03 IS 2639 - Lesson 3: Network Technologies and Topologies (copy)
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Topology
describes the lay of the land
Network Topology
describes how a network is physically laid out and how signals travel from one device to another
True
True or False
Physical layout of the devices and cables doesn’t describe how signals travel from one device to another
Physical and Logical Topologies
Network topologies are categorized into 2 kinds of topologies, what are these?
Physical Topology
Arrangement of cabling and how cables connect one device to another in a network is considered the network’s
Logical Topology
path data travels between computers on a network is considered the ___________
Bus
Star
Ring
Point-to-point
All network designs today are based on these basic physical topologies:
Physical bus topology
defined as a continuous length of cable connecting one computer to another in daisy-chain fashion
Physical Bus Topology
simplest and at one time the most common method for connecting computers
Electrical Pulses
________ (signals) travel the cable’s length in all directions
Signal Propagation
Signals traveling across the medium and from device to device is called __________
Terminator
Signals traveling across the medium and from device to device are called signal propagation, signal continues until it weakens or is absorbed by ________
Terminator
an electrical component called a resistor that absorbs the signal instead of allowing it to bounce back up the wire
Signal Bounce
If not terminated, the signal bounces or is “reflected” at the end of the medium
________ is the term used when electricity bounces off the end of a cable and back in the other direction
Physical Star Topology
Use a central device (hub or switch) to connect computers
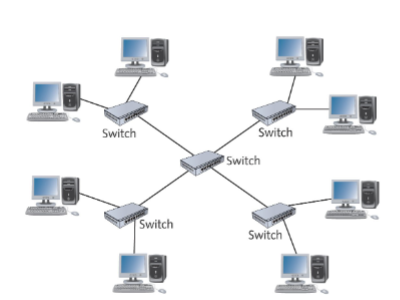
Extended Star
most widely used in networks containing more than just a few computers
Central device
A __________ sits in the middle and instead of attached computers, other switches or hubs are connected to the central switch’s ports
Hierarchical Star
Extended Star is sometimes referred to as a __________
Extended Star
This topology is most effective when the center of the star is running at a much faster speed than other devices
Extended Star Topology Network
What kind of topology is shown in the picture?
True
True or False
How Data Travels in a Physical Star
Details of how data travels in a physical start depend on the type of central device
The central device determines the ‘logical’ topology
Physical Ring Topology
like a bus and devices are daisy-chained one to another. Instead of terminating each end, the cabling is brought around from the last device back to the first device to form a ring
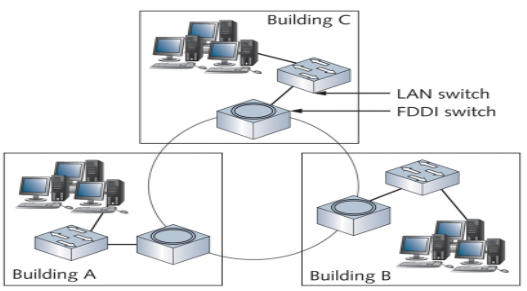
Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI)
Physical Ring Topology was most widely used to connect LANs with a technology called _______
FDDI
most often used as a network backbone, which is cabling used to communicate between LANs or between hubs and switches
Dual Ring
FDDI uses a _________, which means data travels in both directions, one ring failure doesn’t break network
Physical Ring Topology
What kind of topology is this?
Point-to-Point
a direct link between two devices
It is mostly used in WANs
Point-to-Multipoint Technology
an arrangement where a central device communicates with two or more other devices. All communication goes through the central device
Point-to-Multipoint Technology
often used in WANs where a main office has connections to several branch offices via a router
Mesh Topology
connects each device to every other device in a network. Multiple point-to-point connections for the purposes of redundancy and fault tolerance
To ensure that if one or more connections fail, there’s another path for reaching all devices on the network
purpose of creating a mesh topology
Large Wans, Internetwork
Mesh Topology is found in ______ and _______
Logical Topology
Describes how data travels from computer to computer
Physical Topology
Logical topology is sometimes same as ____
True
True or False
In a physical bus and physical ring, the logical topology mimics the physical arrangement of cables
Physical Star
A logical ring using a __________ implements the ring inside the central device’s electronics, which is a MAU in the token ring technology
Switched Topology
there is always an electrical connection between the computer and the switch but when no data is being transferred there is no logical connection or circuit between the devices
Network Technology
The method a network interface uses to access the medium and send data frames and the structure of these frames
Network interface layer technologies
Network architectures
Data link layer technologies
Other Terms for Network Technologies
Ethernet, 802.11 Wireless
A network uses __________, ___________ wireless, or some combination of these to move data from device to device in your network
Frame Format, Media
The network technology often defines ______ and _______
Unshielded Twisted Pair
most common media type in LANs
Consists of 4 pairs of copper wires each twisted together
True
True or False
In Unshielded Twisted Pair, the higher the number, the higher the cable’s bandwidth potential
Fiber-optic Cabling
uses thin strands of glass to carry pulses of light long distances and at high data rates
Isn’t susceptible to electrical interference
Coaxial Cable
obsolete as a LAN medium but it is used as the network medium for Internet access via cable modem
Baseband
sends digital signals in which each bit of data is represented by a pulse of electricity or light. Sent at a single fixed frequency and no other frames can be sent along with it
Broadband
uses analog techniques to encode binary 1s and 0s across a continuous range of values. Signals flow at a particular frequency and each frequency represents a channel of data
Ethernet
most popular LAN technology. Advantages include ease of installation, scalability, media support, and low cost
10 Mbps to 10 Gbps
Ethernet Networks supports a broad range of speeds
True
True or False
Ethernet can operate a in physical bus or physical star and logical bus or switched logical topology
Frame
Unit of network information that NICs and Switches work with
Media Access Method
a set of rules governing how and when the medium can be accessed for transmission
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Ethernet uses ________
Collision Domain
extent to which signals in an Ethernet bus topology network are propagated
True
True or False
All devices in a collision domain are subject to the possibility that whenever a device sends a frame, a collision might occur
Network Protocols
Ethernet relies on _________ to ensure delivery
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
Error-checking code in an frame’s trailer is __________
Half-duplex Communication
works like a two-way radio; you can talk and listen but not both at the same time
Full-Duplex Communication
means NIC/switch can transmit/receive simultaneously
True
True or False
CSMA/CD is not used because a collision cannot occur in full-duplex mode
True
True or False
Most switches operate in full-duplex
Using the IEEE document number defining the standard (IEEE 802.3)
XBaseY – 10BaseT, 100BaseT, 100BaseFX
Ethernet standards are expressed in one of two ways:
10BaseT Ethernet
Uses two of the four wire pairs
Runs over Category 3 or higher UTP cabling
Highly susceptible to collisions and is obsolete
100BaseTX Ethernet
Most common Ethernet variety
Runs over Category 5 or higher UTP
Uses two of four wire pairs
Also sometimes called “Fast Ethernet”
100BaseFX Ethernet
Runs over two strands of fiber optic cabling
Typically used as backbone cabling between hubs or switches
Also used to connect clients or servers when immunity to noise and eavesdropping is required
1000BaseT Ethernet
Usually called “Gigabit Ethernet”
Runs over Category 5e or higher UTP and uses all four wire pairs
To support full-duplex transmission over a single pair of wires:
1000BaseT uses hybrid and canceller technology, which combines multiple signals and cancels interference
2.5GBaseT and 5GBaseT
This specification was largely in response to increasing Wi-Fi speeds
Faster wired Ethernet speeds are needed as uplink ports from new 802.11ac APs
Runs over Cat 5e/6 cabling
10GBaseT Ethernet
Runs over four pairs of Category 6A or 7 UTP
Operates only in full-duplex mode
No hubs, only switches support 10GBaseT
Still considered an expensive option, although prices are dropping
Good for network servers so they can keep up with desktop systems that commonly operate at 1 Gbps
100BaseT4
Uses all four pairs of wires in UTP Category 3 cable
Obsolete
1000BaseLX
Uses fiber-optic media
“L” stands for “long wavelength” laser
Supports a maximum cable segment length of 5,000 meters
Some manufacturers have extended it by using specialized and proprietary optical transceivers
1000BaseSX
Uses fiber-optic media
“S” stands for “short wavelength” laser
Can’t cover as much distance as long-wavelength lasers, but are less expensive
1000BaseCX
Uses specially shielded, balanced, copper jumper cables
Might also be called “twinax” or “short-haul” copper cables
10 Gigabit Ethernet IEEE 802.3ae Standards
Much like the others in frame formats and media access
Defined to run only on fiber-optic cabling and specifies a maximum distance of 40 kilometers
Primarily used for network backbones
Varieties:
10GBaseSR, 10GBaseLR, 10GBaseER, 10GBaseSW, 10GBaseLW, and 10GBaseEW
40 Gigabit and 100 Gigabit Ethernet
Very high cost is still prohibitive
Adoption has been slow
Fiber-optic cabling is primary medium
Although there are provisions to use special copper assemblies over short distances
802.11 wireless
also referred to as Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi)
Hotspot
In most towns you can usually find a public Wi-Fi network, called a _____
Airwaves
802.11 is essentially an extension to Ethernet. Using _______ instead of cabling as the medium
Infrastructure mode use a central access point (AP)
Ad hoc mode is a mode of operation where there is no central device
Wi-Fi can operate in one of two modes
Infrastructure mode use a central access point (AP)
Stations connect through a wireless AP before they can communicate with other devices
Ad hoc mode is a mode of operation where there is no central device
Data travels from device to device like a bus
Sometimes called “peer-to-peer mode”
2.4GHz and 5.0 GHz
Wi-Fi networks operate at one of two radio frequencies:
2.4 GHz
actually 2.412 thru 2.484 divided into 14 channels spaced 5 MHz apart
5.0 GHz
actually 4.915 thru 5.825 GHz divided into 42 channels of 10, 20, or 40 MHz each
TV Channel
A wireless channel works like a _______:
You must tune to the correct channel to connect
True
True or False
If you are configuring several Wi-Fi networks:
Choose channel five apart from other known APs
Transmitted, Receiver
The antenna on a Wi-Fi device is both ____and ____
Characteristics and placement determine how well a device transmits or receives Wi-Fi signals
Omnidirectional antennas
signals radiate out from the antenna with equal strength in all directions
Unidirectional antenna
signals are focused in a single direction
Ideal for placement at one end of long, narrow spaces
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
Wi-Fi devices use __________
Absorption
solid objects absorb radio signals, causing them to attenuate (weaken)
Refraction
the bending of a radio signal as it passes from a medium of one density through a medium of a different density
Diffraction
the altering of a wave as it tries to bend around an object
Reflection
occurs when a signal hits a dense, reflective material, resulting in signal loss
Scattering
when a signal changes direction in unpredictable ways, causing a loss in signal strength
Signal-to-noise ratio
the amount of noise compared with the signal strength, Noise can come from equipment, other wireless devices, and other wireless networks
Throughput
the actual amount of data transferred
Not counting errors and acknowledgements
Goodput
actual application-to-application data transfer speed
Overhead
Packet frame headers, acknowledgements, and retransmissions are collectively known as
802.11a
requires more power and has a shorter indoor range, transfers data at 54 Mbps
802.11b
was the most widely accepted standard because of its low cost and good indoor range