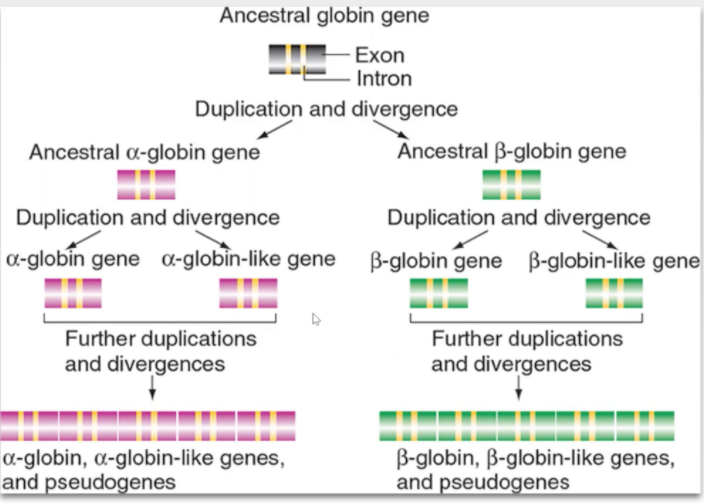
Gene Duplication
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
Paralogs
* copies that coalesce at a duplication event
2
New cards
Duplication event
* type of mutation in which one or more copies of a DNA segment is produced
* arises from %%unequal crossing over%% during %%meiosis%% between %%misaligned homologous chromosomes%%
* arises from %%unequal crossing over%% during %%meiosis%% between %%misaligned homologous chromosomes%%
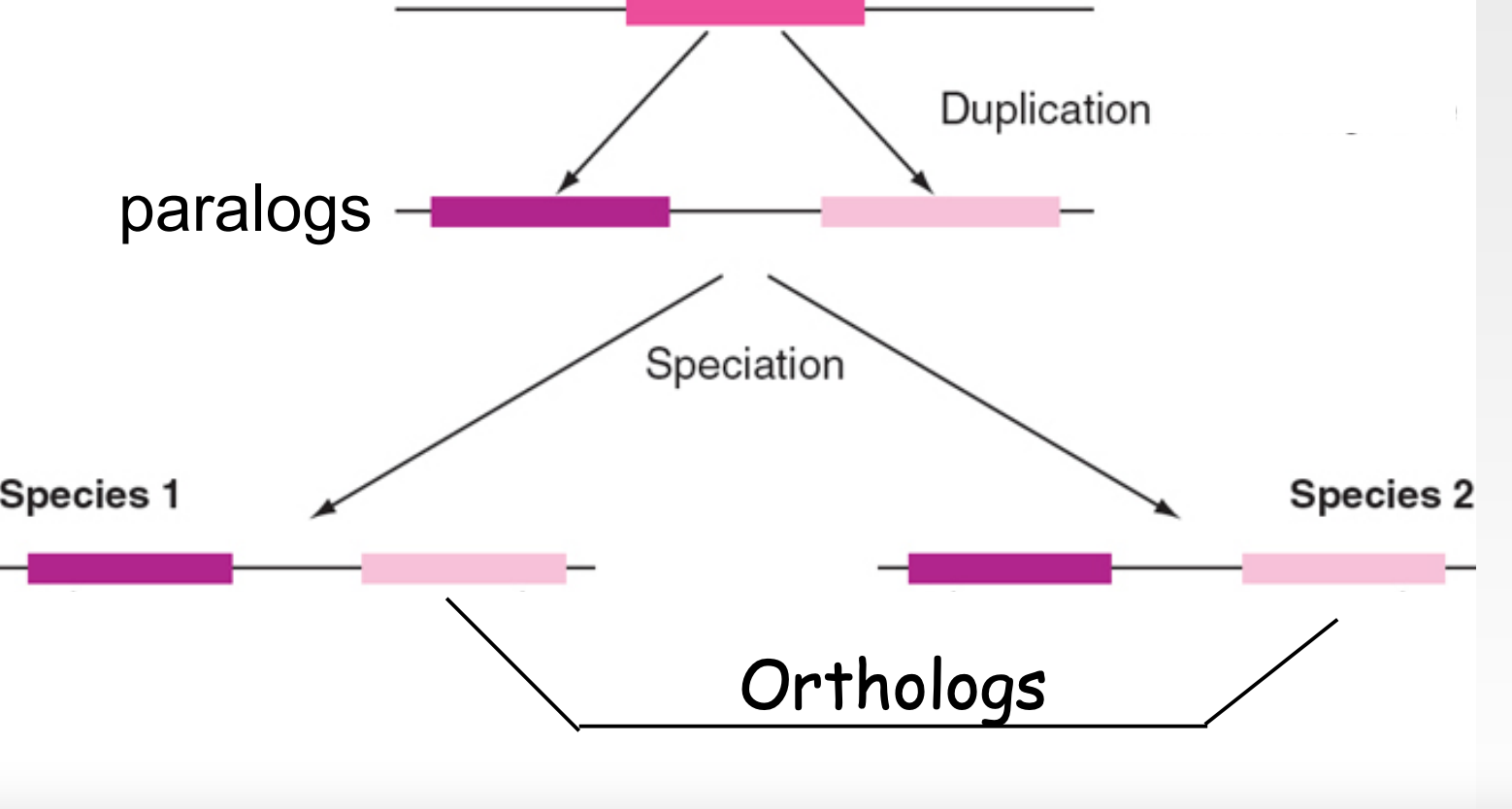
3
New cards
Orthologs
* coalesce at a ^^speciation^^ event
4
New cards
Another diagram of speciation and duplication events
* first duplication occurs
* ^^speciation^^ event into A and B
* red and blue in each species
* ^^speciation^^ event into A and B
* red and blue in each species
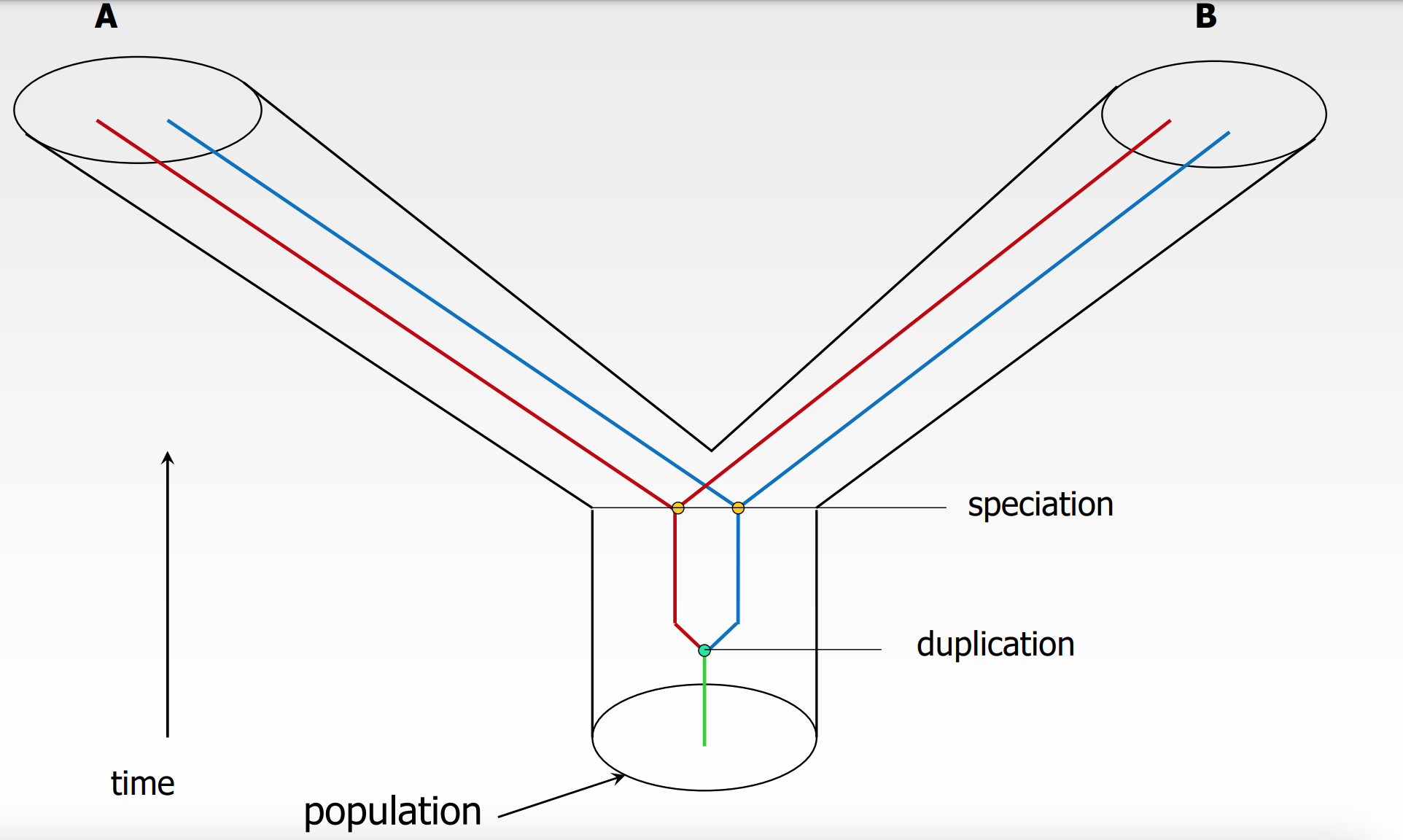
5
New cards
when duplication occurs assume…
* assume through multiple generations that the single duplication event which would have occurred in a single individual gets PASSED on and now everybody in that entire population has that duplication event
* and now everyone in the population has 2 copies 2 loci
* and now everyone in the population has 2 copies 2 loci
6
New cards
during speciation event…
* lineage gets split into two different groups (A and B) (represented by tubes)
7
New cards
since everyone got both copies from duplication event …
* both of these species lineages (A and B) will inherit both copies (blue and red)
8
New cards
same colors are…
* orthologs
9
New cards
different colors are…
* paralogs
10
New cards
Draw diagram with
1. duplication event
2. speciation event for both copies (2)
3. duplication event for one of the copies
4. 2 speciation event
1. duplication event
2. speciation event for both copies (2)
3. duplication event for one of the copies
4. 2 speciation event
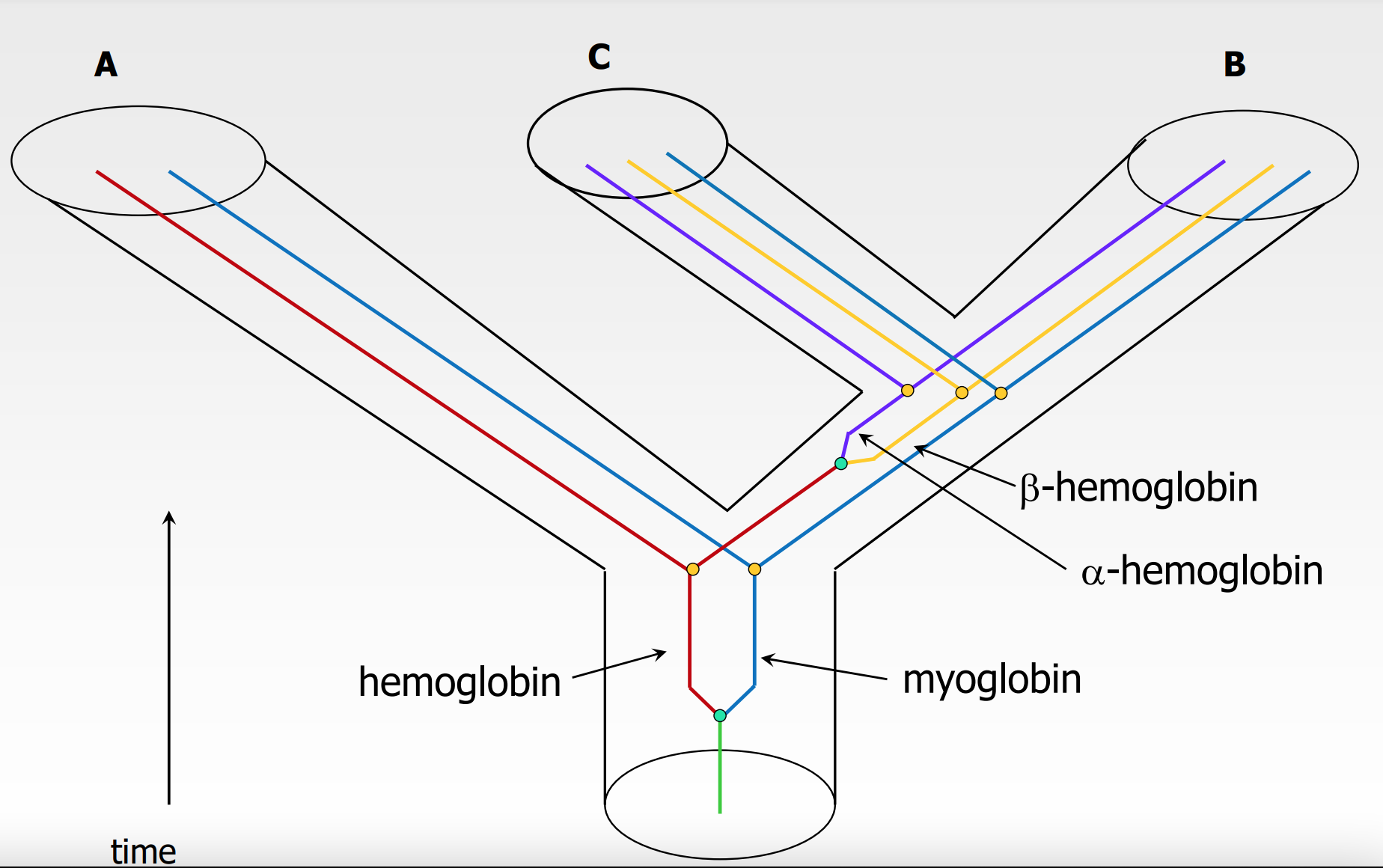
11
New cards
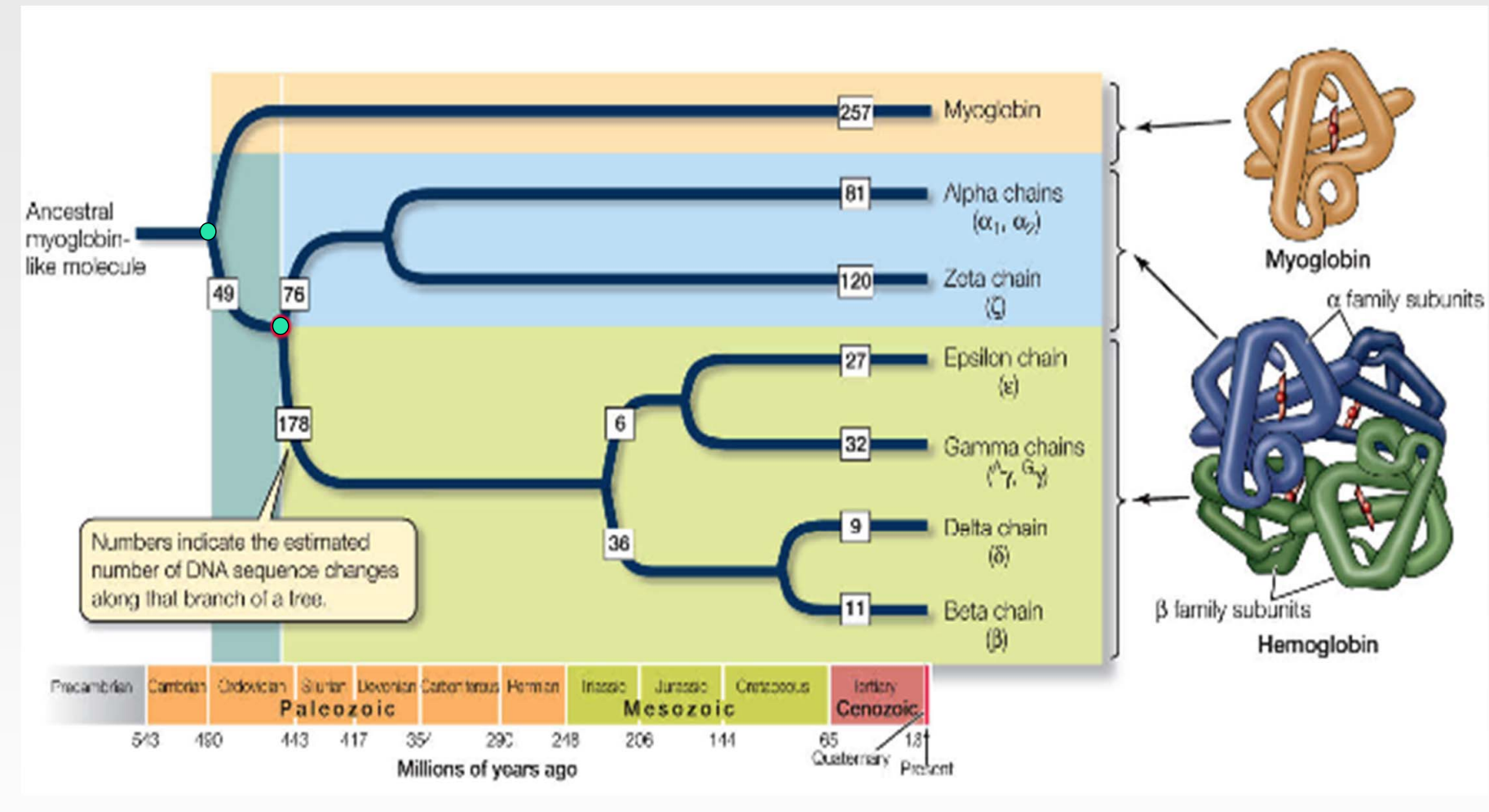
Real world example of speciation and duplication event like the graph represented:
* split in ancestral globin gene
* in some species (a vertebrate) there was duplication and one of them became primitive for of %%HEMOGLOBIN%% and the other %%MYOGLOBIN%% (550 million years ago)
* Another duplication event occurs in hemoglobin
* @@B-hemoglobin@@
* @@a-hemoglobin@@
* we need both types to produce the oxygen carrying molecules in blood
* in some species (a vertebrate) there was duplication and one of them became primitive for of %%HEMOGLOBIN%% and the other %%MYOGLOBIN%% (550 million years ago)
* Another duplication event occurs in hemoglobin
* @@B-hemoglobin@@
* @@a-hemoglobin@@
* we need both types to produce the oxygen carrying molecules in blood
12
New cards
disentangle the diagram
* name each line
* m(A), m(C), m(B) → myoglobin in species A, B, and C
* h(A)
* α(C), α(B)
* β(C), β(B)
* remove the species (tubes)
* move all colors away from each other (still attached to the tree)
* m(A), m(C), m(B) → myoglobin in species A, B, and C
* h(A)
* α(C), α(B)
* β(C), β(B)
* remove the species (tubes)
* move all colors away from each other (still attached to the tree)
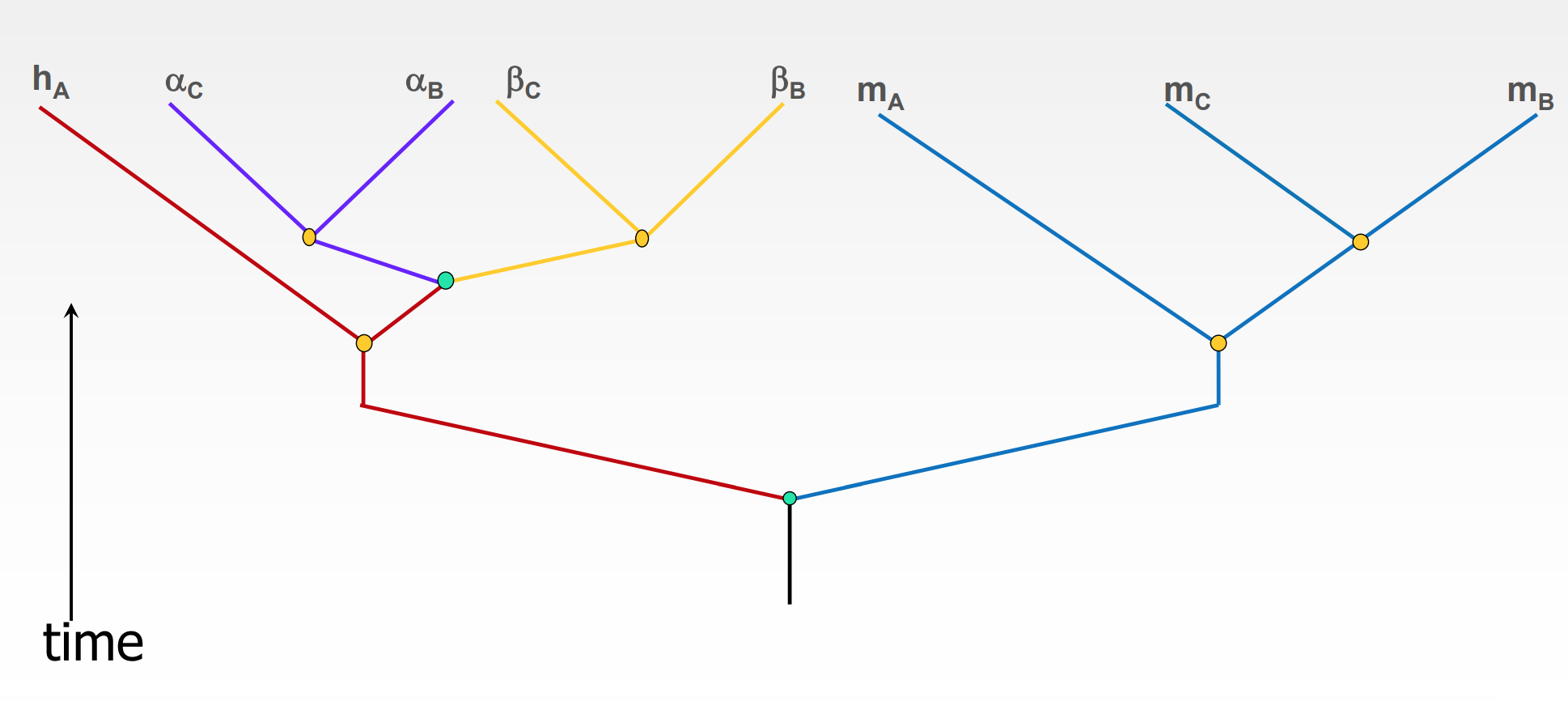
13
New cards
Duplication tree for ancestral myoglobin like molecule
14
New cards
Getting rid of speciation events from original disentangled diagram
* only keep one branch per color
* doesn’t matter which branches are removed
* doesn’t matter which branches are removed
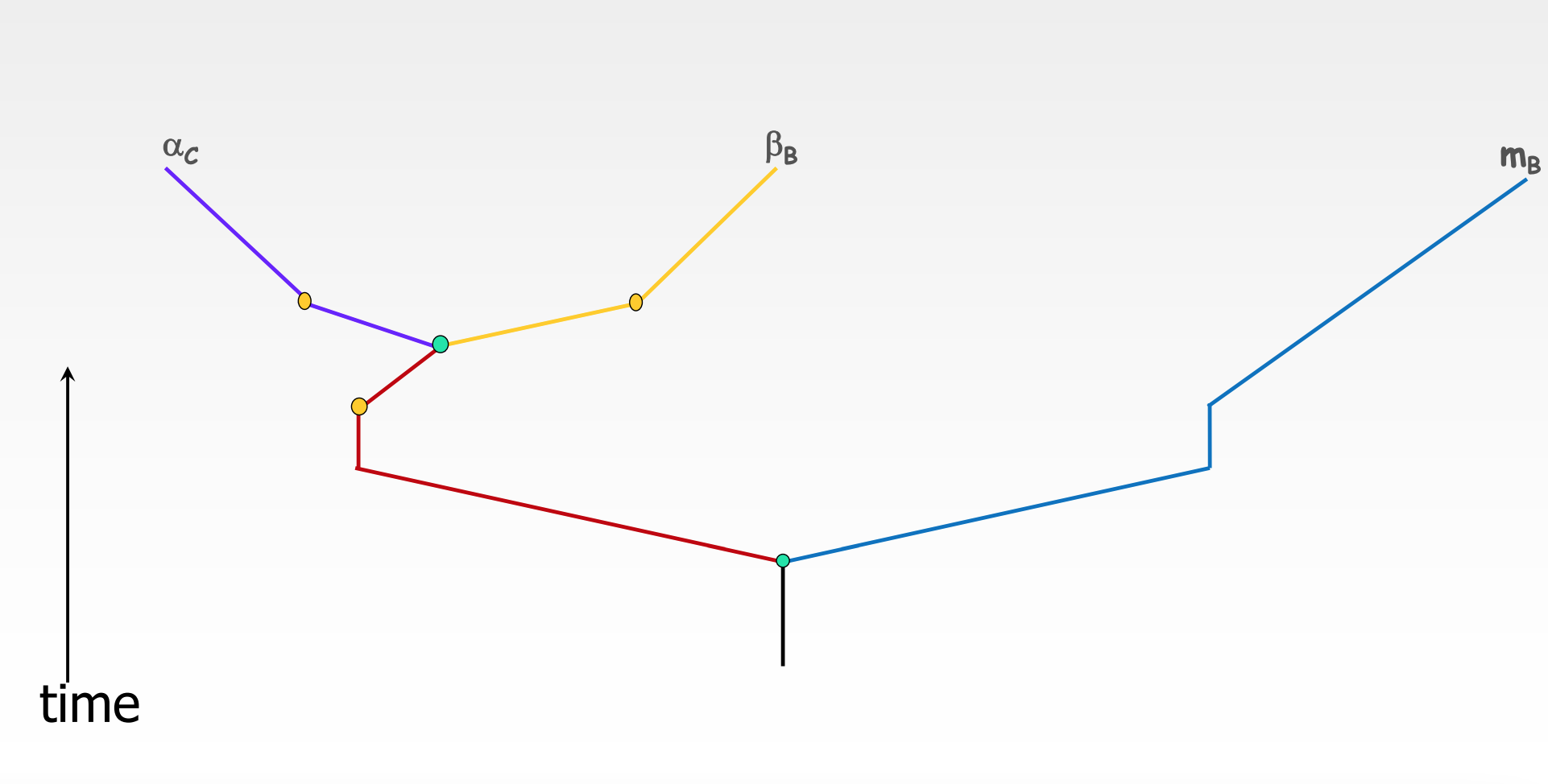
15
New cards
Why do we get rid of speciation events?
* strip away the noise
* tens of thousands of vertebrate species since first globins evolved
* looking only at duplication
* tens of thousands of vertebrate species since first globins evolved
* looking only at duplication
16
New cards
Hagfish example
* lineage that ==never== had a ==duplication event== in the hemoglobin
* no alpha or beta hemoglobin
* red line only
* no alpha or beta hemoglobin
* red line only
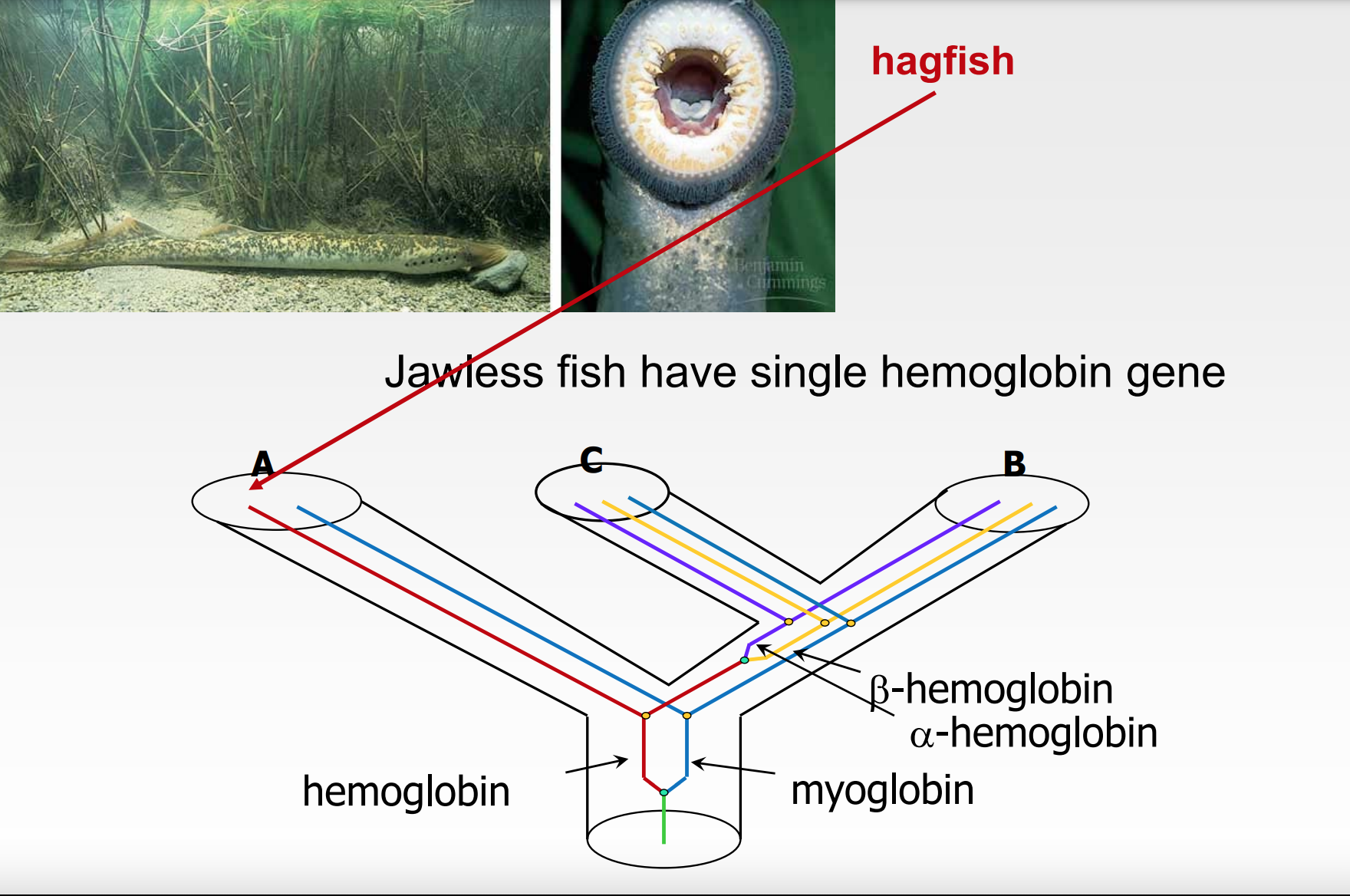
17
New cards
jawed fish and land vertebrates have …
distinct alpha and beta globin genes
18
New cards
Why did B-globin gene go through additional duplication events
* evolution of %%fetal hemoglobins%% in mammals
* fetal hemoglobin: makes the hemoglobin in fetus have a %%greater affinity for oxygen%%
* fetus gets %%97-98%%% of oxygen
* %%selective advantage%%: grows faster (and possibly larger)
* fetal hemoglobin: makes the hemoglobin in fetus have a %%greater affinity for oxygen%%
* fetus gets %%97-98%%% of oxygen
* %%selective advantage%%: grows faster (and possibly larger)
19
New cards
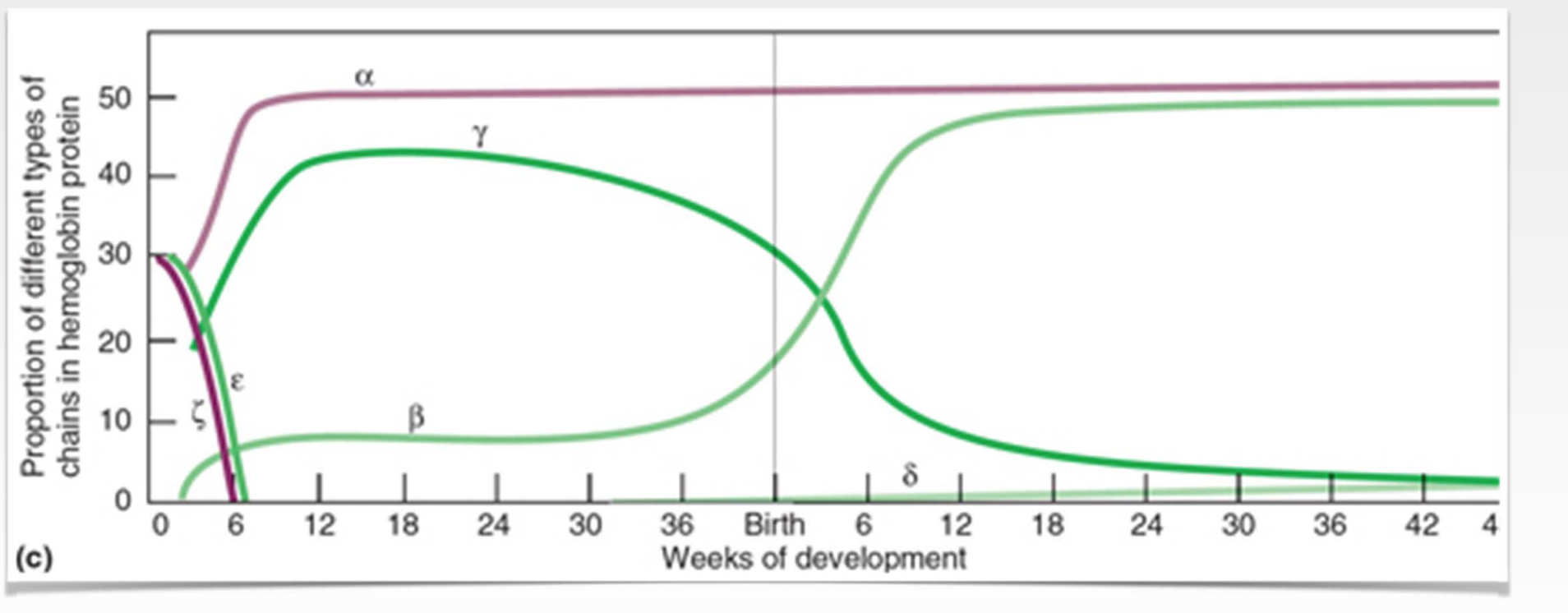
Expression of human hemoglobin genes as a function of developmental age
* alpha hemoglobin gets developed early on when the fetus starts to develop the circulatory system and gets express all throughout life
* %%gamma%% is main fetal hemoglobin
* while fetus is gestating and the embryo is gestating it produces gamma version of the beta hemoglobin
* gamma has HIGHER affinity for oxygen
* Once baby is born there is a ^^switch^^
* ==stops== expressing ==gamma== type of beta hemoglobin
* %%starts%% expressing regular %%beta%% hemoglobin
* %%gamma%% is main fetal hemoglobin
* while fetus is gestating and the embryo is gestating it produces gamma version of the beta hemoglobin
* gamma has HIGHER affinity for oxygen
* Once baby is born there is a ^^switch^^
* ==stops== expressing ==gamma== type of beta hemoglobin
* %%starts%% expressing regular %%beta%% hemoglobin
20
New cards
Why does there have to be a switch from gamma type beta hemoglobin to beta hemoglobin being expressed after being born
\*switching works exactly the same way in males and females
* when females became pregnant, if they still use gamma there ==won’t be any advantage== for fetus having a higher affinity for oxygen
* when females became pregnant, if they still use gamma there ==won’t be any advantage== for fetus having a higher affinity for oxygen
21
New cards
HOW does gamma type beta being expressed switch to beta hemoglobin being expressed
change in transcription factors
* shuts down transcription of gamma type of beta hemoglobin
* up-regulates the transcription of regular beta hemoglobin
* shuts down transcription of gamma type of beta hemoglobin
* up-regulates the transcription of regular beta hemoglobin
22
New cards
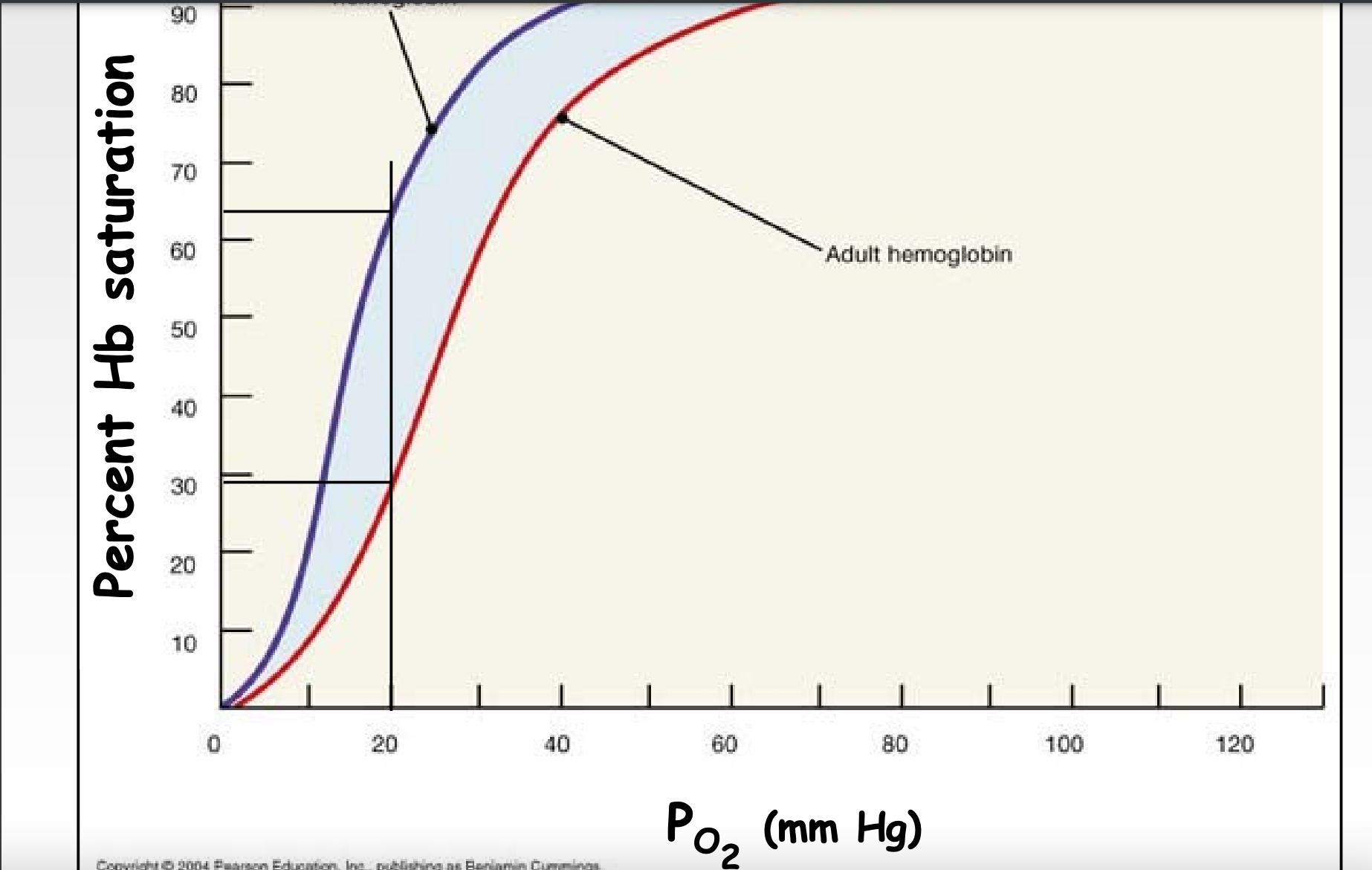
Partial pressure (O2) and percent Hb saturation graph
23
New cards
pseudogenes
Pseudogenes are **nonfunctional segments** of DNA that ***resemble functional*** genes.
24
New cards
if an organisms has a gene, the gene has been retained because
it has some positive function value
25
New cards
Why is the most efficient way for new functions to evolve through gene duplication and NOT pleiotropy
* Pleiotropy: a single gene having multiple functions by influencing more than one trait
* evolution of new functions still highly constrained, as it allows new function to work well, it degrades original function
* evolution of new functions still highly constrained, as it allows new function to work well, it degrades original function
26
New cards
Exon shuffling
* once there are two or more copies recombination can occur (exon shuffling)
* thus, you can start making combinations amongst the one different duplicated genes
* further allows you to potentially produce new function
* thus, you can start making combinations amongst the one different duplicated genes
* further allows you to potentially produce new function
27
New cards
what happens to one locus after gene duplication
1. turns into pseudogene
2. Both copies retain OG function
3. one copy evolves new function
1. neofunctionalization
4. the copies optimize different original, pleiotropic functions
1. subfunctionalization
28
New cards
probability of new function is actually…
quite low
* lose function, because mutation is not a directed process
* lose function, because mutation is not a directed process
29
New cards
How could both copies retain original function after going through gene duplication
* especially when a lot of gene product is needed
* you need a LOT of ribosomes to make all those different proteins collectively
* if selection favors OG functions
* you need a LOT of ribosomes to make all those different proteins collectively
* if selection favors OG functions
30
New cards
Ribosomal RNA genes are a case of
lots and lots of DNA duplication
31
New cards
Repeated gene duplication can lead to
gene clusters on the same chromosome
32
New cards
what can produce gene families
* chromosomal breakage and re-anealing
33
New cards
what ARE gene families
gene clusters occurring on two or more chromosomes
34
New cards
Some important gene families
* hemoglobin family \~10 genes
* Olfactory receptor family (\~900 genes; over 60% pseudogenes in humans)
* Immunoglobulin family (\~800 genes)
* Olfactory receptor family (\~900 genes; over 60% pseudogenes in humans)
* Immunoglobulin family (\~800 genes)
35
New cards
How did cells evolve to create chemical mechanisms to protect themselves as O2 levels increased
* prokaryotic globin binds and “detoxifies” oxygen present in cell’s environment
36
New cards
globin gene duplication and divergence diagram