Fundamentals of Welding 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Joining
welding, brazing, soldering, and adhesive bonding
Assembly
mechanical methods of fastening
Welding definition
joining process in which two or more parts are coalesced at their contacting surfaces by application of heat/pressure
Welding Importance/Pros
Provides a permanent joint, is economically stable, not restricted to a factory environment
Limitations of Welding
Performed manually and labor cost are expensive, High energy and inherently dangerous, welded joints do not allow for convenient disassembly, difficult detection of defects
Two Categories of Welding Processes
Fusion welding, Solid State welding
What is Fusion Welding? What is Autogenous welding?
Joining processes that melts the base metal. Fusion welding with no addition of a filler metal.
List Three Fusion Welding Processes
Arc, resistance, oxyfuel gas
What is Arc Welding + Basics?
Melting of metals is done by electric arc. 1. before the weld 2. during the weld base metal melted and filler meal is added to molten pool 3. the completed weldment
Fusion: What is Resistance Welding?
Melting accomplished by heat from resistance to an electrical current between faying surfaces held together under pressure
Fusion: What is Oxyfuel gas welding?
melting is accomplished by an oxyfuel gas such as acetylene
What is Solid State Welding?
Joining processes in which coalescence results from application of pressure alone or a combination of heat and pressure
Solid State: Describe Diffusion Welding
coalescence by solid state fusion between two surfaces held together under pressure at elevated temperature
Solid State: Define Friction Welding
coalescence by heat of friction between two surfaces
Solid State: Define Ultrasonic Welding
coalescence by ultrasonic oscillating motion in a direction parallel to contacting surfaces of two parts held together under pressure
Applications of Welding
Construction, piping, shipbuilding, aircraft, automotive, railroad
The welder controls…
the path or placement of the welding gun
Fitter…
Arranges the parts prior to welding
Safety Concerns
high temperatures of molten metals, gas fuels are hazardous, most processes use electrical power + shock is a hazard
Special Hazards
UV exposure (dark viewing helmet), sparks + spatters of molten, smoke and fumes
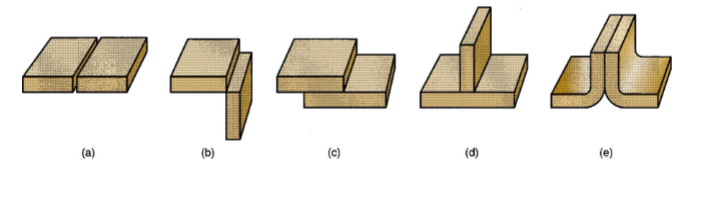
What are the five types of joints?
butt, corner, lap, tee, and edge
To accomplish fusion a source of __________ must be supplied to the _________.
high density het energy, faying surfaces
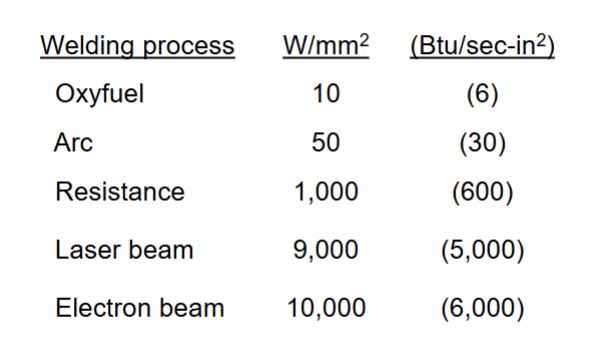
Power Density
Power transferred to work per unit surface area W/mm²
What happens when Power density is too low and when it is too high?
Low: heat is conducted into work so melting never occurs. High: localized tmeperatures vaporize metal in affected region
Power Densities for Welding Processes
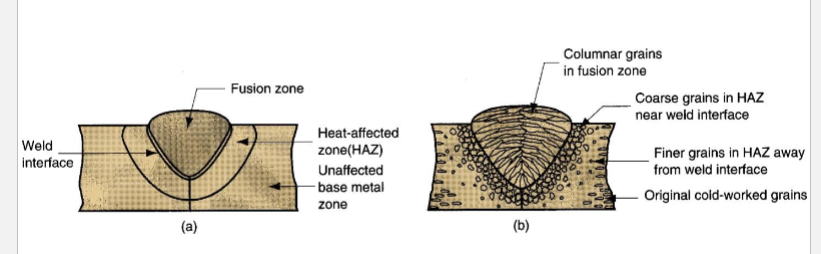
What are (a) and (b) in this fusion welded joint cross-section?
(a) principal zones, (b) typical grain structure
What is the Heat Effected Zone? What happens in this areas?
Metal experiences below melting but high enough for microstructural changes. The effect on HAZ is usually negative and welding failure often occurs here