Chapter 3: Markets (Macro)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Why is specialization important to understand regarding trade?
People and countries tend to produce goods where there is a lower opportunity cost. Everyone cannot produce everything because we are confronted with resource, time, and talent constraints.
Market
The buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service.
What are 4 characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
1. Standardized goods
2. No transaction costs (Limited Barrier of entry)
3. Full information
4. Buyers and sellers are price takers
Examples of perfectly competitive markets:
Farmers Markets
Foreign exchange markets
Basic commodities such as wheat, eggs, or corn
What are consumers usually driven by in the market?
maximize the utility (satisfaction) they get from available incomes.
What are businesses driven by in the market?
maximize profits by selling goods that satisfy demand while keeping costs low.
What are governments driven by in the market?
maximize the general welfare of society, constrained by a budget (sources?) and the laws of society.
market economy
an economy in which private individuals, rather than a centralized planning authority, make the decisions
market
buyers and sellers who trade a particular good or service
competitive market
a market in which fully informed, price-taking buyers and sellers easily trade a standardized good or service
price taker
a buyer or seller who cannot affect the market price. In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price takers as a consequence of many sellers selling standardized goods
standardized good
a good for which any two units have the same features and are interchangeable
Participants are price takers
Neither buyers nor sellers have the power to affect the market price
Full Information
Market participants know everything about the price and features of the good
Demand
How much people are willing and able to buy under certain circumstances
quantity demanded
the amount of a particular good that buyers will purchase at a given price during a specified period
law of demand
An increase in the price of a good lowers the quantity demanded of that good, while a decrease in the price of a good raises the quantity demanded of that good.
Nonprice detriments
all the factors (other than price) that affect how much of a product people want to buy or companies want to sell.
Examples of Nonprice Detriments for demand
Income - If people earn more money, they usually buy more stuff
Preferences - If a product becomes trendy or goes out of style
Population - More people in an area means more potential buyers
Prices of related goods - If Coke gets expensive, people might buy more Pepsi
Future expectations - If people think prices will rise next month, they might buy more now
Examples of Nonprice Detriments for supply
Production costs - If materials or labor get cheaper, companies can sell more profitably
Technology - Better machines can produce more goods more efficiently
Number of sellers - More companies in the market means more total supply
Government policies - Taxes, subsidies, or regulations that affect production
Future expectations - If companies think demand will increase, they might produce more now
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase (demand) at various prices
demand curve
a graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that consumers will demand at various prices
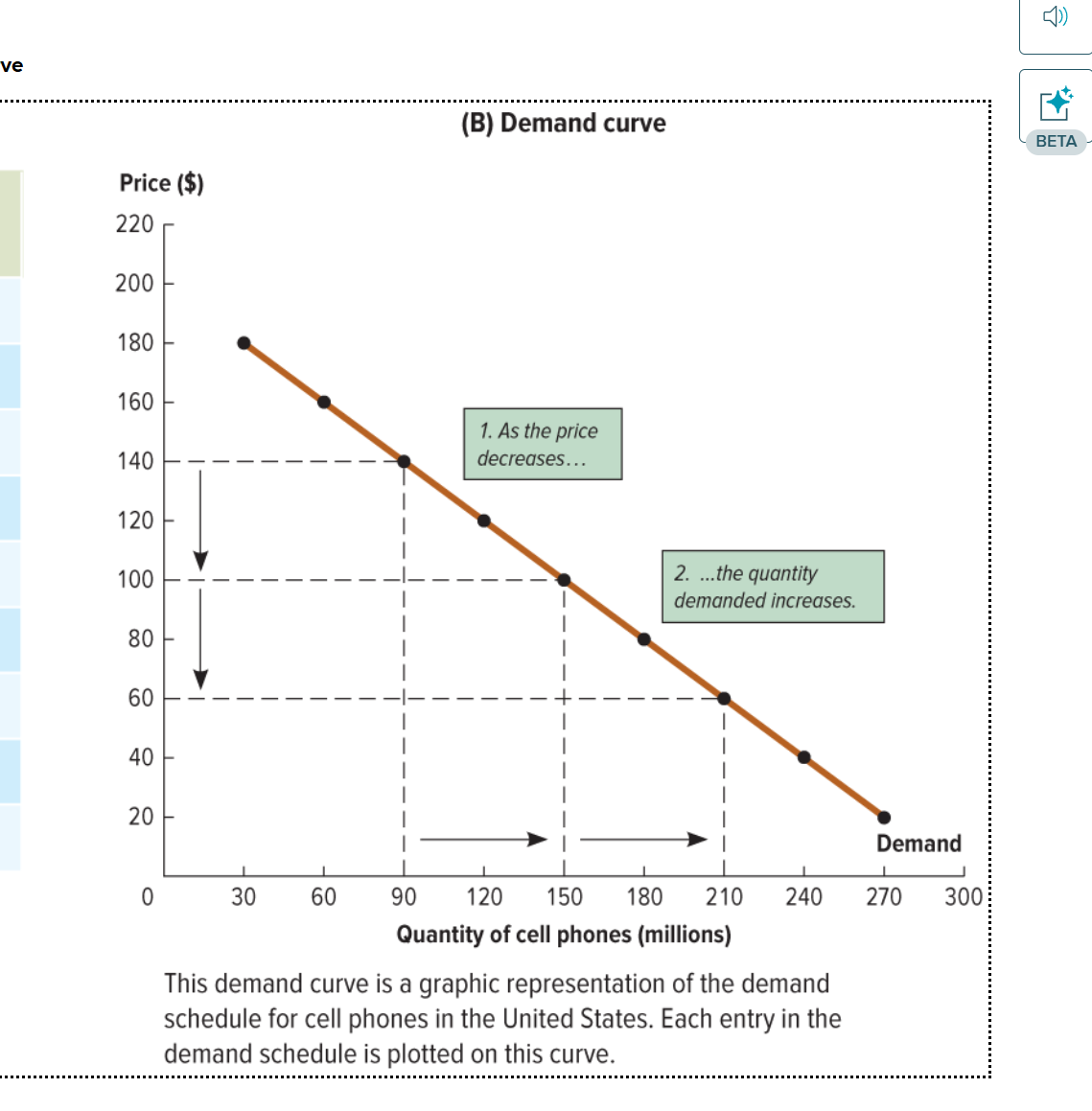
What does the demand curve show?
A decrease in price increases the quantity demand
substitutes
goods that serve a similar-enough purpose that a consumer might purchase one in place of the other.
Ex: Sandals and flip flops, Coke and Pepsi, Books and Kindle, etc.
What happens to the opportunity cost for pasta when the price of pasta remains the same while the price of rice doubles?
The opportunity costs for pasta decreases because you sacrifice less of the expensive good to get each unit of the cheaper good.
complements
goods that are consumed together, so that purchasing one will make consumers more likely to purchase the other
Examples of complimentary goods:
Peanut Butter and Jelly
Cereal and Milk
Guns and Bullets
Knives and Cutting Boards
normal goods
goods for which demand increases as income increases. Ex: Suits, Jewelry, buying organic food
inferior goods
goods for which demand decreases as income increases. Ex: Instant Ramen
quantity supplied
the amount of a particular good or service that producers will offer for sale at a given price during a specified period
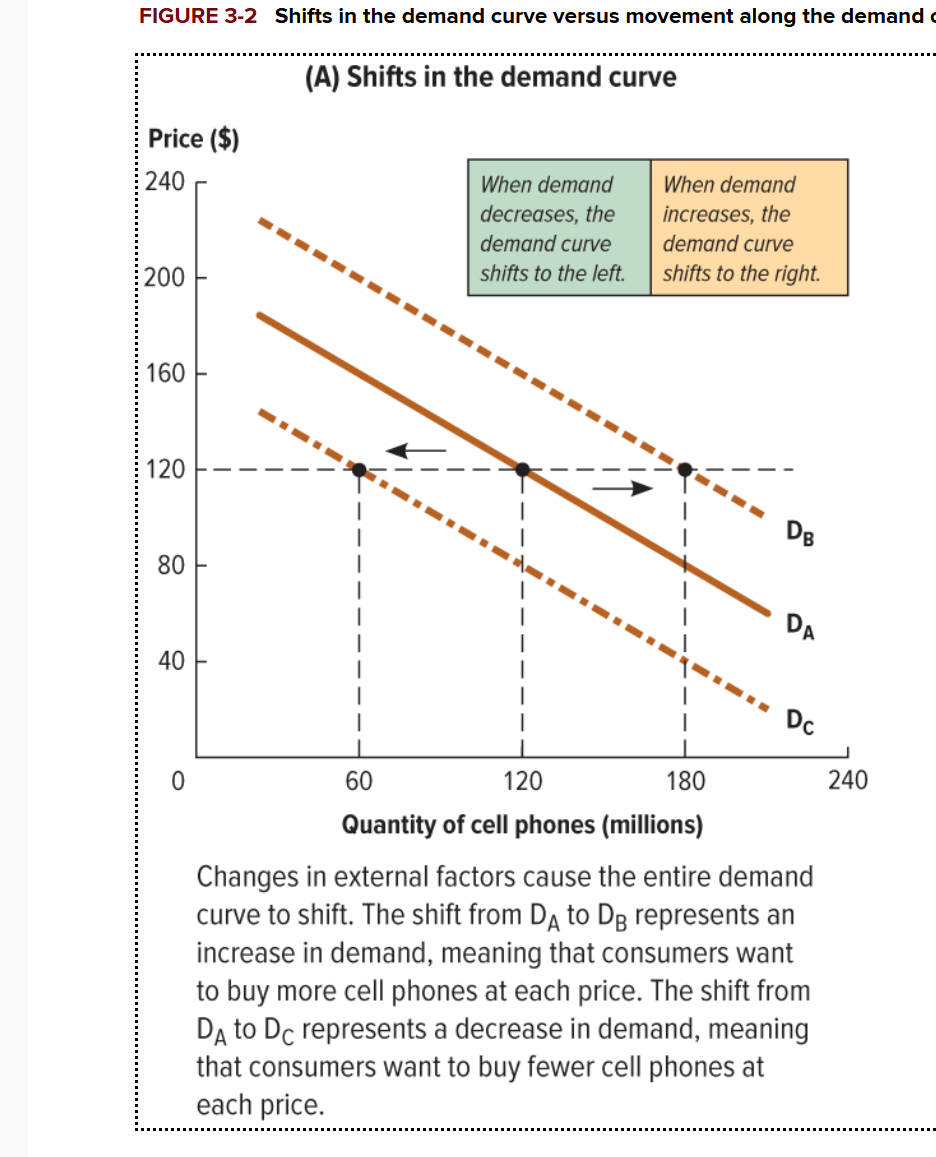
What happens when the demand curve shifts to the left?
The demand decreases
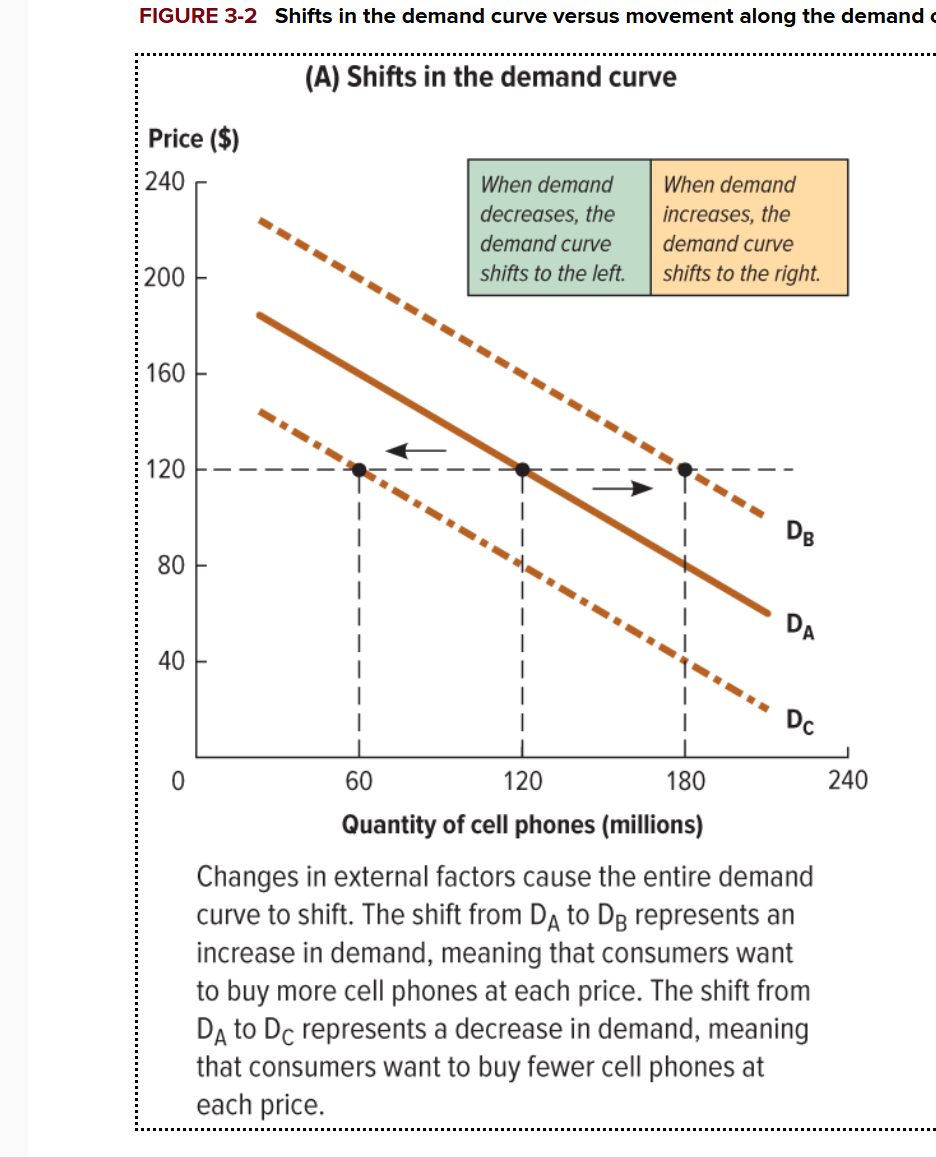
What happens when the demand curve shifts to the right?
The demand increases
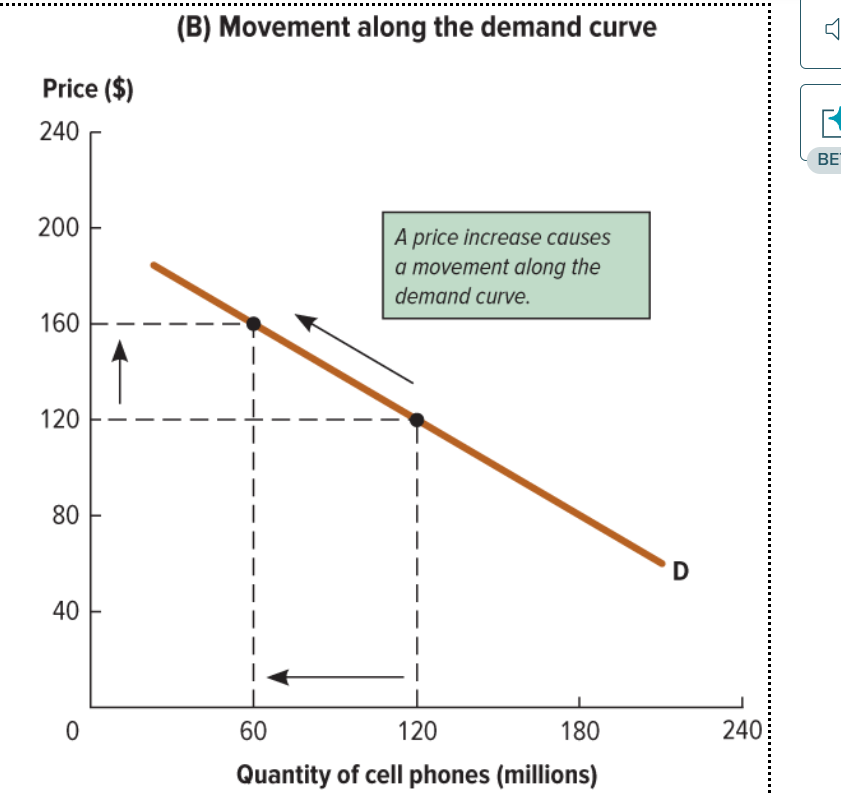
What happens when a price change occurs on the demand curve?
A movement along the demand curve occurs but the curve itself is constant
quantity supplied
the amount of a particular good or service that producers will offer for sale at a given price during a specified period
Supply
How much of a good or service producers are willing to offer under certain circumstances
law of supply
a fundamental characteristic of supply that states that, all else equal, quantity supplied rises as price rises
supply schedule
a table that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will supply at various prices
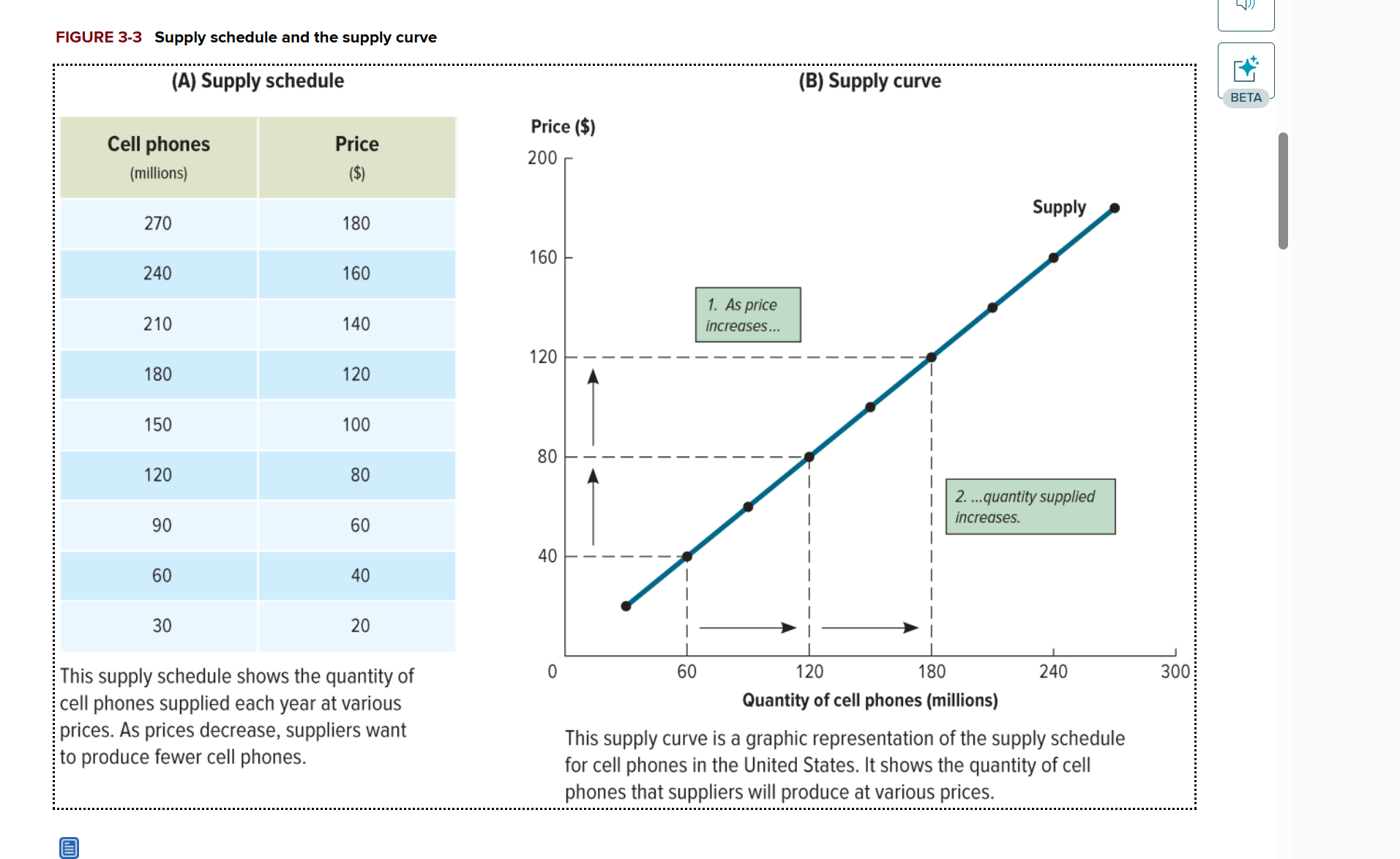
How does the price of a product affect the quantity supply on the supply curve?
Prices Rise = Increase in quantity supply
Prices Decrease = Decrease in quantity supply
supply curve
a graph that shows the quantities of a particular good or service that producers will supply at various prices
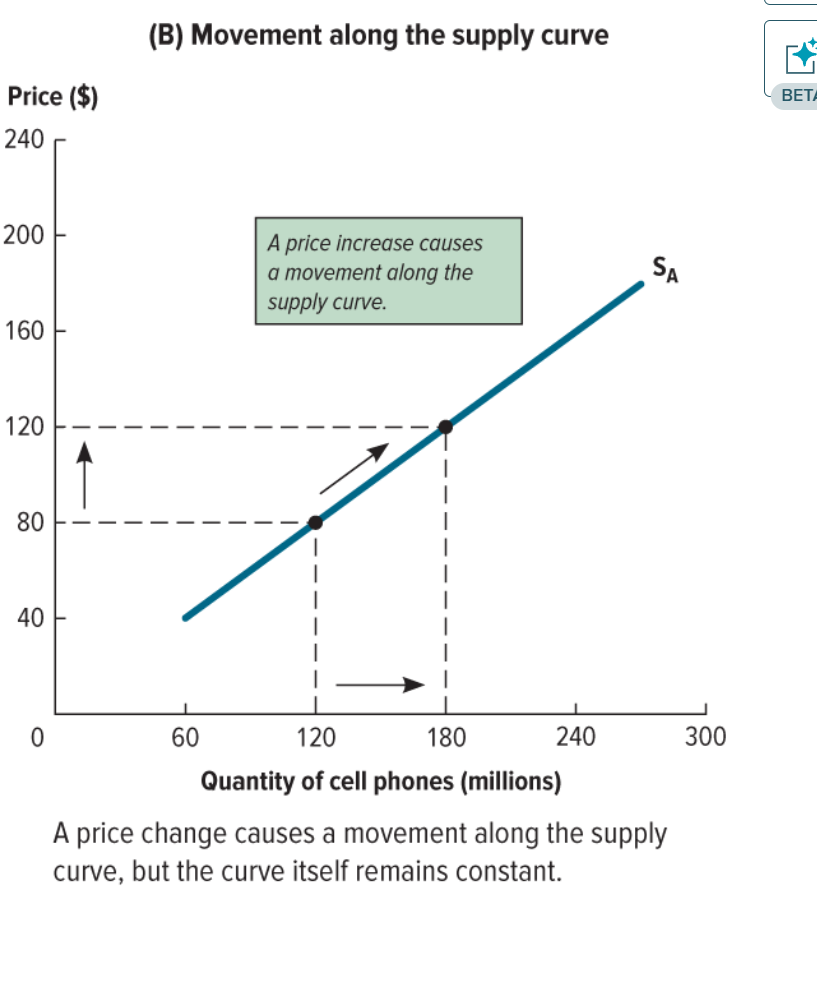
How does a change in price affect the supply curve?
It causes movement on the supply curve, but the supply curve itself remains constant