Ch. 9: Autonomic Nervous System
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
What are do autonomic neurons do
Innervate organs not under voluntary control
What are the three effector organs of the autonomic neurons
cardiac muscle, Smooth muscle of visceral organs and blood vessels, and Glands
Neurons are motor, but there are sensory neurons from
the viscera for control
Somatic motor neurons have
cell bodies in the spinal cord and just one neuron traveling from spinal cord to effector.
The autonomic motor system has two sets of neurons in the PNS: The first has
cell bodies in the brain or spinal cord and synapses in an autonomic ganglion
The autonomic motor system has two sets of neurons in the PNS: The second has
cell bodies in the ganglion and synapses on the effector
Preganglionic neurons originate in the
midbrain or hindbrain or from the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral spinal cord (CNS)
Postganglionic neurons originate in the
ganglion (PNS)
Autonomic ganglia are located in the
head, neck, and abdomen as well as in chains along either side of the spinal cord
Somatic motor neurons release only
acetylcholine which is always excitatory.
Autonomic neurons release mainly
acetylcholine and norepinephrine but may be excitatory or inhibitory
Neurons in the somatic nervous system can be up to 10x larger than
autonomic nervous system neurons
What are the two divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions
What's another word for the sympathetic division of the ANS
The Thoracolumbar division
sympathetic Preganglionic neurons come from the
thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
sympathetic Preganglionic neurons synapse in
sympathetic ganglia that run parallel to the spinal cord; These are called the paravertebral ganglia. These ganglia are connected, forming the sympathetic chain of ganglia
Splanchnic nerves continue through the paravertebral ganglia and make their first synapse at a
collateral ganglion.
Because preganglionic neurons can branch and synapse in ganglia at any level, there is
Divergence and Convergence
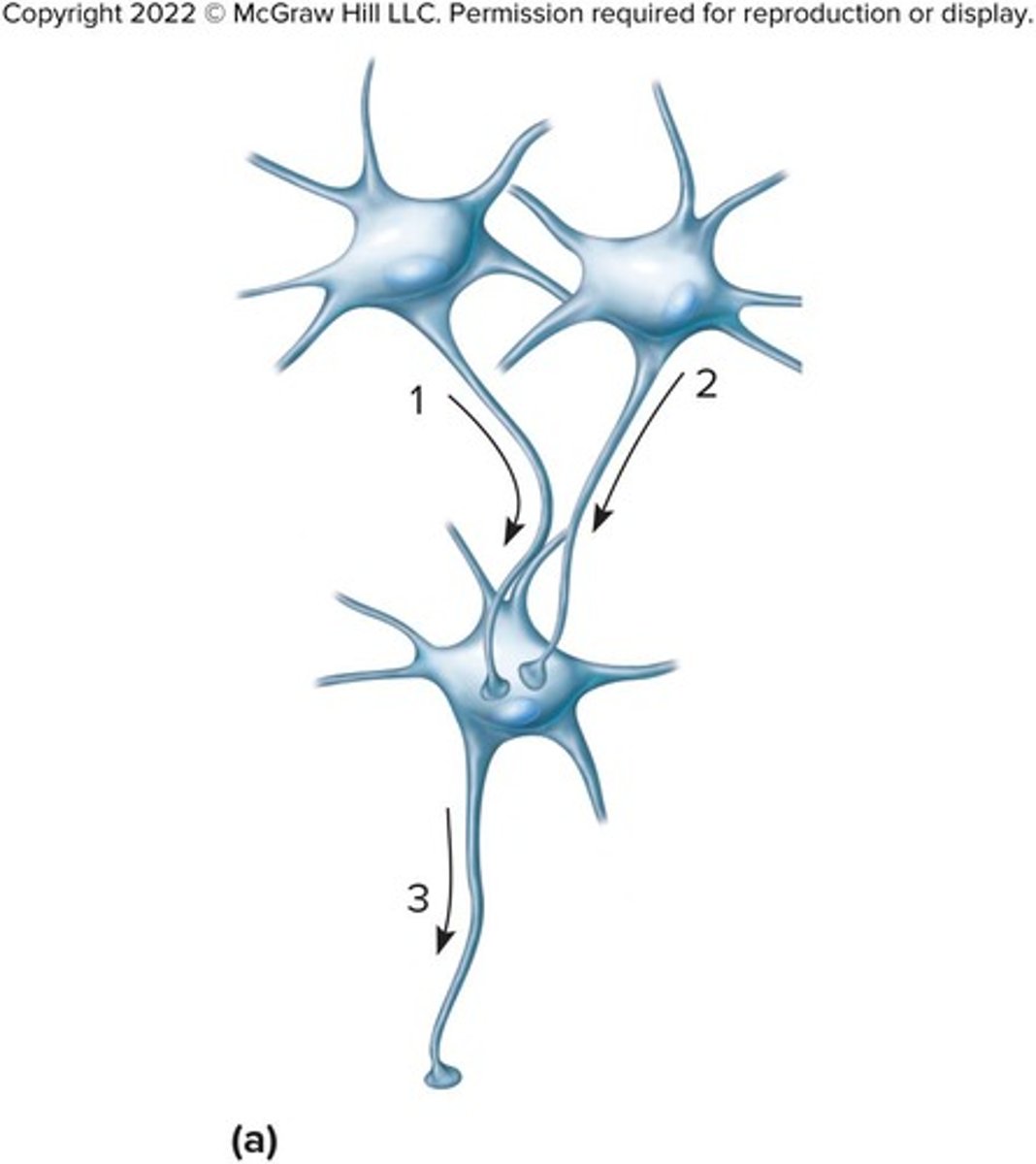
What is Divergence
One preganglionic neuron synapses on several postganglionic neurons at different levels.
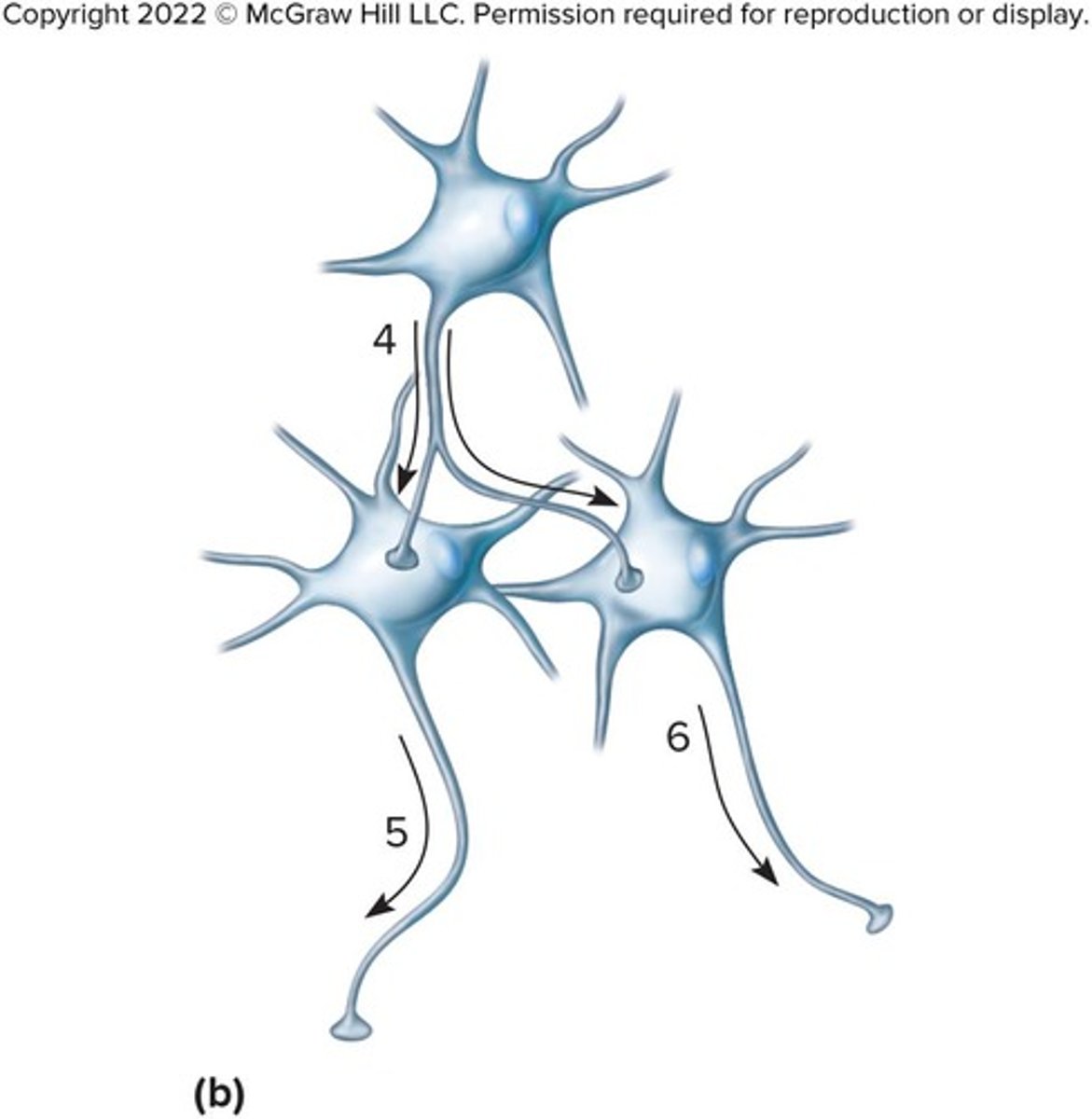
What is Convergence
Several preganglionic neurons at different levels synapse on one postganglionic neuron.
Convergence Allows the sympathetic division to act as a
single unit through mass activation and to be tonically active
The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine when stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system as a part of
mass activation
Embryologically, the adrenal medulla is a modified ganglion and is innervated directly by
preganglionic sympathetic neurons.
What's another word for the parasympathetic division of the ANS
Craniosacral division
parasympathetic Preganglionic neurons come from the
brain or sacral region of the spinal cord.They synapse on ganglia located near or in effector organs; called terminal ganglia
parasympathetic Preganglionic neurons do not travel
with somatic neurons (as sympathetic postganglionic neurons do). Terminal ganglia supply very short postganglionic neurons to the effectors
What four cranial nerves have autonomic system functions
The oculomotor (III), facial (VII), glossopharyngeal (IX), and (X) vagus nerves
The oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves carry
parasympathetic preganglionic neurons.
The facial (VII) and glossopharyngeal (IX) nerves stimulate
flow of saliva
The Oculomotor Nerve (III) constricts the
pupils
The Vagus Nerve has effects on varying organs, it
constricts bronchi, slows heartbeat, stimulates peristalsis, stimulates bile release, and contracts bladder.
Preganglionic nerves from the sacral region of the spinal cord provide innervation to the lower part of the
large intestine, rectum, urinary and reproductive organs. Terminal ganglia are located within these organs.
The sympathetic division activates the body for "fight or flight" through the release of
norepinephrine from postganglionic neurons and the secretion of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla.
The flight or fight response Prepares the body for intense physical activity in emergencies by
Increasing heart rate and blood glucose levels and by diverting blood to skeletal muscles; Tonically regulates heart, blood vessels, and other organs
The parasympathetic division is antagonistic to the
sympathetic division.
The parasympathetic system allows the body to
"rest and digest" through the release of ACh from postganglionic neurons; Slows heart rate, and increases digestive activities
Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by all
preganglionic neurons (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
Acetylcholine is also It is also the neurotransmitter released from
parasympathetic postganglionic neurons.
Some sympathetic postganglionic neurons that innervate sweat glands and skeletal muscle blood vessels) release ACh. These synapses are called
cholinergic
Norepinephrine is the neurotransmitter released by most sympathetic postganglionic neurons. These are synapses are called
adrenergic
Axons of postganglionic neurons have various swellings called
varicosities that release neurotransmitter along the length of the axon.
Sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons innervate the same tissues but release different
neurotransmitters
Response to adrenergic stimulation can be
epinephrine in the blood or norepinephrine from sympathetic nerves; Can stimulate or inhibit, depending on receptor
What are the two types of α (alpha) Adrenergic receptors
α1 and α2
What are Three types of β (beta) Adrenergic receptors
β1 β2 and β3
α and β Adrenergic Receptors act using
G-proteins and second messenger systems
α receptors use a
Ca2+ second messenger system to constrict organs
What do α1 receptors do
they Constrict blood vessels
(vasoconstriction)
What do α2 receptors do
they inhibit the release of Norepinephrine
β receptors uses
cAMP to dilate organs
What do β1 receptors do
Increase contraction, contractility, HR
What do β2 receptors do
relax smooth muscle of bronchiole muscle
What do β3 receptors do
regulate metabolism (brown fats)
Alpha receptors are more sensitive to
norepinephrine
Beta receptors are more sensitive to
blood epinephrine
Agonists are drugs that
promote the process stimulated by the NT
Antagonists are drugs that
block the action of the NT
ACh released from preganglionic neurons of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic division is
stimulatory.
ACh from postganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic division is
usually stimulatory, but some are inhibitory, depending on receptors.
In general, sympathetic and parasympathetic effects
are antagonistic
Where are nicotinic receptors found
in autonomic ganglia
Nicotinic receptors Serve as
ligand-gated ion channels for Na+ & K+ = Ionotropic receptors; blocked by curare
Where are muscarinic receptors found in
visceral organs and stimulated by release of Ach from postganglionic neurons
Muscarinic receptors can be
stimulatory or inhibitory (opening K+ or Ca2+ channels); Use G-proteins and second messenger system = Metabotropic receptors; Blocked by atropine
Most visceral organs are innervated by both
sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons.
The parasympathetic system causes
heart rate to decrease, digestive functions to increase, and pupil diameter to decrease
What are complimentary effects
when both divisions produce similar effects on the same target (Ex: salivary gland secretion: Parasympathetic division stimulates secretion of watery saliva; sympathetic constricts blood vessels so the secretion is thicker.)
What are Cooperative effects
when both divisions produce different effects that work together to promote a single action. (Ex: Erection and ejaculation: Parasympathetic division causes vasodilation and erection; sympathetic causes ejaculation)
What organs are only intervated by the sympathetic division
Adrenal medulla, Arrector pili muscles in skin, Sweat glands in skin, Most blood vessels; Regulated by increase and decrease in sympathetic nerve activity; Important for body temperature regulation through blood vessels and sweat glands
Many visceral functions are regulated by
autonomic reflexes.
Sensory input is sent to brain centers (usually by the vagus nerve), which integrate the information and modify the activity of
preganglionic neurons.
The Medulla oblongata controls
many cardiovascular, pulmonary, urinary, reproductive, and digestive functions.
The Hypothalamus controls
major regulatory center of the ANS - body temperature, hunger, thirst, pituitary gland
The Limbic system is responsible for
autonomic responses during emotional states (blushing, pallor, fainting, cold sweating, racing heart rate)
The Cerebellum controls
motion sickness nausea, sweating, cardiovascular changes
The Frontal & temporal lobes control
emotion and personality
What two things is aging associated with
increased levels of sympathetic activity, and Increased sympathetic tone
in the lungs we have stretch receptors that
respond to lung inflation by sending signals via the vagus nerve to the brainstem.
In the aorta we have chemoreceptors and baroreceptors where
baroreceptors act as pressure sensors, detecting changes in blood pressure, while chemoreceptors monitor blood chemistry, sensing levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH
The heart has atrial and stretch receptors that
detect increased blood volume and pressure (atrial stretch) and trigger the Bainbridge reflex.
The gastrointestinal tract has stretch receptors that
detect distension (stretching) from food or feces
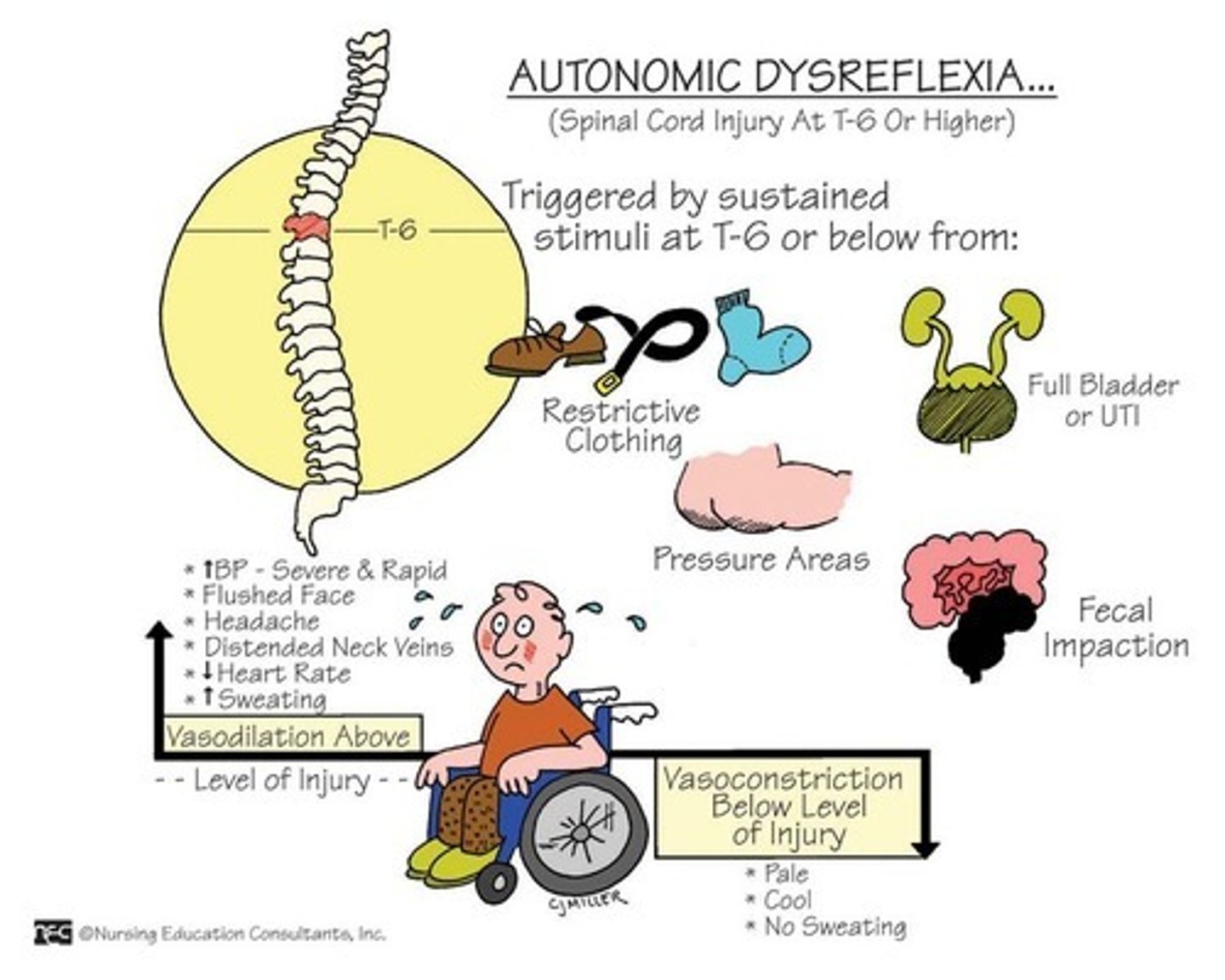
What is Autonomic Dysreflexia
a life-threatening medical emergency that can occur in people with spinal cord injuries (SCIs) above the sixth thoracic vertebra (T6).
as we get older there is an Increased risk for
hypertension and cardiovascular diseases
What is adrenaline
also known as epinephrine, is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the body's "fight or flight" response.
What is noradrenaline
also known as norepinephrine, is a neurotransmitter and hormone that plays crucial roles in various bodily functions.
What is dopamine
a chemical messenger in the brain . It plays a key role in movement, motivation, learning, reward, and mood
What is serotonin
mood NT that contributes to well being and happiness;
What is GABA
the calming NT that calms firing nerves in the CNS, high levels improve focus
What is Glutamate
the memory NT, being the most common NT involved in learning and memory
What are endorphins
the Euphoria NT, released during exercise, excitement & sex, producing well-being & euphoria, reducing pain
What is the Olfactory (I) nerve responsible for
Sense of smell
What is the Optic (II) nerve responsible for
Sense of vision
What is the Oculomotor (III) nerve responsible for
Moves the eye (most extraocular muscles), constricts the pupil, and controls the upper eyelid
What is the Trochlear (IV) nerve responsible for
Moves the eye down (superior oblique muscle)
What is the Trigeminal (V) nerve responsible for
Sensation (pain, temperature, touch) for the face, scalp, and teeth (three main branches: ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular); controls muscles of mastication (chewing)
What is the Abducens (VI) nerve responsible for
Moves the eye horizontally (lateral rectus muscle)
What is the Facial (VII) nerve responsible for
Controls muscles of facial expression; provides the sense of taste for the anterior two-thirds of the tongue; controls salivary and lacrimal (tear) glands
What is the Vestibulocochlear (VIII) nerve responsible for
Sense of hearing and balance (equilibrium)
What is the Glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve responsible for
Sense of taste for the posterior one-third of the tongue; controls the pharynx (swallowing); monitors blood pressure and O2 /CO2 levels in the blood
What is the Vagus (X) nerve responsible for
It controls muscles for swallowing and speaking; provides parasympathetic control to the heart, lungs, and digestive tract