Human Anatomy Unit 3
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
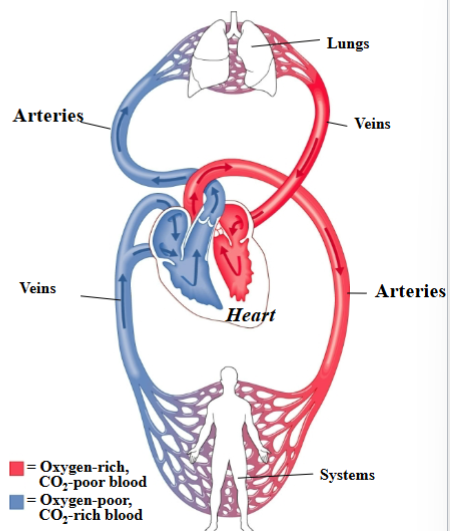
Cardiovascular System
Heart: Pumps blood
Arteries: carries blood away from heart
Veins: carries blood toward the heart
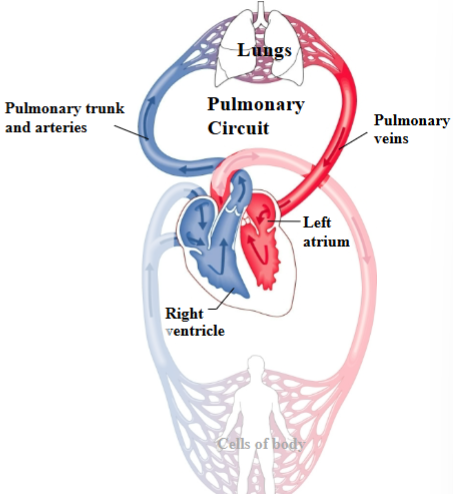
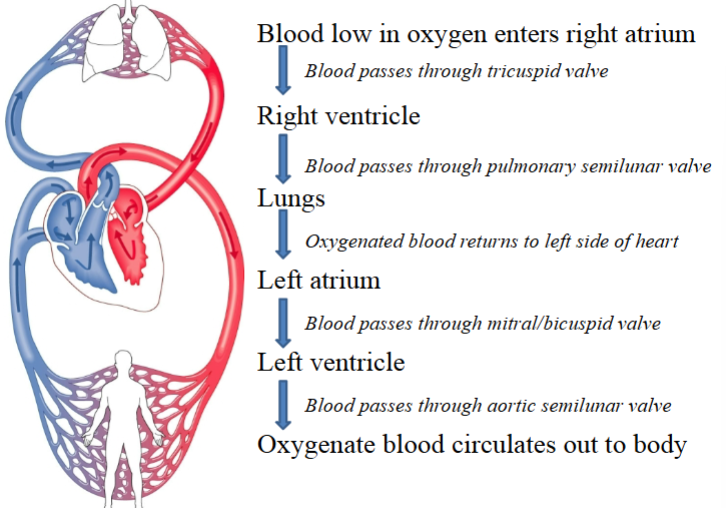
Pulmonary Circuit
Route between heart & lungs that allows blood to pick up oxygen.
Right ventricle of heart → Pulmonary trunk and arteries → Lungs → Pulmonary veins → Left atrium of heart
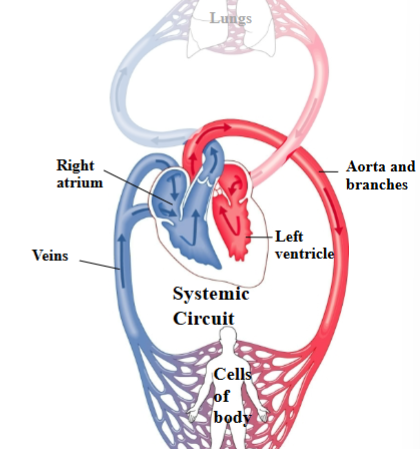
Systemic Circuit
Route between heart & tissues of the body (other than the lungs) that brings oxygen out to cells.
Left ventricle of heart → Aorta & branches → Cells of the body → Veins → Right atrium of heart
Heart Basics
Pumps ~1800 gallons/day through 60,000 miles of blood vessels
Approximately fist-sized
Sits to the left of the midline & on top of the diaphragm
4 distinct chambers
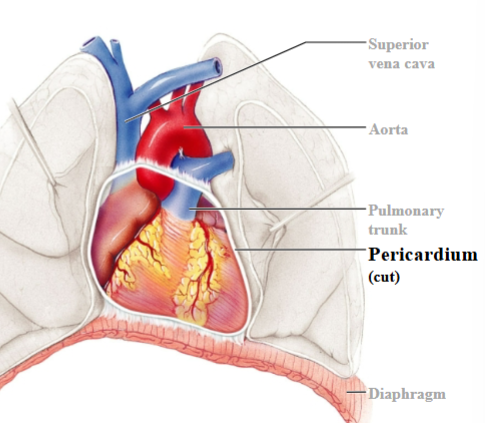
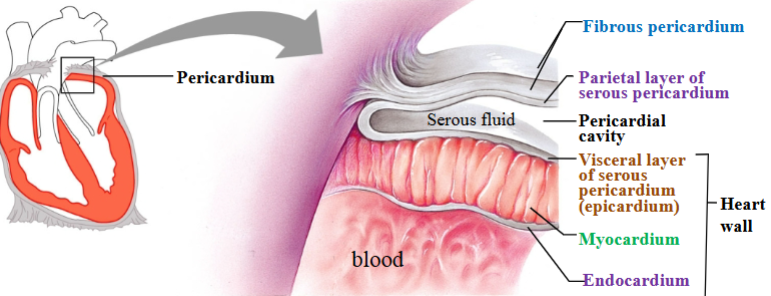
Pericardium
Heart is contained within a pericardial sac known as the pericardium.
Fibrous pericardium
Touch outer layer of sac that anchors heart and prevents overfilling; dense irregular CT
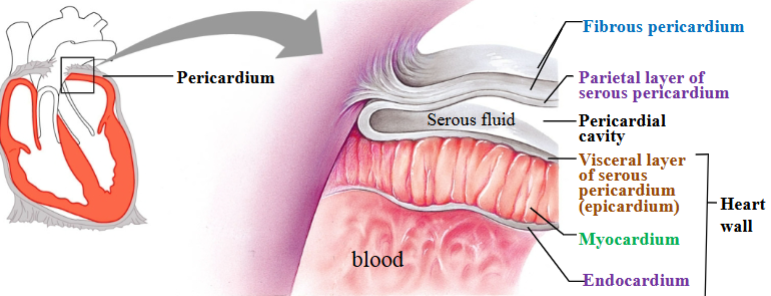
Serous pericardium
Serous membrane around heart
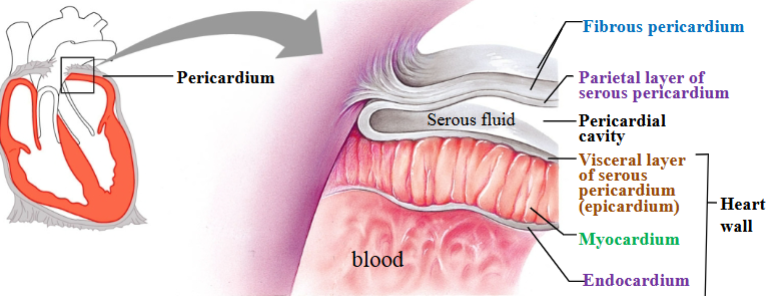
Parietal layer of serous pericardium
Inner layer of sac, secretes serous fluid
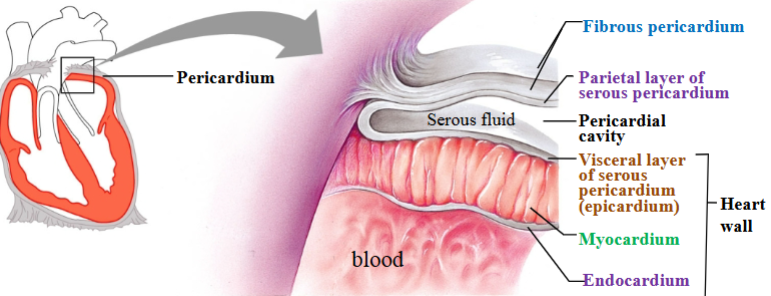
Visceral layer of serous pericardium
Outer layer of heart, secretes serous fluid (epicardium)
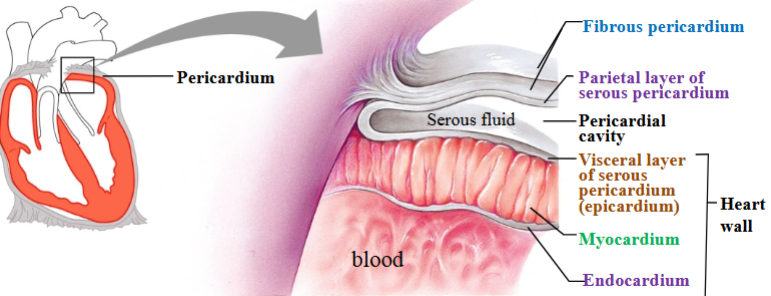
Pericardial cavity
Space between parietal & visceral layers; filled with serous fluid
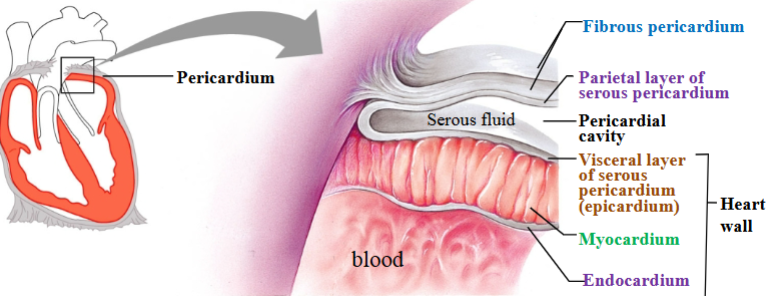
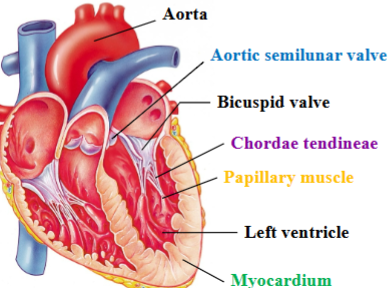
Myocardium
Cardiac muscle tissue; left ventricle has thickest layer of cardiac muscle
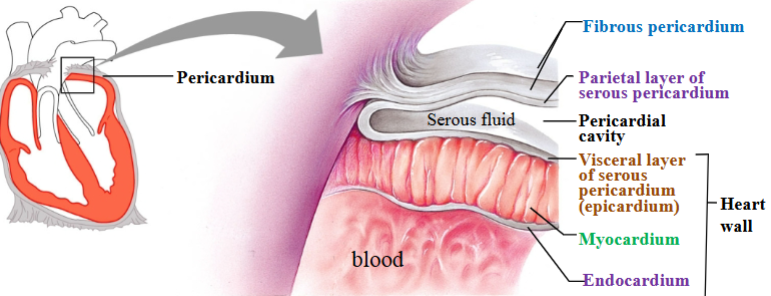
Endocardium
Simple squamous epithelium
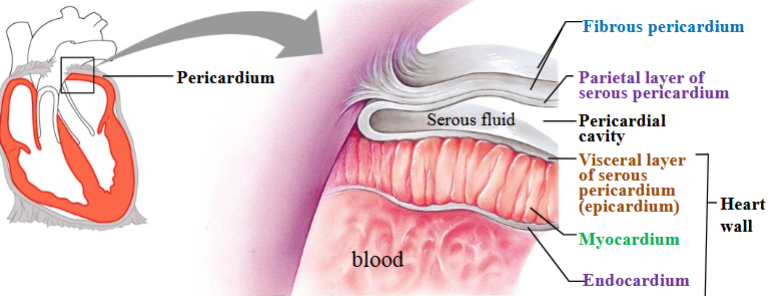
Heart wall
Visceral layer (epicardium)
Myocardium
Endocardium
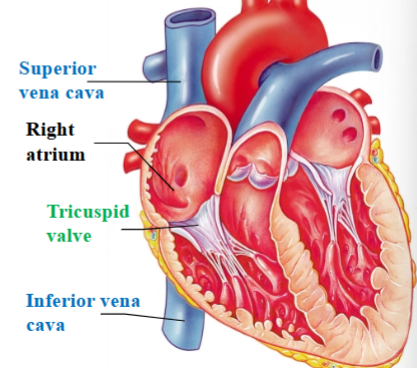
Superior & Inferior vena cava
Large veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium
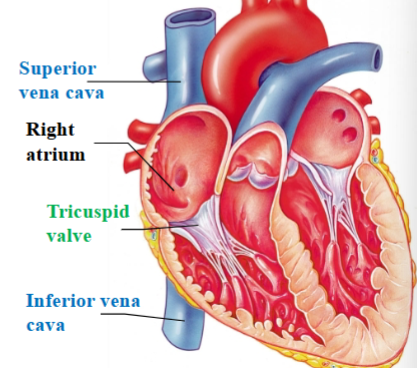
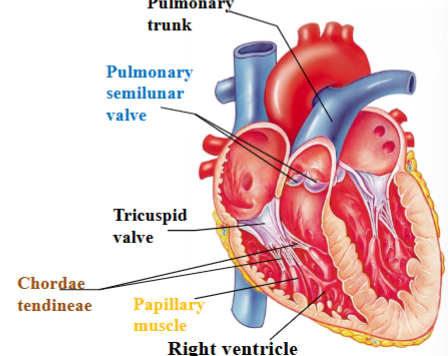
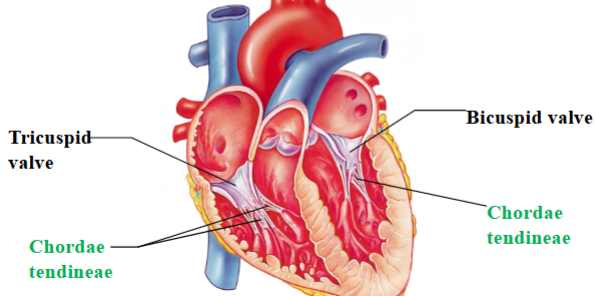
Tricuspid (right atrioventricular) valve
separates right atrium from right ventricle
Chordae tendineae
Dense regular CT that attaches cusps of tricuspid valve to ventricle wall and other end attaches to papillary muscles.
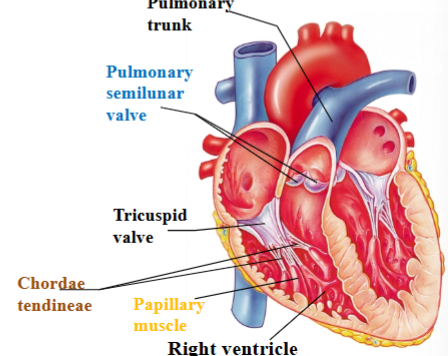
Papillary muscle
Projection of cardiac muscle in the ventricular walls; right ventricle contains 3 papillary muscles that attach to the tricuspid valve
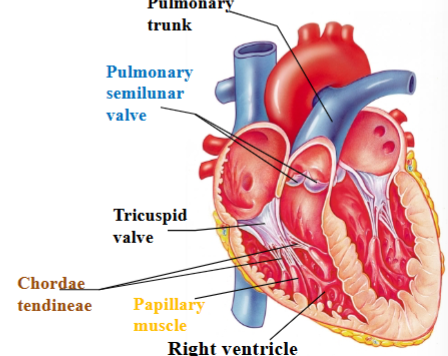
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Separates right ventricle from pulmonary trunk (artery)
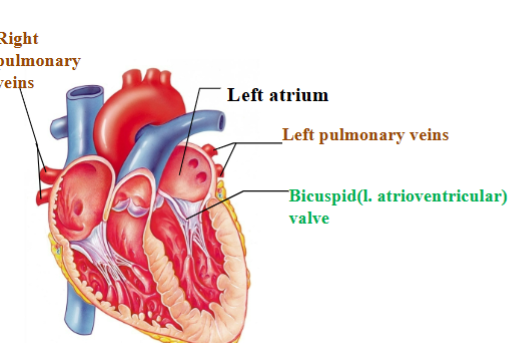
Pulmonary veins
return oxygenated blood to heart from lungs
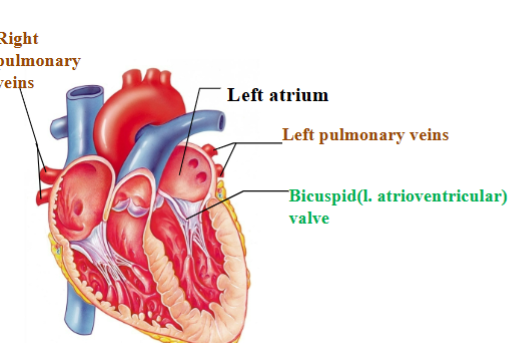
Bicuspid/mitral (left atrioventricular) valve
Separates left atrium from left ventricle
Aortic semilunar valve
Separates left ventricle from the aorta
Blood flow through the heart
Tricuspid & Bicuspid/Mitral (right & left atrioventricular) valves
Named by # of cusps per valve
Cusps formed of endocardium reinforced with dense CT
Chordae tendineae prevent valves from inverting into the atria when the ventricles contract
Function of the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & bicuspid)
Atrioventricular valves open as gravity and atrial contraction moves blood from the atria to the ventricles. Ventricles are at rest.
Pulmonary & Aortic Semilunar valves
Valve cusps resemble pockets
Blood pushes them open when the ventricles contract
When ventricles relax, blood fills the pockets and forces the valve closed
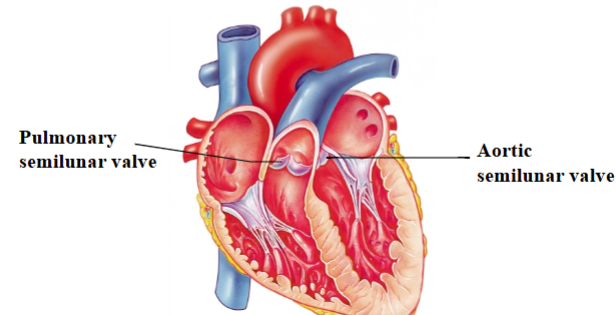
Function of the semilunar valves
As ventricles contract, blood is pushed up against the semilunar valves, forcing them open.
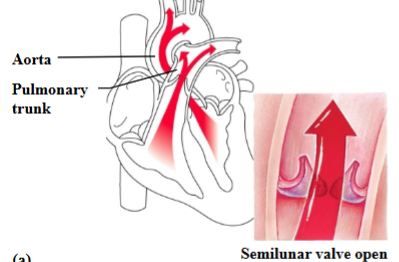
Heart Murmur
Noise in the heart caused by blood leaking past a closed valve
Mitral valve prolapse
Most common; weakness in the collagen of the valve or chordae tendinae
Stenosis
Narrowed opening between valves, may be caused by calcium deposits or illness
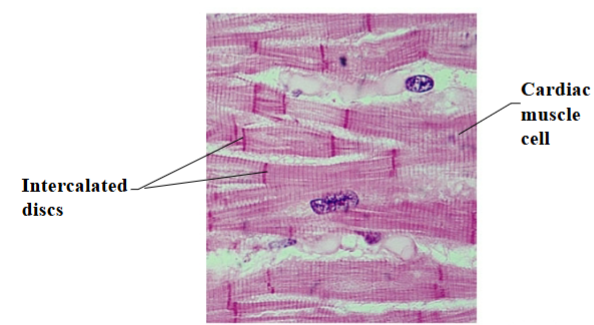
Cardiac muscle
Striated muscle cells connected by intercalated discs
Some of the cells are adapted to conduct an impulse instead of contracting
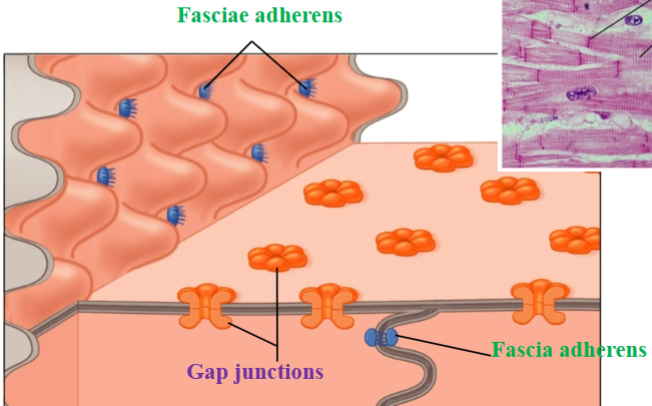
Gap junctions
Allow for quick communication between cells for a coordinated contraction
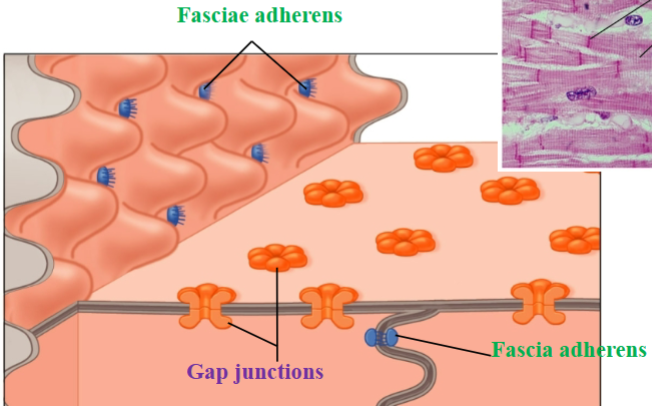
Fascia adherens
Desmosome-like connections; provide strength
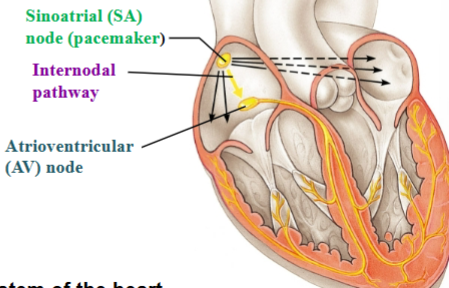
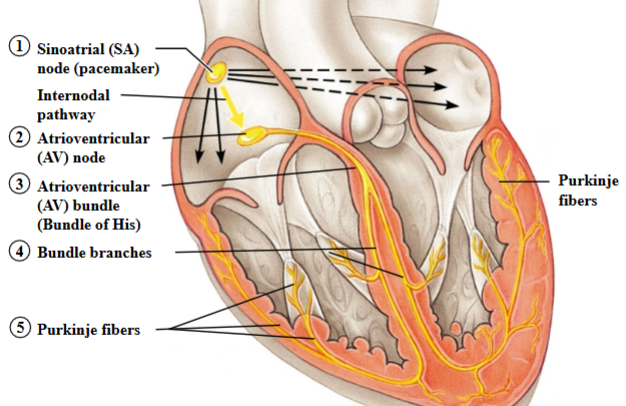
Sinoatrial (SA) node
In the right atrium; initiates the electrical impulse
Pacemaker
Inherent Rhythmicity (automaticity)
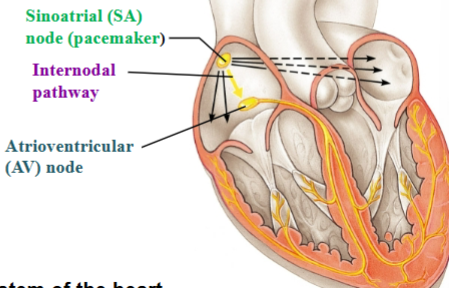
Internodal pathway
Carries impulse away from SA node to AV node
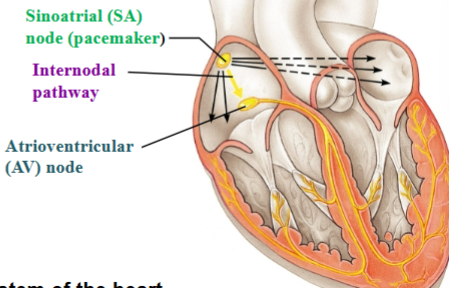
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Delays impulse before it is passed on to the ventricles
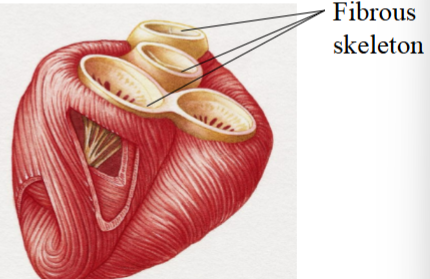
Fibrous skeleton
Barrier between the atria and ventricles that prevents an electrical impulse from passing
Only one pathway from atria to ventricles: AV node
The conducting system of the heart
Atria contract top to bottom
Ventricles contract bottom to top
Cardiac cycle
Cardiac Cycle: 1 heartbeat; ~0.8 seconds/cycle
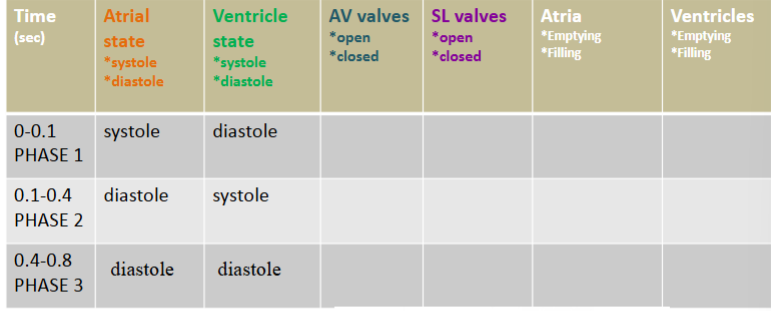
Systole
Contraction (forcing blood out)
Diastole
Relaxation (filling with blood)
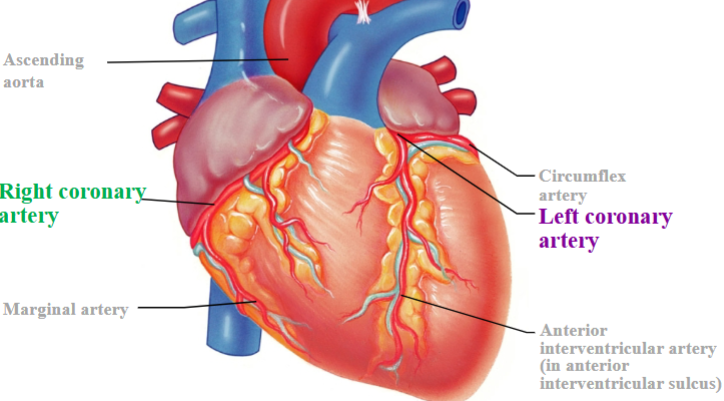
Heart needs an external blood supply
Right coronary artery & branches
Left coronary artery & branches
Atherosclerosis
Build-up of plaques which cause narrowing of artery
Most common cause of arteriosclerosis (any hardening of arteries)
Some causes:
Damage to inner surface (endothelium) caused by inflammatory response to smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, etc.
Cholesterol, calcium, and lipids can attach damaged lining and harden into plaques
Myocarial Infarction
Heart Attack; Result of blood not reaching cardiac muscle tissue
Thrombus
Blood clot
Ischemic
Restriction in blood supply resulting in oxygen and glucose deprivation of tissues
Balloon angioplasty without stent
Procedure used to open up a narrowed or blocked blood vessel (usually an artery) using only a balloon catheter, without placing a stent afterward; One alternative to bypass surgery
Coronary bypass
A type of open-heart surgery used to restore blood flow to the heart muscle when one or more of the coronary arteries are blocked or severely narrowed.
Blood vessels
Transport blood
Continuous circuit between heart and capillaries
Lymph vessels
Transports lymph: fluid that has accumulated in tissues
One way: not a circuit
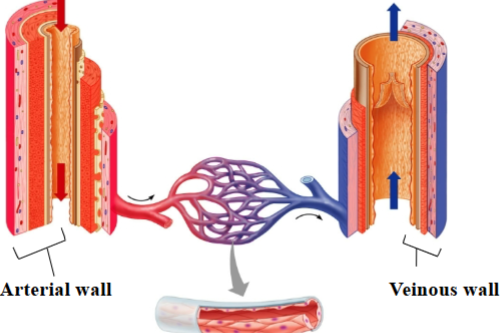
Tunica intima
Endothelium: simple squamous epithelium
Subendothelial layer: loose areolar CT
Veins forms valves
A layer of the vessel walls
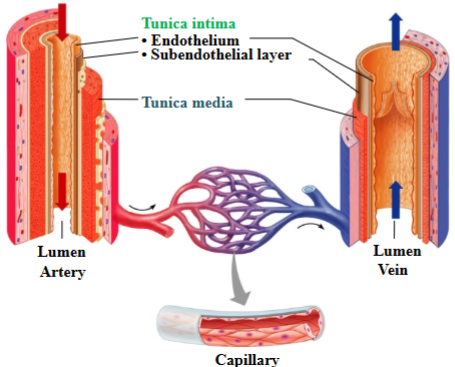
Tunica media
Smooth muscle arranged circularly to allow for vasoconstriction; artery is thicker with more elastic fibers; a layer of the vessel walls
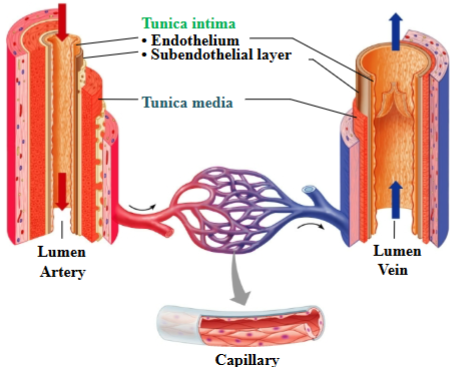
Tunica externa
loose areolar CT
Vaso vasorum: blood vessels that run through this layer and supply cells of vessel wall
Tunica externa of veins have equal thickness or thicker than arteries
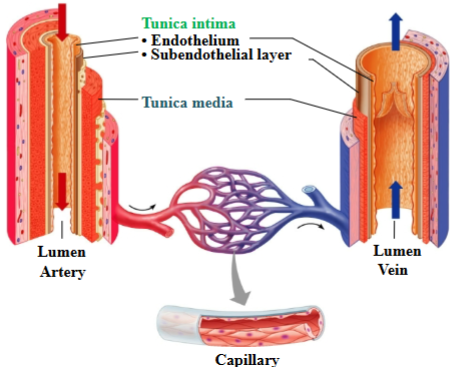
Arterial walls are thicker and stronger than veins:
must withstand the higher pressure of blood pumped from the heart.