Communication & Networking - A Level Comp Sci
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
What are the 2 main types of data transmission?
Serial
Parallel
How does serial transmission work? (+ what distances is it best for?)
Data is sent 1 bit at a time along 1 wire
best for medium/long distance
How does parallel transmission work? (+ what distances is it best for?
Multiple bits are sent simultaneously across multiple wires
Short distance - generally less than 5 metres
What is data skew in parallel transmission? (+why does it occur?)
The time delay between data from different wires reaching the receiver in parallel transmission
due to slightly differing electrical properties between each wire/medium
Why is serial better than parallel transmission? (4 reasons)
No data skew (only 1 wire) - more reliable
Cheaper to install (only 1 wire, less complex)
Less interference between wires (crosstalk) with use of shielded cables
Lower power consumption
What is synchronous transmission? (+ serial or parallel?)
Mostly parallel data transmission; can be serial
data is sent at regular intervals using a clock signal shared between transmitter & receiver
When & where is synchronous data transmission used?
Where? In control bus of a CPU
When? during the fetch-execute cycle
What is asynchronous data transmission?
A method of serial data transmission;
Data is sent without a clock signal, so transmitted when it’s ready
Involves the use of start, stop & parity bits for tracking data and error checking
When & where does asynchronous transmission occur?
When? For small intermittently-sent data
Where? In the computer’s communication ports for connecting peripherals
What is the purpose of a start bit in asynchronous transmission?
Signals the beginning of data packet/byte to the reciever’s clock
What is the purpose of a stop bit in asynchronous transmission?
Signals the end of a data packet/byte for the receiver to process the received data
What is latency (in computer communication)?
Time delay between when an instruction is transmitted and when it’s received
What is latency measured in?
milliseconds (ms)
What is bit rate?
Number of bits transmitted over a communication medium in 1 second
What is baud rate?
Number of distinct signal changes/symbols transmitted over a communication channel per second
What is bandwidth?
Maximum range of frequencies / rate of data transfer over a communication channel
What is bandwidth measured in?
bits per second (bps)
What is the relationship between bandwidth and bit rate?
It is directly proportional
Higher bandwidth = higher bit rate
In what circumstances is the baud rate NOT equal to the bit rate?
When each symbol is encoded with more than 1 bit - bit rate will be higher
How does odd parity work in asynchronous data transmission?
Parity bit = 1 when number of 1s is odd (otherwise is 0)
How does even parity work in asynchronous data transmission?
Parity bit = 1 when number of 1s is even (otherwise is 0)
What is a network topology?
The physical and logical arrangement of devices & its connections in a network
What is the order of devices that data arrives at in home networking?
Modem
Router
Switch
W.A.P (wireless access point)
What is the purpose of the Modem in home networking?
Device that:
Recieves the internet signal from the ISP (internet service provider)
Converts it into a format suited for home network
What is the purpose of the Router in home networking?
Device that:
Receives data from the Modem & manages network traffic (incl the internet)
Uses IP addresses to determine data travel across networks
What is the purpose of the Switch in home networking?
Device that:
Connects devices within same network & forwards data packets to correct device using MAC (media access control) addresses
What is the purpose of the W.A.P (wireless access point) in home networking?
Device that:
Allows wireless devices to connect to network by receiving & transmitting data signals via radio waves
What are the 3 main types of network topology?
Bus, Star, Ring
What are the pros of using a ring topology?
Cheap to expand & add new devices
Fast data travel - only 1 direction
No reliance on central device/hub
What are the cons of using a ring topology?
Slows down with lots of devices (as data moves in 1 direction only)
If 1 computer in topology fails, entire network fails
What is a NIC (network interface card)?
A hardware component that allows a computer to connect to a network, whether wired or wireless
What is a physical network topology?
The physical architecture of the connections in a computer system
What is the most common type of physical network topology?
Physical STAR topology
What is a logical network topology?
How data packets flow within a network, irrespective of physical arrangement
How can a physical star topology behave as a logical bus topology?
A bus protocol is run on the hub for it to distribute packets to all connected devices in a network
When are star topologies most commonly used?
Home networks
Schools
Small businesses
What is the issue with using a star topology both physically and logically?
The Ethernet Protocol is only designed to work on a bus topology
What is a server? (In a client-server network)
A specialised computer that manages resources & provides functionality to clients within a network
What is a client? (In a client-server network)
A computer that requests the services/resources provided by a server
What are the main features of a client-server network? (Management, storage, suitability)
Central server manages security
Performs some processing tasks
Suitable for any size organisation or network that requires centralised management
What are 2 pros of client-server networks?
Pros:
Easy centralised management - increased reliability
Easy to add new clients
What are 2 cons of client-server networking?
Dependency on central server - entire network fails if it fails
Expensive to set up and maintain - requires specialist management
What are the 4 main features of peer-to-peer networking?
No centralised management of files or security
Easy communication between computers w/o a central server
Each peer has equal status in the network
Most suitable for homes, small businesses, live streaming
What are 2 pros of peer-to-peer networking?
Pros:
Cheaper set up & maintenance than client-server
No dependency on central server
What is a con of peer-to-peer networking?
Data/files from a computer can’t be accessed by peers if computer is off
What is Wi-Fi?
= A type of WLAN & a family of protocols based on international standards
What 2 components are needed for wireless networking? (+ what is their purpose?)
Wireless access point (converts wired signals from router into Wi-Fi signals)
Wireless network adapter (allows wired device to send & recieve Wi-Fi signals)
How does WPA/WPA2 encryption secure wireless networks?
Encrypts wireless traffic & requires user to enter password/credentials to gain access
How does disabling Service Set Identifier (SSID) secure wireless networks?
SSID is not displayed so user must manually enter network name to access network
How does MAC address filtering secure wireless networks?
Whitelist created so only users with authorised MAC address can access network
What are 3 methods of securing wireless networks?
WPA/WPA2 encryption
Service Set Identifier (SSID) disabled
MAC address filtering
What is Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)?
= A protocol used in wireless networks to avoid data collisions when multiple devices communicate simultaneously
How does CSMA/CA work? (Explain the steps)
When ready to transmit, device listens to communication channel to check its idle
If idle, device waits for a back off period (random amount of time), then data is transmitted
If busy, device waits for another back off period & checks channel again (repeats until idle)
Data is transmitted
What is Request To Send / Clear To Send (RTS/CTS)?
= A protocol used in addition to CSMA/CA to get around the hidden node problem
How does RTS/CTS work?
After device has checked whether channel is idle, a “Request to Send” message is sent to the server
If server is idle, it responds with “Clear to Send” message & data is transmitted
If “Clear to Send” message is not received, then server is communicating with hidden node & CSMA process restarts
What is a potential problem of using CSMA/CA without RTS/CTS?
Risk of the hidden node problem = when 2 nodes in a wireless network can’t connect with each other, but can connect with a 3rd node (eg an access point)
May lead to a collision & corrupted data
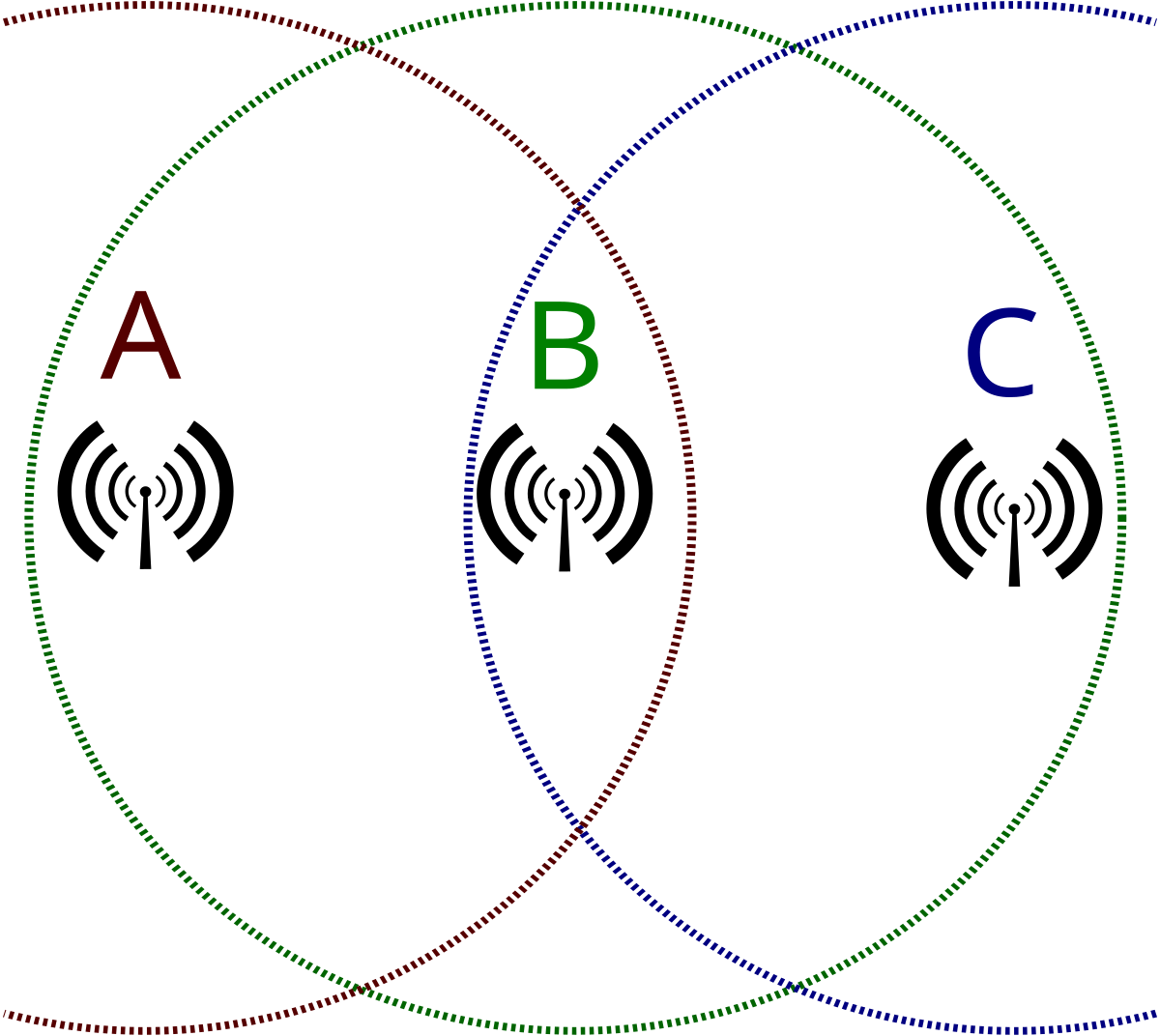
What is a Service Set Identifier?
= a unique identifier that allows devices to connect to a Wi-Fi network
What is the Internet?
= A global WAN of interconnected computer networks that uses an end-to-end communication (TCP/IP)
What is the World Wide Web?
= A interconnected system of public web pages accessible via the Internet
What protocol is used to transfer resources on the internet?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
What is an Internet Service Provider?
= A company/3rd party that provides its customers with access to the Internet
What is a packet?
= A container in which data is transmitted over a network
What is packet switching? (+ how it works) *
= Process of transferring data over a network by sending it in packets
Data is split into packets, sent via best possible route, and reassembled into order when received
Data is passed through routers (each pass = a hop), that use recipient address to determine where to send it
What are the 5 main components of a packet?
Sender’s address
Recipient’s address
Packet contents
Time To Live (TTL): number of hops packet can do until being dropped
Sequence number: contains number of packets in a message + a packet’s position compared to the others
What is a packet’s Time To Live (TTL)?
= Number of hops a packet can do until being dropped
What is the purpose of a sequence number in a packet?
Allows packets to be reassembled in the correct way order
Missing packets can be identified
What does a router & gateway both do?
= Directs packets being transmitted across networks towards their destinations
How are gateways used for 2 networks with different protocols?
Gateway strips away packet details (except packet contents)
New sender & recipient addresses are given to packet to comply with new protocol
What is a Uniform Resource Locator (URL)?
= A unique text-based address of a file/resource on the internet
What is a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)?
= The complete unique address that specifies an exact resource
(Contains: host name, domain name, top level domain
What is a domain name?
= The part of a URL that locates a domain on the internet
What is the purpose of a domain name server?
Stores domain names and their corresponding IP addresses
What is an IP address?
= A unique numerical address assigned to a device using Internet Protocol to identify its host & location
How are domain names organised? (Outline the DNS System hierarchy)
Root server
Top Level Domains (TLD)
Second Level Domains (2LD)
Subdomains
Hosts
What is the purpose of the Root Name Server?
Directing DNS queries to the right TLD server during the DNS lookup process
Explain the DNS lookup process
User enters URL & browser checks its local cache for the IP address (if there, process stops)
If not there, DNS query is sent to a DNS server (normally the ISP) to get the IP address
Recursive resolver checks its cache to find IP address & starts recursive process if not there
Resolver sends query to root server & it directs the resolver to the right TLD server
TLD server tells resolver address of the authoritative name server
Authoritative name server responds to resolver with final IP address
IP address is sent back to browser & user can connect to the web server
What is a Recursive Resolver?
= A server that translates a human-readable domain name into its corresponding IP address
What is an Internet Registry? (+ their purpose)
= An organisation responsible for allocating IP adresses within a geographical area
What is encryption?
= The encoding & scrambling of data using a key so it cannot be intercepted/understood
What is are the 2 types of encryption?
Symmetric encryption
Asymmetric encryption
How does symmetric encryption work?
Both sender & receiver share the same private key that is used for both encryption and decryption
Sender encrypts data with the shared key
Key is exchanged/shared to recipient over a network
Recipient uses key to decrypt message
What is the main drawback of symmetric encryption?
Security risk: is key is intercepted when exchanged over a network → encryption is broken
How does asymmetric encryption work?
2 pairs of mathematically linked keys are generated
2 pairs of keys; sender & recipient each have public and private key
Sender encrypts message with recipient’s public key, available to anyone
Message can only be decrypted with recipient’s private key
What is a digital signature used for?
Verifies the sender of the message + checks it hasn’t been tampered with during transmissions
How is a digital signature made?
A digest of the message is created (a unique value) often by hashing/checksum algorithm
Digest encrypted using sender’s private key & appended onto message (anyone with sender public key can
Appended message is encrypted using recipient’s public key (only recipient can decrypt)
To decrypt it fully: recipient private key → sender’s public key
What is a digital certificate & its purpose?
An electronic document that proved ownership of a key pair used in asymmetric encryption
checks that fake key isn’t used by an imposter
What does a digital certificate contain?
Serial number
Owner number
Expiry date
Owner public key
Certificate authority’s signature
What is a firewall?
A security checkpoint software/hardware that:
monitors network/packet traffic
prevents unauthorised user access to a network
What are the 3 main types of firewalls?x
Packet filtering
Proxy servers
Stateful inspection
How does a packet filtering firewall work?
Inspects the header of a packet & accepts and blocks it based on set of filters:
Its source IP address, destination IP address, port numbers, and protocol type
How does a stateful inspection firewall work?
Internal contents of the packet are scanned + compares it to a state table (a log of all active connections) to check if it:
Belongs to a legitimate, existing connection
Is not part of an existing malware database
If yes, packet is allowed through
What is a proxy server?
= An separate intermediate device between a user and a remote web server that traffic must pass through
How does a proxy server firewall work?
It uses its own IP address instead of the user’s one when receiving requests
Privacy/security measure against threats
What is a worm?
= A type of malware that can self-replicate and spread across networks independently without user interaction
What type of vulnerabilities do worms exploit?
Network flaws
Unpatched systems
What is a Trojan horse?
= A type of malware that disguised as a benign file, often via email attachments & malicious website downloads
What type of vulnerabilities do Trojan horses exploit?
Ignorant user trust via social engineering
What is a virus?
= A type of malware that requires a host program/file to spread & corrupt a system