Ch. 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM334
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
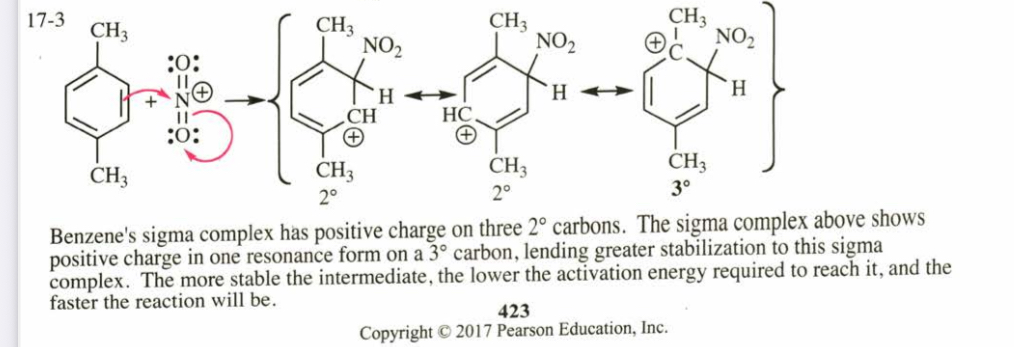
(17.3) p-Xylene undergoes nitration much faster than benzene. Use resonance forms of the sigma complex to explain this accelerated rate.
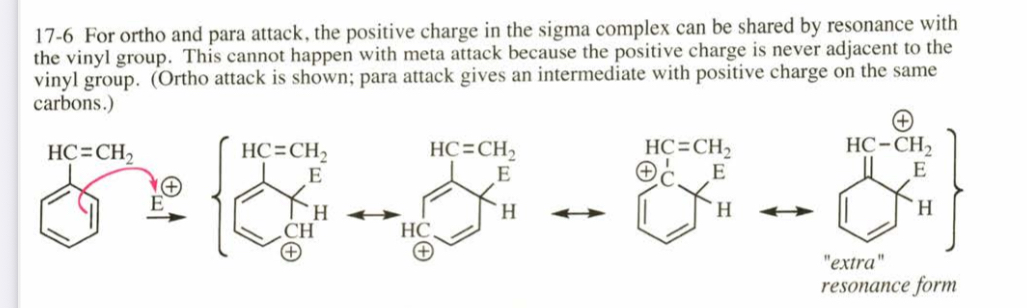
(17.6) Styrene (vinylbenzene) undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution much faster than benzene, and the products are found to be primarily ortho- and para-substituted styrenes. Use resonance forms of the intermediates to explain these results.
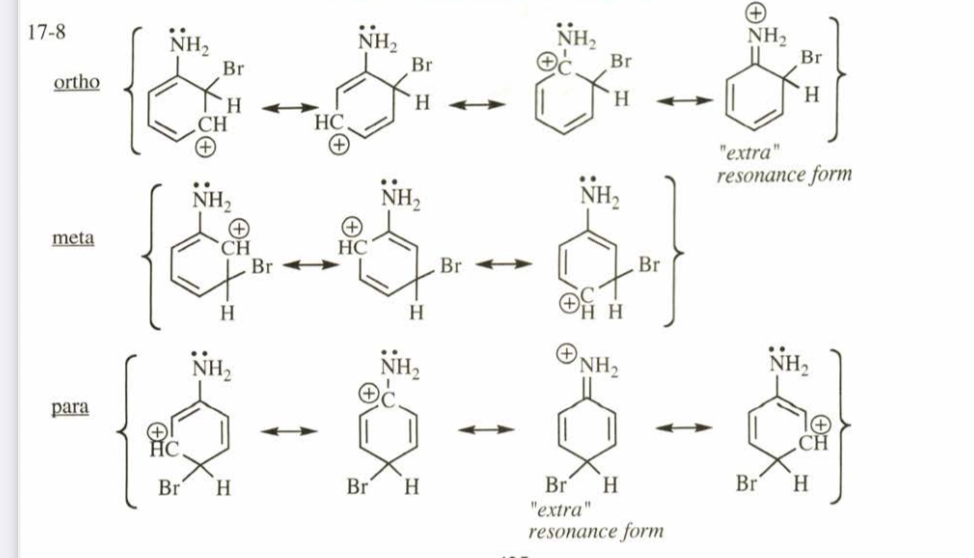
(17.8) Draw all the resonance forms for the sigma complexes corresponding to bromination of aniline at the ortho, meta, and para positions.
(17.12) Predict the mononitration products of the following compounds.
(a) o-nitrotoluene
(c) o-bromobenzoic acid
(e) m-cresol (m-methylphenol)
(b) m-chlorotoluene
(d) p-methoxybenzoic acid (f) o-hydroxyacetophenone
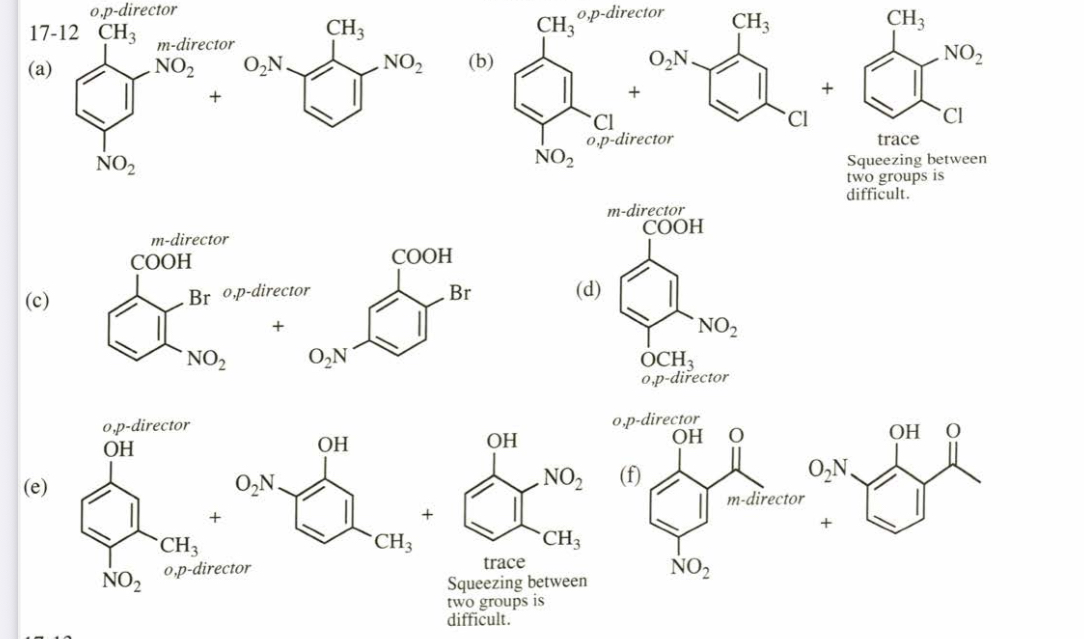
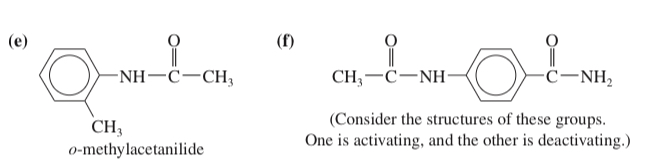
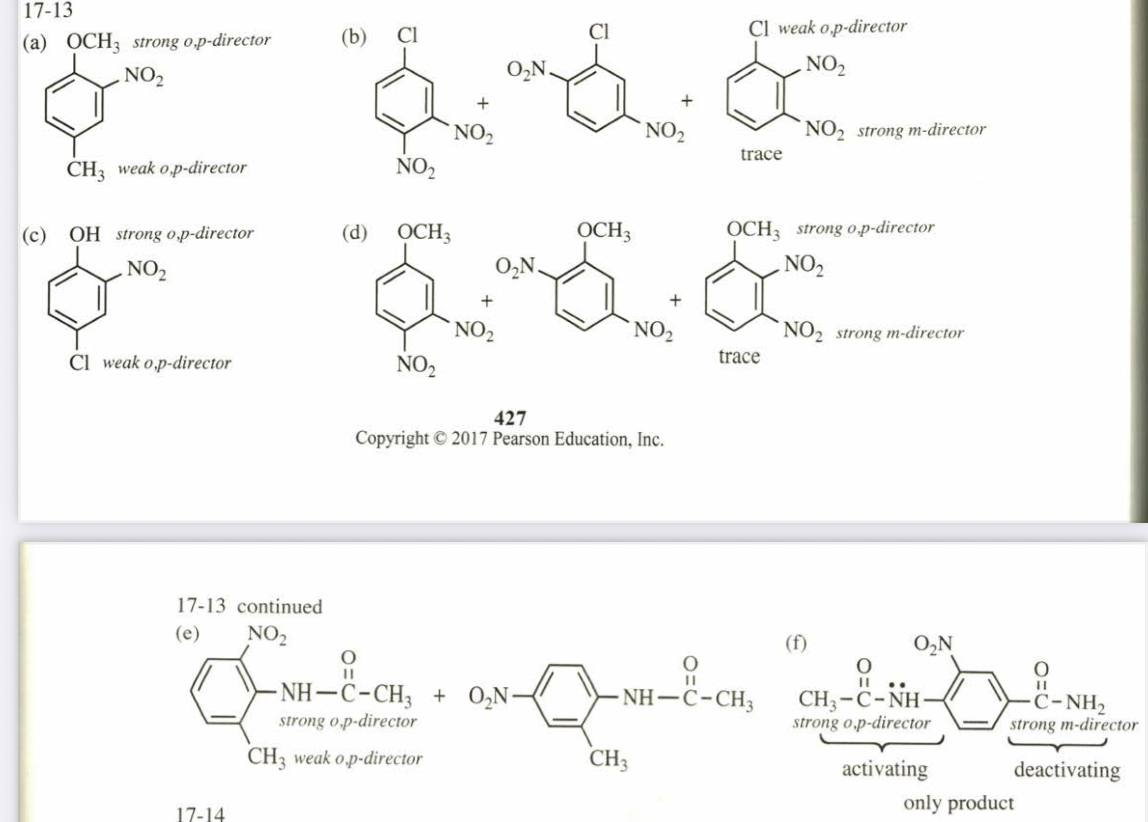
(17.13) Predict the mononitration products of the following aromatic compounds. (a) p-methylanisole (b) m-nitrochlorobenzene
(c) p-chlorophenol (d) m-nitroanisole
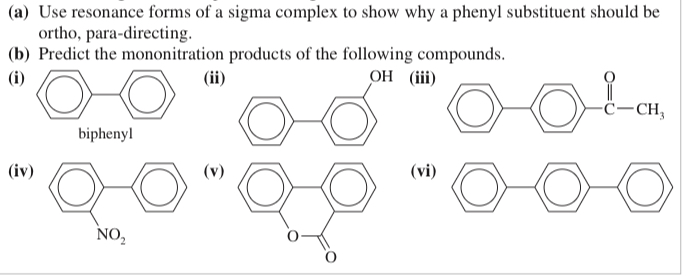
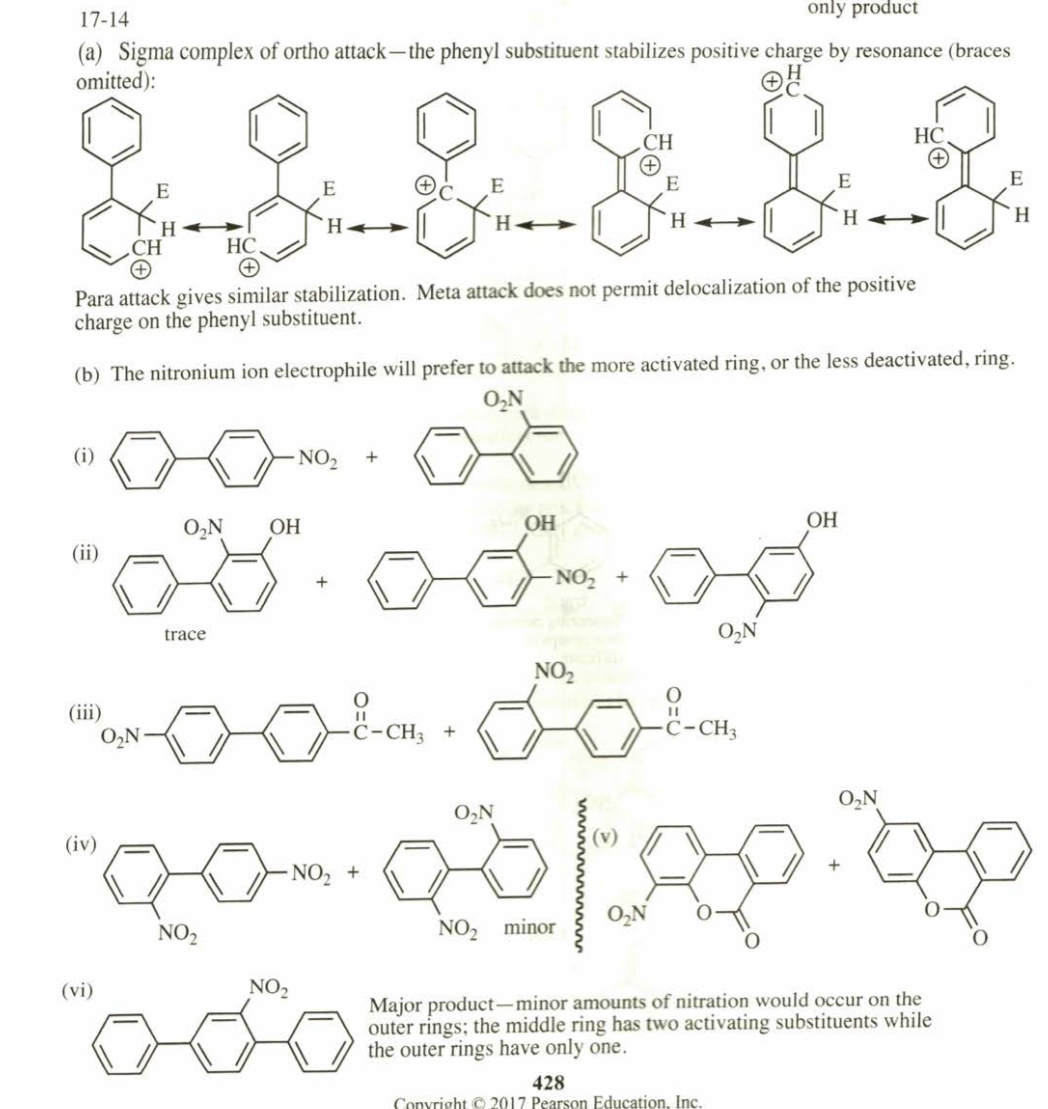
(17.14) Biphenyl is two benzene rings joined by a single bond. The site of substitution for a biphenyl is determined by (1) which phenyl ring is more activated (or less deactivated), and (2) which position on that ring is most reactive, using the fact that a phenyl substitu- ent is activating and ortho, para-directing.
(a) Use resonance forms of a sigma complex to show why a phenyl substituent should be ortho, para-directing.
(b) Predict the mononitration products of the following compounds.
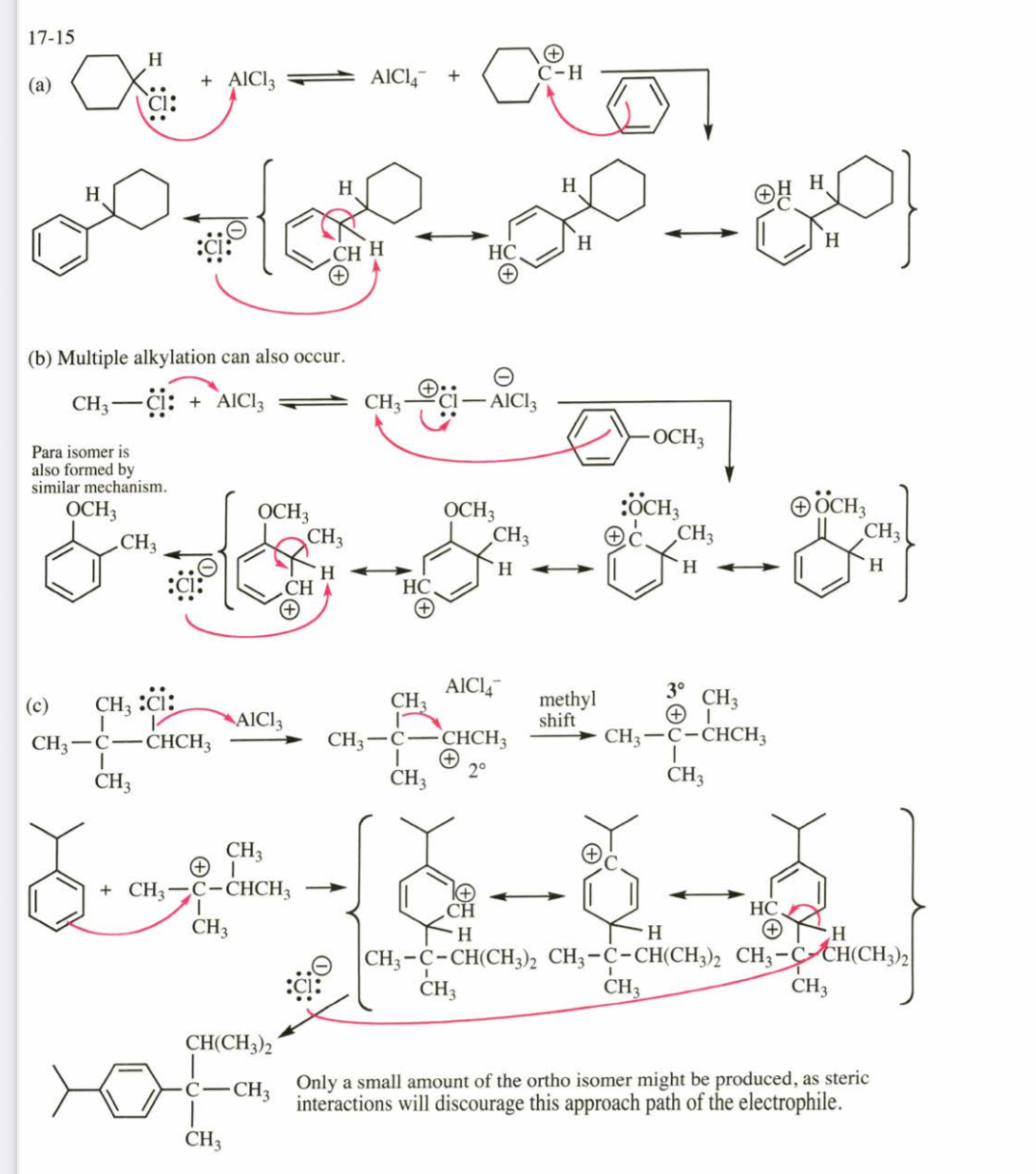
(17.15) Propose products (if any) and mechanisms for the following AlCl3@catalyzed reactions: (a) chlorocyclohexane with benzene
(b) methyl chloride with anisole
*(c) 3-chloro-2,2-dimethylbutane with isopropylbenzene
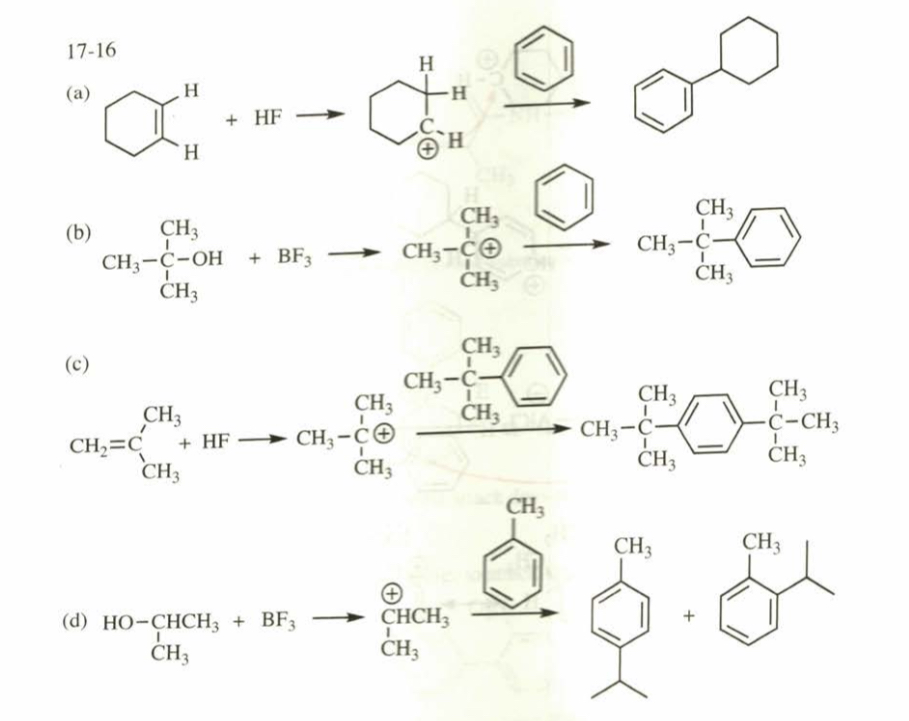
(17.16) For each reaction, show the generation of the electrophile and predict the products.
(a) benzene + cyclohexene + HF (b) tert@butyl alcohol + benzene + BF3 (c) tert@butylbenzene + 2@methylpropene + HF (d) propan@2@ol + toluene + BF3
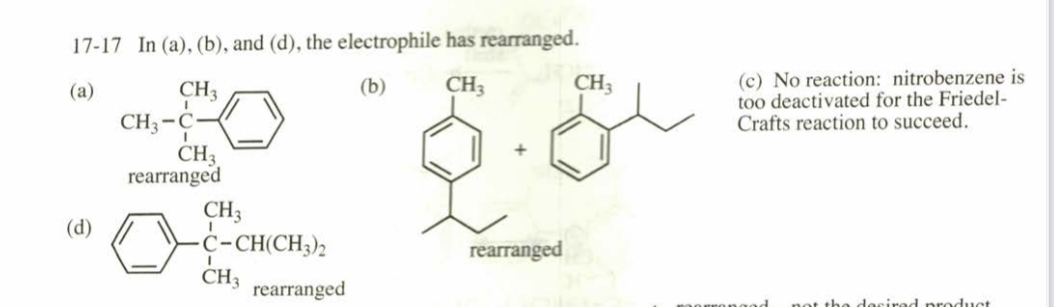
(17.17) Predict the products (if any) of the following reactions. (a) (excess) benzene + isobutyl chloride + AlCl3
(b) (excess) toluene + butan@1@ol + BF3
(c) (excess) nitrobenzene + 2@chloropropane + AlCl3 (d) (excess) benzene + 3,3@dimethylbut@1@ene + HF
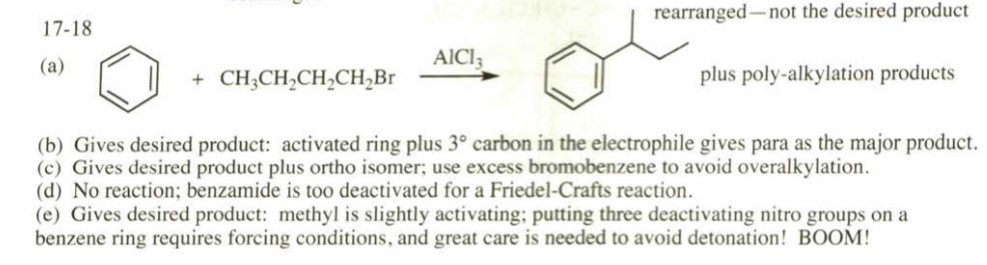
(17.18) Which reactions will produce the desired product in good yield? You may assume that aluminum chloride is added as a catalyst in each case. For the reactions that will not give a good yield of the desired product, predict the major products.
Reagents
(a) benzene + n-butyl bromide
(b) ethylbenzene + tert-butyl chloride (c) bromobenzene + ethyl chloride
(d) benzamide (PhCONH2) + CH3CH2Cl (e) toluene + HNO3, H2SO4, heat
Desired Product
n-butylbenzene p-ethyl-tert-butylbenzene p-bromoethylbenzene p-ethylbenzamide 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT)
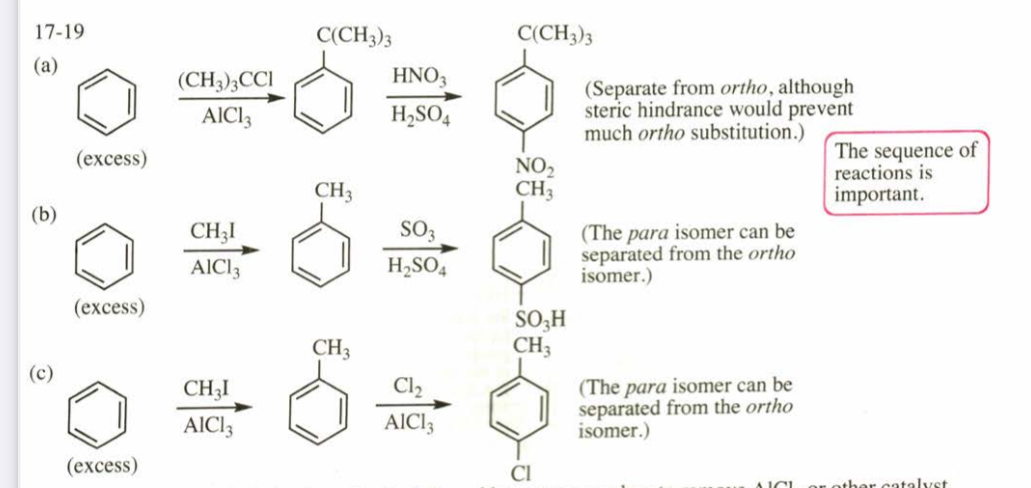
(17.19) Show how you would synthesize the following aromatic derivatives from benzene. (a) p-tert-butylnitrobenzene (b) p-toluenesulfonic acid (c) p-chlorotoluene
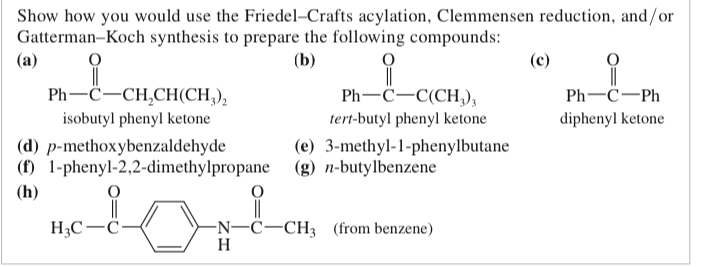
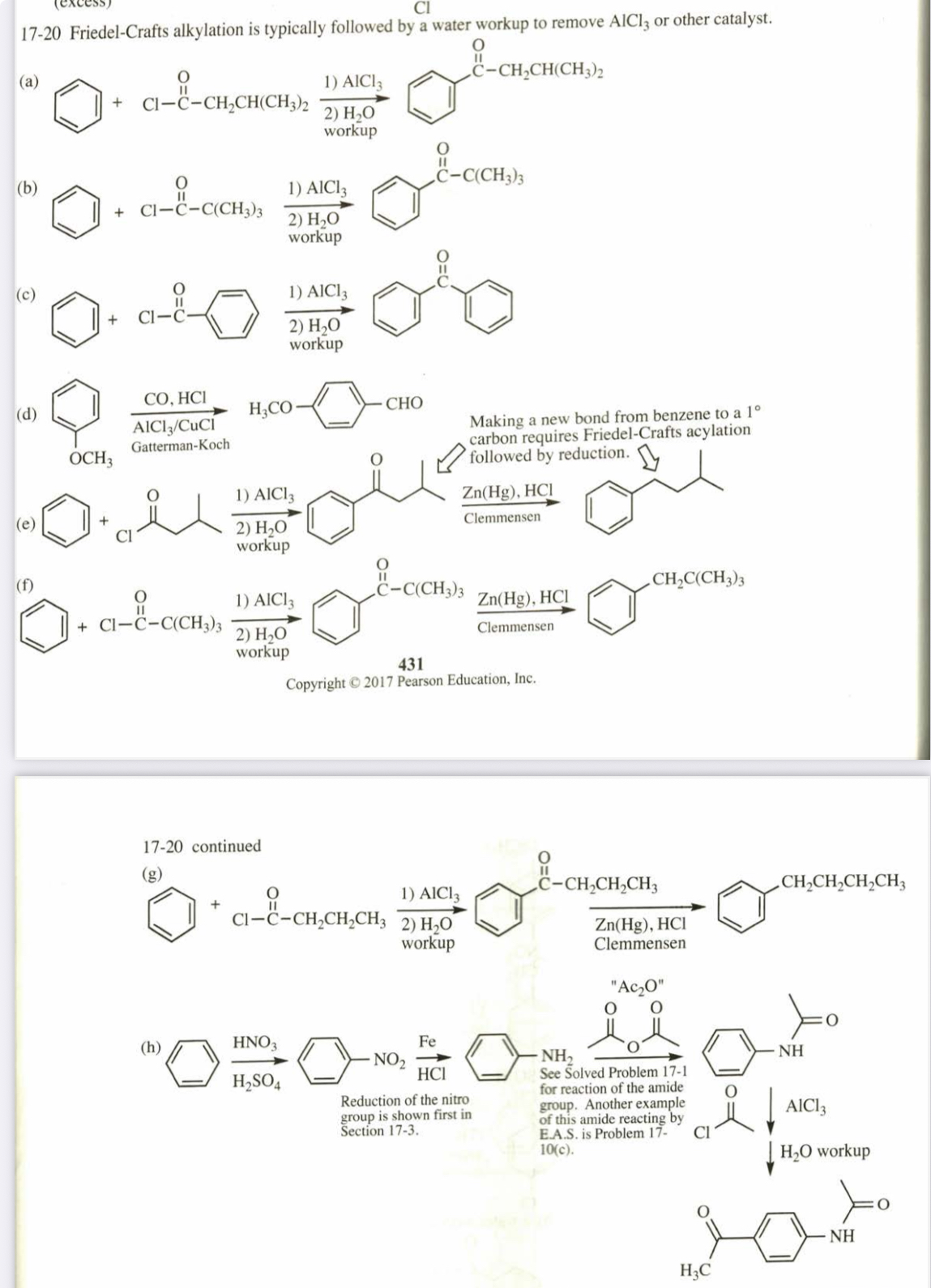
(17.20) Show how you would use the Friedel-Crafts acylation, Clemmensen reduction, and/or Gatterman-Koch synthesis to prepare the following compounds:

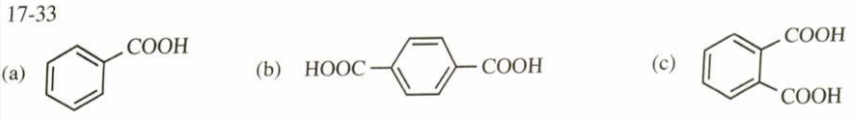
(17.33) Predict the major products of treating the following compounds with hot, concentrated potassium permanganate, followed by acidification with dilute HCl.
(17.35) What would be the ratio of products in the reaction of chlorine with ethylbenzene if chlorine randomly abstracted a methyl or methylene proton? What is the reactivity ratio for the benzylic hydrogens compared with the methyl hydrogens?

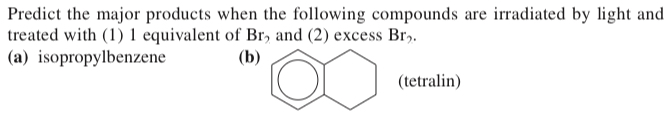
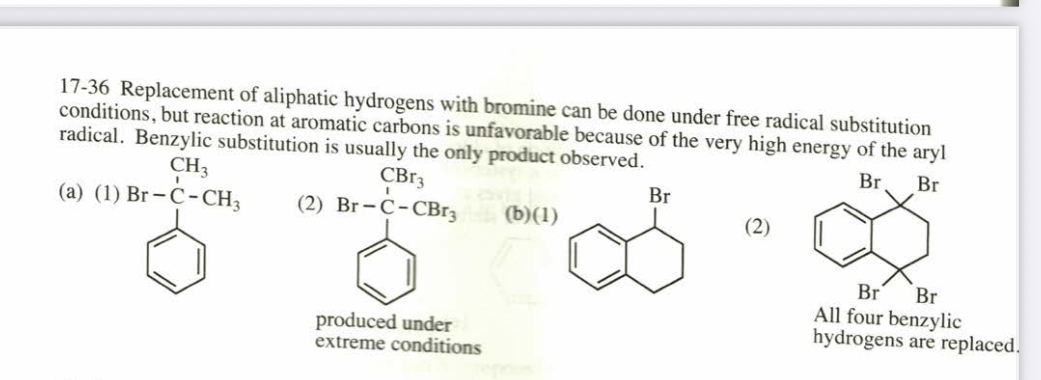
(17.36) Predict the major products when the following compounds are irradiated by light and treated with (1) 1 equivalent of Br2 and (2) excess Br2.
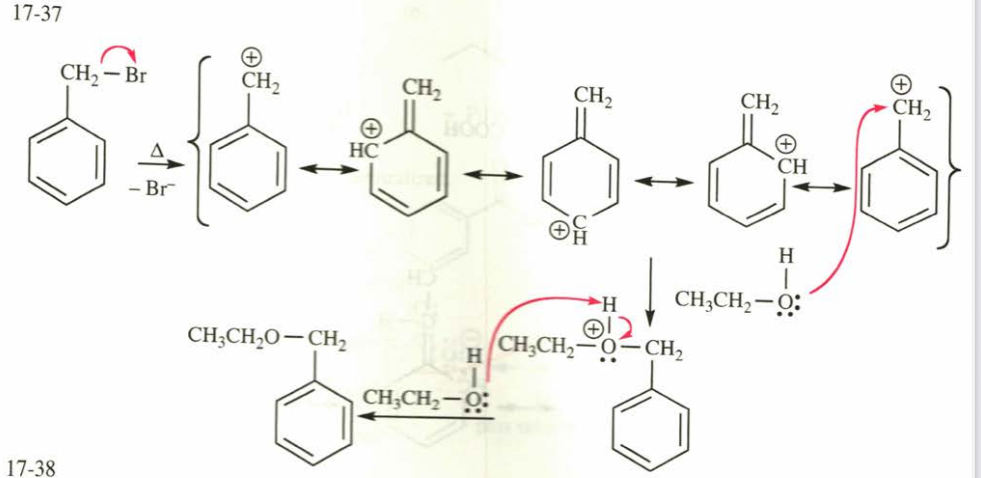
(17.37) Propose a mechanism for the reaction of benzyl bromide with ethanol to give benzyl ethyl ether (shown above).
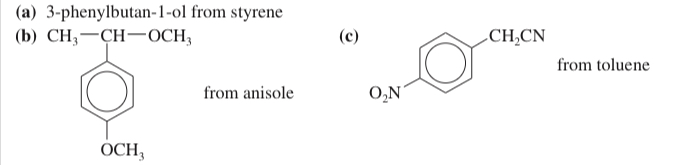
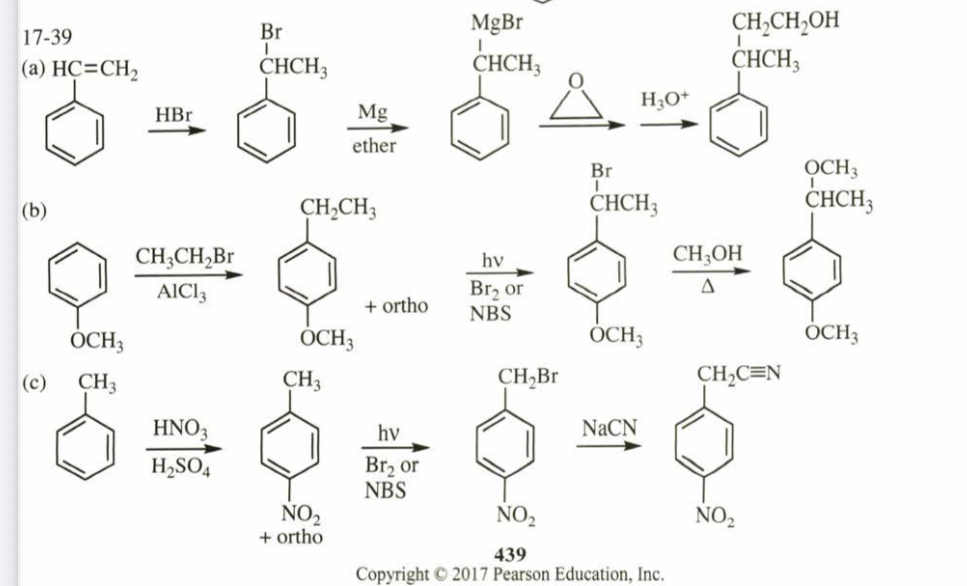
(17.39) Show how you would synthesize the following compounds, using the indicated starting materials.
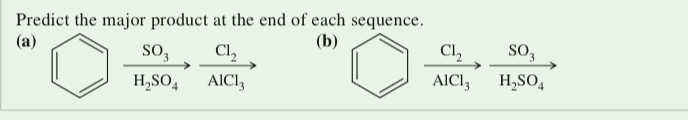
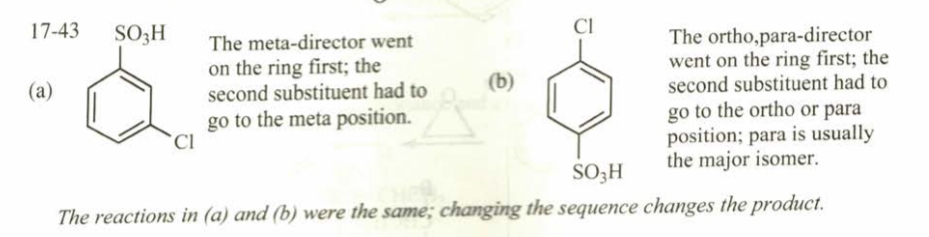
(17.43) Predict the major product at the end of each sequence.

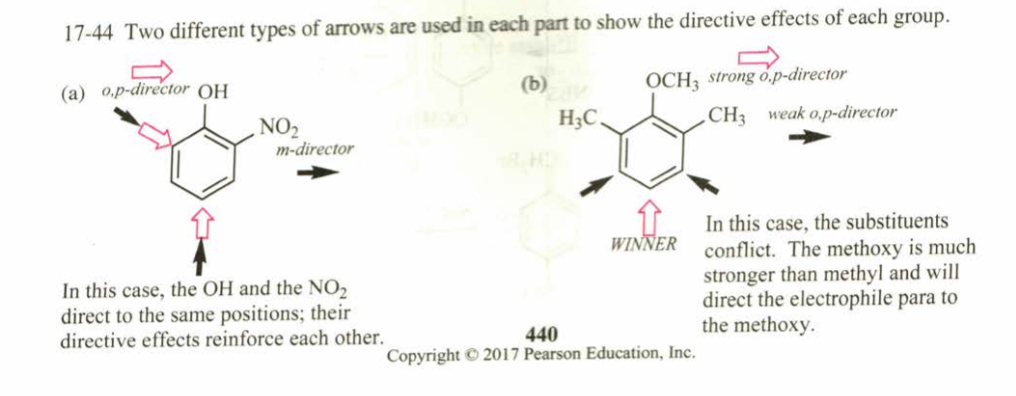
(17.44) Predict the site(s) of electophilic attack on these compounds.
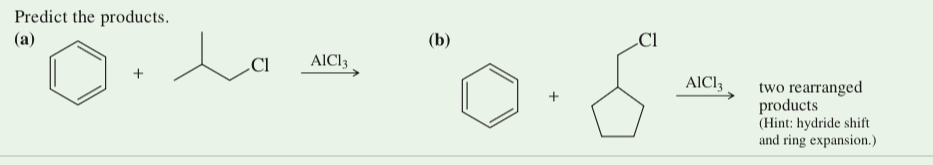
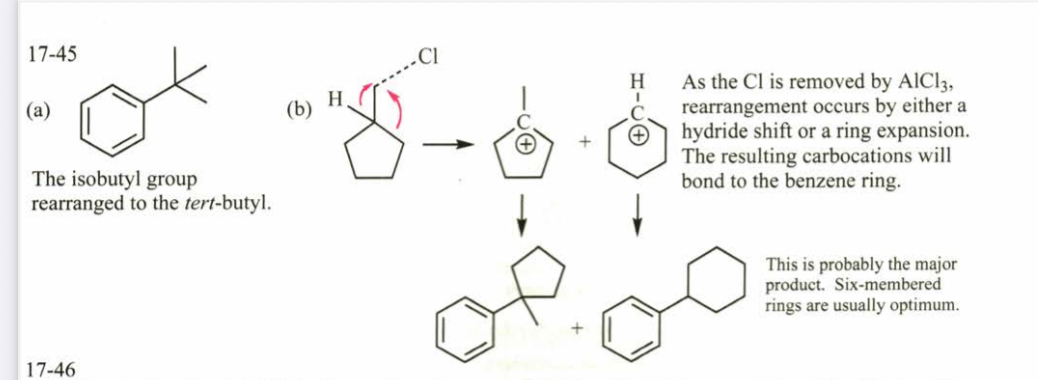
(17.45) Predict the products.
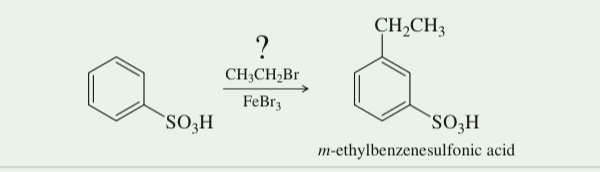
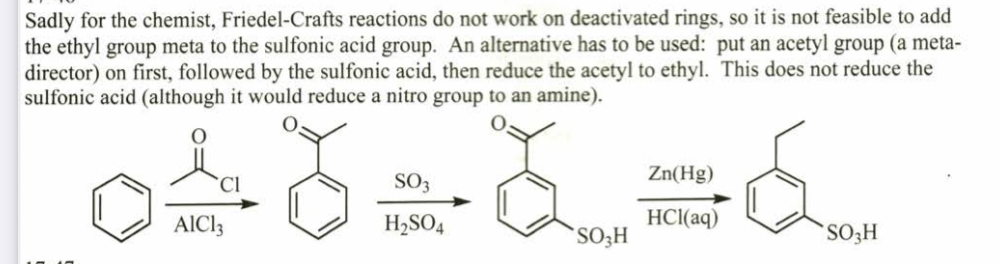
(17.46) To synthesize m-ethylbenzenesulfonic acid, a student attempted the Friedel–Crafts alkyl- ation of benzenesulfonic acid with bromoethane. Do you predict that this reaction was successful? If not, propose an alternative synthesis.
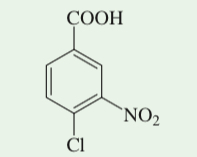
(17.47) Propose a synthetic sequence of this trisubstituted benzene starting from toluene.
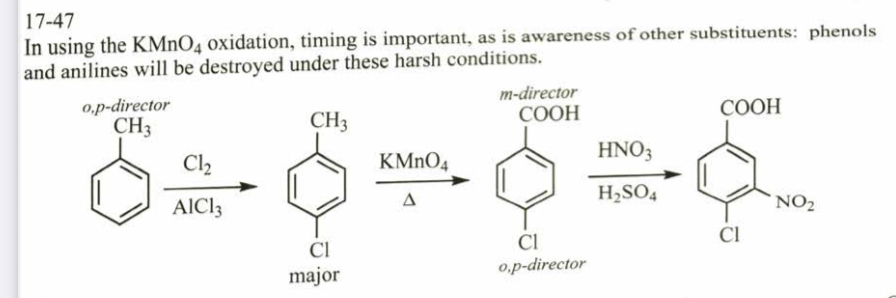
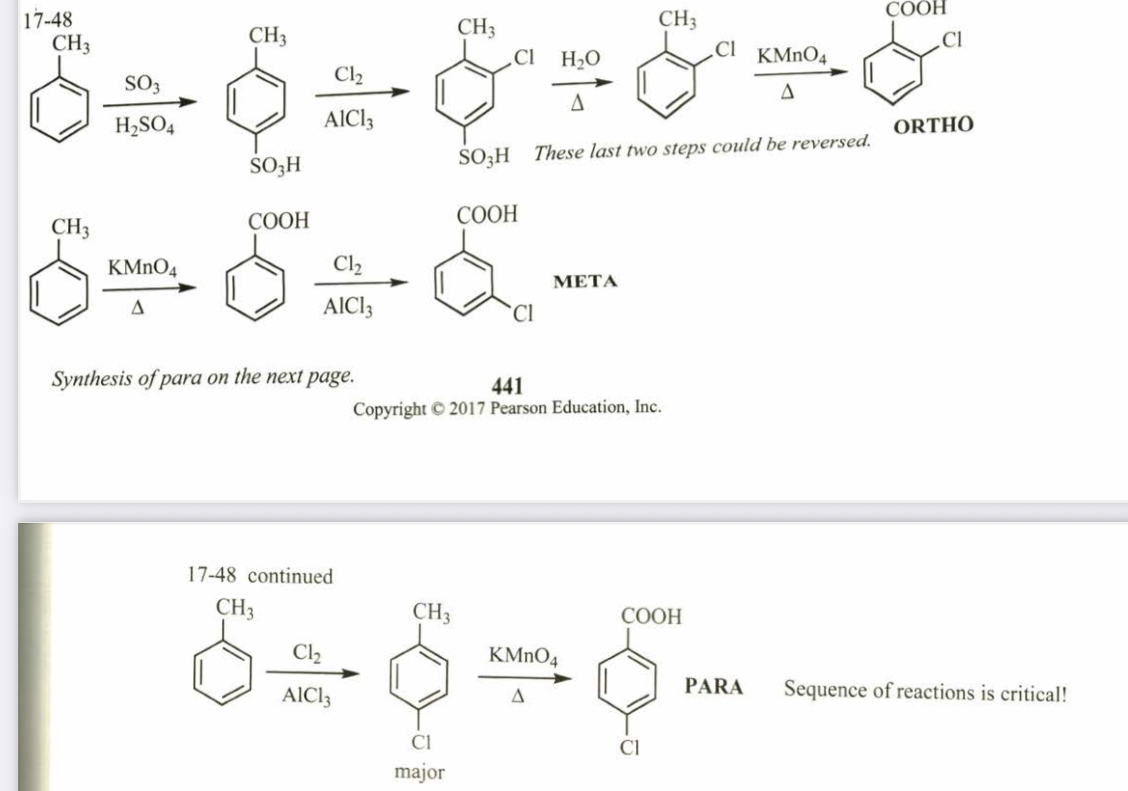
(17.48) Starting from toluene, propose syntheses for ortho-, meta-, and para-chlorobenzoic acid.
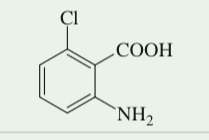
(17.49) Starting from toluene, propose a synthesis of this trisubstituted benzene.
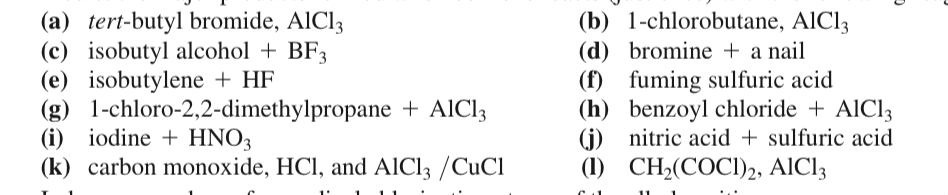
(17.50) Predict the major products formed when benzene reacts (just once) with the following reagents.
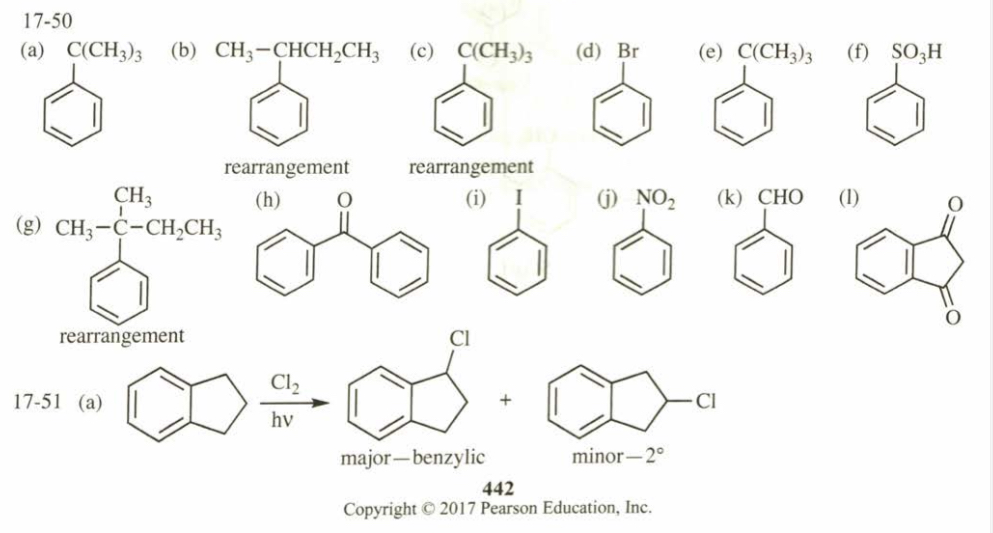
(17.52) Show how you would synthesize the following compounds, starting with benzene or toluene and any necessary acyclic reagents. Assume para is the major product (and separable from ortho) in ortho, para mixtures.
(a) 1-phenyl-1-bromobutane
(d) ethoxybenzene
(g) p-aminobenzoic acid
(j) 3-nitro-4-bromobenzoic acid (m) 2-(4-methylphenyl)butan-2-ol
(b) 1-phenyl-1-methoxybutane (c) 3-phenylpropan-1-ol
(e) 1,2-dichloro-4-nitrobenzene (f) 1-phenylpropan-2-ol
(h) 2-methyl-1-phenylbutan-2-ol (i) 5-chloro-2-methylaniline (k) 3-nitro-5-bromobenzoic acid (l) 4-butylphenol
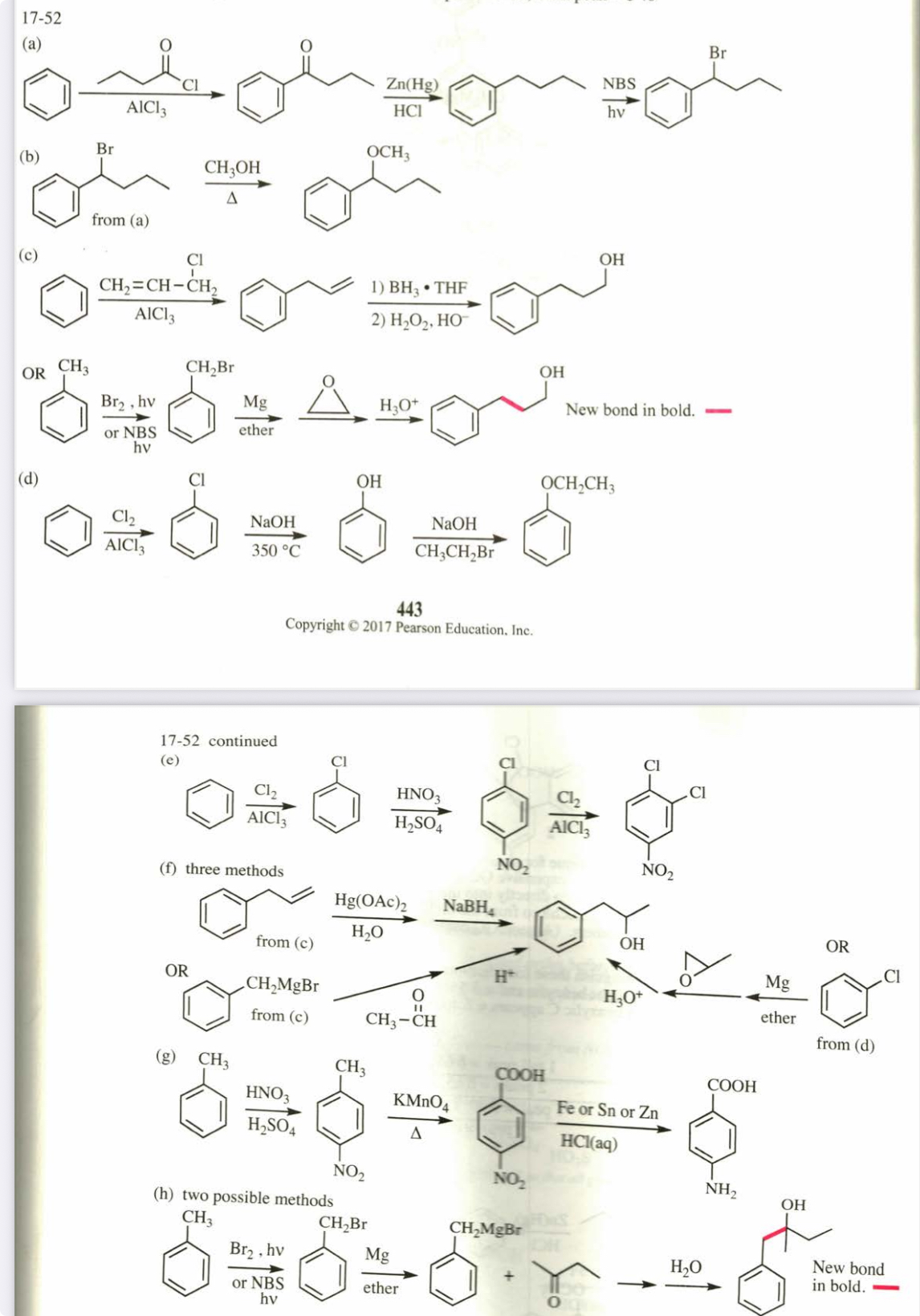
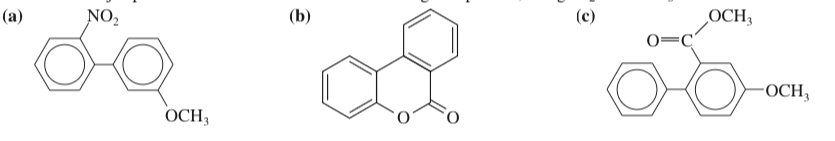
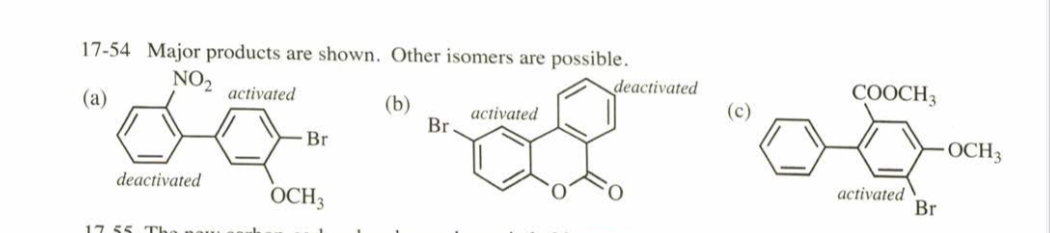
(17.54) Predict the major products of bromination of the following compounds, using Br2 and FeBr3 in the dark.
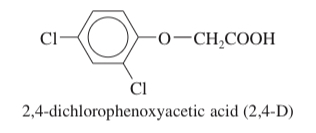
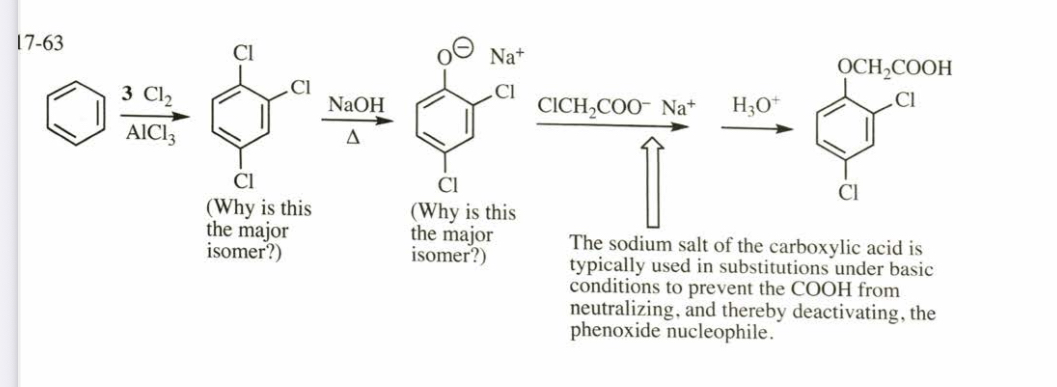
(17.63) The most common selective herbicide for killing broadleaf weeds is 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Show how you would synthesize 2,4-D from benzene, chloroacetic acid (ClCH2COOH), and any necessary reagents and solvents.
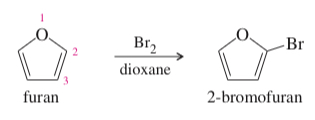
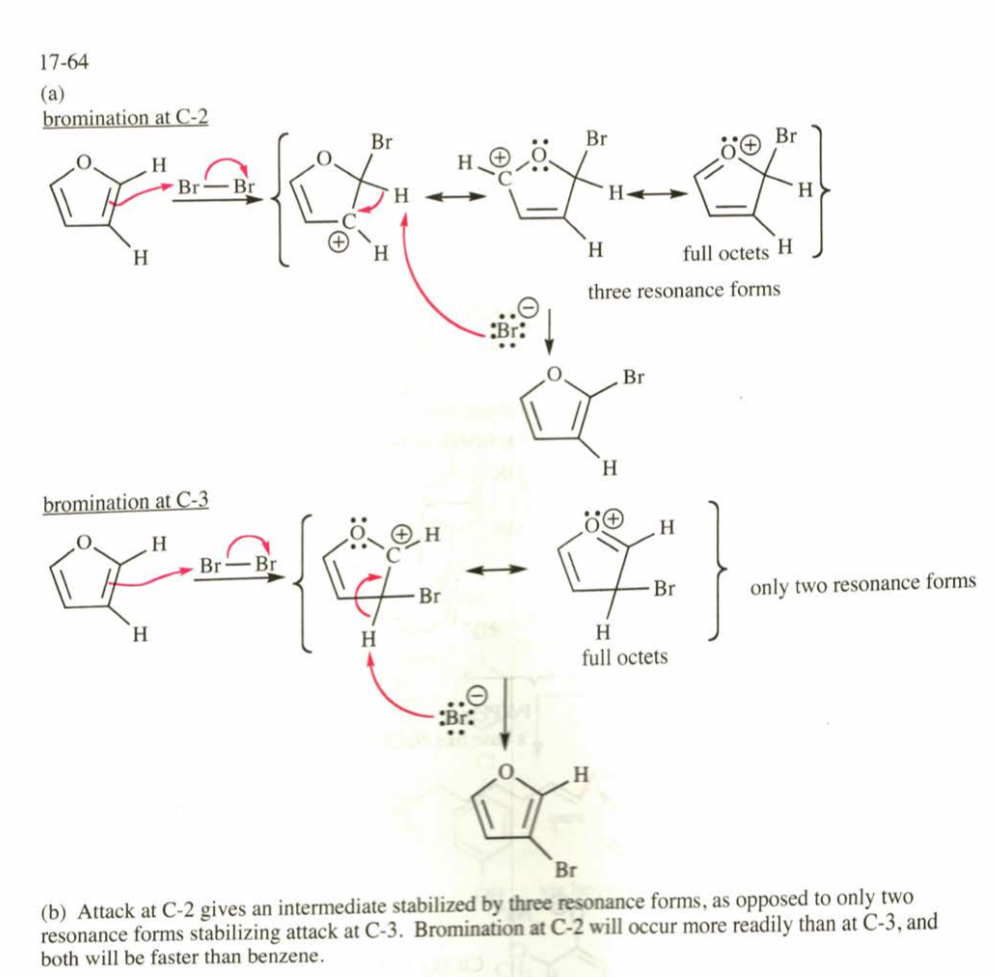
(17.64) Furan undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily than benzene; mild reagents and conditions are sufficient. For example, furan reacts with bromine to give 2-bromofuran.
(a) Propose mechanisms for the bromination of furan at the 2-position and at the 3-position. Draw the resonance forms of
each sigma complex, and compare their stabilities.
(b) Explain why furan undergoes bromination (and other electrophilic aromatic substitutions) primarily at the 2-position.
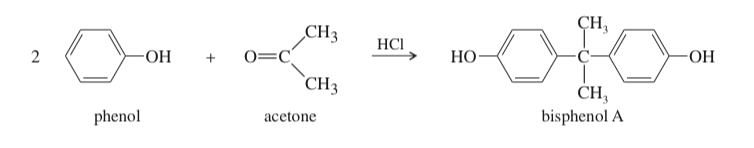
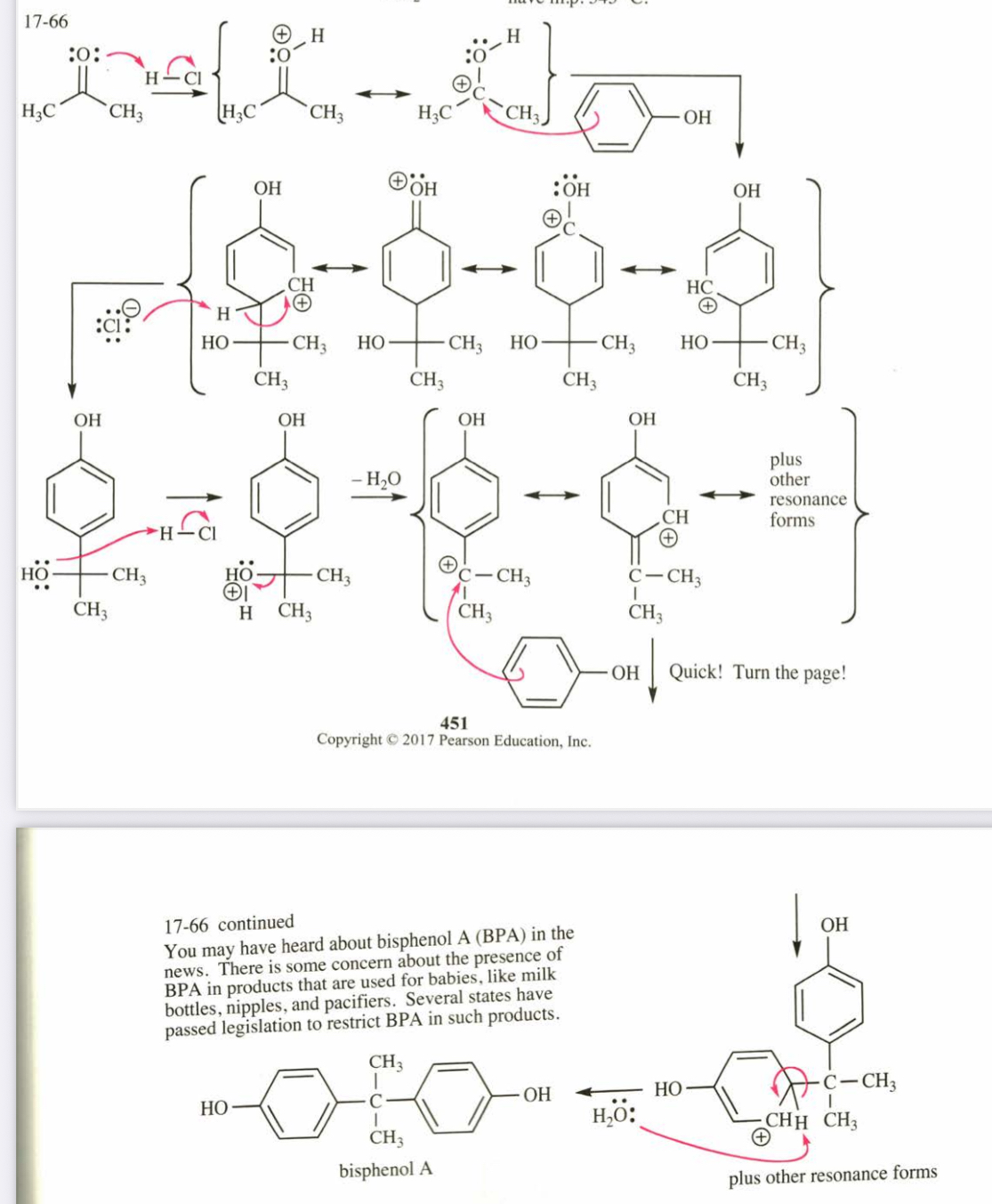
(17.66) Bisphenol A is an important component of many polymers, including polycarbonates, polyurethanes, and epoxy resins. It is synthesized from phenol and acetone with HCl as a catalyst. Propose a mechanism for this reaction.
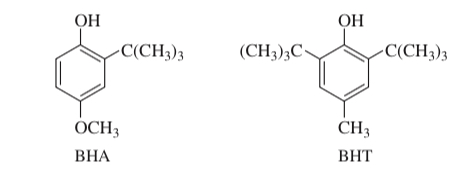
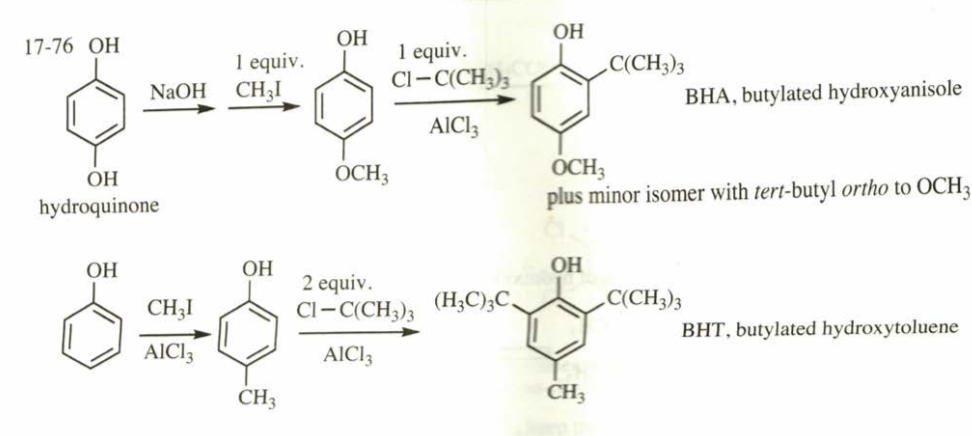
(17.76) The antioxidants BHA and BHT are commonly used as food preservatives. Show how BHA and BHT can be made from phenol and hydroquinone.
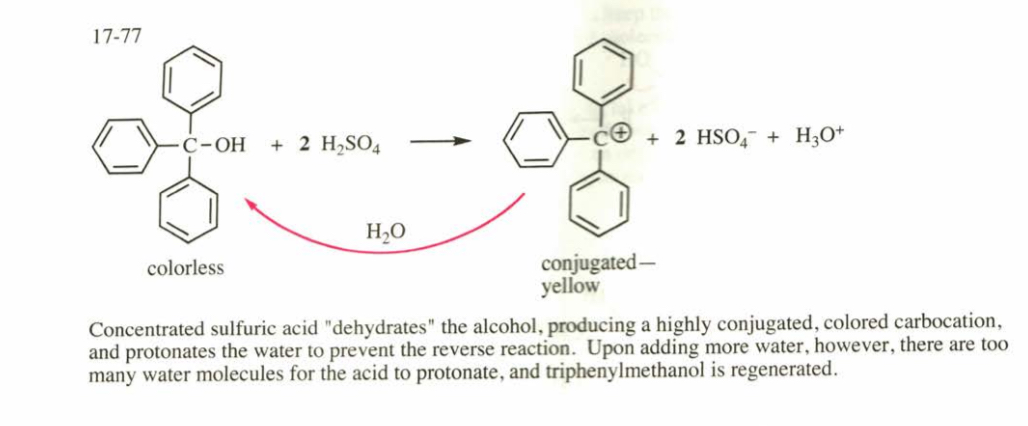
(17.77) Triphenylmethanol is insoluble in water, but when it is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid, a bright yellow solution results. As this yellow solution is diluted with water, its color disappears and a precipitate of triphenylmethanol reappears. Suggest a structure for the bright yellow species, and explain this unusual behavior.