Earth and ocean science 111-First part
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Isolated system
A physical system that does not exchange matter or energy with its surroundings, remaining completely self-contained.
fixed and finite energy and matter
Closed system
A physical system that can exchange energy but not matter with its surroundings, allowing for energy transfer while maintaining a fixed amount of matter.
eg earth
Open system
A physical system that can exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings, allowing for continuous interaction and transfer.
System
Any portion of the universe that can be separated from the rest for measuring and observing change
Remote sensing
The continuous or repetitive collection of information about a target from a distance
Geographical information system (GIS)
Computer-based system that can store large amount of spatially referenced data points
Spatially
Store, use, etc in a way that relates to space and the position, area, and size of things within it.
Geostationary Satellites
Fixed in orbit at high altitudes
Sun-synchronous satellites
Circle from pole to pole at lower altitudes and thus have higher resolution.
Swaths
Overlapping strips of data
Flux
The constant exchange of energy and matter between Earth’s reservoirs
Steady state
Matter in and out of a reservoir is equal
Sink
Matter into the reservoir is greater than matter leaving
Receives energy or matter
Source
Matter leaving the reservoir is greater than matter going in
Donates energy or matter
Residence time
Average length of time water spends in a reservoir
Sequester
isolate or hide away.
Sequestration
When a substance has a very long residence time in a reservoir
The four great reservoirs
Biosphere
Atmosphere
Geosphere
Hydrosphere
What is the amount of matter in a closed system?
Fixed and finite
What happens of changes are made in one part of a closed system
The result of those changes eventually will effect other parts of the system
What is earths energy system powered by?
External: Sun
Internal: Radioactive decay and Gravitational energy
Gravitational energy
Heat still being lost from planetary formation
Life zone
Where earths 4 reservoirs interact most intensively. It is 10km above and below the surface
Cryosphere
Perennially frozen parts of the hydrosphere
Negative feedback
The systems response is in the opposite direction to the stimulus/initial input
Positive feedback
Increase in output leads to a further increase in output
Biogeochemical cycle
Movement of a chemical element or compound that cycles through earths reservoirs and has a role in earths stability
Cycles
The physical materials of the Earth system and the energy contained within it are continually recycled in numerous overlapping cycles.
How do we learn about the earth?
By measuring the mass or volume of materials and energy
Mineral requirements
Naturally forming/occurring
Inorganic
Solid Crystalline structure
Specific chemical compound
Rocks
Collections of minerals and other natural materials and organic matter
Solids with a crystal structure are?
Crystalline
Solids without a crystal structure are?
Amorphous
Most abundant mineral groups
Most abundant: Silicates
Second abundant: simple oxides
Most abundant minerals
Feldspars ~60%
Quartz ~15%
What does a crystal require?
The angle between any two faces to be the same on each crystal
Luster
Quality and intensity of light reflected
Hardness
Relative resistance of a mineral to being scratched
Density
Average mass per unit volume
Rock requirements
Naturally forming
Non-living
Firm
Combination of solid matter containing part of a planetary object
Igneous rock
Formed by the cooling and consolidation of MAGMA
Sedimentary rocks
Formed by either chemical precipitation of material dissolved in water or by the deposition of particles suspended and transported by water
Metamorphic rock
Either an igneous or sedimentary rock that has changed due to high TEMPERATURE and high PRESSURE
Texture
Overall appearance of a rock
Mineral assemblage
Amounts and kinds of minerals present
Plutonic igneous rock
Crystalize from magma underground
Volcanic igneous rock
Crystalizes from magma above ground
Regolith
A layer of broken disintegrated rock matter produced by rock weathering
What happened when the big bang cooled enough?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons combined into hydrogen atoms
Nucleosynthesis
the process of creating new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nuclei and nucleons
Big bang nucleosynthesis
Nuclear fusion formed H and He atoms
Stellar nucleosynthesis
forming elements in the stars
Created heavier element
Supernovae
Creates elements heaver then Fe
How are planets formed?
Gravity pulls together materials to make new stars and a surrounding accretionary disk.
the accretionary disk starts to coalesce to make planetesimals which collide to make protoplanets and eventually planets
Coalesce
combine elements together to form one mass or whole
planetesimals
a body which could come together with many others under gravitation to form a planet.
Differentiation
the process by which a planet's chemical elements separate into distinct layers. This happens when a planet melts and its materials separate by density
Chondrite
a type of meteorite that's made of iron, magnesium, silicon, and oxygen. Chondrites are the oldest known rocks and provide important clues about the formation of the solar system.
Planet types
Terrestrial: small, dense, rocky
Jovian: large, low density, gas giant
When did earths layering form?
Planetary differentiation
Primary waves
Travel the fastest
Can travel through solids and liquids
Refracted when passing through the core
Travel faster through colder materials
When can earths layers be transported
During volcanic eruptions
Secondary waves
Travel slower
Cannot travel through liquid
Cannot travel through the earths core
Compositional layers
Continental Crust
Oceanic Crust
Mantle
Core
Strength layers
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Mesosphere
Lithosphere
Strong, cool, and rigid
Only layer that reliably breaks when put under pressure
Where earthquakes generate
Asthenosphere
Can flow/bend when under pressure
Solid, weak, easily deformed
Cannot generate earthquakes reliably
Mesosphere
High temperature and pressure
Strong and solid
Participated in convention
What are plate tectonics a response to?
Earth trying to cool down
Convection cells
patterns of fluid motion that occur when warm, less dense material rises and cold, denser material sinks
conduction
The transfer of energy, such as heat or an electric charge, through a substance
Divergent margins
the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving apart
Convergent margins
the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving apart
Transform margin
a fault where two tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally.
Why is the mantle the densest layer
Closest to the core
Solid rock
Lithospheric plates
Have nothing to do with the shape of continents
Can be covered in continental or oceanic crust
3 major and many more minor plates
Divergent plate margins
Seismicity: Shallow earthquakes
Melting: Decompression melting
Volcanism: Creation of oceanic crust and mid ocean ridge
Hydrothermal energy
Mid ocean ridges and continental rifts
Continental rifts
Plates are continental and only produces oceanic crust
Pressure created from magma became great enough for the crust to separate
The rift valley formed mimics what is happening below the surface
Mid-Ocean Ridges
The plates pull apart causing the asthenosphere to rise up.
Decompression melting occurs lowering the melting point and creating the partial melting of the mantle creating magma
Magma cools and new oceanic crust is formed
Convergent plate margins
Seismicity: Ranges from shallow to deep
Melting: Flux melting
Volcanism: Creation of continental crust at volcanic arc
Accretionary wedge
Subduction and continental collision zone
Subduction zones
Oceanic →Oceanic or Continental →Oceanic
Trench and volcanic arcs are formed
Continental collision zone
Continental →Continental lithosphere
Forms mountains and thick crustal root
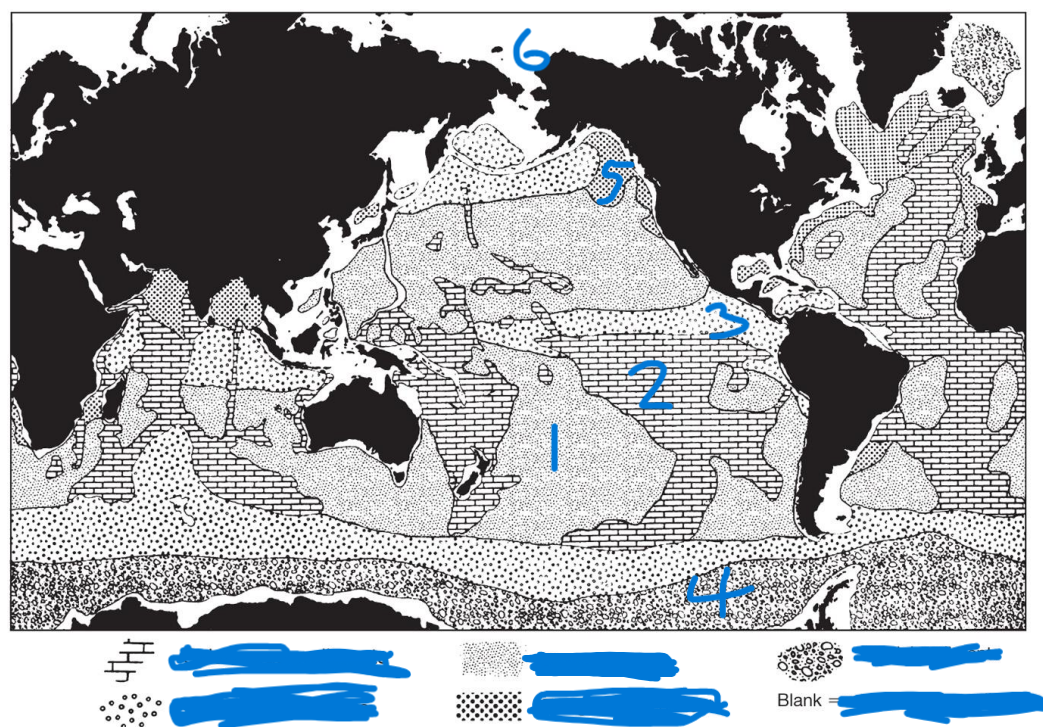
Deep Sea clay
Calcareous ooze
Siliceous ooze
Glacio-marine sediment
Terrigenous sediments
Ocean margins
Two kinds of metamorphic rock and where they are found.
Slate, Schist, Areas of uplift eg Pleasent valley
Three kinds of igneous rock and where they are found.
Obsidian, pumice (volcanic), Gabbro (Plutonic), Near volcanic arcs eg Boatmans Harbour
Two Sedimentary rock types and where they are found.
Conglomerate, Sandstone, Along the coastline eg Koekohe beach
How is hydrogen formed.
A few minutes after the big bang during the period called the big bang nucleosynthesis
How is oxygen formed
created within stars through nuclear fusion
Differeces between sea water and fresh water
Seawater, Contains lots of ions, Denser, 3.5% salt, -2 freezing point. Freshwater: Contains few ions, less dense, <0.5% salt, 0 freezing point
Speed of sound in water
1500 m/s