Exam 3 - Geological Oceanography
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Methods of Absolute Dating
Historic events
Annual layers
Radiometric Dating
Petrology
study of the chemical composition and mineral associations in rocks
Hyaloclastic
Brecciated in a glassy basalt matric and typically forms when there are landslides of submarine basalt flows
SONAR
Sound Navigation and Ranging (developed during WWII for submarine detection)
Diagenesis
compaction and chemical reactions of sediments and pore fluids that change the chemistry of the water and solids accumulated
cotectic
Describing the conditions of pressure, temperature and composition at which multiple solid phases crystallize at the same time from a single liquid when cooled
Guyots
seamounts with a flat top with evidence of shallow or subaerial exposure that are more than 1000 m in elevation
formation of seamounts
an example of an endogenic process
olivine and nephilene
which two minerals found in basalt do not exist if the silica concentration is too high
200-400 kHz
Using SONAR, typical frequencies for shallow-water marine bathymetry surveys are:
1500 m/s
The speed of sound in water is approximately
siliceous ooze
a sediment that is 63% made up of radiolarian remains is called a _____
young seafloor
no sediment accumulation around Mid-Ocean ridge indicating that the seafloor is spreading
sources of dissolved matter
Weathering of rocks
continental weathering
calcium ions released into rivers transported to the ocean when silicate and carbonate rocks weather
Acid rain
accelerates dissolution of rocks
Hydrothermal vents
Biological processes
corals, mollusks, and plankton
Annual layers
Lamination
couplet
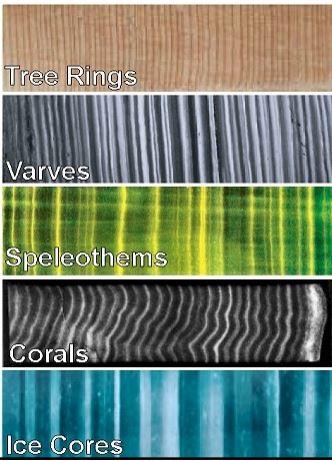
lamination
layers of sediment differing in composition
couplet
pair of adjacent different layers
Varves
sediment laminations found in anoxic basins
Biogenous-rich sediments in a spring thaw bloom and fall mixing bloom
Lithogenous-rich sediments in winter
Radioactive decay
process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation
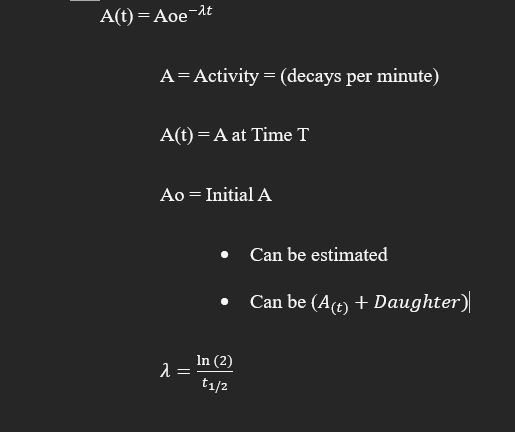
Parent isotope
decays to daughter isotope and decay particle
234U-230Th Method
U2+ is abundant and can replace Ca2+ in carbonate
Th is rare in seawater, so initial carbonate has little
Uo + Ut +Thf
234U-230Th
(10-450ka) corals, calcareous oozes, mollusks shells
Peking Man is an early hominin fossil (<100 ka). The fossils were partly encrusted with calcium carbonate. What Radioisotope is best?
sediment record from south oahu
(>2 Ma), and found a change from pelagic sediments to turbidites
210Pb
(<100 yr) terrigenous sediments
14C
(100a-40Ka) organic matter
40K-40Ar
(<500ky) Rocks containing K (constrain pelaeomag timescale)
Basis of 14C-Method
Cosmic Ray Bombardment
Nuclear reaction with the atmosphere
rapid chemical reaction with O2 in the atmosphere
Equilibrium between atmosphere and biosphere
Cosmic ray bombardment
creates free neutrons
nuclear reaction with atmospheric 14N(n,p)14C
produces and average ratio of 14C/12C=10-12
rapid chemical reaction with O2 (21%)
in the atmosphere
12C + 1/2O2 → 14CO + O
14CO + HO → 14CO2 + H
within 6-8 years
equilibrium between atmosphere and biosphere

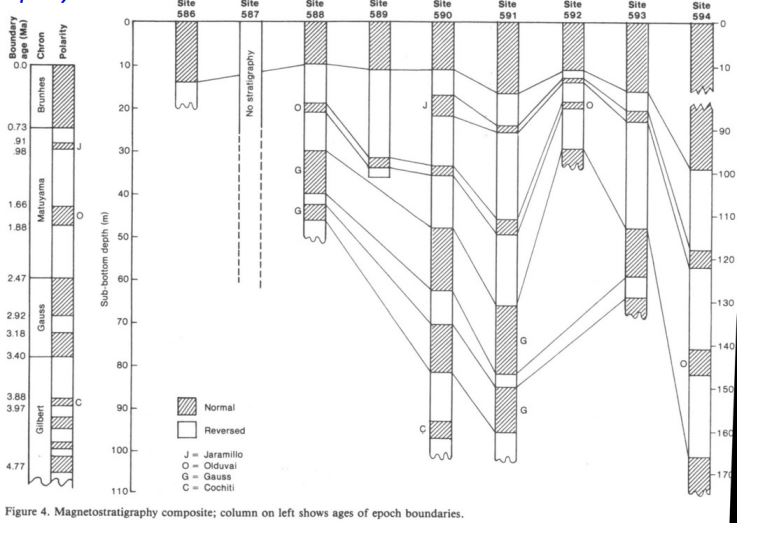
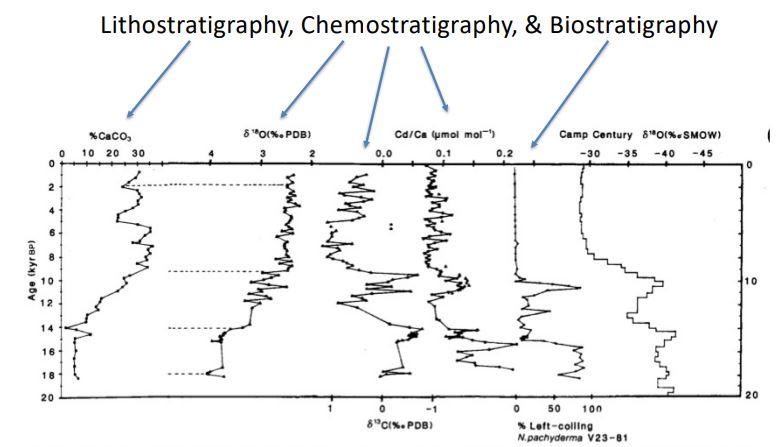
What principles of Magnetostratigraphy are show here?
Superposition
Lateral continuity
orignal horizontality
1.42 cm/ka
Calculate the sedimentation rate over the last 0.73 Ma.
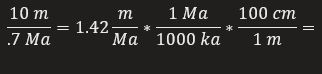
594
Which core had the fastest sedimentation rate?
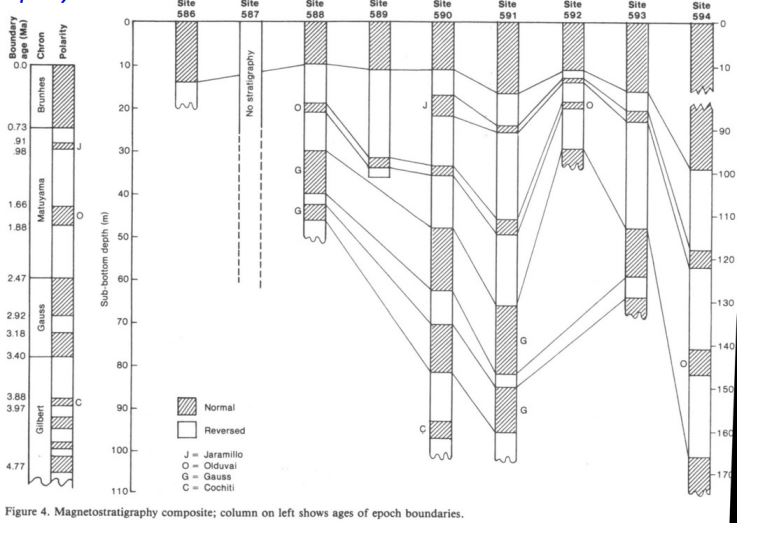
588 or 592
Which cores has the slowest sedimentation rate?
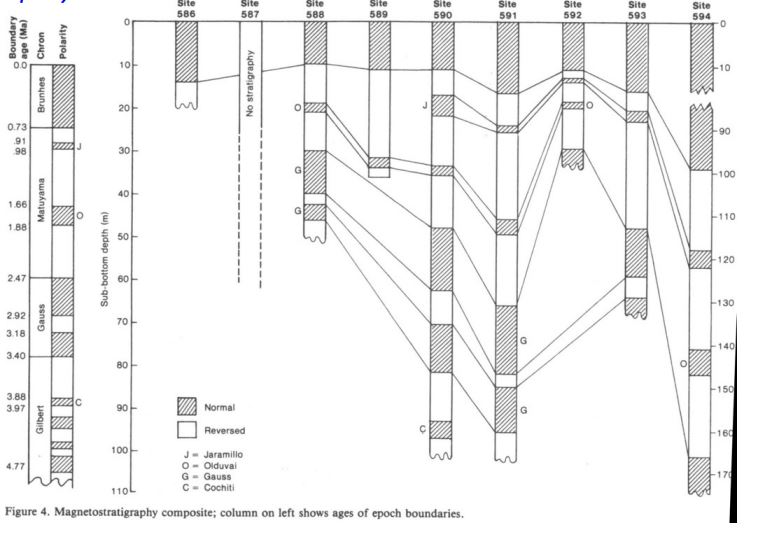

590 Cochiti
Which core collected the oldest sediment?
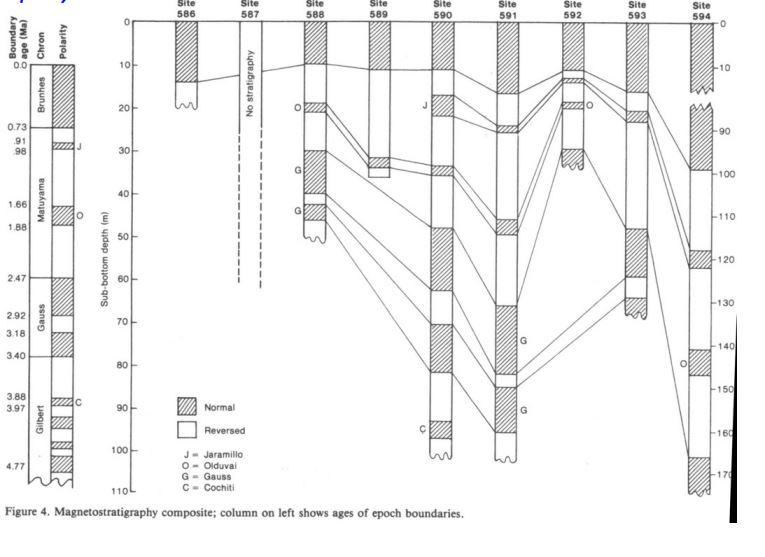
Biostratigraphy
tracking the changes in fossil fauna and flora
typically planktonic microfossil
diversity, abundance, rapid evolution, wide distribution
Biostratigraphy useful for
Age dating
environmental information (temp, nuts)
Smear slides used
to determine the composition of sediment recovered during coring
Quickly determine presence-absence, relative abundance
microfossil
communities that are also isolated to specific time periods
relative dating
the fixing of a geologic structure or event in a chronological sequence relative to other geologic structures or events
fossil succession used
to identify biostratigraphic zones
index fossil
abundant, cosmopolitan, existed for a relatively short span of time
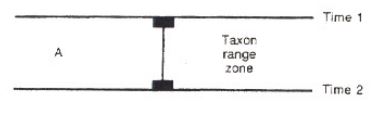
Taxon Range
define a period of time
Concurrent range zone
period of time where two fossil overlap

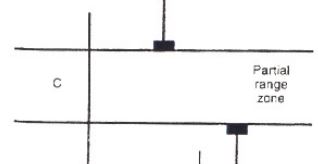
Partial range zone
one fossil exist for a long period of time where the two other fossils don’t exist in the same time period with a biozone in the middle
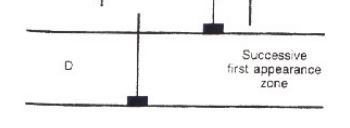
successive first appearance zone
period of time where only one fossil exists is the biozone and once the second fossil appears the sediment is younger
successive last appearance zone
period of time where one fossil is the last to die off and another fossil dies off before it

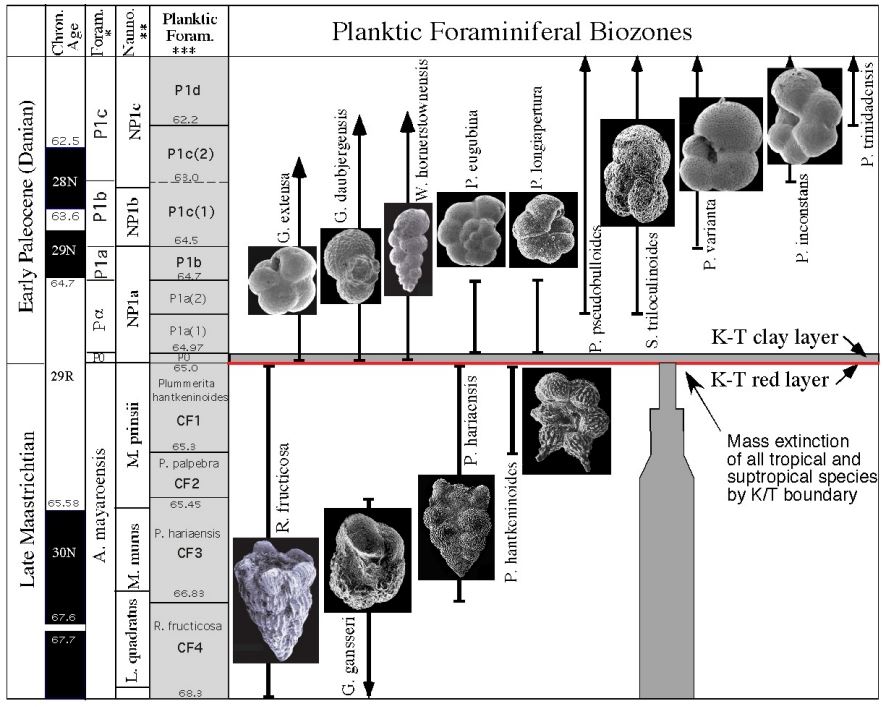
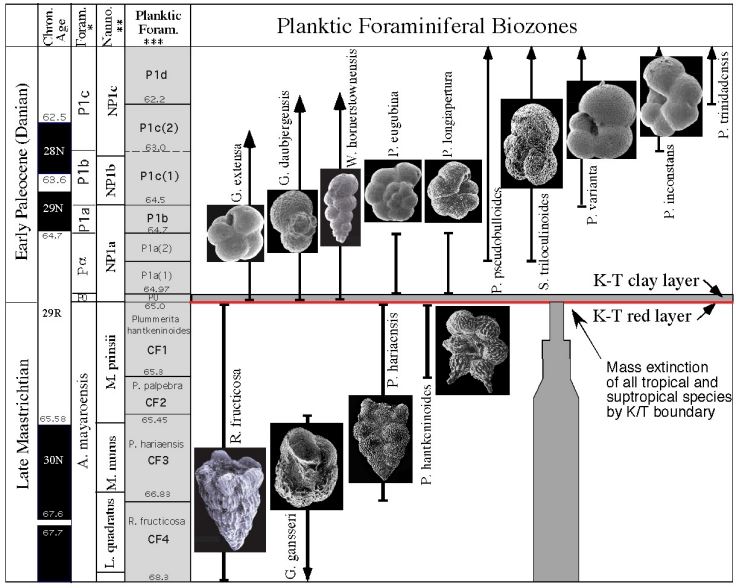
Which zone based on range
CF1 (Taxon range)
P1a(2) (Concurrent range)
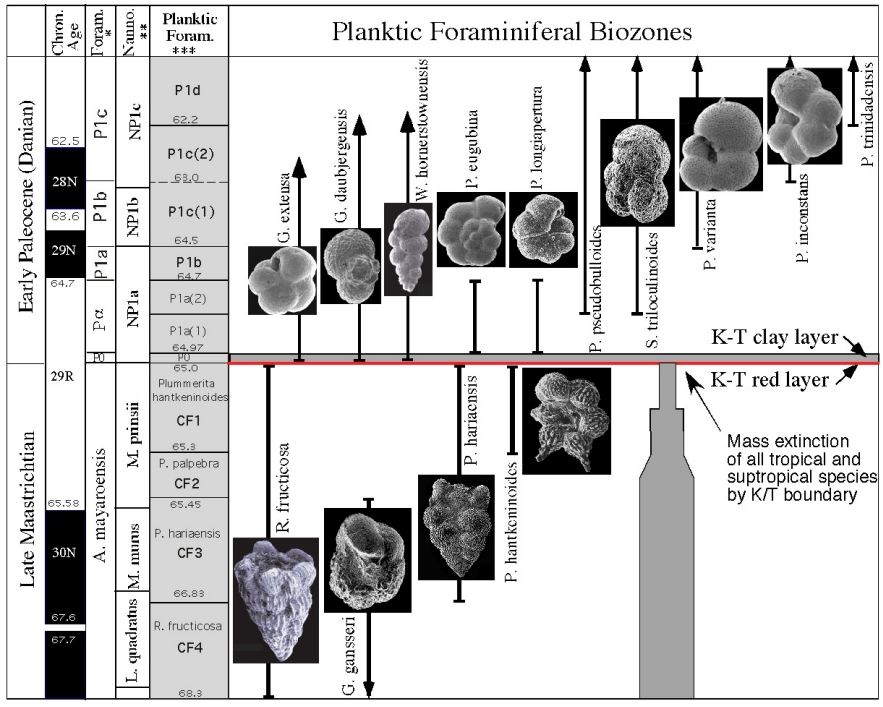
Successive First appearance
P0
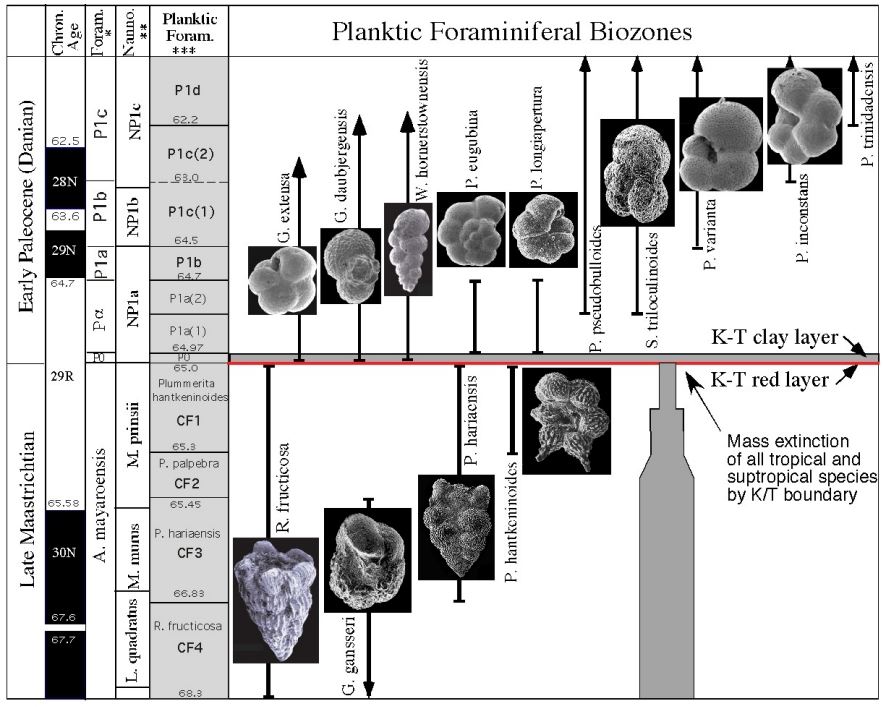
Partial range
P1b
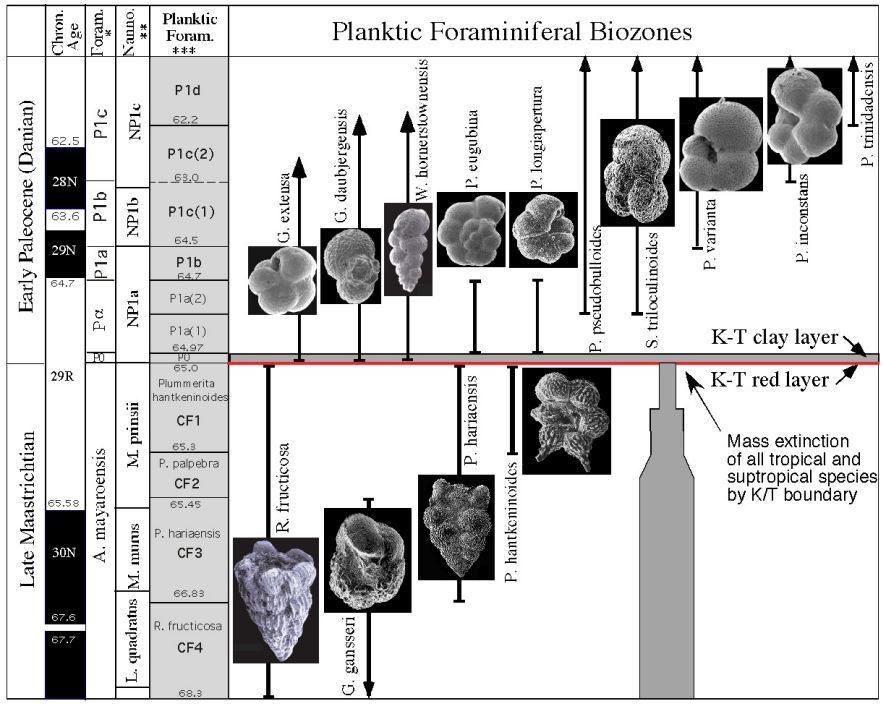
Biozone
CF1
Foraminiferans
unicellular, heterotrophic plankton with calcite shells (CaCO3)
Most studied marine microfossil
Make up 2.5% of all known animal species of the last 550 Ma
The foundation of marine paleoecology
Large (50-400 µm)
high diversity
occur in all marine environments, at all latitudes, within all oceans
Climate Indicators in sediments
foraminifera
Viscosity and Drag
decrease with warmer water
compensate for high density shell
tropical shells thinner, more porous, exaggerated apertures, spines
Tropical foram
globigerinoides sacculife

polar foram
neogloboquadrina pachyderma
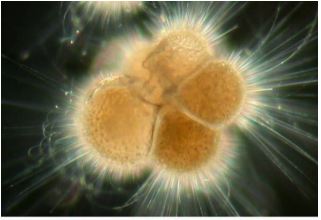
Foram N. Pachy test
Changes with temperature
left-coiling (sinestral) in cold water
right-coiling (dextral) in warmer water
changes in species with temperature
water started cold; conditions change with a period of warm water; ended cold
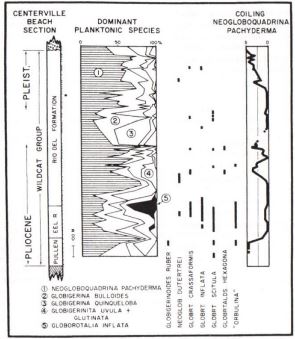
regional biostratigraphic relationships
are developed because of changes in species with temperature
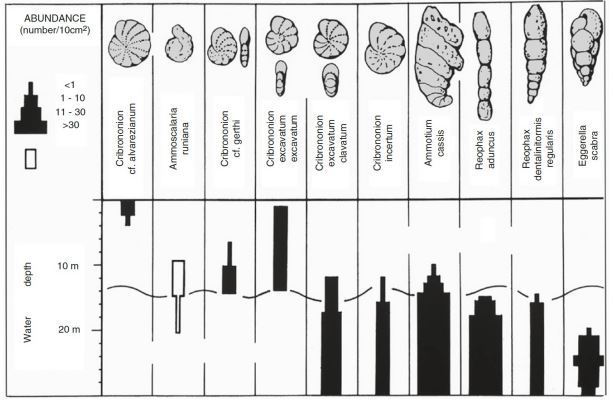
Benthic forams
indicators of water depth
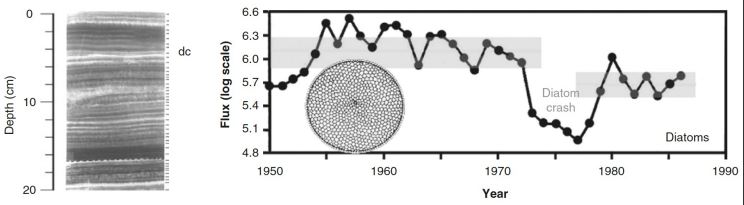
diatoms
are indicators of primary production
More diatoms, must have been more nutrients and more production
Diatom crash in Santa Barbara Basin
Strong upwelling, but Si-limited
Shifting baseline-reduced accumulation of diatoms after 1980
Distribution of coral reefs
tropics and subtropics
skewed to western side of oceans
no coral reefs in upwelling regions (except equator)
annual layers in coral cores
Faster, lower-density growth during summer months
massive corals typically
Aragonite skeleton records:
changes in accessory elements
changes in isotopic ratio
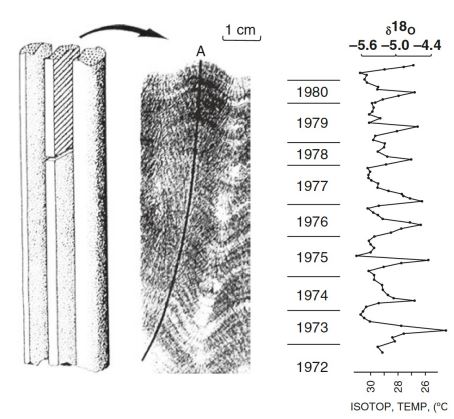
changes in accessory elements in coral cores
Temp: Mg, Sr
pH: Basic
Nutrients, salinity: Ba, Li
Changes in isotopic ration
Growth rate: 13C/12C
Temperature: 18O/16O
Seafloor imprint of glaciers
Iceburg-carved ravines on the shelf
Dropstones (grain size larger than anticipated for the region)
Isotopes of elements
the chemical characteristic of an element is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus
92 naturally occurring elements
some are stable; some are radioactive
Atomic number
= # Protons = define the chemistry
Atomic weight
= protons + neutrons = referred to as isotopes
Different elements can have different numbers of neutrons and thus atomic weights (the sum of protons plus neutrons
All isotopes of a given element
have the same chemical properties
small differences of all isotopes of a given element
due to the fact that heavier isotopes typically form stronger bonds and diffuse slower
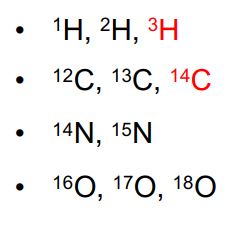
examples for H, C, N, and O
Except for 1H, even atomic weights are more abundant than odd
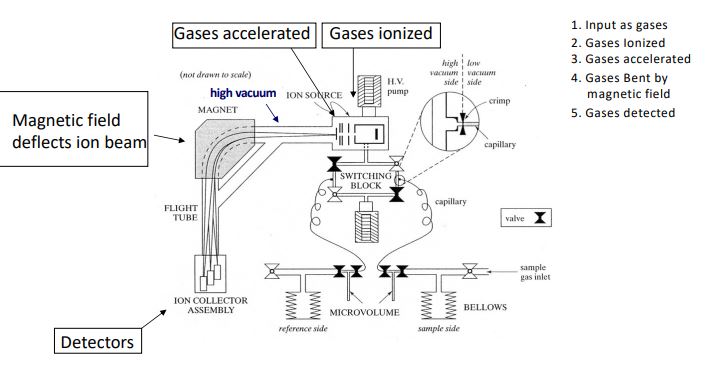
mass spectrometer
isotopes are measured as ratios of two isotopes by various kinds of detectors. Standards are run frequently to correct for instrument stability
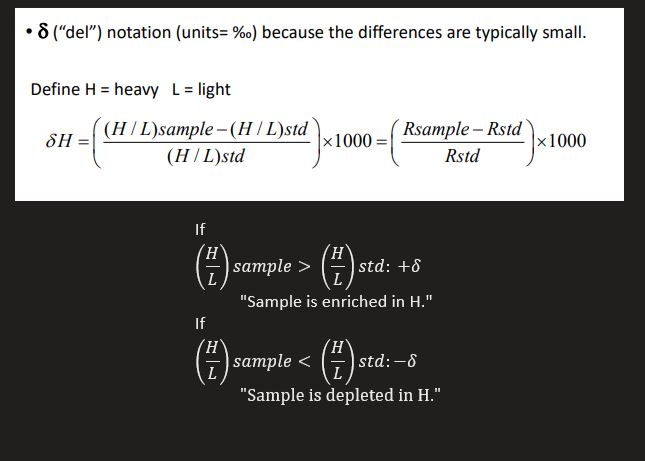
Define H = heavy and L = light
Report stable isotope abundance as ratio to most abundant isotope (e.g. 13C/12C)
Isotope ratio of a sample is reported relative to a standard
Standard for H
Standard Mean Ocean Water (SMOW)
Standard for C
Belemnitella americana from the Cretaceous Peedee formation, South Carolina (PDB)
Standard for N
Atmospheric N2
Standard for O
Standard Mean Ocean Water (SMOW)
Belemnitella americana from the Cretaceous Peedee formation, South Carolina (PDB)
Standard for S
Troilite (FeS) from the Canyon Diablo iron meteorite (CD)
Fractionation
variations in isotope abundance are caused by reactions which preferentially use one isotope resulting in a different fraction in the product than in the reactant
equilibrium isotope effects
Partial separation of isotopes between two (or more) substances in equilibrium. Usually inorganic (CaCO3), not organic
larger isotope
tends to be more stable
ex) water is enriched in D218O vs. vapor
HCO3- is enriched in 13C vs. CO2
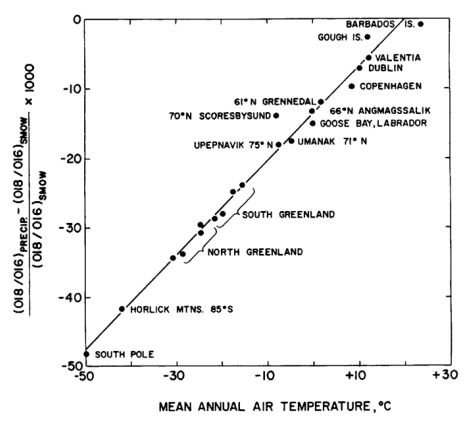
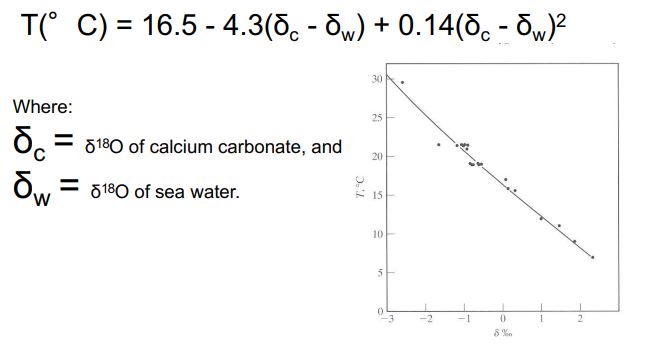
paleothermometer
Fractionation during ppt. of CaCO3 as a result of temperature
As temperature gets colder, 18O increases
As temperature gets warmer, 18O decreases
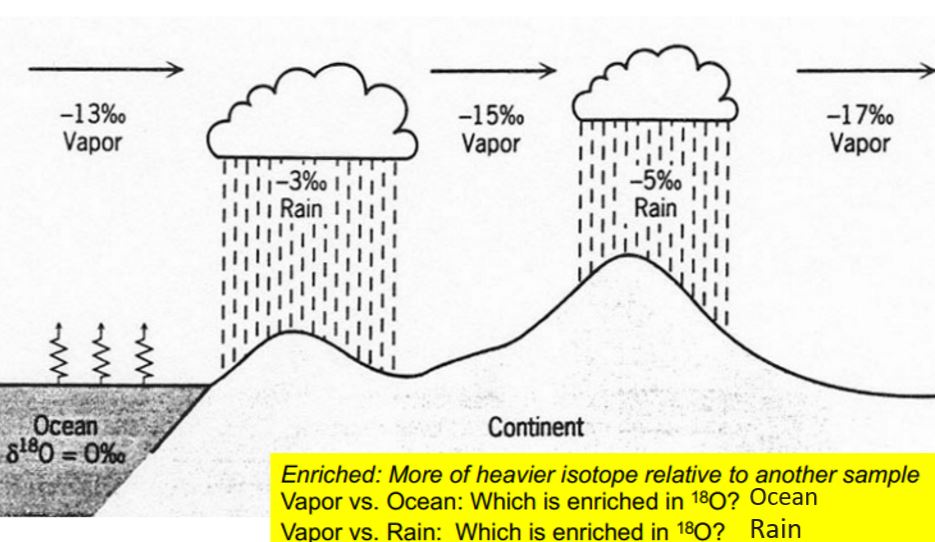
Raleigh Distillation
condensed phase is in isotopic equilibrium with the surrounding vapor and immediately removed
Results in equilibrium fractionation: H216O(v) + H218O(v) = H216O(l) + H218O(l)

Foram 18O records
Change in temperature
Change in ice volume = ~1‰
Deep benthic forams
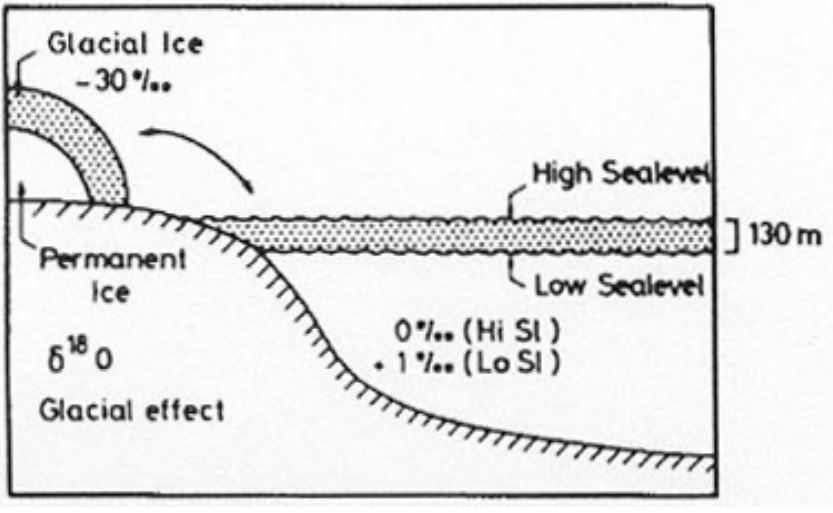
glacial effect
a result of the Raleigh Distillation, during ice ages the oceans are enriched in 18O
Local effects of 18O
elevation and storms
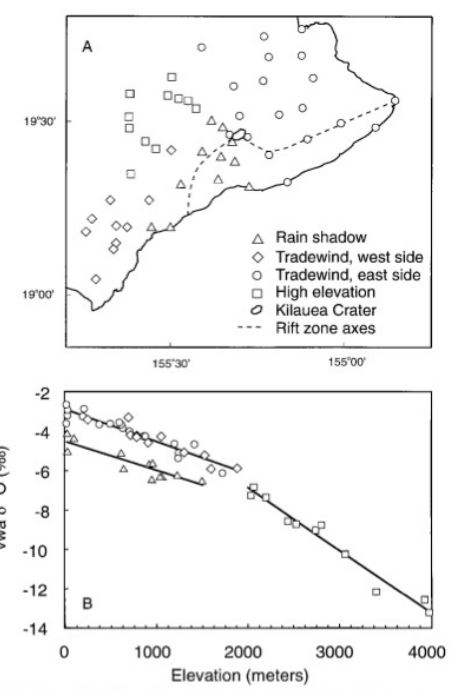
Continental effects of 18O
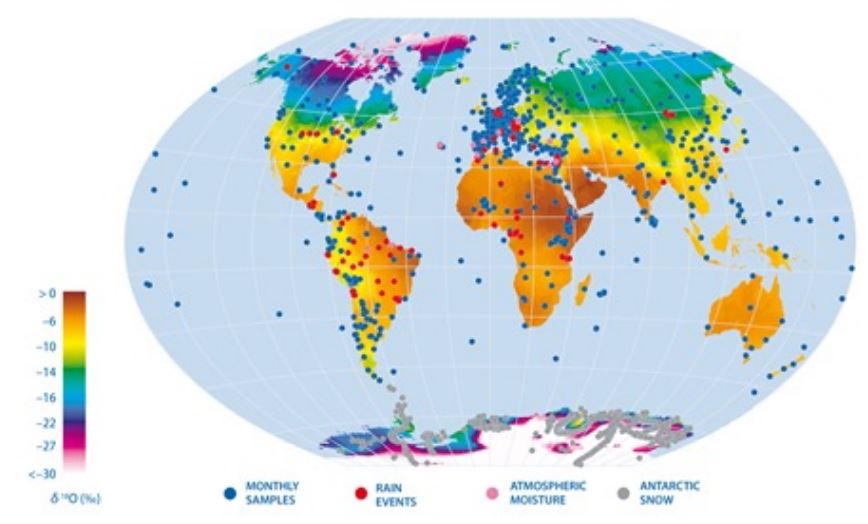
global atmospheric circulation
assumptions of estimating temps in ancient ocean environment
Organisms ppted CaCO3 in isotopic equilibrium with dissolved CO32-
The 18O of the original water is known
The 18O of the shell has remained unchanged
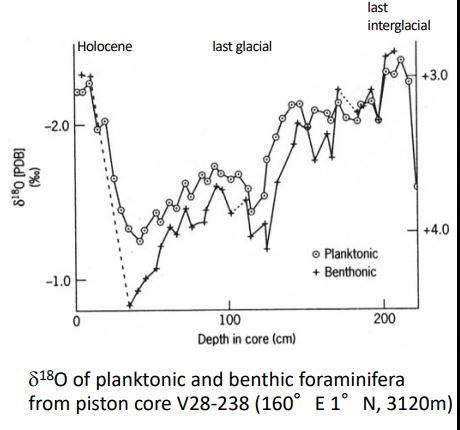
estimation of temps in ancient ocean environments
Planktonic forams measure sea surface temperature and benthic forams measure benthic temperature
Glacial-Interglacial cycles
extend back more than 1Ma
Isotope stages (relative dating technique)
Odd = warm periods
Even = cold periods
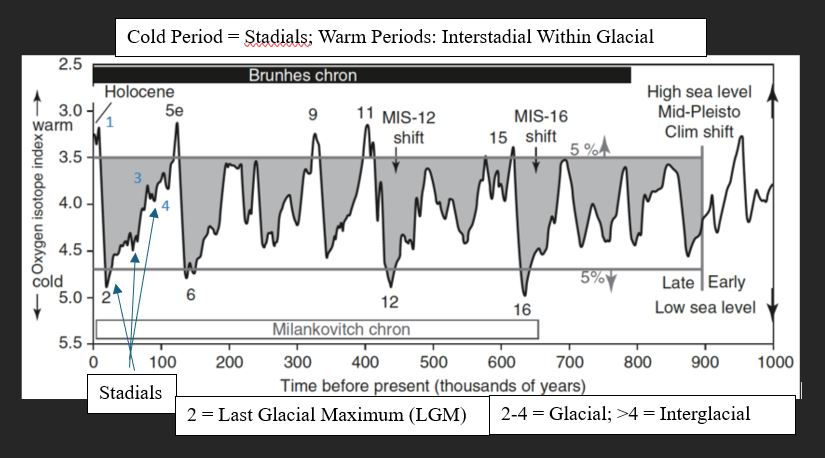
Cold Periods
Stadials
Warm Periods
Interstadial
Insolation
incoming solar radiation
High Insolation
Earth close to sun, hemisphere pointed towards sun
Low Insolation
Earth far from sun, hemisphere pointed away from sun