Ocular Anatomy: eyebrow + eyelashes
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
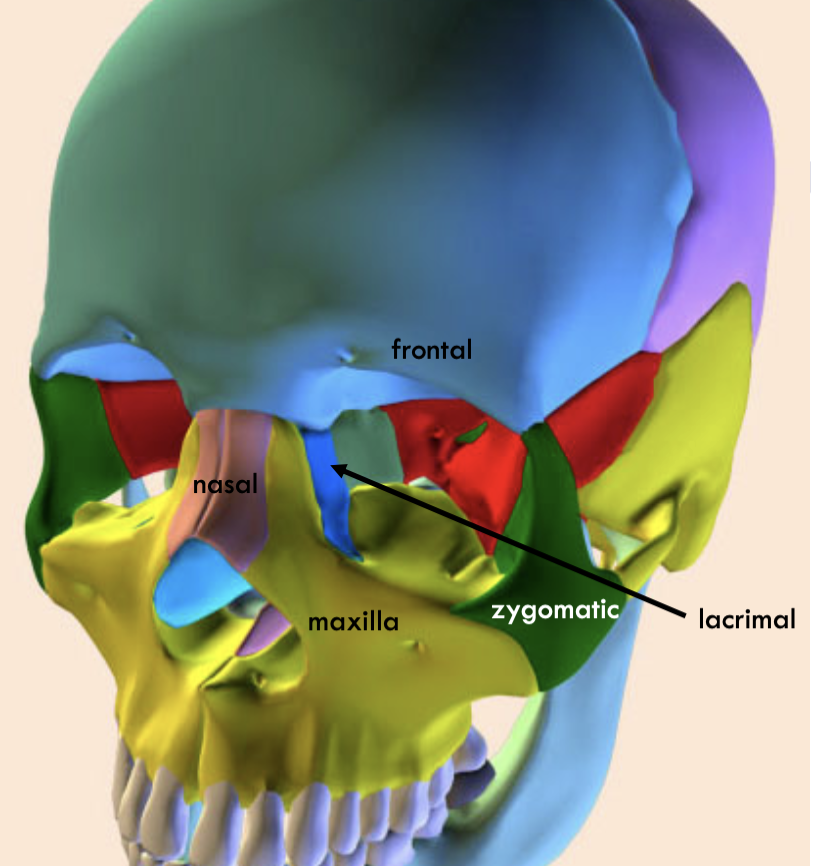
Where is the frontal
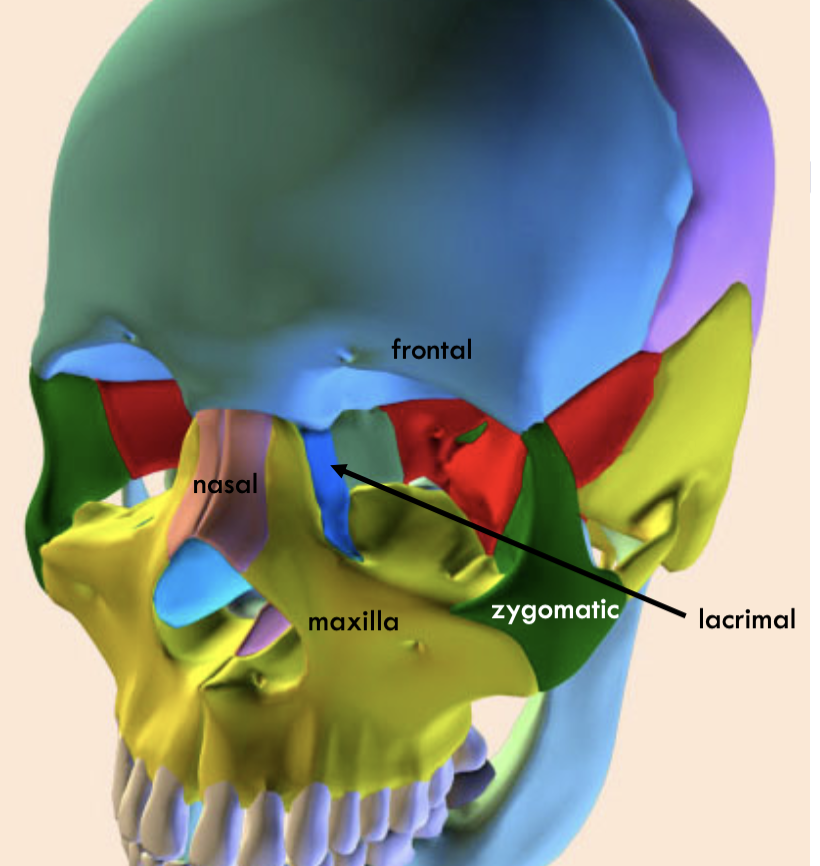
Where is the nasal
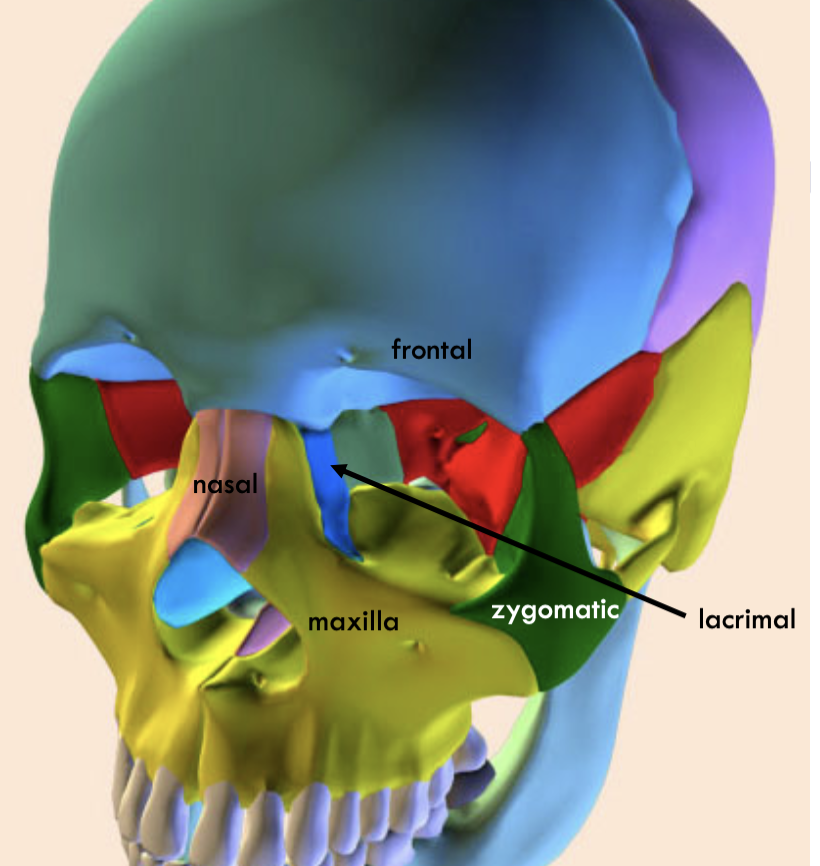
where is the lacrimal
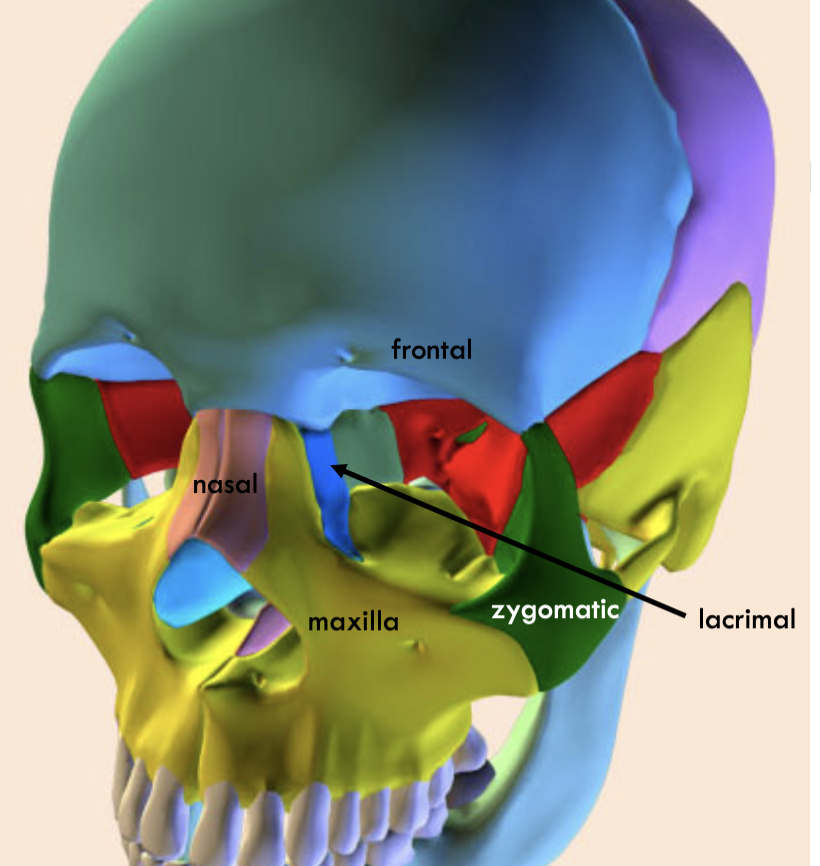
where is the maximal
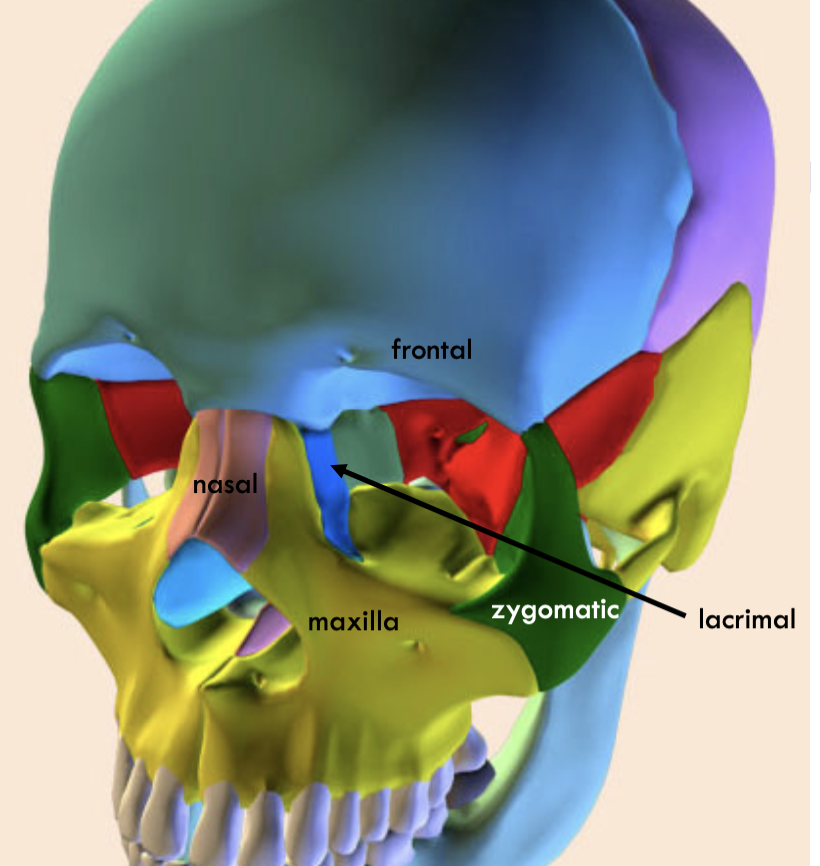
where is the zygomatic
What are the different fascia
Orbital, periorbita, orbital periosteum
What is fascia
lining of tissue
fascia attachment mechanism
attaches better on corner, more loose on surfaces of the skull.
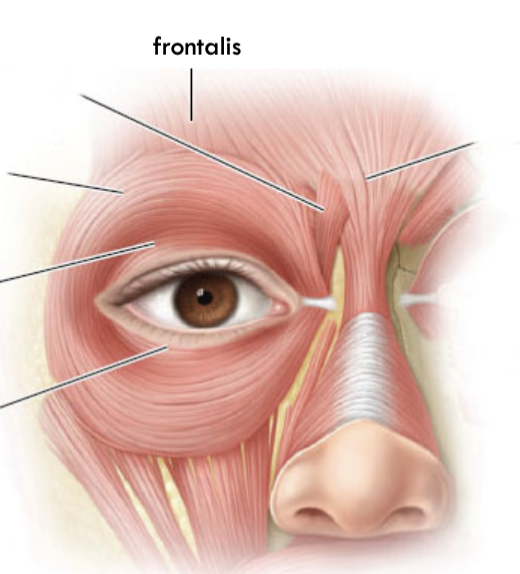
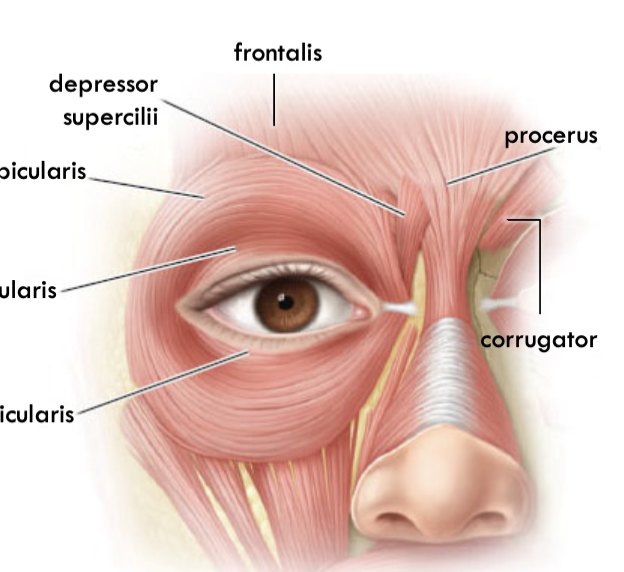
Frontalis:
origin, insertion and innervation
origin: scalp
insertion: superior orbital rim
Innervates CN 7 Temporal Branch
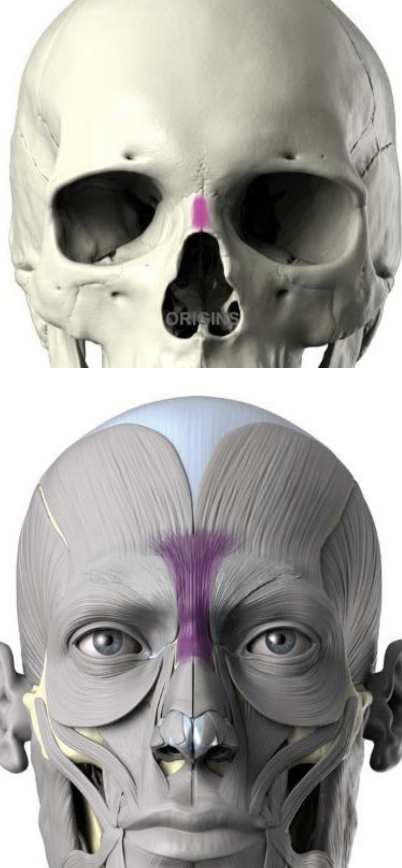
Procerus:
origin, insertion and innervation
origin: nasal bone
insertion: medial side of frontalis
Innervates CN 7 Temporal Branch
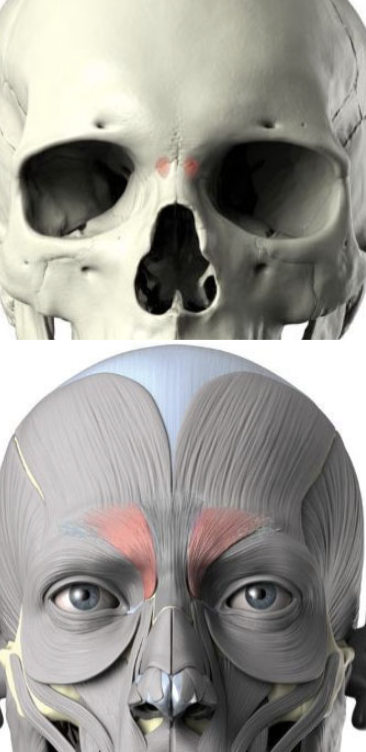
Depressor supercilii
origin, insertion and innervation
origin: superior maxilla bone
insertion: dermis under medial brow
Innervates CN 7 Temporal Branch
corrugated supercilii
origin, insertion and innervation
origin: frontal bone
insertion: skin superior to medial eyebrow
Innervates CN 7 Temporal Branch
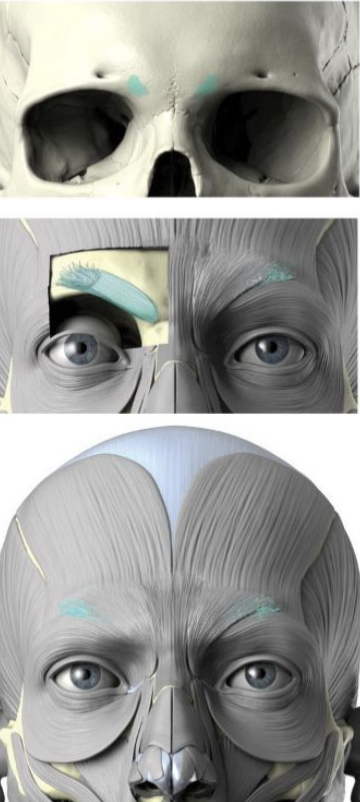
orbicularis occuli
origin, innervation
origin: medial bony orbit
Innervates CN 7 Temporal, zygomatic Branch
What is plapebrae
Eyelids
Function of plapebrae
movement of tears, protection, produce tears.
What is lagopahthalmos
non-functioning/ closing eyelids
results in improper tear drainage and corneal ulceration and inflammation
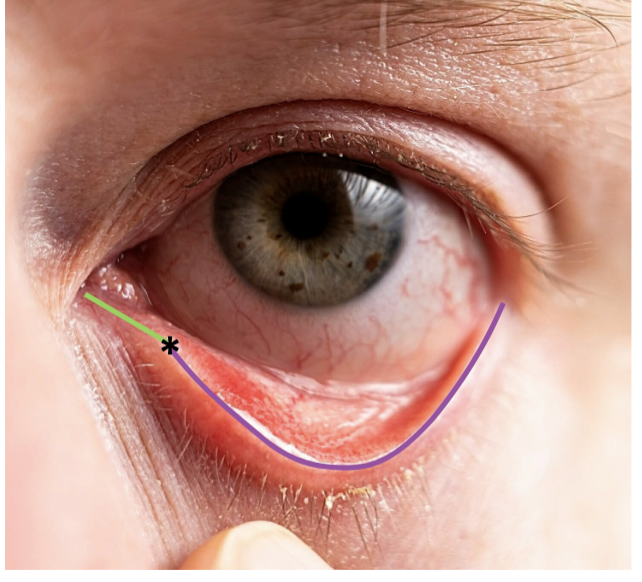
Tarsal portion
thin delicate part of eyelids that cover the orbit. sticks onto eyes
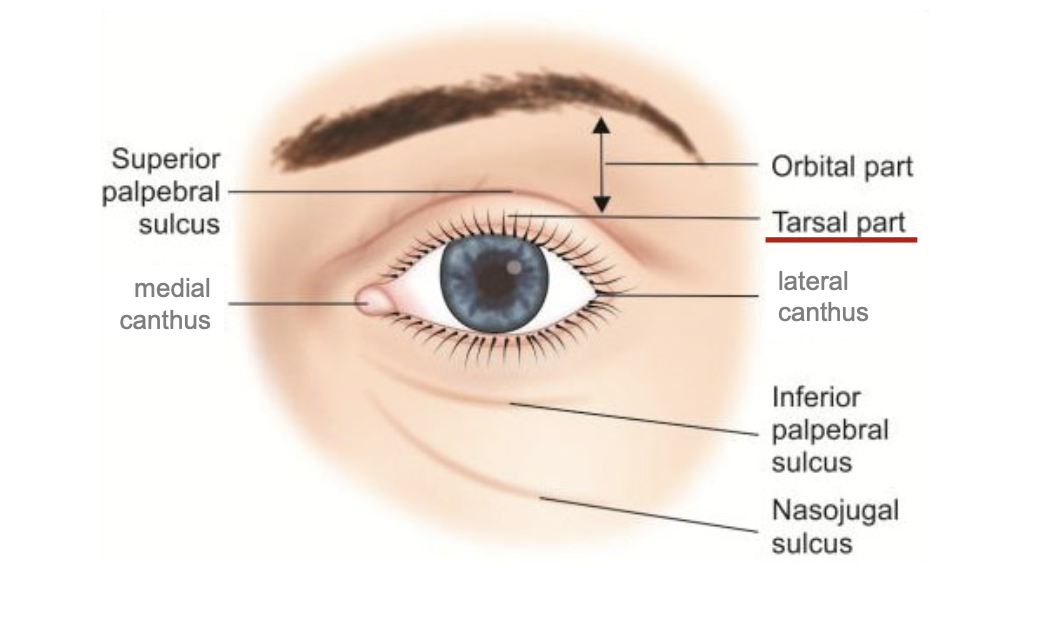
Orbit portion
Thicker fatty part of eyelids that is loosely attached to the eye. more protective
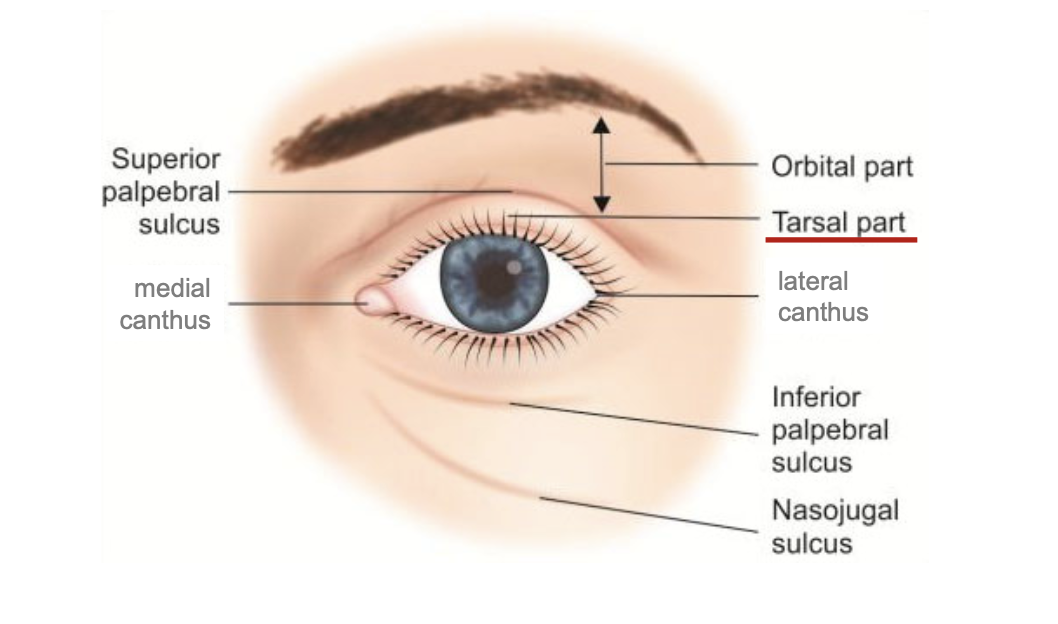
Palpebral sulcus
furrow/ depression that separates orbit and tarsal.
palpebral fissure
empty space where eyes go.
canthus
medial and lateral canthus. located on the corners of palpebral fissure.
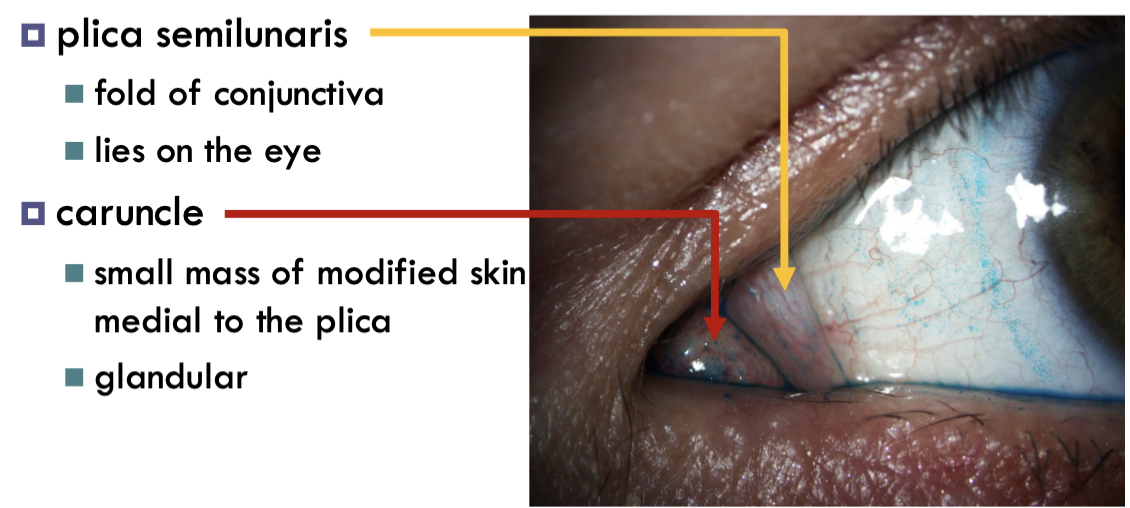
plica semilunari
folds of conjunctiva that allow for temporal movement of eyes
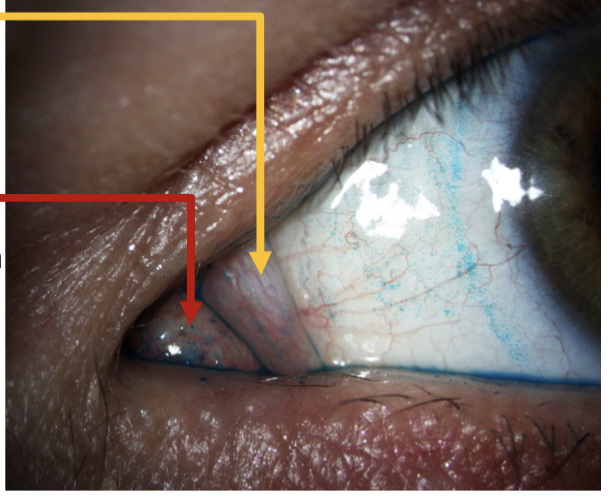
caruncle
gland further in the corner of medial canthus.
lacrimal papilla
Elevation on both superior and inferior eyelid. Contains the puncta
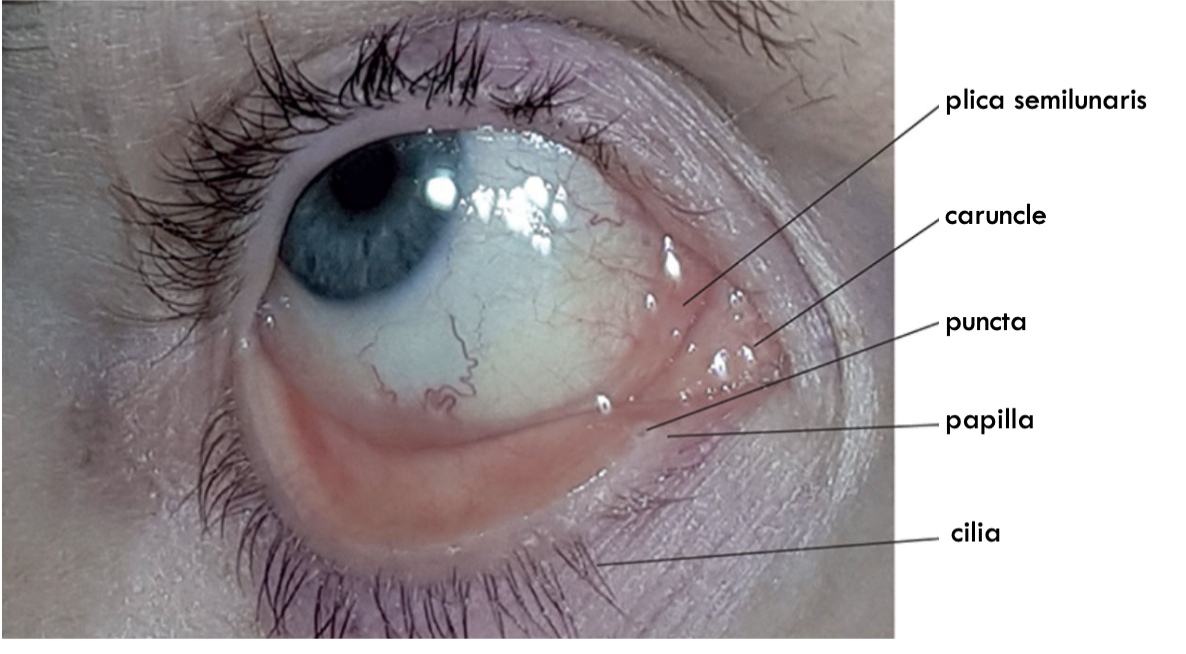
puncta
drainage found on the papilla. divides the lid margins into lateral ciliary and nasal lacrimal.
Epicanthic
asian monolid.
covers the caruncle and plica semilunaris. Present in young children but goes away as nose develops.
what is cilia
eyelashes.
more cilia on upper lid, supplied with nerves and plays a role in sensory reflex.
What is madarosis
loss of eyelashes
what is poliosis
general name of white hairs due to lack of melanin. can be marker of potential disease.
what is trichiasis
misdirected growth of eyelashes.
What is meibomian gland
found in ciliary portion (more in superior)
what is the grey line
insertion of the obicularis oculi, between cilia and meibomian gland. Weak spot of the tissue (often entry for surgery)
what are the layers of the skin
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous areolar.
Subcutaneous areolar
loose connective tissue containing fat and blood.
orbicularis oculi
cranial nerve 7 (temporal, zygomatic), surrounds palpebral fissure
What is blepharospasm
spasm of the orbicularis. response to pain not from lack of sleep and caffine.
orbital portion of orbicularis oculi
Origin, action, opposing muscle
origin: medial bony orbit
action: tightly closing eyes
Opposing muscle: frontalis
multiple insertion around the orbicularis oculi.
Palpebral portion of orbicularis oculi
origin: medial palpebral ligament
insertion: lateral palpebral ligament
action: closure of eye gently; involuntary blinking
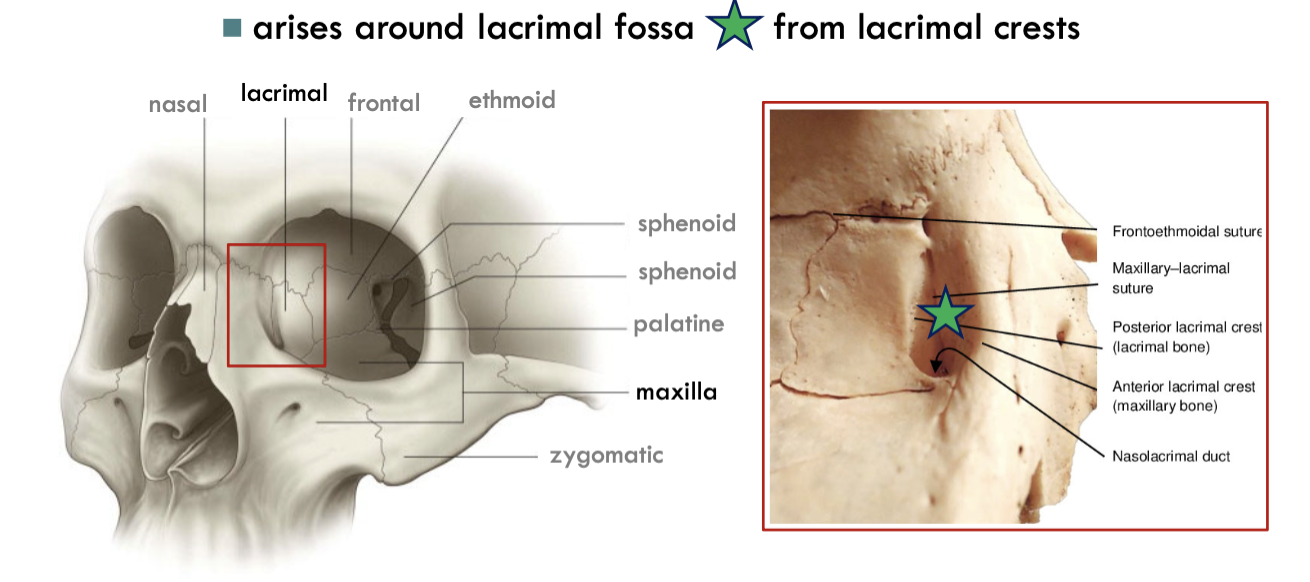
Horner’s muscle (pars lacrimalis)
muscle that arises from the lacrimal fossa (hole in the skull). Section of the palpebral obicularis oculi
located medially to the palpebral portion
Canaliculi
tubes that receive tears from puncta.
Surperior and inferior meet to form the common canaliculus
Lacrimal sac
Receives tears. lives in the lacrimal fossa.
What is the function of the horner’s muscle
encircles canaliculi, and contraction helps move tears down the drainage system.
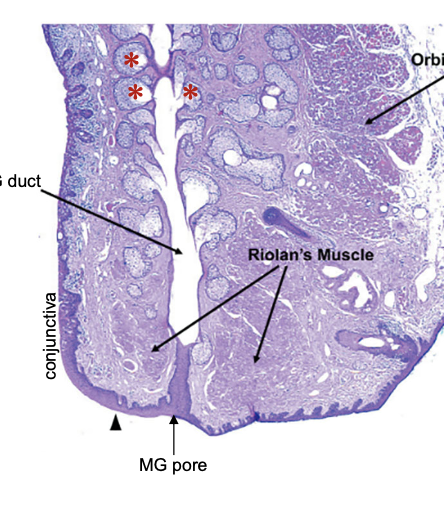
Riolan’s muscle (pars ciliaris)
located near lid margin posterior to cliia on both sides of meibomian pores. aka grey line
insertion: lateral palpebral ligament(blinking) & grey line (tone).
Function of Riolan’s muscle
insertion of obicularis oculi to the eyelid skin. holds lid margin close contact with the globe.
squeezes on meibomian gland and secretes gland secretion.
loss of muscle tone leads to sag.
Entropion
inversion of lid margin.
differs to trichiasis.
ectropion
eversion of lid margin. caused by loss of tone.
epiphora
overflow of tears
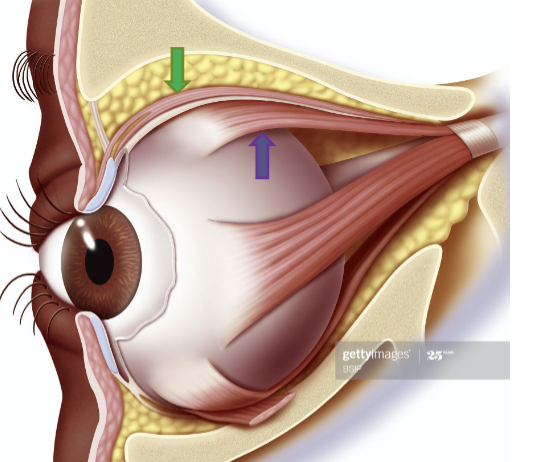
levator palpebrae
Origin
superior palpebral levator.
striated muscle
Origin: lesser wing of sphenoid bone. above and anterior to optic foramen.
levator sheath attaches to what?
sheath of the superior rectus muscle. Fascia sheath touch each other (focal adhesion).
coordinates movement between eyes and eyelids.
levator palpebrae
insertion, action
insertion: skin of superior eyelids and tarsal plate. has to pass between orbicularis oculi
action: elevates eyelid
levator palpebrae innervation
cranial nerve 3 (superior branch)
levator aponeurosis
tendinous fanning out of levator.
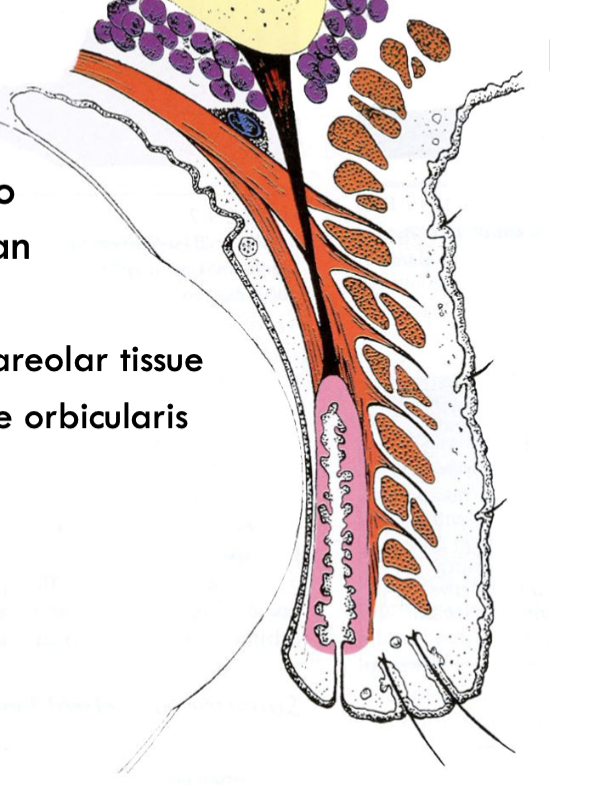
potential space
areas of subcutaneous areolar between muscles.
Eg. space between obicularis that levator aponuerosis enter through
pretarsal space
potential space inbetween tarsal plate and obicularis oculi where levator aponeurosis attaches anteriorly to the tarsal plate and goes through the obicularis oculi.
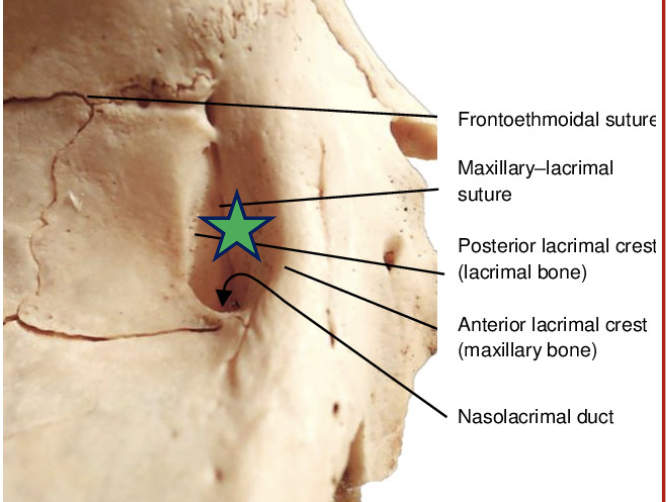
What bones make up the lacrimal fossa?
Anterior lacrimal crest (maxillary bone) and posterior lacrimal crest (lacrimal bone)
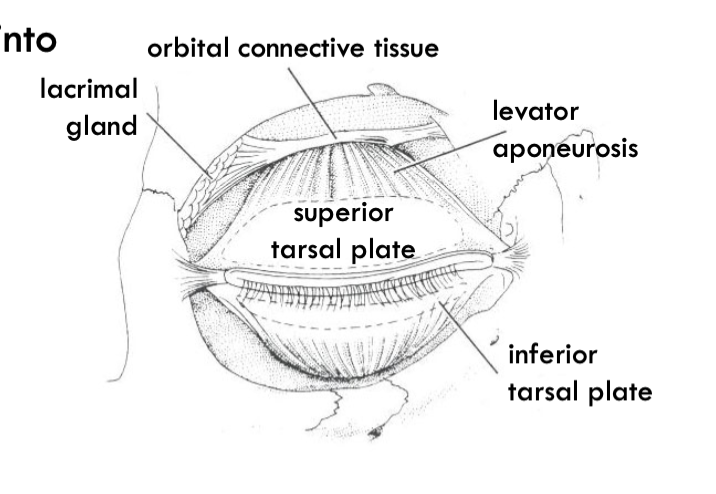
lacrimal gland
lacrimal gland surround superior palpebral levator aponeurosis. divided into tow lobes
Orbital and palpebral.
medial horns attachment
attaches near fronto lacrimal suture and medial palpebral ligament.
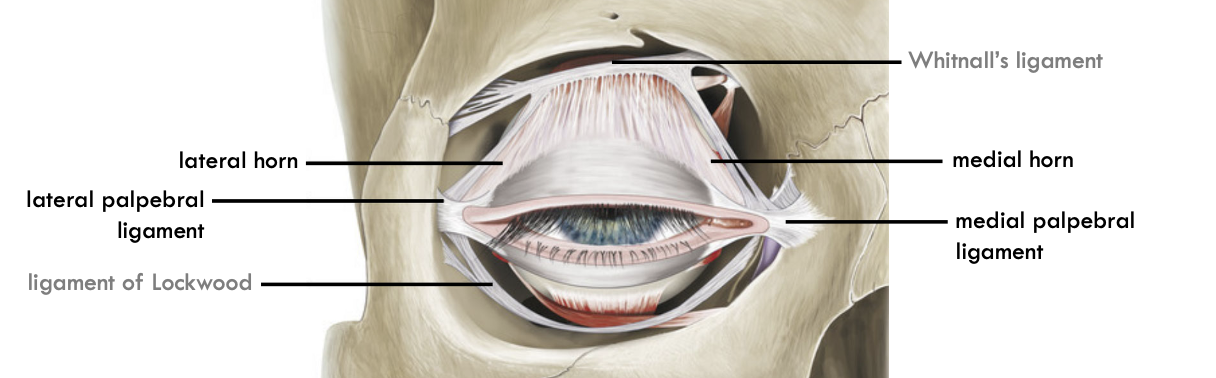
Lateral horn attachment.
attaches to zygomatic bone and palpebral ligament
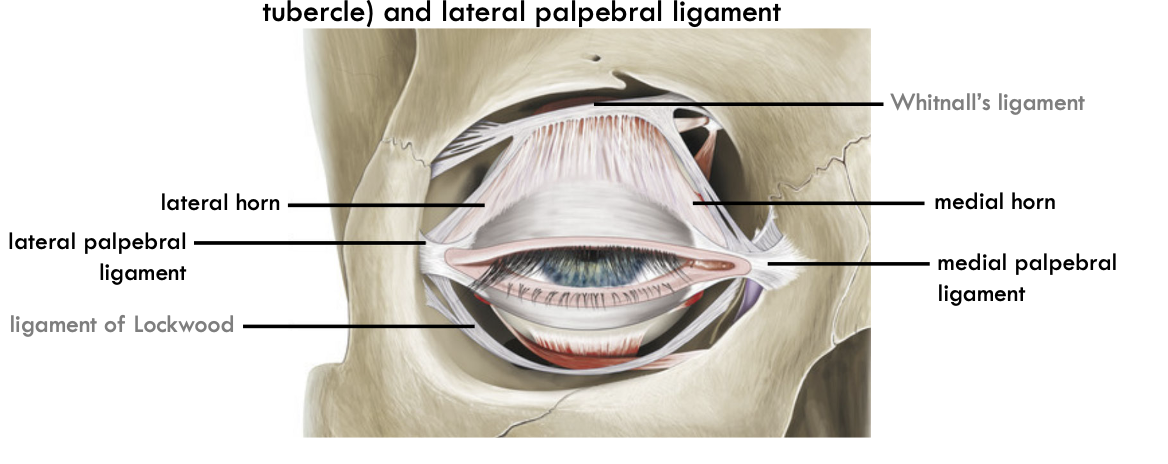
Function of medial and lateral horn
firm attachment for smoother movement of eyelid.
What is ptosis
issue with the levator nerves causing drooping of eyelid
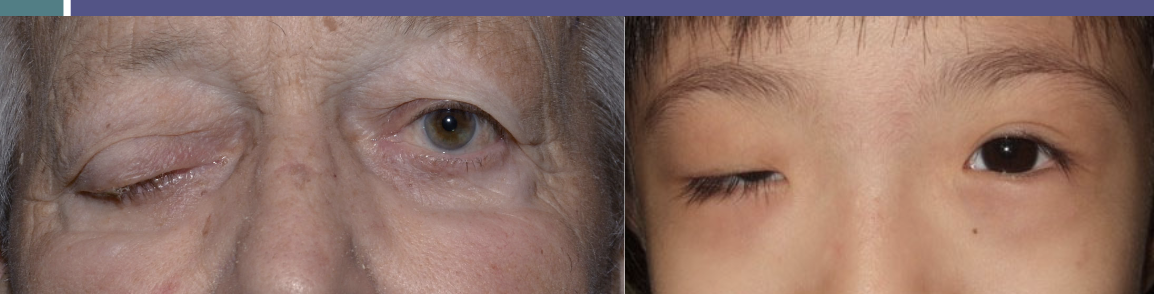
Degree of ptosis
Big droop indicated by bigger levator muscle
small droop indicated by smaller muller’s muscle
Muller’s muscle (superior tarsal muscle)
smooth muscle that originates from the levator and attaches to the superior tarsal plate.
contributes to involuntary lid elevation.
inferior tarsal muscle
origin and insertion
Origin: inferior extraocular muscle sheath
insertion: lower conjunctiva and inferior border of lower tarsal plate.
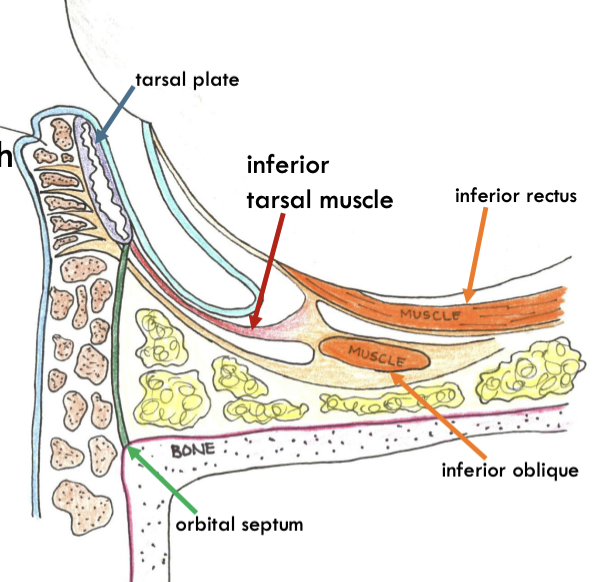
inferior tarsal muscle innervation
sympathetic
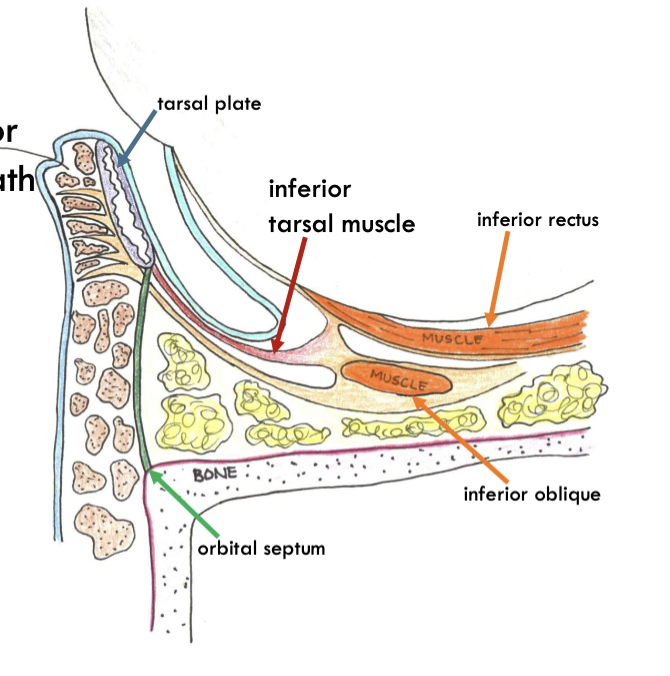
inferior aponeurosis
origin and insertion
similar to superior but inferior
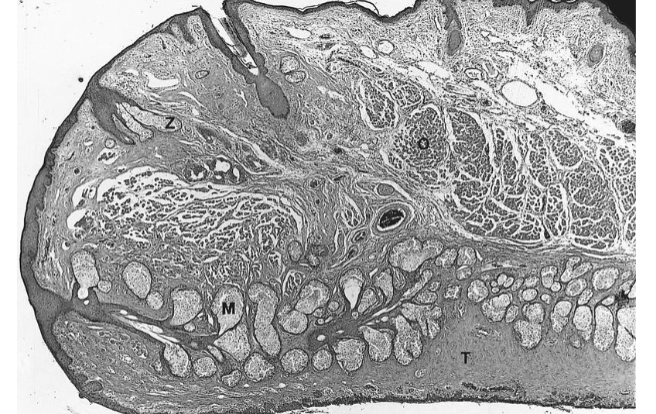
Tarsal plate
dense connective tissue of uniform collagen fibrils
Function of tarsal plate
adds rigidity
Palpebral conjunctiva
lines inner surface of the eyelid
stroma tightly adherent to tarsal plate
contains goblet cells
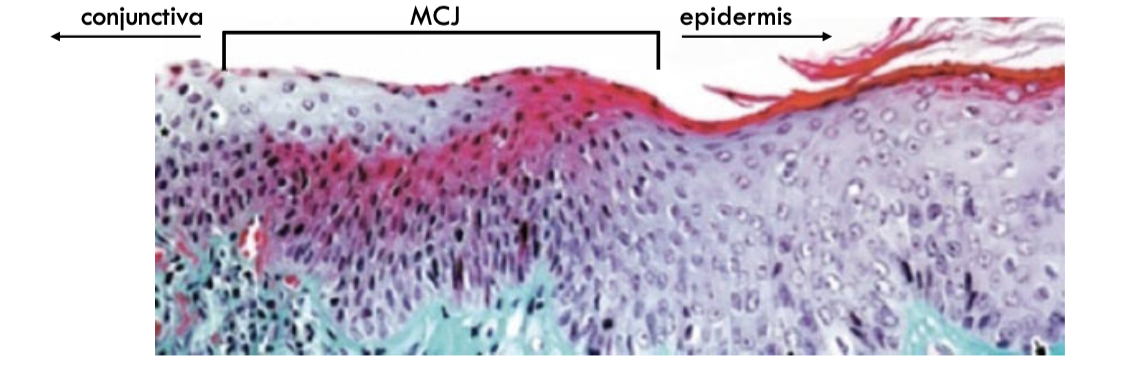
mucocutaneous junction
epithelial transition between skin and conjunctiva.
from keratinized skin to unkeratinized epithelium.
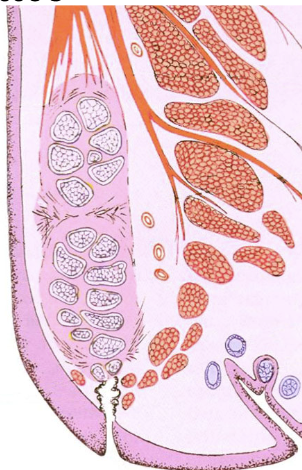
meibomian gland
embedded in tarsal plate
duct that opens at eyelid margin
long branching acini (grape cluster)
Function of meibomian gland
produce sebum called meibum
type of holocrine gland
What is holocrine secretion
When the whole cell becomes what is secreted
meibum secretion
acinar cells are compressed by myoepithelial cells.
holocrine cells fill the cell, and are filled with sebaceous granules (gives a fuzzy appearance)
as cells exit the acinar cell they degenerate and decompose.
Chalazion
non-infection meibomian gland clogging
meibomian dysfunction
reduction in secretion due to thickened lipid secrition or keratinized ducts.
usually due to shift in hormones - older women are more susceptible
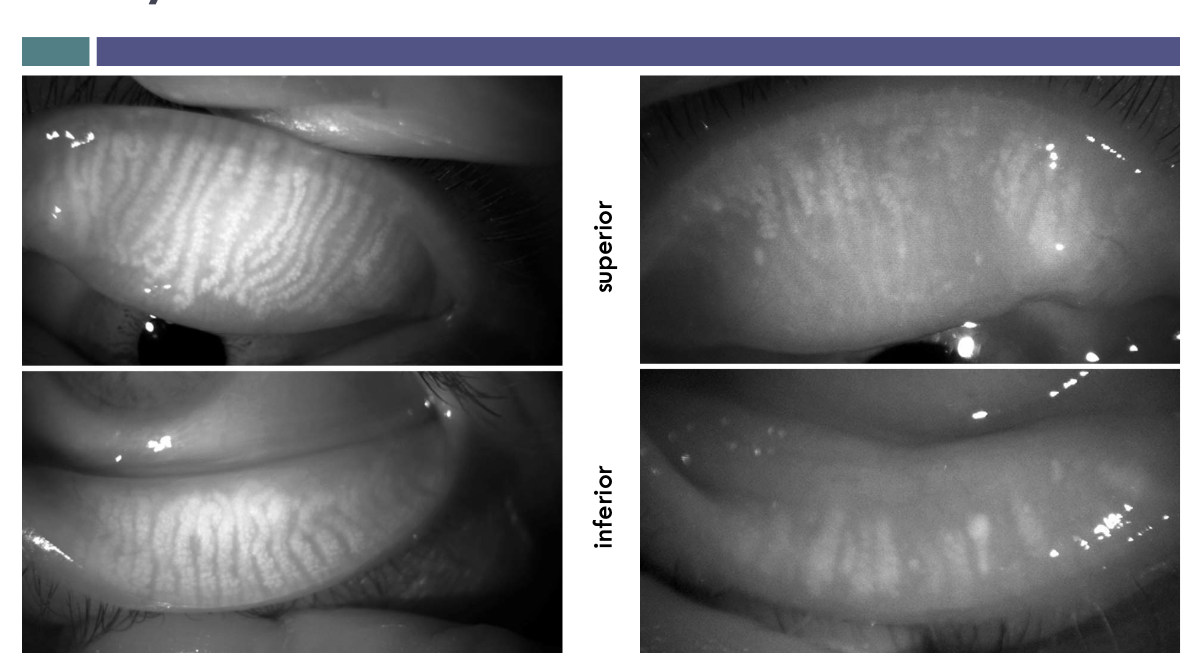
Zeis gland
histologically the same as meibomian glands (holocrine)
function as lubricating eyelashes and protection of eyes.
positioned little inferior, posterior of the cillia.
Glands of Moll
serous glands (aqueous secretion filled with proteins)
large lumen with cuboidal secretory cells and myoepithelium
what type of gland is gland of moll
apocrine gland
where are Glands of moll found?
ducts open anywhere along the ciliary margin.
External hordeolum
stye
infected zeis or moll gland
internal hordeolum
stye infection of meibomian gland
accessory lacrimal glands
gland of krause
superior to the conjunctiva fornix
gland of wolfring
anterior to palperbral conjunvtiva
orbital septum
thin but dense connective tissue associated with the eyelids
starts at the orbital margin
Protective function of the orbital septum
lays anterior to the lacrimal gland to protect it from external environment
lays posterior to the lacrimal duct to separate old tears from the eyes
attachement of orbital septum
lateral
attaches to the bony orbital margin at the zygomatic bone
medial
attaches to medial bony margin
orbital seuptum attachment
fuses at the tarsal plate.
interrupted by levator aponeurosis. fuses to create tight barrier
orbital septum with age
loss of integrity and elasticity.
fluid accumulation and loose tissue.
orbital septum ASIAN PEOPLE
orbital septum fuses further anterior causing natural droop
Function of Tear film
refractive index
nutrition
mechanical
antibacterial
immune response
structure of tear film
3 layers:
outer- lipis
middle- aqueous
inner- mucin
lipid layer of tear film
prevents evaporation of tears
produced by meibomian glands and zeis glands
aqueous layer tear film
produced by lacrimal gland and krause and wolfring accessory glands
function: transport tear components and moisture
inner layer: mucin tear film
produced by goblet cells and ocular surface cells
soluble and transmembrane mucins
Function
hydrophilic coating for cornea to reguate surface tension
lid wiper theory
thin band of palpebral conjunctiva makes contact with ocular surface
accessory lacrimal glands
wolfring and krause
secretes aquesous layer for basal secretion
merocrine glands
ducts also have secretions
lacrimal gland
secretes aqueous fluid for basal and reflex secretion
secretions from lacrimal glands
Merocrine
what does lacrimal gland consist of
central lumen
secretory cells
myoepithelium
Duct structure of lacrimal gland
many tubules connect into 12 main ducts
Tear film pathway
down by gravity
medial by capillary action