Unit 2: Economics Indicators
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Factor payments
The income earned by the owners of factors of production, such as wages of labor, rent for land, interest for capital, and profits for entrepreneurship
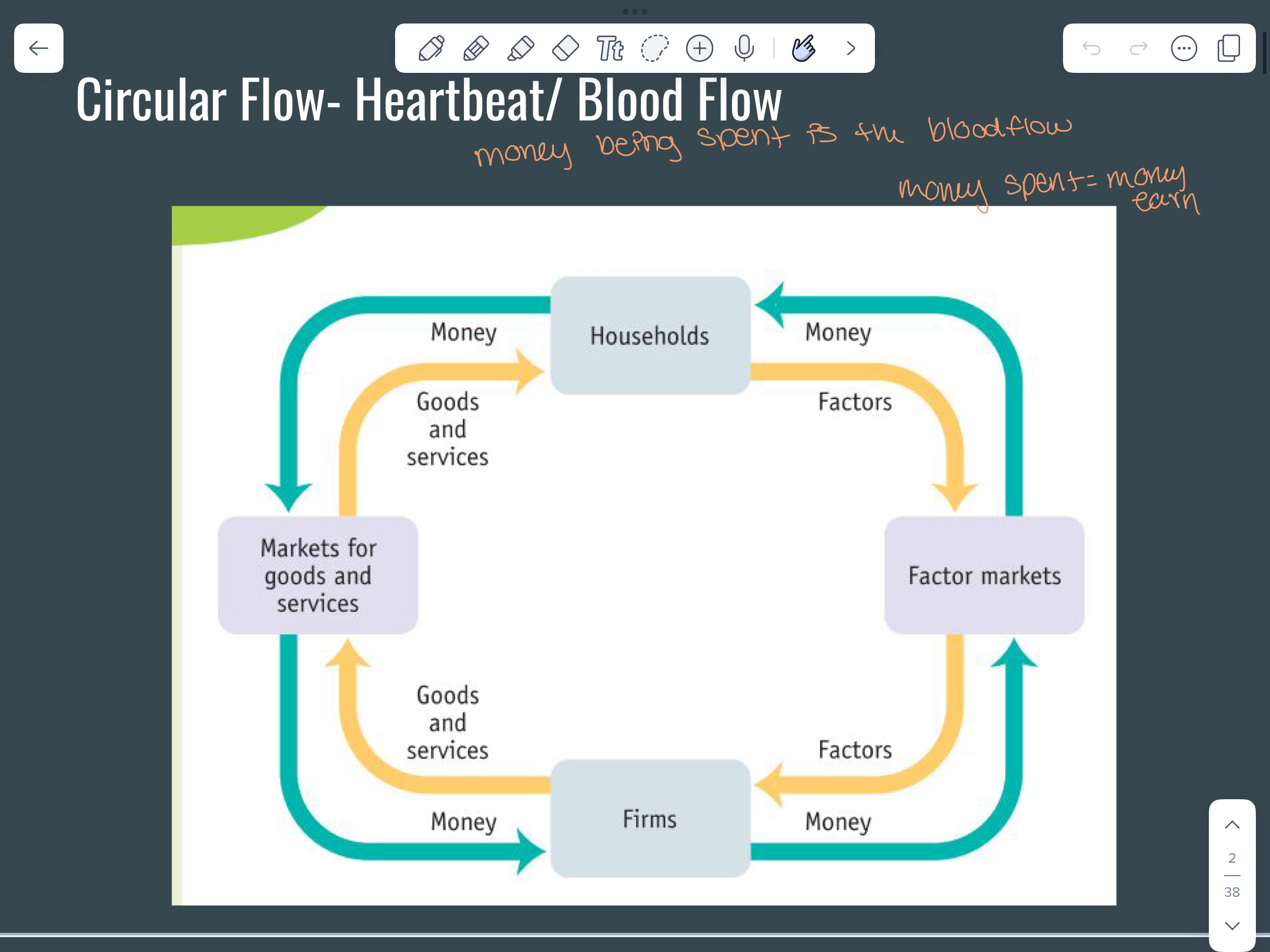
Circular flow model
Shows how goods and services, resources, and money all flow in the economy
Transfer payments
Payments made by the government without any goods or services being exchanged, such as welfare, unemployment compensation, social security, stimulus checks, or subsidies, etc
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country in one year
3 ways to measure GDP
Expenditures approach
Income approach
Value added approach
Expenditures approach
A method of calculating a country’s total economic output (GDP) by summing all spending on final goods and services
GDP=C+I+G+Xn
Expenditures approach equation
GDP=C+I+G+Xn
Income approach
A method for calculating a country’s total economic output (GDP) by summing all income earned in the production of goods and services.
wages+rent+interest+profit
Income approach equation
wages+rent+interest+profit
Value added approach
A method of calculating a country’s total economic output (GDP) by summing the additional value created at each stage of production.
Labor force
Individuals aged 16+ who are either employed or actively seeking employment but currently unemployed, excluding those who are retired, full-time students, homemakers, or otherwise not seeking work.
Labor force participation rate (equation)
(number of people in the labor force/ working age population)x100
Unemployment rate
and its formula
The percentage of the labor force (those working or actively seeking work) that does not have a job
(number of people unemployed/number of people in the labor force)x100
Discouraged workers
given up looking for jobs so they’re no longer counted as unemployed because they’re no longer in the labor force
Frictional unemployment
A person chooses to leave their job for another or between jobs or is searching for the first time, they have skills
Structural unemployment
Changes in demand in an economy cause other skills and abilities to become unneeded or obsolete.
Caused by a fundamental shift in the economy, such as when a new technology removed the need for a worker or when an industry is no longer needed
Cyclical unemployment
Demand for a certain good or service decreases, leading to unemployment.
A decrease in spending overall in the economy
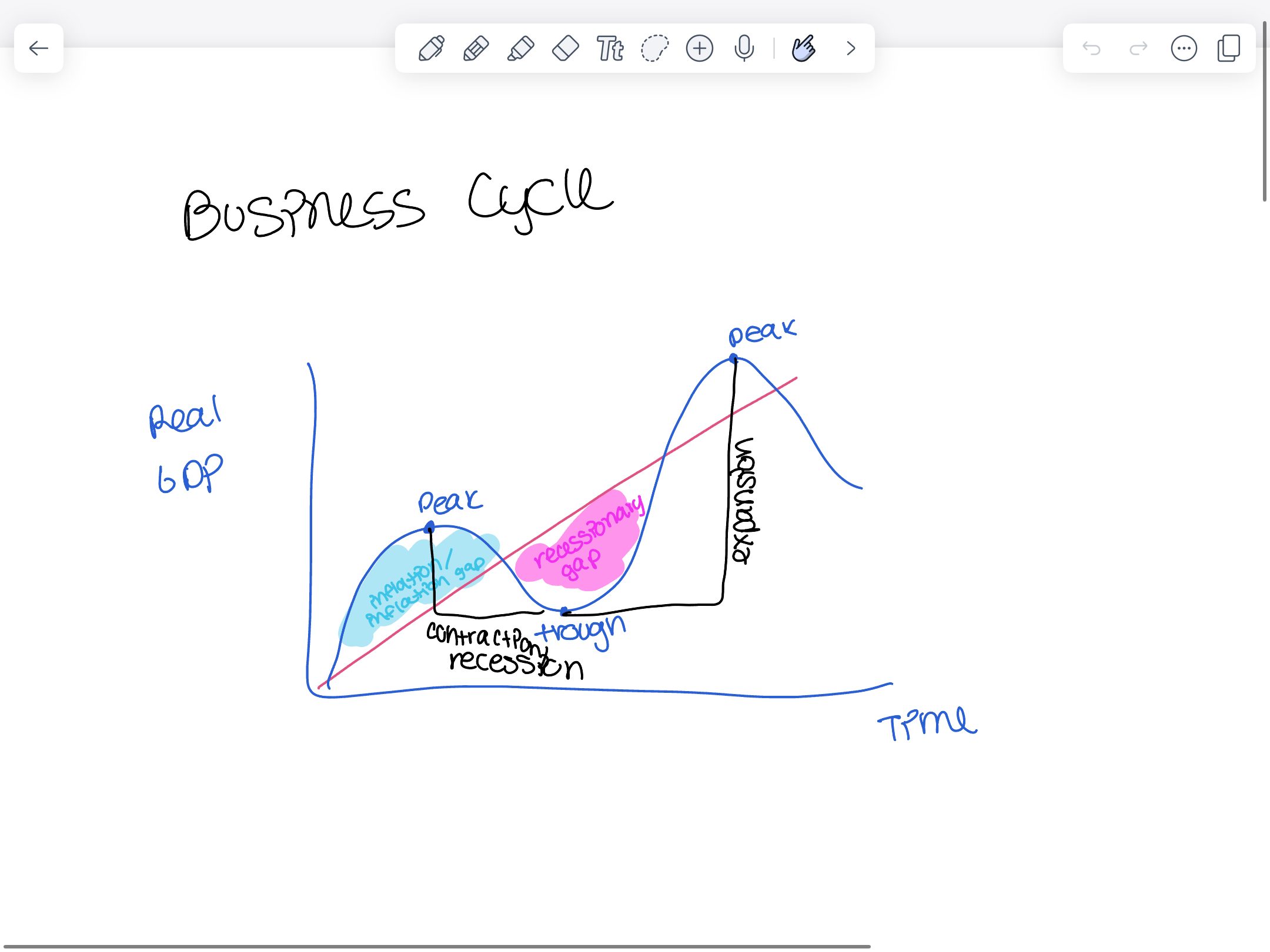
Connection to the business cycle is unemployment due to a recession
Natural rate of unemployment
The level of unemployment that exists when the economy is at full employment, including only frictional and structural unemployment, but not cyclical unemployment
What unemployment types are present when an economy is in a recession?
Frictional, structural, and cyclical
What unemployment types are present when an economy is at full employment?
Only frictional and structural unemployment
When can a economy actually be outside of the PPC graph in terms of unemployment?
Economy can only be here when there’s really low structural and frictional unemployment
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Measures the average change over time in the prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households
(value of a basket in a given year/value of the basket in the base year)x100
Consumer price index (CPI) equation
(value of a basket in a given year/value of the basket in the base year)x100
Inflation
increase in average level of prices
Deflation
decrease in average level of prices
Disinflation
prices are still going up but at a slower rate so basically a decrease in the rate of inflation
Unanticipated infaltion hurts lenders that lends at ___ interest rates and ppl with ____ incomes
fixed
fixed
People who benefit from unanticipated inflation are borrowers who borrow at a ____interest rate
fixed
GDP Deflator
An economic metric that measures the changes in prices of all goods and services produced within a country, providing a broad indicator of inflation
(Nominal GDP/Real GDP)x100
GDP Deflator formula
(Nominal GDP/Real GDP)x100
Key expenditures in GDP
Personal consumption (C)
Government Purchases (G)
Private investment(buying capital)(I)
Net exports (Nx)
Personal Consumption (C)
-the biggest one
Household consumption
2/3 of US economy
Must be purchases of NEW items
Government purchases (G)
-Purchases by all levels of government: national, state, county, city, etc
-Must be purchases of goods and services, not all government spending
-Does not include transfer payments
Private investment (I)
-Goods produced for use in the production of other goods and services (capital)
-Gross Private Investment includes 3 categories: 1(Firms’ spending on new buildings, plants, tools, capital) 2(purchases of new residential housing) 3(additions to firms; resources)
-Must be new items
-Investment is a highly volatile component of GDP
-How businesses think consumers will buy in the future.
-Not stocks and bonds
Net exports (Nx)
Net exports=Exports-Imports
Negative net exports= trade deficit
Positive net exports= trade surplus
Nominal GDP
just total number
Real per capita GDP equation
Real GDP/Population
Real GDP formula
Real GDP = Nominal GDP/Deflator
GDP and GNP
GDP refers to the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country, while GNP includes the value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of location.
Higher (per capita) GDP correlates with
Higher literacy rate
Higher life expectancy
Lower infant mortality
Higher standard of living
Full employment
level of employment when the economy is operating exactly at its full potential
Seasonal unemployment
unemployment caused by the weather or calender
Underemployment
when workers take on work that is beneath their skill level or for fewer level or for fewer hours than full-time employment
Disguised employment
when “true” unemployment is not visible to statistics, such as when companies are overstaffed
Unemployment
when workers who are able and willing to work cannot find jobs
NAIRU
Non Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment
Price index
number whose movement reflects movement in average level of prices
Core CPI
excludes energy and food
Who wins when inflation is higher than expected— borrower or lender?
Borrower
Who wins when inflation is lower than expected— borrower or lender?
Lender
Price index formula
(Current cost of basket/ base period cost of basket)
Rate of inflation formula
(change in index/ initial value of idex)x100
(new-old)/old x100
Business cycle graph