Chapter 4: Greek Art
0.0(0)Studied by 12 people
Card Sorting
1/61
Last updated 7:59 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
Pericles
________ used the extra funds in the Persian war treasury to build the Acropolis; Greek allies were furious that the funds were not returned to them.
2
New cards
Poseidon
________ made saltwater spring from the ground on the Acropolis.
3
New cards
Temples
________ are built with the post- and- lintel system in mind, the columns are never too widely set apart.
4
New cards
krater
The ________ was a bowl for mixing water and wine because the Greeks never drank their wine straight.
5
New cards
Polykleitos
He wrote a famous (no longer existing) book on the canon of human proportions
6
New cards
Iktinos
He wrote on the nature of ideal architecture
7
New cards
Contrapposto
The fluid body movement and relaxed stance that was unknown in freestanding sculpture before this
8
New cards
Encaustic
a type of painting in which colors are added to hot wax to affix to a surface
9
New cards
Peplos
a garment worn by women in ancient Greece, usually full length and tied at the waist
10
New cards
Canon
a body of rules or laws; in Greek art, the ideal mathematical proportion of a figure
11
New cards
Isocephalism
the tradition of depicting heads of figures on the same level
12
New cards
Panathenaic Way
a ceremonial road for a procession built to honor Athena during a festival
13
New cards
Nike
ancient Greek goddess of victory
14
New cards
Stele
an upright stone slab used to mark a grave or a site
15
New cards
Athena
Greek goddess of war and wisdom; patron of Athens
16
New cards
Zeus
King of the ancient Greek gods; known as Jupiter to the Romans; god of the sky and weather
17
New cards
Gigantomachy
a mythical ancient Greek war between the giants and the Olympian gods
18
New cards
Shaft
the body of a column
19
New cards
Metope
a small relief sculpture on the façade of a Greek temple
20
New cards
Architrave
a plain, unornamented lintel on the entablature
21
New cards
Entablature
the upper story of a Greek temple
22
New cards
Portico
an entranceway to a building having columns supporting a roof
23
New cards
Pediments
These are seated over the tops of columns, contain sculptures representing the heroic deeds of the god or goddess housed inside
24
New cards
Cornice
It separates the upper and lower parts of a Greek temple
25
New cards
Agora
a public plaza in a Greek city where commercial, religious, and societal activities are conducted
26
New cards
Bouleuterion
a chamber used by a council of 500 citizens, called a boule, who was chosen by lot to serve for one year
27
New cards
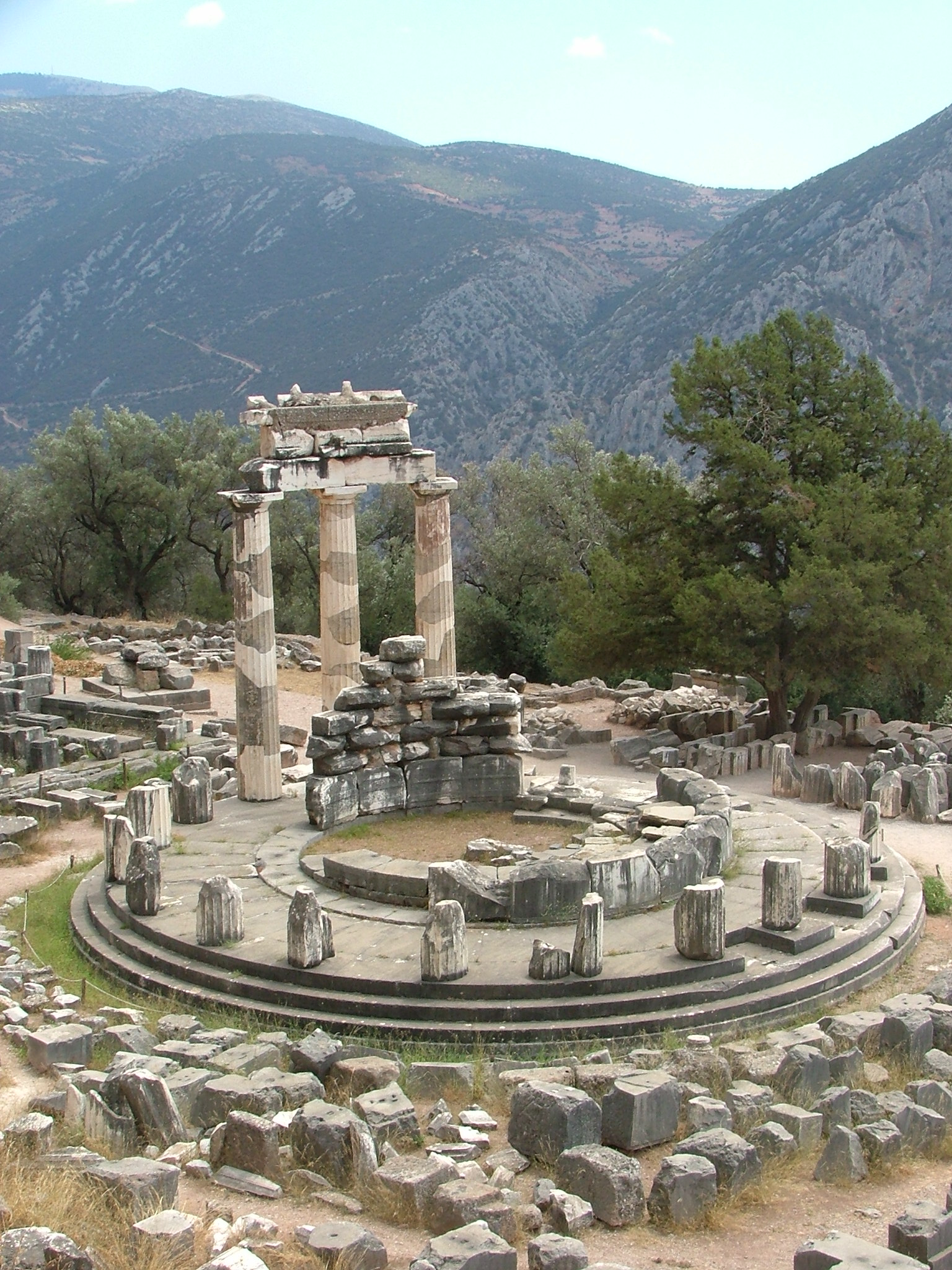

Tholos
a round structure manned by a group of senators 24 hours a day for emergency meetings; served as a dining hall where the prytaneis (executives) of the boule often met
28
New cards
Stoas
Covered walkway with columns on one side and a wall on the other
29
New cards
Cella
the main room of a temple where the god is housed
30
New cards
Amphiprostyle
having four columns in the front and four in the back
31
New cards
Niobe
the model of a grieving mother; after boasting of her fourteen children, jealous gods killed them
32
New cards
Mosaic
a decoration using pieces of stone, marble, or colored glass, called tesserae, that are cemented to a wall or a floor
33
New cards
Peloponnesian War
The worst of these internal struggles happened during the \_____ (431–404 B.C.E.) when Athens was crushed by Sparta.
34
New cards
Alexander the Great
Peloponnesian War did not end until the reign of __________, who, in the fourth century B.C.E., briefly united Macedonians and Greeks, by establishing a mighty empire that eventually toppled the Persians.
35
New cards
nudity
Greek sculpture is unafraid of \_______.
36
New cards
acropolis
Elaborate Greek temple complexes were placed on a high hill, or \____, overlooking the city.
37
New cards
propylaea
Gateways, called \____, prepared the visitor for his or her entrance into the complex.
38
New cards
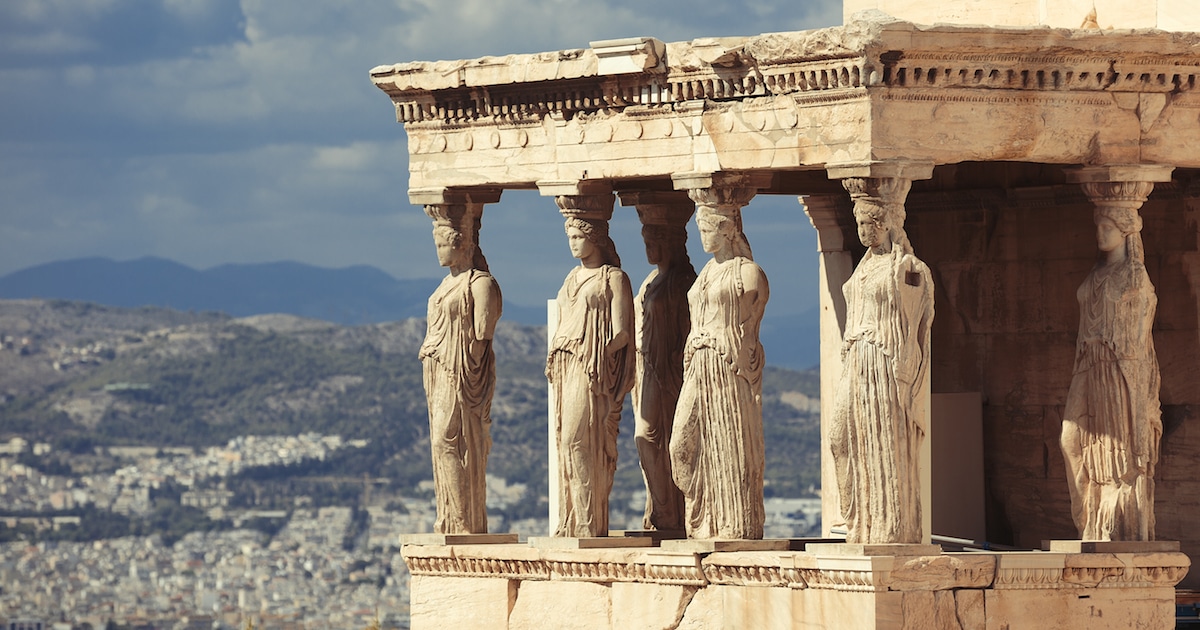

caryatids
The introduction of columns carved as figures, the female version of which are called \____.
39
New cards
peristyle
Temples are built with the post-and-lintel system in mind, the columns are never too widely set apart. The columns completely surround the temple core in a design called a \_____.
40
New cards
Erechtheum
A temple near the Parthenon, houses Poseidon's trident marks, the salt water well, and the sacred olive tree.
41
New cards
kylix
A \____, with its wide mouth and shallow dimensions, was a drinking cup, ideal for the display of scenes on the relatively flat bottom.
42
New cards
amphora
The portable \_____ stored provisions like oil or wine with an opening large enough to admit a ladle.
43
New cards
black figure
In the Archaic period, artists painted in a style called \_______, which emphasized large figures drawn in black on the red natural surface of the clay.
44
New cards
Andokides
At the end of the Archaic period, red-figure vases were introduced by \_______; in effect, they are the reversal of black figure-style pots.
45
New cards
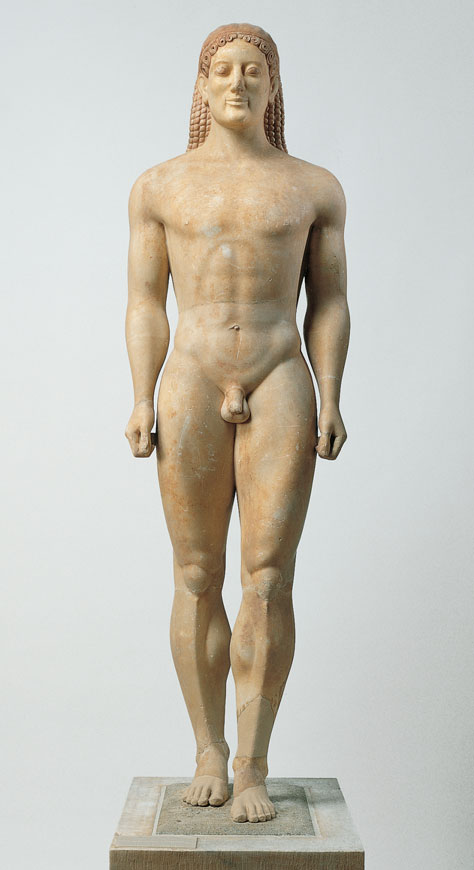

Anavysos Kouros
* Hair is knotted and falls in neatly braided rows down the back.
* “Archaic smile” meant to enliven the sculpture.
* Grave marker, replacing huge vases of the Geometric period.
* Sponsored by an aristocratic family.
* “Archaic smile” meant to enliven the sculpture.
* Grave marker, replacing huge vases of the Geometric period.
* Sponsored by an aristocratic family.
46
New cards
Kroisos
Not a real portrait but a general representation of the dead.
Anavysos Kouros is named after a young military hero ________.
Anavysos Kouros is named after a young military hero ________.
47
New cards
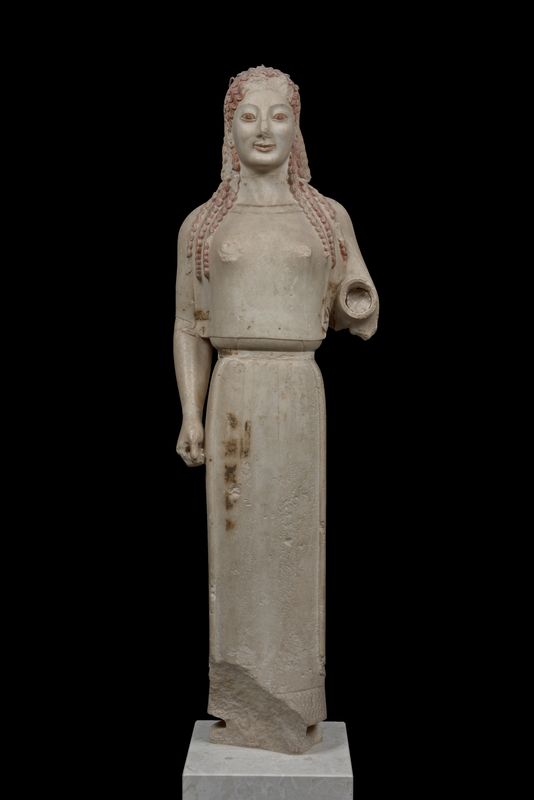

Peplos Kore
* Hand emerges into the viewer’s space
* Breasts revealed beneath drapery; Indented waist.
* Broken hand was fitted into the socket
* she is the goddess, either Athena or Artemis
* Breasts revealed beneath drapery; Indented waist.
* Broken hand was fitted into the socket
* she is the goddess, either Athena or Artemis
48
New cards
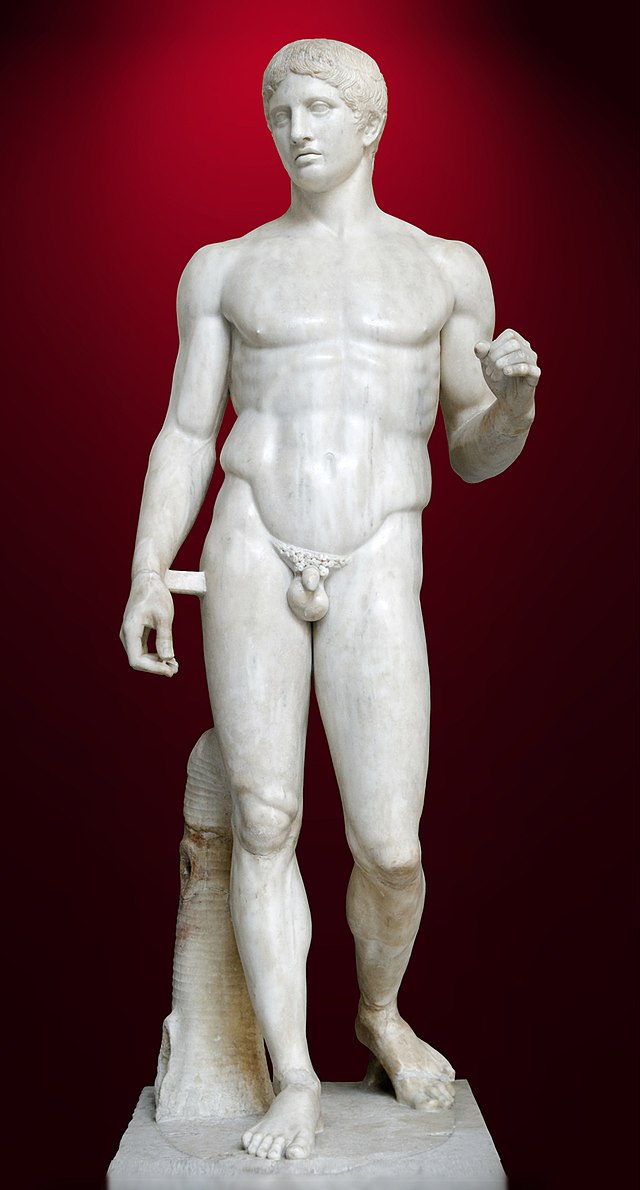

Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
**Details:**
* A sculpture of Polykleitos
* original: c. 450–440 B.C.E.
* A Roman marble copy of a Greek bronze original,
* Found in National Archaeological Museum, Naples
* A sculpture of Polykleitos
* original: c. 450–440 B.C.E.
* A Roman marble copy of a Greek bronze original,
* Found in National Archaeological Museum, Naples
49
New cards
Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
* Represents Polykleitos’s ideal masculine figure.
* Marble Roman copy of a bronze Greek original
* Found in Pompeii in a place for athletic training
* Marble Roman copy of a bronze Greek original
* Found in Pompeii in a place for athletic training
50
New cards

Helios, Horses, and Dionysus (Heracles?)
* Figures seated in the left-hand corner of the east pediment of the Parthenon
* contains figures who are present at the birth of Athena, which is the main topic at the center of pediment—now lost.
* Part of the Parthenon sculptures, also called the **Elgin Marbles**.
* contains figures who are present at the birth of Athena, which is the main topic at the center of pediment—now lost.
* Part of the Parthenon sculptures, also called the **Elgin Marbles**.
51
New cards
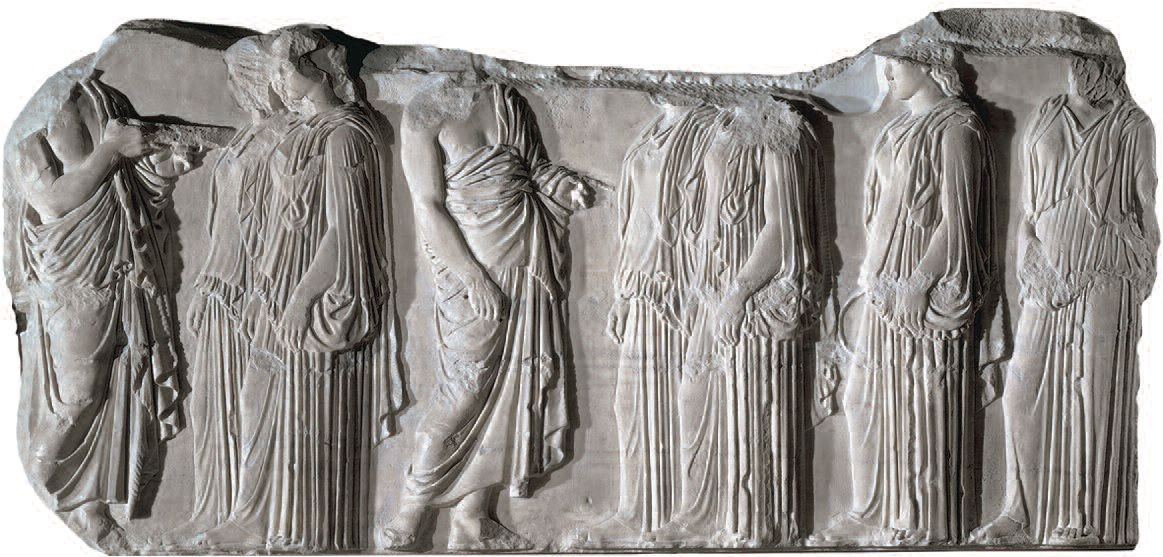

Plaque of the Ergastines
* Part of frieze from Parthenon
* Scene from Panatenaic friend
* first time in Greek art that human events are depicted on a temple.
* contains a religious procession of women dressed in contemporary drapery and acting nobly
* Scene from Panatenaic friend
* first time in Greek art that human events are depicted on a temple.
* contains a religious procession of women dressed in contemporary drapery and acting nobly
52
New cards

Victory adjusting her sandal
* Part of the balustrade on the Temple of Athena Nike, a war monument.
* One of many figures on the balustrade
* Not a continuous narrative but a sequence of independent scenes.
* One of many figures on the balustrade
* Not a continuous narrative but a sequence of independent scenes.
53
New cards
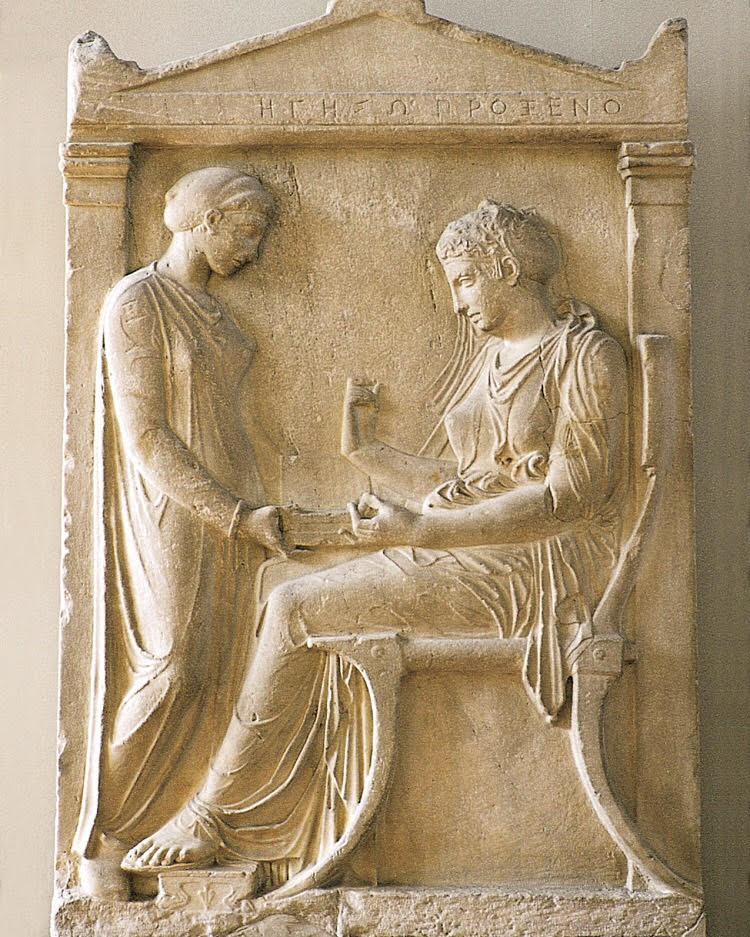

Grave stele of Hegeso
* Grave marker.
* Use of contrapposto in the standing figure.
* Text includes name of the deceased.
* Erected in the Dipylon cemetery in Athens
* Use of contrapposto in the standing figure.
* Text includes name of the deceased.
* Erected in the Dipylon cemetery in Athens
54
New cards
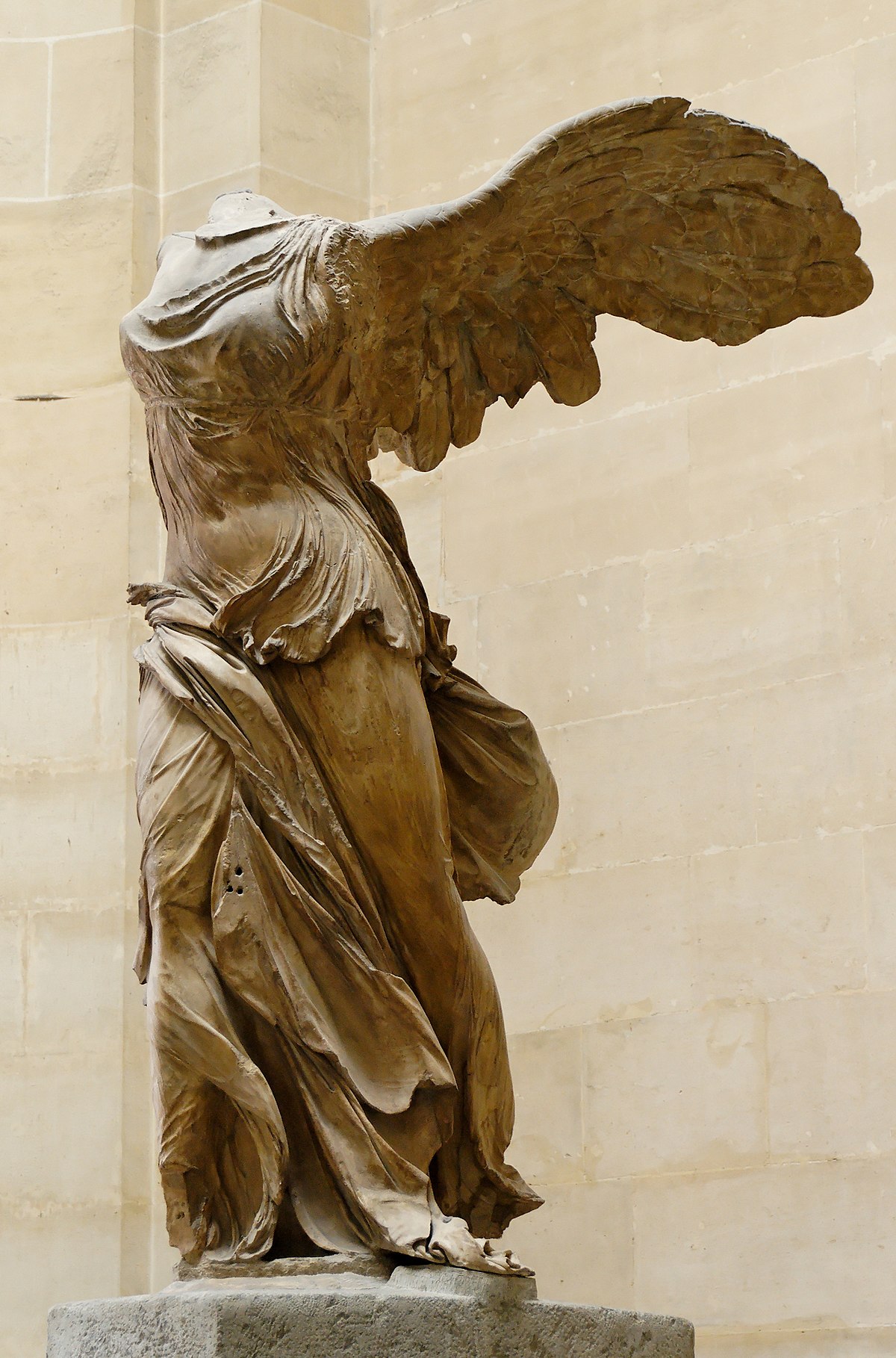

Winged Victory of Samothrace
* Large heroic figure of Nike placed above the marble prow of a naval vessel.
* Monumental figure.
* made to commemorate a naval victory in 191 B.C.E.
* Found in 1863 in situ on Samothrace.
* Monumental figure.
* made to commemorate a naval victory in 191 B.C.E.
* Found in 1863 in situ on Samothrace.
55
New cards
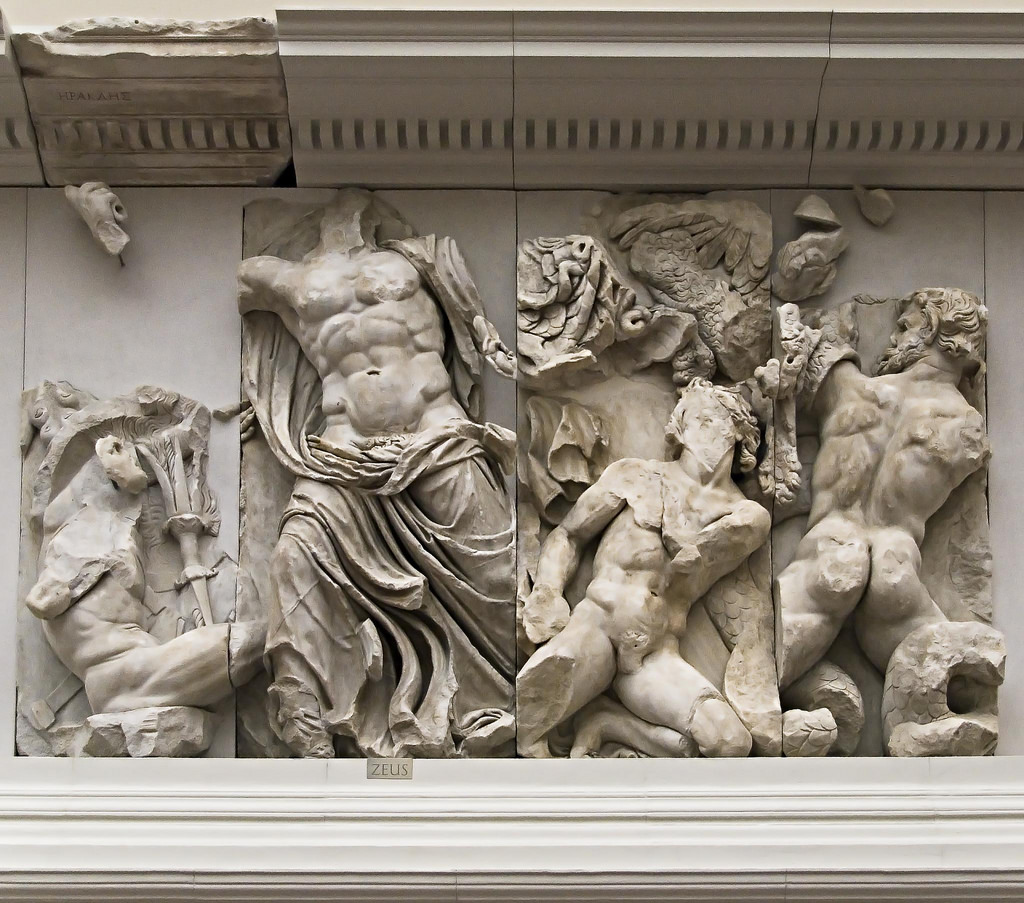

Athena, from the Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
* Describes the battle between the gods and the giants
* The gods’ victory over the giants offers a parallel to Alexander the Great’s defeat of the Persians.
* Also acts as an allegory of a Greek military victory by Eumenes II.
* The gods’ victory over the giants offers a parallel to Alexander the Great’s defeat of the Persians.
* Also acts as an allegory of a Greek military victory by Eumenes II.
56
New cards
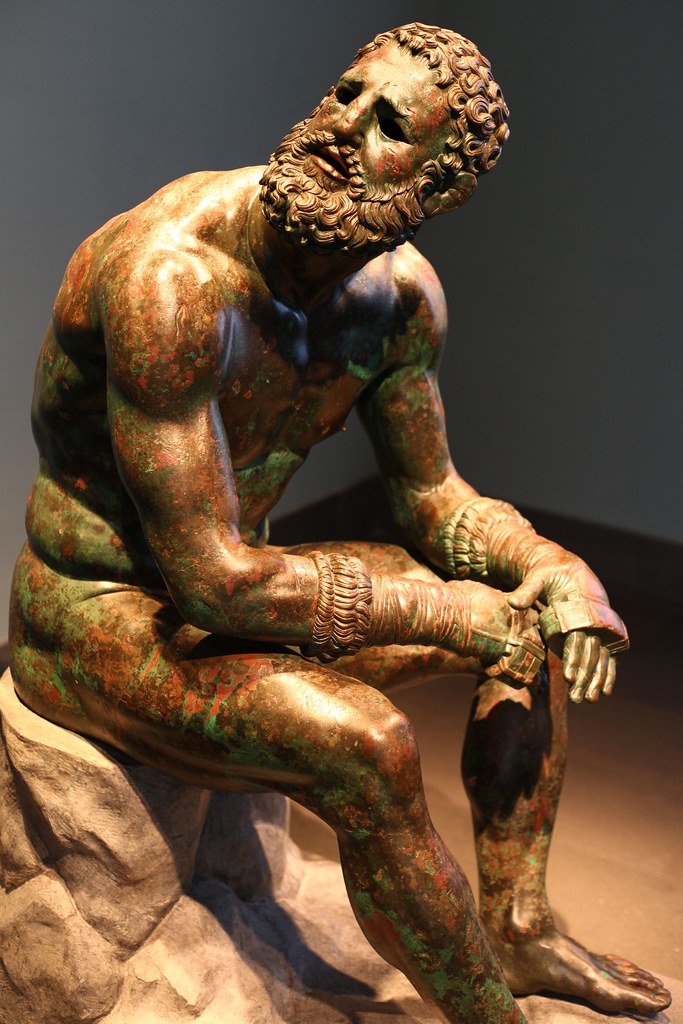

Seated Boxer
* Rare surviving Hellenistic bronze.
* Older man, past his prime, looks defeated.
* May have been a good luck charm for athletes
* Nude fighter; hands wrapped in leather bands
* Older man, past his prime, looks defeated.
* May have been a good luck charm for athletes
* Nude fighter; hands wrapped in leather bands
57
New cards
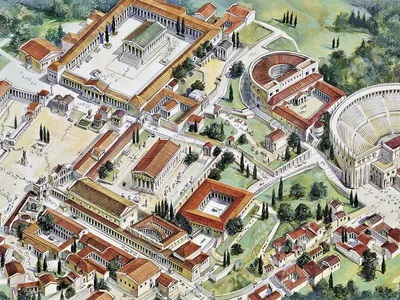
Athenian Agora
A plaza at the base of the Acropolis in Athens with commercial, civic, religious, and social buildings where ceremonies took place.
58
New cards

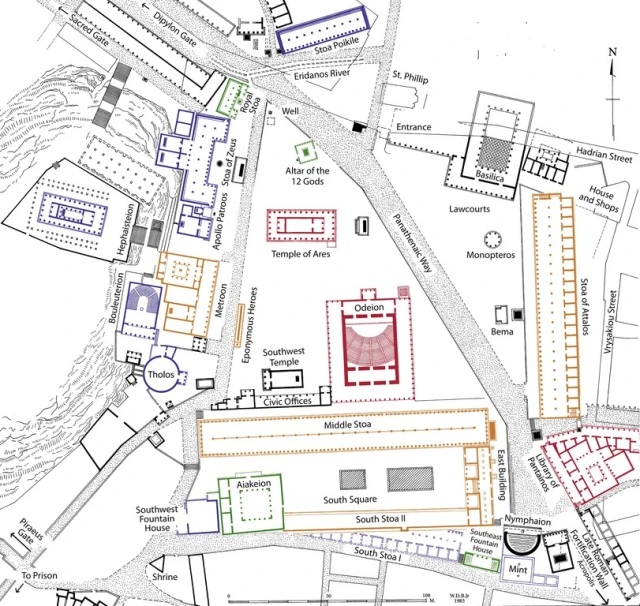
Parthenon
* Architects: Iktinos
* Interior built to house a massive statue of Athena
* also included the treasure of the Delian League
* Greek predilection for algebra and geometry is omnipresent in the design of this building
* Constructed under the leadership of Pericles
* Interior built to house a massive statue of Athena
* also included the treasure of the Delian League
* Greek predilection for algebra and geometry is omnipresent in the design of this building
* Constructed under the leadership of Pericles
59
New cards
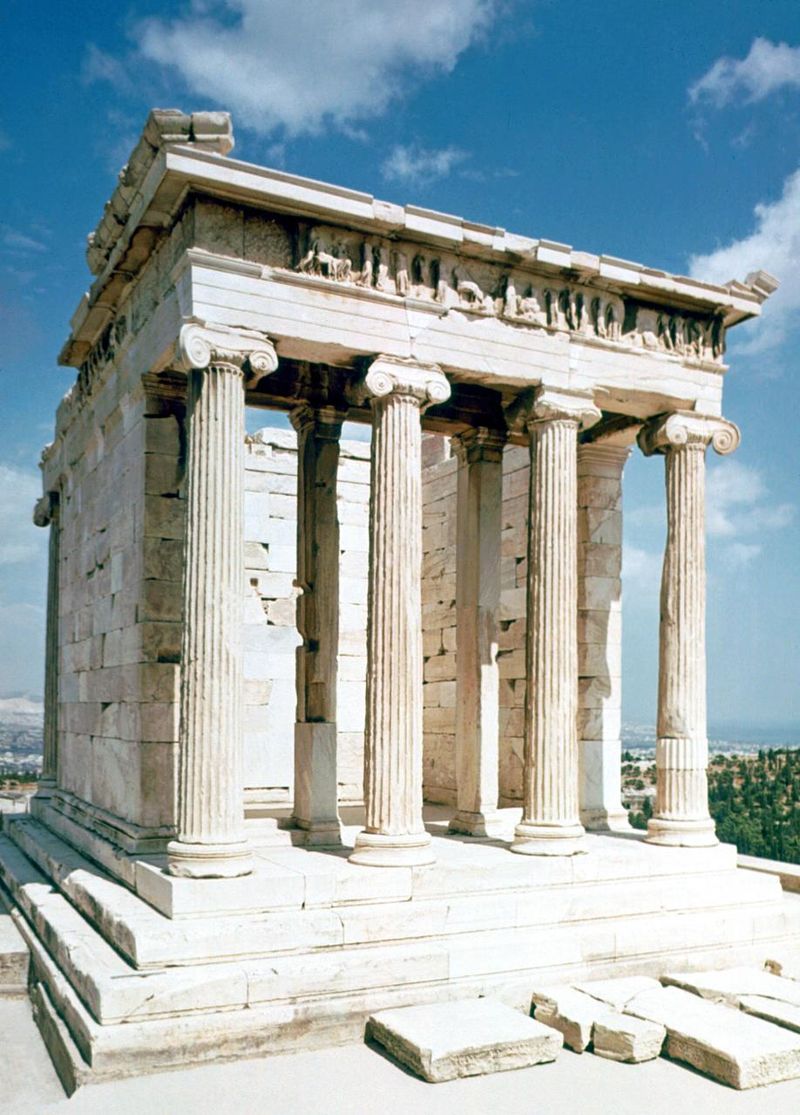

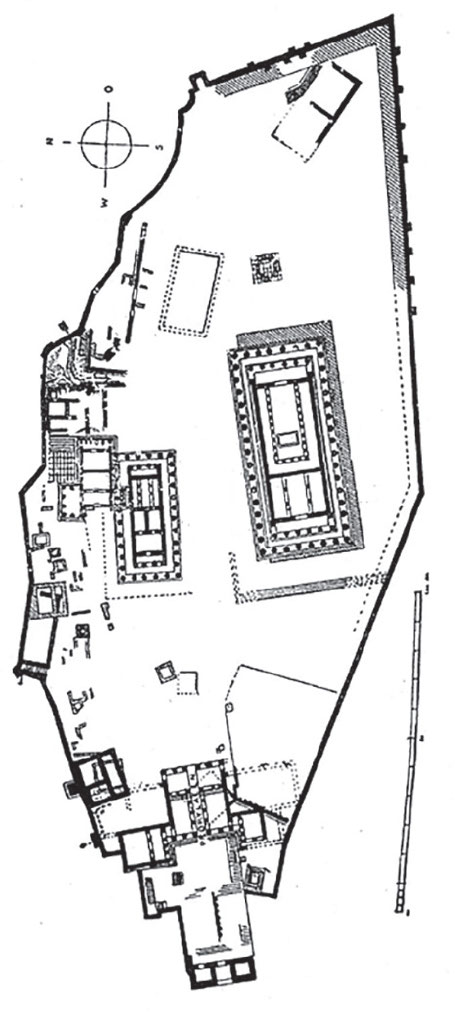
Temple of Athena Nike
* Architect: Kallikrates
* Amphiprostyle | Ionic Temple
* Built to commemorate the Greek victory over the Persians in the Battle of Marathon
* Amphiprostyle | Ionic Temple
* Built to commemorate the Greek victory over the Persians in the Battle of Marathon
60
New cards
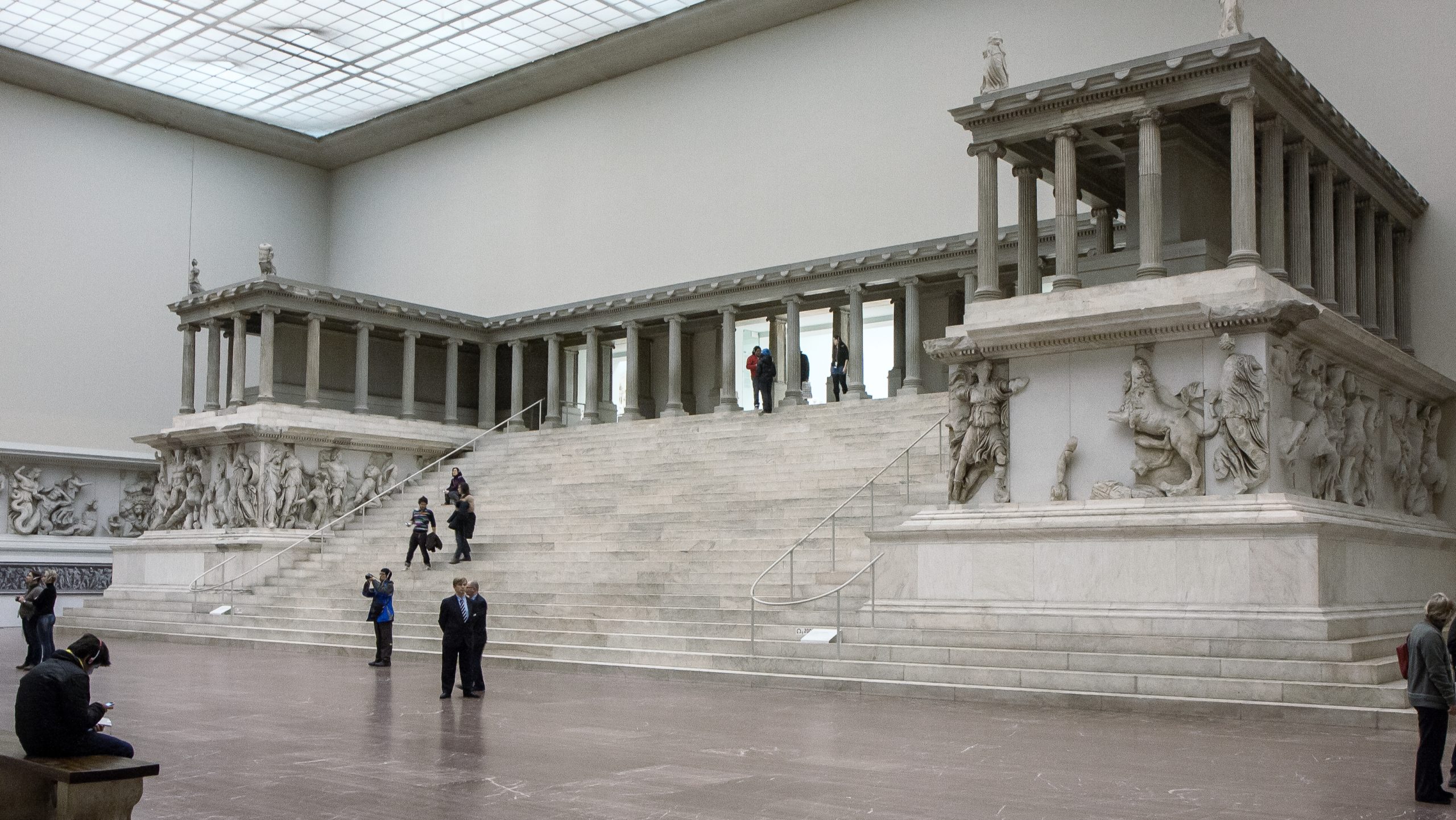

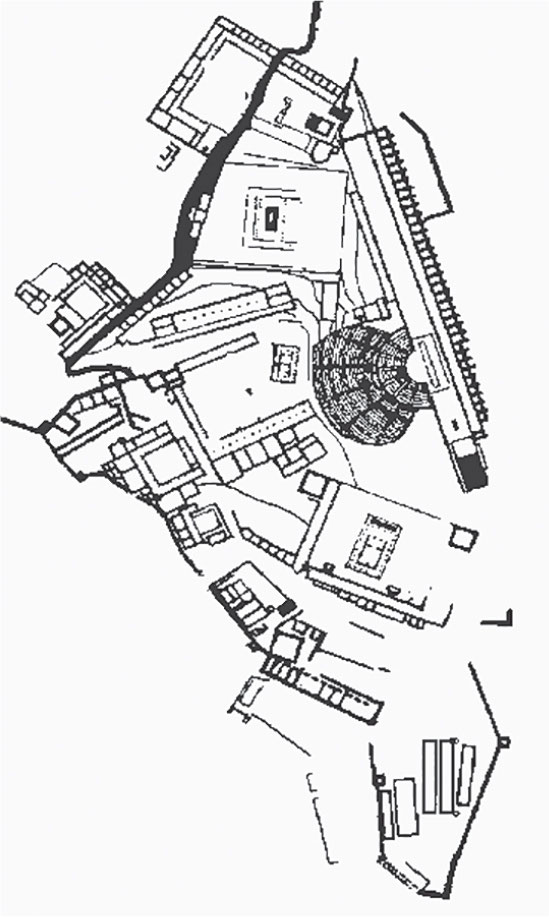
Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
* Altar is on an elevated platform at the top of a dramatic flight of stairs.
* A frieze 7.5 feet high and more than 400 feet long wraps around the monument.
* Altar dedicated to Zeus and Athena
* A frieze 7.5 feet high and more than 400 feet long wraps around the monument.
* Altar dedicated to Zeus and Athena
61
New cards
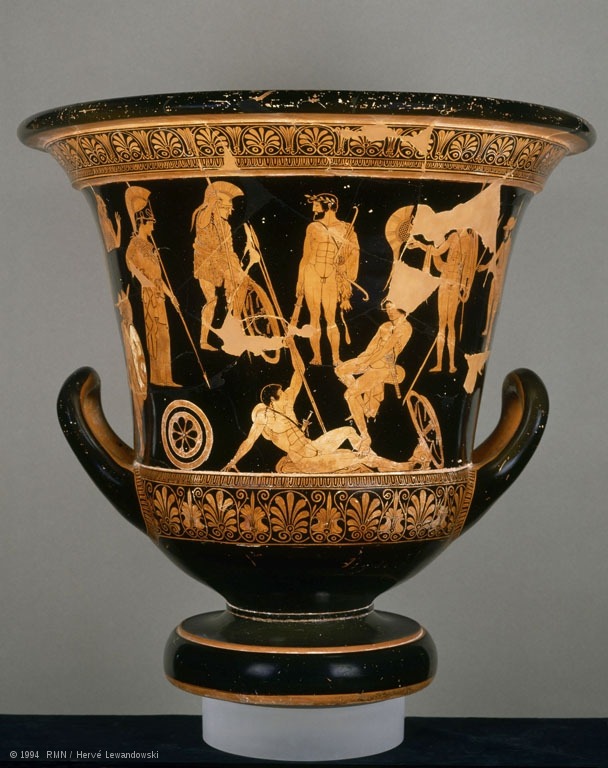

Niobides Krater
* First time in vase painting that isocephalism
* For ceremonial use
* Called in that name because the killing of Niobe’s children is depicted on one side.
* For ceremonial use
* Called in that name because the killing of Niobe’s children is depicted on one side.
62
New cards
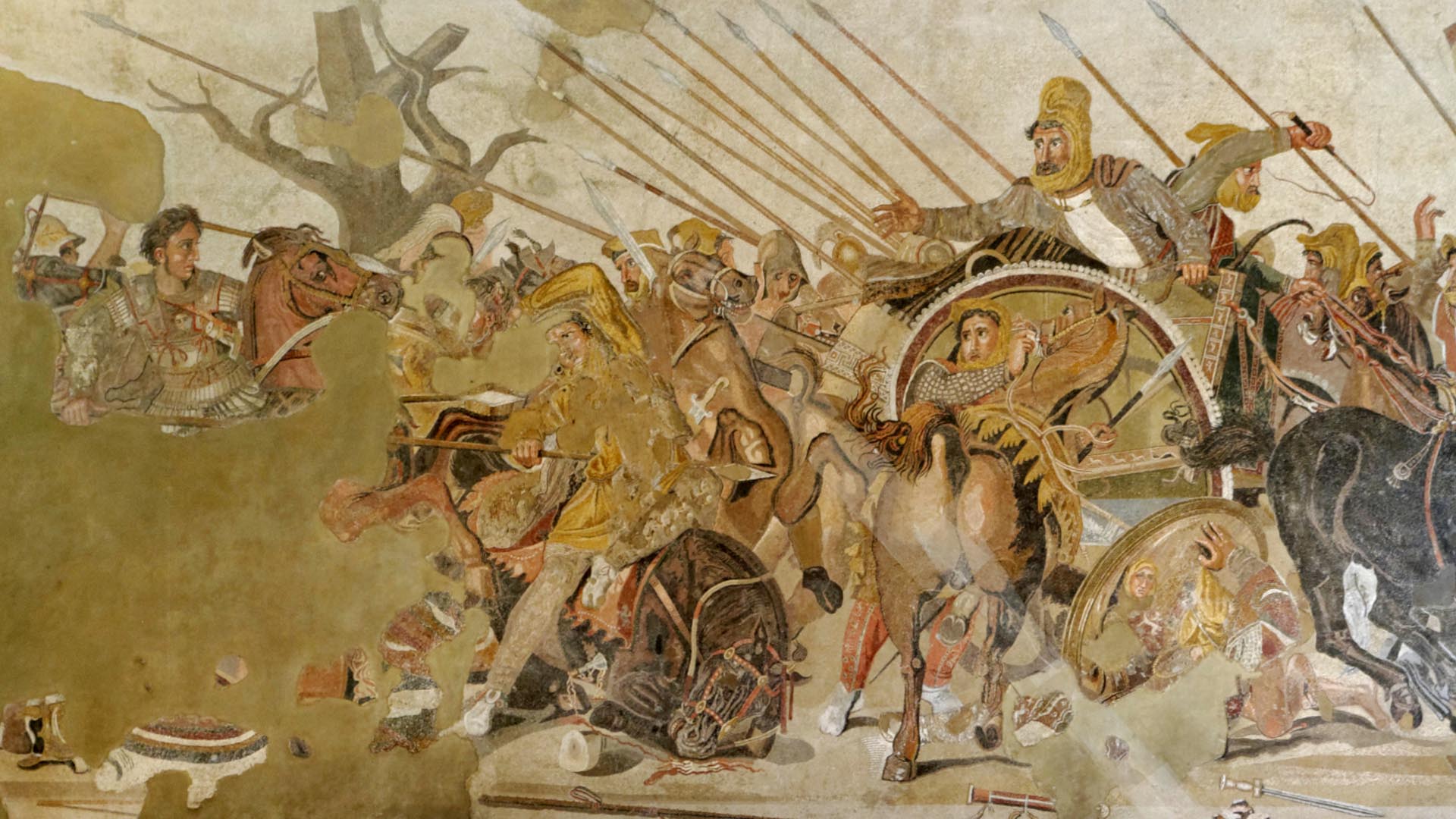

Alexander Mosaic
* Extremely complex interweaving of figures; spatial illusionism through foreshortening, chiaroscuro, reflection in shield.
* Use of tesserae instead of previously used pebbles.
* A copy of a mural made by Piloxenos of Eretria for King Cassander.
* Use of tesserae instead of previously used pebbles.
* A copy of a mural made by Piloxenos of Eretria for King Cassander.