human bio general: Respiratory system
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
4 main components of blood
Plasma
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) (Erythrocytes)
White Blood Cells (WBCs) (Leukocytes)
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Plasma
The liquid portion of blood (about 55% of total blood volume)
Mostly water (about 90%), but also contains proteins, hormones, nutrients, salts, and waste products
Functions: transports nutrients, hormones, and waste; helps regulate body temperature and pH
RBCs
Make up about 40–45% of blood
Contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and returns carbon dioxide to the lungs.
Give blood its red color.
WBCs
Make up less than 1% of blood
Part of the immune system, protecting the body against infections, bacteria, viruses, and foreign invaders.
Platelets
Tiny cell fragments in the blood
Essential for clotting, helping stop bleeding when an injury occurs.
What is the function of the respiratory system
?
Brings oxygen (O₂) into the body for energy production.
Removes carbon dioxide (CO₂), a waste product.
Helps maintain blood pH balance.
Assists with speech and sense of smell.
function of epiglottis
Acts as a flap of tissue at the entrance of the larynx.
Closes during swallowing to prevent food or liquid from entering the airway.
Opens during breathing to allow air to pass into the trachea.
Describe cellular respiration and write the word equation:
A process in cells that releases energy by breaking down glucose with oxygen.
Produces ATP (energy), which powers cell activities, along with carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
C6H12O6+6O2⟶6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP)
How many alveoli are in each lung?
Each lung contains about 300 to 500 million alveoli.
Combined, the two lungs have around 600 million alveoli.
This large number creates a huge surface area (~70 m²) for efficient gas exchange.
Do you think there is a higher concentration of oxygen in the blood or in the alveoli?
There is a higher concentration of oxygen in the alveoli compared to the blood.
This difference in concentration allows oxygen to diffuse from the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries.
At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood (where its concentration is higher) into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Do you think there is a higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood or in the alveoli?
There is a higher concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood compared to the alveoli.
This concentration gradient allows carbon dioxide to diffuse from the blood into the alveoli, where it can be exhaled from the body.
During inhalation and exhalation, the pressure in the lungs changes. Determine whether the pressure is high or low for inhalation and exhalation and explain why this is.
Inhalation
Pressure in lungs: Low
The diaphragm contracts and moves down, and the rib cage expands, increasing lung volume.
Lower pressure lets air flow into the lungs.
Exhalation
Pressure in lungs: High
The diaphragm relaxes and moves up, and the rib cage contracts, decreasing lung volume.
Higher pressure pushes air out of the lungs.
What does spirometer test for, and measure
?
Tests for:
Lung function and breathing capacity
Detects respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD
Measures:
Volume of air inhaled and exhaled
Rate of airflow during breathing
What does oximeter test for, and measure
?
Tests for:
Oxygen levels in the blood (oxygen saturation, SpO₂)
Pulse rate
Measures:
Percentage of hemoglobin carrying oxygen in the blood
Heart rate (beats per minute)
What does stethoscope test for, and measure
?
Tests for:
Heart sounds (e.g., heartbeat, murmurs)
Lung sounds (e.g., breathing, wheezing, crackles)
Bowel sounds in the abdomen
Measures:
Not a numerical measurement itself; it listens to sounds to assess function and detect abnormalities.
Describe the process of inhalation through the: thoracic cavity, intercostal muscles and ribs, diaphragm, and lungs
During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens while the external intercostal muscles lift the ribs upward and outward, expanding the thoracic cavity, which lowers the pressure inside the lungs and allows air to flow in.
Describe the process of exhalation through the: thoracic cavity, intercostal muscles and ribs, diaphragm, and lungs
During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and rises, the intercostal muscles relax causing the ribs to move downward and inward, which decreases the thoracic cavity’s volume, increases the pressure in the lungs, and forces air out.
movement of substances in the alveoli
gas exchange occurs by diffusion
oxygen moves from alveoli (high conc.) into the blood (low conc.)
co2 moves from the blood (high conc.) into the alveoli (low conc.) to be exhaled
Arteries - “A” for away
Carry blood away from heart
Most oxygen-rich, except pulmonary artery
Thick muscular walls, elastic tissue
Narrow lumen
Examples: aorta, carotid, femoral
Veins
Carry blood toward heart
Most oxygen-poor, except pulmonary veins
Thin walls, less muscle and elastic
Wide lumen, valves prevent backflow
Examples: vena cava, jugular, saphenous
Capilleries
Connect arteries and veins
Site of gas, nutrient, and waste exchange
One cell thick walls for diffusion
Very narrow lumen, slow blood flow
Found throughout body tissues
What does pulmonary refer to?
lungs
What is considered a healthy bp?
120/80 mmHg (systolic = top, diastolic = bottom #)
which side of the heart has thicker walls and why?
Left side thicker: pumps blood to whole body, needs higher pressure
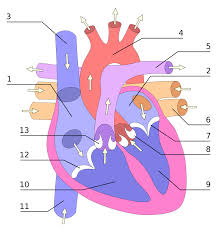
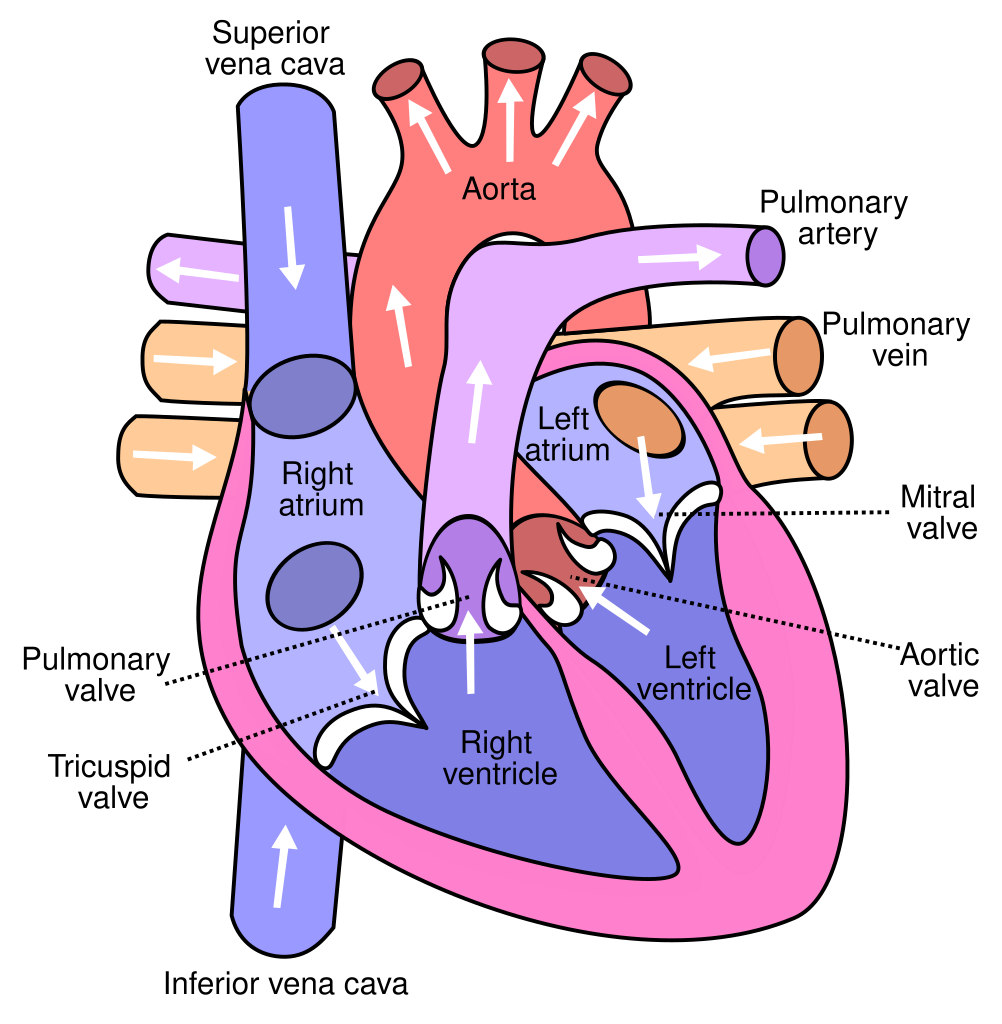
Heart diagram