CBL 9: The Routine Fertility Farm Animal Visit
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
What are the main factors impacting the onset of puberty in cows?
genetics, nutrition, body composition and weight
How can poor nutrition be caused in cows?
bullying and competition from other cows
Does poor nutrition delay or cause early onset of puberty?
delay
Does good nutrition delay or cause an early onset of puberty?
early onset
Does seasonality affect puberty?
yes
How do longer daylight hours affect puberty?
delay puberty
How does shorter daylight hours affect puberty?
accelerate it
Do higher temperatures in the summer delay or cause early onset of puberty?
delay
What is the site of secretion of oestrogen?
granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles
What effect on the ovaries does high levels of oestrogen cause?
LH surge during oestrus
What is the site of secretion of progesterone?
corpus luteum
What are the effects of progesterone on the ovaries?
prepares uterus for initiation and maintenance of pregnancy
How does progesterone affect other hormones?
inhibits FSH, LH & oestrogen
What is the site of secretion of FSH?
anterior pituitary gland
What are the effects of FSH on the ovaries?
stimulates follicle growth
What is the site of secretion of LH?
anterior pituitary gland
What effect does LH have on the ovaries?
maintenance of the corpus luteum
What is the site of secretion of PGF2α?
uterus
What effect does PGF2α have on the ovaries?
induces regression of corpus luteum (luteolysis)
What is the site of secretion of GnRH?
hypothalamus
What effect does GnRH have on the ovaries?
stimulates ant pit to release FSH and LH
What is the site of secretion of inhibin?
granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles
What effects does inhibin have on the ovaries?
inhibits release of FSH
What hormones are involved in the reproductive cycle?
oestrogen, progesterone, FSH, LH, PGF2α, GnRH, inhibin
Outline the steps of the process of ovulation
hypo secrete GnRH
FSH & LH released from pit
follicle maturation
What happens after follicle maturation?
follicle reaches max size & ruptures to release ovum
Where does the oocyte pass post ovulation?
down uterine tube into uterus
How does the oocyte pass down the uterine tube?
muscular contractions and cilia
What does the remaining tissue from the follicle become after being fertilised in the uterus?
CL
Outline the places the female gametes are transported to prior to fertilisation
ovaries - fimbriae of infundibulum - uterine tube - uterotubal junction - uterine horns
What is the fimbriae of infundibulum?
ovarian end of uterine tube/oviduct
What does the fimbriae of infundibulum do after ovulation?
engulf oocyte and prevent it being lost into abdominal cavity
How many parts does the uterine tube/oviduct have?
3
What are the 3 parts of the uterine tube called?
infundibulum, ampulla and isthmus
Where does fertilisation most commonly occur?
ampulla
Outline the places the sperm is transported prior to fertilisation
seminiferous tubules of testes - rene testis - epididymus - deferent duct - pelvic urethra (cervix - uterine body - uterine horns - uterine tubes)
Where is sperm produced?
seminiferous tubules of testes
Where does sperm mature?
epididymus
What happens to the sperm at the epididymus?
it matures
How does sperm move through the epididymus?
peristaltic contractions of muscular duct and hydrostatic pressure
What are the 5 stages of fertilisation?
contact
acrosome reaction (& completion of zona pellucida penetration)
fusion of plasma membranes and entry of sperm into nucleus
cortical reaction
fertilisation
acrosome
membrane which surrounds the anterior part of the sperm nucleus
What is the acrosome reaction triggered by?
penetration of cumulus and zona pellucida
What enzymes are involved in the acrosome reaction during fertilisation?
hydrologic enzymes
What does the cortical reaction block during fertilisation?
polyspermy
What happens during the cortical reaction?
cortical granules in egg fuse with plasma membrane
Where are cortical granules found?
egg cytoplasm
What does the embryo release when it attaches to the uterine lining in implantation to communicate its existence to the mother?
proteins and hormones
What does embryo signalling prevent?
luteolysis (CL breakdown)
Implantation
embryo comes into contact with the receptive parts of the uterus
What are the 2 types of implantation?
invasive and non-invasive
What is the role of progesterone in pregnancy and parturition?
maintain uterus, maintain quiescence of myometrium, promote cervical closure
What is oestrogen’s role in pregnancy and parturition?
increase contractive potential of uterus
What is the role of prolactin in pregnancy and parturition?
alveolar development during prepartum period
When and why do prolactin levels rise during pregnancy and parturition?
latter part of gestation because of oestrogen
What is the role of ACTH in pregnancy and parturition?
adrenal cortex becomes more sensitive to foetal ACTH
What is the role of cortisol in pregnancy and parturition?
changes in secretion by foetus causes release of PGF2a from uterus
What is the role of PGF2a in pregnancy and parturition?
increases (due to increased oestrogen) and initiates parturition
What is the role of oxytocin in pregnancy and parturition?
stimulates uterine contractibility softening cervix and relaxation of birth canal
What is the role of relaxin in pregnancy and parturition?
enhance luteal activity and support pregnancy
follicle
small pocket-like sac located inside ovary
What are follicles responsible for?
monthly growth, maturation and release of an egg
What species are monovular?
horse, cow
What species are polyovular?
sheep, pig, dog, cat
What do you do to identify dominant follicles of an animal?
rectal palpation
How are follicles detected during rectal palpation?
fluctuating, turgid, fluid-filled bodies usually smooth and protruding slightly from the surface
What does a corpus luteum when fully formed feel like during rectal palpation?
firm, solid unyielding body embedded in ovary
What is the optimal sign for mating/AI?
12 hours after primary oestrus signs are observed
What are the behavioural signs of proestrus?
increasingly restless, mount other heifers, calling
What hormones do the behavioural signs of proestrus occur due to?
oestrogens
Are primary or secondary heat signs seen during proestrus?
secondary
Are primary or secondary heat signs seen during oestrus?
primary
What are the behavioural signs of oestrus seen during oestrus?
stand to be mounted, display bulling string of mucus from vulva
What is the function of the corpus luteum?
progesterone secretion to prepare the uterus for pregnancy
Luteolysis
regression of CL
Why is cows being seasonally polyoestrous good regarding maximising productivity in cattle?
there can be almost constant reproduction of new offspring
How can optimising fertility reduce environmental impacts?
decrease methane emissions
What is rectal palpation important for diagnosing in cows?
pregnancies
What body condition score should replacement heifers have?
3 when weaned at 8 months
What percentage of their mature weight should replacement heifers be at at their first mating?
60%
What age are heifers served at?
15 months
When should heifers have their first calving?
24 months
How are vaginal exams in cows performed?
vulvar lips parted and speculum with lubricant inserted into vestibule
What direction should the speculum be inserted into the vestibule during a vaginal exam?
dorsocranially
Why should the speculum be inserted into the vestibule dorsocranially during a vaginal exam?
to avoid external urethral orifice
What is the role of vaginal examination in assessment of a cow?
detect infection from birthing process (find any abnormal discharge)
What could finding abnormal discharge in a vaginal examination be a sign of?
endometrius, metritis or cervicitis
What does a normal cow’s vaginal discharge look like?
clear
What does abnormal cow’s vaginal discharge look like?
purulent, malodorous, blood
What is post partum lochia?
normal discharge after calving
What diagnostic imaging can be used to identify pregnancy in cows?
trans-rectal ultrasonography
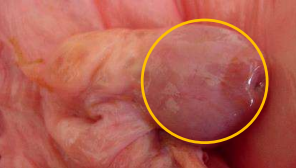
Corpus luteum or follicles?
corpus luteum
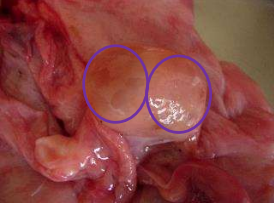
Corpus luteum or follicles?
follicles
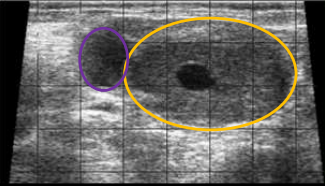
Corpus luteum or follicles?
Corpus luteum
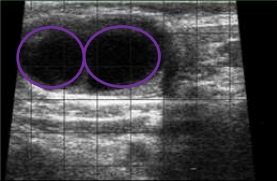
Corpus luteum or follicles?
follicles
What colour is CL on ultrasound?
grey (hypoechoic)
What colour are follicles on ultrasound?
black (anechoic centre)
What does CL look like on ultrasound?
grey with black “lacuna” in centre
Does CL have a thin or thick wall?
thick
Do follicles have a thick or thin wall?
thin