Year 10 Biology, cells and stuff
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
MRS GREEN
movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, equilibrium (homeostasis), excretion, nutrition
Unicellular
Made of a single cell
multicellular
Consisting of many cells
5 kingdoms
Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, (MAPPF)
Monera
bacteria, a biological kingdom made of prokaryote, single cell, no nucleus
Protista
a kingdom of mostly one-celled eukaryotic organisms that are different from plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. large group of cells like cholera
Anamalia
animals, basic groups of living things that comprises all animals, multicellular organisms
Plantae
plants, all organisms that have chlorophyll
Autotrophic
make their own food, like trees
Heterotrophic
Organisms that obtain their nutrients or food from consuming other organisms.
Eukaryote
Multicellular organism, DNA in nucleus with chromosomes and membranes
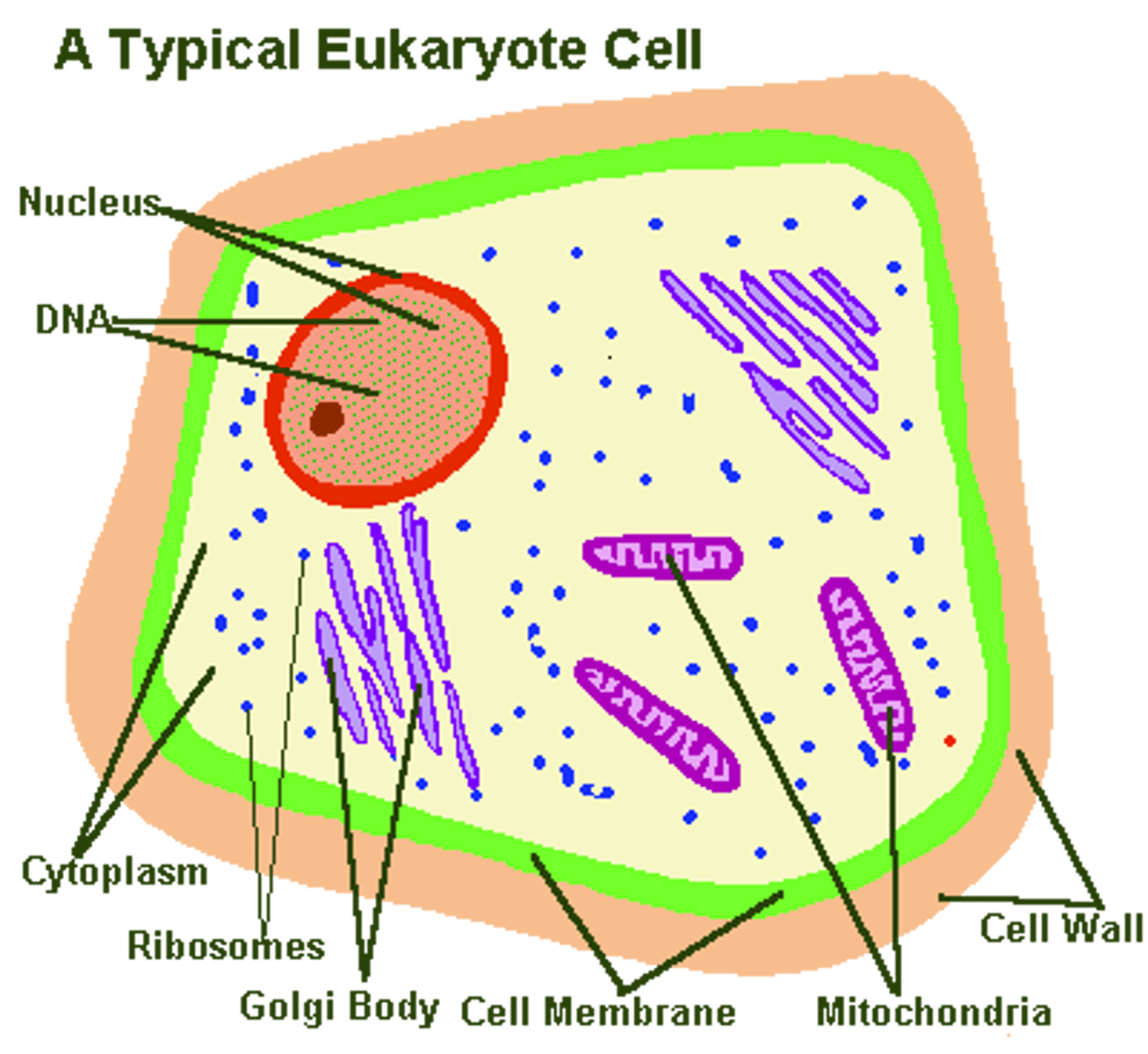
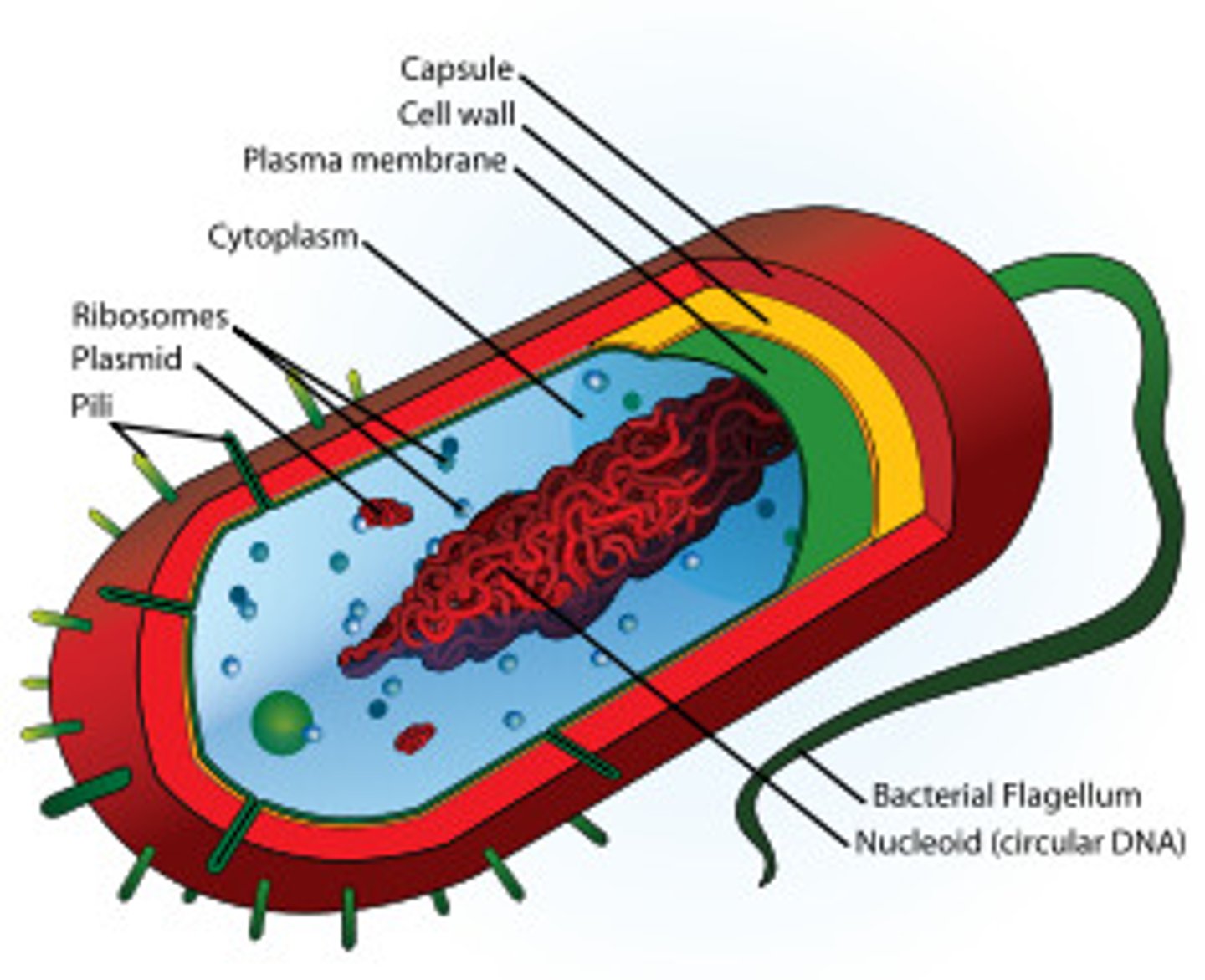
Prokaryote
Single celled organism, distinct nucleus, no membrane
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Building blocks of protein, carbs, nucleic acid and lipids
amino acid, simple sugars like glucose, fatty acid, glycerol
stem cell
unspecialized cell that can give rise to one or more types of specialized cells
How can stem cells be used in medicine?
To replace damaged tissues and cells
totipotent and example
meaning whole. Unlimited self renewal capabilities, can differentiate into any cell under appropriate condition. Like cell of embryo
Pluripotent cell and example
meaning many. Able to differentiate into any type of cell. Like blastocyst
Multi-potent cell and example
meaning several, able to limited range of cells. like foetal tissue.
Unipotent cell and example
Meaning one. Differentiate into one cell type, somatic cells, like neurons and muscle cels.
enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things, speed up reactions. made of proteins
How enzymes work
they have an active site that connects to substrate, like a lock and key
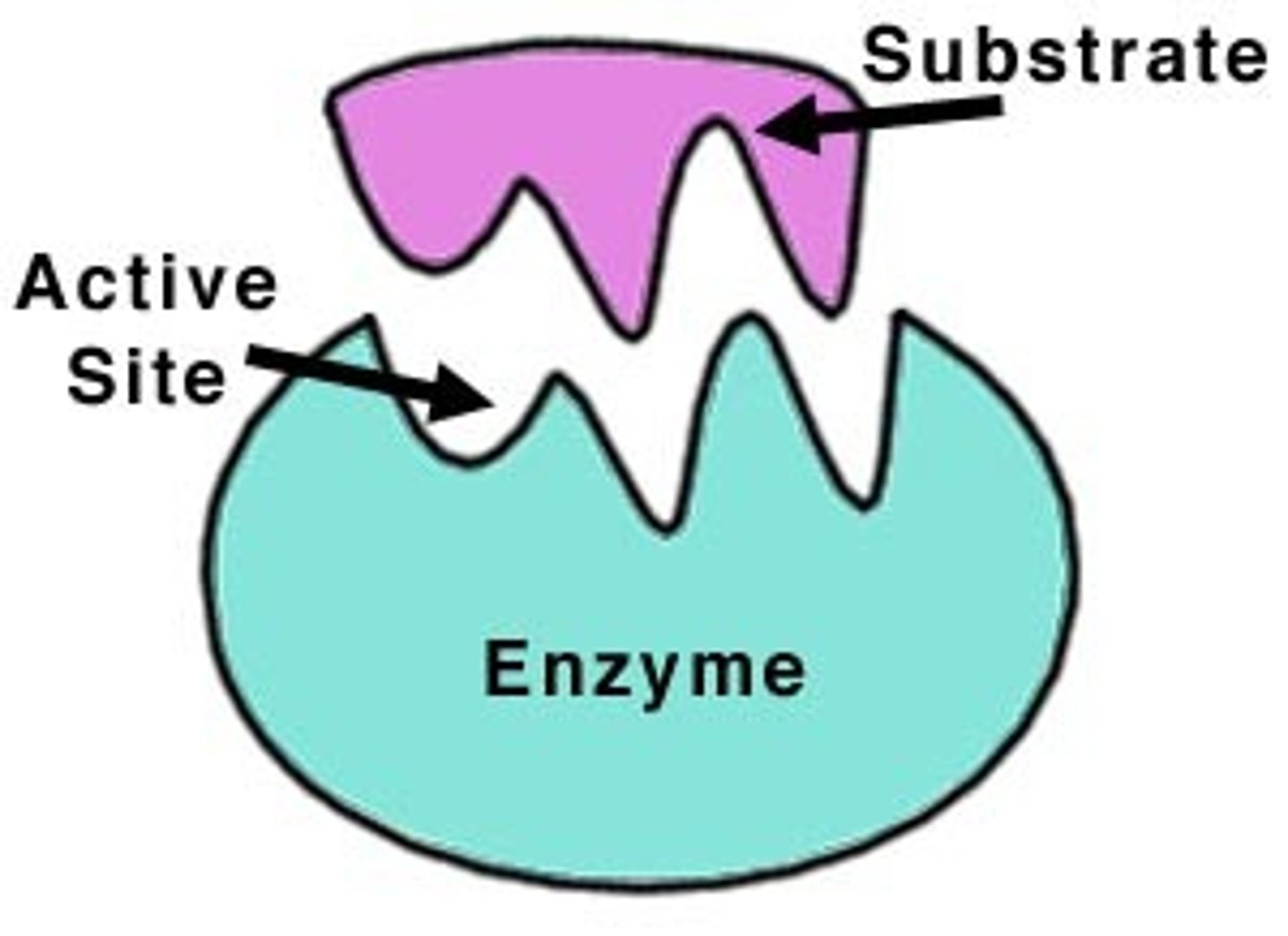
simple diffusion
high to low concentrations, doesn't need energy (passive)
facilitated diffusion
high to low concentration, requires ATP (energy)
active transport
low concentration to high concentration, needs energy (active) moves against concentration gradient.
Osmosis
movement of solvent from a region of lower solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. No energy required (passive)
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
Red Blood Cell when isotonic
normal state
RBC when hypotonic
diluted, swollen/turgid
RBC when hypertonic
Shrunken/Flaccid in concentrated solution
Endocytosis
entering the cell
exocytosis
exiting the cell
Phagocytosis
ingestion of bacteria, engulf large particles
Pinocytosis
Ingestion of liquids into the cell through the cell membrane, known as the "fluid endocytosis."
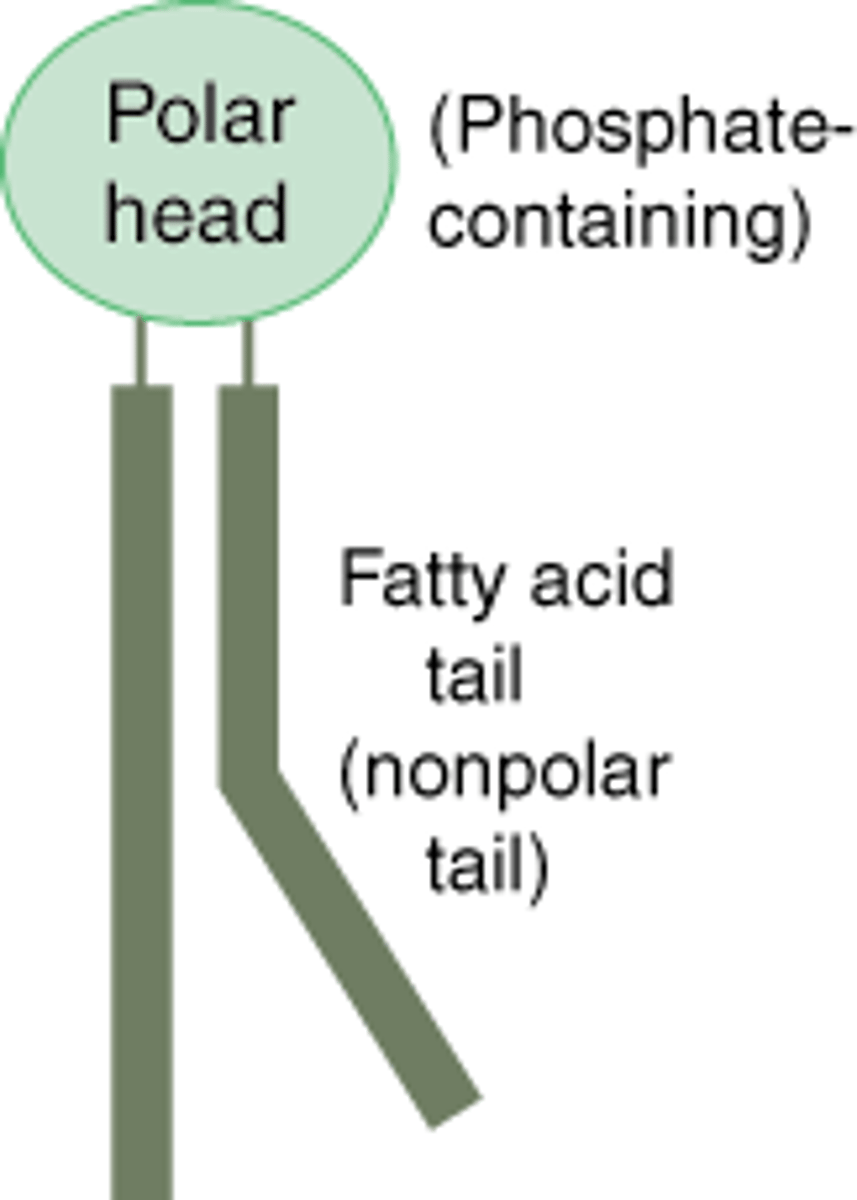
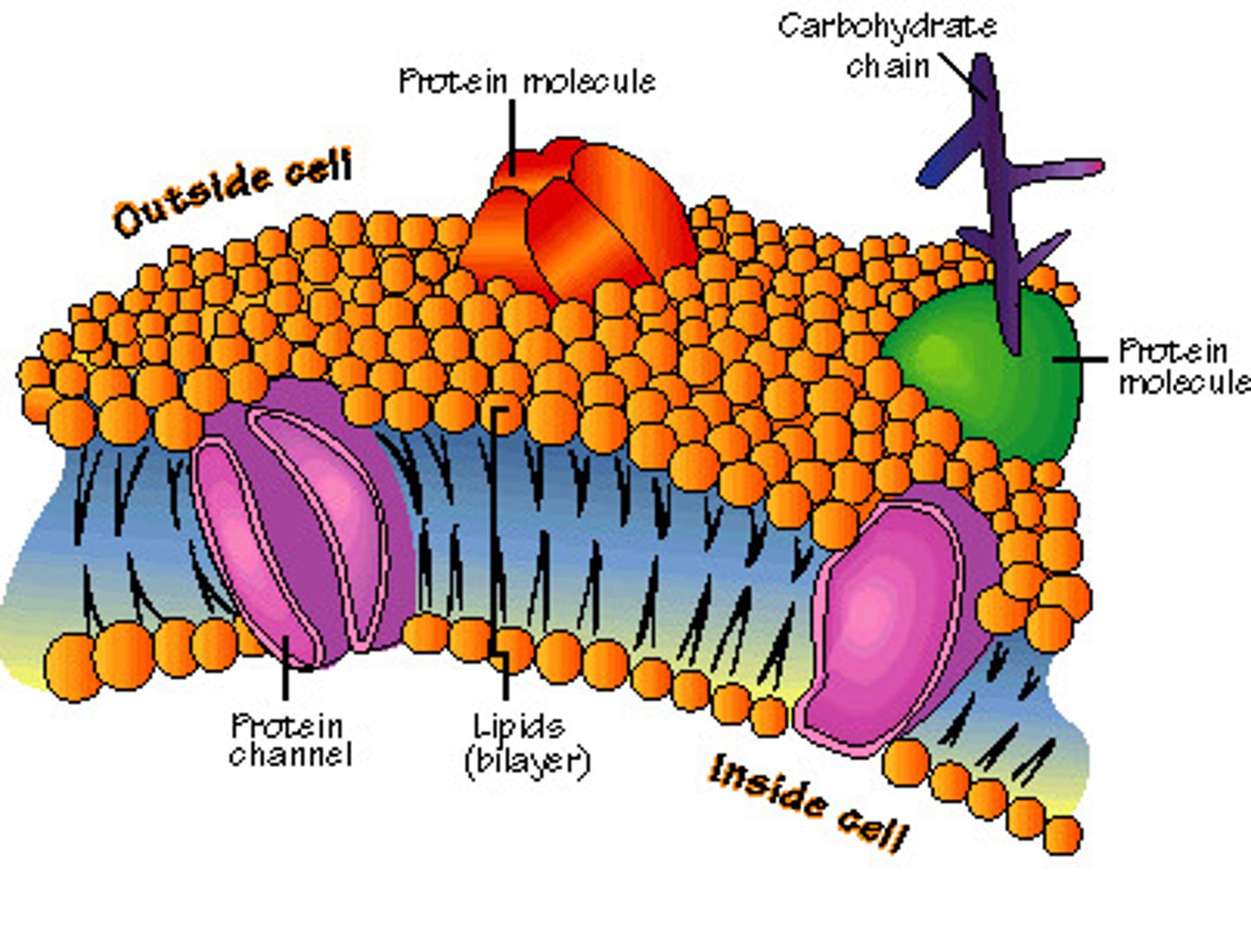
Phospholipids
controls what goes in an out of the cell as it has a selective. The fluid inside and outside is aqueous (water is solvent)
Diagram of a phospholipid
polar head is hydrophilic (attracted to water), two non polar tails are hydrophobic (repel water) which helps maintain homeostasis.
Plasma membrane parts
Peripheral proteins attach to chemical/integral proteins for cell communication. Carbohydrates identify the cell and act as binding site. Channel proteins are passageways from specific materials to go in and out of the cell. Cholesterol helps keep the membrane fluid by preventing the phospholipids from sticking, also adds rigidity so cell holds shape.
CNS
central nervous system; brain and spinal cord
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System, the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Neurons
a cell that carries electrical signals around the body
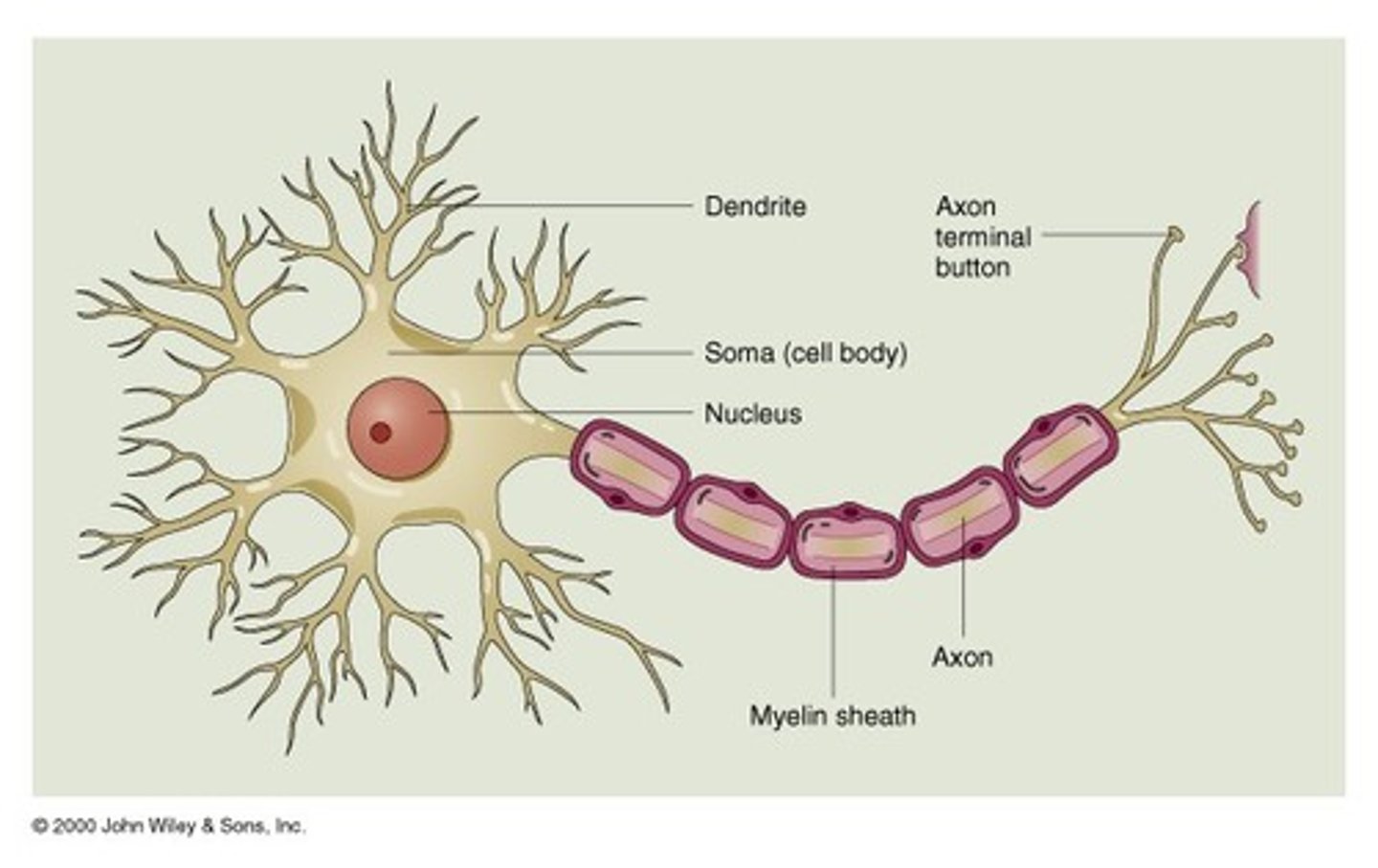
Dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
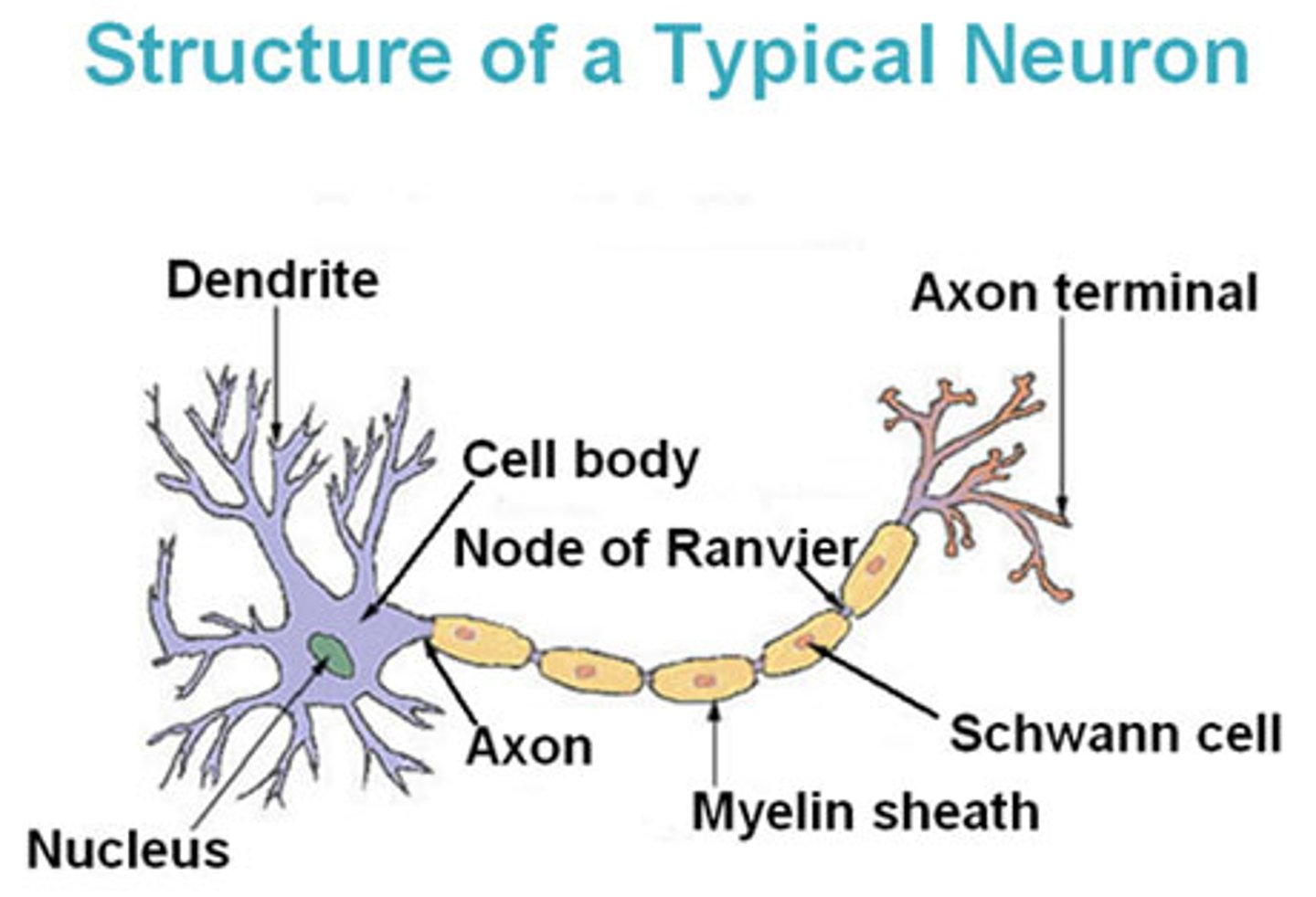
myelin sheath
insulates the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that transfers electrical signals
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended, where cellular reactions and processes occur
cell/plasma membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
neurotransmitter
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
receptor
A small area on the dendrite that receives the signal from the other neuron
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
photosynthesis word formula
Carbon dioxide, water and light energy ---------> glucose and oxygen
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production, cellular respiration- Glucose + Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide and Water
immune system
protects the body from pathogens and diseases, fights an infection.
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease
two lines of defense
non-specific (physical/chemical barrier) like skin and mucus. Specific defense (immune response) Antigens, T and B cells
second line of defense
blood vessels dilate to allow WBC/phagocytes to enter infected tissue, infected tissue become red and swollen, fever may occur to kill pathogens.
Antigen
The substance that triggers an immune response
antibodies
Y-shaped proteins that attach to particular kinds of antigens, neutralising pathogens
B cells
Type of WBC that produces antibodies
Helper T cells
Activate Killer T cells and B cells
Cytoxic T cells
directly attacks pathogen that have invaded the inside of a cell
Phagocytes
engulf a pathogen and presents antigens on its surface, activating helper T cells
Memory B cells
Remain in body for years, produces more antibodies if your infected by the same pathogen again
Innate Immunity
Immunity you are born with, depends on genetic factors
Acquired Immunity
Life experience. Active or Passive
Active immunity
appears after exposure to pathogen. Memory B cells used providing long term immunity. Natural active immunity is exposure to the antigen or artificial is a vaccine.
Passive immunity
also called borrowed immunity. A person is given a medication that contains antibodies obtained from another person or animal. It has very fast acting but short lived, the body eventually destroys the foreign antibodies.
Different glands
Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, testes/ovaries
Hormone
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
Target tissue
cells of an organ that are affected or stimulated by specific hormones
what do hormones control
growth, metabolism, reproduction, stress
pituitary gland
master gland, controls other endocrine glands
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
positive feedback homeostasis
have a stimulus that causes a response to not solve but enhance it -- less common
negative feedback example
body temperature regulation
positive feedback example
childbirth and blood clotting
How body cools down
hypothalamus detects warmer blood, it then activates sweat glands, water evaporates and heat is lost, then temperature returns to normal
how body heats up
hypothalamus detects heat loss, activates muscles which shiver to generate heat, heat is gained and temperature returns to normal