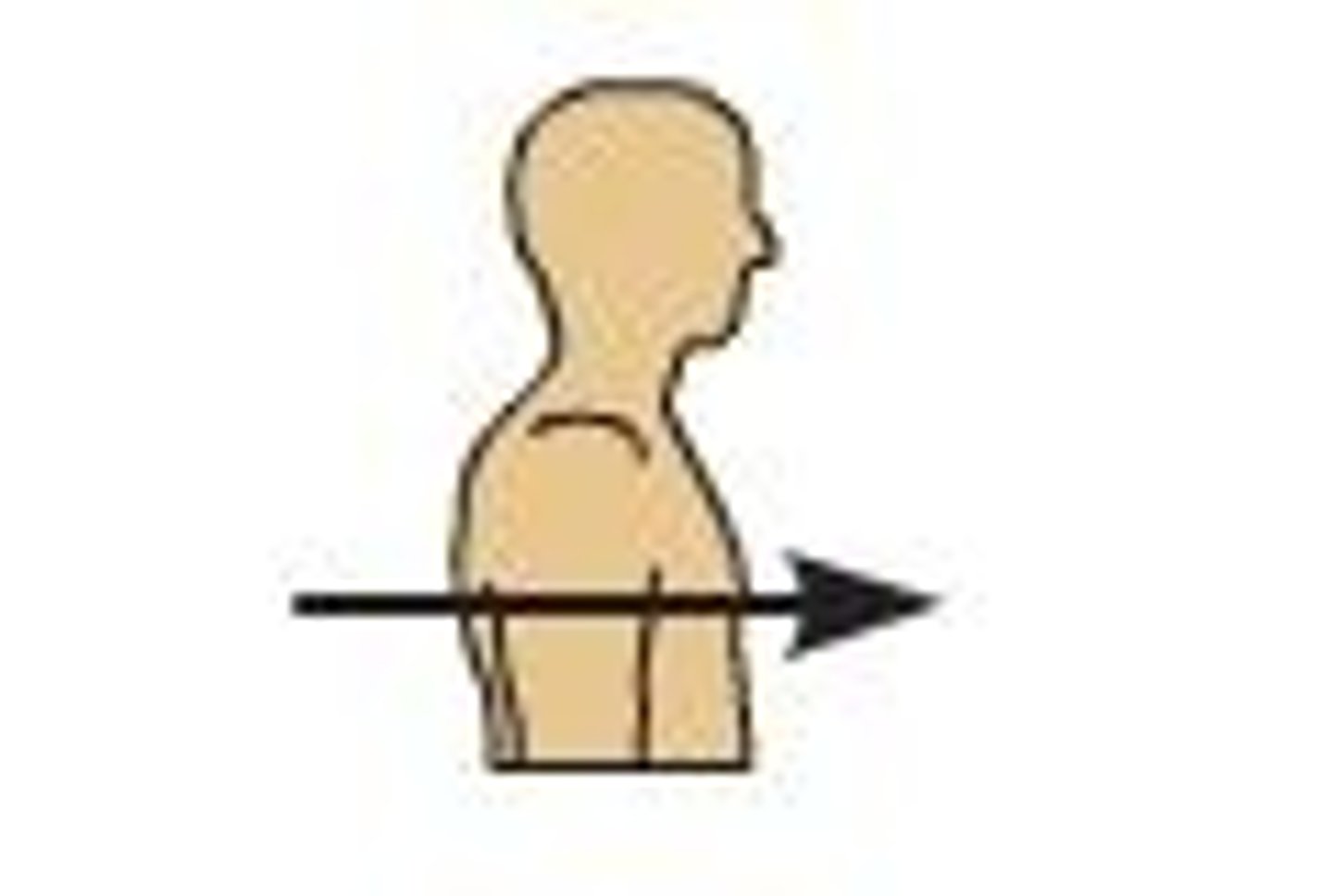
posterior (dorsal)
describes the back or direction toward the back of the body
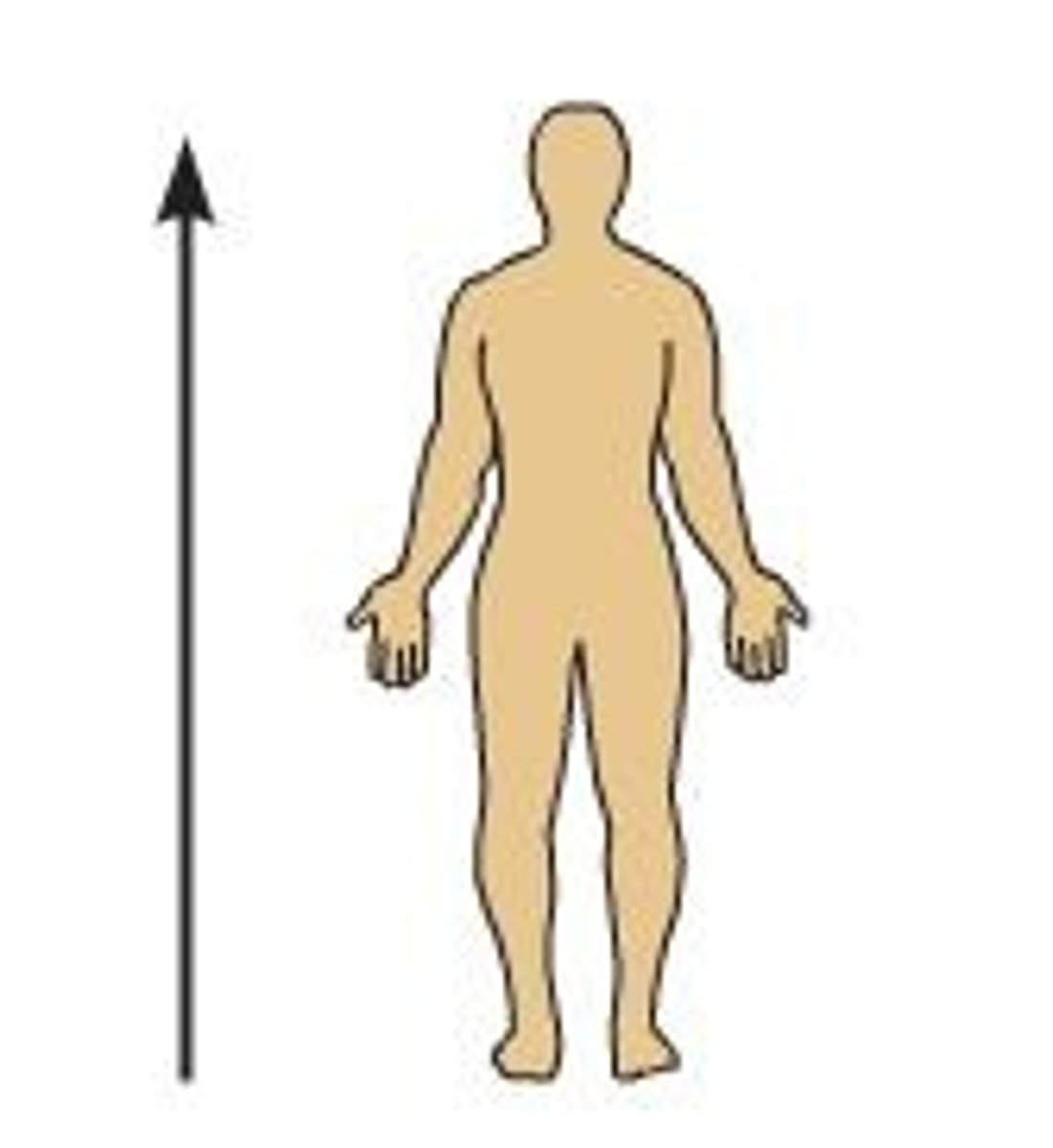
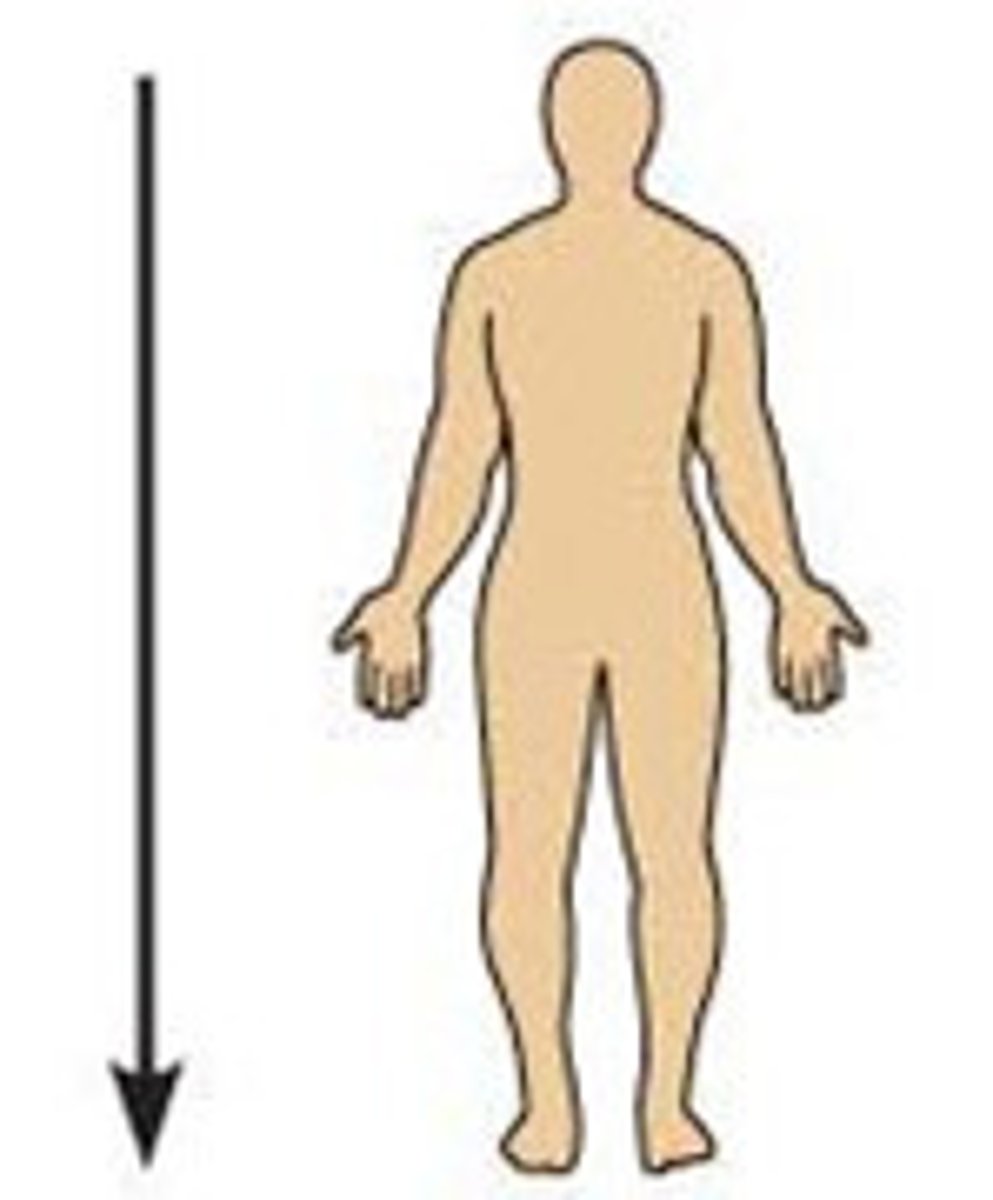
superior (cranial)
describes a position above or higher than another part of the body proper
inferior (caudal)
describes a position below or lower than another part of the body
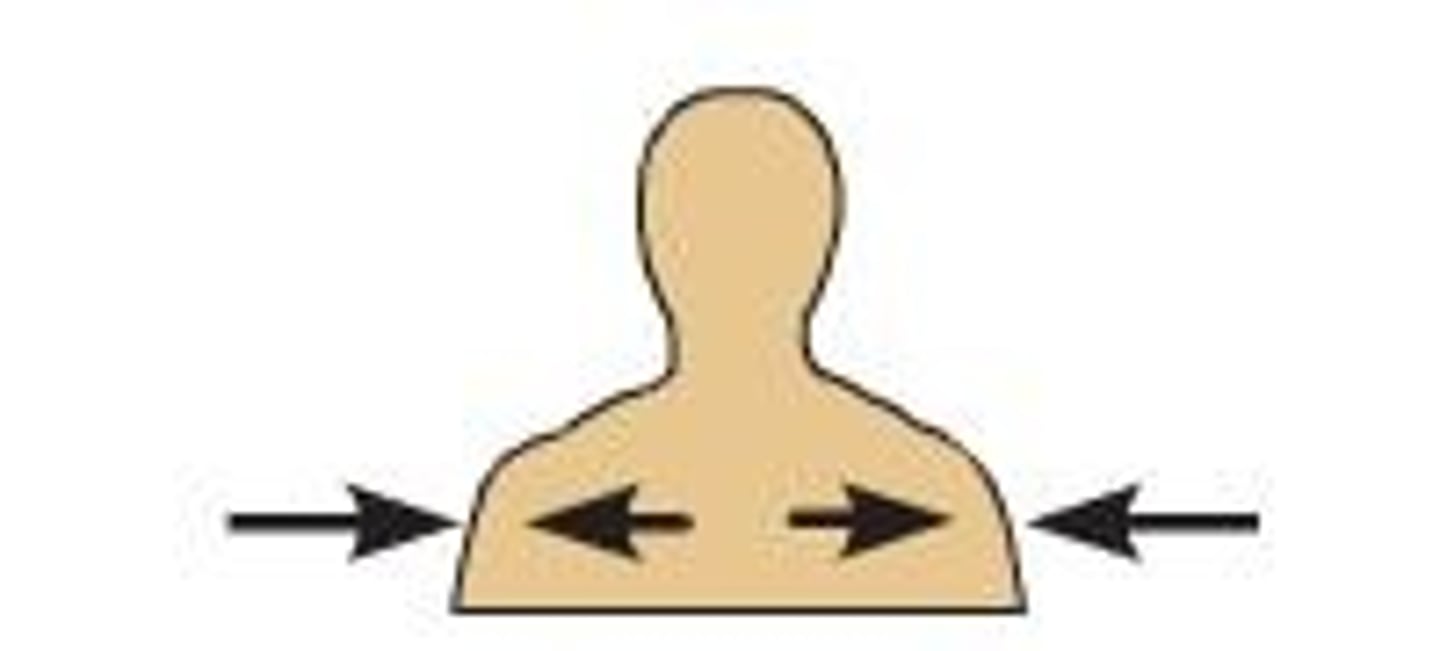
medial
describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body
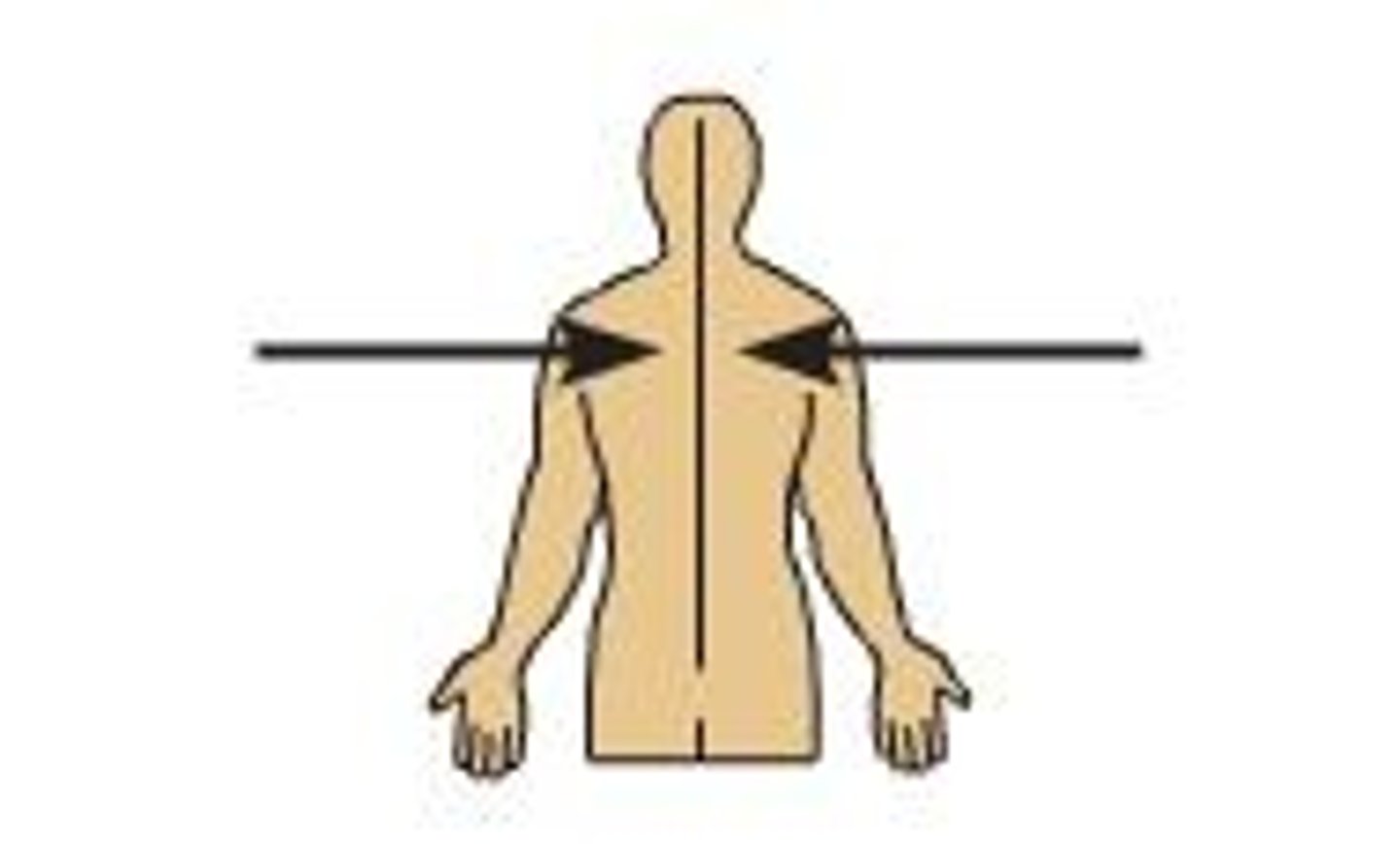
lateral
describes the side or direction toward the side of the body
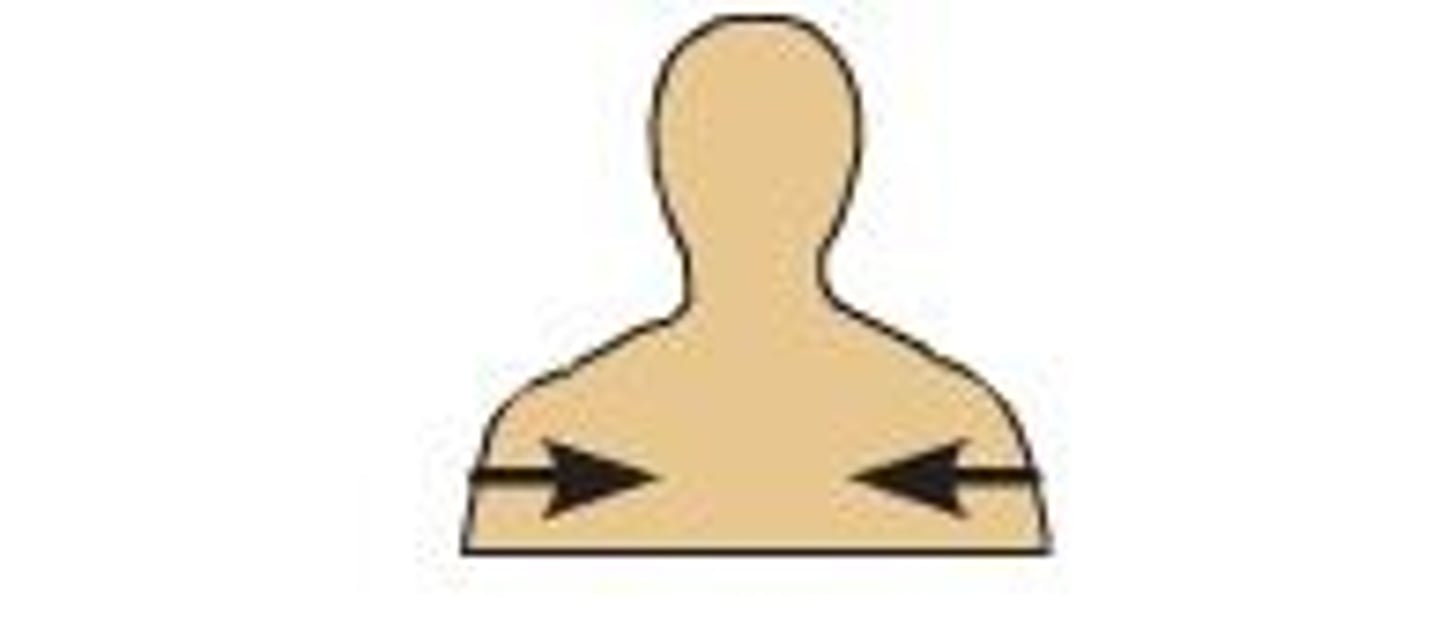
superficial
describes a position closer to the surface of the body
deep
describes a position farther from the surface of the body
concave
exhibiting a depression, a hollow surface; a surface exhibiting an inward curve
convex
having an outline or surface curved like the exterior of a circle or sphere.
projection
a feature or part extending beyond the level of its surroundings
recession
a feature or part withdrawn within the level of its surroundings
depression
a hollow or shallow concave area in a surface
protrusion
the state of being projected beyond a surrounding surface
bilateral
having or relating to two sides
frontal
from the front
profile
an outline of something, especially a person's face, as seen from one side
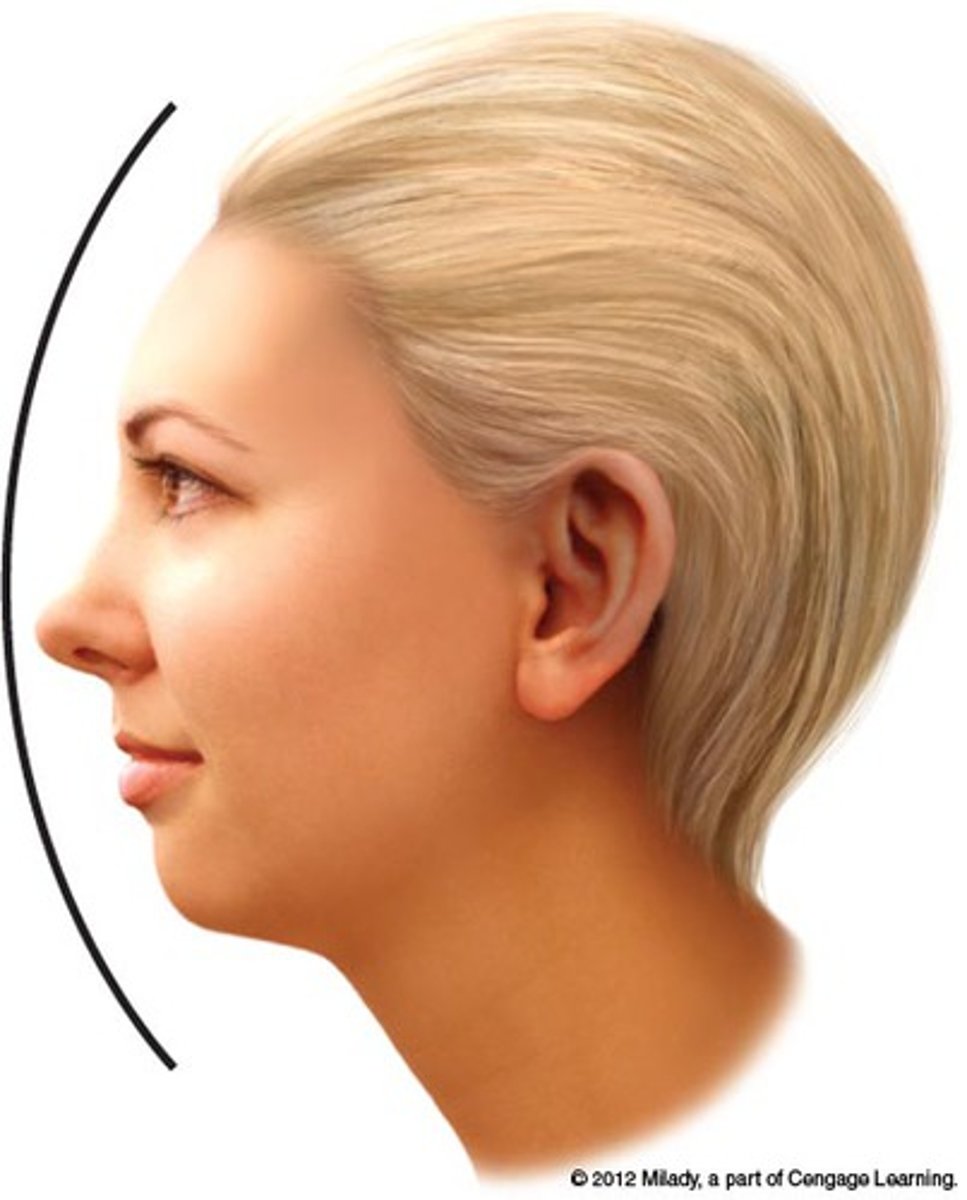
inclination
a slope or a slant; deviation from the vertical or horizontal
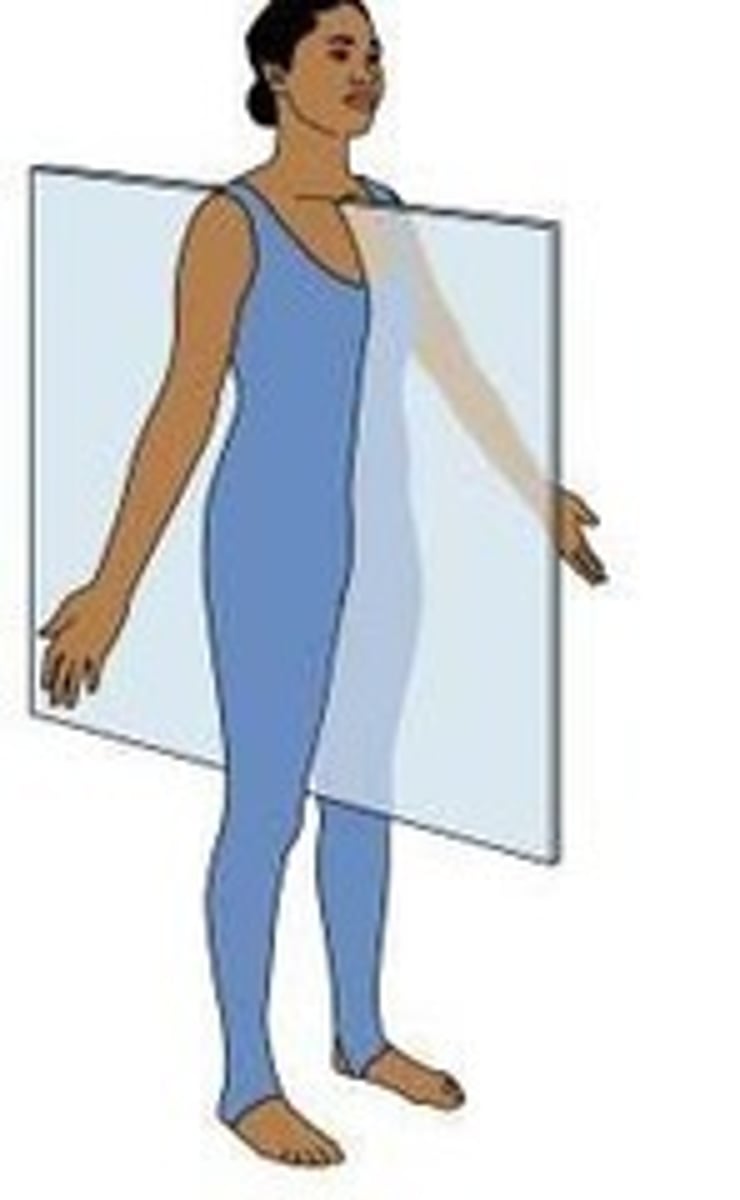
medial plane (mid-sagittal)
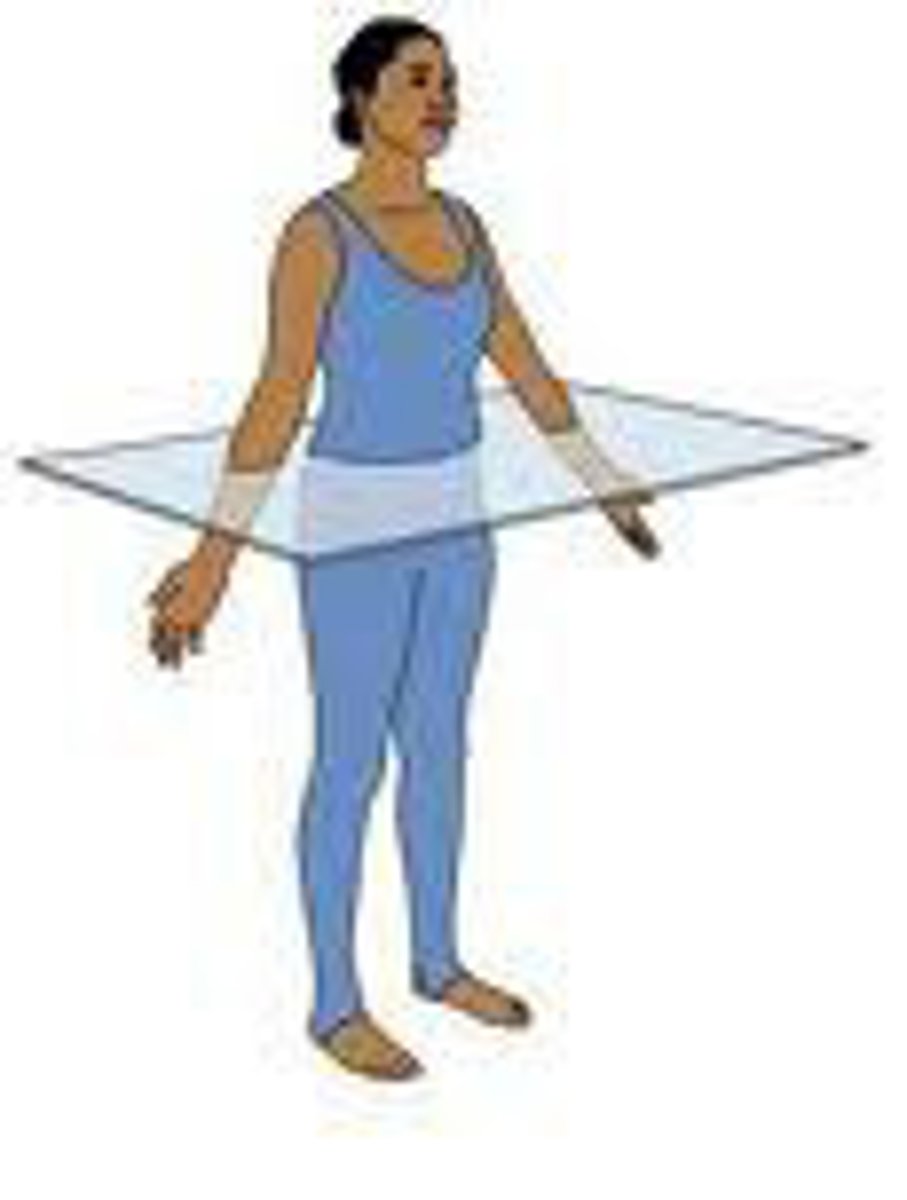
horizontal plane (transverse)
oblique plane
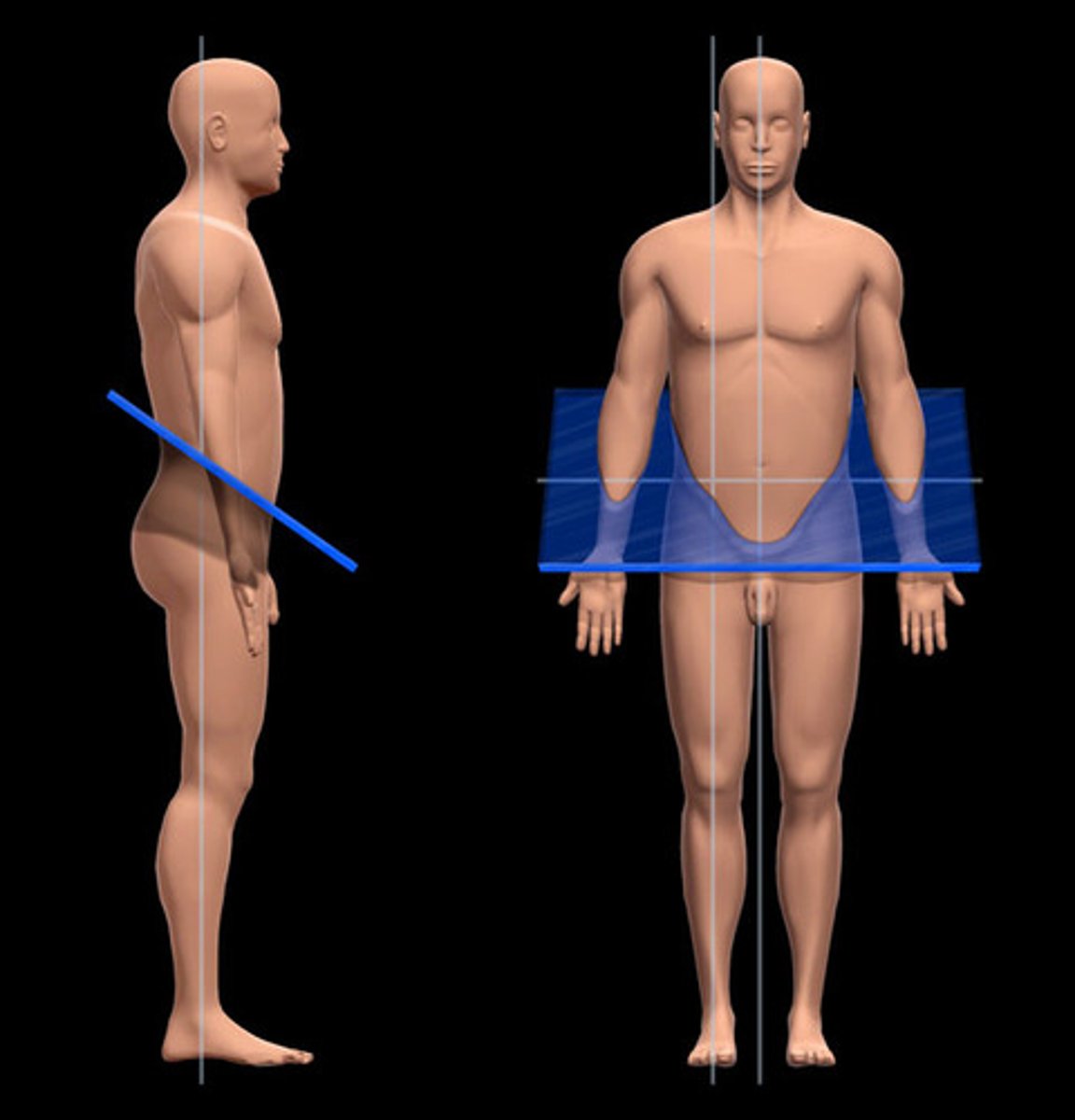
frontal plane (coronal)

major restoration
a restoration requiring a long period of time, extensive in nature, and requiring advanced technical skill
minor restoration
a restoration requiring minimum time, effort, and skill to complete
symmetry
correspondence in size, shape, form, and relative position of parts that are on opposite sides of the face
2/3 rule
unless at least two-thirds of the facial structures remain intact, no restoration is ordinarily attempted
• Major restorations - outside the norm
• Extra invasive procedures
when to request authorization for restorative work:
• moles
• warts
• scars
• birthmarks
characteristics that are typically NOT concealed:
Dr. Thomas Holmes
Modern restorative techniques in North America were influenced by the result of the embalming techniques developed by:
Joel E. Crandall
published information about new techniques and included before and after photographs of mutilated remains; founded the science of restorative art as we know it
Egyptians
the roots of restorative art can be traced back to the _______________
restorative waxes
a significant development took place in the mid-1920s when embalming chemical companies made available ______________ ________
oval
the geometric form of the skull (viewed from the top, front, and side)
puberty
the male and female skulls remain similar in development until ____________
10%
the female skull is lighter and smaller, by about ____%
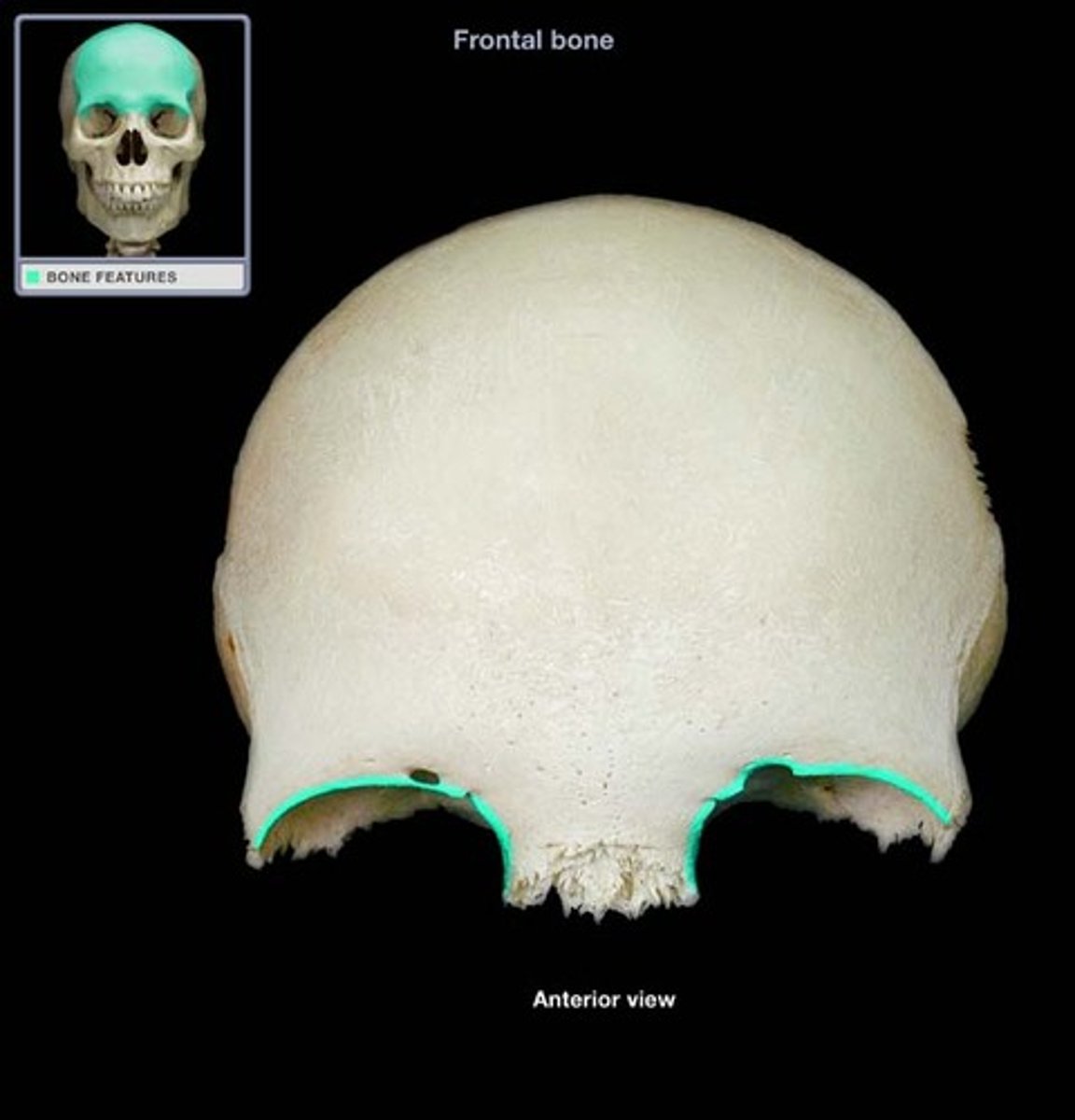
coronal, lambdoidal, and squamosal
the three major sutures of the adult skull:
fontanelles
"soft spots"; spaces that exist to help the baby be born physically, these regions also permit growth of the brain and skull during early childhood
seven
the infant skull has __________ bones
two
sutures remain flexible, giving a baby's brain time to grow until the bones fuse at about age ______
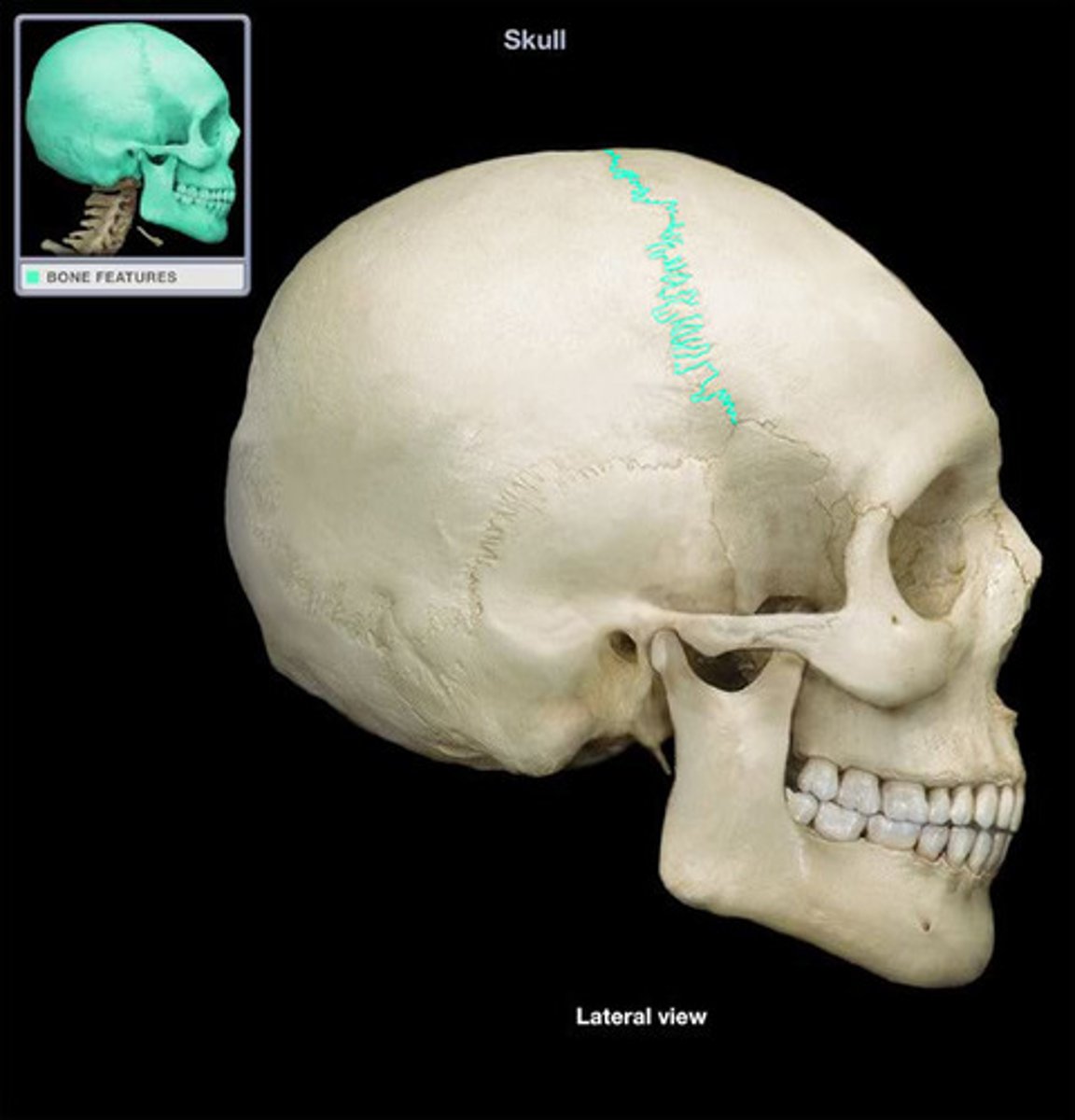
coronal suture
junction between frontal and parietal bones
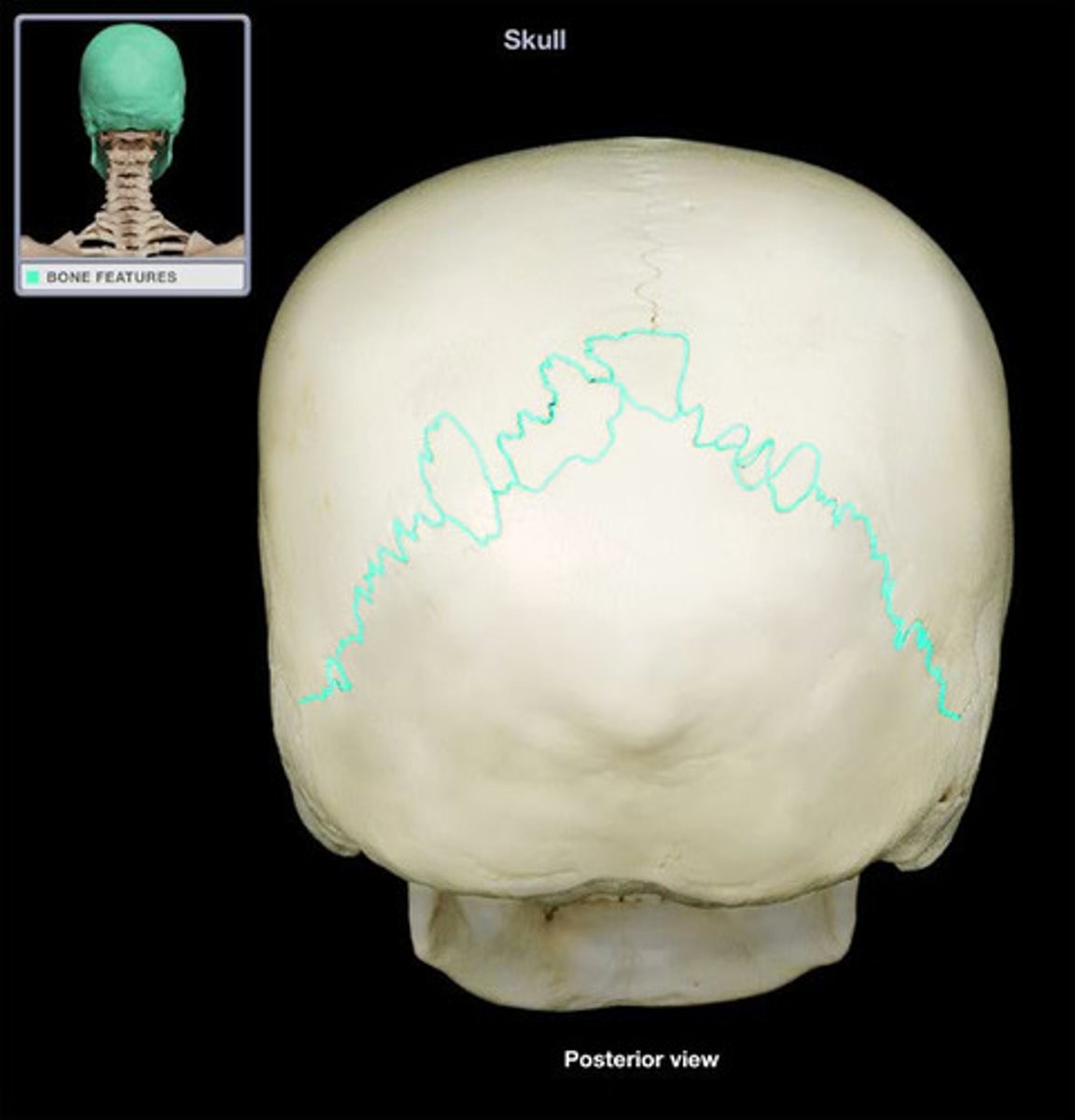
lambdoidal suture
junction between the parietal and occipital bones
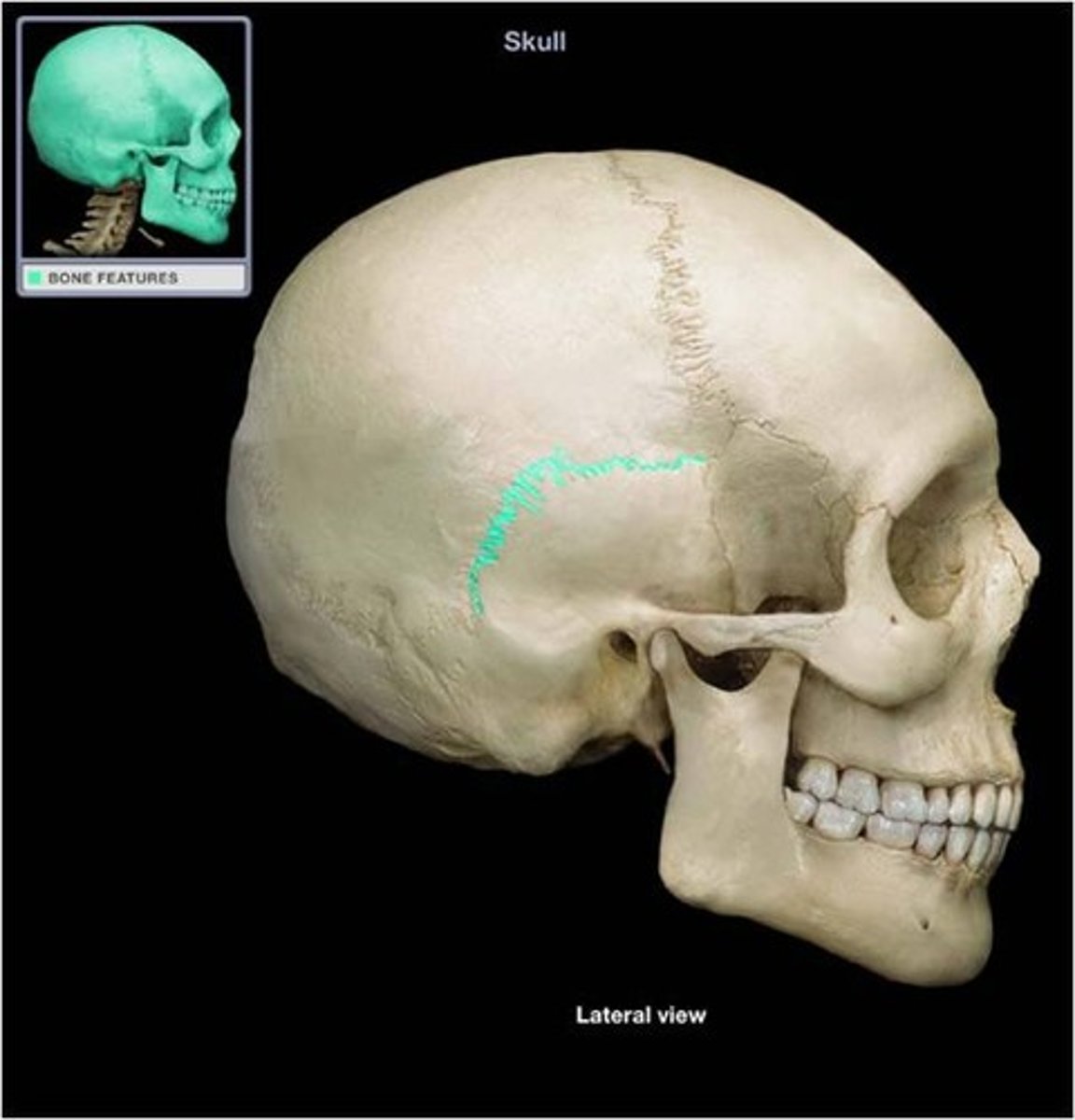
squamosal suture
junction between the parietal and temporal bones
jaws
the most obvious characteristic of old age is the reduction of the size of the upper and lower ________
unpaired
occipital bone: paired or unpaired?
paired
parietal bone: paired or unpaired?
paired
temporal bone: paired or unpaired?
unpaired
frontal bone: paired or unpaired?
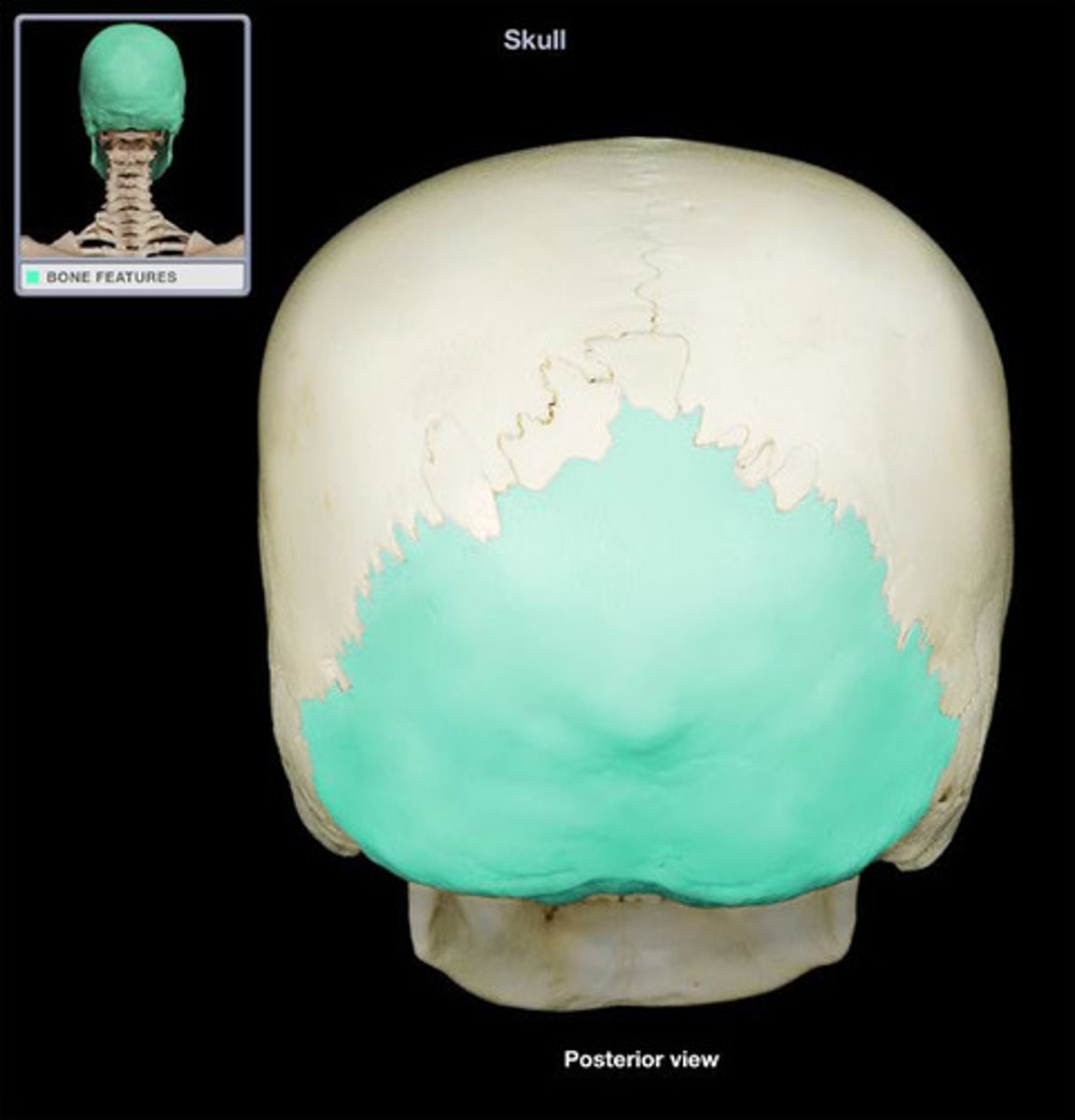
occipital bone
the lowest part of the back and base of the cranium, forming a cradle for the brain
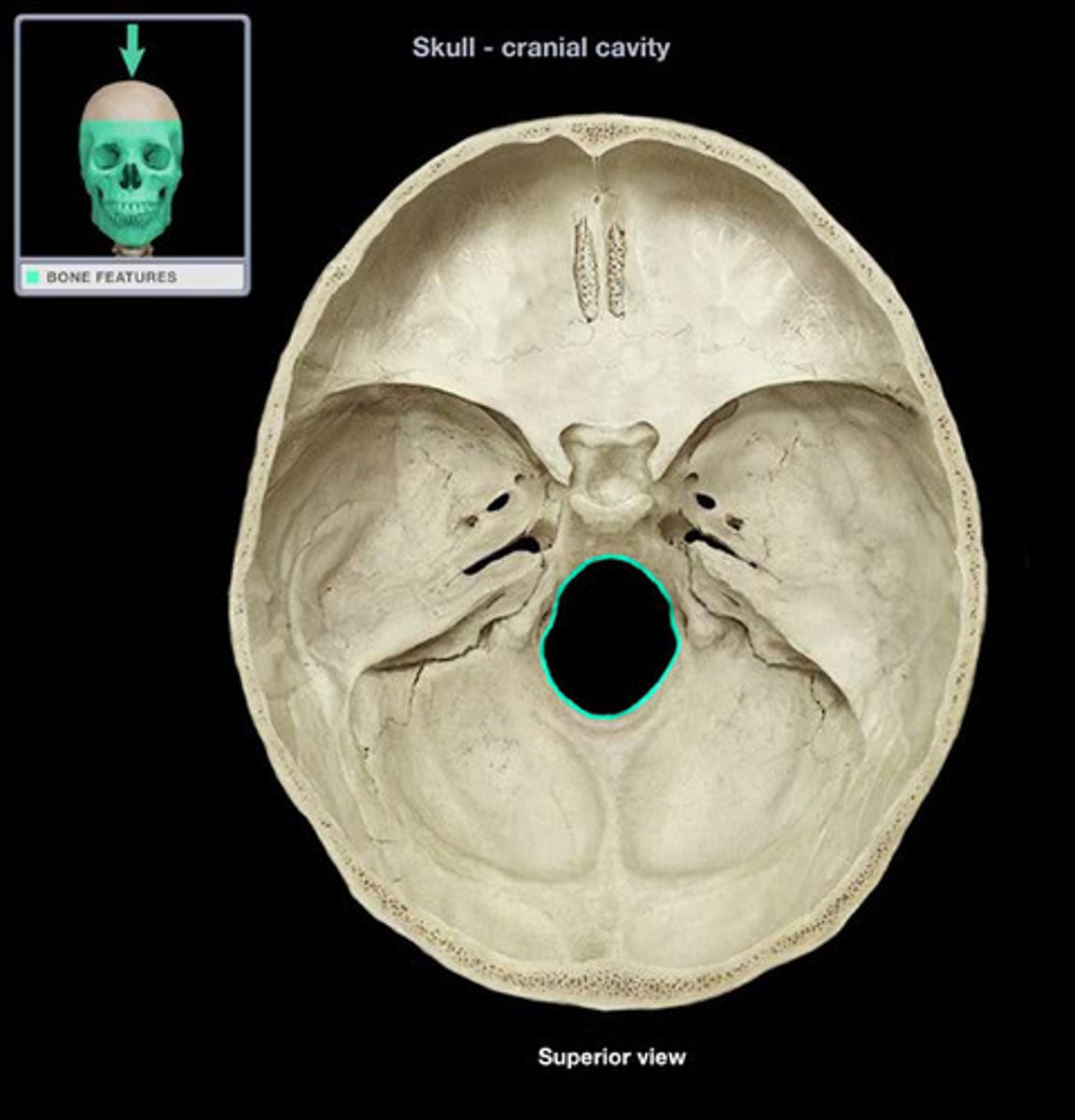
foramen magnum
opening in the occipital bone through which the spinal cord passes
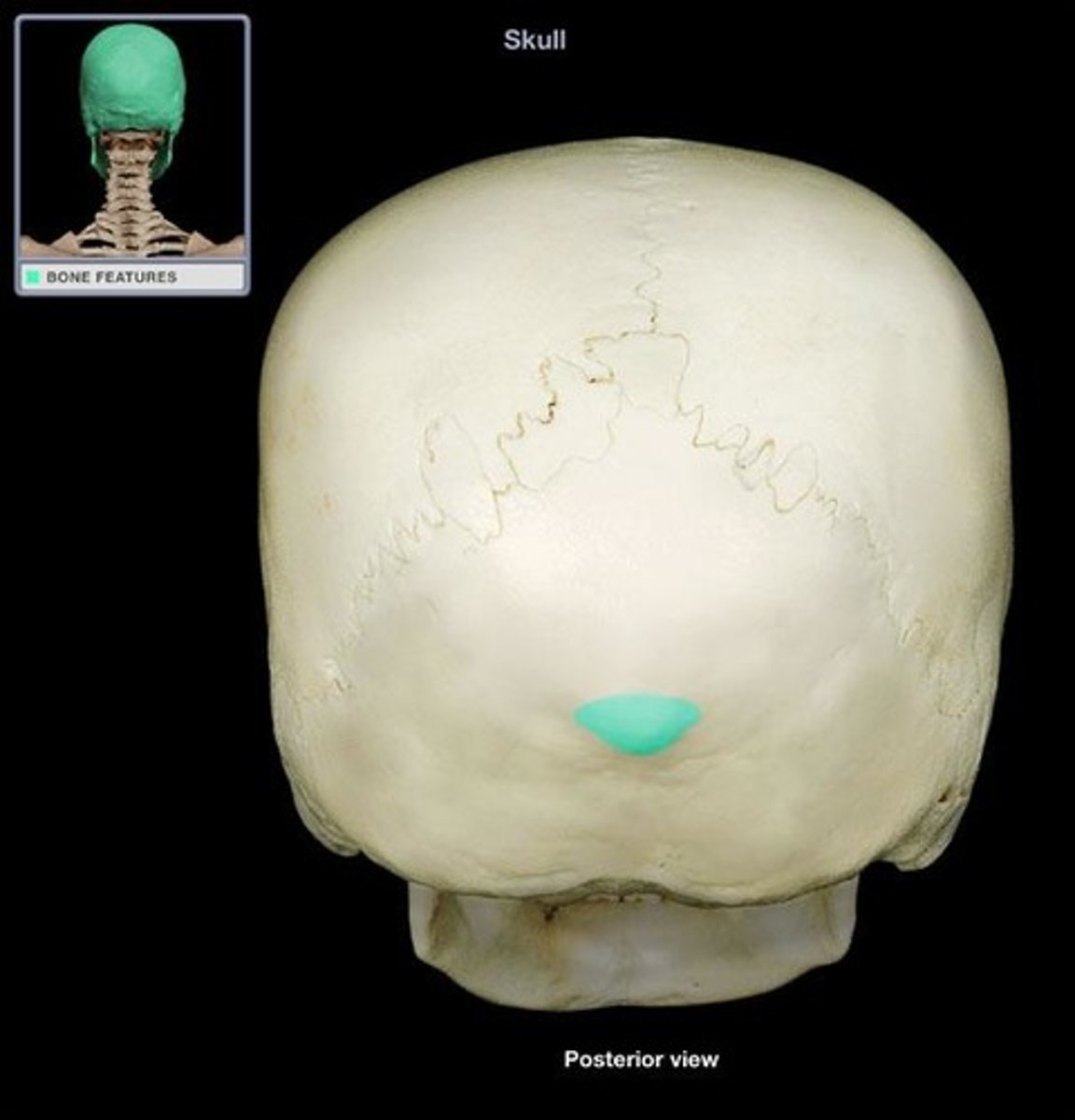
occipital protuberance
the prominence at the center of the external surface of the occipital bone
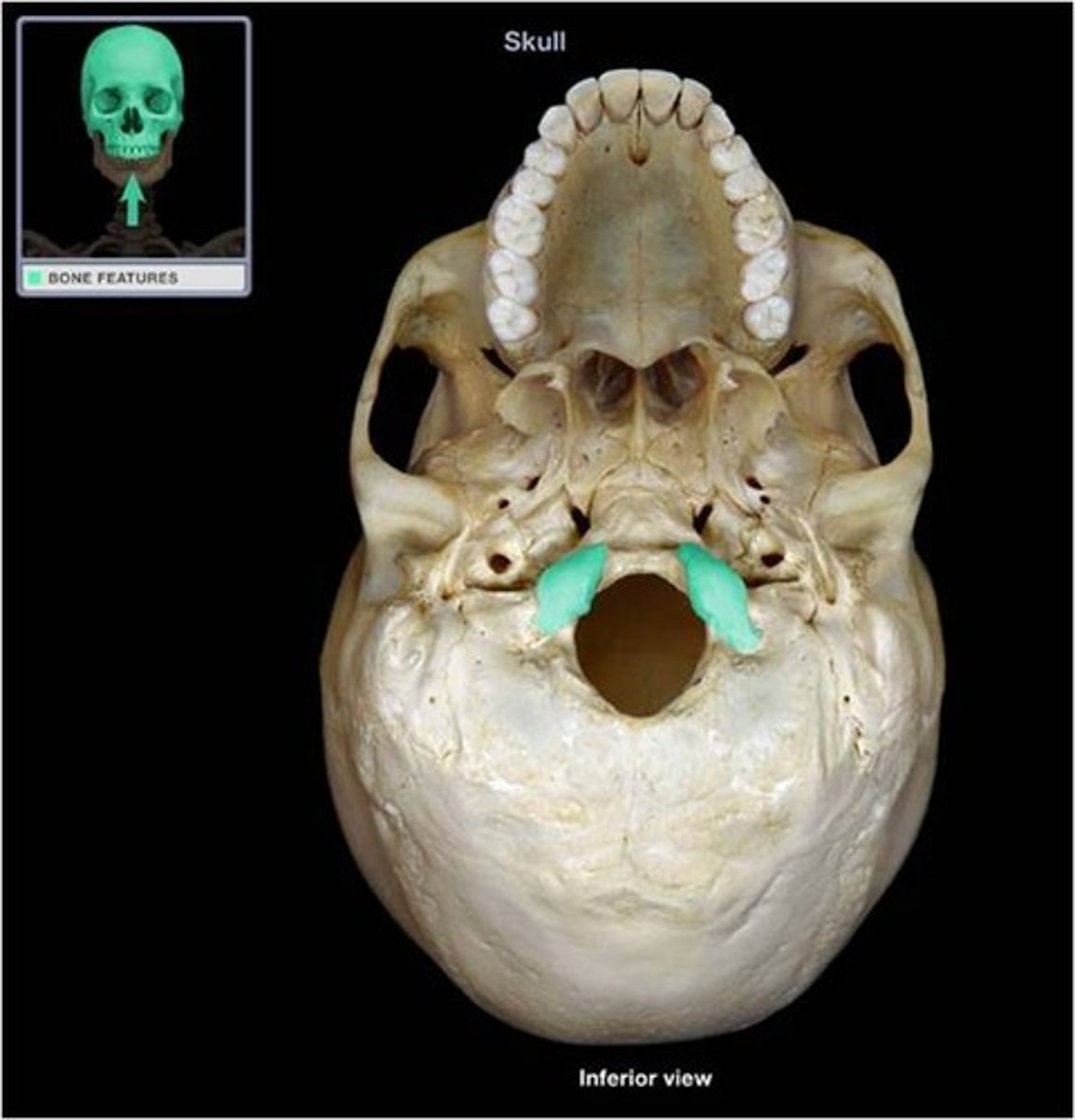
occipital condyles
each of two rounded knobs on the occipital bone that form a joint with the first cervical vertebra.
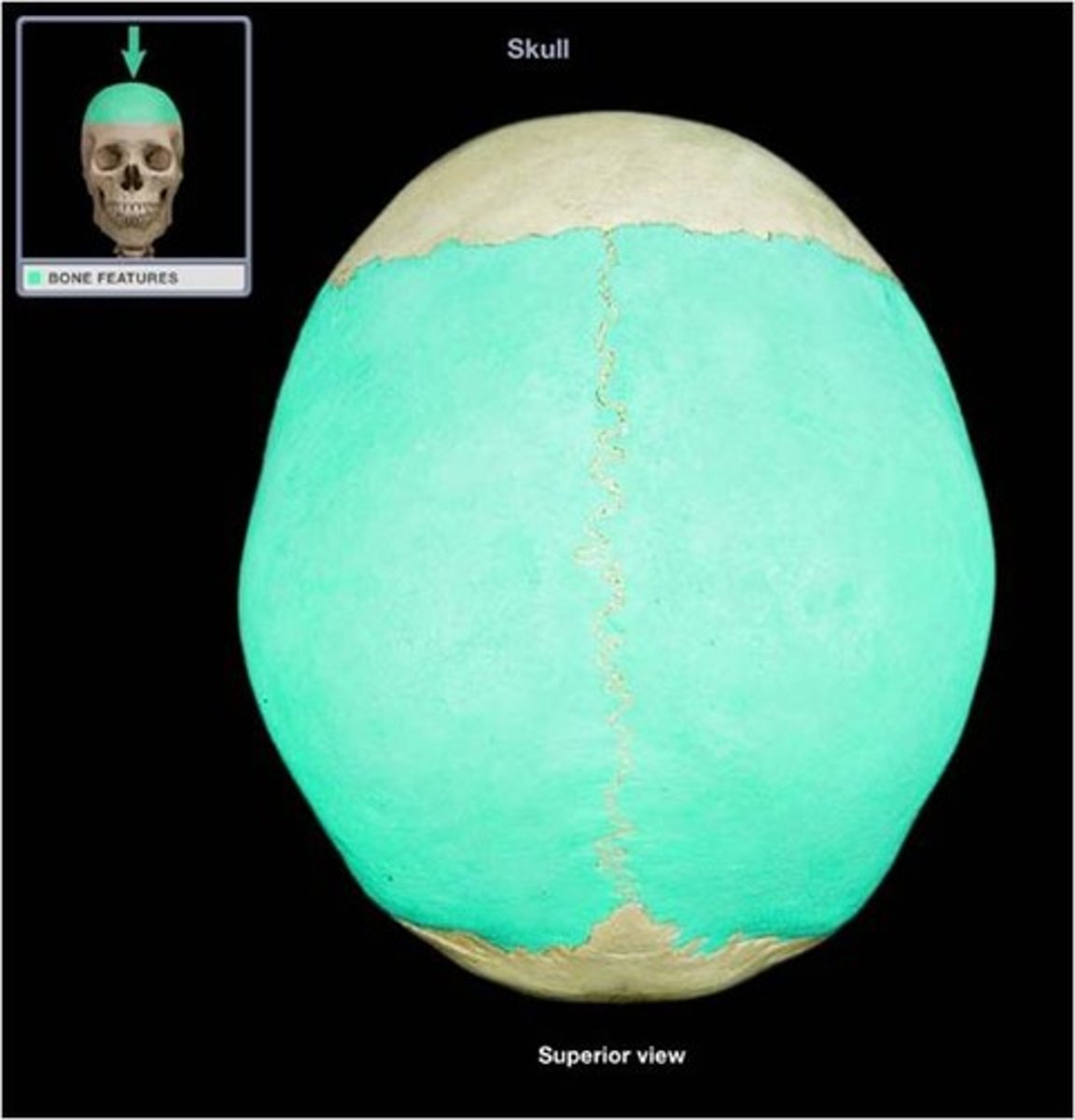
parietal bones (2)
the superior portion of the sides and back of the cranium, as well as the posterior two-thirds of the roof of the cranium
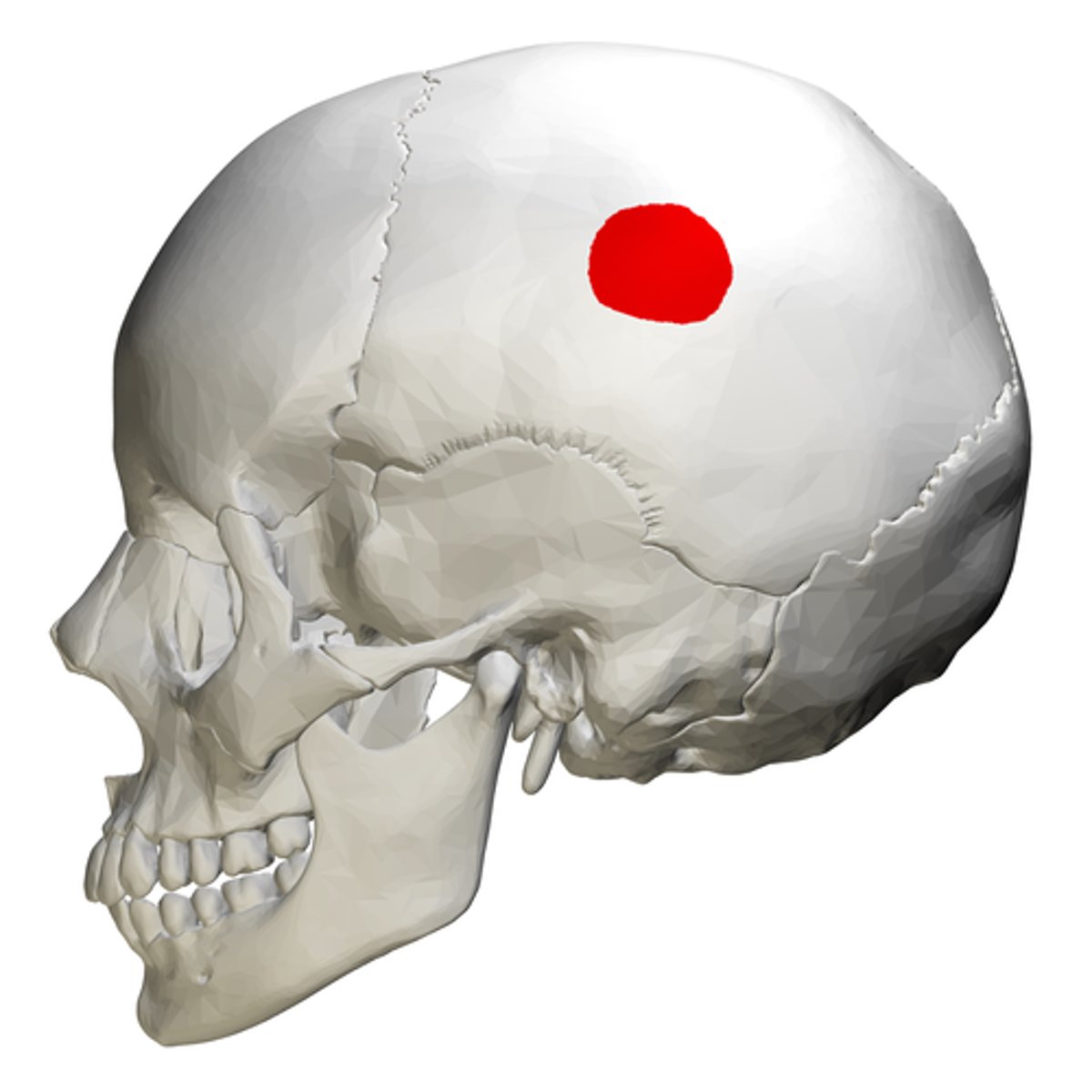
parietal eminence
the rounded peak of the external convexity of the parietal bones; determines the widest part of the cranium (note: may be helpful when attaching the modeled ear to the side of the cranium)
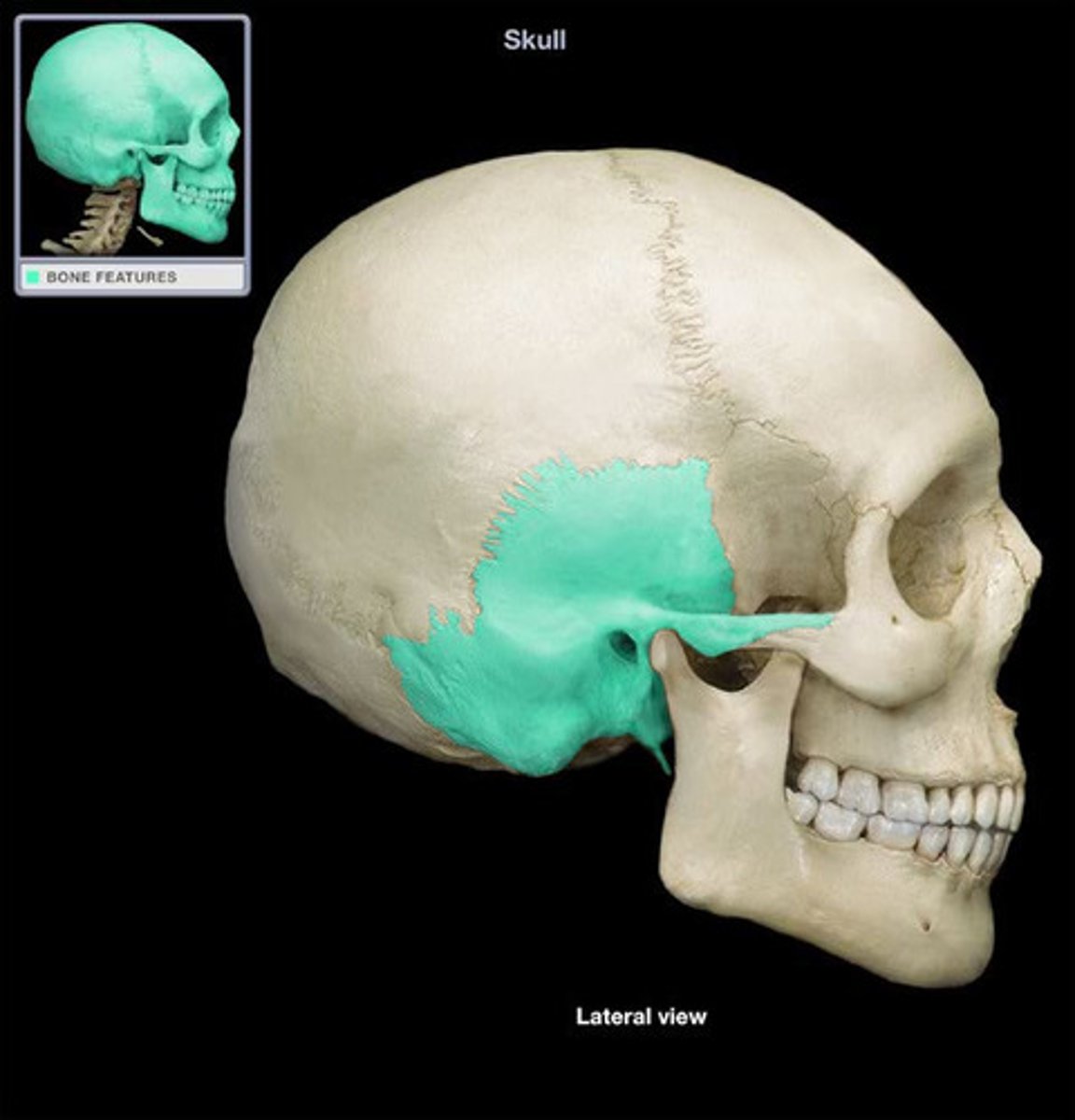
temporal bones (2)
the inferior portion of the sides and base of the cranium, inferior to the parietal bones and anterior to the occipital bone
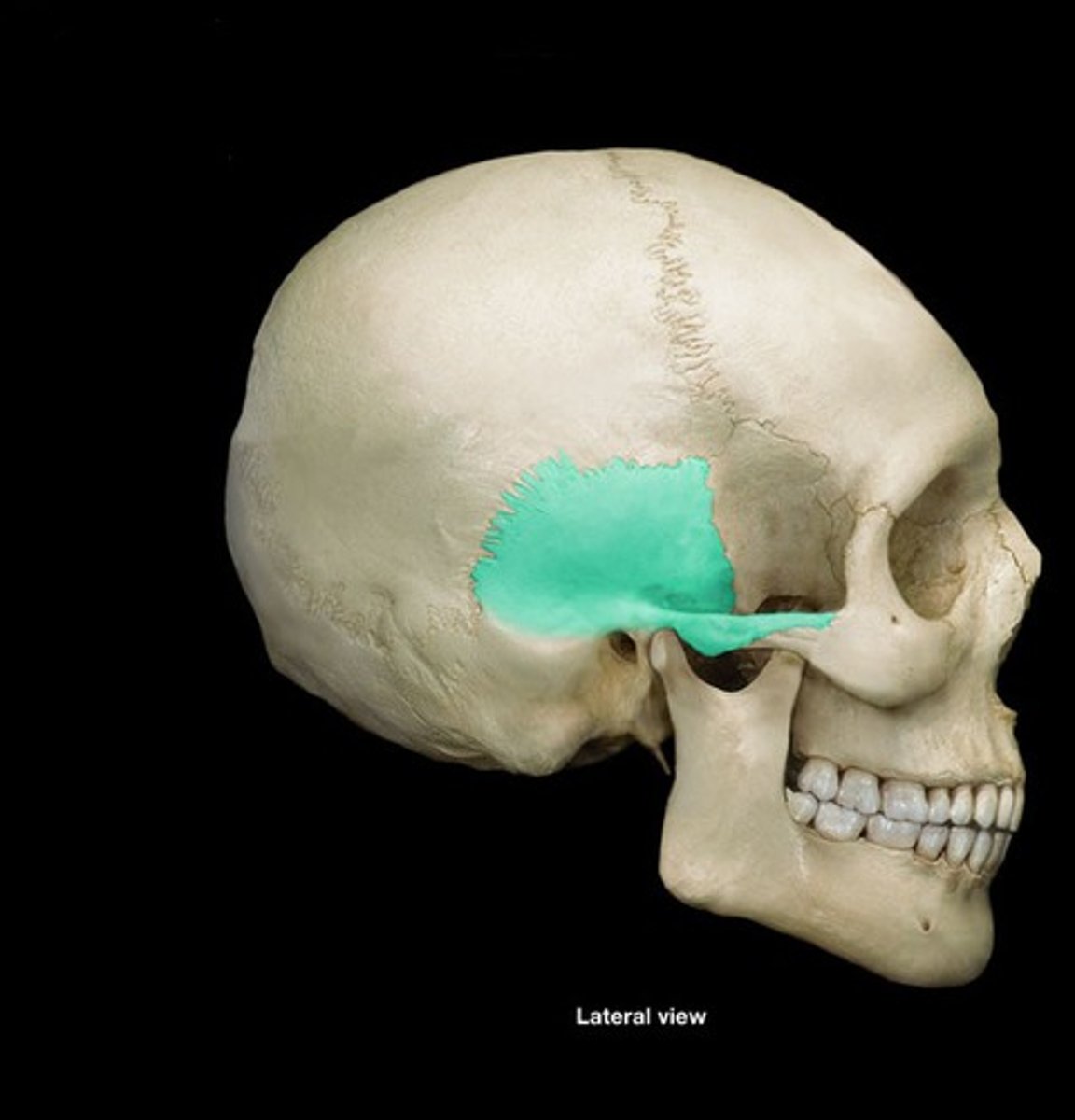
squama
the vertical surface of the temporal bone
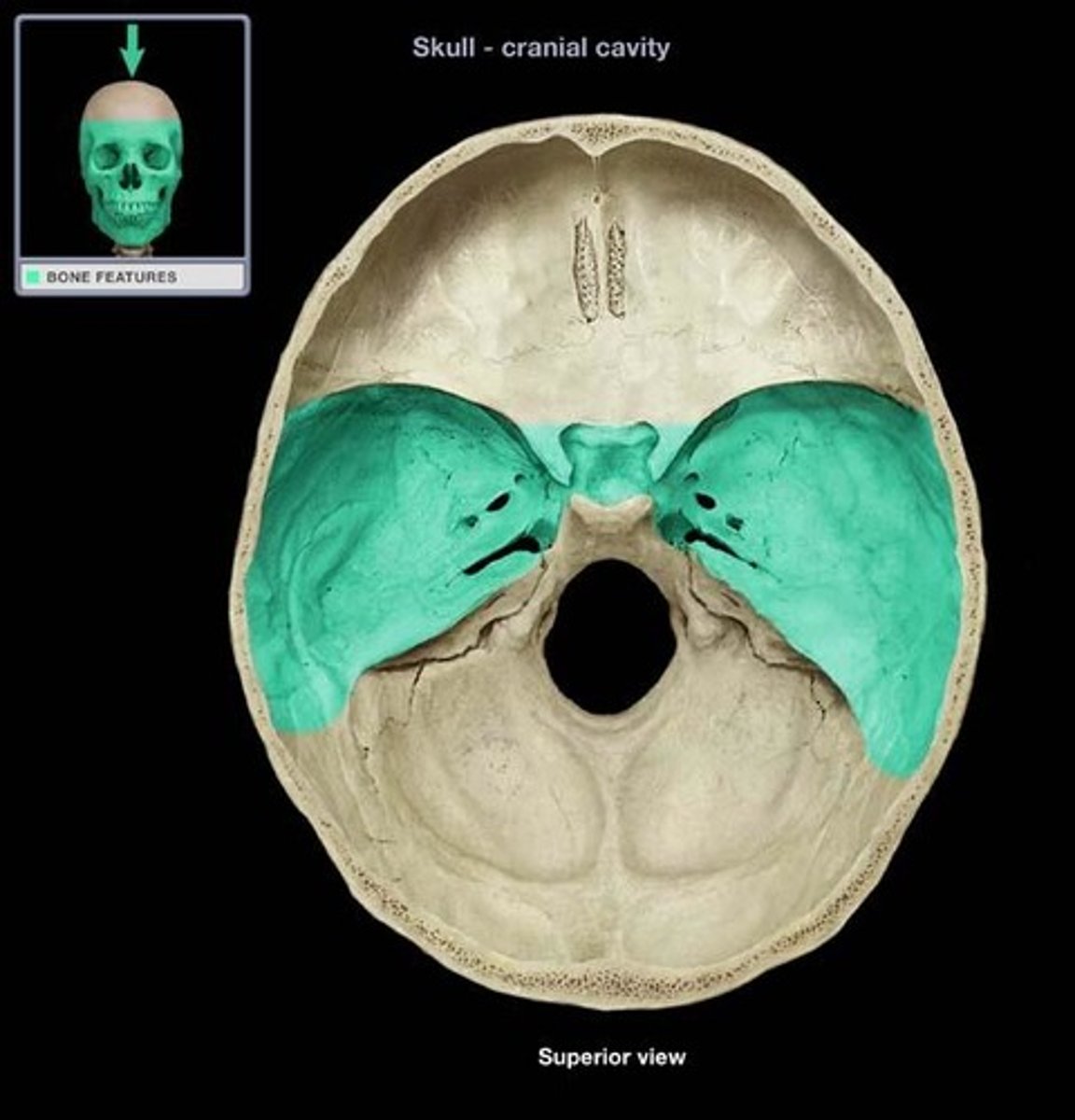
temporal cavity
the concave surface of the head overlying the temporal bone
1. external auditory meatus
2. zygomatic arch
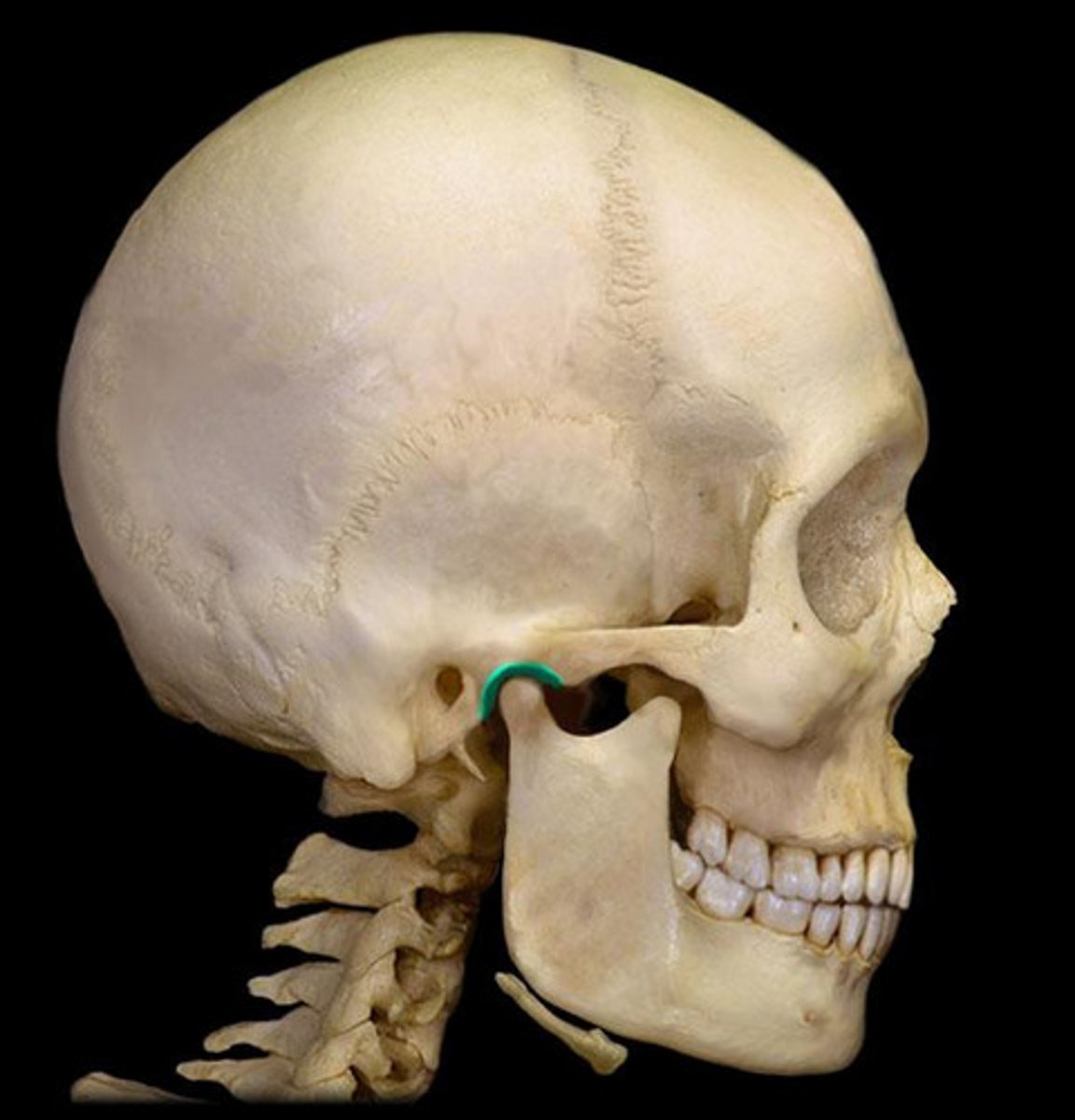
3. mandibular fossa
4. mastoid process
anatomical structures (4) of the temporal bone used for locating the modeled ear:
external auditory meatus
ear passage; deep hole located on the inferior portion of the medial 1/3 of the ear on the anterior border
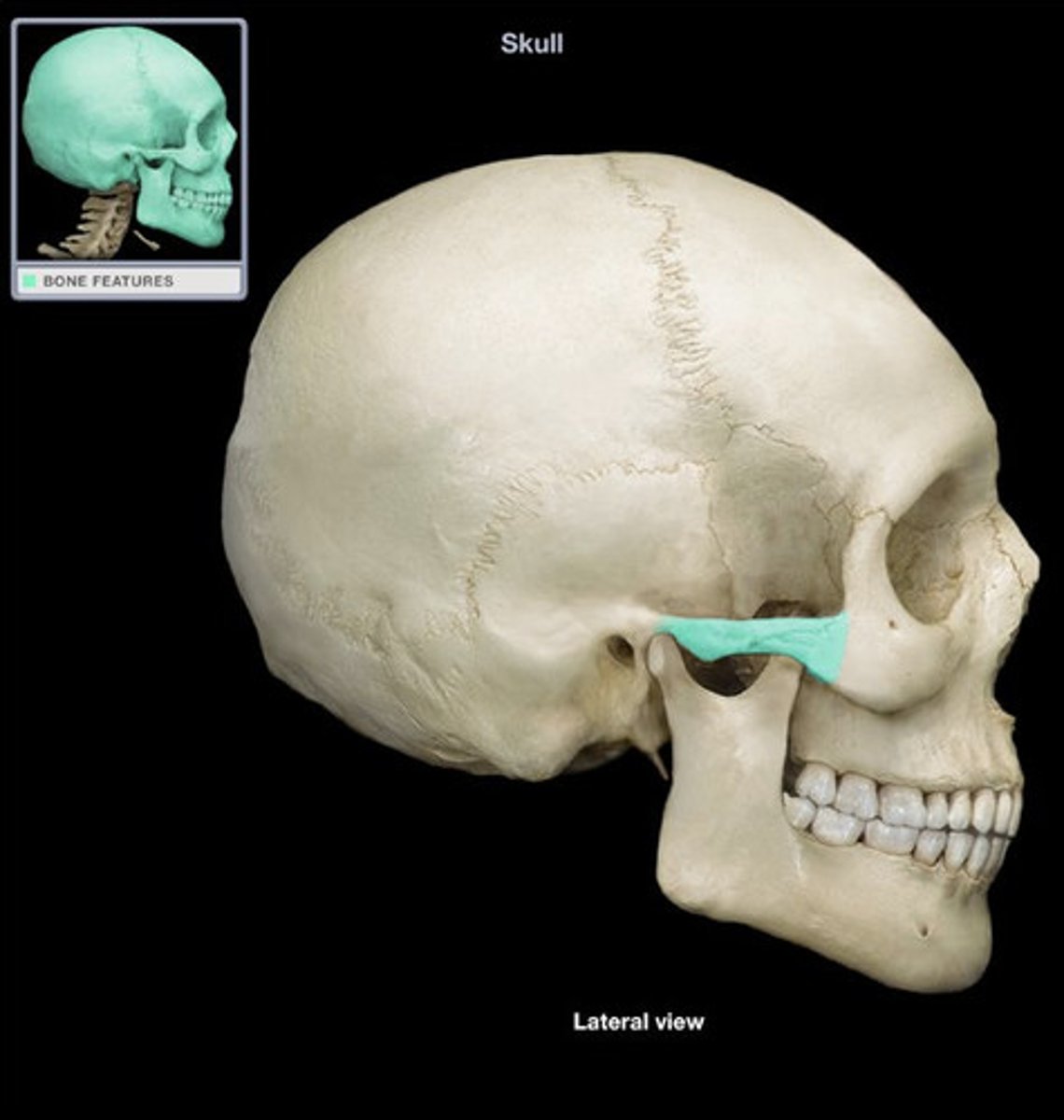
zygomatic arch
the processes on the temporal and zygomatic bones; determines the widest part of the face
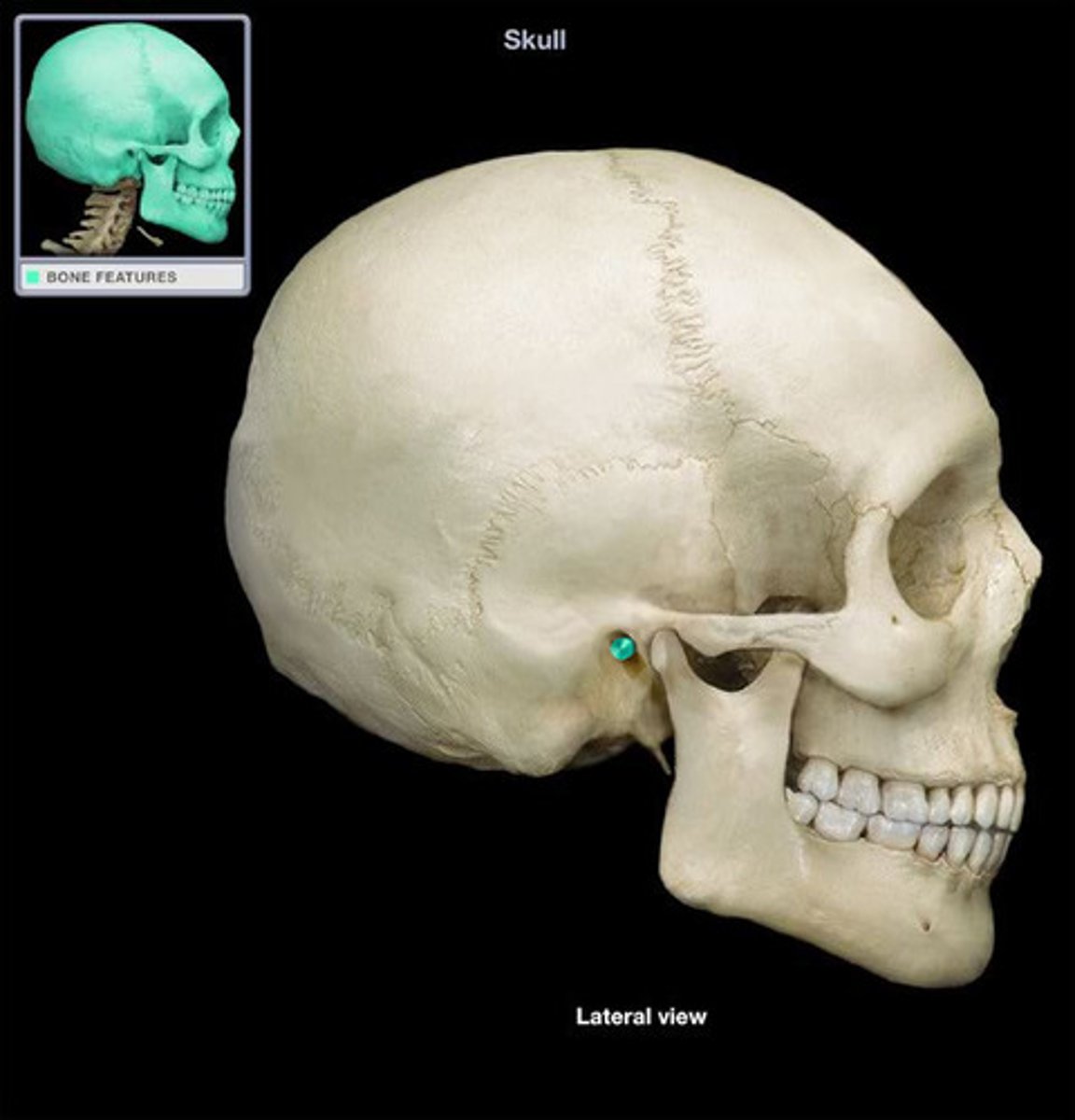
mandibular fossa
the small oval depression on the zygomatic process of the temporal bone into which the condyle of the mandible articulates, just anterior to the external auditory meatus
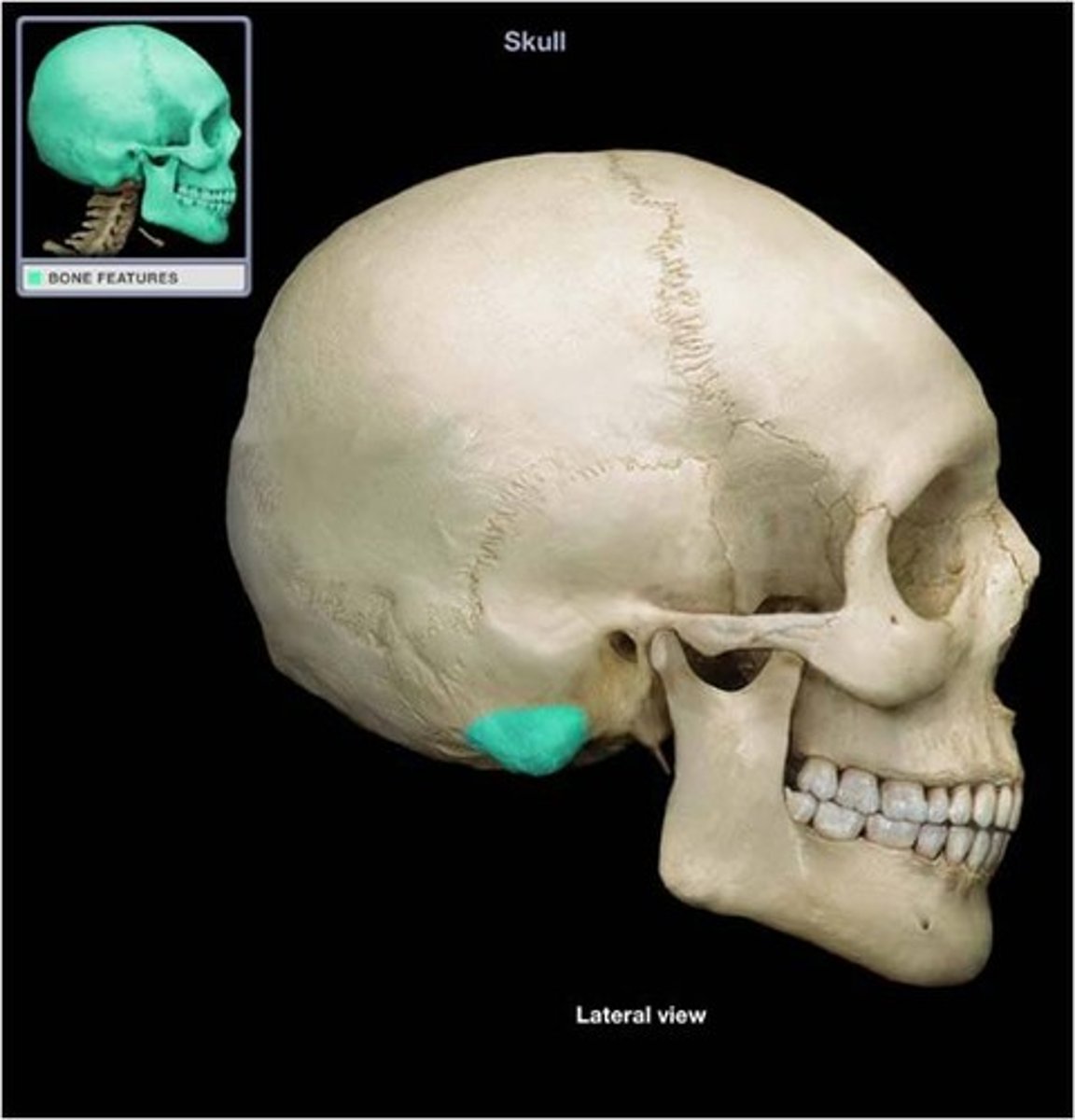
mastoid process
the rounded projection on the inferior portion of the temporal bones just posterior to the lobe of the ear
frontal bone
the anterior third of the cranium, forming the forehead and the anterior portion of the roof of the skull
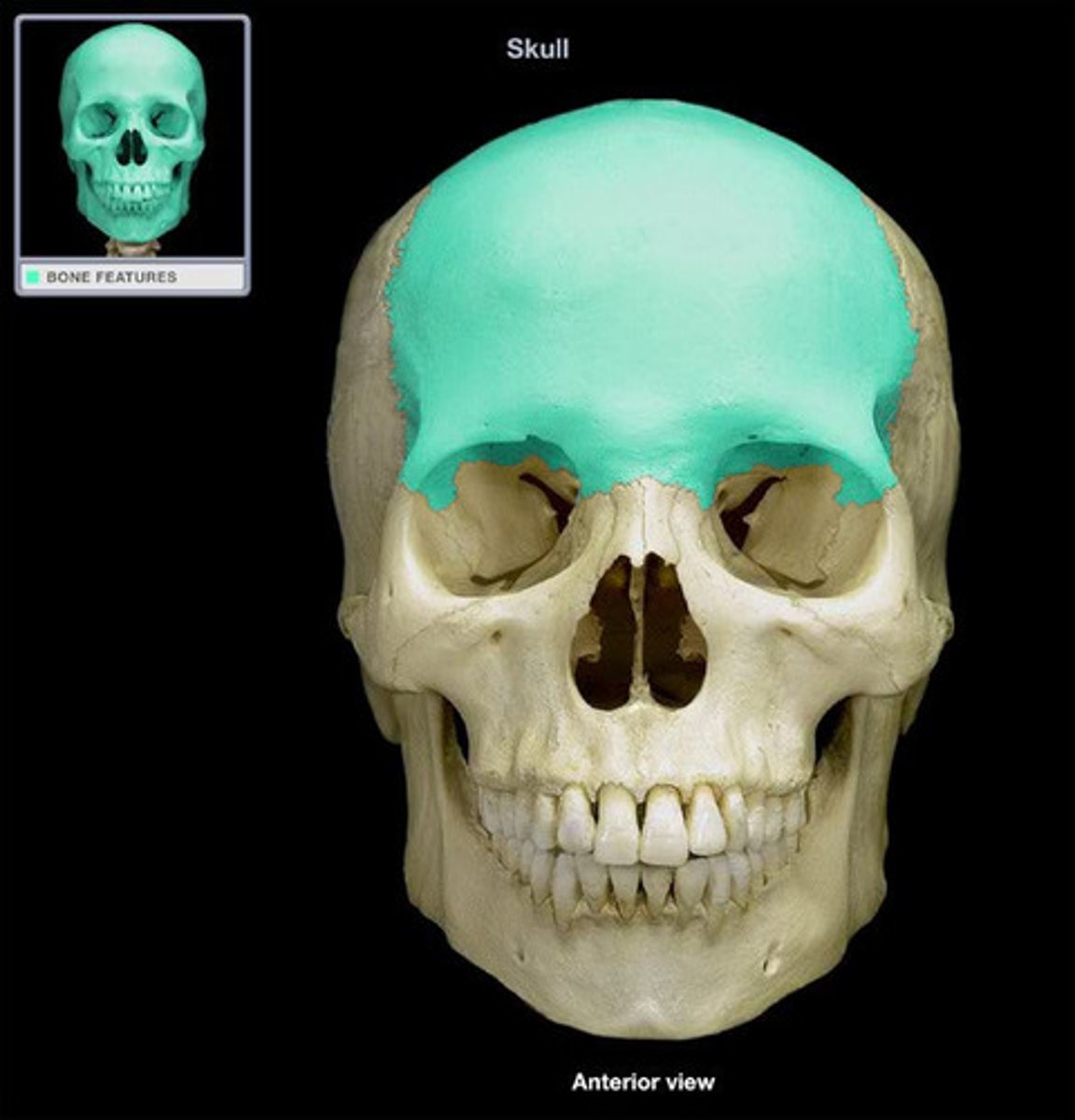
vertical surface (forehead)
this surface extends from the upper margin of the eye sockets to the level of the two frontal eminences
horizontal surface (crown)
this surface continues to ascend superiorly until it reaches the parietal bones
• Fontal eminences (paired)
• Supraorbital margins (paired)
• Superciliary arches (paired)
• Glabella (unpaired)
eminences of the frontal bone:
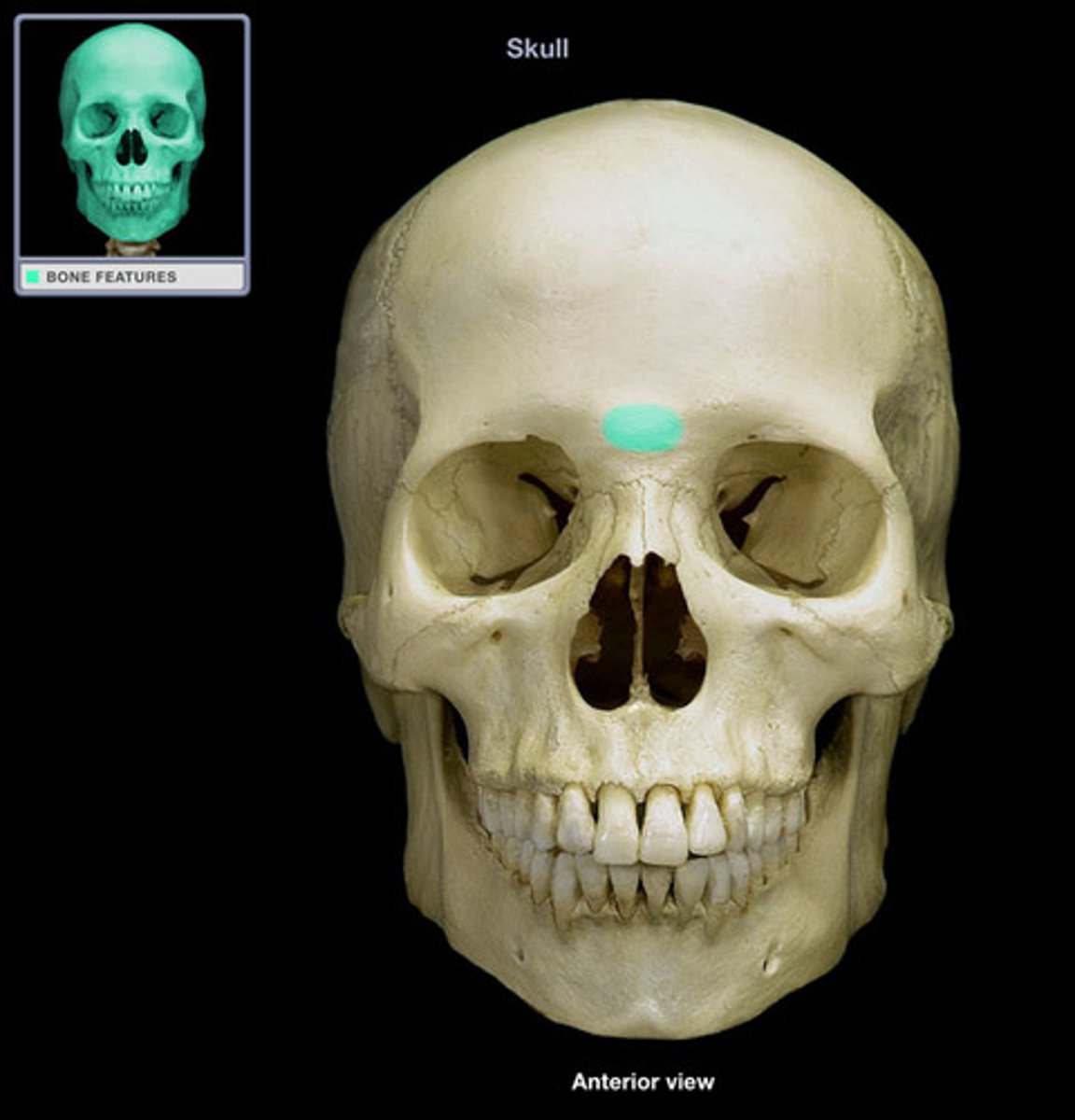
glabella
a single bony prominence of the frontal bone located between the superciliary arches in the inferior part of the frontal bone above the root of the nose
frontal eminences
rounded prominences on either side of the median line and a little inferior to the center of the frontal bone
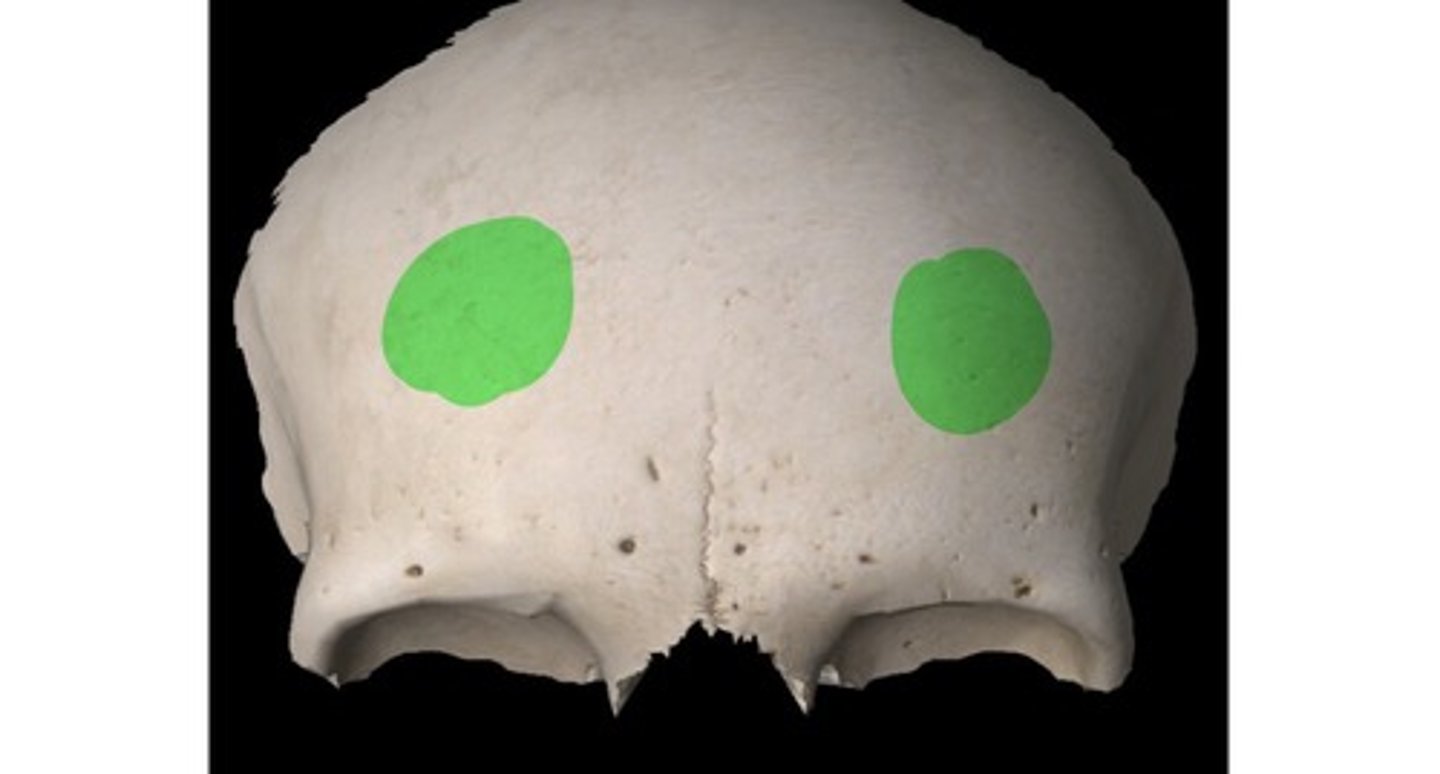

supraorbital margins
the superior rim of the eye sockets
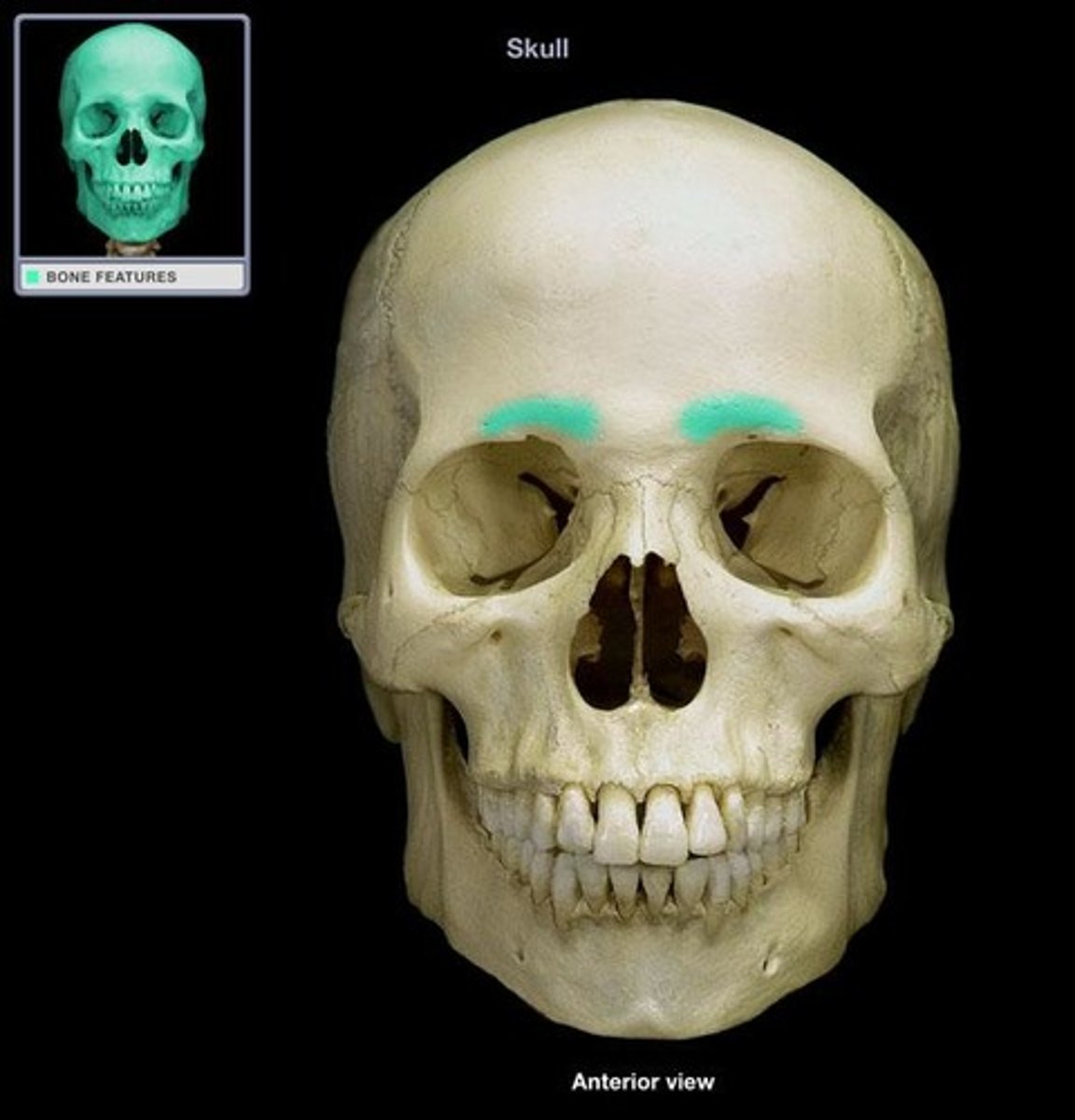
supercilliary arches
located on the inferior part of the forehead just superior to the median ends of the eyebrows
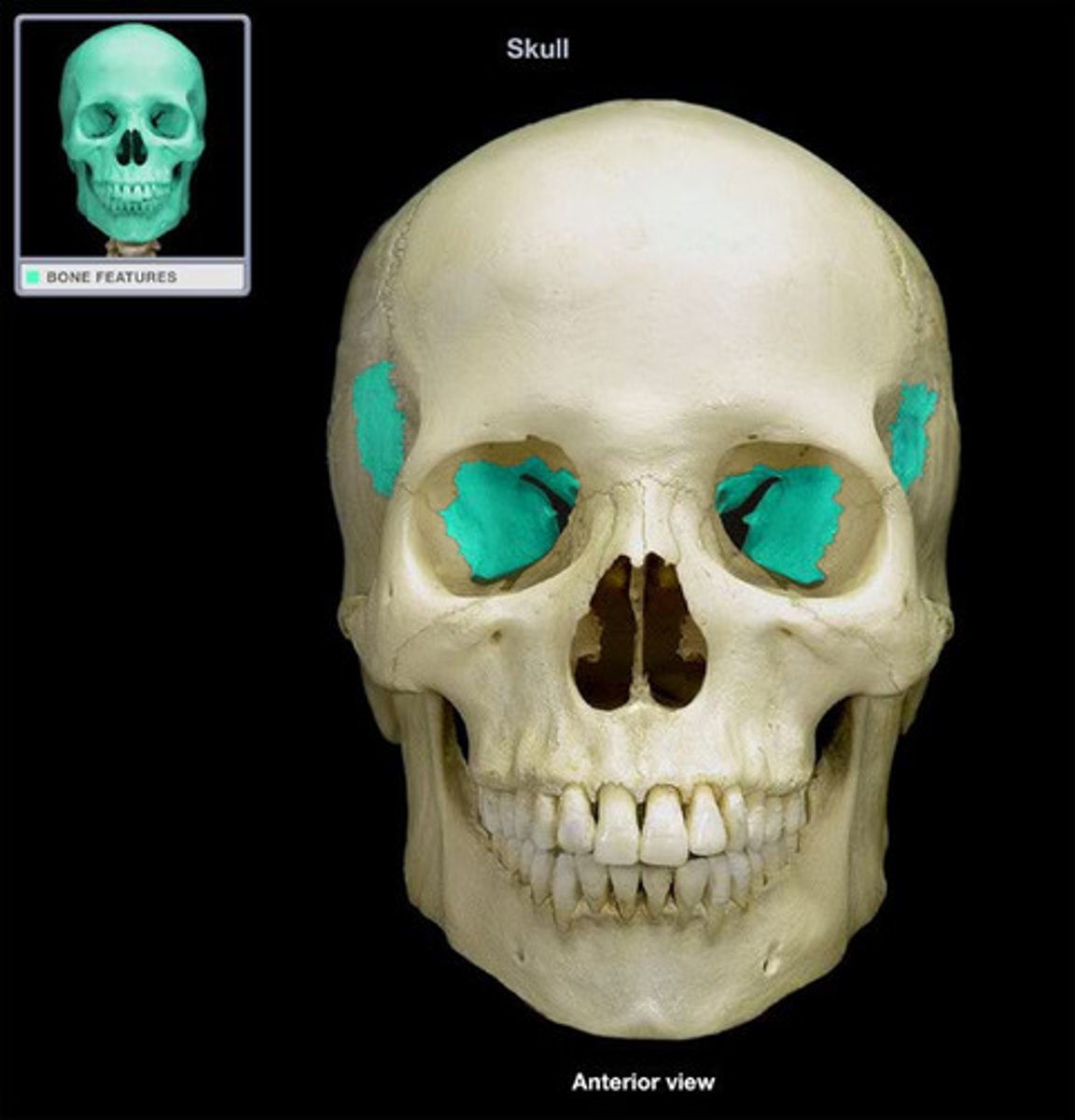
sphenoid
an unpaired bone of the neurocranium
ethmoid
this bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes
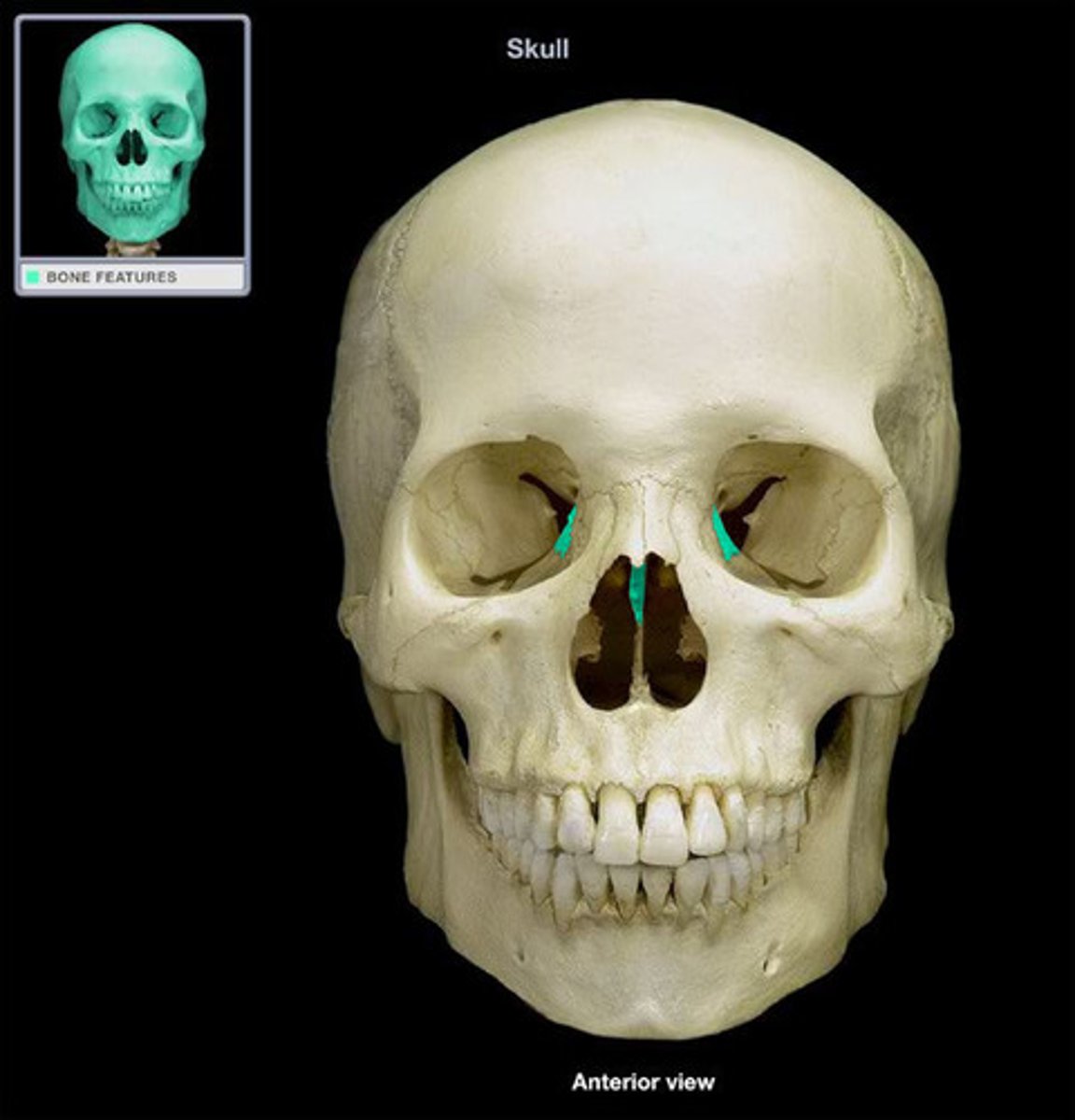
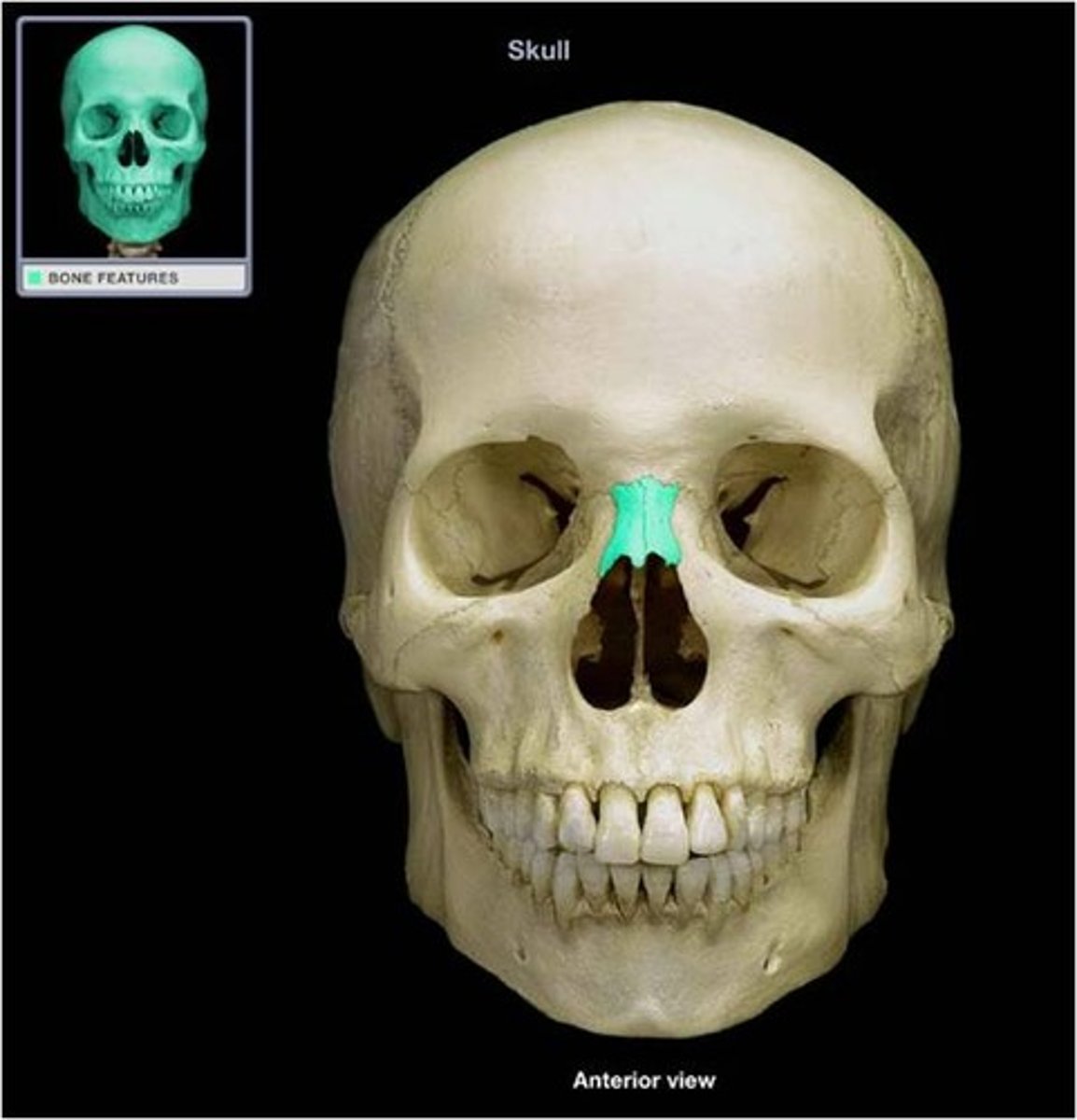
nasal bones (2)
directly inferior to the glabella and forming a dome over the superior portion of the nasal cavity
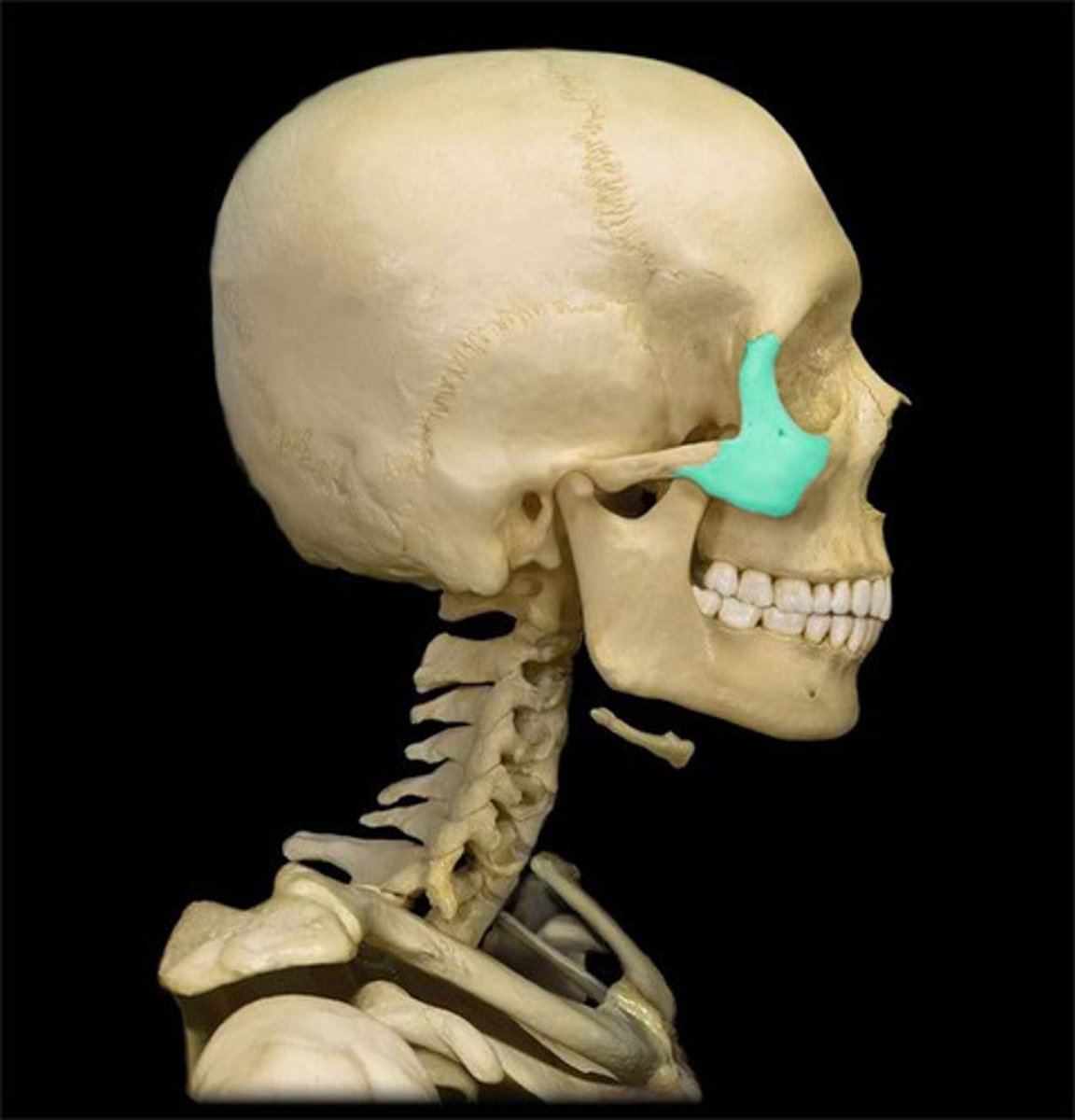
zygomatic bones (2)
bones of the cheek; often described as being diamond shaped and form the cheek bones
nasal cavity
the orifice in the bony face bounded by the margins of the nasal bones and the maxilla
zygomatic arch depression
one of the lesser concavities of the face located on the lateral portion of the cheek inferior to the zygomatic arch
zygomaticofrontal process
the lateral rim of the eye socket formed by a process of the frontal bone and a process of the zygomatic bone
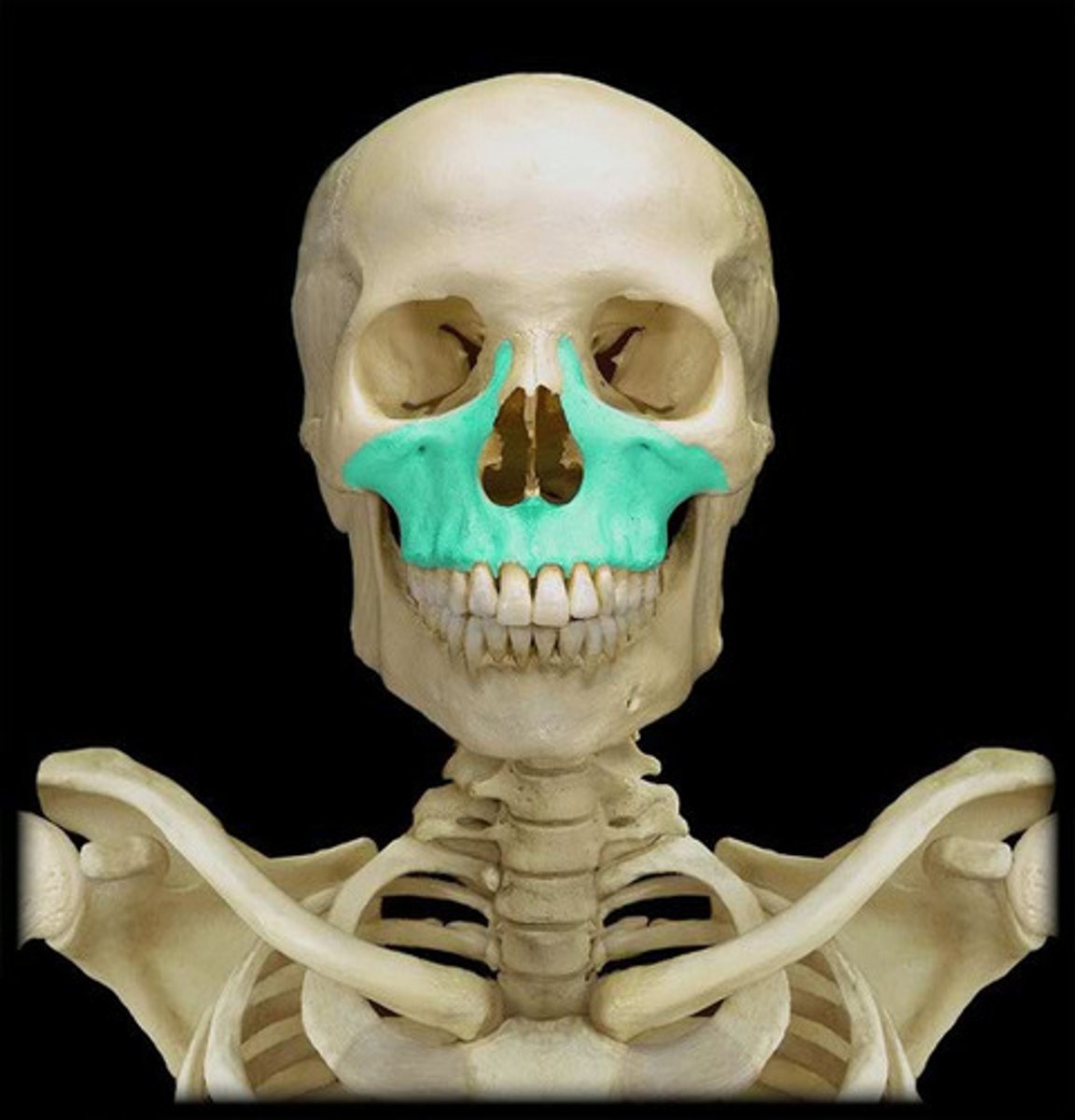
maxilla bones (2)
paired bone with several processes that forms the skeletal base of most of the superior face, roof of the mouth, sides of the nasal cavity, and floor of the orbit
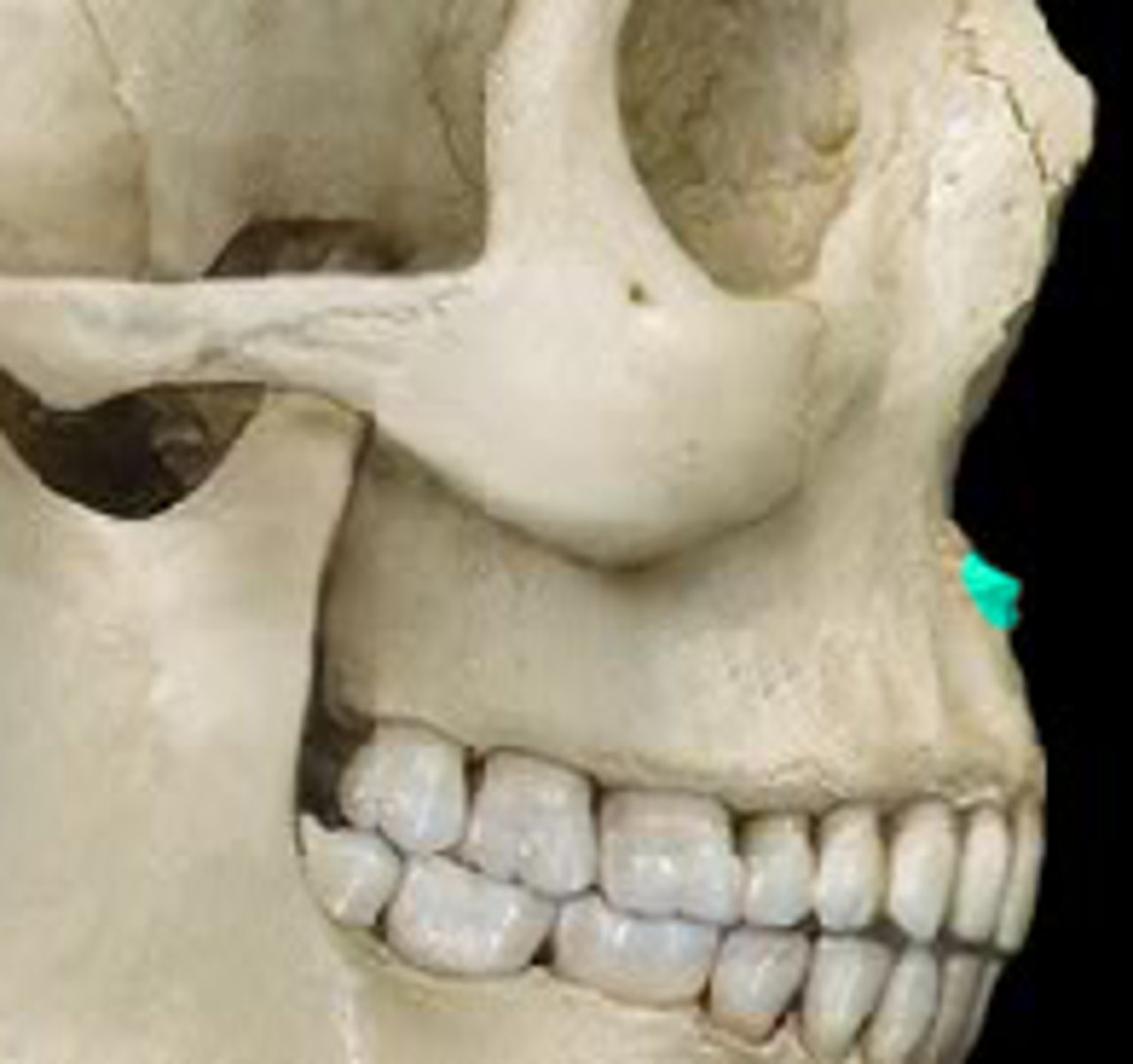
nasal spine of the maxilla
small bony projection located on the median line at the inferior margin of the nasal cavity
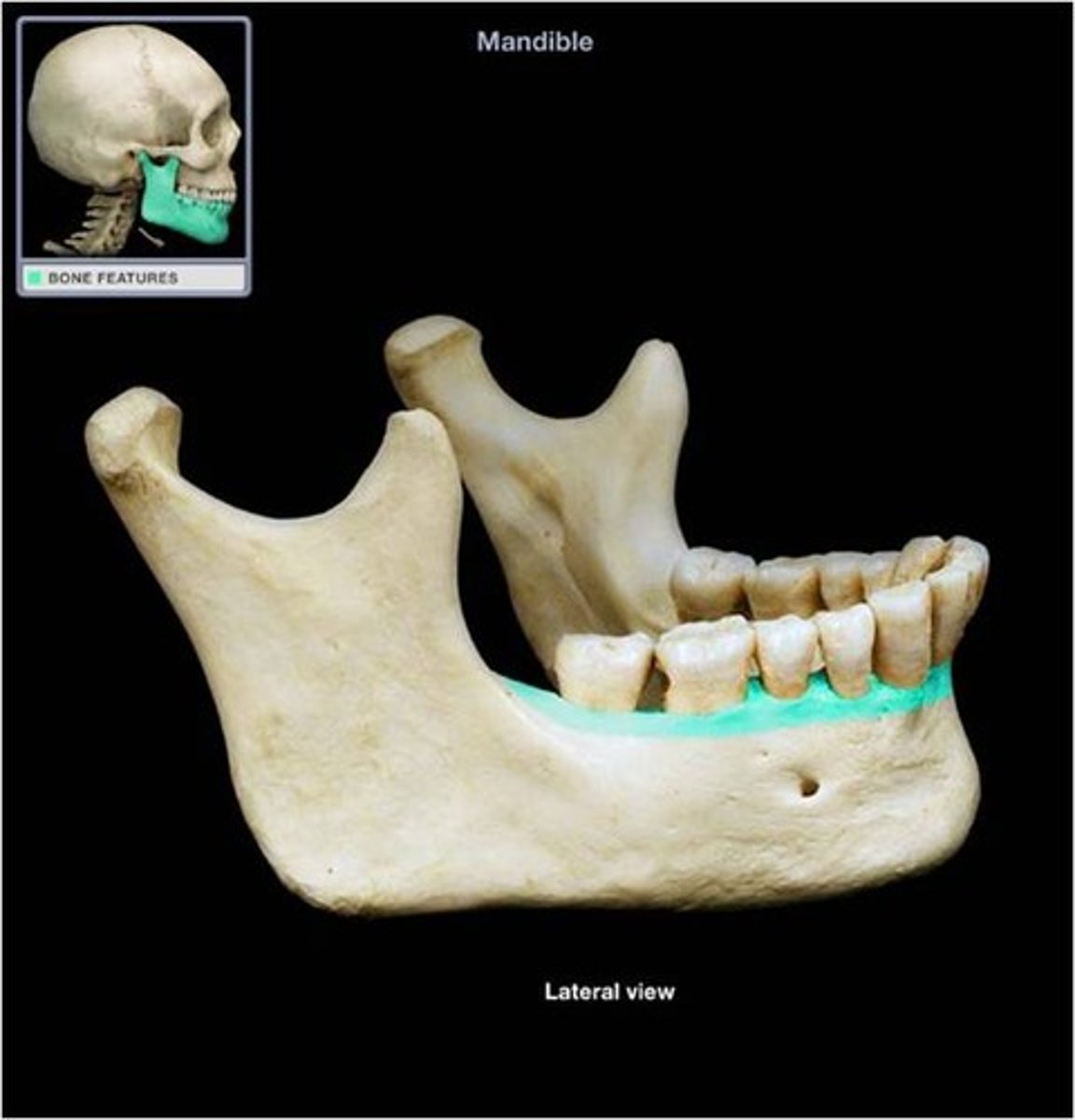
alveolar processes
bony ridges found on the inferior surface of the maxilla and the superior surface of the mandible which contain sockets for the teeth
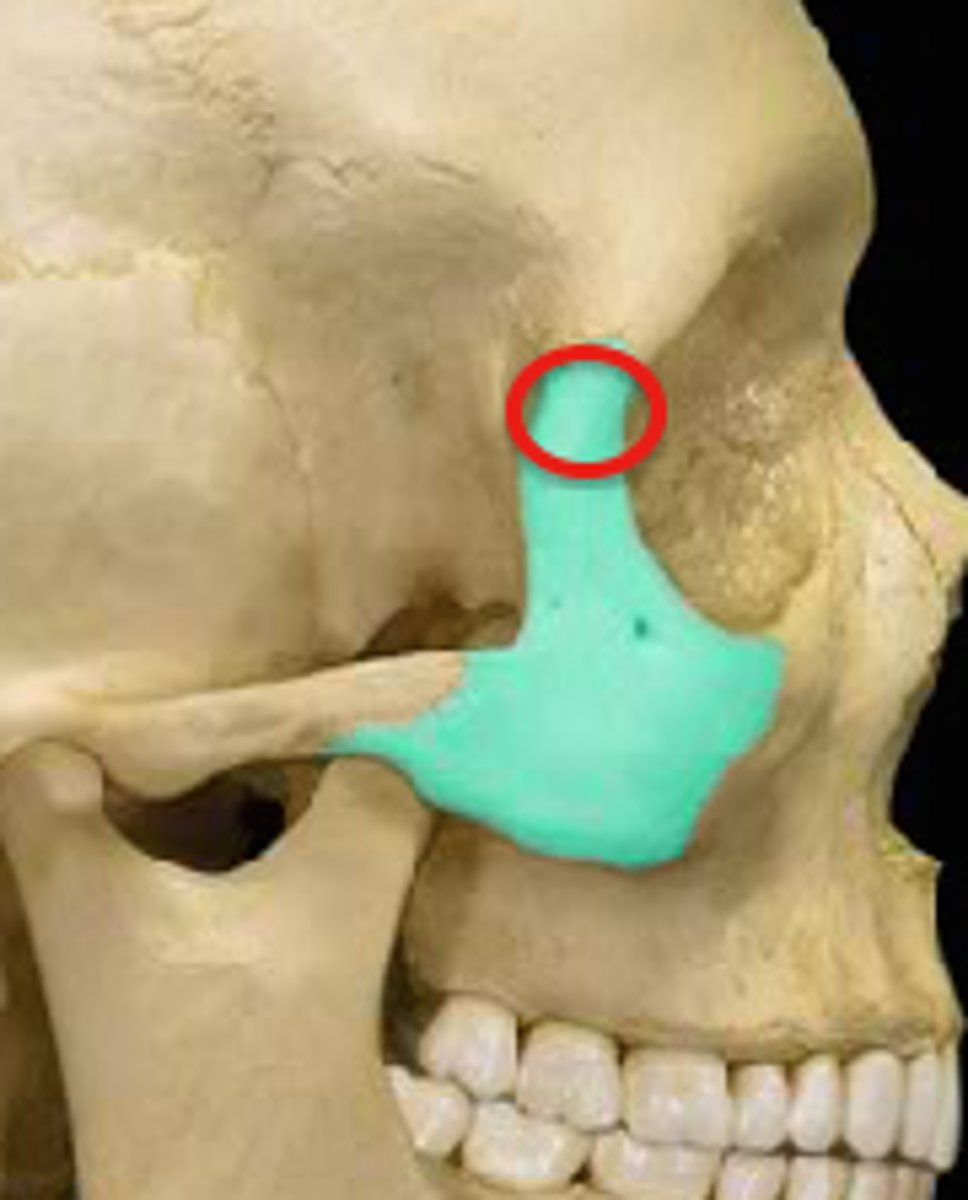
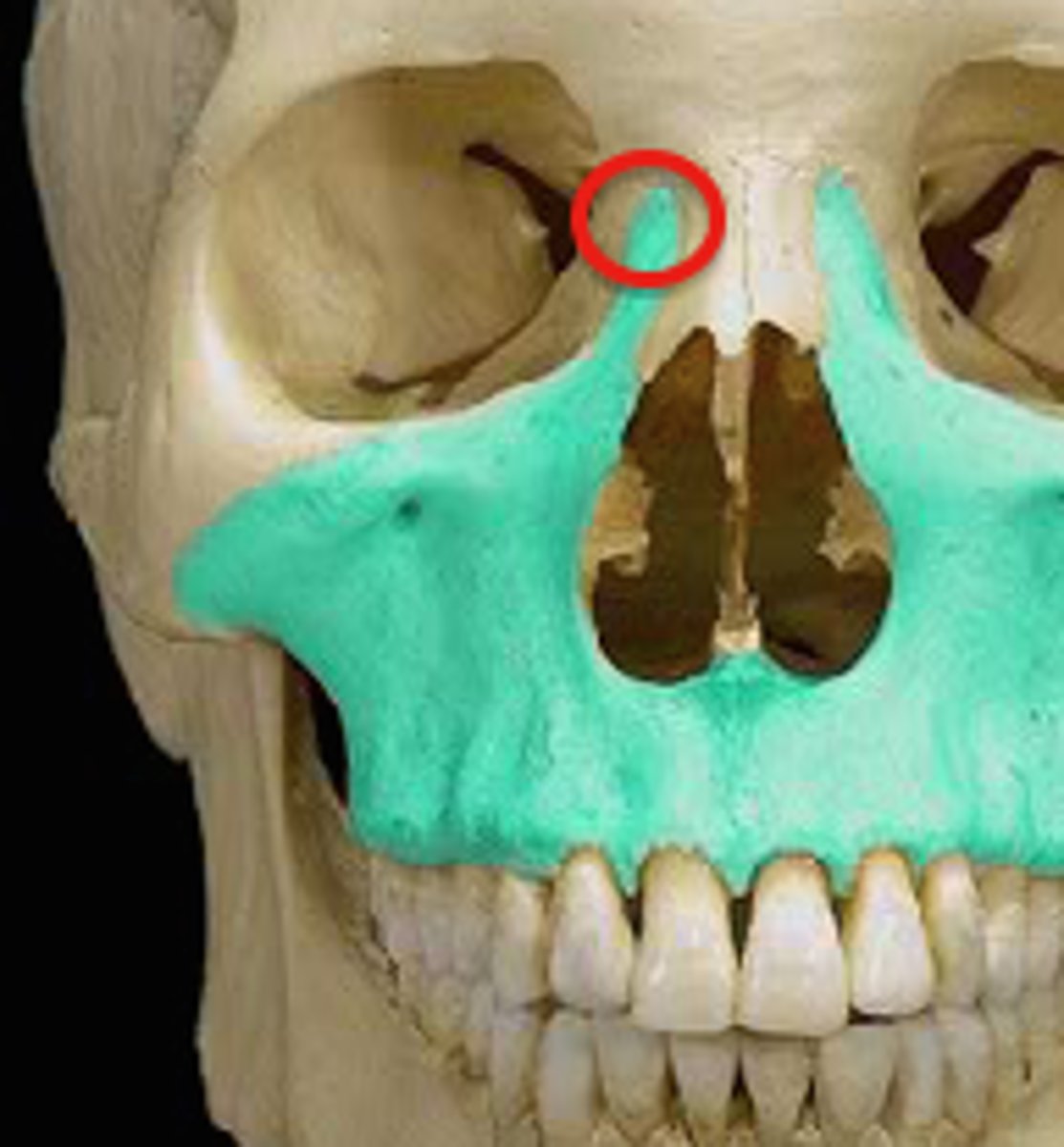
frontal process of the maxilla
the ascending part of the upper jaw which gradually protrudes as it rises beside the nasal bone to meet the frontal bone
mandible
the horseshoe-shaped bone forming the inferior jaw
body and the ramus
the mandible is divided into the:
mental eminence
a triangular projection on the inferior portion of the anterior mandible
incisive fossa
the depression between the mental eminence and the mandibular incisors
• Alveolar processes
• Mental eminence
• Incisive fossa
the three parts of the body of the mandible:
• Coronoid process
• Mandibular condyle
• Mandibular notch
the three parts of the ramus:
coronoid process
the anterior, non-articulating process of the ramus of the mandible which serves as the insertion for the temporalis muscle
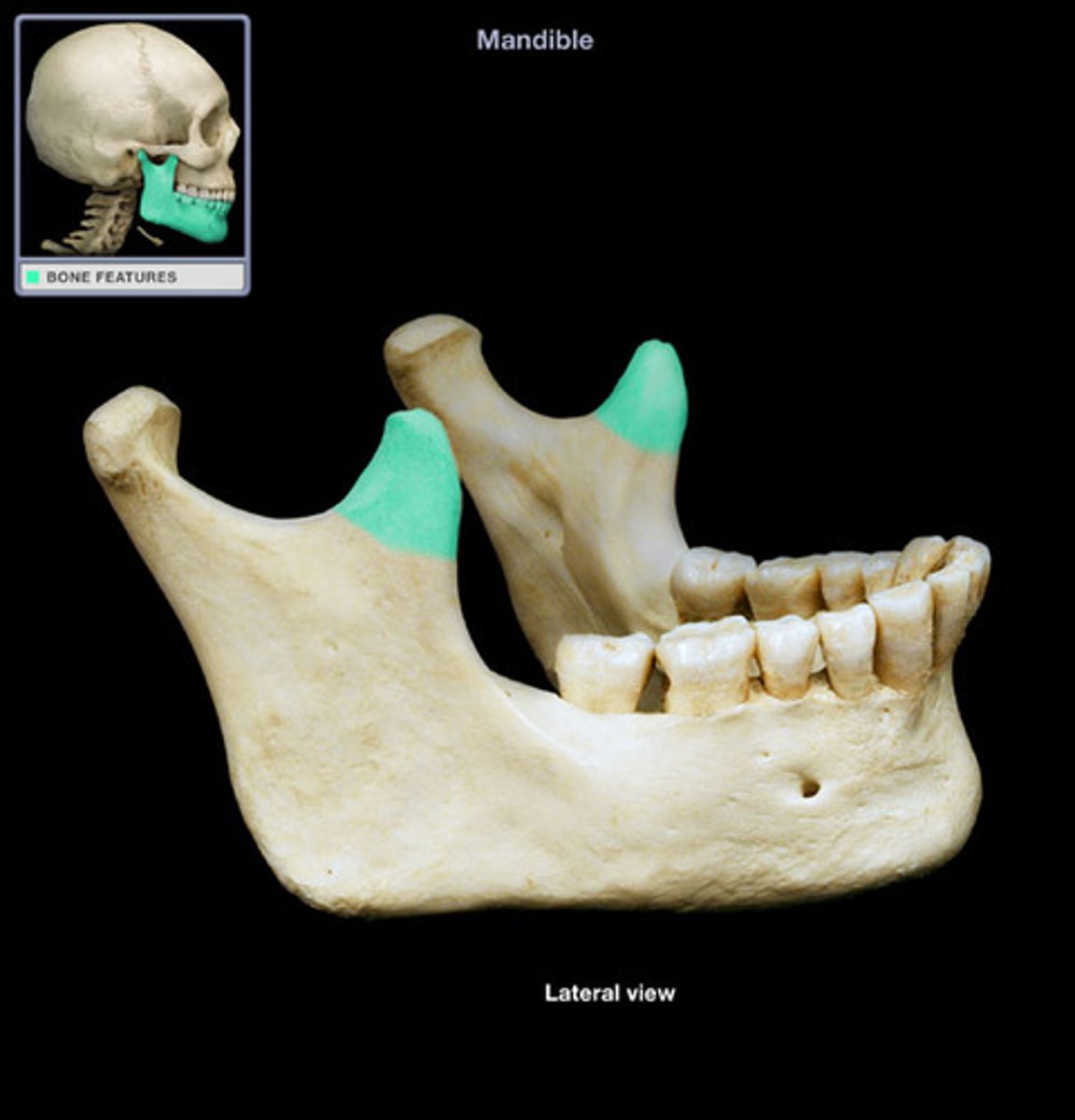
mandibular condyle
a rounded prominence at the end of a bone forming an articulation; the posterior process of the ramus of the mandible
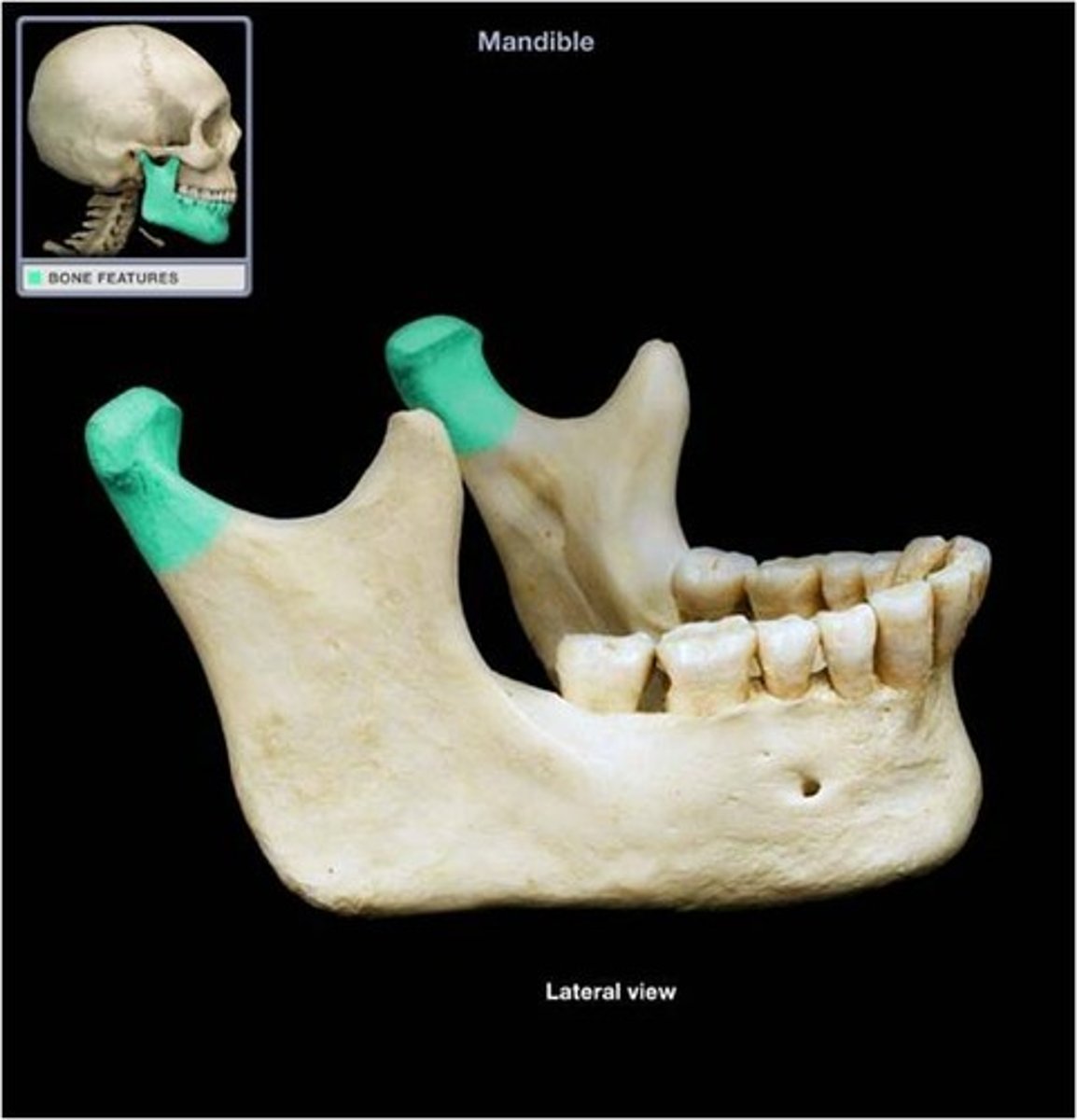
mandibular notch
a relatively deep indentation between the condyle and coronoid process of the mandible
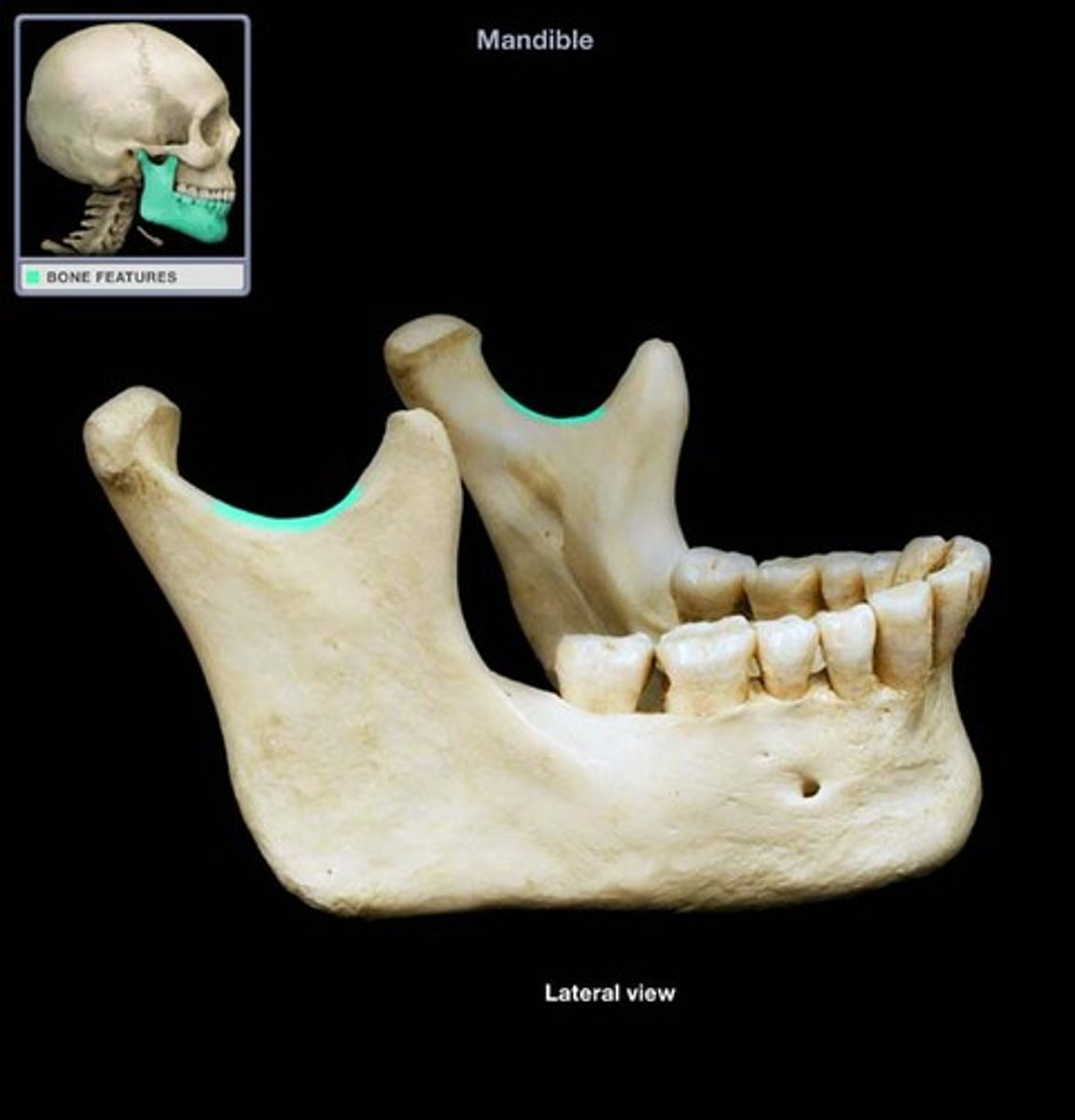
angle of the mandible
a bony angle formed by the junction of the posterior edge of the ramus of the mandible and the inferior surface of the body of the mandible; marks widest part of lower 1/3 of face
parietal eminences
mark the widest part of the cranium
zygomatic arches
mark the widest part of the face
angle of the mandible
marks the widest part of the lower 1/3 of the face
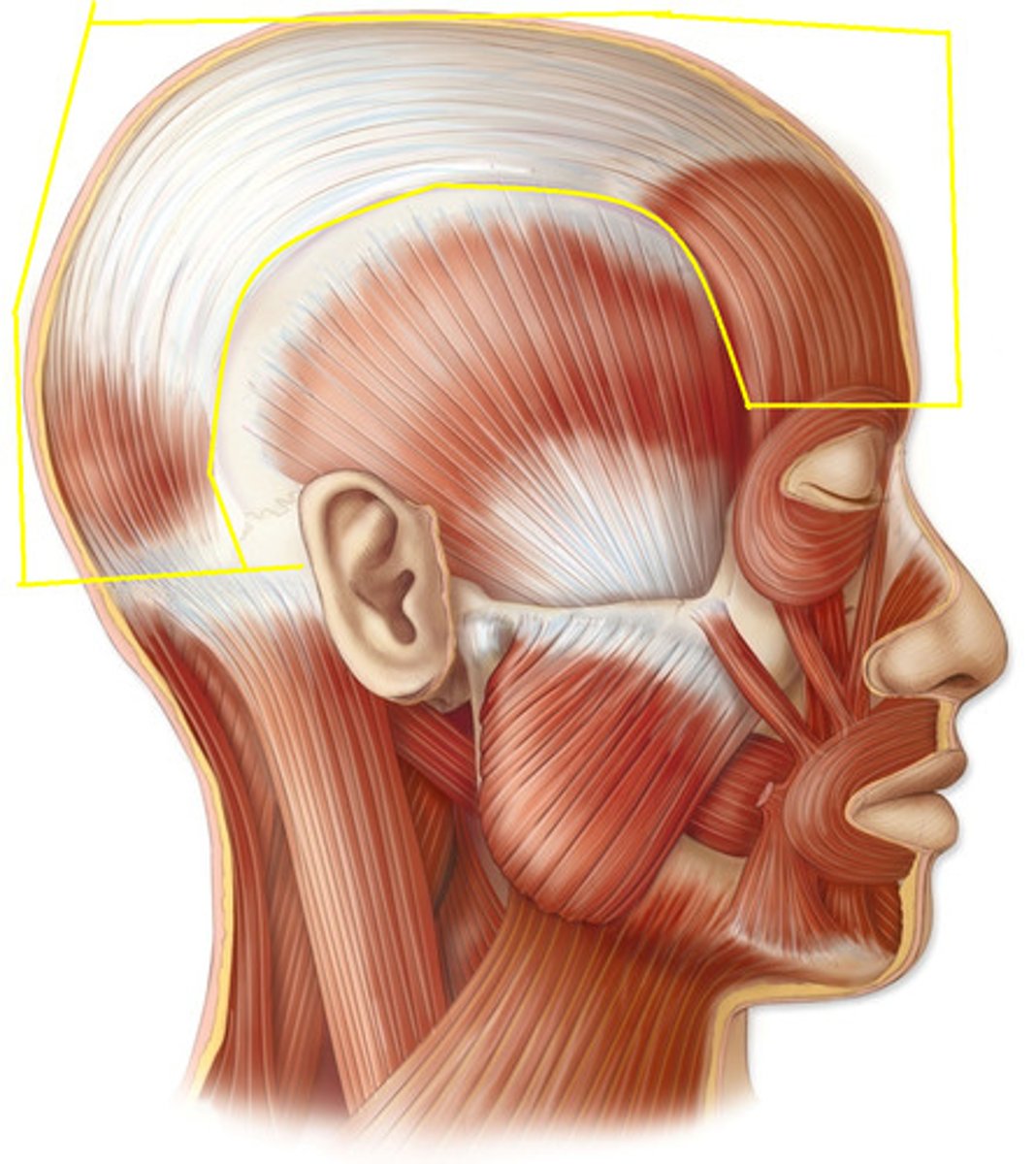
occipitofrontalis