Biology ELLIE RYAN 9B
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Name two groups of cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells info
Smaller (cell membrane, cytoplasm and cell wall and NO nucleus), genetic material not in a nucleus- single DNA loop and may contain small circular DNA called plasmid
Example of a prokaryotic cell
Bacteria
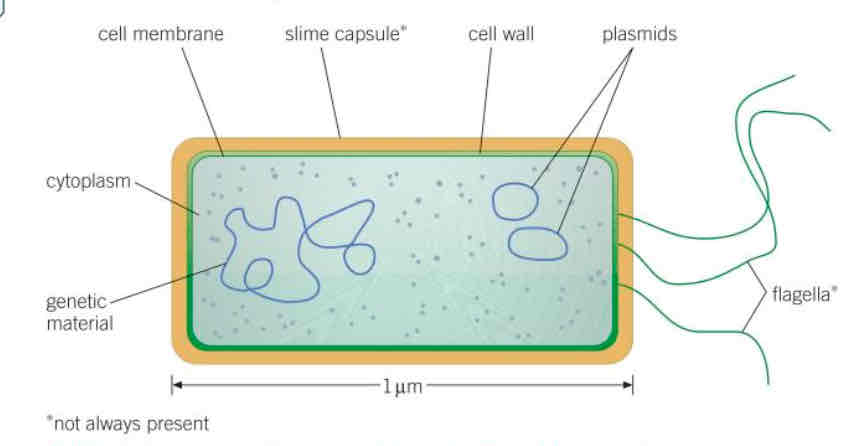
Diagram of a bacteria cell
Genetic information, cytoplasm, cell membrane, slime capsules*, cell wall, plasmids, flagella* (* not always included)
Eukaryotic cells info
More complex (cell membrane, cytoplasm- may or may not have a cell wall), have a nucleus which contains the genetic information
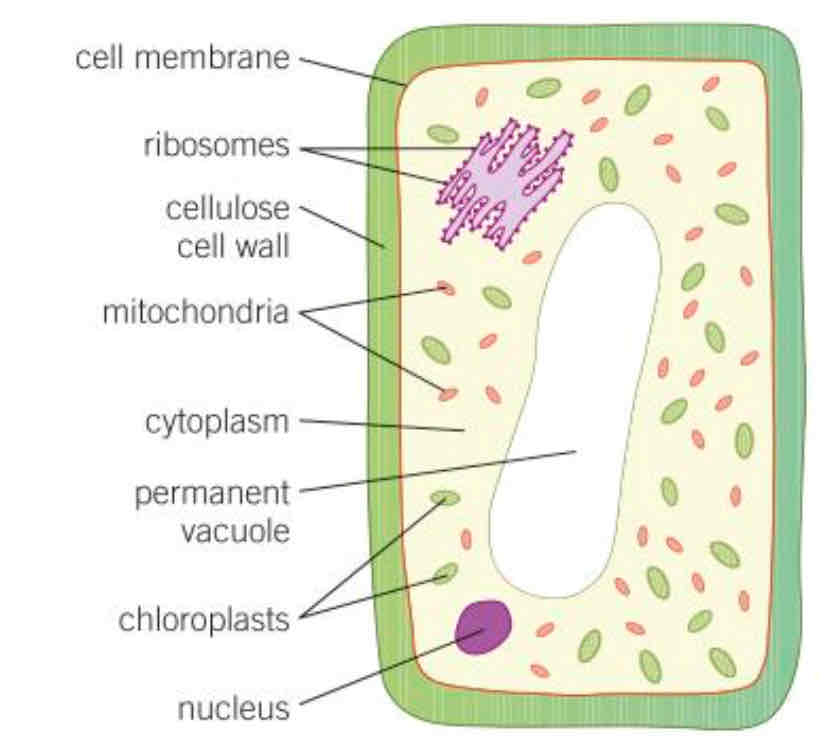
Example of eukaryotic cells
PLANT CELL Cell membrane, ribosomes, cell wall, mitochondria, cytoplasm, permanent vacuole, chloroplast and nucleus
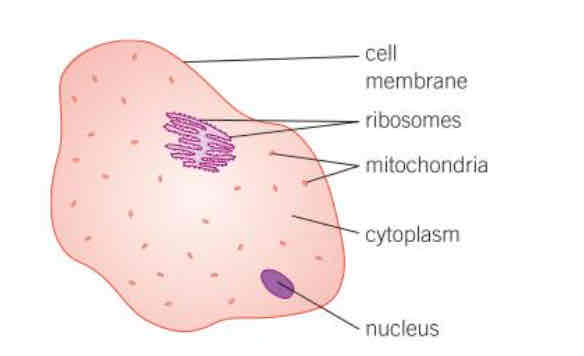
Example of eukaryotic cells
ANIMAL CELL Cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria, cytoplasm and nucleus
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration (release of energy)
Nucleus
Controls cell activity - contains genetic material
Cell membrane
Controls movement of substances in and out of cells
Cytoplasm
Liquid gel where most of cell reactions happen (e.g anaerobic respiration)
Cell wall
Cellulose for strength (algae have too)
Chloroplast
Contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Vacuole
Contains cell sap - keeps it rigid
The difference between chlorophyll and chloroplast
Chloroplast is the organelle structure- chlorophyll is the green pigment that absorbs sunlight
As an organism develops
Cells differentiate to form specialised cells
What is a specialised cell
A cell that has got different sub-cellular structure, so its structure is linked to its function- specific to its job
What are examples of specialised cells in animals
Nerve cells - long axons to carry electrical impulses over long distances, special ends that release chemicals to transfer messages to other nerves, lots of mitochondria to release energy from respiration
Muscle cells
Many mitochondria for high rate of respiration to contract, stores of glycogen as energy source for respiration
Sperm cells
Tail to swim towards egg, mid-section has lots of mitochondria to release energy for respiration, acrosome (head)has enzymes that breakdown egg layers to gain access.
Examples of specialised cells in plants
Root hair cells - have extensions (hairs) to increase SA for fast absorption of water/nutrients, many mitochondria to provide energy for active transport of nutrients against con gradient, have thin cell walls to provide a short diffusion/osmosis distance.
Xylem cell
Long hollow dead tube cells for fast movement of water up the plant, cell wall strengthened with lignin
Phloem cells
Special sieve holed walls to allow movement of dissolved substances, no internal structure to obstruct flow
In mature animals, what is most cell division for?
Repair and replacement
When does cell division occur?
Animal - at early embryos stage, plants retain the ability to differentiate throughout life
Types of microscopes
Light and electron
Why is the electron microscope useful
To study cells in finer detail
Advantages of electron microscope?
Has a bigger magnification and better resolution
Resolution and magnification
Resolution- the ability to distinguish between two separate points which are close together, magnification = how many times bigger the object gets
The magnification equation
Magnification (m)= image size (I) x object size (o), image size = magnification x object size, object size= image size/magnification
What is it important to remember before using the equation?
Getting all the data into the same units
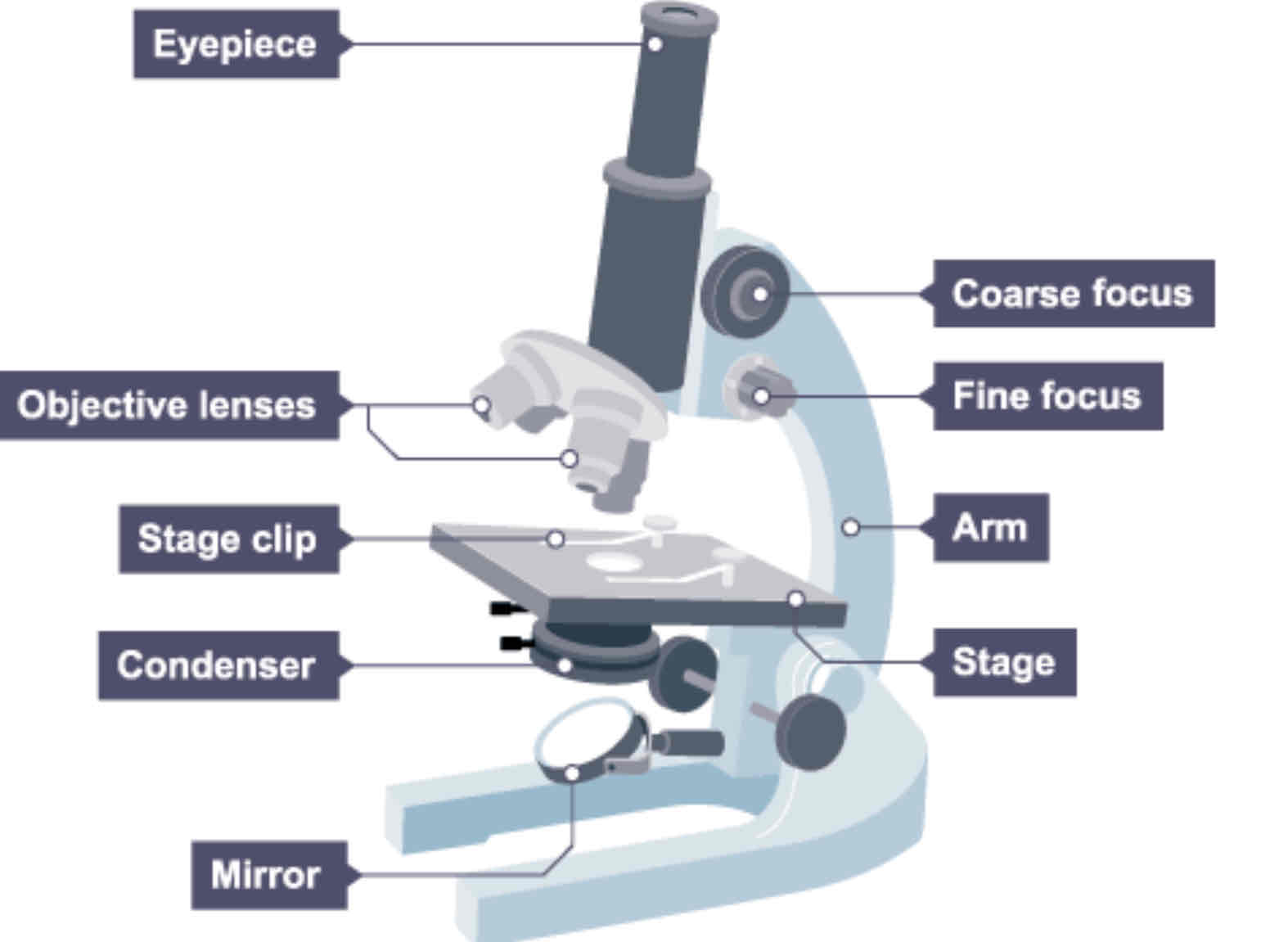
Labels of the light microscope
eyepiece lens
Coarse focus
Fine focus
High power objective lens
Low power objective lens
Slide stage
Mirror
Orders of magnitude
10 times bigger = 10(1) bigger = 1 order
100 times bigger = 10(2) bigger = 2 orders
1000 times bigger = 10(3) bigger = 3 orders
How to work out how many time bigger objects are?
Divide the bigger number by the smaller one - answer should be 10,100,1000
What are three ways substances can move
Diffusion, osmosis and active transport
Why do substances need to move
Life processes need gases and other dissolved substances before they can happen.
E.g respiration requires glucose and oxygen to be inside cells
Photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide and water to get into the plant
What is diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Down the concentration ( high concentration to low concentration).
Passive process - require no energy
Occurs until equilibrium
Examples of diffusion
oxygen from the air into the bloodstream
Co(2) from the bloodstream into the air
Oxygen into cells do body from the blood to supply respiration
Carbon dioxide into actively photosynthesising cells
What causes diffusion
passive - no energy required: relies on molecules moving randomly due to the energy they have
Factors that affect the rate of diffusion (ROD) and what makes diffusion quicker
difference in concentration - the larger concentration gradient = faster ROD
Temperature/thermal energy- higher temperature = faster ROD
Surface area - larger SA = faster ROD
What is osmosis
The movement of water molecules from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
Down the concentration gradient (high concentration to low concentration)
Passive process- requires no energy
Occurs until equilibrium
A high concentration of water is also known as
dilute solution
A low concentration of water is known as
A concentrated solution
importance of osmosis in plants
To keep tugor of cell - vacuole fills with water and cell becomes hard and rigid
What is active transport
the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to high concentration
Against the concentration gradient
Active process- requires energy
Example of active transport
glucose from low concentration in small intestine into the blood
Glucose re-absorption in the kidney
Uptake of mineral ions in the root of plants
Genetics size rule
cells contain nucleus, which contain chromosomes, which are made up of genes, which have a genetic code nahe from the molecule DNA
What are chromosomes
structure of inheritance- made up of many genes
what are genes
section of DNA that codes for a particular trait
what are alleles
Different versions of a particular gene, eg blue eyes or green eyes
what is DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid- the molecule of inheritance = the genetic code
what shape is DNA
double helix
what is the genetic code used for
to combine amino acids in a specific order to make proteins such as enzymes
in humans, how many chromosomes do cells have
normal body- cells 46 gamete 23
what are gametes
the sex cells, sperm or egg
why do most organisms have an even number of chromosomes
they occur in pairs, one inherited from each parent
the pairs are called?
homologous pairs- two of each chromosome
what does this mean
we have two copies of each gene
what is cell division
a cell splitting its nucleus and membrane to create new cells
what are the two types
mitosis and meiosis
what is mitosis
the production of two genetically identical cells from an original cell which have the same numbers of chromosomes
what is it important for
growth, tissue repair and replacement
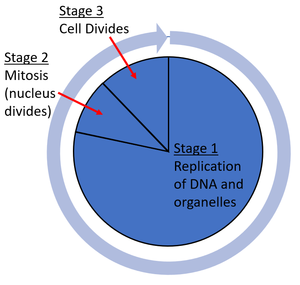
what happens during mitosis division
DNA replicates and divides once
what is the cell cycle
series of stages that cause cells to divide
stages of the cell cycle
cell grows and makes more mitochondria and ribosomes, DNA replicates
one set of chromosomes moves to each end of cell, nucleus divides (mitosis)
cytoplasm and cell membrane divides to form two genetically identical cells
what are stem cells
in specialised cells that can differentiate into any specialised cell of an organism
what is differentiation
stem cells becoming specialised- being assigned a specific job
when does differentiation happen in animals
manly during early stages of development in womb
in plants
they keep some stem cells even whah mature in their meristem tissue (root and shoots)
what can stem cells be used for in plants
cloning plants - creating genetically identical plants for research, horticulture and agriculture protecting rare species from extinction
human stem cells- sources
embryonic stem cells- human embryos
adult stem cells- bone marrow
problems with adult stem cells
keeping some specialism and so cannot be made to differentiate into all types of cells but can turn into lots of cells including blood cells
human stem cell use
cloned to differentiate into cells tissue organs for medical therapy
examples
nerve cells - paralysis
pancreatic cells - diabetes
organs - e.g kidney for transplant
heart cells - heart attack recovery
how are these cells made
embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient - this means that the cells tissue organs are not rejected by the patient’s immune system
Evaluation of stem cell therapy
Pros: reduce suffering by treating diseases/ save NHS money/ no rejection issues
Cons: expensive and not always effective : ethical issues with discarding embryos / possible transfer of viral infections
Summary: the high cost spent research a developing the treatment will be outweighed by saving to NHS once treatment is established so i think its a good idea.
what is health
a state of physical and mental wellbeing
what are the types of diseases
non communicable diseases and communicable diseases
what is the difference
communicable is infectious
what else can meal us ill
diet - overeating= risk of type 2 diabetes
stress - linked to heart disease/ cancer
life situations- where you live = access to medication
example of NCD
Coronary heart disease, stroke, COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
what contributes to NCD
risk factors- aspects of a person lifestyle or substance present in a person body/environment that have been shown to be linked to an increased rate of disease
most diseases
are cause by the interaction of the numbers of factors

what is a casual relationship ( but we’re knee deep in the passenger seat and you’re eating my out)
for some ncd have been proved that a certain risk caused the disease
if there is no casual relationship what do we describe the increase risk as?
a correlation- as a risk factor increases so does disease however correlation is not causation another factor may be involved eg genetics
how can different types of diseases interact
defect the immune system means you are more likely to to suffer infectious disease
viruses living in cells can be triggers for cancer (eg HPV - cervical cancer)
immune reactors caused by a pathogen can trigger allergies (asthma/ rashes)
what are the known risk factors for disease
the effects of diet smoking and exercise on cardiovascular disease
obesity as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes
the effects of alcohol on the liver and the brain function
the effects of smoking on lung disease and lung cancer
the effects of smoking and alcohol on unborn babies
carcinogens, including ionising radiation, as a risk factor for cancer
what do you need to be aware of in terms of effects of non-communicable diseases
the human cost (death) the financial cost (treatment) for an individual, community, nation or globally
explain the effects of poor diet?
a poor diet increases your risk of developing cardiovascular disease directly through cholesterol levels caused CAD and indirectly through obesity (body stress of being overweight)
what is the effect of exercise
reduces the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease
obesity is a strong risk factor for
type 2 diabetes
explain the effects of high alcohol consumption
alcohol is toxic and damages the liver causes cirrhosis and liver cancer- it also causes brain damage and can affect unborn babies’ development
explain the effects of smoking
smoking causes cardiovascular disease including coronary heart disease, lung cancer and COPD
if a foetus is exposed to smoke?
has restricted oxygen levels and carbon monoxide takes the place of oxygen in red blood cells this leads to low birth weight premature and still birth
what is cancer
a change in cells that lead to uncontrolled cell growth and division. uncontrolled cell growth can cause cancers to grow very large
what changes in a cancer cell
the DNA in the nucleus
this change in called a mutation
what are the two types of tumours
benign and malignant
features of benign tumours
growth of abnormal cells which are contained in one area usually within a membrane
they do not invade other parts of the body
features of a malignant tumour
generally referred to as cancers
some of the cancers cells split off and travel to different parts of the body in the blood
they settle in different organs and form secondary tumors