BIOL 108 Topic 5: Evolution by Natural Selection
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What does the theory of evolution describe?
The theory of evolution describes a mechanism for the gradual change and diversification of species over time, including the appearance of new species
Who was Charles Darwin?
A British naturalist who developed a theory of evolution based on natural selection.
-In 1859, Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection
What two main points did Darwin make in his book?
1. Species show evidence of "descent with modification" from common ancestors (evolution)
2. Natural selection is the mechanism for "descent with modification".
How many simple main principles of natural selection are there?
3
What does the first main principle of natural selection say about variation?
There is variation within a population of organisms and this variation can be inherited (passed to the next generation)
What does the second main principle of natural selection say about individuals with inherited traits?
Individuals with inherited traits are better suited for growth and reproduction in a given environment contribute disproportionately to the next generation.
What does the third main principle of natural selection say about natural selection?
Natural selection his the process by which individuals with favourable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
What was the commonly held view prior to Darwin's work? What is an example of what Linnaeus believed?
Prior to Darwin's work, Earth was viewed as being geologically young and inhabited by unchanging species.
e.g. Linnaeus believed that similarities between organisms reflected their pattern of creation.
The study of what helped to lay the groundwork for Darwin's ideas?
Fossils
What are fossils?
Fossils are remains or traces of organisms from the past, usually found in sedimentary rock, which appear in strata (layers).
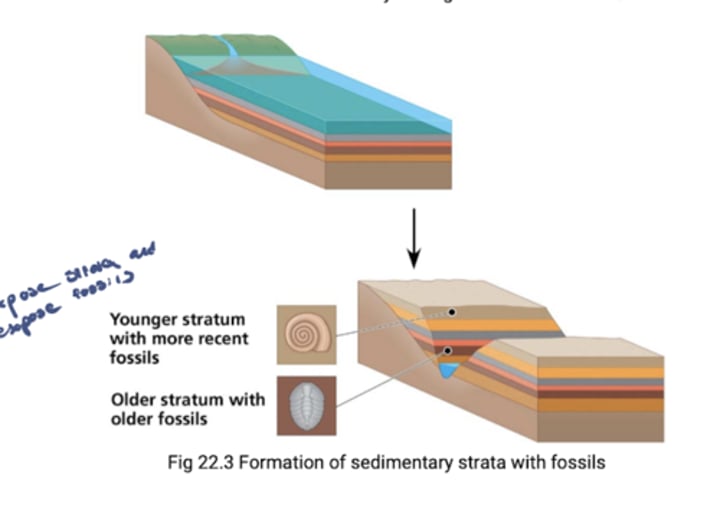
What had others noted about fossils?
Others had noted that fossil organisms often did not resemble living ones, so the extinction of species must occur.
What did Georges Cuvier note?
French naturalist Georges Cuvier noted that fossils from older strata were dissimilar to living organisms and that fossil species changed between strata (extinction).
What was Cuvier's idea of catastrophism?
Cuvier proposed that the fossil record represented catastrophism: each boundary between strata represents a catastrophic event.
What did Cuvier believe?
Cuvier believed that species did not change over time, i.e. no evolution.
Instead of evolution what did Cuvier believe?
The succession of life forms in the Earth's strata (over time) due to:
-catastrophe —> local extinction —> presence of fossils in the stratum
-after a catastrophe, different species moved into the area —> new fossils in a new stratum following another catastrophe
What did Jean-Baptiste Lamarck hypothesize?
French zoologist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck hypothesized (1809) that the apparent disappearances of species was one species slowly changing into another
-Lamarck was philosophically opposed to extinction.
What was Lamarckism?
Lamarck hypothesized that species "evolved" through the inheritance of acquired characteristics.
What does inheritance of acquired characteristics mean?
An organism can pass on characteristics that it acquired during its lifetime to its offspring
-the use and disuse of a structure lead to heritable changes

Is Lamarck's theory correct? Explain.
Not a plausible mechanism for evolution; not supported by genetic inheritance or experimental evidence.
-Weismann (1891): cut the tails off of 901 mice (19 successive generations) —> each generation grew full-length tails!
What did Darwin realize on his travels? (3)
1. He noted tat species traits match the environments they inhabit.
2. He observed that fossils resembled living species from the same region and that living species resembled other species from nearby regions.
3. He experienced an earthquake in Chile and observed the uplift of rocks and fossils.
What did Darwin hypothesis after the Beagle's month-long visit to the Galápagos Islands?
Darwin hypothesized that species from South America had colonized the Galapagos and formed new species
What did Darwin write his essay on?
Natural selection as the mechanism of descent with modification, but did not introduce it publicly.
What is natural selection?
A process in which individuals with favourable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
What is the history of life like in Darwin's view? Did Darwin's theory agree with Linnaeus' hierarchical classification?
a tree with branches representing life's diversity
-Darwin's theory agreed with Linnaeus' hierarchical classification.
-Darwin reasoned that large morphological gas between related groups could be explained by this branching process and past extinction events.
What two points did Darwin make?
1. Species show evidence of "descent with modification" from common ancestors (evolution).
2. Natural selection is the mechanism for "descent with modification
What does this mean: Species show evidence of "descent with modification" from common ancestors (evolution).
All organisms are related through descent from an ancestor that lived in the past.
What is evolution?
The process by which living organisms descend with modification from ancestral organisms.
What does descent with modification explain?
Explains the duality of unity and diversity in living organisms.
What is unity?
Similar traits among organisms are dye to descent from common ancestors.
What is diversity?
Differences among organisms due to the accumulation of heritable changes.
What does descent with modification describe?
The origin of new species (speciation) from ancestral species.
What did Darwin observe during the voyage of the HMS Beagle?
Many examples of species adaptation to the environment.
What are adaptations?
Adaptations are the inherited characteristic of an organism that enhances its survival and reproduction in a specific environment.
What did Darwin realize?
Adaptation and the origin of new species were closely related processes
-research on the Galapagos finches demonstrates the connection between adaptation and speciation.
What did Darwin observe in the finches?
Finch species on different Galápagos Islands were similar yet had distinct differences.
What is the similar appearances of finches from one island or habitat to another?
Unity due to common ancestry.
What did Darwin observe that was dissimilar in finches?
Beak shape adaptations
-variation in beak shape influences a species' food sources (e.g. seeds, insects, and cactus flowers) and their mechanisms of feeding.
-diversity due to descent with modification
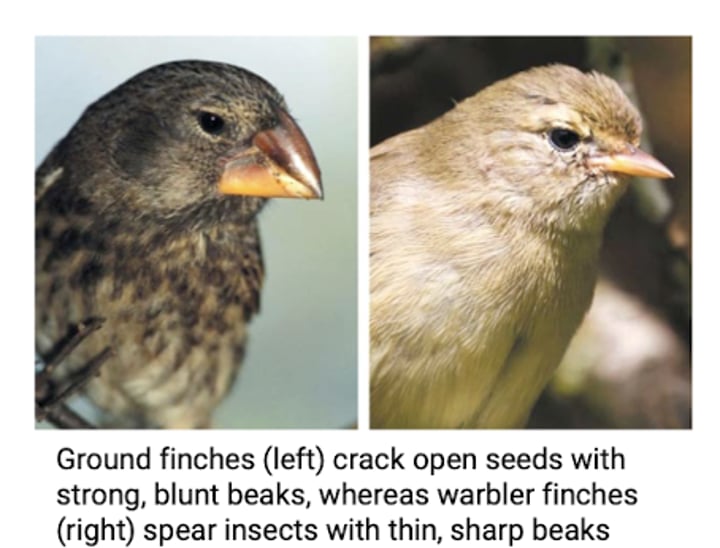

What was Darwin's hypothesis about the beaks of ancestral species?
The beak of an ancestral species had adapted over time to form descendant species that are adapted to different food sources.
What kind of group do the Galapagos finch species form?
A monophyletic group
-they descended from a single common ancestor.
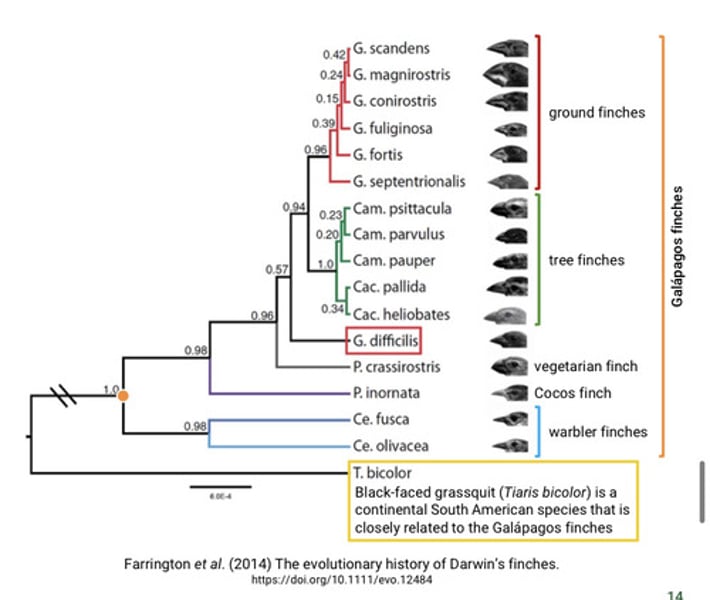
What did Darwin propose natural selection as the mechanism for?
Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism for "descent with modification" (evolution) that gives rise to adaptation and speciation.
What did Darwin note about artificial selection?
Humans have modified other species by selecting and breeding individuals with desired traits
e.g. artificial selection for crops, ornamental plants, livestock, and companion animals.
-Darwin described how a similar process occurs in nature
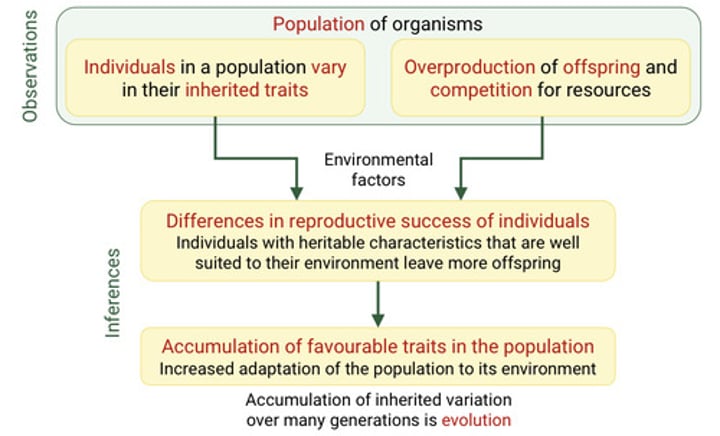
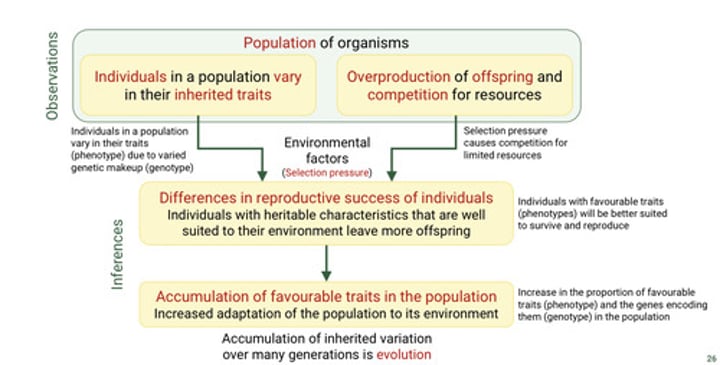
What are the two observations of evolution by natural selection?
1. Members of a population vary in their inherited traits
2. Populations produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce.
Explain observation 1. What is a population? What do most populations show a lot of? What is the raw material that natural selection acts upon?
-A population is a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offspring.
-Most populations show considerable variation, i.e. all individuals are different.
-Variation in populations (genetic diversity) is the raw material that natural selection acts upon
(genetic diversity is the genetic variation within a population and between populations within a species
Explain observation 2. Provide an example. What leads to competition for resources? What is competition?
e.g. a single female sockeye salmon spawns 2,000-5,000 eggs before dying (1 in 1000 eggs will survive and return to spawn at maturity)
-insufficient resources to support all offspring leads to competition for resources
-Competition is most intense among individuals of the same species (i.e. with populations) because they compete for identical environmental requirements
What are the two inferences of evolution by natural selection?
1. Individuals whose inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment leave more offspring than other individuals.
2. The unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favourable traits in the population over generations.
Explain inference 1.
If some heritable variation provides a competitive advantage or is better suited to their environment, individuals wirth this variation will survive and reproduce at a higher rate than individuals with deleterious variation.
Explain inference 2.
-If some heritable traits are advantageous, these traits will accumulate in the population over time, increasing the frequency of individuals with these traits.
i.e. increase the frequency of individuals with advantageous variation in subsequent generations
-evolution occurs because of the unequal reproductive success of individuals
What does natural selection result in?
The adaptation of populations to their environment. Under natural selection the environment "selects" for adaptive traits (beneficial traits)
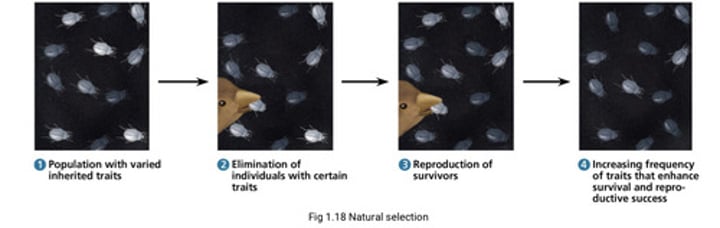
Know this diagram
What are two types of variation?
Genotypes and phenotypic
What is genotype?
The genetic makeup of an organism, i.e. an organism's complete set of genes
What is genotypic variation?
The difference in DNA among individuals in populations.
Is genotypic variation heritable?
Yes
-i.e. the traits or variants encoded in DNA are passed from parent to offspring during reproduction.
What does the expression of the genotype contribute to?
an individual's observable traits (phenotype), but not all genotypic variation is expressed
e.g. redundancy in genetic code
What is phenotype?
An organism's observable characteristics
-e.g. morphology, biochemical or physiological properties, and behaviour
What is phenotypic variation?
The variability in phenotypes that exists in a population.
What is an organism's phenotype determined by?
Interaction of environmental factors and its genotype
e.g. blue hydrangea flowers when grown in acidic soils
What can phenotype sometimes be determined by?
solely by the environment, and is not heritable.
What does natural selection act on?
Acts on genetic variation expressed in the phenotype.
What must happen for natural selection to act on variation?
it must be 'seen' by the environment (expressed in the phenotype) and be heritable (caused by genotype)
How does genetic variation arise in populations>?
Randomly, but natural selection is not a random process
What is the raw material that natural selection acts upon?
Variation (genetic diversity)
What are selective agents?
Environmental factors acting on populations to effect the survival and/or reproduction of individuals in the population
What are two examples of selective agents?
Biotic and abiotic
What is an example of a biotic selective agent?
Predators, disease, competitors
What is an example of an abiotic selective agent?
space, light, temperature, and water
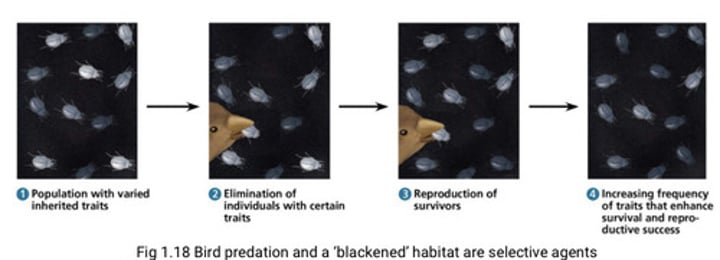
What is a selection pressure?
When a selective agent consistently causes differences in survival and/or reproduction in a population
-the intensity with which a selective agent causes a selective pressure varies with environmental conditions
What can natural selection not act without?
Selection pressure.
Natural selection is _______-______
context-dependent
What happens if the selection pressure changes?
The direction of natural selection will change (context dependent)
-the direction of adaptable change is dependent on the environment
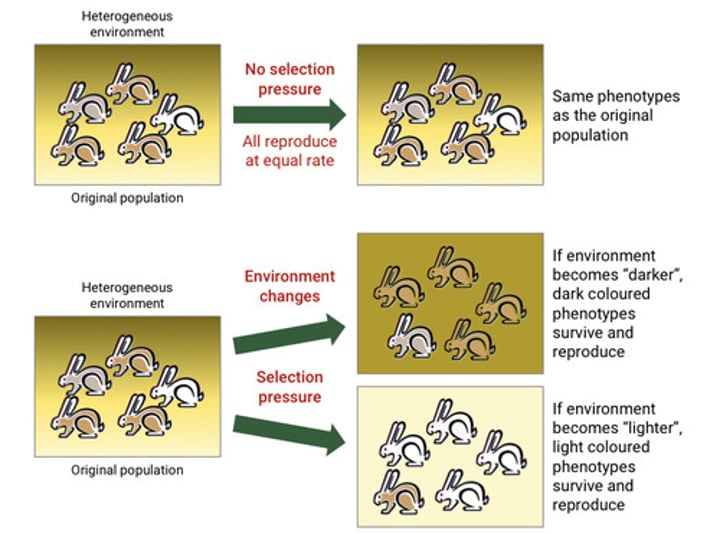
What does consistent selection pressure lead to?
a directional change in the population (natural selection)
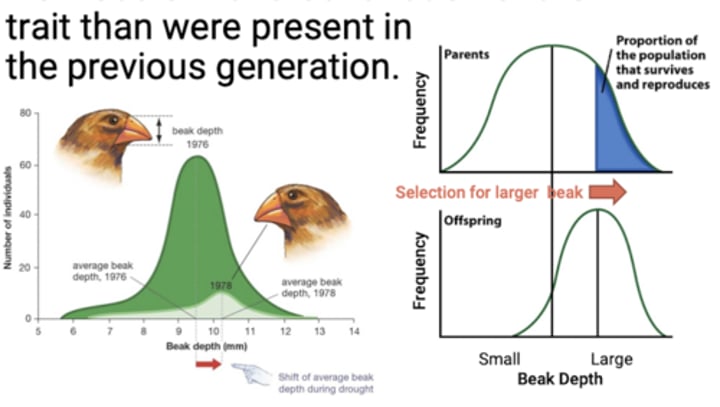
Know this diagram
Make sure you know this example

The direction of what may change as selection pressures change?
Natural selection.
Is the direction of evolutionary change in a population predetermined and reversible?
Yes
Know this about the birds
A drought in 2004 and competition from large ground finch (a recent immigrant with a substantially larger beak) severely decreased the number of large seeds available.

What does natural selection occur as a result of?
Unequal reproductive success of individuals in populations.
What happens in the next generation following unequal reproductive success of individuals in populations?
There are more. individuals with that variation of the trait than. were present in the previous generation
What did Darwin provide?
Darwin provided a logical mechanism by which natural forces (selection pressures) can select for advantageous variations.
-environment "selects" for beneficial traits
-natural selection result in adaptive change in populations over generations (adaptive evolution)
-Darwin termed this process "descent with modification"
What is adaptation?
An inherited characteristic of an organism that enhances its survival and reproductive in a specific environment.
What is natural selection (summary definition/review)?
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
What is all that is needed for reproduction?
But increased survival and reproduction are not necessary:
all that is needed is greater reproductive success.
-e.g. if two individuals have the same lifespan but one produces twice as many offspring as the other, then that's sufficient enough for natural selection to act on the trait for the production of more offspring.
What happens to individuals with beneficial inherited traits?
Survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals.
What does natural selection increase?
The adaptation of populations to their environment over time.
What happens if an environment changes over time?
Natural selection may result in adaptation to new conditions.
-adaptations vary in different environments
What happens as populations adapt to different environments?
New species may arise over time (over many generations), e.g. speciation of Galapagos finches from a single common ancestor.
Do selection pressures act on individuals or populations?
Selection pressures act on individuals but only populations evolve.
Do organisms change as the population adapts? Explain.
NO
-Rather, adaptation changes the proportion of beneficial traits across multiple populations.
What does natural selection act on? (review/duplicate term)
Existing variation
What does natural selection do?
Natural selection can only increase or decrease the frequency of heritable traits that vary in a population.
Does natural selection create new traits?
NO