OPT 114 Ciliary Body
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What part of the eye is the ciliary body a part of?
UVEA (middle vascular layer along with iris and choroid)
Where in the eye does the ciliary body start?
just outside of the limbus, a small portion of the longitudinal muscle fibers are within the limbus)
What is the ciliary body continuous with anteriorly?
iris, trabecular meshwork, scleral spur
What is the ciliary body continuous with posteriorly?
choroid and retina
What is the transition between the ciliary body and the retina/choroid?
ora serrata
What are the two regions of the ciliary body?
1) Pars plana (orbicularis ciliaris)
2) Pars plicata (corona ciliaris)
Where are 70-80% of ciliary processes located?
pars plicata
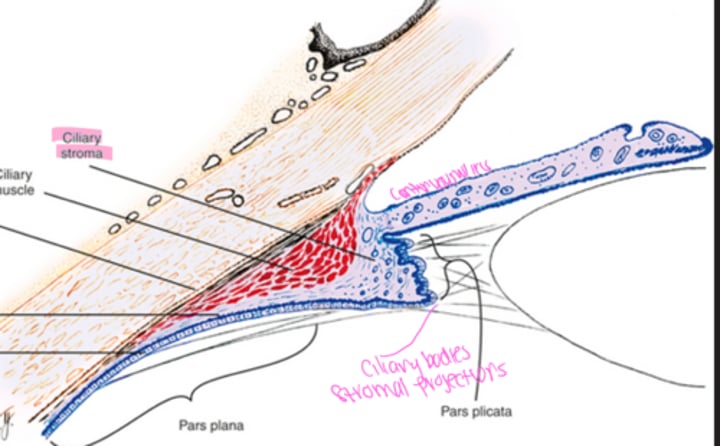
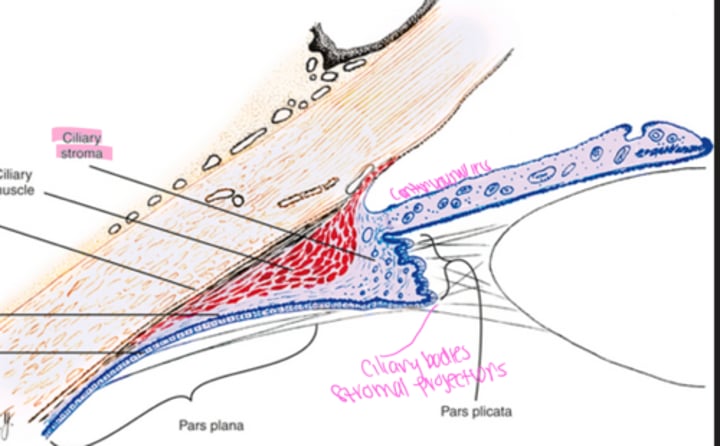
What region of the ciliary body has wider anterior region?
pars plicata
Projections of the ciliary stroma are covered by what type of epithelium?
pigmented and non pigmented epithelium
What does the pars plicata extend into?
posterior chamber
What do ciliary processes do?
produce aqueous
Describe the flow of aqueous humor
flows into posterior chamber, between the lens and the iris, through the pupil, into the anterior chamber
Where are the valleys of Kuhnt located?
between ciliary processes
What region has a flatter posterior surface?
pars plana
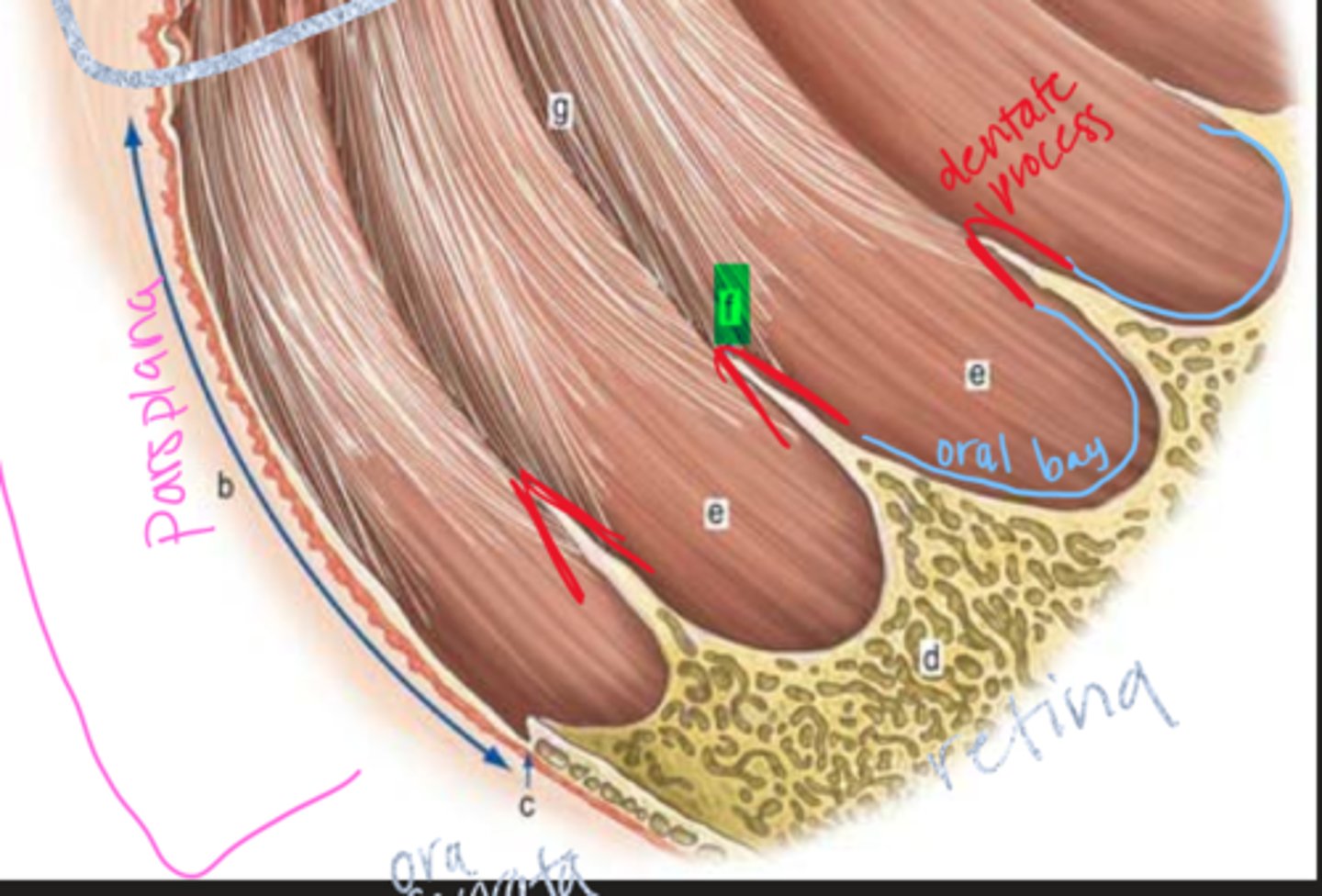
Where does the pars plana extend from?
posterior pars plicata to ora serrata
Where do oral bays project into?
peripheral retina, composed of ciliary stroma covered by pigmented and nonpigmented epithelium
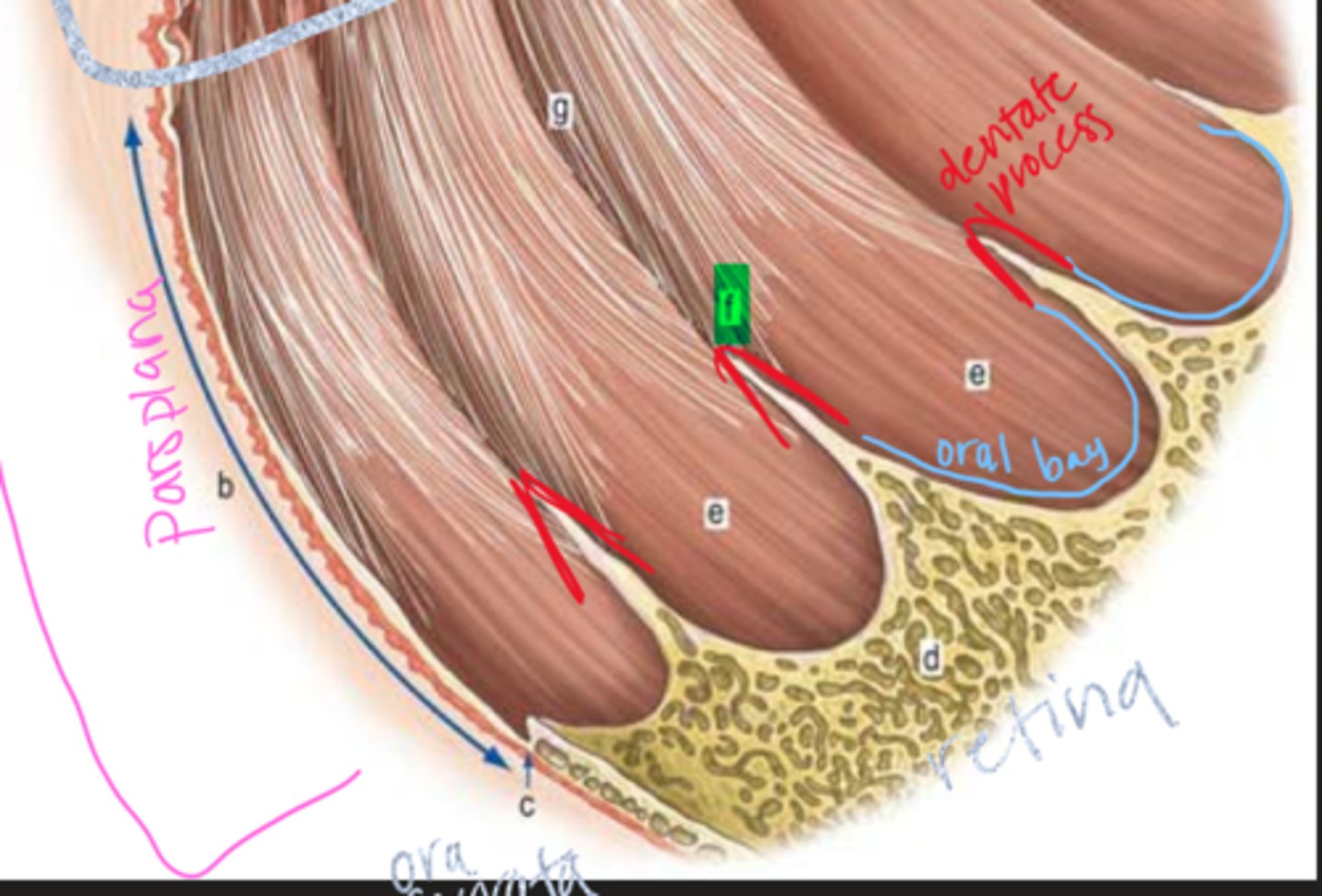
Where are dentate processes located in the ciliary body?
between oral bays, they are projections of the peripheral retina
What are the layers (inner to outer) of the ciliary body?
1. nonpigmented epithelium
2. pigmented epithelium
3. stroma
4. muscle
5. supraciliaris
where is the nonpigmented layer located?
most inner layer, lines posterior chamber and part of the vitreous chamber
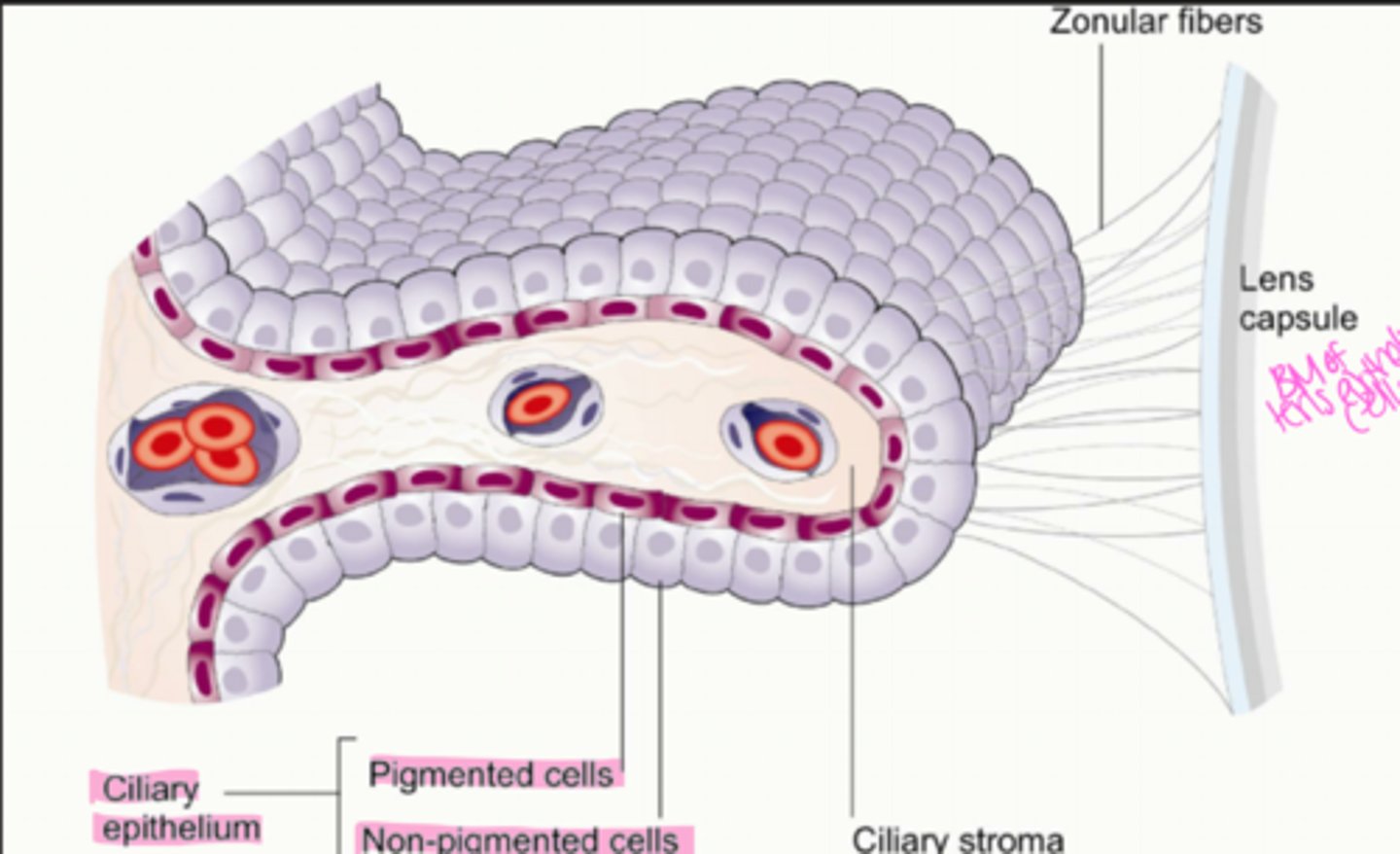
What is the nonpigmented epithelium composed of?
single layer of columnar epithelial cells with tight junctions in between them
Where do zonules arise from?
basement membrane of non pigmented epithelium
Where do zonules insert?
lens capsule in the equatorial regions of the lens
What do zonules do?
suspend the lens in the anterior chamber
What is the non pigmented epithelium continuous with anteriorly?
posterior pigmented epithelium of the iris (basement membranes are continuous with one another)
What is the non pigmented epithelium continuous with posteriorly?
neurosensory retina (basement membrane is continuous with inner limiting membrane of the retina)
Cells of the non pigmented and pigmented epithelium sit ______ to __________
apex to apex
Where is the pigmented epithelium located?
outer to the non pigmented epithelium
Describe the cells making up the pigmented epithelium
single layer of cuboidal epithelium cells
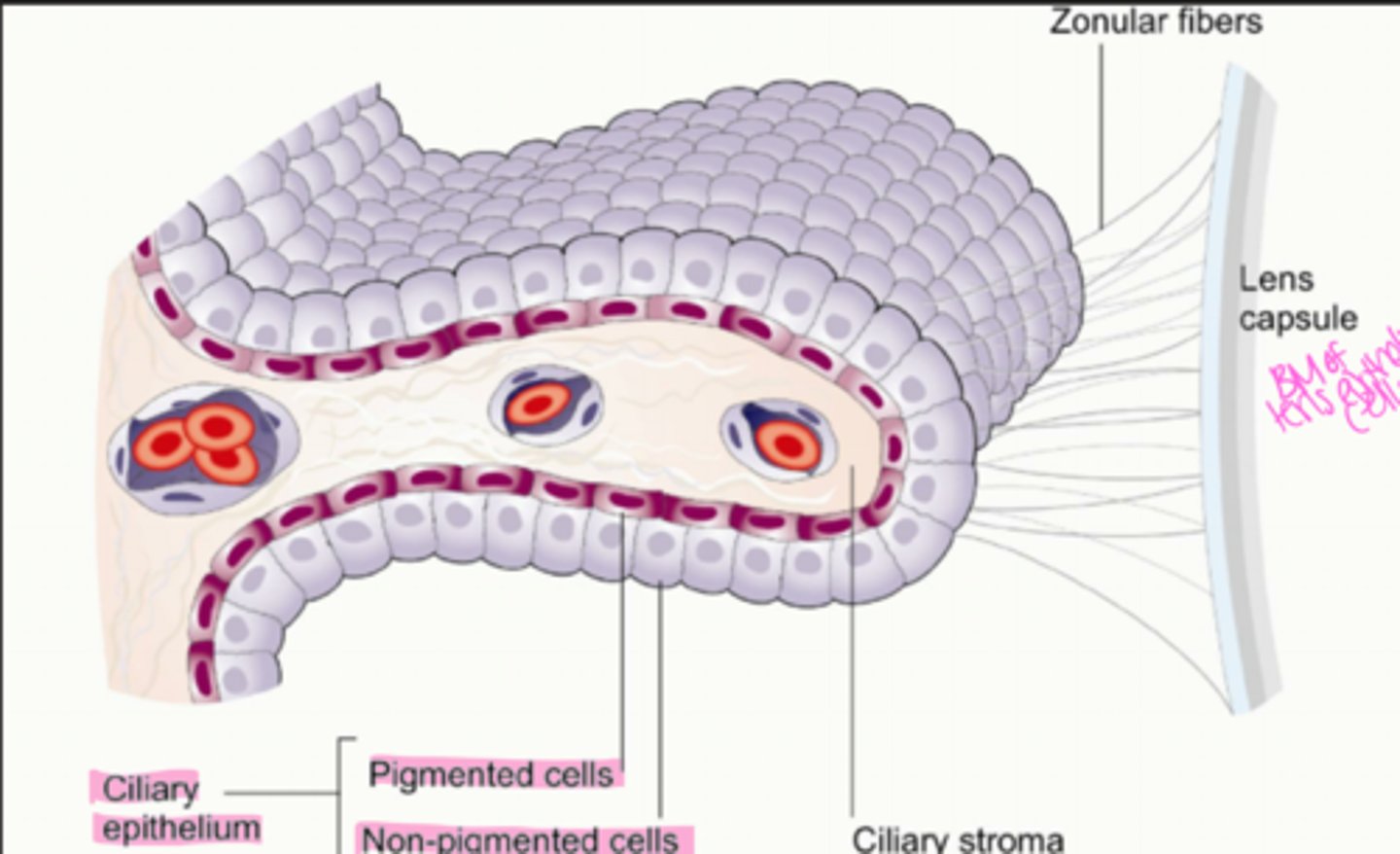
What is the pigmented epithelium continuous with anteriorly?
anterior pigmented epithelium of the iris (basement membranes are continuous with one another)
What is the pigmented epithelium continuous with posteriorly?
retinal pigment epithelium (basement membranes are continuous with one another)
What is the ciliary stroma composed of?
vascularized, loose connective tissue (collagen, fibroblasts, ground substance) and melanocytes + WBCs
What is the ciliary stroma continuous with anteriorly?
iris stroma
What is the ciliary stroma continuous with posteriorly?
choroidal stroma
What is the ciliary muscle layer composed of?
smooth muscle fibers with longitudinal, radial, and circular orientations
Where do longitudinal muscle fibers of the ciliary muscle run?
parallel to the sclera
Anteriorly, what do longitudinal fibers attach to?
scleral spur and trabecular meshwork
Posteriorly, where do longitudinal fibers attach?
choroid in form of stellate shaped terminations
Where are circular muscle fibers located?
anterior and inner region of the ciliary body
What is the supraciliaris?
potential space between ciliary body and sclera
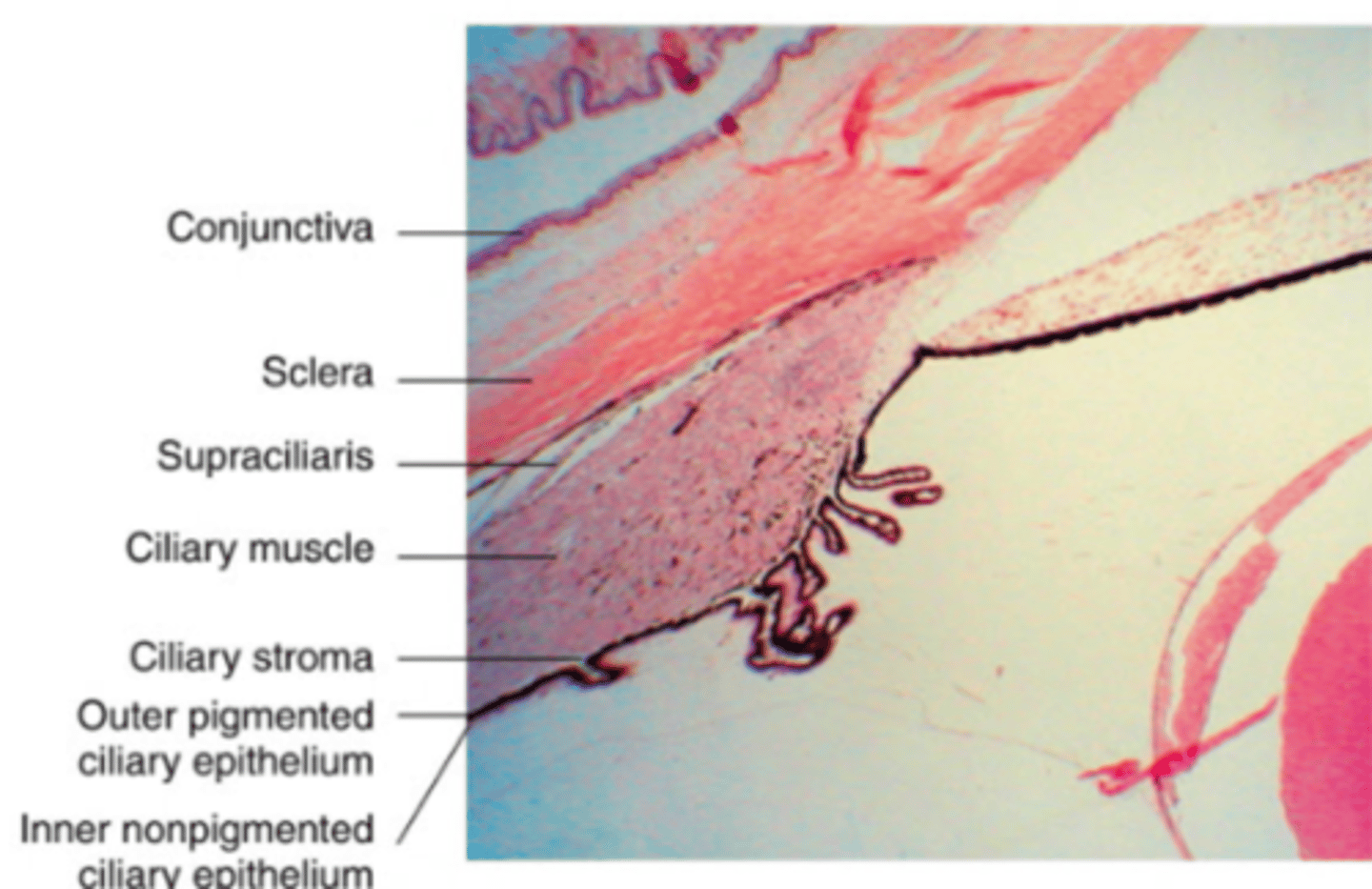
What is the supraciliaris continuous with?
Suprachoroid (space between choroid and sclera)
What is the function of the ciliary process?
secretes aqueous humor
How does contraction of the ciliary muscle affect surrounding structures?
increase size of pores of trabecular meshwork responsible for aqueous humor drainage
What does contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscle do?
controls the shape of the lens
What happens when ciliary muscles contract?
muscle thickens moving inward and causing zonules to relax thickening the lens
What occurs during accommodation?
anterior surface of the lens becomes steeper, increasing the refractive power
What nerve off the ophthalmic nerve innervates the ciliary body?
nasociliary nerve--> long ciliary nerves
Describe motor innervation to the ciliary muscle
parasympathetic fibers of smooth muscle (involuntary autonomic)
Is the ciliary body vascular?
Yes.
What supplies the ciliary body?
Major arterial circle of the iris (MACI)
Why are capillaries of the ciliary stroma highly fenestrated?
allows molecules to leak out of the capillaries and enter the stroma
Describe the path of drainage of the ciliary body
Ciliary veins -> vortex veins -> superior and inferior ophthalmic veins
What arteries form the major arterial circle of the iris?
muscular arteries anastomose with long posterior ciliary arteries
What does the major arterial circle of the iris form?
minor arterial circle around the collarette