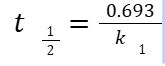PHA6120: UNIT 1: MATH CONCEPTS, RATES, HALF-LIFE
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
x
In the expression: 𝑁 = 𝑏x
is the exponent
b
In the expression: 𝑁 = 𝑏x
is the base
N
In the expression: 𝑁 = 𝑏x
is the number when b is raised to the xth power (bx)
logarithm
The _ of a positive number N to a given base b is the exponent x to which the base must be raised to equal the number N.
pH
_ of biological fluids can affect LADME
logarithmic
pH scale is is a _ scale
Time
independent variable, plotted on the abscissa (x axis)
Drug concentration
dependent variable, plotted on the ordinate (y axis)
RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
SEMILOG COORDINATES
CURVE FITTING
Implies that there is some sort of relationship between variables x and y (ie. drug vs. pharmacologic effect).
CURVE FITTING
Continuous function of x and y
x
y=mx+b
Where
_ = independent variable
y
y=mx+b
Where
_ = dependent variable
b
y=mx+b
Where
_ = the y-intercept
m
y=mx+b
Where
_ = the slope of the straight line
EQUATION OF A STRAIGHT LINE
y=mx+b
POSITIVE
ZERO
NEGATIVE
LINEAR REGRESSION
This method is often encountered and used in clinical pharmacy studies to construct a linear relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable
Coefficient of determination (r2)
expresses how much variability in the outcome is explained by the input factor
RATE PROCESSES
The rate of chemical reaction is the velocity with which the reaction occurs
RATE PROCESSES
is used to describe processes such as drug absorption or drug elimination
ORDER OF REACTION
The way in which the concentration of the drug or reactant in a chemical reaction affects the rate of chemical reaction or process
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
Proceeds over time (t) independent from the concentration of the drug (C)
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
Fixed amount of drug is removed per unit time
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
The rate of a first-order process is dependent upon the concentration of the drug (C)
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
Fixed percentage of drug is removed per unit time
HALF-LIFE
The time required for one-half of the drug concentration to disappear (t½ )
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
Dependent on:
Concentration at time zero Rate constant
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
Independent of:
Concentration at time zero
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
Plot the data on a semi-log graph
If the data appear to form a straight line with good correlation using linear regression, then the data likely follow _
non-zero order
Plot the data on a rectangular graph
If the data appear to be a curve rather than a straight line, the reaction rate for the data is _
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
Fixed amount of drug is removed per unit time
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
Concentration independent
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
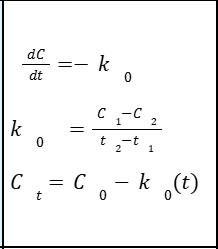
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
(mg/L)/h
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
A plot of C vs time on a rectangular graphing paper yields a straight line.
ZERO-ORDER KINETICS
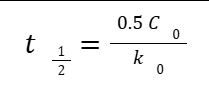
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
Fixed percentage of drug is removed per unit time
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
Concentration dependent
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
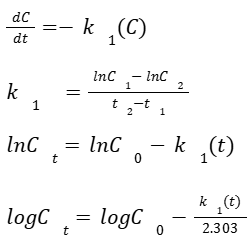
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
1/h
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS
A plot of C vs time on semi-log graphing paper yields a straight line.
FIRST-ORDER KINETICS