Monomers and Polymers of Carbs, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Four Key Organic Molecules of Life
Lipid, Protein, Amino Acid, Carbohydrate
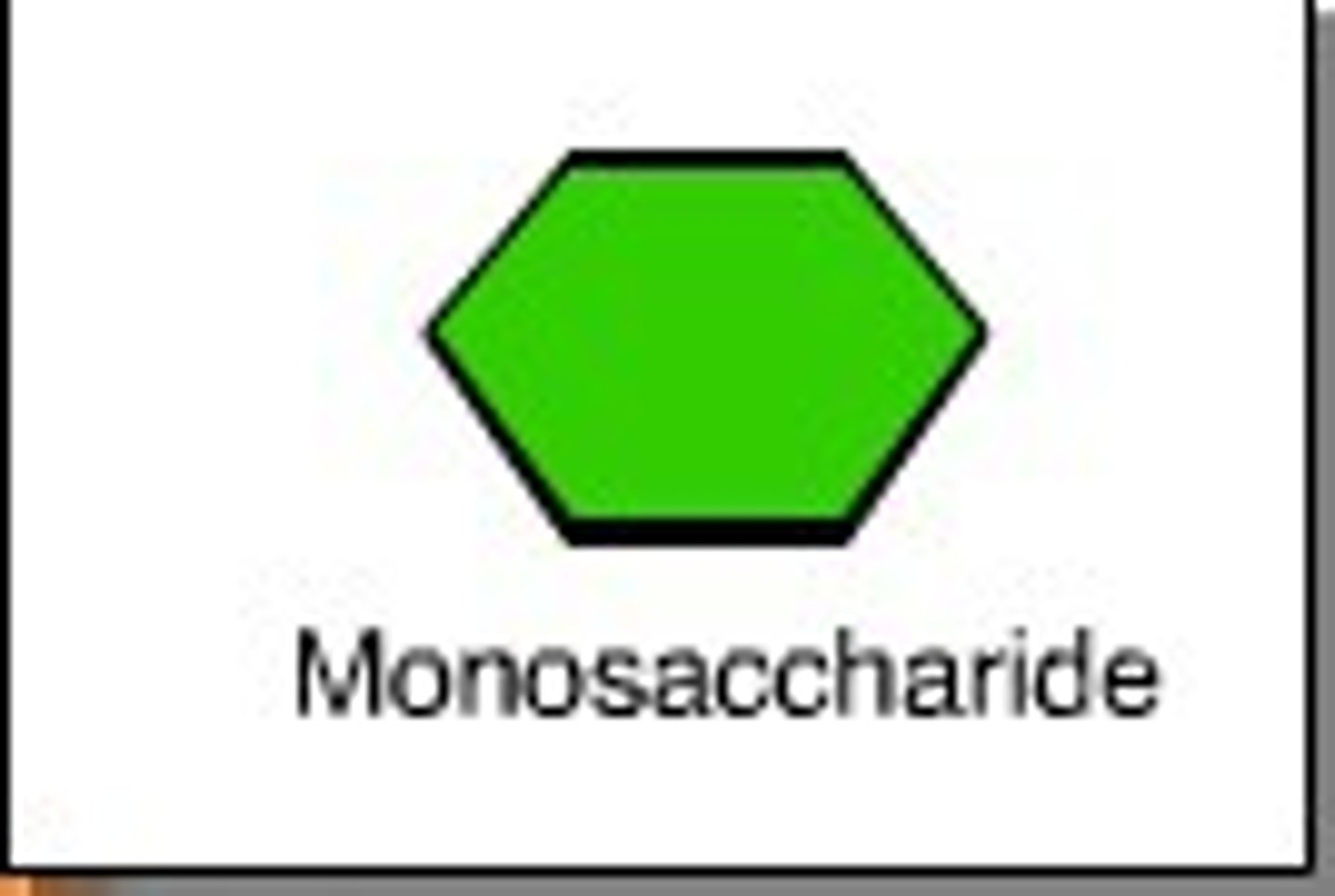
Carbohydrate Monomer
glucose
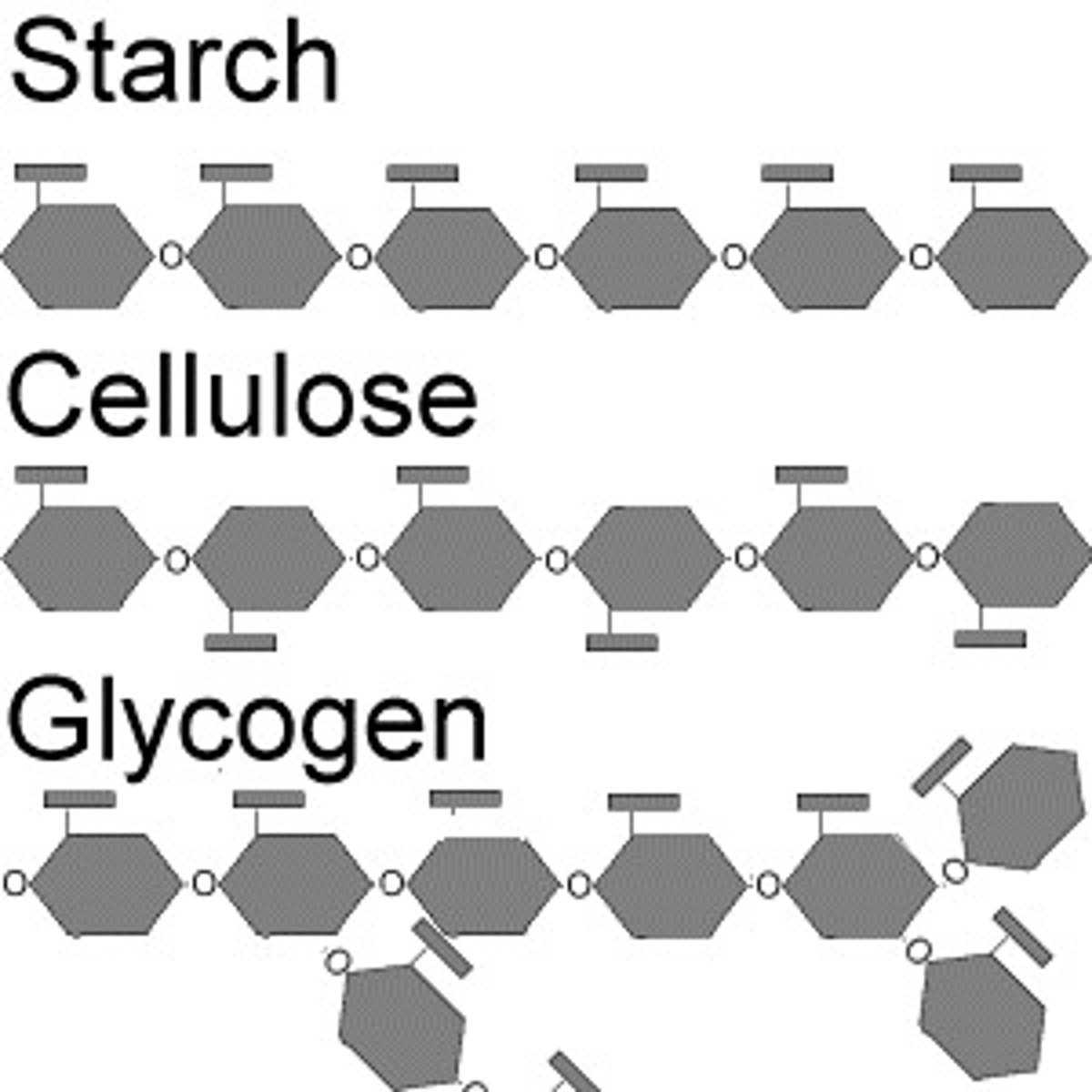
Carbohydrate Polymer
Polysaccharide: starches, glycogen, cellulose
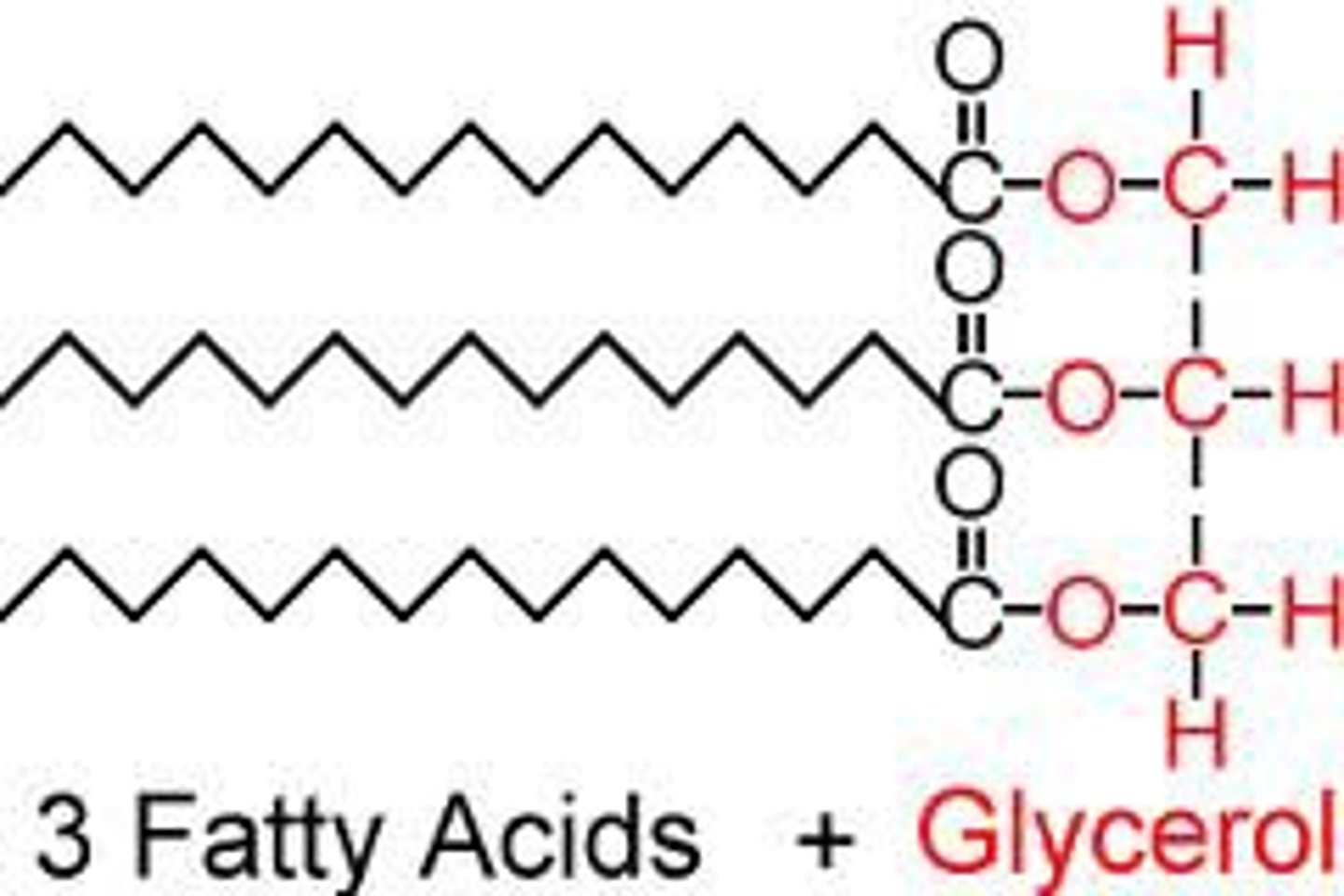
Lipids Monomer
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
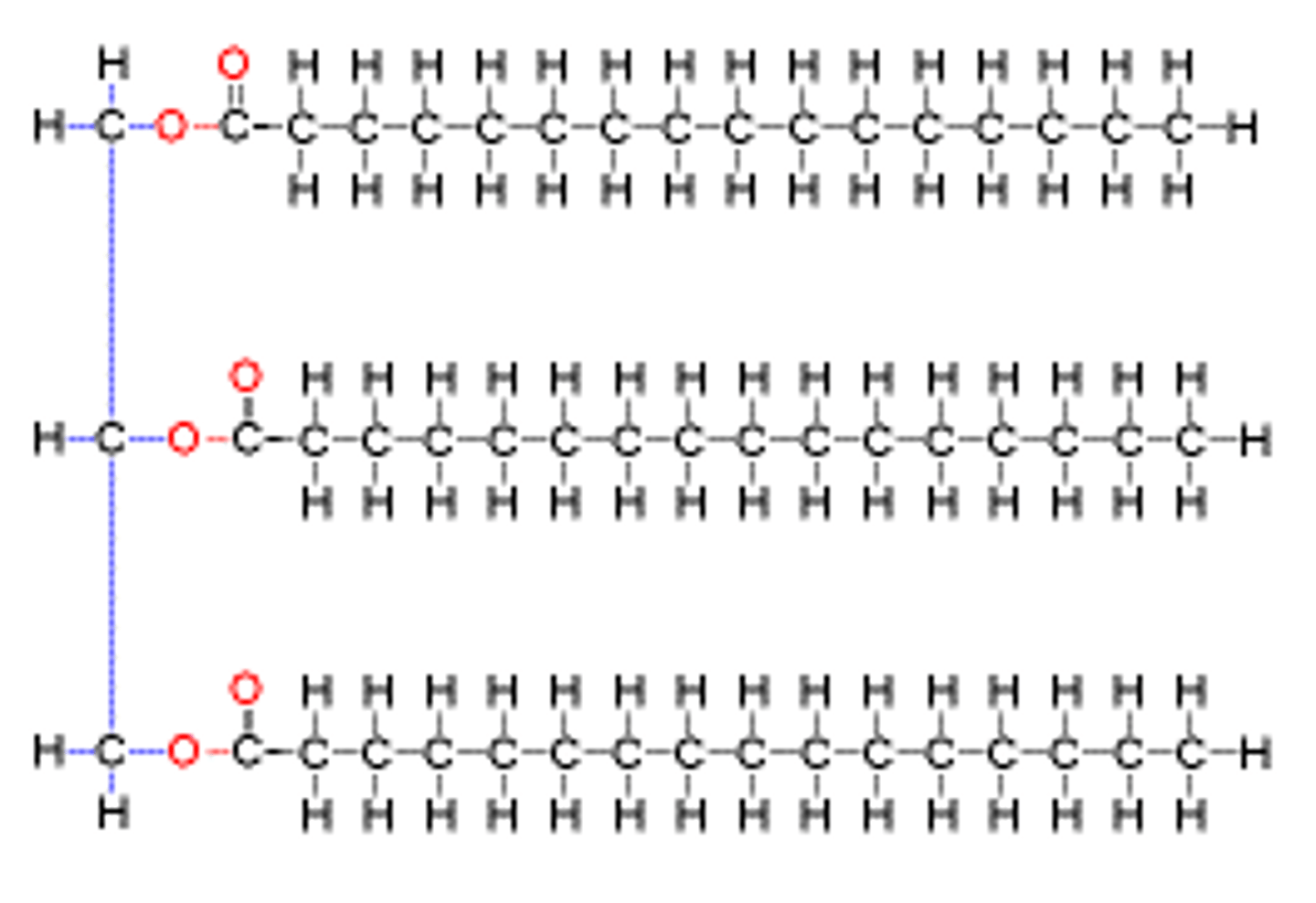
Lipids Polymer
saturated fat, unsaturated fat, phospolipids, steroids.
Nucleic Acid Monomer
Nucelotide
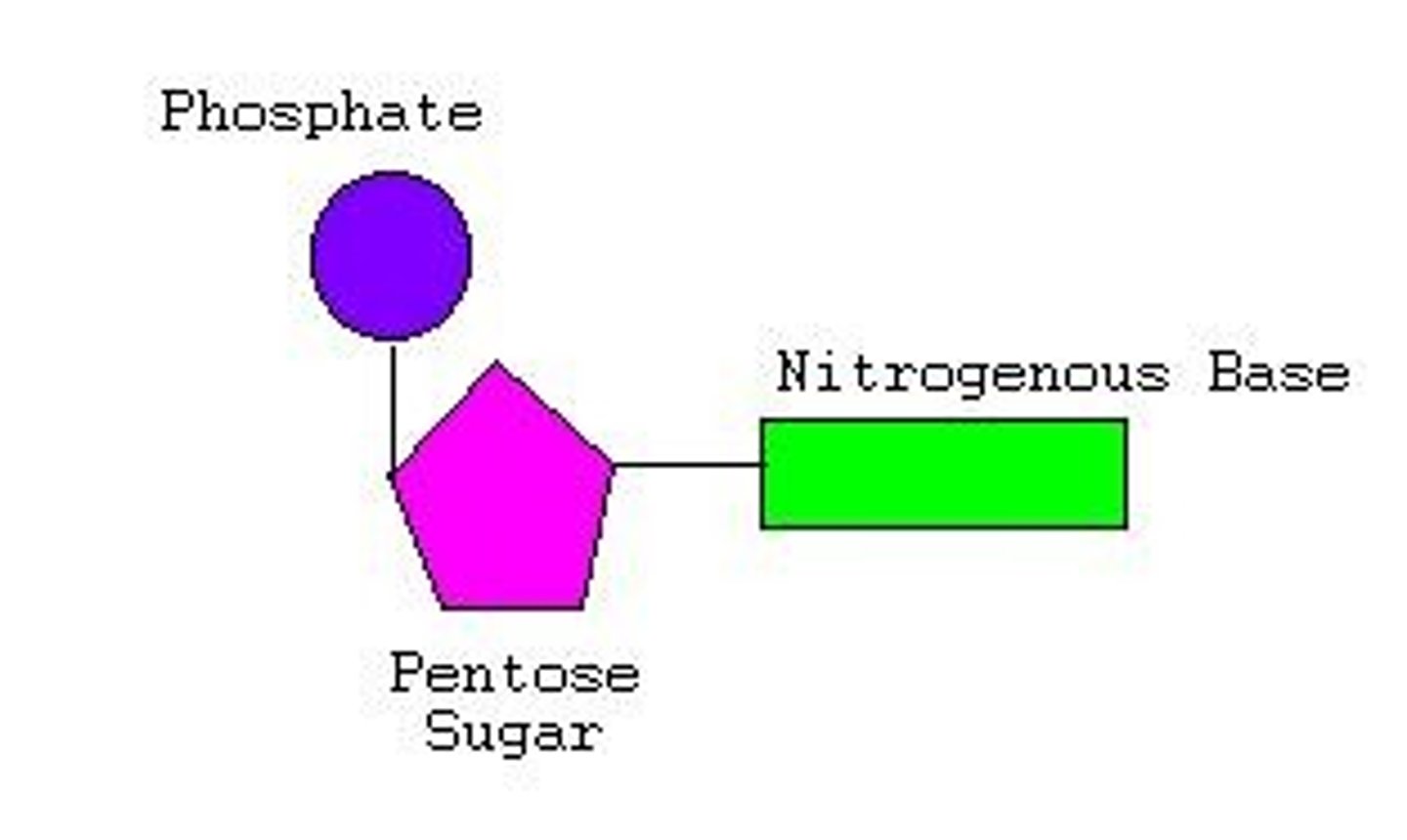
Nucleic Acid Polymer
Nucleic Acid (DNA and RNA)
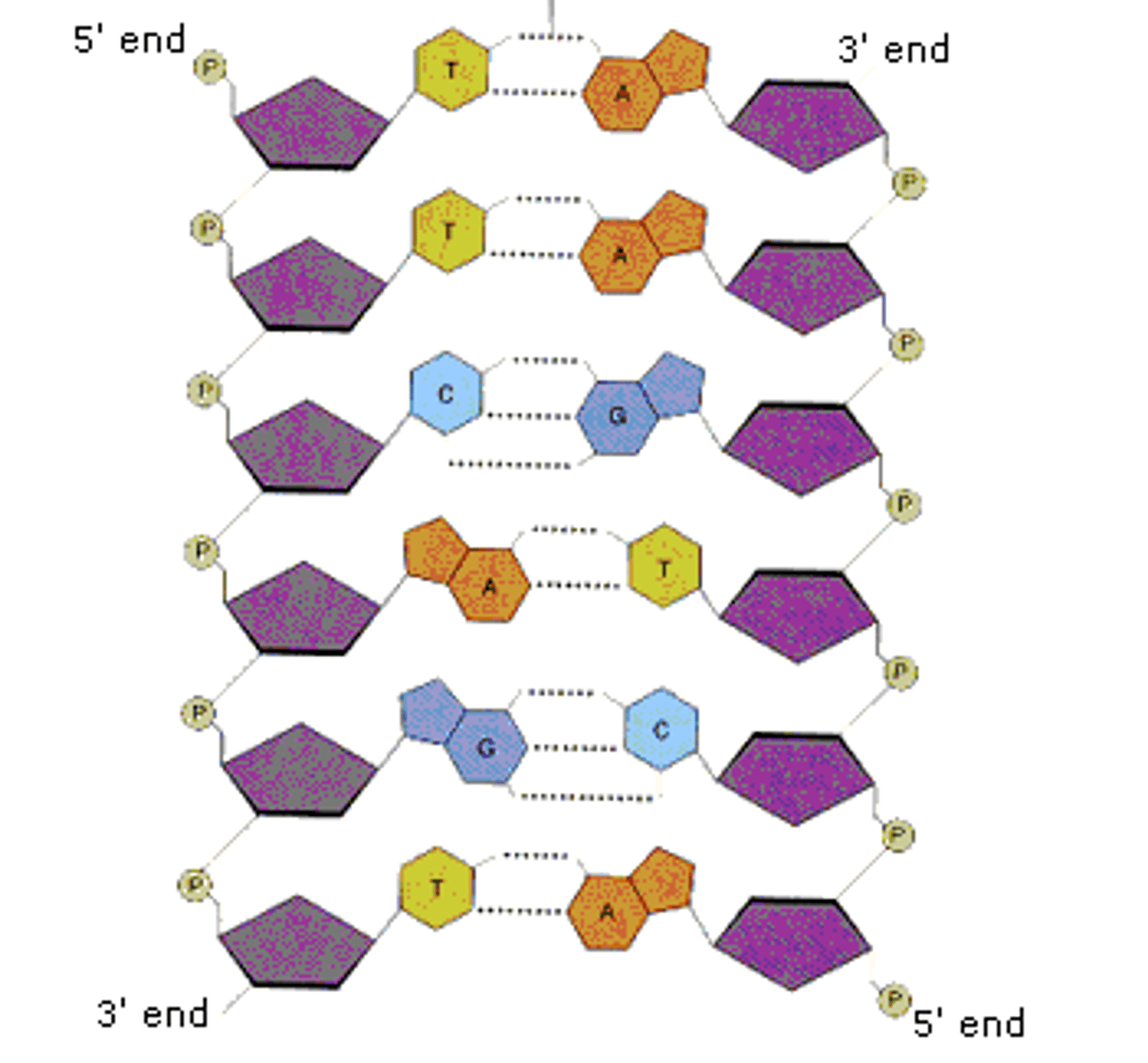
Proteins Monomer
Amino Acids
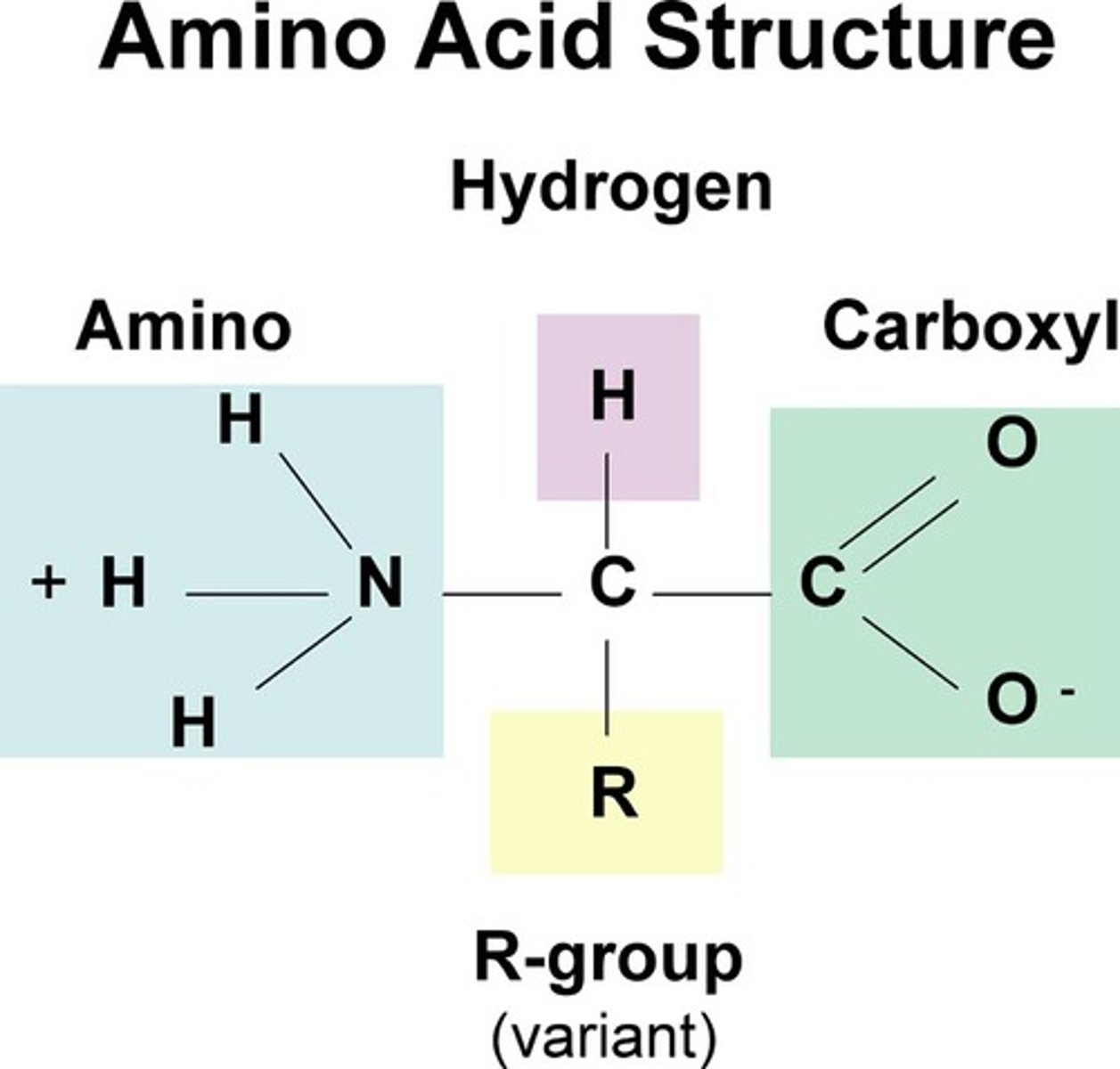
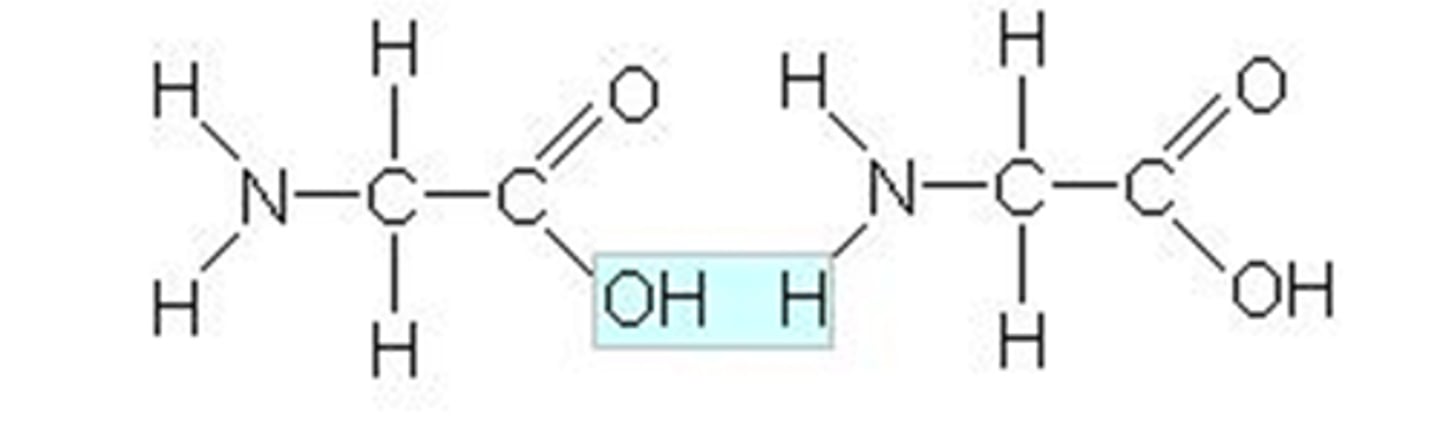
Proteins Polymer
Polypeptide Chain
Monomer of Carbohydrate
Glucose: a monosaccharide and the most basic unit of a carbohydrate.
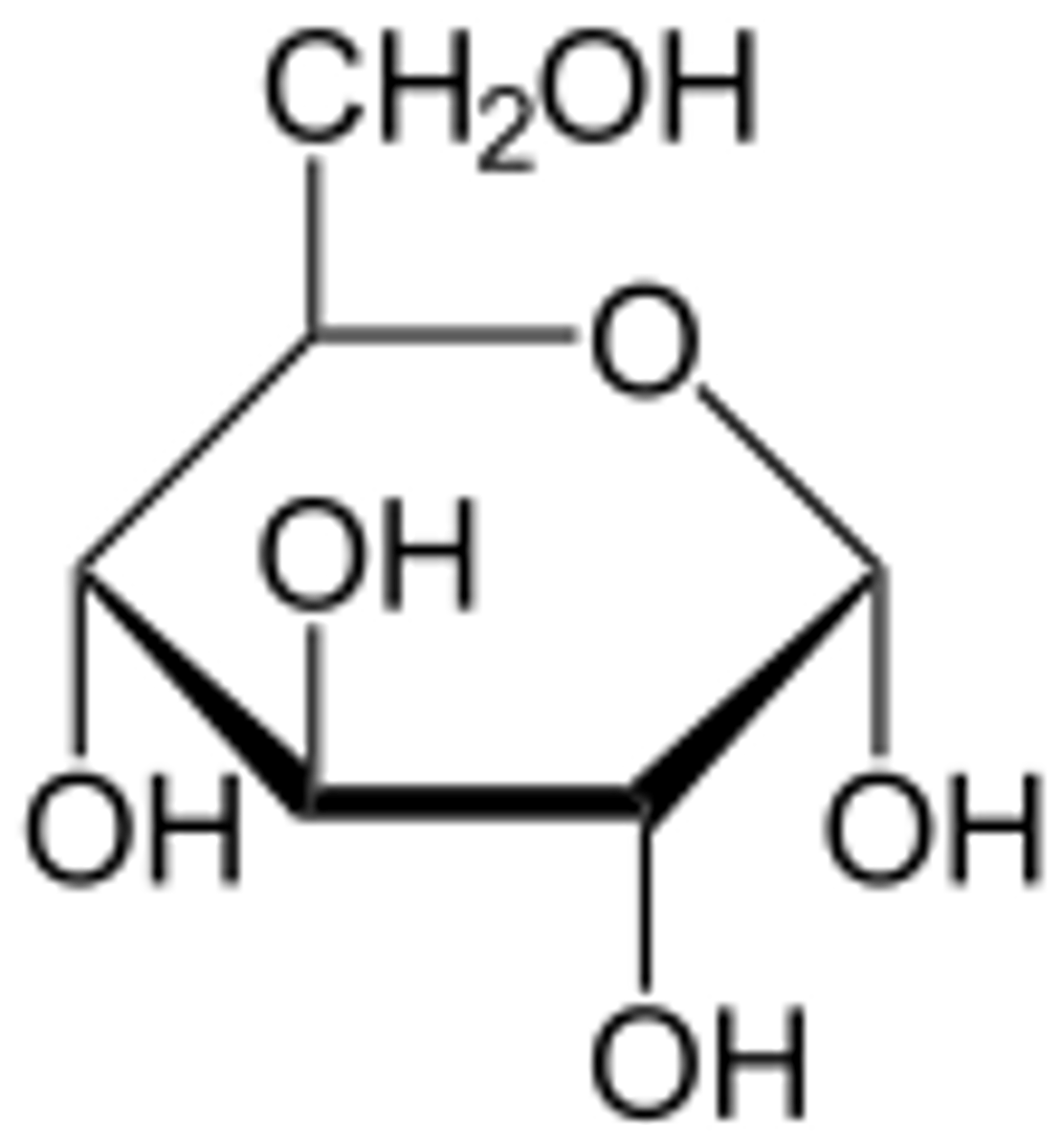
Monomer of Nucleic Acid
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Polymer of Nucleic Acid
DNA and RNA
Polymer of Protein
Polypeptide chain
Monomer examples
RNA, DNA, glucose, glycerol, fatty acid, saturated fat,
polysaccharides
phospholipid
lipid used for cell structure/membrane
Organic compounds
makes up living matter: contains Carbon:
protein, nucleic acid, carbohydrate, lipid, CO2
Inorganic compounds
makes up non-living matter: does not contain carbon
H2O, O2,
Monomer
a small molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
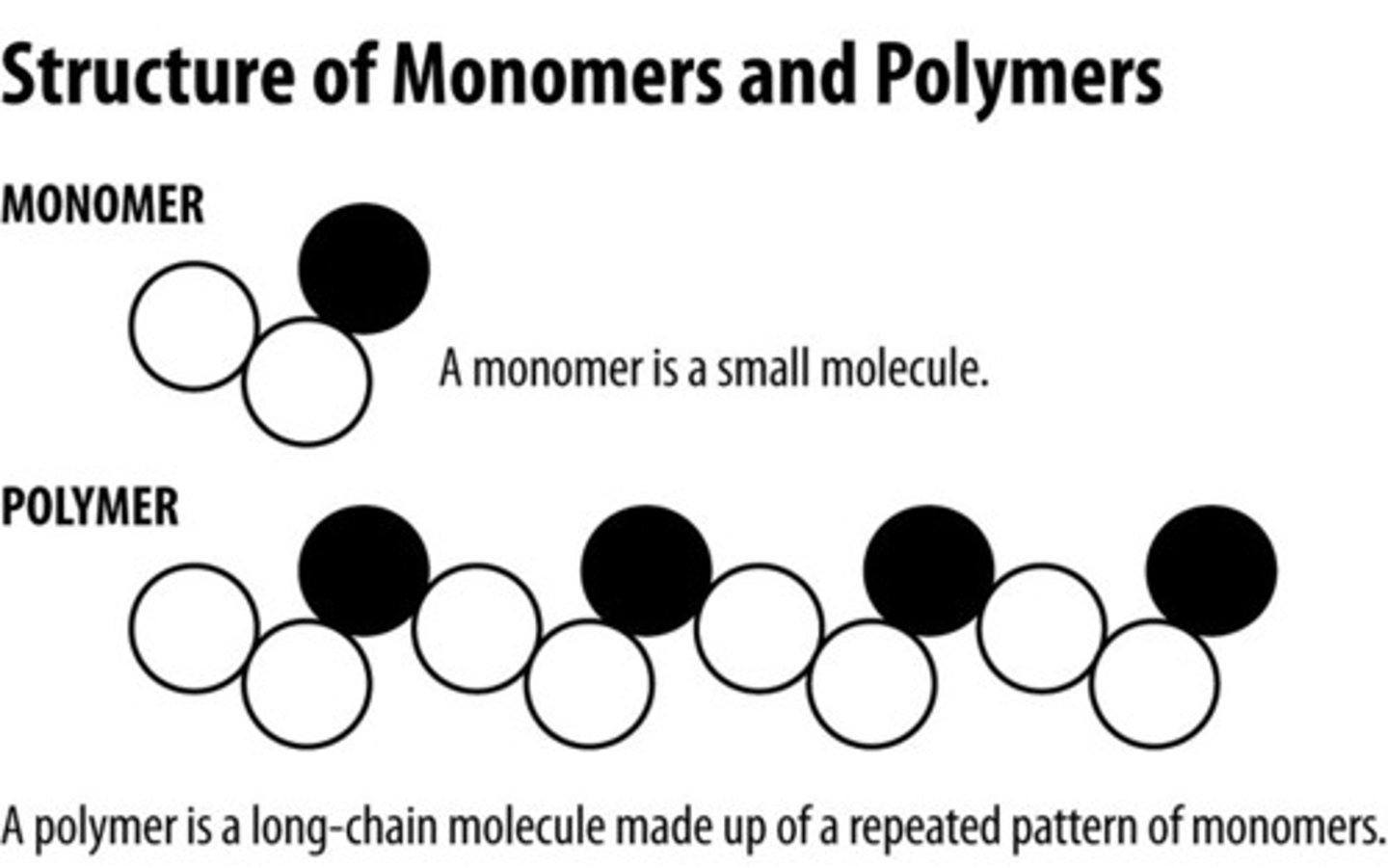
Polymer
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules. Polymers make up macromolecules
phospholipid
Phospholipid consist of 2 major component - a glycerol attached to a phosphate molecule and two fatty acid chain attached to the glycerol. Phospholipid is a polymer of lipids. Structure of cell membrane
activation energy
the minimum quantity of energy that the reacting species must absorb in order to undergo a specified reaction.
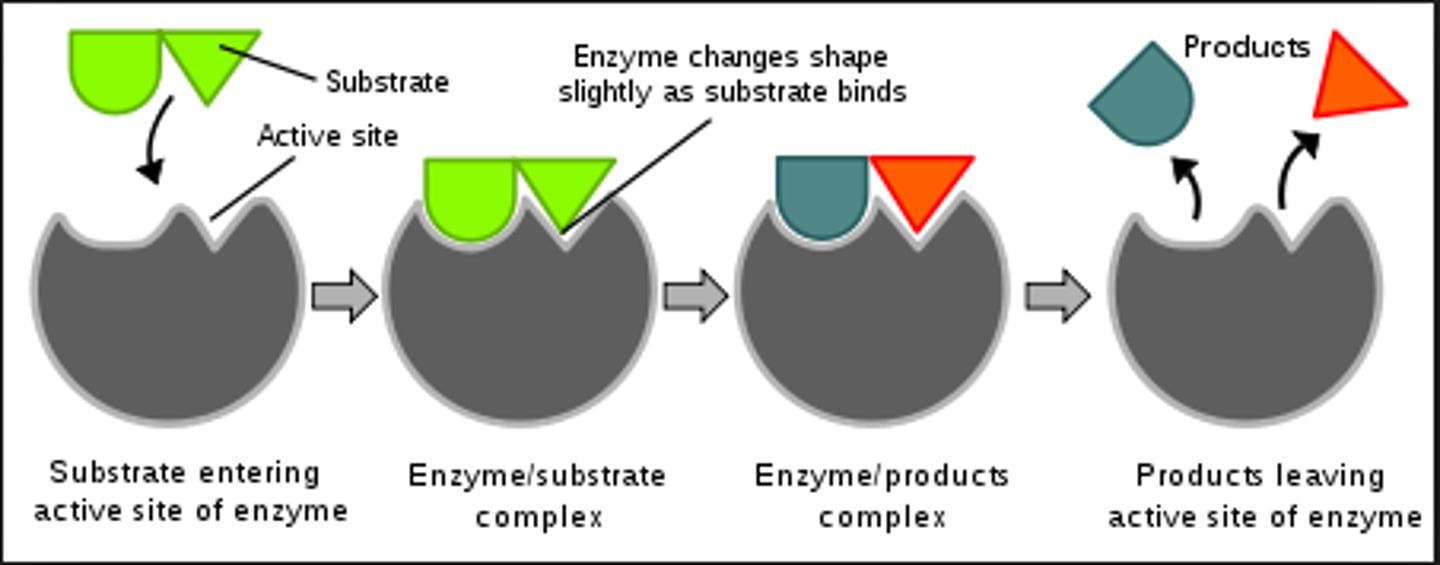
enzyme
a catalyst that lowers the activation energy required of the substrate. The substrate bonds at the active site of the enzyme. The resulting reaction creates a product.
Lipid
Lipids have three major roles in cells. First, they provide an important form of energy storage. Second, and of great importance in cell biology, lipids are the major components of cell membranes. Third, lipids play important roles in cell signaling, both as steroid hormones
carbohydrate
One of the four macro molecules. Monomer is glucose. polymers are: starch,glycogen,cellulose. Starch and cellulose are from plants. Glucose is both. Starch come from animals.