C1.3 Photosynthesis
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Light energy
Plants + photosynthetic organisms (algae, plants, cyanobacteria) start food chains using photosynthesis to transform light energy from Sun into chemical energy in form of glucose
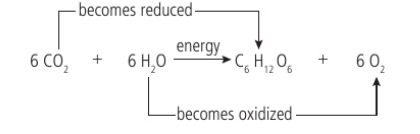
Photosynthesis equation
Water split for hydrogen and oxygen (released)
Released hydrogens reduce CO2 to form glucose
Photosynthetic pigments
Variety in chloroplasts, mostly chlorophyll
Also carotenoids including specific ones- carotene, xanthophyll
Type and concentration is unique to a plant species and can be seperated using chromatography
Chromatography
Allows determination of pigments in chloroplasts
Pigments with higher Rf values are smaller and more soluble
Electromagnetic spectrum
Plants use visible light section- has many colours but can be considered in three regions:
Red end
Green middle
Blue end
Plant reactions to different wavelengths of light
Absorb it (energy absorbed and used)
Reflect it (energy not absorbed, we see the colour)
Ability of photoautotrophs to absorb light
Determined by pigments on chloroplast membranes
Absorption spectrum
Created by plotting amount of light absorbed against light wavelength
Varies depending on type of photosynthetic pigment present
Represents amount of light energy absorbed by pigment
Chlorophylls a+b have high light absorption in violet and red wave lengths
Pigments like carotenoids absorb light at different wavelengths compared to chlorophylls a+b
Other pigments less efficient at light absorption compared chlorophyll a+b
Action spectrum
Indicates rate of photosynthesis at different light wavelengths
Varies depending on type of photosynthetic pigment present
Represents rate of photosynthesis carried out by pigment
Chlorophylls a + b have relatively high rates of photosynthesis
Pigments like carotenoids allow photosynthesis at different wavelengths
Other pigments have less effective rate of photosynthesis compared to chlorophylls a + b
How light energy transforms into chemical energy
When a pigment absorbs light, energy is used to raise an electron to a higher energy level (excitation of electrons)
Requires a specific amount of energy (specific light photons)
Explains why different pigments absorb different wavelengths
Once electrons are excited to a higher level, energy is used for chemical bonds
Measuring rate of photosynthesis
Measure rate of oxygen production or carbon dioxide intake
Measure change in plant’s biomass (indirect reflection as many factors impact growth)
Law of limiting factors
Proposed by Frederick Frost Blackman in 1905
States a process with many limiting factors will have a rate limited by lowest value
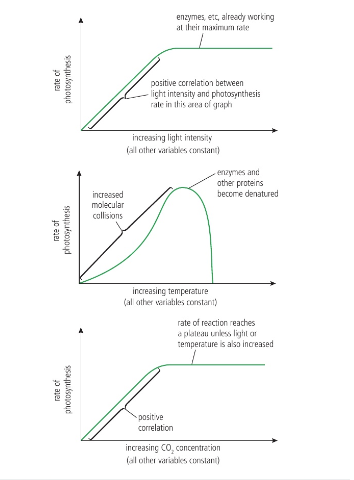
Photosynthesis limiting factors
Amount of water, sunlight, temperature, carbon dioxide, chloroplasts, chlorophyll
Rising carbon dioxide levels and photosynthesis
Many experiments on this showed weed growth increases more than that of plants or trees
Peter Wayne’s study in controlled greenhouses showed doubling carbon dioxide led to 61% more ragweed growth
Experiments in natural settings, FACE
Air-free carbon dioxide enrichments experiments
Allows effect of increasing carbon dioxide to be seen in more natural + agricultural ecosystems→ more reliable