MR DALTON MID TERM QUESTIONS
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
When a solution is heated in an open test tube, the test tube should always be pointed ___
away from others
The reason for wafting or fanning a small amount of chemical vapors toward the nose as a mean to detect odors in a test tube is to ___
protect the respiratory tract against potentially harmful vapors
What safety precautions should be taken if a chemical reaction produces toxic gases?
Do not directly inhale the fumes (waft, if necessary)
Before you complete a lab assignment, what should you inspect your glassware for?
No chips or cracks and is clean from residue to prevent cross contamination
In a lab that involves heating glassware, how can you tell if the glass is hot or cold?
There are a few ways to test the glass, but the key way is to use caution.
Describe a good hypothesis.
A hypothesis is a testable and measurable statement.
If the plant is left out in the sun, then it will grow more.
Differentiate between a theory, law, hypothesis, and inference.
Theory: an idea that is well researched and supported by many scientists/experiments
Law: can not be explained, just happens; about the natural world
Hypothesis: a testable statement
Inference: an explanation that is necessarily supported by collected data
Differentiate between the independent variable, dependent variable, controlled variables, and experimental control.
Independent variable: what the scientist is changing in the experiment
Dependent variable: what the scientist measures as a result of the change
Controlled variables: everything that stays the same in an experiment
Experimental control: the most normal scenario that is used for comparing your results to
Differentiate between precision and accuracy.
Precision: how close the measurements are to each other
Accuracy: how close the measurements are to the correct answer
Describe the precise equipment when measuring volume.
Equipment that is tall, skinny, and has a lot of markings
Graduated cylinders, pipettes, burettes, and volumetric flasks.
A technician experimentally determined the boiling point of octane to be 124.1°C. The actual boiling point of octane is 125.7°C. Calculate the percent error.
1.3%
(accepted - experimental) (100) = (125.7 - 124.1) (100) = 1.3% accepted 125.7
How many significant figures are in the measurement of 204.30 meters?
5; trailing zeros only count if there is a decimal point
How many significant figures are in the measurement 2.700 meters?
4; trailing zeroes only count if there is a decimal point
How many significant figures are in the measurement 0.000130 cm?
3; trailing zeroes only count if there is a decimal point
Convert 3.59 × 10^8 to long form. (consider the rules for significant figures)
359,000,000; you MUST have the same number of significant figures in the original number vs the scientific notation value. NO DECIMAL should be written.
Convert the following measurement to scientific notation: 202,000 grams (SF RULES!)
2.02 ×10^5 grams (DONT FORGET UNITS!!)
Subtract: 7.987 m - 0.54 m (consider sf rules)
7.45 m ; when adding or subtracting, round your final answer to the same number of decimal places, as the measurement with the fewest decimal places, not the fewest total sig figs.
0.54 has 2 digits after the decimal
7.987 has 3 digits after the decimal
ANSWER: 7.45m with 2 DIGITS AFTER THE DECIMAL
When performing the calculation, 34.430 g + 12.1 g +2,222.34 g, the final answer is ____. (SF rules!)
2,268.9 g
34.430 has 3 digits after the decimal
12.1 has 1 digit after the decimal
1,222.34 has 2 digits after the decimal
Solve: 923 g divided by 20,312 cm3 = ?? (SF RULES)
0.0454 g/cm3 (rules of multiplication and division)
923 has 3 SF
20,312 has 5 SF
Solve: 123,000 m × 6,234 m = ?? (SF Rules)
7.67 × 10^8 m²
(766,782,000 m² rounded to 3 SF)
Identify each of the descriptions as either a physical change or chemical reaction:
a. concrete cracking
b. sucralose dissolving
c. food spoiling
d. ice melting
a. physical
b. physical
c. chemical
d. physical
Objects with a higher density than water (sink/float) and less dense objects will (sink/float)
More dense will sink and less dense will float.
a block of maple wood with a volume of 405 cm³ and a density of 0.67g/cm³ is cut in half. The density of the two smaller blocks is now ___.
0.67g/cm²
density does not change unless it turns properties like solid, liquid, or gas.
A proton has a ___ charge and is located _______. An electron has a ___ charge and is located _______. A neutron has a ___ charge and is located ______.
positive; nucleus
negative; electron cloud outside of the nucleus
neutral; nucleus
A substance has 7 protons, 8 neutrons, and 10 electrons. Identify the element, its mass number, and charge.
Nitrogen - 15
-3 charge
A substance that does not chemically nor physically separate into other substances can be classified as ___
an element
The atomic number is always the same as the number of ______.
protons
What is the difference between an average atomic mass (amu) and a mass number?
The AMU is the weighted average. You must know the percentages of each isotope to calculate the atomic mass and it is the same as the atomic mass on most periodic tables.
The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. It is the mass of a single isotope of an element.
Describe the location of the non-metals, metals, and metalloids on the periodic table.
metals: left of staircase
metalloids: along the stair case
non-metals - right of the staircase
Elements in the same (group/period) have similar chemical properties
Group (horizontally)
A nucleus occupies a large (volume/mass) of an atom and a small (volume/mass). The electron cloud occupies a large (volume/mass) of an atom and a small (volume/mass).
A nucleus occupies a large mass and a small volume while the electron cloud occupies a large volume and small mass.
Use dimensional analysis to convert 982,347 seconds to days.
11.3698 days (6 sig figs)
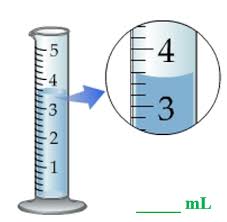
The volume of liquid being measured in the graduated cylinder below is ___.
3.55cm³
Complete the following problem: A piece of stone has a mass on 24.595 grams and a volume of 5.34 cm³. What is the density of the stone?
4.61 g/cm³
Density = Mass/Volume
Don’t forget to use division sig figs to report the proper answer
Identify each statement as describing a physical change or chemical reaction:
A. as orange drink mix dissolves in water, the water changes color
B. as an iron rusts, it turns brownish red
C. as an egg white is cooked, it turns white
D. as silver tarnishes, it turns black
A. physical
B. chemical
C. chemical
D. chemical
Identify the mass number, number of protons, neutrons & electrons for 42 - Ca²+
Mass number - 42
Protons - 20
Neutrons - 22
Electrons - 18
Identify the ion charge formed by each of the following:
A) Na
B) O
C) He
D) Mg
A) 1+
B) 2-
C) none
D) 2+
Which element is the most electronegative element on the periodic table?
Fluorine
Small atomic size and high effective nuclear charge
Determine the number of electrons the following elements will donate or accept to become a more stable ion:
A) Be
B) Al
C) N
D) He
A) donate 2
B) donate 3
C) accept 3
D) neither (stable with 2 valence electrons)
Alkali metals are in group __.
Alkaline earth metals are in group ___.
Halogens are in group ___.
Noble Gases are in group ___.
A) group 1
B) group 2
C) group 17
D) group 18
Determine the number of valence electrons for each of the elements below:
A) Xenon
B) Carbon
C) Selenium
D) Calcium
A) 8
B) 4
C) 6
D) 2
Identify the number of electrons in the outer most energy level for each element:
A) B
B) Ba
C) P
A) 3
B) 2
C) 5
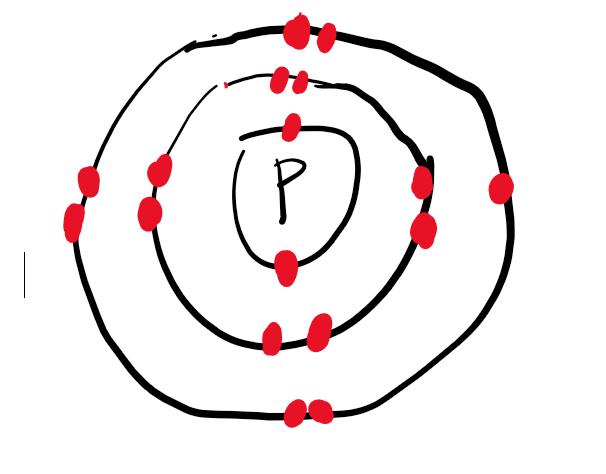
Draw the Bohr electron model for P

Draw the Bohr electron model for P ion
Draw the electron dot structure for Aluminum

Draw the ion dot structure for Aluminum
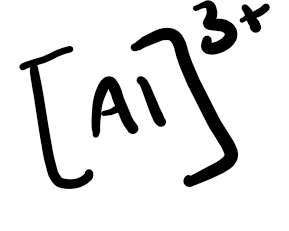
Identify each of the following elements as a solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature/pressure.
A) Mercury
B) Oxygen
C) Sulfur
D) Aluminum
A) liquid
B) gas
C) solid
D) solid
Identify each of the following elements as a metal or non-metal
A) Mercury
B) Oxygen
C) Sulfur
D) Aluminum
A) metal
B) non-metal
C) non-metal
D) metal
Describe how the atomic radius changes as you go left to right across a period on the Periodic Table and going down a group.
The atomic radius decreases (more compacted) as you go left to right across a periodic table.
The atomic radius increases (gain space) as you go down a group on the periodic table.
Describe how the atomic masses change going left to right across a period on the Periodic Table and going down a group.
Atomic masses increase going left to right across a period and increase going down a group.
Which group on the periodic table is most readily accepts electrons? Why?
Halogens (group 17)
They have 7 electrons and is just one away from fulfilling its full octet and becoming stable.
Which group on the periodic table is most resistant to forming compounds? Why?
Noble Gases (group 18)
They already have 8 valence electrons, making them stable and having a full octet.
A cation is a (+/-) ion and an anion is a (+/-) ion. The type of bond that exists between them is a/an ____ bond.
Cation is a positive ion.
Anion is a negative ion.
The type of bond that sits between them is an ionic bond.
In a covalent bond, electrons are (shared/transferred). In an ionic bond, electrons are (shared/transferred).
In a covalent bond, electrons are shared.
In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred.
Name the following acids
A) H2 SO4
B) HCl
C) HNO3
D) H3 PO4
A) Sulfuric acid
B) Hydrochloric acid
C) Nitric acid
D) Phosphoric acid
Write the chemical formula for strontium iodide.
SrI2
Name P2O5
Diphosphorus pentaoxide
Name CS2
Carbon Disulfide
What is the charge/oxidation number of Cu in Cu2S?
1+
Sulfur has a charge of -2.
What is the charge/oxidation number of Fe in Fe2O3?
3+
Oxygen has a 2- charge and there are 3 of them.
Fe should have a 3+ charge since there are only 2 of them.
Write the formula for copper (II) carbonate.
CuCO3
Since carbonate ends in -ate, this is a polyatomic compound, so look for the carbonate charge first.
Write the formula for calcium oxide.
CaO
This is an ionic compound, since oxide ends in -ide.
Name SCl4
Sulfur tetrachloride
This is an example of a molecular compound since sulfur and chloride are both non-metals.
Name MgI2
Magnesium iodide
Magnesium ion - since it is a cation, it does not need -ide
Iodide ion - since it is an anion, it needs the -ide suffix
What happens to ionization energy when moving across a period and down a group?
Ionization energy increases when moving across a period because the radius is decreasing.
Ionization energy decreases when going down a group because the radius is increasing.
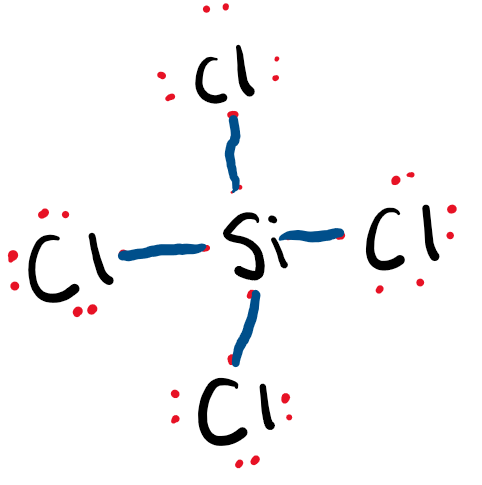
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for SiCl4
Draw and name VSEPR shape of the following compounds. Use the VSEPR chart.
A) CH4
B) OF2
C) BeF2
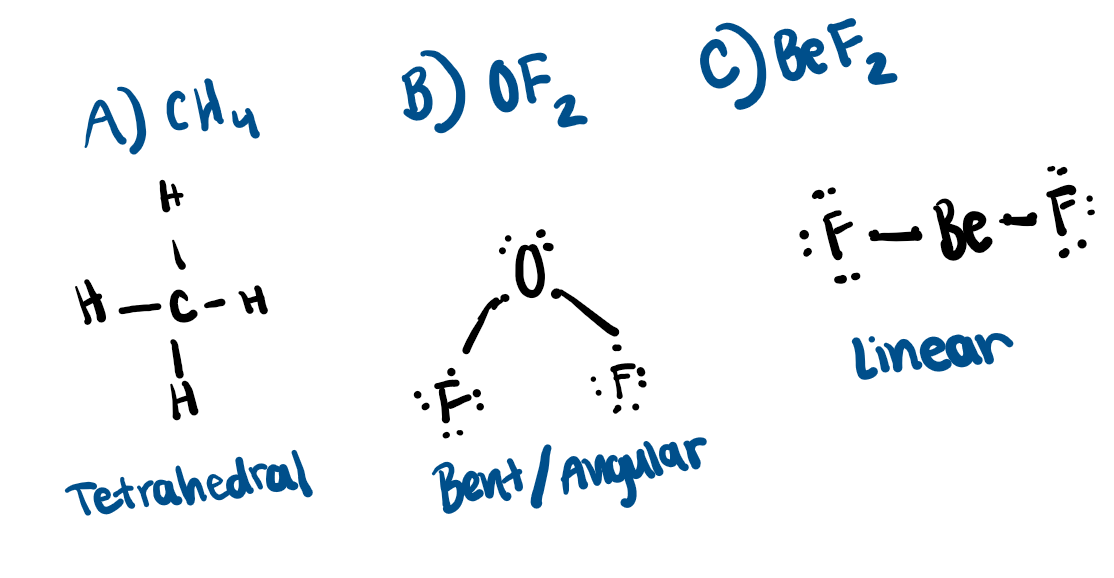
Use dimensional analysis to solve the following problems.
A) How many grams are in 35.6 mg?
B) How many kilometers are in 257 cm?
C) How many milliliters are in 245.2 kl?
A) 0.0356g
B) 0.00257km
C) 2.452 × 108mL