BIOMI 2900: Lecture 40 Review Problems
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 40: Transmission
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are airborne disease agents in
Aerosols
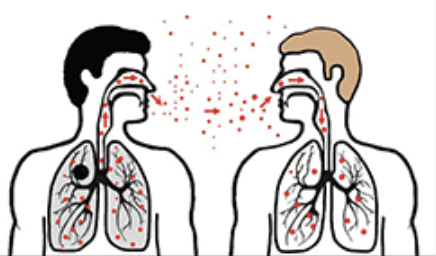
How many people get killed globally from respiratory infections?
>4 million people annually
What are STIs (STDs)?
Pathogens banking on out survival
State the following for mumps: agent, transmission, symptoms
Agent: virus (-)ssRNA
Transmission: virus found in saliva and respiratory secretions – CONTAGIOUS
Symptoms: pain, swelling of parotid glands that may extend down to other salivary glands, fever, headache, loss of appetite, muscle aches, tiredness
What is the incubation period for mumps? What can it lead to?
Incubation period: 14-18 days. Patients are infectious from 2 days before until 5 days after symptoms begin, symptomatic 7-10 days, most people recover completely after a few weeks
Can lead to testicular inflammation, deafness, meningitis, very rarely encephalitis and death
What are some examples of mumps outbreaks in the US?
2016-17: Penn State, 77 confirmed cases
2015-16: several campuses in Iowa and Illinois, hundreds of cases
2014-15: several campus outbreaks, one outbreak affected the NHL
2011-13: several smaller contained outbreaks on college campuses
2009-10: NYC 3000+ cases, mostly high school students
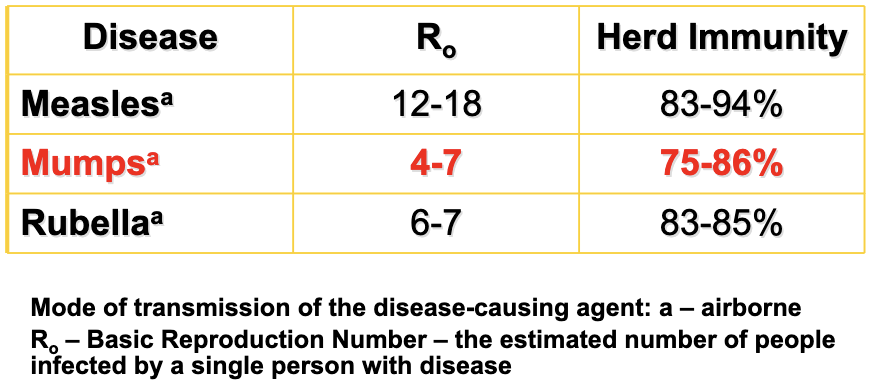
How effective is the MMR vaccine?
MMR vaccine is 49 - 91% effective (single dose), 66 - 95% effective (2 doses), a third boost does not improve effectiveness against Mumps
State the following for mumps: treatment, vaccine, epidemiology
Treatment: none; wait it out
Vaccine: MMR - Mumps, Measles and Rubella or now available MMRV – with Varicella (chicken pox) Live attenuated virus, required in all 50 states and DC for kids entering preschool or college
Epidemiology
A common disease in many parts of the world, including areas in Europe, Asia, and Africa
Mumps is a human disease, no animal or environmental reservoir
In US, incidence peaks in late winter, early spring
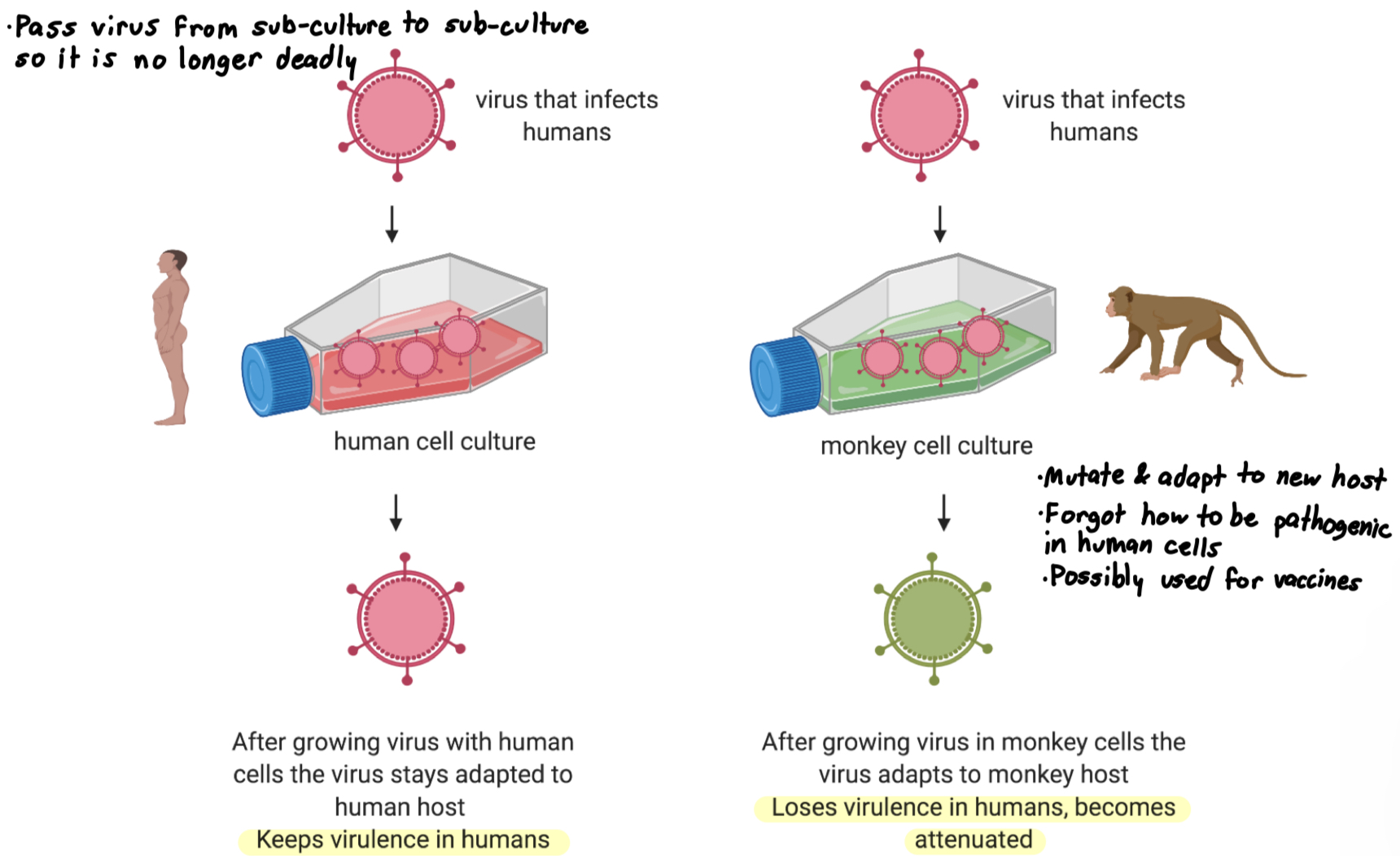
What is Attenuation - passaging?
Attenuation: the process of reducing the virulence or pathogenicity of a virus
Passaging: when a virus is grown repeatedly in controlled conditions to make it weaker
How can we limit the spread of mumps?
Limiting the spread of “mumps is centered on good hygiene:
Always cover your nose and mouth when you cough or sneeze
Wash your hands frequently
Dispose of used tissues and other similar objects appropriately
Do not share drinking glasses, eating utensils, water bottles, cigarettes, lipstick/makeup, etc.”
State the following for tuberculosis: agent, transmission, symptoms
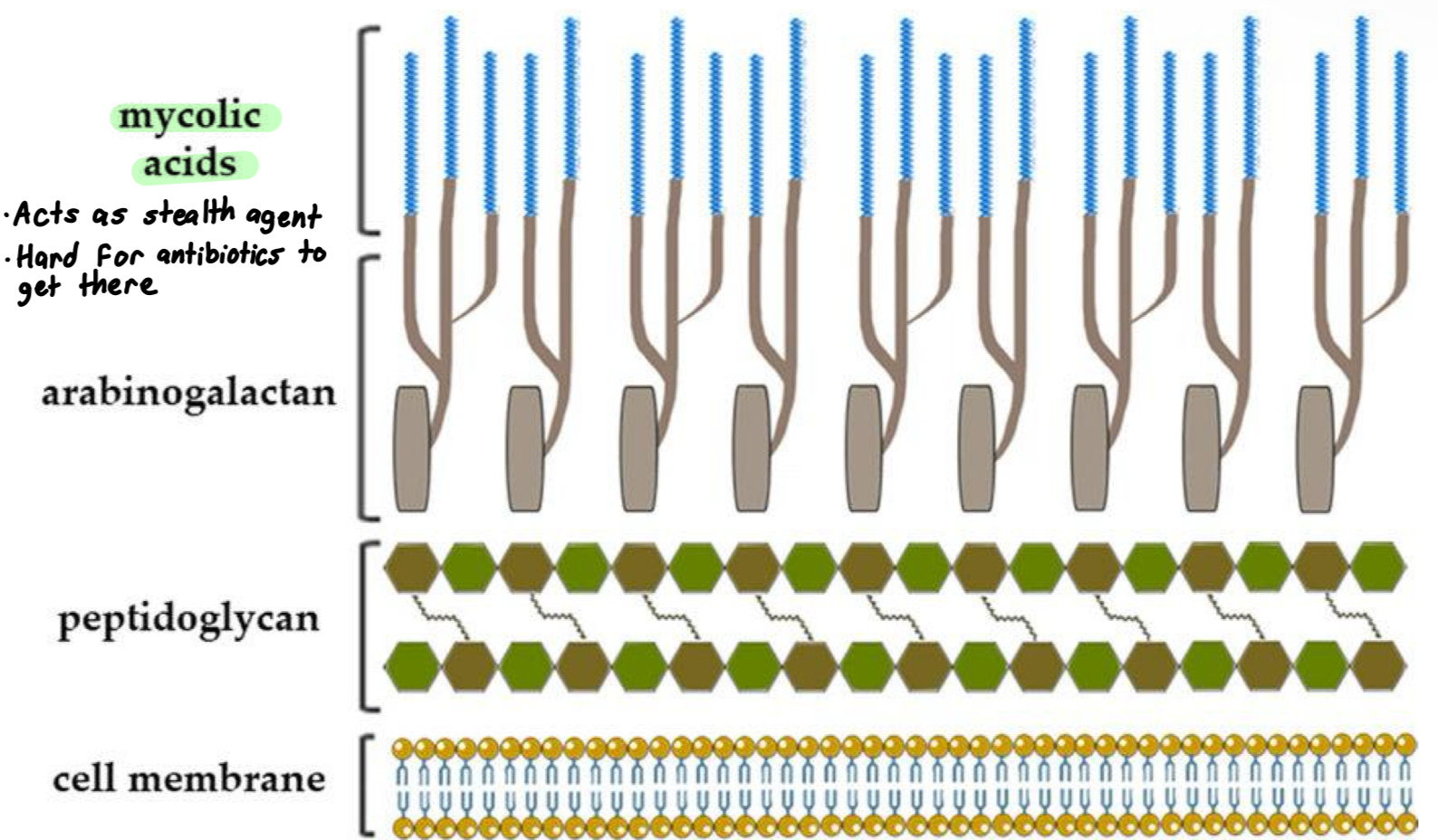
Agent: Mycobacterium tuberculosis very slow growing (24 hr generation time) gram-positive Actinobacteria but with an unusual, thick outermost layer of glycolipids including mycolic acid
Transmission: airborne droplets
Symptoms: bad cough that lasts 3 weeks+, chest pain, coughing up blood or sputum, fatigue, weight loss, chills, fever, progressive irreversible lung damage, bacterium can go systemic → death
Regarding tuberculosis, what does latent infection refer to?
Latent infection: live bacteria in the lungs but not growing, no symptoms, not contagious
Active TB disease
What does mycolic acid do to tuberculosis?
Mycolic acid helps TB to avoid host immune response, also to be less sensitive to antibiotics
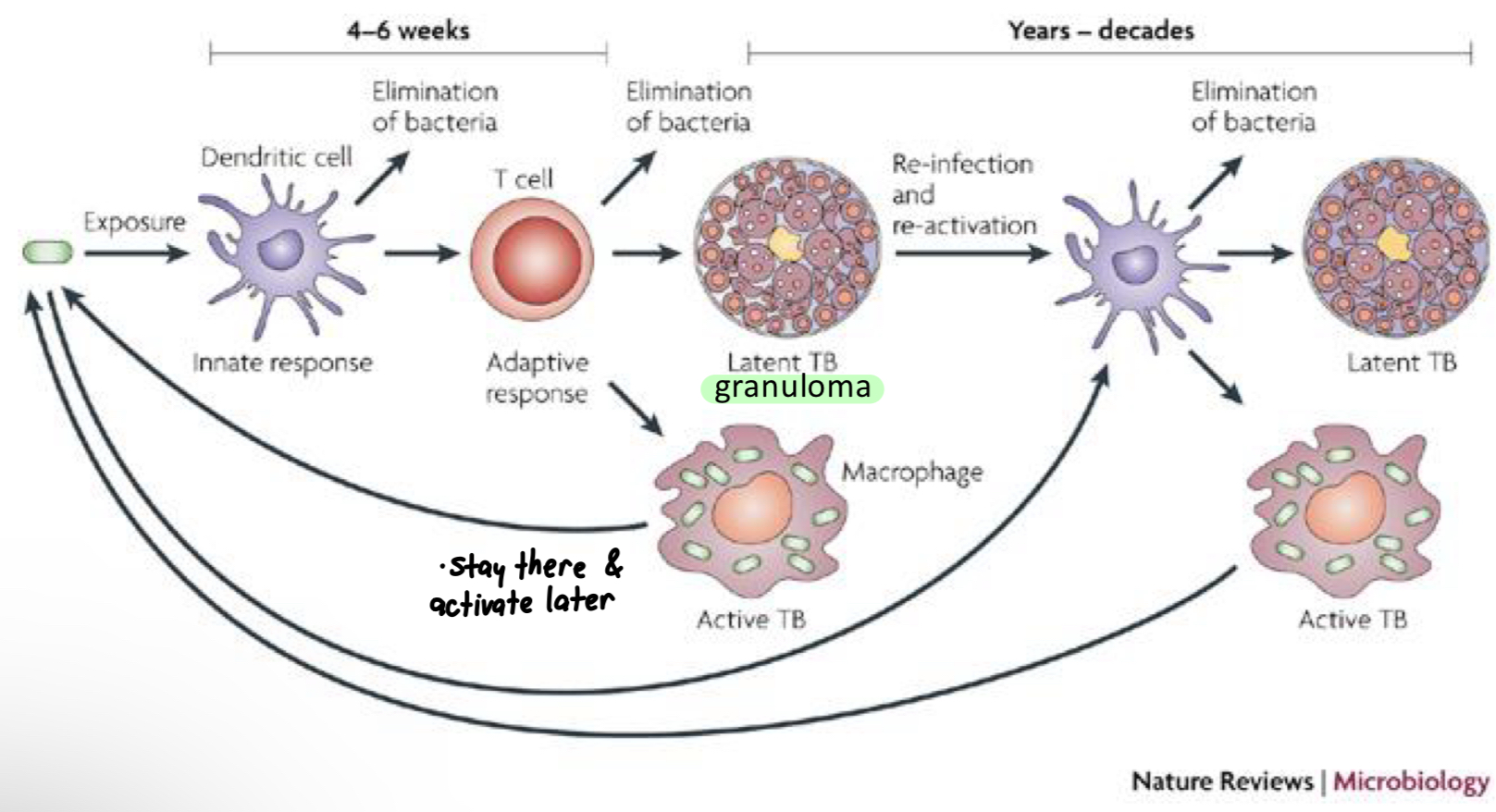
Regarding tuberculosis, what are macrophages? What if immune response is not strong enough? What do granulomas do?
Macrophages: can help clear infection or serve as a host to grow M. tuberculosis
If immune response is not strong enough, long term infection
Granulomas form to contain bacteria: Latent TB
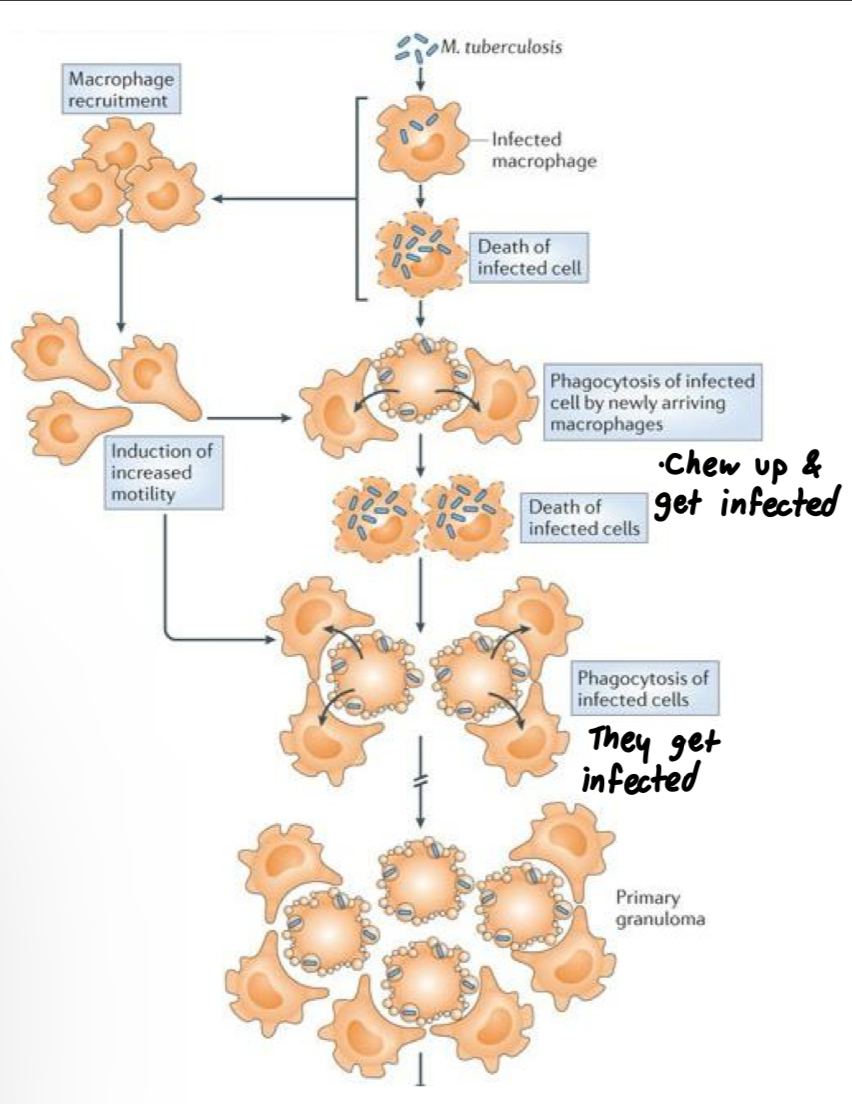
How does M. tuberculosis thrive in macrophages?
M. tuberculosis specifically infects macrophages, and recruits MORE macrophages to grow in
Keeps pH inside phagosome relatively neutral
Produces lipids that prevent fusing of
phagosome with lysosome
State the following for tuberculosis: virulence factors, treatment, epidemiology
Virulence factors
Can live inside macrophages by preventing lysosome fusion
Inhibits apoptosis of infected cells
Long term survival within walled-off lesions (granulomas)
Treatment: 3 or more antibiotics
Epidemiology
1/3 of the world’s population is infected, 1.5 million TB-related deaths each year, est. 2 billion latent infections
Leading killer of people with AIDS
In the US, inexpensive screening and effective treatment lead to reduction of disease but still 9,287 cases reported in 2016
Multi Drug Resistant (MDR) TB resistant to at least 2 of the antibiotics used in treatment. (XDR TB)
TB is a human disease, not known to infect other animals or have an environmental reservoir.
What is the vaccine for tuberculosis?
Vaccine: BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guérin, attenuated M. bovis) available but poor efficacy against pulmonary TB disease
Under development: boosting the BCG and a cell-mediated response
State the following for chlamydia: agent, transmission, symptoms, treatment
Agent: Chlamydia trachomatis – an obligate intracellular pathogen that lives off the organic molecules taken from the host cell, small genome ~1 Mb
Transmission: Intimate contact
Symptoms: women - often mild or no symptoms (in 75% of those infected), men - painful urination some mucoid or watery discharge; advanced infections in female fallopian tubes leads to pelvic inflammatory disease, scarring may cause infertility; active infection during pregnancy can lead to premature birth, can be passed on to child during birth – conjunctivitis or pneumonia
Treatment: When detected (urine test or PCR test of vaginal sample), easily treated with antibiotics (azithromycin)
Regarding the life of Chlamydia trachomatis, what are elementary bodies? What does reticulate bodies take over? Is the host cell killed?
The elementary body (EB) is a tough, non-reproductive “spore-like” form, it forces host cell to engulf it, then within its own membrane-bound compartment it transforms to reticulate body (RB)
RB takes over the host cell, assimilates nutrients and replicates.
Host cell is not always killed!
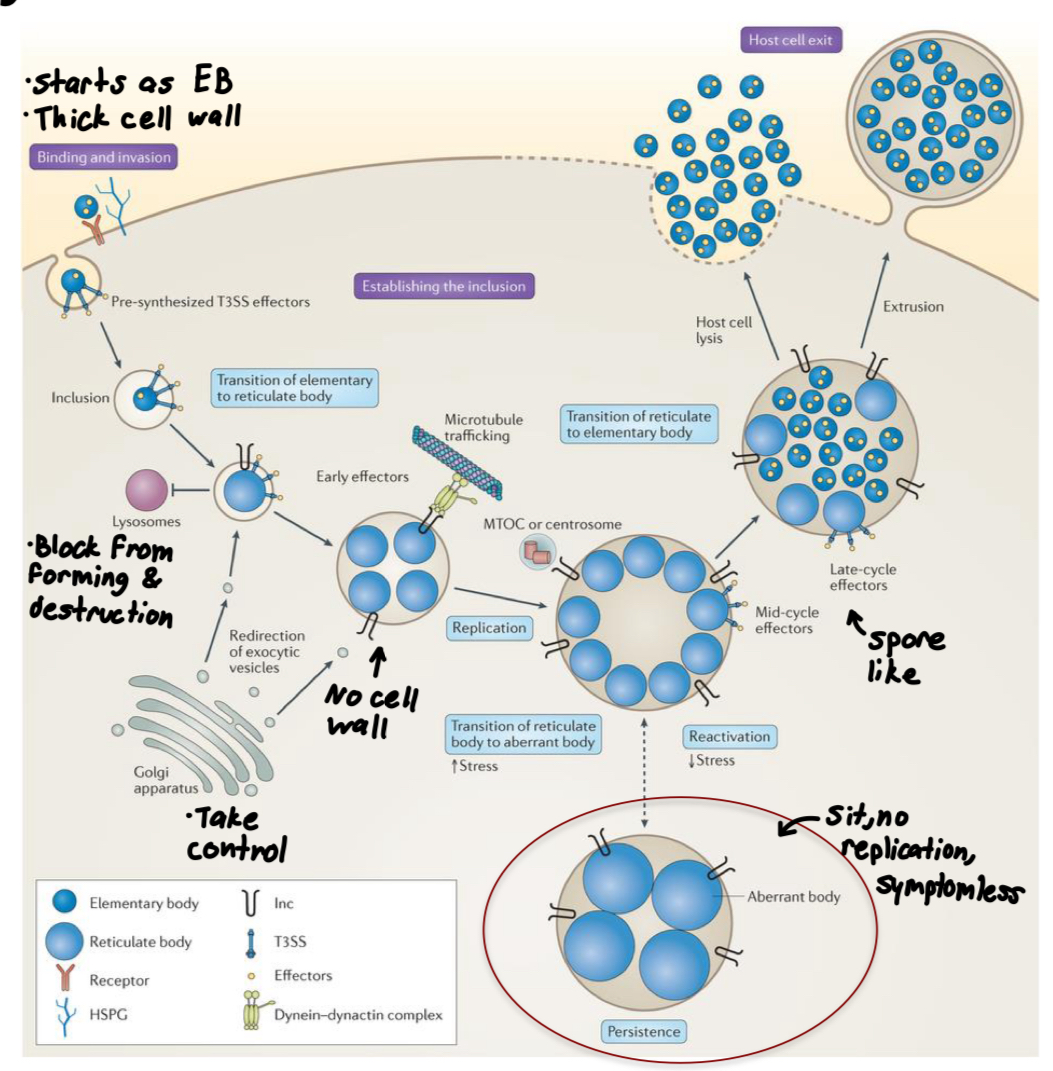
Regarding Chlamydia trachomatis, what do bacterial adhesins aid in? What do T3SS do? What do effectors do?
Bacterial adhesins aid attachment to epithelial cells
T3S: injects effector proteins into cytoplasm to induce host actin remodeling, forcing endocytosis
Effectors prevent fusion with lysosome, redirect vesicle trafficking in the host, aid in acquisition of nutrients from host, inhibit apoptosis of host cell
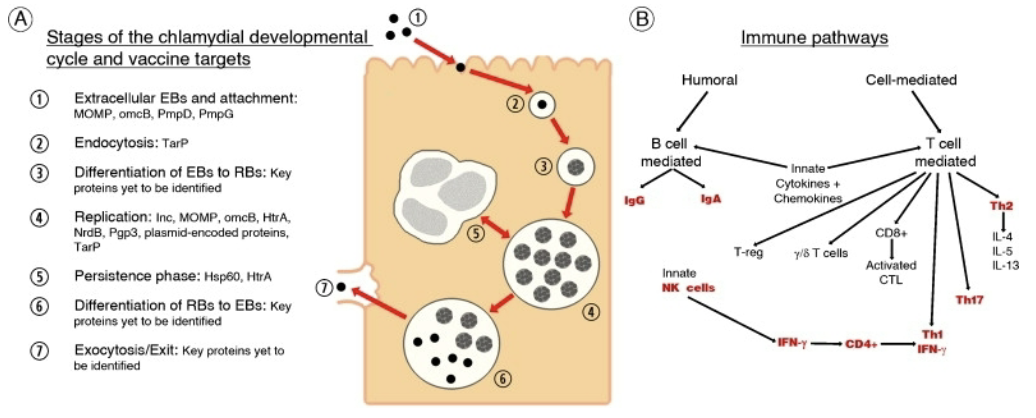
State the following for Chlamydia trachomatis: epidemiology, globally anually estimated cases, disease reserviors, prevention, vaccine
Epidemiology: cause of the most frequently reported STI in the US. In 2014, >1,400,000 infections reported to CDC but estimated 2.9 million infections
Globally estimated 100,000,000 new cases every year
Disease reservoirs – infected humans.
Prevention: condoms, long-term monogamous relationship,
abstinenceVaccine: None available. Whole-cell vaccines have not been effective. In animal tests, stimulating helper T cells actually increased spread of Chlamydia in the individual!
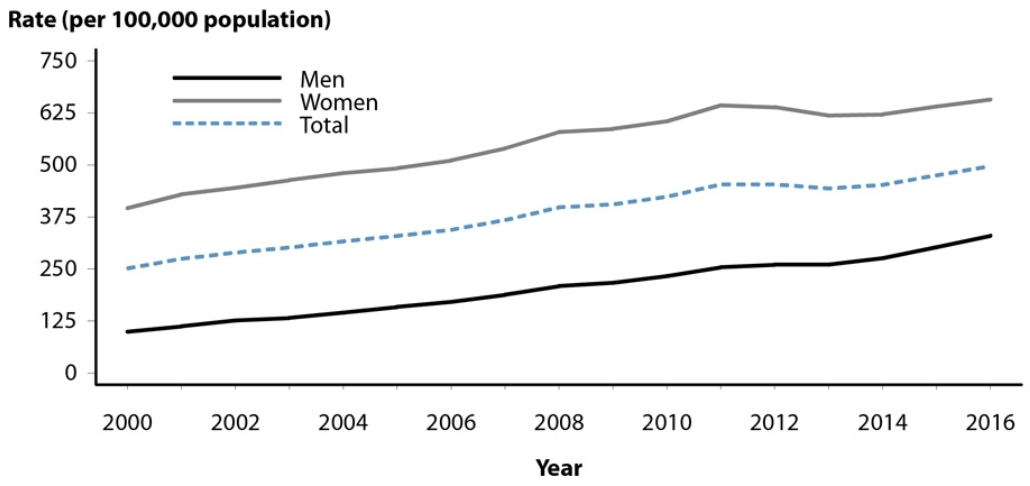
What is the infection rate trend graph in the US of Chlamydia trachomatis reported cases?